Important Note - Please Read:
|
|
|
- Letitia Mosley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help menu and selecting About SAFE... If your version of SAFE is not at least version 6.01 and you want to run this tutorial, then you should call Computers and Structures at (510) for information on upgrading SAFE. 1
2 SAFE Problem 3 One-Way Beam-Slab System With Opening Design Information E = 3600 ksi, Poissons Ratio = 0.2, Unit Weight = 150 pcf f c = 4 ksi, fy = 60 ksi X direction top rebar cover = 2.5 (to rebar centroid) Y direction top rebar cover = 1.5 (to rebar centroid) X direction bottom rebar cover = 1.5 (to rebar centroid) Y direction bottom rebar cover = 2.5 (to rebar centroid) All columns are 12 by 12. Column height below is 10 feet. All beams are 12 wide by 18 deep (12 deep below slab). Design beams as rectanglar beams (not T-beams). Slab is 6 thick. Dead load in addition to self-weight is 35 psf. Live load is 100 psf. To Do Use the ACI code. Review the factored beam moments. Review the calculated beam flexural reinforcing. Note: Dimensions are to column and beam centerlines A B Opening Note: Our intent is that you try this problem on your own first. After you have solved it on your own, you can step through our solution if desired. If you have problems trying to create the model, then follow the steps in our solution. 2
3 SAFE Problem 3 Solution 1. Click the drop down box in the status bar to change the units to kip-ft. 2. From the File menu select New Model From Template. This displays the Slab Templates dialog box. 3. In this dialog box: Click on the Ribbed Slab button to display the Ribbed Slab dialog box. In this dialog box: À In the Along X Direction area verify that 0.5 is entered in the Left Edge Distance and Right Edge Distance edit boxes. À In the Along X Direction area type 1 in the Number of Spans edit box. À In the Along X Direction area verify that 24 is entered in the Spacing edit box. À In the Along Y Direction area verify that 0.5 is entered in the Left Edge Distance and Right Edge Distance edit boxes. À In the Along Y Direction area type 1 in the Number of Spans edit box. À In the Along Y Direction area verify that 24 is entered in the Spacing edit box. À Type.5 in the Slab Thickness edit box. À Verify that 1 is entered in the Column Size (square) edit box. À Type 10 in the Column Height Below edit box. À In the Load area type.035 in the Dead Load (Additional) edit box. Since the units are kips and feet,.035 is equivalent to 35 psf. À In the Load area type.1 in the Live Load edit box. Since the units are kips and feet,.1 is equivalent to 100 psf. À Leave the Create Live Load Patterns check box unchecked. Note: Checking the Create Live Load Patterns check box causes the program to create all sorts of automatically generated skip loading patterns for the live load. These patterns are automatically added to the defined static load cases and are identified with a Load Type called Pattern Live. In addition, these live load patterns are included in the load combinations automatically created for design. 3
4 À In the Joist area type 6 in the Spacing edit box. À In the Joist area verify that the Y Direction option is selected This means that the joists will be defined parallel to the Y- axis.. Note: We will define and assign actual beam/ joist sizes later. À Click the OK button. 4. From the Edit menu select Edit Grid... to display the Define X Grid dialog box. 5. In this dialog box: In the Display area select the Y Grid option. In the Display Grid As area verify that the Ordinates option is selected. Click in the 3rd row of the spreadsheet. In the Grid Line #3 area select the Secondary Line option. Note: Secondary grid lines do not have Grid ID bubbles. We will not specify a Grid ID for these secondary lines. Type 4 in the Coordinate column of the 3rd row of the spreadsheet. Type 20 in the Coordinate column of the 4th row of the spreadsheet. Click the OK button. The model now appears as shown in Figure Delete the center joist (beam) by clicking on it to select it and then pressing the Delete key on the keyboard. 7. Verify that the Snap to Points button on the side toolbar is depressed. Alternatively, you could click on the Draw menu, select Snap To and verify there is a check mark next to Points on the submenu. 8. Click the Snap to Intersections button on the side toolbar. After you click on the button it will remain depressed indicating that this snap option is active. Alternatively, you could click on the Draw menu, select Snap To and click on Intersections in the submenu to activate this snap option. Note: The snap options buttons act like toggle switches. You can use them to turn snap options on or off. If a snap option button appears depressed then that snap option is active. Clicking any snap option button toggles it between active(depressed) and inactive (not depressed). Similarly, the snap option items on the Draw menu act like toggle switches. If a snap option on the Snap To submenu has a check mark next to it 4
5 then that snap option is active. Clicking a snap option on the Snap To submenu toggles the state of that option. J K L M Delete this joist Figure 3-1: Model After Step 5 9. Click the Draw Line Object button on the side toolbar (or select Draw Line Object from the Draw menu). 10. Draw a line object by clicking on the point labeled J in Figure 3-1 and then double clicking on the point labeled K to complete the line object. Note: With the Intersection snap option activated the mouse cursor will snap to the intersection of the beam and grid line at points J and K. Note: We could also single click on the point labeled K and then press the Enter key on the keyboard to complete the line object. 11. Draw a line object by clicking on the point labeled L in Figure 3-1 and then double clicking on the point labeled M to complete the line object. The model now appears as shown in Figure
6 P O Q R Figure 3-2: Model After Step Click the Snap to Intersections button on the side toolbar to deactivate this snap option. 13. Click the Snap to Middle and Ends button on the side toolbar to activate this snap option. 14. Run the mouse cursor along the beam near the point labeled O in Figure 3-2 until the cursor snaps to the midpoint of the beam and a text box which says Mid Point appears. Left click the mouse to start drawing a new beam from this midpoint location. 15. Move the mouse up to the point labeled P in Figure 3-2. Again the mouse cursor will snap to the midpoint of the beam. Double click at point P to finish drawing this beam. 16. Similarly, click on the point labeled Q in Figure 3-2 and then double click on the point labeled R to draw another beam. Note that both points Q and R are at the midpoints of beams. The model now appears as shown in Figure Now we will draw the area object that will define the slab opening. Click the Draw Rectangular Area Object button on the side toolbar (or select Draw Rectangular Object from the Draw menu). 6
7 S U T Figure 3-3: Model After Step Single click on the point labeled S in Figure 3-3 and then double click on the point labeled T to draw the area object. 19. Click the Pointer/Select button to switch from Draw mode to Select mode. 20. Right click near the point labeled U in Figure 3-3 to display the Rectangular Slab Information dialog box for the just drawn area object. 21. In this dialog box: In the Locate Slab area select the By Center option. In the Identification and Location area verify that Center X and Center Y are both 12. These are the X and Y coordinates of the center of the area object. In the Identification and Location area type 11 in the X Dimension and type 15 in the Y Dimension edit boxes. Click the OK button. 7
8 22. Left click near the point labeled U in Figure 3-3 to select the just dimensioned area object. 23. From the Assign menu select Opening. This area is now designated as an opening. 24. Click the drop down box in the status bar to change the units to kip-in. 25. From the Define menu select Slab Properties... to display the Slab Properties dialog box. 26. In this dialog box: In the Slab Property area highlight the property named SLAB and then click the Modify/Show Property button to display the Slab Property Data dialog box. In this dialog box: À In the Analysis Property Data area: ä Verify that the Modulus of Elasticity is ä Verify Poisson s ratio is 0.2. Note: We will verify the unit weight later. ä Verify that the Bending Thickness (X), Bending Thickness (Y) and Twisting Thickness are all 6. Note: These values will all be 6 because we entered the footing thickness in the Ribbed Slab dialog box in Step 3. ä Verify that the Slab Type option is selected. ä Verify that the Thick Plate check box is checked. Note: Checking the Thick Plate check box tells the program to consider slab shear deformations in the analysis. If this box is not checked then slab shear deformations are not included in the analysis. À In the Design Property Data area: ä Verify that the Thickness is 6. ä Type 2.5 in the X Cover Top (to Centroid) edit box. ä Type 1.5 in the Y Cover Top (to Centroid) edit box. ä Type 1.5 in the X Cover Bottom (to Centroid) edit box. ä Type 2.5 in the Y Cover Bottom (to Centroid) edit box. 8
9 ä Verify the Concrete Strength, fc is 4. ä Verify the Reinforcing Yield Stress, fy is 60. ä Verify that the No Design check box is not checked. À Click the OK button twice. 27. From the Define menu select Beam Properties... to display the Beam Properties dialog box. 28. In this dialog box: Click the drop-down box in the Click To area and click on Add Rectangular Beam to display the Property Data For Rectangular Beam dialog box. In this dialog box: À Type XBEAM in the Beam Property name edit box. À In the Analysis Property Data area: ä Verify that the Modulus of Elasticity is ä Verify Poisson s ratio is 0.2. Note: We will verify the unit weight later. ä Verify the width is 12. ä Type 18 in the Depth edit box. À In the Design Property Data area: ä Verify the width is 12. ä Type 18 in the Depth edit box. ä Type 2.5 in the Cover Top (to Centroid) edit box. ä Type 1.5 in the Cover Bottom (to Centroid) edit box. ä Verify the Concrete Strength, fc is 4. ä Verify the Reinforcing Yield Stress, fy is 60. ä Verify the Shear Steel Yield Stress, fys is 60. ä Verify the Concrete Shear Strength, fcs is 4. 9
10 ä Verify that the No Design check box is not checked. À Click the OK button. Click the drop-down box in the Click To area and click on Add Rectangular Beam to display the Property Data For Rectangular Beam dialog box. In this dialog box: À Type YBEAM in the Beam Property name edit box. À In the Analysis Property Data area: ä Verify that the Modulus of Elasticity is ä Verify Poisson s ratio is 0.2. Note: We will verify the unit weight later. ä Verify the width is 12. ä Type 18 in the Depth edit box. À In the Design Property Data area: ä Verify the width is 12. ä Type 18 in the Depth edit box. ä Type 1.5 in the Cover Top (to Centroid) edit box. ä Type 2.5 in the Cover Bottom (to Centroid) edit box. ä Verify the Concrete Strength, fc is 4. ä Verify the Reinforcing Yield Stress, fy is 60. ä Verify the Shear Steel Yield Stress, fys is 60. ä Verify the Concrete Shear Strength, fcs is 4. ä Verify that the No Design check box is not checked. À Click the OK button twice. 29. Click the drop down box in the status bar to change the units to kip-ft. 30. From the Define menu select Slab Properties... to display the Slab Properties dialog box. 10
11 31. In this dialog box: In the Slab Property area highlight the property named SLAB and then click the Modify/Show Property button to display the Slab Property Data dialog box. In this dialog box: À Verify that the unit weight is À Click the OK button twice to exit all dialog boxes. 32. From the Define menu select Beam Properties... to display the Beam Properties dialog box. 33. In this dialog box: In the Beam Property area highlight the property named XBEAM and then click the Modify/Show Property button to display the Property Data For Rectangular Beam dialog box. In this dialog box: À Verify that the unit weight is À Click the OK button. In the Beam Property area highlight the property named YBEAM and then click the Modify/Show Property button to display the Property Data For Rectangular Beam dialog box. In this dialog box: À Verify that the unit weight is À Click the OK button twice to exit all dialog boxes. 34. Click in the plan view window titled Slab Properties to make sure it is active. When the window is active its title bar is highlighted. 35. Click the Select All button on the main toolbar to select all elements. 36. From the Assign menu select Beam Properties... to display the Beam Properties dialog box. 37. In this dialog box: In the Beam Property list box click on YBEAM to highlight it. Click the OK button. The model now appears as shown in Figure
12 V Figure 3-4: Model After Step Select the four X-direction beams that are circled in Figure 3-4 by clicking on them. 39. From the Assign menu select Beam Properties... to display the Beam Properties dialog box. 40. In this dialog box: In the Beam Property list box click on XBEAM to highlight it. Click the OK button. 41. Right click somewhere on the slab area object not in the opening, for example at the point labeled V in Figure 3-4 to display the Rectangular Slab Information dialog box. 42. In this dialog box: Note that the Slab Property is SLAB and recall that we have already defined these properties. 12
13 Note that the Load Case drop-down box says DEAD and that the associated w/area edit box says This is the dead load we initially input (see step 3). Select LIVE from the Load Case drop-down box and note that the associated w/area edit box says 0.1. This is the live load we initially input (see step 3). Click the OK button. 43. From the Options menu select Preferences... and then select the Concrete Tab. 44. In this dialog box: Verify that ACI is selected in the Concrete Design Code drop-down box. Verify that in the Reinforcement Results Units area the Sq-in and Sq-in/ft option is selected. Click the OK button. 45. On the Design menu choose Select Design Combos to display the Design Load Combinations Selection dialog box. 46. In this dialog box: In the Design Combos list box click on DCON2 to highlight it and then click the Show button. Note that this load combination is defined as 1.4DL + 1.7LL. Also note that the Use For Design check box is checked. Note: SAFE automatically creates design load combinations based on the selected design code and on the static load types. In this case where the defined static load types are DEAD and LIVE (see Static Load Cases on the Define menu) and the design code is ACI , the program automatically creates two load cases. They are 1.4DL (DCON1) and 1.4DL + 1.7LL (DCON2). If we wanted to add an additional design load combination we could define it by selecting Load Combinations... from the Define menu and then clicking the Add New Combo button, to display the Load Combination data dialog box. In this dialog box we can define the load combination and we can check the Use For Design check box if we want the load combination to be used in design. Click the OK button twice to exit all dialog boxes. 47. From the Analyze menu select Set Options to display the Analysis Options dialog box. 48. In this dialog box: 13
14 In the Analysis Type area verify that the Normal option is selected. Accept the default maximum mesh dimension of 4 feet. Note: To automatically mesh the model the program first develops a mesh that is broken at each grid line, at the edge of any area objects, at the ends of each line object and at each point object. If the dimension of any elements meshed in this manner exceeds the specified maximum mesh dimension then those elements are subdivided such that the maximum mesh dimension is no longer exceeded. Note: In general, the maximum mesh size should be based on the span length. It is good practice to have at least four elements in a span, and generally it is not necessary to have more than eight elements in a span. Thus if the typical span length is less than sixteen feet, it may be advisable to reduce the default maximum mesh size to something less than 4 feet. In this example we are accepting the default maximum mesh of four feet. This means that the slab spanning between beams will be modeled using two elements which is less than the four elements recommended in the previous paragraph. If the accuracy of the slab results (moments, etc.) were important to us then we might want to reduce the maximum mesh size to 1.5 feet. Note: The mesh automatically generated by the program can be viewed by clicking the Set Objects button on the main toolbar (or selecting Set Object Options... from the View menu) to display the Set Objects dialog box, checking the Show Mesh check box in the Options area, and clicking the OK button. You can turn off the display of the mesh by unchecking this box. Click the OK button. 49. Click the Run Analysis button on the main toolbar (or select Run Analysis from the Analyze menu). 50. When the initial analysis is complete check the messages in the Analysis window (there should be no warnings or errors) and then click the OK button to close the Analysis window. 51. Click the Show Beam Forces button on the main toolbar (or select Show Beam Forces... from the Display menu) to display the Beam Forces dialog box. 52. In this dialog box: Select DCON2 Combo from the Load drop-down box. In the Component area select the Moment option. 14
15 In the Display options area check the Show Values check box. Note that if the Fill Diagram check box is checked you will have to uncheck it before you can check the Show Values box. Click the OK button to display the moment diagrams. 53. Run the mouse cursor over the beams and read the moment values from the left-hand side of the status bar at the bottom of the SAFE window. 54. If you want to view beam force results for other force components then repeat steps 51 through On the Design menu select Start Design. When the design is complete the calculated X- strip reinforcement is displayed in square inches. 56. From the Design menu select Display Beam Design Info... to display the Beam Reinforcing dialog box. 57. In this dialog box: In the Type of Reinforcing area verify that the Flexural option is chosen. In the Reinforcing Values area verify that the Show Rebar Values at Controlling Station check box is checked. In the Reinforcing Values area verify that the Show Rebar Values at Every Station check box is not checked. Accept the other default values in this dialog box. Click the OK button. 58. Run the mouse cursor over the beams and read the flexural steel values from the left-hand side of the status bar at the bottom of the SAFE window. 15
Important Note - Please Read:
 Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help
Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help
Problem O. Isolated Building - Nonlinear Time History Analysis. Steel E =29000 ksi, Poissons Ratio = 0.3 Beams: W24X55; Columns: W14X90
 Problem O Isolated Building - Nonlinear Time History Analysis Steel E =29000 ksi, Poissons Ratio = 0.3 Beams: W24X55; Columns: W14X90 Rubber Isolator Properties Vertical (axial) stiffness = 10,000 k/in
Problem O Isolated Building - Nonlinear Time History Analysis Steel E =29000 ksi, Poissons Ratio = 0.3 Beams: W24X55; Columns: W14X90 Rubber Isolator Properties Vertical (axial) stiffness = 10,000 k/in
ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode
 ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode Update: September 2018 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT-PT/RC 2017-Tutorial- 1 This ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial
ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode Update: September 2018 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT-PT/RC 2017-Tutorial- 1 This ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial
ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode
 ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode Update: January 2014 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT-PT/RC 2014-Tutorial- 1 This ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial
ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode Update: January 2014 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT-PT/RC 2014-Tutorial- 1 This ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial
SAFE DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE. Tutorial
 Tutorial SAFE DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE Tutorial ISO SAF112816M3 Rev. 0 Proudly developed in the United States of America November 2016 Copyright Copyright
Tutorial SAFE DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE Tutorial ISO SAF112816M3 Rev. 0 Proudly developed in the United States of America November 2016 Copyright Copyright
Idealization of Design Strip in ADAPT RC
 ADAPT RC 2010 Tutorial Idealization of Design Strip in ADAPT RC Update: May 2010 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT RC 2010 Tutorial 1 Main Toolbar Menu Bar View Toolbar Structure View
ADAPT RC 2010 Tutorial Idealization of Design Strip in ADAPT RC Update: May 2010 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT RC 2010 Tutorial 1 Main Toolbar Menu Bar View Toolbar Structure View
TUTORIAL INCLUDING PUSHOVER ANALYSIS
 SAP2000 Integrated Finite Elements Analysis and Design of Structures DETAILED TUTORIAL INCLUDING PUSHOVER ANALYSIS Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 6.20 Beta June 1998 COPYRIGHT
SAP2000 Integrated Finite Elements Analysis and Design of Structures DETAILED TUTORIAL INCLUDING PUSHOVER ANALYSIS Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 6.20 Beta June 1998 COPYRIGHT
CHECK STRESS ON DECK BASED ON SDI REQUIREMENTS
 ANALYSIS OF NON-COMPOSITE CONCRETE SLAB ON METAL DECK Lab #7 Question #2 A 6" total depth lightweight concrete slab with compressive strength of 3000psi is placed simply supported on a galvanized steel
ANALYSIS OF NON-COMPOSITE CONCRETE SLAB ON METAL DECK Lab #7 Question #2 A 6" total depth lightweight concrete slab with compressive strength of 3000psi is placed simply supported on a galvanized steel
Bridge Design using the STAAD.Pro/Beava AASHTO Code
 Bridge Design using the STAAD.Pro/Beava AASHTO Code By IEG Group, Bentley Systems Bentley Systems Inc. March 12, 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction.1 2.0 Creating the Bridge Geometry/Structural Analysis
Bridge Design using the STAAD.Pro/Beava AASHTO Code By IEG Group, Bentley Systems Bentley Systems Inc. March 12, 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction.1 2.0 Creating the Bridge Geometry/Structural Analysis
STRUCTURAL CONCRETE SOFTWARE ADAPT-ABI 2009 GETTING STARTED GUIDE. Copyright 2009
 STRUCTURAL CONCRETE SOFTWARE ADAPT-ABI 2009 GETTING STARTED GUIDE Copyright 2009 Copyright ADAPT Corporation 2009 all rights reserved support@adaptsoft.com www.adaptsoft.com ADAPT Corporation, Redwood
STRUCTURAL CONCRETE SOFTWARE ADAPT-ABI 2009 GETTING STARTED GUIDE Copyright 2009 Copyright ADAPT Corporation 2009 all rights reserved support@adaptsoft.com www.adaptsoft.com ADAPT Corporation, Redwood
ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE CONCRETE SLAB ON METAL DECK
 ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE CONCRETE SLAB ON METAL DECK Assignment #5 Select a Vulcraft composite deck to support 150 psf service live load on a 10 ft clear span. The steel deck is to be used on a three-span
ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE CONCRETE SLAB ON METAL DECK Assignment #5 Select a Vulcraft composite deck to support 150 psf service live load on a 10 ft clear span. The steel deck is to be used on a three-span
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC6 Two Span Reinforced Concrete Slab System Example
 AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC6 Two Span Reinforced Concrete Slab System Example AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training 6" A A 30'-0" 30'-0" B #11's #11's 1'-6"
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC6 Two Span Reinforced Concrete Slab System Example AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training 6" A A 30'-0" 30'-0" B #11's #11's 1'-6"
Advanced 3-D Tutorial
 Advanced 3-D Tutorial Introduction To demonstrate some of the features of VisualAnalysis we have put together this advanced tutorial for you to use. This tutorial assumes that you have a basic knowledge
Advanced 3-D Tutorial Introduction To demonstrate some of the features of VisualAnalysis we have put together this advanced tutorial for you to use. This tutorial assumes that you have a basic knowledge
1. Define the material properties. Activate the Data Entry menu if it s not already visible, and click on Materials.
 CE 533, Fall 2014 Guide for Using RISA3D 1 / 9 Example Structure. The procedure for calculating frequencies and modes shapes of a multidegree of freedom (MDOF) system will be demonstrated using the following
CE 533, Fall 2014 Guide for Using RISA3D 1 / 9 Example Structure. The procedure for calculating frequencies and modes shapes of a multidegree of freedom (MDOF) system will be demonstrated using the following
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
2D Tutorial. Project Description: Running VisualAnalysis: Setting Up the Project:
 2D Tutorial Project Description: This project has been set-up to demonstrate the basic features of VisualAnalysis. You will model and analyze the following two-dimensional frame with a curved glue-laminated
2D Tutorial Project Description: This project has been set-up to demonstrate the basic features of VisualAnalysis. You will model and analyze the following two-dimensional frame with a curved glue-laminated
WoodWorks Design Office User Guide U.S. Sizer Tutorial Instructions
 WoodWorks Design Office Sizer Shearwalls Connections Database Editor 2017 User Guide U.S. Sizer Tutorial Instructions For U.S. Design Office 11 Canadian Wood Council American Wood Council Developed by
WoodWorks Design Office Sizer Shearwalls Connections Database Editor 2017 User Guide U.S. Sizer Tutorial Instructions For U.S. Design Office 11 Canadian Wood Council American Wood Council Developed by
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
SAP 2000 Problem II Homework Problem P5.45. Recall from Lab #6 the Global and Local Reference Coordinate Systems for 2D Problems
 SAP 2000 Problem II Homework Problem P5.45 Recall from Lab #6 the Global and Local Reference Coordinate Systems for 2D Problems Z 2 Global (XYZ) Coordinate System Joint Displacements Applied Point Loads
SAP 2000 Problem II Homework Problem P5.45 Recall from Lab #6 the Global and Local Reference Coordinate Systems for 2D Problems Z 2 Global (XYZ) Coordinate System Joint Displacements Applied Point Loads
AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015
 AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015 M N D O T B R I D G E S T A T E A I D Page 1 PS1 - Simple Span Prestressed I Beam Example (BrR 6.7.1) 1. From the Bridge Explorer create
AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015 M N D O T B R I D G E S T A T E A I D Page 1 PS1 - Simple Span Prestressed I Beam Example (BrR 6.7.1) 1. From the Bridge Explorer create
System Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006
 System Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation SYSTEM COMPONENTS FOR PRECAST CONCRETE ii
System Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation SYSTEM COMPONENTS FOR PRECAST CONCRETE ii
Concrete Plate Concrete Slab (ACI )
 Tutorial Tutorial Concrete Plate Concrete Slab (ACI 318-08) Tutorial Concrete Plate All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced,
Tutorial Tutorial Concrete Plate Concrete Slab (ACI 318-08) Tutorial Concrete Plate All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced,
Piping Design. Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index
 Piping Design Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-2001. All rights reserved. Site Map Piping Design member member
Piping Design Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-2001. All rights reserved. Site Map Piping Design member member
Steel Structures Tutorial
 AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Steel Structures Tutorial STL8 Pin and Hanger Rolled Beam Example Topics Covered Steel rolled beam with cover plates input as girder system. Schedule based input. Pin and hanger
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Steel Structures Tutorial STL8 Pin and Hanger Rolled Beam Example Topics Covered Steel rolled beam with cover plates input as girder system. Schedule based input. Pin and hanger
Finite Element Analysis of a 10 x 22 FRP Building for TRACOM Corporation
 Finite Element Analysis of a 10 x 22 FRP Building for TRACOM Corporation May 29, 2007 A. Background TRACOM Corporation designs and constructs Fiber Reinforced Plastic Buildings for use as shelters around
Finite Element Analysis of a 10 x 22 FRP Building for TRACOM Corporation May 29, 2007 A. Background TRACOM Corporation designs and constructs Fiber Reinforced Plastic Buildings for use as shelters around
Tutorial. External Application Checks using Excel
 Tutorial External Application Checks using Excel External Application Checks for Excel All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced,
Tutorial External Application Checks using Excel External Application Checks for Excel All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced,
cover to the center of the bars depth of bottom reinforcement (h cover) depth of top reinforcement (h cover)
 Interaction (ACI318) Checker today Input Column dimensions Reinforcement Materials (steel, concrete, bolts) Output Moment capacity Column interaction diagram RC Column Capacity - Axial Force - Bending
Interaction (ACI318) Checker today Input Column dimensions Reinforcement Materials (steel, concrete, bolts) Output Moment capacity Column interaction diagram RC Column Capacity - Axial Force - Bending
Steel Structure Tutorial
 AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Steel Structure Tutorial STL5 - Two Span Rolled Beam Example BrD and BrR Training STL5 - Two Span Rolled Beam Example Topics Covered Steel rolled beam with cover plates input as
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Steel Structure Tutorial STL5 - Two Span Rolled Beam Example BrD and BrR Training STL5 - Two Span Rolled Beam Example Topics Covered Steel rolled beam with cover plates input as
Basic Modeling 1 Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006
 Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents 3 1 5 1.1 Start Tekla Structures 6 1.2 Create a New Model BasicModel1 7 1.3 Create Grids 10 1.4
Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents 3 1 5 1.1 Start Tekla Structures 6 1.2 Create a New Model BasicModel1 7 1.3 Create Grids 10 1.4
Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu.
 1. BEAM MODEL Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a new model with the New Icon. In the dialogue
1. BEAM MODEL Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a new model with the New Icon. In the dialogue
Version October 2015 RFEM 5. Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method. Introductory Example
 Version October 2015 Program RFEM 5 Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method Introductory Example All rights, including those of translations, are reserved. No portion of this book may be
Version October 2015 Program RFEM 5 Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method Introductory Example All rights, including those of translations, are reserved. No portion of this book may be
FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING
 FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Purpose of FB-MultiPier Validation testing Performing validation of structural analysis software delineates the capabilities and limitations
FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Purpose of FB-MultiPier Validation testing Performing validation of structural analysis software delineates the capabilities and limitations
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
Advance Design. Tutorial
 TUTORIAL 2018 Advance Design Tutorial Table of Contents About this tutorial... 1 How to use this guide... 3 Lesson 1: Preparing and organizing your model... 4 Step 1: Start Advance Design... 5 Step 2:
TUTORIAL 2018 Advance Design Tutorial Table of Contents About this tutorial... 1 How to use this guide... 3 Lesson 1: Preparing and organizing your model... 4 Step 1: Start Advance Design... 5 Step 2:
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
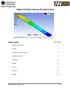 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
RSPile. Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis. Pile Analysis Software. Grouped Pile Analysis
 RSPile Pile Analysis Software Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis Grouped Pile Analysis Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate how to model grouped piles under a cap. The finished product of this tutorial
RSPile Pile Analysis Software Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis Grouped Pile Analysis Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate how to model grouped piles under a cap. The finished product of this tutorial
CME-TRUSS (Version 2.1) User's Manual
 CME-TRUSS (Version 2.1) User's Manual INTRODUCTION CME-TRUSS is an interactive program for structural analysis of two-dimensional trusses. The software is written in the Microsoft Visual Basic for Windows
CME-TRUSS (Version 2.1) User's Manual INTRODUCTION CME-TRUSS is an interactive program for structural analysis of two-dimensional trusses. The software is written in the Microsoft Visual Basic for Windows
SAFI Sample Projects. Design of a Steel Structure. SAFI Quality Software Inc. 3393, chemin Sainte-Foy Ste-Foy, Quebec, G1X 1S7 Canada
 SAFI Sample Projects Design of a Steel Structure SAFI Quality Software Inc. 3393, chemin Sainte-Foy Ste-Foy, Quebec, G1X 1S7 Canada Contact: Rachik Elmaraghy, P.Eng., M.A.Sc. Tel.: 1-418-654-9454 1-800-810-9454
SAFI Sample Projects Design of a Steel Structure SAFI Quality Software Inc. 3393, chemin Sainte-Foy Ste-Foy, Quebec, G1X 1S7 Canada Contact: Rachik Elmaraghy, P.Eng., M.A.Sc. Tel.: 1-418-654-9454 1-800-810-9454
Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution
Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution
AASHTOWare BrR/BrD 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC1 Single Span Reinforced Concrete Tee Beam Example
 AASHTOWare BrR/BrD 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC1 Single Span Reinforced Concrete Tee Beam Example BrR and BrD Training RC1 - Single Span Reinforced Concrete Tee Beam Example From the Bridge
AASHTOWare BrR/BrD 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC1 Single Span Reinforced Concrete Tee Beam Example BrR and BrD Training RC1 - Single Span Reinforced Concrete Tee Beam Example From the Bridge
AISIBEAM User's Manual (Version 3.0)
 AISIBEAM User's Manual (Version 3.0) Shabin Taavoni, Ph.D., PE, title Structural Software Inc. location John C. Huang Ph.D., PE, Principal CHC Engineering, LLC Herndon, VA Scope of Software The software
AISIBEAM User's Manual (Version 3.0) Shabin Taavoni, Ph.D., PE, title Structural Software Inc. location John C. Huang Ph.D., PE, Principal CHC Engineering, LLC Herndon, VA Scope of Software The software
WinAqua TUTORIAL WinAqua
 WinAqua TUTORIAL WinAqua WinAqua TUTORIAL Copyright SOFiSTiK AG, D-81514 Műnchen, 1990-2002 This documentation is protected by copyright. No part of it may be reproduced, translated or rewritten in any
WinAqua TUTORIAL WinAqua WinAqua TUTORIAL Copyright SOFiSTiK AG, D-81514 Műnchen, 1990-2002 This documentation is protected by copyright. No part of it may be reproduced, translated or rewritten in any
discontinuity program which is able to calculate the seam stress and displacement in an underground mine. This program can also
 LAMODEL- This is a full-featured featured displacement- discontinuity program which is able to calculate the seam stress and displacement in an underground mine. This program can also reasonably calculate
LAMODEL- This is a full-featured featured displacement- discontinuity program which is able to calculate the seam stress and displacement in an underground mine. This program can also reasonably calculate
Three- Span Continuous Horizontally Curved. Composite Steel TUB Girder Bridge
 Three- Span Continuous Horizontally Curved Composite Steel TUB Girder Bridge WIZARD, ANALYSIS AND DESIGN TUB Girder Curved Contents Bridge Information Material and Section Properties Wizard Modelling Tweaks
Three- Span Continuous Horizontally Curved Composite Steel TUB Girder Bridge WIZARD, ANALYSIS AND DESIGN TUB Girder Curved Contents Bridge Information Material and Section Properties Wizard Modelling Tweaks
General Information Project management Introduction... 4 Getting Started Input geometry... 7
 Tutorial Shell Tutorial Shell All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database or retrieval system or published,
Tutorial Shell Tutorial Shell All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database or retrieval system or published,
User s Manual ❹ Tools
 User s Manual ❹ Tools 2 CONTENTS I. THE NEW UPGRADED INTERFACE of SCADA Pro 5 II. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE NEW INTERFACE 6 1. Tools 6 1.1 Structural Elements 6 1.2 USC-WCS 12 1.3 Model 13 1.4 Members
User s Manual ❹ Tools 2 CONTENTS I. THE NEW UPGRADED INTERFACE of SCADA Pro 5 II. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE NEW INTERFACE 6 1. Tools 6 1.1 Structural Elements 6 1.2 USC-WCS 12 1.3 Model 13 1.4 Members
STL1 - Simple Span Plate Girder Example
 STL1 - Simple Span Plate Girder Example 1'-9" 47'-6" 44'-0" 1'-9" 10" including 1/2" int. wearing surface 4'-3" 3 spaces @ 13'-0" = 39'-0" 4'-3" 13'-0" 13'-0" 13'-0" 6 spaces @ 26'-10" 161'-0" Framing
STL1 - Simple Span Plate Girder Example 1'-9" 47'-6" 44'-0" 1'-9" 10" including 1/2" int. wearing surface 4'-3" 3 spaces @ 13'-0" = 39'-0" 4'-3" 13'-0" 13'-0" 13'-0" 6 spaces @ 26'-10" 161'-0" Framing
Step by Step. Tutorial for AxisVM X4. Edited by: Inter-CAD Kft.
 Step by Step Tutorial for AxisVM X4 Edited by: Inter-CAD Kft. 2018 Inter-CAD Kft. All rights reserved All brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks. Intentionally blank page Step
Step by Step Tutorial for AxisVM X4 Edited by: Inter-CAD Kft. 2018 Inter-CAD Kft. All rights reserved All brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks. Intentionally blank page Step
Revit Structure 3 ETABS Data Exchange
 Revit Structure 3 ETABS Data Exchange Overview This document describes how to exchange Building Information Modeling (BIM) data between Revit Structure 3 and ETABS, a three-dimensional physical object
Revit Structure 3 ETABS Data Exchange Overview This document describes how to exchange Building Information Modeling (BIM) data between Revit Structure 3 and ETABS, a three-dimensional physical object
Tekla Structures Analysis Guide. Product version 21.0 March Tekla Corporation
 Tekla Structures Analysis Guide Product version 21.0 March 2015 2015 Tekla Corporation Contents 1 Getting started with analysis... 7 1.1 What is an analysis model... 7 Analysis model objects...9 1.2 About
Tekla Structures Analysis Guide Product version 21.0 March 2015 2015 Tekla Corporation Contents 1 Getting started with analysis... 7 1.1 What is an analysis model... 7 Analysis model objects...9 1.2 About
Tutorial 3: Constructive Editing (2D-CAD)
 (2D-CAD) The editing done up to now is not much different from the normal drawing board techniques. This section deals with commands to copy items we have already drawn, to move them and to make multiple
(2D-CAD) The editing done up to now is not much different from the normal drawing board techniques. This section deals with commands to copy items we have already drawn, to move them and to make multiple
Revised Iain A MacLeod
 LUSAS User Guidelines Revised 01.07.15 Iain A MacLeod Contents 1 Geometrical features and meshes... 1 2 Toolbars... 2 3 Inserting points... 2 4 Inserting a line between two points... 2 5 Creating a dataset...
LUSAS User Guidelines Revised 01.07.15 Iain A MacLeod Contents 1 Geometrical features and meshes... 1 2 Toolbars... 2 3 Inserting points... 2 4 Inserting a line between two points... 2 5 Creating a dataset...
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis
 Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis 1. The software is available at the Open Access Labs (OAL) and the Virtual OAL at http://voal.tamu.edu in Programs under the Windows Start menu. The software can also
Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis 1. The software is available at the Open Access Labs (OAL) and the Virtual OAL at http://voal.tamu.edu in Programs under the Windows Start menu. The software can also
Concept Mode Tutorial 5 Two Storey House (CDN)
 Concept Mode Tutorial 5 Two Storey House (CDN) The Sizer file (.wwa) created from going through this tutorial can be downloaded by clicking here. 5.1 Introduction In this tutorial you will create and design
Concept Mode Tutorial 5 Two Storey House (CDN) The Sizer file (.wwa) created from going through this tutorial can be downloaded by clicking here. 5.1 Introduction In this tutorial you will create and design
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Truss Bridge Analysis Using SAP2000
 Truss Bridge Analysis Using SAP2000 SAP2000 is a structural analysis and design program that allows users to create and test a computer animated model of their figure. The program calculates dead loads,
Truss Bridge Analysis Using SAP2000 SAP2000 is a structural analysis and design program that allows users to create and test a computer animated model of their figure. The program calculates dead loads,
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Floor System Tutorial FS1 - Girder Floorbeam Stringer Example
 AAHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Floor ystem Tutorial F1 - Girder Floorbeam tringer Example CL 2'-0" 15'-0" 15'-0" 2'-0" 9" 21WF62 (typ) 5 spaces @ 6 = 30-0 Concrete curb & railing = 0.3k/ft each side Fy = 36ksi
AAHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Floor ystem Tutorial F1 - Girder Floorbeam tringer Example CL 2'-0" 15'-0" 15'-0" 2'-0" 9" 21WF62 (typ) 5 spaces @ 6 = 30-0 Concrete curb & railing = 0.3k/ft each side Fy = 36ksi
Exam 1 Problem #1. Exam Solution - Problem #1. Given information. Temperatures. Thermal Resistance
 Exam 1 Problem #1 Calculate the coefficient of thermal transmittance, U, and the thermal gradient through the wall. Exam Solution - Problem #1 Given information Temperatures To Ti 32 F 68 F Thermal Resistance
Exam 1 Problem #1 Calculate the coefficient of thermal transmittance, U, and the thermal gradient through the wall. Exam Solution - Problem #1 Given information Temperatures To Ti 32 F 68 F Thermal Resistance
3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) Figure 3.1 Geometry of a circular footing on a sand layer
 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
TABLE OF CONTENTS WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN? INSTALLING ADVANCE DESIGN... 8 System requirements... 8 Advance Design installation...
 Starting Guide 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Welcome to Advance Design... 5 About this guide... 6 Where to find information?... 6 Contacting technical support... 6 WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN?...
Starting Guide 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Welcome to Advance Design... 5 About this guide... 6 Where to find information?... 6 Contacting technical support... 6 WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN?...
CONCRETE DESIGN SOFTWARE LIBRARY
 CONCRETE DESIGN SOFTWARE LIBRARY DESIGN AND INVESTIGATION OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTINUOUS BEAMS PORTLAND CEMENT ASSOCIATION 5420 Old Orchard Road, Skokie, Illinois 60077-1083 Telephone: (847) 966-4357
CONCRETE DESIGN SOFTWARE LIBRARY DESIGN AND INVESTIGATION OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTINUOUS BEAMS PORTLAND CEMENT ASSOCIATION 5420 Old Orchard Road, Skokie, Illinois 60077-1083 Telephone: (847) 966-4357
Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran
 Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode 2
 5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 5 minutes Discipline: Concrete Shell Reinforcement
5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 5 minutes Discipline: Concrete Shell Reinforcement
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 2
 ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 2 In this homework assignment you will use your rapidly developing ANSYS skill set to model and analyze three different
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 2 In this homework assignment you will use your rapidly developing ANSYS skill set to model and analyze three different
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Floor System Tutorial
 AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Floor System Tutorial FS3 - Floorbeam Stringer Floor System Example Topics Covered Superstructure composed of floorbeams and stringers System Superstructure Definition Rolled beam
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Floor System Tutorial FS3 - Floorbeam Stringer Floor System Example Topics Covered Superstructure composed of floorbeams and stringers System Superstructure Definition Rolled beam
Background CE 342. Why RISA-2D? Availability
 Background CE 342 RISA-2D RISA-2D is a structural analysis program, which can model: Beams, frames, trusses and plates. Any linear elastic structural material. Typical supports, such as pins, rollers and
Background CE 342 RISA-2D RISA-2D is a structural analysis program, which can model: Beams, frames, trusses and plates. Any linear elastic structural material. Typical supports, such as pins, rollers and
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
Tutorial AISC Steel Frame Building
 Tutorial AISC 360-05 Steel Frame Building Tutorial Frame Steel All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database
Tutorial AISC 360-05 Steel Frame Building Tutorial Frame Steel All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database
General Information... 1 Introduction... 2 Getting started Starting a project Project management... 6
 Tutorial Tutorial Steel Hall AISC (AISC Steel 360-10) Hall Tutorial Frame Steel All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced,
Tutorial Tutorial Steel Hall AISC (AISC Steel 360-10) Hall Tutorial Frame Steel All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced,
ADAPT MAT RC Tutorial (SI units with European Code EC2) Update: April 2010 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved
 ADAPT MAT RC Tutorial (SI units with European Code EC2) Update: April 2010 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT MAT RC Tutorial (SI units with European Code EC2) I TABLE OF CONTENTS 1
ADAPT MAT RC Tutorial (SI units with European Code EC2) Update: April 2010 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT MAT RC Tutorial (SI units with European Code EC2) I TABLE OF CONTENTS 1
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis
 Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
EXAMPLE 1. Static Analysis of Cantilever Column (Fixed-Base Column)
 EXAMPLE 1 Static Analysis of Cantilever Column (Fixed-Base Column) Calculate the top displacement, axial force, shear force and bending moment diagrams for the fixed base column described in the figure
EXAMPLE 1 Static Analysis of Cantilever Column (Fixed-Base Column) Calculate the top displacement, axial force, shear force and bending moment diagrams for the fixed base column described in the figure
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
Dynamics and Vibration. Tutorial
 Dynamics and Vibration Tutorial Startup To use Dynamics and Vibration Analysis (DVA), you must first start TK Solver. Once in TK, select Dynamics & Vibration from the Applications Menu. The DVA Menu will
Dynamics and Vibration Tutorial Startup To use Dynamics and Vibration Analysis (DVA), you must first start TK Solver. Once in TK, select Dynamics & Vibration from the Applications Menu. The DVA Menu will
Quick Start Guide. ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. Toll free: Fax:
 Quick Start Guide ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. Toll free: 1-800-818-2051 Phone: 604-539-0122 e-mail: support@asrsoft.com Fax: 604-539-1334 www.asrsoft.com Copyright 1991-2014 ASR Automated Systems
Quick Start Guide ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. Toll free: 1-800-818-2051 Phone: 604-539-0122 e-mail: support@asrsoft.com Fax: 604-539-1334 www.asrsoft.com Copyright 1991-2014 ASR Automated Systems
RISA-3D TO REVIT Structure Grid Lines Columns, Beams, and Braces Footings Boundary Conditions Structural Walls...
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 3 Why Revit Structure and RISA?... 4 Install the RISA-Revit Structure Link Component... 4 Version Information... 5 Component Information... 5 Compatibility
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 3 Why Revit Structure and RISA?... 4 Install the RISA-Revit Structure Link Component... 4 Version Information... 5 Component Information... 5 Compatibility
Oasys GSA. Getting Started
 Getting Started 13 Fitzroy Street London W1T 4BQ Telephone: +44 (0) 20 7755 3302 Facsimile: +44 (0) 20 7755 3720 Central Square Forth Street Newcastle Upon Tyne NE1 3PL Telephone: +44 (0) 191 238 7559
Getting Started 13 Fitzroy Street London W1T 4BQ Telephone: +44 (0) 20 7755 3302 Facsimile: +44 (0) 20 7755 3720 Central Square Forth Street Newcastle Upon Tyne NE1 3PL Telephone: +44 (0) 191 238 7559
RISA-2D. Tutorials. Rapid Interactive Structural Analysis 2-Dimensional. risa.com
 RISA-2D Rapid Interactive Structural Analysis 2-Dimensional Tutorials RISA Tech, Inc. 26632 Towne Centre Drive, Suite 210 Foothill Ranch, California 92610 (949) 951-5815 (949) 951-5848 (FAX) risa.com Copyright
RISA-2D Rapid Interactive Structural Analysis 2-Dimensional Tutorials RISA Tech, Inc. 26632 Towne Centre Drive, Suite 210 Foothill Ranch, California 92610 (949) 951-5815 (949) 951-5848 (FAX) risa.com Copyright
Revised Iain A MacLeod
 LUSAS User Guidelines Revised 20.06.14 Iain A MacLeod Contents 1 Geometrical features and meshes... 1 2 Toolbars... 1 3 Inserting points... 1 4 Inserting a line between two points... 1 5 Creating a dataset...
LUSAS User Guidelines Revised 20.06.14 Iain A MacLeod Contents 1 Geometrical features and meshes... 1 2 Toolbars... 1 3 Inserting points... 1 4 Inserting a line between two points... 1 5 Creating a dataset...
SAFE 2014 (v14.1.0) Release Notes
 SAFE 2014 (v14.1.0) Release Notes Copyright Computers and Structures, Inc., 2015 Notice Date: 2015-06-12 This file lists all changes made to SAFE since the previous version. Most changes do not affect
SAFE 2014 (v14.1.0) Release Notes Copyright Computers and Structures, Inc., 2015 Notice Date: 2015-06-12 This file lists all changes made to SAFE since the previous version. Most changes do not affect
TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior Initial Project Space Setup Static Structural ANSYS ZX Plane
 TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior In this tutorial you will learn how to recognize and deal with a common modeling issues involving stress concentrations
TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior In this tutorial you will learn how to recognize and deal with a common modeling issues involving stress concentrations
v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Underwater Slope Use a slope geometry line to build a model in UTEXAS of an underwater slope
 v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial Use a slope geometry line to build a model in UTEXAS of an underwater slope Objectives Illustrate how to build a UTEXAS model in GMS that uses a slope geometry line. This tutorial
v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial Use a slope geometry line to build a model in UTEXAS of an underwater slope Objectives Illustrate how to build a UTEXAS model in GMS that uses a slope geometry line. This tutorial
SAP2000, ETABS and Revit Structure 2014 Data Exchange Documentation
 SAP2000, ETABS and Revit Structure 2014 Data Exchange Documentation ISO XRV070113M1 Rev. 0 Version 2014 Berkeley, California, USA June 2013 2 Copyright Copyright Computers and Structures, Inc., 2013 All
SAP2000, ETABS and Revit Structure 2014 Data Exchange Documentation ISO XRV070113M1 Rev. 0 Version 2014 Berkeley, California, USA June 2013 2 Copyright Copyright Computers and Structures, Inc., 2013 All
Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids
 Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Custom Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006
 Custom Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents...i 4...3 4.1 Define Custom Part of Fastener Plate...3
Custom Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents...i 4...3 4.1 Define Custom Part of Fastener Plate...3
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Tutorial. Parametric input
 Tutorial Parametric input Tutorial Parametric Input All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database or retrieval
Tutorial Parametric input Tutorial Parametric Input All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database or retrieval
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Step 3. Rectangle. Fig. 1. Step 6. For the Placement Point, click the bottom left gray rectangle and click OK, Fig. 2. to fit the drawing on screen.
 Chapter 24 BOAT SOLID A. Name Level. Hold down ALT and press Z. Step 2. Key-in block for Name and click OK, Fig. 1. B. Create Rectangle. Step 3. Rectangle. Fig. 1 Step 4. 1 Point. Step 5. Key-in 9 for
Chapter 24 BOAT SOLID A. Name Level. Hold down ALT and press Z. Step 2. Key-in block for Name and click OK, Fig. 1. B. Create Rectangle. Step 3. Rectangle. Fig. 1 Step 4. 1 Point. Step 5. Key-in 9 for
UTEXAS Underwater Slope
 GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS Figure 1. Underwater Slope Excavation Problem. 1 Introduction This tutorial illustrates how to build a UTEXAS model in GMS that uses a slope geometry line. This tutorial is similar to
GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS Figure 1. Underwater Slope Excavation Problem. 1 Introduction This tutorial illustrates how to build a UTEXAS model in GMS that uses a slope geometry line. This tutorial is similar to
General Section Designer
 Contents GSD Overview General Section Designer Step : Material Properties Step : Section Step : Rebars Step : Load Combination Step 5: Design Options Step 6: Results Data Exchange: AutoCAD, midas Gen Design
Contents GSD Overview General Section Designer Step : Material Properties Step : Section Step : Rebars Step : Load Combination Step 5: Design Options Step 6: Results Data Exchange: AutoCAD, midas Gen Design
Multiframe Windows Version 16. User Manual
 Multiframe Windows Version 16 User Manual Bentley Systems, Incorporated 2013 License & Copyright Multiframe Program & User Manual 2013 Bentley Systems, Incorporated iii Table of Contents License & Copyright...
Multiframe Windows Version 16 User Manual Bentley Systems, Incorporated 2013 License & Copyright Multiframe Program & User Manual 2013 Bentley Systems, Incorporated iii Table of Contents License & Copyright...
1 General Principles. General Principles. In this chapter 1-1
 1 General Principles In this chapter 1 General Principles 1.1 User Interface 1.2 Title bar 1.3 Menu bar 1.4 Standard Toolbar 1.5 The drawing area 1.6 Component tabs 1.7 Status Bar 1.8 Manipulating Components
1 General Principles In this chapter 1 General Principles 1.1 User Interface 1.2 Title bar 1.3 Menu bar 1.4 Standard Toolbar 1.5 The drawing area 1.6 Component tabs 1.7 Status Bar 1.8 Manipulating Components
Steel connections design According to EC3. User s Manual
 Steel connections design According to EC3 User s Manual Version 1.0 April 2017 Contents 1 COPYRIGHT... 5 2 DISCLAIMER... 6 3 PRAXIS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 7 4 BASE PLATE CONNECTION... 10 4.1 Column...
Steel connections design According to EC3 User s Manual Version 1.0 April 2017 Contents 1 COPYRIGHT... 5 2 DISCLAIMER... 6 3 PRAXIS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 7 4 BASE PLATE CONNECTION... 10 4.1 Column...
DRY EXCAVATION USING A TIE BACK WALL
 3 This example involves the dry construction of an excavation. The excavation is supported by concrete diaphragm walls. The walls are tied back by prestressed ground anchors. Silt Sand 10 m 2 m 20 m 10
3 This example involves the dry construction of an excavation. The excavation is supported by concrete diaphragm walls. The walls are tied back by prestressed ground anchors. Silt Sand 10 m 2 m 20 m 10
SAP2000, ETABS, SAFE and Revit 2018 Data Exchange Documentation
 SAP2000, ETABS, SAFE and Revit 2018 Data Exchange Documentation ISO XRV080317M1 Rev. 0 Version 2018.0 Proudly developed in the United States of America August 2017 Copyright Copyright Computers and Structures,
SAP2000, ETABS, SAFE and Revit 2018 Data Exchange Documentation ISO XRV080317M1 Rev. 0 Version 2018.0 Proudly developed in the United States of America August 2017 Copyright Copyright Computers and Structures,
