This chapter deals with CSM LIM Configuration:
|
|
|
- Justin Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
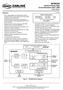
1 CHAPTER 14 This chapter deals with LIM Configuration: General, page 14-1 Circuit Emulation Service (CES), page Application, page 14-3 Line Configuration, page 14-4 Maintenance, page CES Configuration, page History, page Statistics, page CES Configuration Procedures, page General The Compact Subscriber Module () supports Circuit Emulation Services (CES) on an E1/DS1 interface. The (DS1 and E1 interfaces) provides adaptation from time-division multiplexed (TDM) equipment (i.e. PBX s, WAN multiplexers, channel banks, video codecs, etc.) and traffic to ATM. In both E1 and DS1 modes structured and unstructured services can be provided with a maximum of 96 and 120 connections supported on each module. The Network Module has 4 ports which support fractional DS1 services (n x 56 kbps/n 64 kbps) where 1 to 24 contiguous or non-contiguous DS0 channels are mapped to a single ATM VCC not to exceed 127 total connections. Structured services provide digital access and cross-connect system connectivity where n x 64 kbps and n x 56 kbps digital signal level zero (DS0) channels are adapted to ATM cells and mapped to unique ATM virtual connections (VCCs). Unstructured services provide support and maintenance of a single full bandwidth Mbps (DS1) or Mbps (E1) clear channel across a single ATM virtual connection. Configurations of both the DS1 and the E1 version of the module are detailed in this chapter. The, shown in Figure 14-1 utilizes the AAL1 SAR and enables transferring PBX calls over an ATM network. Its front panel is shown in Figure 1-5 (chapter 1). Figure 14-1 in system 14-1
2 Circuit Emulation Service (CES) Chapter 14 Ethernet IP Telephone 0, 1, 23 D:0, D:0...D:0 AAL5 SAR Management (DS1/E1) TDM CBR PBX (DS1/E1) (DS1/E1) (DS1/E1) AAL1 SAR - CES Cells Cells Cisco 8110 E3 ATM Figure 14-2 ATM Layers CES AAL1 ATM DS1 E Circuit Emulation Service (CES) The Cisco 8110 supports up to two 7810 modules, each providing 4 CES User ports. Port and Service modes and parameters can be configured. CES is an option supported by Cisco 8110 software release 4.0 and up. To add CES support to the Cisco 8110 at least one CM7810 module should be installed in interface slots 1 or 3 (User side). The Cisco 8110 supports two of these modules. Each 7810 supports 4 ports than can be configured to be 4xT1 or 4xE1 interfaces. CES mode can be selected for each port to be UDT or SDT. 14-2
3 Chapter Application Figure 14-3 Circuit Emulation Service Signal Flow TDM ATM 4xT1 or 4xE1 interface AAL1 adapter Cisco 8110 LIM Application TDM Ports The four TDM ports can be selected to be either E1 or T1, for each The framing format and line code can be selected. Supported line codes are: For T1: B8ZS and AMI For E1: HDB3 Supported framing formats are: For T1: SF and ESF For E1: FAS, MFAS, FAS+CRC, MFAS+CRC Channels may be programmed individually to carry CAS signaling or not. Different option of trunk conditioning in case of failures are provided. Maintenance and statistics are accumulated for each port in a similar way to other LIM cards, but no cells related parameters are accumulated (Ingress, Egress and Errored cells), since the interface is TDM and not ATM. The 7810 can provide the Cisco 8110 clock source from the recovered clock of any of its input signals. CES modes UDT and SDT modes are supported on a per port basis. In UDT mode only one service can be configured per port. The alarms handling can be selected to handle only LOS alarms, to handle LOS and monitor all other frame alarms, or to monitor and handle all frame alarms. In SDT mode up to 24 (T1) or 31 (E1) services can be configured per port. Each service may include between one and all channels of a port. Each service can be selected to carry or not CAS signaling. 14-3
4 Line Configuration Chapter 14 In both modes the clock recovery scheme can be selected. The supported schemes are: Internal, Adaptive and Loop timed. Cells fill level can be set to reduce delay. ATM Level Each service should be associated with a VC. The VC features are the same as for a regular VC in the Network side. In the User side no OAM generation or handling is performed, since the ATM Interface in the User side is internal to the Cisco By default CES related alarms will not force VC-AIS alarms. VC alarms are reported to the CES level for consequent actions. Line Configuration The card is configured on both the CBR and ATM side. Configuration of the CBR side of the may be performed using the following menus. Access to configuration is via the DSX1 configuration menu. Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 When you log into the Cisco 8110 and type? at the prompt, the Root Menu is displayed Type any portion of the word configuration and press RETURN. Then type? and press RETURN. The Configuration Menu is displayed. Type dsx1 at the prompt and press RETURN. Then type? and press RETURN to display the DSX1 Configuration menu: Figure 14-4 DSX1 Configuration Menu Cisco 8110::host:configuration:dsx1$? line_typebuild_out attenuation line_bal payloadcoset csm> alarm> pm>up top exit? LINE_TYPE This command allows the user to select the protocol (E1, T1) This selection remains until reconfigured. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: line_type <lim 1..3> (t1 e1) <lim 1..3> e1 t1 LIM selection Selects E1 mode Selects T1(DS1) mode BUILD_OUT This command sets the physical interface line buildout characteristics for -T1 and LIM-T1 modes. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: T-1 Mode Only usage: build_out <lim1..3> ( all) short long) 14-4
5 Chapter 14 Line Configuration <lim 1..3> LIM selection short less than 133 feet feet feet feet feet long Over 655 feet. ATTENUATIONThis command is used to set the attenuation in LIM-T1 and CMS-T1 (when build-out is long). At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: attenuation <lim 1..3> ( all) (0db 7.5db 15db 22.5db) <lim 1..3> LIM selection 0db 0 db attenuation 7.5db 7.5 db attenuation 15db 15 db attenuation 22.5db 22.5 db attenuation LINE_BAL This command is used to enable or disable line balance for LIM-E1. usage: line_bal <lim 1..3> (balance unbalance) <1..3> LIM selection balnce unbalance Enable / disable line balance PAYLOAD This command enables the payload scrambling at the ATM level for all types of LIM (i.e. LIM-E1, LIM-T1). usage: payload <lim 1..3> ( all) (scrambling none) <1..3> LIM selection 14-5
6 Line Configuration Chapter 14 scramling none enables payload scrambling disabled COSET An ATM parameter which indicates when to calculate the header error correction bit if it is to be ORed with another value or not (known as the COSET Polynomial). It is applicable for LIM-E1 and LIM-T1. usage: coset <lim 1..3> ( all) (enable disable) <1..3> LIM selection enable disable activates / deactivates Coset This command configures the Circuit Emulation Services. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following screen is displayed: Figure 14-5 Configuration submenu Cisco 8110::host::configuration:dsx1:csm$? t1_framing e1_framing line_code trunk_condition dt_mode udt_alarm clock_source clock_recovery up top exit? T1_FRAMING This command is used to enable or disable CAS (Channel Associated Signalling). the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: t1_framing <lim 1..3> ( all) (esf sf) At <lim 1..3> LIM selection esf Extended super-frame sf Super-frame E1_FRAMING This command is used to enable or disable Channel Associated Signalling. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: e1_framing <lim 1..3> ( all) (e1 crc_e1 mf crc_mf) <lim 1..3> LIM selection 14-6
7 Chapter 14 Line Configuration e1 crc_e1 mf crc_mf E1 mode Cyclic redundancy Check. in E1 mode Multiframe (SDT Mode Only) CRC and Mutiframe mode (SDT Mode Only) LINE_CODE This command defines the line encoding in T1 mode only and allows selection between two standards: AMI or B8ZS. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: line_code <lim 1..3> ( all) (b8zs ami) <lim 1..3> LIM selection b8zs ami Selection of standard TRUNK_CONDITION This command is used to enable the trunk conditioning option for SDT mode. This configures the a,b,c,d (a,b in T1-SF mode) bit. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: trunk_condition {<ch val 0..0xff>} <lim 1..3> ( all) (mode_01 mode_10 only_1 only_0 none) <lim 1..3> LIM selection mode_01 mode 01 enabled mode_10 mode 10 enabled only_1 mode 1 enabled only_0 mode 0 enabled none no mode selected <0..0xff> channel value DT_MODE This command is used to select the type of data transfer ( structured or unstructured). At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: dt_mode <lim 1..3> ( all) (sdt udt) <lim 1..3> LIM selection 14-7
8 Line Configuration Chapter 14 sdt structured data transfer selected udt unstructured data transfer selected (not in E1-MF mode) UDT_ALARM This command is used to select the Unstructured Data Transfer, UDT, option and determine when to declare an alarm and which action is to be taken. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: udt_alarm consequent_action) <lim 1..3> ( all) (los monitor_all <lim 1..3> LIM selection los Monitor LOS only monitor_all Monitor any alarm consequent_ Send VC-AIS in UDT Mode action CLOCK_SOURCE This command defines the transmitted clock source At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: clock_source <lim 1..3> <port 1..4> <lim 1..3> <port 1..4> LIM selection Port selection CLOCK_RECOVERY This command is used to select the clock recovery scheme. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: usage: clock_recovery <lim 1..3> ( all) (internal loop_timed adaptive) <lim 1..3> LIM selection internal internal (built-in) clock source selected loop_timed loopback clock source selected adaptive adaptive clock source selected ALARM This command enters the DSX1 alarm configuration submenu. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following screen as shown in Figure 14-6 is displayed: 14-8
9 Chapter 14 Line Configuration Figure 14-6 DSX1 Alarm Configuration Submenu Cisco 8110::host:configuration:dsx1:alarm$? show high_ber low_ber up top exit? SHOW This command displays the DSX1 alarm configuration. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following information as shown in Figure 14-7 is displayed: Figure 14-7 DSX1 Alarm Configuration Display Cisco 8110::host:configuration:alarm$ show 1 1 DSX1 Alarm Parameters High BER : 10E-4 Low BER : 10E-6 HIGH_BER This command sets BER high alarm threshold to 10 -x. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: high_ber <lim 1..3> ( all) <3..6> <1..3> LIM selection <3..6> BER selection LOW_BER This command sets BER low alarm threshold to 10 -x. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: low_ber <1..3> ( all) <5..9> <1..3> LIM selection <5..9> BER selection PM This command enteres the DS1 Performance Monitoring submenu. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The screen shown in Figure 14-8 is displayed: Figure 14-8 DS1 LIM Performance Monitoring Submenu Cisco 8110::host:configuration:lim:pm$? show clear degraded unacceptable unavailable up top exit? SHOW This command displays the DS1 LIM performance monitoring thresholds. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The type of information shown in Figure 14-9 is displayed: 14-9
10 Line Configuration Chapter 14 Figure 14-9 LIM Performance Monitoring Configuration Cisco 8110::host:configuration:dsx1:pm$ show 1 DSX1 PM Configuration Port LCV LCV UAS UAS FE FE SES PM id Degraded Unacceptable Degraded Unacceptable Degraded Unacceptable th state Enabled Enter show to display the following prompt: Usage: show <lim 1..3> ( all) <lim 1..3> LIM selection DEGRADED This command defines how many Line Code Violations should have occurred in the previous 24 hours to declare a degraded performance. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: degraded (es ses sefs fe lcv uas hcs) <lim 1..3> ( all) <int> es ses sefs fe lcv uas Errored Seconds - Enter the number of ES alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Severely Errored Seconds - Enter the number of SES alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Severely Errored Frame Seconds - Enter the number of SEFS alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Frame Error - Enter the number of FE alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Line Code Violation - Enter the number of Line CV alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Unavailable Seconds - Enter the number of UAS alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance hcs Header Check Sequence - Enter the number of HCS alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance <1..3> LIM selection <int> CV count 14-10
11 Chapter 14 Line Configuration UNACCEPTABLE This command defines how many Line Code Violations should have occurred in the previous 15 minute to declare an unacceptable performance. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: unacceptable (es ses sefs fe lcv uas hcs) <lim 1..3> ( all) <int> es ses sefs fe lcv uas Errored Seconds - Enter the number of ES alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Severely Errored Seconds - Enter the number of SES alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Severely Errored Frame Seconds - Enter the number of SEFS alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Frame Error - Enter the number of FE alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Line Code Violation - Enter the number of Line CV alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance Unavailable Seconds - Enter the number of UAS alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance hcs Header Check Sequence - Enter the number of HCS alarms required to declare Unacceptable and Degraded performance <1..3> LIM Selection <int> CV count: Default 5000 Range 0 to , 0 = disabled SES_THRESHOLD This command defines the number of errored seconds (ES) in the previous 15 minutes to declare a severely errored second. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: ses_threshold <lim 1..3> ( all) < > <1..3> LIM selection < > Range of seconds: Default = 6 STATUS This command enables or disables the performance monitoring (PM). At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: status <lim 1..3> ( all) (enable disable) 14-11
12 Maintenance Chapter 14 <1..3> LIM selection enable monitoring enabled disable monitoring disabled CLEAR This command clears the relavent performance monitoring (PM) current or history parameters. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: clear (current history) <lim 1..3> ( all) current Selects current data files history Selects history data files <lim 1..3> LIM selection s UNAVAILABLE This command defines unavailable seconds. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: unavailable <1..3> <0..10> <1..3> LIM selection <0..10> Set the number of seconds Maintenance Step 1 Step 2 When you log into the Cisco 8110 and type? at the prompt the Root Menu is displayed. Type any portion of the word maintenance and press RETURN. Then type? and press RETURN The Maintennce Menu is displayed. Step 3 Select dsx1 to display the screen shown in Figure Figure Maintenance DSX1 submenu Cisco 8110::host: maintenance:dsx1$? loopback det_loop_codes send_code up top exit? LOOPBACK This command sets the DSX1 interface loopback mode. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: loopback <lim 1..3> ( all) (none payload line diagnostic){(forever)} 14-12
13 Chapter 14 Maintenance The parameters are defined as follows: 1..3 LIM Selection none No looback payload Sets payload loopback line Sets line loopback diagnostic Sets internal loopback forever When this parameter is present, the loop continues until the command is issued with the NONE option DET_LOOP_CODES This command enables dection of loop codes sent by the remote system. Usage: det_loop_codes <lim 1..3> ( all) (enable disable) The parameters are defined as follows: lim 1 3 selects LIM enable enables loopback code detection disable disables loopback code detection SEND_CODE This command sends the pattern of loop code using BOP protocols in order to set loopback in the remote side. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: send_code <1..3> ( all) (line_remote_loop payload_remote_loop reset_remote_loop) (Fd1 inband) The parameters are defined as follows: 1..3 Selects DS1 LIM line_remote_loop Sends remote line loopback code payload_remote_loop Sends remote payload loopback code reset_remote_loop Clears remote loopback code Fdl Sends the code in FDL inband Sends the code inband 14-13
14 CES Configuration Chapter 14 CES Configuration The card is configured on both the CBR and ATM side. Configuration of the ATM side of the may be performed using the following menus. Step 1 Step 2 When you log into the Cisco 8110 and type? at the prompt, the Root Menu is displayed. Any portion of the word configuration and press RETURN. Then type? and press RETURN. The Configuration Menu is displayed. Type ces at the prompt and press RETURN. Then type? and press RETURN to display the CES Configuration menu. Figure CES Configuration Menu Cisco 8110::host:configuration:ces$? show> new delete cas oam_alarm_gen partial_fill buf_max_size cdv_rx_t loss_integ_time enable disable activity_timout shaping_class remote_addr first_interval retry_limit restart clear up top exit? SHOW This command displays CES configuration parameters as shown in the sample screen in Figure PCR and CDV computations are implemented for CES connections. The PCR computation complies with af-vtoa par The CDV depends on the number of active connections. As the CBR traffic is already shaped as required, no policing is needed to be performed by these connections. These computed parameters may be used by the user to configure the PVCs in the Network switches. Class 0 is assigned as a default class of highest priority for CBR connections. Other connections will use class 31 as default. This will assure that when there is a contention on the network port (traffic coming from ethernet and native ATM LIM) the CBR traffic will always be serviced
15 Chapter 14 CES Configuration Figure CES show submenu Cisco 8110::host:configuration:ces:show$? service config up top exit? Figure DS0 Status Display SERVICE This command is used to select the status of each service. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: service <limid 1..3> lim 1 3 selects LIM Note The If index presented is the one that should be used in commands that use the If index as a parameter (e.g..delete, CAS etc.) Figure Service status display Cisco 8110::Cisco 8110_b~ co ce sh ser 1 CES Services for LIM IfIndex Port Channels ConnType Vpi Vci CbrType Admin pvc SDT Up Up pvc SDT Up Up Oper Note To see CES services of other LIMs, reference Figures 14-17, and CONFIG This command is used to display the configuration. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: config Interface Index of a service Figure Service status display for LIM 3 Cisco 8110::Cisco 8110_b~ co ce sh ser 3 CES Services for LIM IfIndex Port Channels ConnType Vpi Vci CbrType Admin Oper 14 1 fffffff pvc UDT Up Unkown pvc SDT Up Unknown e080 pvc SDT Up Unknown Figure shows details of service configuration CBR type UDT and its computed values for service
16 CES Configuration Chapter 14 Figure CES Configuration Display for Service 14 Cisco 8110::Cisco 8110_b~ co ce sh con 14 CES Configuration for service Limid : 3 PortId : 1 Channels : All ConnType : pvc Vpi : 3 Vci : 234 CBR Type : SDT Admin Status : Up Oper Status : Unknown Clock Mode : adaptive CAS : Basic Partial Fill : 0 Max Buf Size : 400 CDV Receive : 200 CDV Traansmit : 15 PCR : 4107 Cell Loss Int : 2500 OAM Alarm Gen : Disable Figure shows details of service configuration CBR type UDT and its computed values for service 256. Figure CES Configuration Display for Service 256 Cisco 8110::Cisco 8110_b~ co ce sh con 256 CES Configuration for service Limid : 3 PortId : 3 Channels : 7,8,9,10 ConnType : pvc Vpi : 3 Vci : 234 CBR Type : SDT Admin Status : Up Oper Status : Unknown Clock Mode : adaptive CAS : Basic Partial Fill : 0 Max Buf Size : 400 CDV Receive : 200 CDV Traansmit : 15 PCR : 697 Cell Loss Int : 2500 OAM Alarm Gen : Disable Figure shows details of service configuration CBR type UDT and its computed values for service
17 Chapter 14 CES Configuration Figure CES Configuration Display for Service 257 Cisco 8110::Cisco 8110_b~ co ce sh con 257 CES Configuration for service Limid : 3 PortId : 2 Channels : 7,13,14,15 ConnType : pvc Vpi : 3 Vci : 234 CBR Type : SDT Admin Status : Up Oper Status : Unknown Clock Mode : adaptive CAS : Basic Partial Fill : 0 Max Buf Size : 400 CDV Receive : 200 CDV Traansmit : 15 PCR : 683 Cell Loss Int : 2500 OAM Alarm Gen : Disable NEW This command is used for assigning some of the time slots into one of the connections by selecting lim, port, channel. The connection is added to the VC table. The command will cause an interface to be created automatically. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: new <limid 1..3> <port 1..4> <channels n-m,l,all> (pvc active_svc passive_svc) <vpi/sel > {<vci >} <limid 1..3> <port 1..4> <channels 1..31> <n-m, l, all> pvc active_svc passive _svc vpi vci selects LIM selects port selects channel Time-slot to be assigned select connection type virtual path identifier virtual channel identifier Example: Usage: new <limid 3> <port 1> <channels 2-3, 4, 6-7, 8> <n-m,l,all> <vpi 0> <vci 233> <limid 1..3> <port 1..4> <channels 1..31> <n-m, l, all> selects LIM selects port selects channel Time-slot to be assigned 14-17
18 CES Configuration Chapter 14 vpi vci virtual path identifier virtual channel identifier DELETE This command is used to erase the connection. RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: delete At the prompt, type the command and press Interface index of a service CAS This command is used to determine whether channel associated signaling should be transferred across the connection. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: cas (enable disable) enable disable Interface index of a service Enable CAS in service Disable CAS in service PARTIAL_FILL This command is used to determine how many of the available bytes in each cell are used before they are deemed full and ready for transmission across the network in order to regulate the transmission quality. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: partial_fill <0..47> Interface Index of a service <0..47> selects number of cells for transmission of loopback codes Default = 0, no partial fill BUF_MAX_SIZE This command is used to determine the amount of buffer space allocated for the nicoming cells. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: buf_max_size <10us > <10us > Selects either ethernet or IP service range in 10 Usec units. Must be twice as large as CDV-RX-T. CDV_RX_T This command is used to set cell delay variation of incoming cells over a specific time span. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: cdv_rx_t <10us > 14-18
19 Chapter 14 CES Configuration <10us > Interface Index of a service range in 10 usec units. Minimum value depends on partial fill and number of frames in this service LOSS_INTEG_TIME This command is used to determine loss integration time. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: loss_integ_time <1msec > <1msec > Interface Index of a service range in 1msec units ENABLE This command is used to enable transfer of data. Data cannot be transferred until configured and enabled with this command. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: enable Interface Index of a service DISABLE This command is used to disable a connection. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: disable Interface Index of a service ACTIVITY TIMEOUT This command defines how much time will pass before a retry is attempted. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: activity_timout < > Interface Index of a service Enter the number of seconds SHAPING CLASS This command defines the shaping classs for CES. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: shaping_class <0..32> Interface Index of a service Select a shaping class value 14-19
20 CES Configuration Chapter 14 REMOTE ADDR This command defines the ATM address of the remote device. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: remote_addr <remote address> remote address Interface Index of a service Address format is: ffe f21a.3641{ d.50.0b.32}.40 FIRST INTERVAL This command defines the first interval timeout. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: first_interval < > Interface Index of a service enter the number of seconds RETRY LIMIT This command defines how many attempts(retry)will be made. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: retry_limit < > Interface Index of a service enter the number of retries RESTART This command restarts the retry procedure. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: restart Interface Index of a service CLEARS This command clears the relavent parameters. At the prompt, type the command and press RETURN. The following prompt is displayed: Usage: clear (current total history) <limid 1..3> current total history <limid 1..3> Selects current data files Selects total data files Selects history data files LIM selection 14-20
21 Chapter 14 History History To view the History data display proceed as follows: Step 1 Step 2 When you log into the Cisco 8110 and type? at the prompt, the Root Menu is displayed. Type any portion of the word statistics and press RETURN. Then type? and press RETURN. The History Menu is displayed. Figure The History sub menu Cisco 8110::host:history$? shaper ces vc lim aps svc> up top exit? Step 3 Type lim and press RETURN. Type? and press RETURN to display the following prompt Usage: lim <1..3> <1..96> <1..3> LIM selection <1..96> select an interval to view. from 96, 15 minute intervals Figure History Report Cisco 8110::host$ his lim 1 1 Monitored Seconds : 0 Port : 1 : ESs : SESs : CVs : UASs : SEFSs Line : 0 : - : 0 : - : - Far End Line : 0 : - : - : - : - Port : 2 : ESs : SESs : CVs : UASs : SEFSs Line : 0 : - : 0 : - : - Far End Line : 0 : - : - : - : - Port : 3 : ESs : SESs : CVs : UASs : SEFSs Line : 0 : - : 0 : - : - Far End Line : 0 : - : - : - : - Statistics To view statistics for LIM T1/E1, proceed as follows: Step 1 When you log into the Cisco 8110 and type? at the prompt, the Root Menu is displayed
22 CES Configuration Procedures Chapter 14 Step 2 Step 3 Type any portion of the word statistics and press RETURN. Then type? and press RETURN. The Statistics Menu is displayed. Type lim and press RETURN. Type? and press RETURN to display the following screen Figure Statistics display Monitored Seconds : 0 Port : 1 : ESs : SESs : CVs : UASs : SEFSs Line : 0 : - : 0 : - : - Port : 2 Line : 0 : - : 0 : - : - Port : 3 Line : 0 : - : 0 : - : - Port : 4 Line : 0 : - : 0 : - : - Note If no LIM number is specified, all LIM statistics will be displayed. Selected LIM statistics, can be shown if the LIM number is added to the LIM command (see Figure 14-20) CES Configuration Procedures Following is a description of the Cisco 8110 CES optional configuration, including commands for the most used operations. Default configuration depends on the selected line type and CES mode. Factory default The 7810 Factory default configuration is as follows: Line Type T1 Line code B8ZS Framing format ESF CES mode UDT Clock recovery scheme adaptive UDT alarms monitor LOS only Trunk Conditioning mode set all signaling bits to 0, then to
23 Chapter 14 CES Configuration Procedures E1 default When the 7810 is changed to E1 the default configuration is as follows: Line Type E1 Line code HDB3 Framing format E1 with CRC CES mode UDT Clock recovery scheme adaptive for UDT, looped timing for SDT UDT alarms monitor LOS only Trunk Conditioning mode none Services default The services default configuration is as follows: No CAS Partial fill 0. Send complete cells, no dummy fill. Port configuration The first step in using the CES option should be to set up the TDM ports operating mode. Selecting E1 or T1 operation The CES may be set to E1 or T1 operation. To change the line type of a installed in slot 1, to E1, perform the following operation: Configure CES line type (from route menu): configuration: dsx1$ line_type 1 e1 To perform this operation no services should be configured. The E1 configuration will be according to the default configuration. Selecting line code In T1 the line code can be selected to be B8ZS or AMI, in E1 the code is always HDB3. To change the line code of port 1, of a installed in slot 3, to AMI, perform the following operation: Configure T1 port line code (from route menu): configuration dsx1 csm line_code 3 1 ami Selecting framing format In T1 the farming can be selected to be ESF or SF, in E1 it can be selected to be FAS, MFAS with and without CRC. To change the framing format of port 4, of a installed in slot 1 and operating in E1 mode, to CRC + MFAS, perform the following operation: 14-23
24 CES Configuration Procedures Chapter 14 Configure E1 port framing format (from route menu): configuration dsx1 csm e1_framing 1 4 crc_mf E1 modes supporting CAS can not be configured if the CES mode is UDT. Selecting CES mode CES mode can be set to UDT or SDT. To configure SDT mode in port 1 of a installed in slot 3 perform the following operation: Configure SDT mode to SDT (from route menu): configuration dsx1 csm dt_mode 3 1 sdt To perform this operation no services should be configured. The SDT configuration will be according to the default configuration. Selecting CES clock recovery scheme Selecting UDT alarms handling CES clock recovery scheme can be set to Adaptive, Loop timed or Internal. To configure Internal mode in port 4 of a installed in slot 1 perform the following operation: Configure SDT mode to SDT (from route menu): configuration dsx1 csm clock_recovery 1 4 internal UDT alarms monitoring can be selected to handle only LOS, to handle LOS and monitor all alarms or to perform consequent actions for all the alarms. To configure LOS only handling in port 2 of a installed in slot 3 perform the following operation: Configure UDT alarms monitoring to LOS only (from route menu): configuration dsx1 csm udt_alarms 3 2 los Service configuration Setting a UDT service Once the port and CES mode have been selected, services can be configured depending on the selected mode and framing format. To configure a service, the service should be defined and then associated to a VC. Once the VC and the Service have been enabled, information starts flowing. Each Service will be assigned an ID that will be used to refer to that service. In the following example we will describe how to set a UDT service associated to port 2 of a 7810 installed in slot 1, that uses VC with VPI = 0, VCI = 100. Set the service (from route menu): configuration ces new 1 2 all
25 Chapter 14 CES Configuration Procedures Verify that service ID number: Note all is the only option for the number of channels in UDT mode configuration ces show service 1 Enable the Service (assume the ID is 5) (from route menu): configuration ces enable 5 Set the associated VC (from route menu): configuration vc new ces1 Enable the associated VC (from route menu): configuration: vc$ enable Setting a SDT service In the following example we will describe how to set a SDT service associated to port 4 of a 7810 installed in slot 1, that uses VC with VPI = 0, VCI = 101. The service will carry channels 5 to 8 with CAS. Set the service (from route menu): configuration ces new Verify that service ID number (from route menu): configuration ces show service 1 Enable the Service (assume the ID is from route menu): configuration ces enable 385 Enable the CAS (from route menu): configuration ces cas 385 enable Set the associated VC (from route menu): configuration vc new ces1 Enable the associated VC (from route menu): configuration vc enable Deleting a service In the following example we will delete the service that was configured in the previous paragraph. Delete the VC (from route menu): configuration vc delete Delete the Service (from route menu): configuration ces delete
26 CES Configuration Procedures Chapter 14 Selecting 7810 as timing source Any port of the 7810 can be used as the Cisco 8110 timing source. To configure port 2 of the 7810 installed in slot 3 as the Cisco 8110 primary timing source, perform the following operation: Select the 7810 as the primary timing source (from route menu): configuration tim primary lim3 Select the port as timing source (from route menu): configuration dsx1 csm clock_source
LIM Configuration Menu
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter deals with configura tion of LIM devices. It is organized as follows:, page 7-1 LIM Maintenance, page 7-4 LIM Alarms, page 7-7 SONET/SDH, page 7-7 SONET Maintenance, page 7-13 DSX1,
CHAPTER 7 This chapter deals with configura tion of LIM devices. It is organized as follows:, page 7-1 LIM Maintenance, page 7-4 LIM Alarms, page 7-7 SONET/SDH, page 7-7 SONET Maintenance, page 7-13 DSX1,
INDEX. Boot Configuration & Defaults A-1 Booting A-3
 INDEX A Abbreviating 16 Administrator Login 14 Alarms Maintenance Submenu 6-28, 7-8, 10-4 Alarms Pinout 3-7 APS History 13-5 APS Statistics 13-3 ATM 2-1 ATM Level 14-4 ATM Parameters 1-4 ATM Statistics
INDEX A Abbreviating 16 Administrator Login 14 Alarms Maintenance Submenu 6-28, 7-8, 10-4 Alarms Pinout 3-7 APS History 13-5 APS Statistics 13-3 ATM 2-1 ATM Level 14-4 ATM Parameters 1-4 ATM Statistics
atm txbuff atm txbuff number no atm txbuff Syntax Description
 atm txbuff atm txbuff To set the maximum number of transmit buffers for simultaneous packet fragmentation, use the atm txbuff interface configuration command. To restore the default value, use the no form
atm txbuff atm txbuff To set the maximum number of transmit buffers for simultaneous packet fragmentation, use the atm txbuff interface configuration command. To restore the default value, use the no form
Configuring Circuit Emulation Services
 CHAPTER 18 Configuring Circuit Emulation Services This chapter describes circuit emulation services (CES) and how to configure the CES T1/E1 port adapters in the Catalyst 8540 MSR, Catalyst 8510 MSR, and
CHAPTER 18 Configuring Circuit Emulation Services This chapter describes circuit emulation services (CES) and how to configure the CES T1/E1 port adapters in the Catalyst 8540 MSR, Catalyst 8510 MSR, and
VC Look-Up Table. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory. Figure 1 - MT90528 Block Diagram
 28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
General Description. Overview. Introduction CHAPTER
 CHAPTER This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page - Introduction, page - Configuration Data, page -3 Management, page -5 Maintenance, page -7 Physical Characteristics, page -8 Timing,
CHAPTER This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page - Introduction, page - Configuration Data, page -3 Management, page -5 Maintenance, page -7 Physical Characteristics, page -8 Timing,
Chapter 4 Front Panel Option Selection
 Chapter 4 Front Panel Option Selection GENERAL FT 100 configuration options, operating status, and diagnostics can be observed or changed using the front panel pushbuttons with the LCD. The unit can also
Chapter 4 Front Panel Option Selection GENERAL FT 100 configuration options, operating status, and diagnostics can be observed or changed using the front panel pushbuttons with the LCD. The unit can also
CHANNELIZED DS-1/E1, DS-3, and OC-3/STM-1 CEM NETWORK MODULES
 CHANNELIZED /E1, DS-3, and OC-3/STM-1 CEM NETWORK MODULES Circuit Emulation Interfaces for ASX, TNX, BXR 400, and BXR1600 Multiservice Switches Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks have long been
CHANNELIZED /E1, DS-3, and OC-3/STM-1 CEM NETWORK MODULES Circuit Emulation Interfaces for ASX, TNX, BXR 400, and BXR1600 Multiservice Switches Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks have long been
Cisco - An Introduction to Circuit Emulation Services
 Page 1 of 14 An Introduction to Circuit Emulation Services Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used CES Concepts Types of Signaling Frame and Cell Processing Types
Page 1 of 14 An Introduction to Circuit Emulation Services Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used CES Concepts Types of Signaling Frame and Cell Processing Types
Cisco Enterprise MIB Objects
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes the common MIB objects used for Cisco enterprise that are used for AXSM, AXSME, PXM1E, PXM45, SRM, SRM-E, FRSM12, RPM-XF, and RPM-PRR. Contents of this chapter include:
CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes the common MIB objects used for Cisco enterprise that are used for AXSM, AXSME, PXM1E, PXM45, SRM, SRM-E, FRSM12, RPM-XF, and RPM-PRR. Contents of this chapter include:
ATM Software Segmentation and Reassembly
 Feature History Release Modification 12.2(2)XB Cisco 2600 Series T1/E1 ATM and Cisco 3660 T1 Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) ATM Adaption Layer 2 (AAL2) Support was introduced. 12.2(8)T This feature
Feature History Release Modification 12.2(2)XB Cisco 2600 Series T1/E1 ATM and Cisco 3660 T1 Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) ATM Adaption Layer 2 (AAL2) Support was introduced. 12.2(8)T This feature
Circuit Emulation over IP
 (CEoIP) provides a virtual circuit through an IP network--similar to a leased line--to integrate solutions that require a time-sensitive, bit-transparent transport into IP networks. Data, with proprietary
(CEoIP) provides a virtual circuit through an IP network--similar to a leased line--to integrate solutions that require a time-sensitive, bit-transparent transport into IP networks. Data, with proprietary
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 Effective Cisco IOS-XE Release 3.14.0S, the Cisco ASR-920-24SZ-IM, ASR-920-24SZ-M, ASR-920-24TZ-M Aggregation Services Router supports the following types of interface modules (IMs): 8x1G Cu IM (A900-IMA8T)
Effective Cisco IOS-XE Release 3.14.0S, the Cisco ASR-920-24SZ-IM, ASR-920-24SZ-M, ASR-920-24TZ-M Aggregation Services Router supports the following types of interface modules (IMs): 8x1G Cu IM (A900-IMA8T)
1-Port and 2-Port HWIC data/voice, 4-Port T1/E1 HWIC, and 8-Port T1/E1 Network Module
 1-Port and 2-Port HWIC data/voice, 4-Port T1/E1 HWIC, and 8-Port T1/E1 Network Module Last Updated: August 18, 2011, This document describes the following Cisco products: Cisco 1-Port and 2-Port Channelized
1-Port and 2-Port HWIC data/voice, 4-Port T1/E1 HWIC, and 8-Port T1/E1 Network Module Last Updated: August 18, 2011, This document describes the following Cisco products: Cisco 1-Port and 2-Port Channelized
Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules
 9 Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules Contents Using an E1- or T1-Carrier Line for Data and Voice................... 9-3 Drop-and-Insert Modules..................................... 9-3 Standards
9 Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules Contents Using an E1- or T1-Carrier Line for Data and Voice................... 9-3 Drop-and-Insert Modules..................................... 9-3 Standards
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
Configuring the SS7 Port Adapter
 CHAPTER 4 To continue your SS7 Port Adapter installation, you must configure the card type as either T1 or E1 and then configure the interfaces. This chapter contains the following sections: Using the
CHAPTER 4 To continue your SS7 Port Adapter installation, you must configure the card type as either T1 or E1 and then configure the interfaces. This chapter contains the following sections: Using the
Technical Committee. Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification Version 2.0. af-vtoa
 Technical Committee Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification Version 2.0 af-vtoa-0078.000 January 1997 af-vtoa-0078.000 CES-IS V2.0 Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification
Technical Committee Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification Version 2.0 af-vtoa-0078.000 January 1997 af-vtoa-0078.000 CES-IS V2.0 Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification
Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter for the Cisco 7500 Series Router
 Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter for the Cisco 7500 Series Router This feature module describes the Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter (PA-MC-STM-1). It includes information on the benefits of this port adapter,
Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter for the Cisco 7500 Series Router This feature module describes the Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter (PA-MC-STM-1). It includes information on the benefits of this port adapter,
Interface Configuration
 CHAPTER 7 You can configure or set up any interface through interface configuration windows, which are associated with each particular line card. This chapter contains the following information: Generic
CHAPTER 7 You can configure or set up any interface through interface configuration windows, which are associated with each particular line card. This chapter contains the following information: Generic
Configuring the Circuit Emulation over Packet Shared Port Adapter
 Configuring the Circuit Emulation over Packet Shared Port Adapter Release History This chapter provides information about configuring the Circuit Emulation over Packet (CEoP) shared port adapters (SPAs)
Configuring the Circuit Emulation over Packet Shared Port Adapter Release History This chapter provides information about configuring the Circuit Emulation over Packet (CEoP) shared port adapters (SPAs)
ACE-2002, ACE-2002E. Multiservice Access Concentrators/ ATM Network Termination Units FEATURES
 Multiservice Access Concentrators/ ATM Network Termination Units FEATURES Multiservice/ATM network demarcation device or access concentrator (ACE-2002), cellular access concentrator () Offer converged
Multiservice Access Concentrators/ ATM Network Termination Units FEATURES Multiservice/ATM network demarcation device or access concentrator (ACE-2002), cellular access concentrator () Offer converged
Configuring an Integrated CSU/DSU WAN Interface
 Configuring an Integrated CSU/DSU WAN Interface Version: 2580 Copyright 2007-2010 ImageStream Internet Solutions, Inc., All rights Reserved. Table of Contents Router Installation and Configuration Manual/Configuring
Configuring an Integrated CSU/DSU WAN Interface Version: 2580 Copyright 2007-2010 ImageStream Internet Solutions, Inc., All rights Reserved. Table of Contents Router Installation and Configuration Manual/Configuring
Real-Time Counters APPENDIX
 APPENDIX E Real-time counters (RTCs) are available through the Diagnostics Center. When the GUI displays the RTCs, the applicability rules would be evaluated by the Cisco MGM server, and the counters will
APPENDIX E Real-time counters (RTCs) are available through the Diagnostics Center. When the GUI displays the RTCs, the applicability rules would be evaluated by the Cisco MGM server, and the counters will
VC Look-Up Table. Segmentation / Reassembly Circular Buffers. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory
 8-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-78.) Supports both Unstructured and Structured
8-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-78.) Supports both Unstructured and Structured
AIM-ATM, AIM-VOICE-30, and AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 on the Cisco 2600 Series and Cisco 3660
 AIM-ATM, AIM-VOICE-30, and AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 on the Cisco 2600 Series and Cisco 3660 Feature History Release 12.2(2)XA 12.2(2)XB Modification The High-Performance ATM Advanced Integration Module (AIM-ATM)
AIM-ATM, AIM-VOICE-30, and AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 on the Cisco 2600 Series and Cisco 3660 Feature History Release 12.2(2)XA 12.2(2)XB Modification The High-Performance ATM Advanced Integration Module (AIM-ATM)
Tandem Switch Application (VoIP Mode)
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides a general description of an application in which a VISM equipped Cisco MGX 8850 and a Cisco VSC 3000 Virtual Switch Controller (Call Agent) combine to provide the functions
CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides a general description of an application in which a VISM equipped Cisco MGX 8850 and a Cisco VSC 3000 Virtual Switch Controller (Call Agent) combine to provide the functions
Configuring Inverse Muliplexing over ATM
 This feature module describes how to configure Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) to transport ATM traffic over a bundle of T1 or E1 cables. This feature s the expansion of WAN bandwidth from T1 speeds,
This feature module describes how to configure Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) to transport ATM traffic over a bundle of T1 or E1 cables. This feature s the expansion of WAN bandwidth from T1 speeds,
Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source
 Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce a new compression technique
Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce a new compression technique
Access Circuit Redundancy Support for IMA
 The Access Circuit Redundancy Support (ACR) for Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) feature provides a converged IP or Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) access network for its mobile users that use
The Access Circuit Redundancy Support (ACR) for Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) feature provides a converged IP or Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) access network for its mobile users that use
Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source
 Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce a new compression technique
Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce a new compression technique
Configuring the Cisco 3825 Mobile Wireless Edge Router in a RAN-O Solution with the Command-Line Interface
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring the Cisco 3825 Mobile Wireless Edge Router in a RAN-O Solution with the Command-Line Interface This chapter describes how to use the Cisco IOS software CLI to configure the Cisco
CHAPTER 4 Configuring the Cisco 3825 Mobile Wireless Edge Router in a RAN-O Solution with the Command-Line Interface This chapter describes how to use the Cisco IOS software CLI to configure the Cisco
Overview of Circuit Emulation
 Circuit Emulation (CEM) is a technology that provides a protocol-independent transport over IP/MPLS networks. It s proprietary or legacy applications to be carried transparently to the destination, similar
Circuit Emulation (CEM) is a technology that provides a protocol-independent transport over IP/MPLS networks. It s proprietary or legacy applications to be carried transparently to the destination, similar
Embedded Management Functions. Signal backhaul xgcp (CAS), Q.931 (PRI) * Call setup/ teardown xgcp * Connection Handling *
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes VISM operation. Figure 5-1 shows the functional blocks of VISM. Items marked with a single asterisk apply to VoIP switching and switched AAL2 PVC modes only. Items marked
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes VISM operation. Figure 5-1 shows the functional blocks of VISM. Items marked with a single asterisk apply to VoIP switching and switched AAL2 PVC modes only. Items marked
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
clock rate through cut-through
 clock rate through cut-through clock rate, page 3 clock rate (interface ATM), page 6 clock rate (interface serial), page 10 clock rate network-clock, page 14 clock recovered adaptive/differential cem,
clock rate through cut-through clock rate, page 3 clock rate (interface ATM), page 6 clock rate (interface serial), page 10 clock rate network-clock, page 14 clock recovered adaptive/differential cem,
Overview of Circuit Emulation
 Circuit Emulation (CEM) is a technology that provides a protocol-independent transport over IP/MPLS networks. It s proprietary or legacy applications to be carried transparently to the destination, similar
Circuit Emulation (CEM) is a technology that provides a protocol-independent transport over IP/MPLS networks. It s proprietary or legacy applications to be carried transparently to the destination, similar
Command Reference. Version: Copyright ImageStream Internet Solutions, Inc., All rights Reserved.
 Version: 2082 Copyright 2007-2010 ImageStream Internet Solutions, Inc., All rights Reserved. Table of Contents Command Reference...1 A...1 abr {pcr} {mcr}...1 B...1 bandwidth {bits_per_second}...1 baud
Version: 2082 Copyright 2007-2010 ImageStream Internet Solutions, Inc., All rights Reserved. Table of Contents Command Reference...1 A...1 abr {pcr} {mcr}...1 B...1 bandwidth {bits_per_second}...1 baud
Understanding the Variable Bit Rate Real Time (VBR rt) Service Category for ATM VCs
 Understanding the Variable Bit Rate Real Time (VBR rt) Service Category for ATM VCs Document ID: 10414 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What is Variable Bit
Understanding the Variable Bit Rate Real Time (VBR rt) Service Category for ATM VCs Document ID: 10414 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What is Variable Bit
Configuring Cisco Integrated Data Service Unit/Channel Service Unit (DSU/CSU) Modules and WAN Interface Cards
 Configuring Cisco Integrated Data Service Unit/Channel Service Unit (DSU/CSU) Modules and WAN Interface Cards Document ID: 10265 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device.
Configuring Cisco Integrated Data Service Unit/Channel Service Unit (DSU/CSU) Modules and WAN Interface Cards Document ID: 10265 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device.
G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD
 G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD This document describes the Multirate Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) feature supported on the Cisco IAD2420 series integrated
G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD This document describes the Multirate Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) feature supported on the Cisco IAD2420 series integrated
Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Router T1/E1 Voice and WAN Network Interface Modules Data Sheet
 Data Sheet Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Router T1/E1 Voice and WAN Network Interface Modules Data Sheet These flexible interface cards support multiple integrated data and voice applications,
Data Sheet Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Router T1/E1 Voice and WAN Network Interface Modules Data Sheet These flexible interface cards support multiple integrated data and voice applications,
Internetworking Part 1
 CMPE 344 Computer Networks Spring 2012 Internetworking Part 1 Reading: Peterson and Davie, 3.1 22/03/2012 1 Not all networks are directly connected Limit to how many hosts can be attached Point-to-point:
CMPE 344 Computer Networks Spring 2012 Internetworking Part 1 Reading: Peterson and Davie, 3.1 22/03/2012 1 Not all networks are directly connected Limit to how many hosts can be attached Point-to-point:
Configuring Layer 2 Local Switching
 CHAPTER 17 The Layer 2 Local Switching feature allows you to switch Layer 2 data between two physical or virtual interfaces of the same type on the same router. The interfaces can be on the same line card
CHAPTER 17 The Layer 2 Local Switching feature allows you to switch Layer 2 data between two physical or virtual interfaces of the same type on the same router. The interfaces can be on the same line card
LANE, CES, and VBR PVCs in Shaped VP Tunnels
 LANE, CES, and VBR PVCs in Shaped VP Tunnels Document ID: 10493 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Assumptions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Troubleshoot
LANE, CES, and VBR PVCs in Shaped VP Tunnels Document ID: 10493 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Assumptions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Troubleshoot
Multiservice Network Termination Unit
 Order from Cutter Networks Ph:727-398-5252/Fax:727-397-9610 www.bestdatasource.com Data Sheet Extending the reach of Ethernet LANs and TDM services over ATM networks Transparent LAN services (TLS) and
Order from Cutter Networks Ph:727-398-5252/Fax:727-397-9610 www.bestdatasource.com Data Sheet Extending the reach of Ethernet LANs and TDM services over ATM networks Transparent LAN services (TLS) and
Technical Committee. Interoperability Abstract Test Suites for the Physical Layer. af-test
 Technical Committee Interoperability Abstract Test Suites af-test-0036.000 April, 1995 af-test-0036.000 Interoperability Abstract Test Suites Interoperability Abstract Test Suites Version 1.0 April, 1995
Technical Committee Interoperability Abstract Test Suites af-test-0036.000 April, 1995 af-test-0036.000 Interoperability Abstract Test Suites Interoperability Abstract Test Suites Version 1.0 April, 1995
LA-140. Advanced ATM IAD FEATURES
 Advanced IAD FEATURES Offers voice, data and LAN to small and medium size businesses over single access line On the user side, supports up to 12 modular analog voice channels, 12 ISDN S0, E1/T1 port, a
Advanced IAD FEATURES Offers voice, data and LAN to small and medium size businesses over single access line On the user side, supports up to 12 modular analog voice channels, 12 ISDN S0, E1/T1 port, a
Circuit Emulation Lab for TDM to IP Migration
 Circuit Emulation Lab for TDM to IP Migration LTRSPG-2716 Speakers: Vincent Ng, Sartaj Khuroo Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: 1. MPLS Flex-LSP Provisioning 2. Basic
Circuit Emulation Lab for TDM to IP Migration LTRSPG-2716 Speakers: Vincent Ng, Sartaj Khuroo Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: 1. MPLS Flex-LSP Provisioning 2. Basic
Performance Monitoring
 CHAPTER 15 The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
CHAPTER 15 The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
Performance Monitoring
 CHAPTER 15 Performance monitoring (PM) parameters are used by service providers to gather, store, set thresholds, and report performance data for early detection of problems. In this chapter, PM parameters
CHAPTER 15 Performance monitoring (PM) parameters are used by service providers to gather, store, set thresholds, and report performance data for early detection of problems. In this chapter, PM parameters
Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source
 Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source Last Updated: April 17, 2012 The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce
Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source Last Updated: April 17, 2012 The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce
Cisco - Understanding the UBR Service Category for ATM Virtual Circuits
 Page 1 of 9 Understanding the UBR Service Category for ATM Virtual Circuits Document ID: 10530 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Advantages and Disadvantages
Page 1 of 9 Understanding the UBR Service Category for ATM Virtual Circuits Document ID: 10530 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Advantages and Disadvantages
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
 ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Protocol Architecture (diag) CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 2 1 Reference Model Planes User plane Provides for user information transfer Control
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Protocol Architecture (diag) CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 2 1 Reference Model Planes User plane Provides for user information transfer Control
ATM Technology in Detail. Objectives. Presentation Outline
 ATM Technology in Detail Professor Richard Harris Objectives You should be able to: Discuss the ATM protocol stack Identify the different layers and their purpose Explain the ATM Adaptation Layer Discuss
ATM Technology in Detail Professor Richard Harris Objectives You should be able to: Discuss the ATM protocol stack Identify the different layers and their purpose Explain the ATM Adaptation Layer Discuss
RADview. Element Management System ACE RAD Data Communications Publication 02/04
 RADview Element Management System ACE-202 1994 2004 RAD Data Communications Publication 02/04 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 Preliminary Hardware Configuration... 1-2 Management Configuration...1-2
RADview Element Management System ACE-202 1994 2004 RAD Data Communications Publication 02/04 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 Preliminary Hardware Configuration... 1-2 Management Configuration...1-2
Configuring Pseudowire
 This chapter provides information about configuring pseudowire features on the Cisco ASR 920 Series Router. Pseudowire Overview, on page 1 CEM Configuration, on page 2 CEM Configuration Guidelines and
This chapter provides information about configuring pseudowire features on the Cisco ASR 920 Series Router. Pseudowire Overview, on page 1 CEM Configuration, on page 2 CEM Configuration Guidelines and
Software Configuration of ATM ISE Line Cards for Cisco Series Routers
 Software Configuration of ATM ISE Line Cards for Cisco 12000 Series Routers This feature module describes the software configuration for the Cisco 4-Port ATM Internet Services Engine (ISE) line cards in
Software Configuration of ATM ISE Line Cards for Cisco 12000 Series Routers This feature module describes the software configuration for the Cisco 4-Port ATM Internet Services Engine (ISE) line cards in
ATM Logical Connections: VCC. ATM Logical Connections: VPC
 ATM Logical Connections: VCC Logical Connections in ATM are referred to as virtual channel connections (VCCs). Virtual channel (VC) is a generic term used to describe unidirectional transport of ATM cells
ATM Logical Connections: VCC Logical Connections in ATM are referred to as virtual channel connections (VCCs). Virtual channel (VC) is a generic term used to describe unidirectional transport of ATM cells
Configuring Automatic Protection Switching
 Application Note Configuring Automatic Protection Switching Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408 745 2000 or 888 JUNIPER www.juniper.net Part Number : 350021-001
Application Note Configuring Automatic Protection Switching Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408 745 2000 or 888 JUNIPER www.juniper.net Part Number : 350021-001
RADview-EMS/NGN. Element Management System for NGN Applications ACE-201/ RAD Data Communications Publication 06/07
 RADview-EMS/NGN Element Management System for NGN Applications ACE-201/622 1994 2007 RAD Data Communications Publication 06/07 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 ACE-201/622 Overview...1-1 1.2 RADview-EMS/NGN
RADview-EMS/NGN Element Management System for NGN Applications ACE-201/622 1994 2007 RAD Data Communications Publication 06/07 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 ACE-201/622 Overview...1-1 1.2 RADview-EMS/NGN
R 155. ZyFLEX. A Fiber Optical Multiplexer For Future-Proof Telecom Solutions.
 F O TA R 155 A Fiber Optical Multiplexer For Future-Proof Telecom Solutions www..com.tw FOM FORTA155 Fiber Optic Multiplexer Scaleable capacity :supports 4, 8, 12, and 16 T1/E1 channels N*64 Kbps with
F O TA R 155 A Fiber Optical Multiplexer For Future-Proof Telecom Solutions www..com.tw FOM FORTA155 Fiber Optic Multiplexer Scaleable capacity :supports 4, 8, 12, and 16 T1/E1 channels N*64 Kbps with
Technical Committee. Voice and Telephony Over ATM - ATM Trunking using AAL1 for Narrowband Services Version 1.0
 Technical Committee Voice and Telephony Over ATM - ATM Trunking using AAL1 for Narrowband Services Version 1.0 AF-VTOA-0089.000 July, 1997 Voice and Telephony Over ATM - af-vtoa-0089.000 ATM trunking
Technical Committee Voice and Telephony Over ATM - ATM Trunking using AAL1 for Narrowband Services Version 1.0 AF-VTOA-0089.000 July, 1997 Voice and Telephony Over ATM - af-vtoa-0089.000 ATM trunking
Chapter 10. Circuits Switching and Packet Switching 10-1
 Chapter 10 Circuits Switching and Packet Switching 10-1 Content Switched communication networks Circuit switching networks Circuit-switching concepts Packet-switching principles X.25 (mentioned but not
Chapter 10 Circuits Switching and Packet Switching 10-1 Content Switched communication networks Circuit switching networks Circuit-switching concepts Packet-switching principles X.25 (mentioned but not
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) ATM concepts
 Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a switching technique for telecommunication networks. It uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing,[1][2] and it encodes data into
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a switching technique for telecommunication networks. It uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing,[1][2] and it encodes data into
Troubleshooting Input Drops on ATM Router Interfaces
 Troubleshooting Input Drops on ATM Router Interfaces Document ID: 8625 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Traditional Reasons for Input Drops Understanding Throttles
Troubleshooting Input Drops on ATM Router Interfaces Document ID: 8625 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Traditional Reasons for Input Drops Understanding Throttles
t1 through tug-2 e1 unframed
 t1 through tug-2 e1 unframed t1, page 3 t1 bert, page 5 t1/e1 cem-group, page 8 t1 clock source, page 9 t1 external, page 11 t1 fdl ansi, page 13 t1 framing, page 15 t1 linecode, page 18 t1 logging-events,
t1 through tug-2 e1 unframed t1, page 3 t1 bert, page 5 t1/e1 cem-group, page 8 t1 clock source, page 9 t1 external, page 11 t1 fdl ansi, page 13 t1 framing, page 15 t1 linecode, page 18 t1 logging-events,
Introduction to ATM Traffic Management on the Cisco 7200 Series Routers
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to ATM Traffic Management on the Cisco 7200 Series Routers In the latest generation of IP networks, with the growing implementation of Voice over IP (VoIP) and multimedia applications,
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to ATM Traffic Management on the Cisco 7200 Series Routers In the latest generation of IP networks, with the growing implementation of Voice over IP (VoIP) and multimedia applications,
Single-router APS for the Cisco Series Router
 Single-router APS for the Cisco 12000 Series Router This feature provides 1+1 single-router automatic protection switching (SR-APS) for the Cisco 12000 series ISE ATM line cards (Engine 3) installed in
Single-router APS for the Cisco 12000 Series Router This feature provides 1+1 single-router automatic protection switching (SR-APS) for the Cisco 12000 series ISE ATM line cards (Engine 3) installed in
ATM. Asynchronous Transfer Mode. (and some SDH) (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy)
 ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode (and some SDH) (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) Why use ATM? Circuit switched connections: After initial setup no processing in network nodes Fixed bit rates, fixed time delay
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode (and some SDH) (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) Why use ATM? Circuit switched connections: After initial setup no processing in network nodes Fixed bit rates, fixed time delay
Communication Networks
 Communication Networks Chapter 3 Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Useful bandwidth of medium exceeds required bandwidth of channel Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency
Communication Networks Chapter 3 Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Useful bandwidth of medium exceeds required bandwidth of channel Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency
G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD
 G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD This document describes the Multirate Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) feature supported on the Cisco IAD2420 series integrated
G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD This document describes the Multirate Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) feature supported on the Cisco IAD2420 series integrated
Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC-192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC-3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module
 Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC-192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC-3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module SDH is a standard that defines optical signals as well as a synchronous frame structure for multiplexed digital traffic.
Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC-192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC-3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module SDH is a standard that defines optical signals as well as a synchronous frame structure for multiplexed digital traffic.
1-, 2-, and 4-Port T1/E1 HWICs and 8-Port T1/E1 Network Module
 1-, 2-, and 4-Pt T1/E1 HWICs and 8-Pt T1/E1 Netwk Module First Published: November 22, 2007 Last Updated: July 11, 2008 This document describes the following Cisco products: Cisco 1-Pt and 2-Pt Channelized
1-, 2-, and 4-Pt T1/E1 HWICs and 8-Pt T1/E1 Netwk Module First Published: November 22, 2007 Last Updated: July 11, 2008 This document describes the following Cisco products: Cisco 1-Pt and 2-Pt Channelized
ATM Hierarchical Shaping ATM VC into VP Shaping, page 1
 ATM Hierarchical Shaping ATM VC into VP Shaping, page 1 Traffic shaping is a quality of service (QoS) mechanism that is used to manage the network traffic by shaping the traffic to a specified rate. Traffic
ATM Hierarchical Shaping ATM VC into VP Shaping, page 1 Traffic shaping is a quality of service (QoS) mechanism that is used to manage the network traffic by shaping the traffic to a specified rate. Traffic
TDM over IP. International Department
 TDM over IP International Department 2010-7-15 RAISECOM TDM over IP TDMoIP Specification 4 E1/T1 TDMoIP product 1 E1/T1 TDMoIP product How to config Nview NNM V5 GUI TDMoIP product family Central RC1201-2GESTM1
TDM over IP International Department 2010-7-15 RAISECOM TDM over IP TDMoIP Specification 4 E1/T1 TDMoIP product 1 E1/T1 TDMoIP product How to config Nview NNM V5 GUI TDMoIP product family Central RC1201-2GESTM1
N:1 PVC Mapping to PWE with Nonunique VPIs
 N:1 PVC Mapping to PWE with Nonunique VPIs The N:1 PVC Mapping to PseudoWire Emulation (PWE) with Nonunique virtual path identifiers (VPIs) feature maps one or more ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs)
N:1 PVC Mapping to PWE with Nonunique VPIs The N:1 PVC Mapping to PseudoWire Emulation (PWE) with Nonunique virtual path identifiers (VPIs) feature maps one or more ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs)
Lesson 3 Network technologies - Controlling
 Lesson 3 Network technologies - Controlling Objectives : Network control or traffic engineering is one of the important techniques in the network. Understanding QoS control, traffic engineering and OAM
Lesson 3 Network technologies - Controlling Objectives : Network control or traffic engineering is one of the important techniques in the network. Understanding QoS control, traffic engineering and OAM
IPmux-11. TDMoIP Gateway DESCRIPTION FEATURES
 IPmux-11 DESCRIPTION FEATURES TDMoIP CPE (Customer Premises Equipment) for the small and medium-sized enterprise sites, offering TDM leased line extension over a packet switched network and controlled
IPmux-11 DESCRIPTION FEATURES TDMoIP CPE (Customer Premises Equipment) for the small and medium-sized enterprise sites, offering TDM leased line extension over a packet switched network and controlled
MPLS AToM Overview. Documentation Specifics. Feature Overview
 MPLS AToM Overview This document provides an introduction to MPLS AToM and includes the following sections: Documentation Specifics, page 14 Feature Overview, page 14 Benefits, page 26 What To Do Next,
MPLS AToM Overview This document provides an introduction to MPLS AToM and includes the following sections: Documentation Specifics, page 14 Feature Overview, page 14 Benefits, page 26 What To Do Next,
1-Port DSU/CSU T1 WIC for the Cisco 1700, Cisco 2600, Cisco 3600, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers
 1-Port DSU/CSU T1 WIC for the Cisco 1700, Cisco 2600, Cisco 3600, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers Feature History Release Modification 11.2 This feature was introduced on the Cisco 1600 series and Cisco
1-Port DSU/CSU T1 WIC for the Cisco 1700, Cisco 2600, Cisco 3600, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers Feature History Release Modification 11.2 This feature was introduced on the Cisco 1600 series and Cisco
Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series)
 Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series) First Published: 2014-11-01 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series) First Published: 2014-11-01 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS
 BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM is a flexible high bandwidth, low delay network technology that is: Capable of handling voice, video and data
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM is a flexible high bandwidth, low delay network technology that is: Capable of handling voice, video and data
4xT1/E1 i nline probe ASE With LinkSafe capabilities
 Visual UpTime Select ASE model 807-0115 4xT1/E1 i nline probe ASE With LinkSafe capabilities Key features Four management ports MLPPP support on IP Transport software Inband management capability LinkSafe
Visual UpTime Select ASE model 807-0115 4xT1/E1 i nline probe ASE With LinkSafe capabilities Key features Four management ports MLPPP support on IP Transport software Inband management capability LinkSafe
Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series)
 Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series) First Published: 2014-11-01 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series) First Published: 2014-11-01 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
PA-A3-T3, PA-A3-E3, PA-A3-OC3MM, PA-A3-OC3SMI, and
 PA-A3-T3, PA-A3-E3, PA-A3-OC3MM, PA-A3-OC3SMI, and PA-A3-OC3SML ATM Port Adapters The PA-A3-T3 and PA-A3-E3 port adapters were introduced in Cisco IOS Release 11.1(18)CC. This feature module has been updated
PA-A3-T3, PA-A3-E3, PA-A3-OC3MM, PA-A3-OC3SMI, and PA-A3-OC3SML ATM Port Adapters The PA-A3-T3 and PA-A3-E3 port adapters were introduced in Cisco IOS Release 11.1(18)CC. This feature module has been updated
Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest (Cisco ASR 920 Series)
 Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.1 (Cisco ASR 920 Series) First Published: 2017-03-23 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose,
Time Division Multiplexing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.1 (Cisco ASR 920 Series) First Published: 2017-03-23 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose,
different problems from other networks ITU-T specified restricted initial set Limited number of overhead bits ATM forum Traffic Management
 Traffic and Congestion Management in ATM 3BA33 David Lewis 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 1 Traffic Control Objectives Optimise usage of network resources Network is a shared resource Over-utilisation -> congestion
Traffic and Congestion Management in ATM 3BA33 David Lewis 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 1 Traffic Control Objectives Optimise usage of network resources Network is a shared resource Over-utilisation -> congestion
Configuring Synchronized Clocking
 Configuring Synchronized Clocking This appendix describes how to configure synchronized clocking. It contains the following sections: Synchronized Clocking Overview, page 791 Synchronized Clocking Configuration
Configuring Synchronized Clocking This appendix describes how to configure synchronized clocking. It contains the following sections: Synchronized Clocking Overview, page 791 Synchronized Clocking Configuration
CPEG 514. Lecture 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) CPEG 514
 Lecture 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode () Outline Introduction Virtual Circuit Setup PVC vs. SVC Quality of Service and Congestion Control IP over and Frame Relay interworking Network (integrated voice,
Lecture 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode () Outline Introduction Virtual Circuit Setup PVC vs. SVC Quality of Service and Congestion Control IP over and Frame Relay interworking Network (integrated voice,
AMX-1344 Access DCS-MUX
 AMX-1344 Access DCS-MUX Description Features : Support DACS (Digital Access Cross-connect System) with full cross-connect Support full DS0 cross-connect, backplane capacity up to 128 Mbps Single controller,
AMX-1344 Access DCS-MUX Description Features : Support DACS (Digital Access Cross-connect System) with full cross-connect Support full DS0 cross-connect, backplane capacity up to 128 Mbps Single controller,
Chapter 1 Configuring ATM
 Chapter 1 Configuring ATM This chapter introduces basic Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) concepts, describes features of the ATM interfaces, and provides information for configuring ATM on E-series routers.
Chapter 1 Configuring ATM This chapter introduces basic Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) concepts, describes features of the ATM interfaces, and provides information for configuring ATM on E-series routers.
Implementing T1 CAS for VoIP
 This chapter describes how to implement the T1 Channel-Associated Signaling (CAS) for VoIP feature. This feature adds support for T1 CAS and E1 R2 signaling with the voice feature card (VFC). The T1 CAS
This chapter describes how to implement the T1 Channel-Associated Signaling (CAS) for VoIP feature. This feature adds support for T1 CAS and E1 R2 signaling with the voice feature card (VFC). The T1 CAS
IPmux-14. TDMoIP Gateway FEATURES DESCRIPTION
 FEATURES TDMoIP CPE (Customer Premises Equipment), offering TDM leased line extension over a packet switched network (PSN) and controlled Ethernet access TDMoIP technology, implementing the emerging IETF,
FEATURES TDMoIP CPE (Customer Premises Equipment), offering TDM leased line extension over a packet switched network (PSN) and controlled Ethernet access TDMoIP technology, implementing the emerging IETF,
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
 CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes the level of support that Cisco ANA provides for ATM, as follows: Technology Description, page 20-1 Information Model Objects (IMOs), page 20-3 Vendor-Specific Inventory
CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes the level of support that Cisco ANA provides for ATM, as follows: Technology Description, page 20-1 Information Model Objects (IMOs), page 20-3 Vendor-Specific Inventory
Interface Commands. Configuring Logical Interfaces chapter in the. Cisco IOS Interface Configuration Guide. Cisco IOS Interface Configuration Guide
 Interface Commands This book describes the basic commands that can be used on different types of interfaces. These commands correspond to the interface configuration tasks included in the Cisco IOS configuration
Interface Commands This book describes the basic commands that can be used on different types of interfaces. These commands correspond to the interface configuration tasks included in the Cisco IOS configuration
N:1 PVC Mapping to PWE with Nonunique VPIs
 The N:1 PVC Mapping to PseudoWire Emulation (PWE) with Nonunique virtual path identifiers (VPIs) feature maps one or more ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs) to a single pseudowire (PW). There are two
The N:1 PVC Mapping to PseudoWire Emulation (PWE) with Nonunique virtual path identifiers (VPIs) feature maps one or more ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs) to a single pseudowire (PW). There are two
Kilomux-2100/2104 KVF.6 E1/T1 Voice Compression Module
 Data Sheet Kilomux-2100/2104 KVF.6 Half or full PBX E1/T1 trunk compression Up to 186 voice channels in a single Kilomux-2100 chassis Group III Fax relay at up to 14.4 kbps, with automatic rate fallback
Data Sheet Kilomux-2100/2104 KVF.6 Half or full PBX E1/T1 trunk compression Up to 186 voice channels in a single Kilomux-2100 chassis Group III Fax relay at up to 14.4 kbps, with automatic rate fallback
Configuring Clear Channel T3/E3 and Channelized T3 and T1/E1 Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 Configuring Clear Channel T3/E3 and Channelized T3 and T1/E1 Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of clear channel T3/E3 controllers and channelized T3
Configuring Clear Channel T3/E3 and Channelized T3 and T1/E1 Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of clear channel T3/E3 controllers and channelized T3
Wireless Networks. Communication Networks
 Wireless Networks Communication Networks Types of Communication Networks Traditional Traditional local area network (LAN) Traditional wide area network (WAN) Higher-speed High-speed local area network
Wireless Networks Communication Networks Types of Communication Networks Traditional Traditional local area network (LAN) Traditional wide area network (WAN) Higher-speed High-speed local area network
