NCERT solution for Fractions-2
|
|
|
- Noreen Waters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NCERT solution for Fractions-2 1 Exercise 7.3 Question 1 Write the fractions. Are all these fractions equivalent? (a) (b) a) We can find fraction in each figure by the formula Dark part/ total parts ½, 2/4= 1/2, 3/6= 1/2, 4/8= ½ These all are equivalent b) We can find fraction in each figure by the formula Dark part/ total part 4/12=1/3, 3/9= 1/3, 2/6= 1/3, 1/3, 6/15 These all are not equivalent
2 Question 2 2 Write the fractions and pair up the equivalent fractions from each row. We can find fraction in each figure by the formula Dark part/ total parts So let s calculate the fraction a) 1/2 I) 6/18 =1/3 b) 4/6=2/3 ii)4/8=1/2 c) 3/9=1/3 iii) 12/16= ¾ d) 2/8=1/4 iv) 8/12= 2/3 e) 3/4 v) 4/16= 1/4 Equivalent fraction would be then a) 1/2 ii)4/8=1/2 b) 4/6=2/3 iv) 8/12= 2/3
3 c) 3/9=1/3 i) 6/18 =1/3 3 d) 2/8=1/4 v) 4/16= 1/4 e) 3/4 iii) 12/16= 3/4 Question 3 Replace in each of the following by the correct number: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) To find an equivalent fraction, we may multiply/divide both the numerator and the denominator by the same number. a) Here in this we have to multiply by 4, so the answer would be 8/28 b) Here in this we have to multiply by 2, so the answer would be 10/16 c) Here in this we have to multiply by 4, so the answer would be 12/20 d) Here in this we have to divide by 3, so the answer would be 15/20
4 e) Here in this we have to divide by 6, so the answer would be 3/4 4 Question 4 Find the equivalent fraction of 3/5 having (a) denominator 20 (b) numerator 9 (c) denominator 30 (d) numerator 27 To find an equivalent fraction, we may multiply/divide both the numerator and the denominator by the same number a) To make denominator 20, we need to multiple both by 4 12/20 b) To make numerator 9, we need to multiple both by 3 9/15 c) To make denominator 30, we need to multiple both by 6 18/30 d) To make numerator 27, we need to multiple both by 9 27/45 Question 5 Find the equivalent fraction of 36/48 with (a) numerator 9 (b) denominator 4
5 a) To make numerator 9, we need to divide both by 4 9/12 5 b) To make denominator 4, we need to divide both by 12 3/4 Question 6 Check whether the given fractions are equivalent: (a) (b) (c) a) for the first fraction 5/9, if multiply both (numerator and denominator) by 6, then we get 30/54 So 5/9 and 30/54 are equivalent fraction b) for the first fraction 3/10, if multiply both (numerator and denominator) by 4, then we get 12/40 and if multiply both (numerator and denominator) by 5 then we get 15/50 So 5/9 and 12/50 are not equivalent fraction c) All the number in both the fraction are prime numbers, so there is no chance of them being equivalent Question 7 Reduce the following fractions to simplest form: (a)
6 6 (b) (c) (d) (e) To reduce the fraction to simplest form, we need to find the HCF of numerator and denominator Let s takes an example of first one 2 48, , ,15 4,5 So HCF will be 2 2 3=12. We can find likewise all the HCF here a) HCF of 48 and 60 is 12, So dividing by 12 on both numerator and denominator b) HCF of 150 and 60 is 12, So dividing by 30 on both numerator and denominator c) HCF of 84 and 98 is 14, So dividing by 14 on both numerator and denominator d) HCF of 12 and 52 is 4, So dividing by 4 on both numerator and denominator 4/5 5/2 6/7 3/13
7 e) HCF of 7 and 28 is 7, So dividing by 7 on both numerator and denominator 7 1/4 Question 8 Ramesh had 20 pencils, Sheela had 50 pencils and Jamaal had 80 pencils. After 4 months, Ramesh used up 10 pencils, Sheela used up 25 pencils and Jamaal used up 40 pencils. What fraction did each use up? Check if each has used up an equal fraction of her/his pencils? Fraction of pencils used by Ramesh = Used pencil/total pencil =10/20 =1/2 Fraction of pencils used by Sheela = Used pencil/total pencil =25/50 =1/2 Fractions of pencils used by Jamaal = Used pencil/total pencil =40/80 =1/2 Yes, they have all used up an equal fraction of his/her pencils. Question 9 Match the equivalent fractions and write two more for each. i) 250/400 a) 2/3 ii) 180/200 b) 2/5 iii) 660/990 c) 1/2 iv) 180/360 d) 5/8 v) 220/550 e) 9/10
8 i) 250/400 = 5/8(Dividing both numerator and denominator by 50) ii) 180/200 =9/10(Dividing both numerator and denominator by 20) iii) 660/990= 2/3(Dividing both numerator and denominator by 330) iv) 180/360= 1/2(Dividing both numerator and denominator by 180) v) 220/550(Dividing both numerator and denominator by 110) d) 5/8 e) 9/10 a) 2/3 c) 1/2 b) 2/5 8 Exercise 7.4 Question 1 Write shaded portion as fraction. Arrange them in ascending and descending order using correct sign <, =, > between the fractions: (a) (b) (c) Show 2/6, 4/6, 8/6, 6/6 on the number line. Put appropriate signs between the fractions given.
9 9 The fractions represented by the shaded portions are as follows: a) 3/8, 6/8, 4/8 1/8 b) 3/8, 4/9, 3/9, 6/9 When we compare two fraction 1) Like Fraction: if the denominator is same, the fraction with the greater numerator is greater. 2) Unlike Fraction: If the denominator is not same, we first get their equivalent fractions with a denominator which is the L.C.M of the denominators of both the fractions The above fractions in a) and b) are like fractions as they have the same denominator. When comparing fractions with same denominator, So, arranging the fractions in ascending order, we have a) 1/8 < 3/8 < 4/8 < 6/8 b) 3/9 < 4/9 < 6/9 < 8/9 c)let us represent the fractions 2/6, 4/6, 8/6, 6/6 on the number line. Again these comparisons are between the like fractions, so numerator will dictate the sign
10 10 Question 2 Compare the fractions and put an appropriate sign. (a) (b) (c) (d) a) Here the fraction is like fraction, so numerator will dictate the sign, since 3 is less than 5 < b) Here the fraction is unlike fraction, we first get their equivalent fractions with a denominator which is the L.C.M of the denominators of both the fractions < LCM of 7 and 4 is 28.
11 Equivalent Fraction for 1/7 will be 4/28 11 Equivalent Fraction for 1/4 will be 7/28 Now as 4 < 7 c) Here the fraction is like fraction, so numerator will dictate the sign, since 4 is less than 5 d) Here the fraction is unlike fraction, we first get their equivalent fractions with a denominator which is the L.C.M of the denominators of both the fractions < > LCM of 5 and 7 is 35. Equivalent Fraction for 3/5 will be 21/35 Equivalent Fraction for 3/7 will be 15/35 Now as 21 > 15 Question 4 Look at the figures and write < or >, = between the given pairs of fractions.
12 12 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) a) < b) > c) >
13 d) = 13 e) < Question 5 How quickly can you do this? Fill appropriate sign ( <, =, > ) (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (I) (j)
14 14 (k) a) If the numerator is same, then the smaller of the denominator fraction is bigger > b) 2/4=1/2 and 3/6=1/2 = c) These are unlike fraction, < So 3/5= 9/15 2/3= 10/15 d) ¾=3/4 > 2/8= 1/4 e) Like fraction < f) Like fraction > g) ¼=1/4 = 2/8=1/4 h) 6/10=3/5 < 4/5=4/5 I) Unlike fraction < j) 6/10=3/5 < 4/5=4/5 k) 5/7=15/21 = Question 6
15 The following fractions represent just three different numbers. Separate them into three groups of equivalent fractions, by changing each one to its simplest form. 15 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (I) (j) (k) (l)
16 16 Simplifying the fraction into simplest form i) 2/12= 1/6 ii) 3/15=1/5 iii) 8/50= 4/25 iv) 16/100= 4/25 v) 10/60=1/6 vi) 15/75=1/5 vii) 12/60=1/5 viii) 16/96=1/6 ix) 12/75=4/25 x) 12/72=1/6 xi) 3/18=1/6 xii) 4/25 1/6 i) v) viii) x) xi) 1/5 ii) vi) vii) 4/25 iii) iv) ix) xii) Question 7 Find answers to the following. Write and indicate how you solved them. (a)?
17 17 (b)? (c)? (d)? We need to first simplify each fraction. After simplication if they are equal, else it is not equal a) Not equal b) Not equal c) equal d) Not equal Question 8 Ila read 25 pages of a book containing 100 pages. Lalita read 2/5 of the same book. Who read less? Total number of pages in the book = 100 pages Number of pages read by Ila = 25 pages Fraction of pages read by Ila = 25/100= 1/4 Lalita read 2/5 of the same book So basically we need to compare the fraction ¼ and 2/5 Since they are unlike fraction, we need to find LCM of 4 and 5 which is 20 So ¼ = 5/20 2/5= 8/20
18 Now 8 > 5 18 So Ila read lesser than Lalita Question 9 Rafiq exercised for 3/6 of an hour, while Rohit exercised for ¾ of an hour. Who exercised for a longer time? Rafiq =3/6 Rohit = ¾ We need to compare the fraction. Since these are unlike fraction, we need to calculate the LCM and 4 and 6. LCM of 4 and 6 is 12 Raft=3/6= 6/12 Rohit= ¾= 9/12 9/12 > 6/12 So clearly Rohit exercised more Question 10 In a class A of 25 students, 20 passed in first class; in another class B of 30 students, 24 passed in first class. In which class was a greater fraction of students getting first class? Total number of students in class A = 25 Number of students passed in first class = 20. Fraction of students of class A who passed in first class = 20/25=4/6
19 Total number of students in class B = Number of students passed in first class = 24. Fraction of students of class B who passed in first class =24/30 =4/6 Both class A and B have the same fraction of students who passed in first class.
**** **** 1=:1 Fractions (iv) TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED. t?t?t?t?t? t?t?t?t?t? Learn and Remember EXERCISE 7.1
 FRACTIONS 7 =: Fractions (iv) (v) Learn and Remember. Fraction means a part of a group or a region. is a fraction. is numerator and is denominator.. Proper fraction is the fraction where numerator is less
FRACTIONS 7 =: Fractions (iv) (v) Learn and Remember. Fraction means a part of a group or a region. is a fraction. is numerator and is denominator.. Proper fraction is the fraction where numerator is less
Exercise 1.1. Page 1 of 22. Website: Mobile:
 Question 1: Exercise 1.1 Use Euclid s division algorithm to find the HCF of: (i) 135 and 225 Since 225 > 135, we apply the division lemma to 225 and 135 to obtain 225 = 135 1 + 90 Since remainder 90 0,
Question 1: Exercise 1.1 Use Euclid s division algorithm to find the HCF of: (i) 135 and 225 Since 225 > 135, we apply the division lemma to 225 and 135 to obtain 225 = 135 1 + 90 Since remainder 90 0,
Fractions and Decimals
 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as
FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as
Month: April No. of Periods: 14
 BLOOM PUBLIC SCHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Subject: MATHEMATICS Class: VII Month: April No. of Periods: 14 Chapter: 1 Integers TTT: 6 WT: 8 CHAPTER Integers Learning Objectives Resources The
BLOOM PUBLIC SCHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Subject: MATHEMATICS Class: VII Month: April No. of Periods: 14 Chapter: 1 Integers TTT: 6 WT: 8 CHAPTER Integers Learning Objectives Resources The
Fractions. Dividing the numerator and denominator by the highest common element (or number) in them, we get the fraction in its lowest form.
 Fractions A fraction is a part of the whole (object, thing, region). It forms the part of basic aptitude of a person to have and idea of the parts of a population, group or territory. Civil servants must
Fractions A fraction is a part of the whole (object, thing, region). It forms the part of basic aptitude of a person to have and idea of the parts of a population, group or territory. Civil servants must
Manipulate expressions containing surds and rationalise denominators (A*) Able to simplify surds (A)
 Moving from A to A* Manipulate expressions containing surds and rationalise denominators (A*) Solve using surds (A*) A* Solve direct and inverse variation three variables (A*) A* Find formulae describing
Moving from A to A* Manipulate expressions containing surds and rationalise denominators (A*) Solve using surds (A*) A* Solve direct and inverse variation three variables (A*) A* Find formulae describing
DECIMAL FRACTIONS. Thus, 0.25=25/100=1/4;2.008=2008/1000=251/125.
 DECIMAL FRACTIONS I. Decimal Fractions : Fractions in which denominators are powers of 10 are known as decimal fractions. Thus,1/10=1 tenth=.1;1/100=1 hundredth =.01; 99/100=99 hundreths=.99;7/1000=7 thousandths=.007,etc
DECIMAL FRACTIONS I. Decimal Fractions : Fractions in which denominators are powers of 10 are known as decimal fractions. Thus,1/10=1 tenth=.1;1/100=1 hundredth =.01; 99/100=99 hundreths=.99;7/1000=7 thousandths=.007,etc
Section 3.2 Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals. 1. Model fractions and/or decimals using blocks, fraction pieces, pattern blocks, etc.
 Section 3.2 Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals We will use several methods to compare and order fractions: 1. Model fractions and/or decimals using blocks, fraction pieces, pattern blocks, etc.
Section 3.2 Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals We will use several methods to compare and order fractions: 1. Model fractions and/or decimals using blocks, fraction pieces, pattern blocks, etc.
What is a Fraction? Fractions. One Way To Remember Numerator = North / 16. Example. What Fraction is Shaded? 9/16/16. Fraction = Part of a Whole
 // Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
// Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
Rational Numbers 11II. Learn and Remember
 11II. Rational Numbers Learn and Remember 1. A rational number can be expressed in the form of J!..., where q p and q are integers and q "* 0. 2. All integers and fractions are rational numbers.. To convert
11II. Rational Numbers Learn and Remember 1. A rational number can be expressed in the form of J!..., where q p and q are integers and q "* 0. 2. All integers and fractions are rational numbers.. To convert
Chapter 1 Section 1 Lesson: Solving Linear Equations
 Introduction Linear equations are the simplest types of equations to solve. In a linear equation, all variables are to the first power only. All linear equations in one variable can be reduced to the form
Introduction Linear equations are the simplest types of equations to solve. In a linear equation, all variables are to the first power only. All linear equations in one variable can be reduced to the form
Rational Numbers CHAPTER Introduction
 RATIONAL NUMBERS Rational Numbers CHAPTER. Introduction In Mathematics, we frequently come across simple equations to be solved. For example, the equation x + () is solved when x, because this value of
RATIONAL NUMBERS Rational Numbers CHAPTER. Introduction In Mathematics, we frequently come across simple equations to be solved. For example, the equation x + () is solved when x, because this value of
i) Natural numbers: Counting numbers, i.e, 1, 2, 3, 4,. are called natural numbers.
 Chapter 1 Integers Types of Numbers i) Natural numbers: Counting numbers, i.e, 1, 2, 3, 4,. are called natural numbers. ii) Whole numbers: Counting numbers and 0, i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,.. are called whole
Chapter 1 Integers Types of Numbers i) Natural numbers: Counting numbers, i.e, 1, 2, 3, 4,. are called natural numbers. ii) Whole numbers: Counting numbers and 0, i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,.. are called whole
The Bracket Strategy
 The Bracket Strategy This strategy will show students how common denominators are actually found. This strategy should be done with fraction bars. Step Create a bracket X Step Fill in the bracket with
The Bracket Strategy This strategy will show students how common denominators are actually found. This strategy should be done with fraction bars. Step Create a bracket X Step Fill in the bracket with
Microsoft Power Tools for Data Analysis #10 Power BI M Code: Helper Table to Calculate MAT By Month & Product. Notes from Video:
 Microsoft Power Tools for Data Analysis #10 Power BI M Code: Helper Table to Calculate MAT By Month & Product Table of Contents: Notes from Video: 1. Intermediate Fact Table / Helper Table:... 1 2. Goal
Microsoft Power Tools for Data Analysis #10 Power BI M Code: Helper Table to Calculate MAT By Month & Product Table of Contents: Notes from Video: 1. Intermediate Fact Table / Helper Table:... 1 2. Goal
Grade 4 Fractions. Answer the questions. For more such worksheets visit (1) Convert into a mixed fraction. (2) Convert
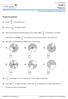 ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
Dawood Public School Course Outline Class IV Math
 Dawood Public School Course Outline 2016-2017 Class IV Math Books: Lu jitan, New Syllabus Primary Mathematics 4 along with practice books 4a and 4b, Singapore; Oxford University Monthly Syllabus for the
Dawood Public School Course Outline 2016-2017 Class IV Math Books: Lu jitan, New Syllabus Primary Mathematics 4 along with practice books 4a and 4b, Singapore; Oxford University Monthly Syllabus for the
Objective A Identify the numerator and the denominator of a fraction. When the numerator is less than the denominator, it is a(n) fraction.
 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.. Pause the video as needed to fill in all blanks.
Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.. Pause the video as needed to fill in all blanks.
 - 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
- 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
Matrix Inverse 2 ( 2) 1 = 2 1 2
 Name: Matrix Inverse For Scalars, we have what is called a multiplicative identity. This means that if we have a scalar number, call it r, then r multiplied by the multiplicative identity equals r. Without
Name: Matrix Inverse For Scalars, we have what is called a multiplicative identity. This means that if we have a scalar number, call it r, then r multiplied by the multiplicative identity equals r. Without
Faculty Expertise Database
 Faculty Expertise Database Log into USCeRA at https://sam.research.sc.edu/uscera Next, click on Faculty Expertise to access your Curriculum Vitae. Click on My Curriculum Vitae to access your vitae information.
Faculty Expertise Database Log into USCeRA at https://sam.research.sc.edu/uscera Next, click on Faculty Expertise to access your Curriculum Vitae. Click on My Curriculum Vitae to access your vitae information.
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
 #2081 GLA Guided Learning Activity Multiplying and Dividing Fractions This packet contains background information for GLA 2081a, 2081b, etc. It is intended for student and tutor use as needed. Author:
#2081 GLA Guided Learning Activity Multiplying and Dividing Fractions This packet contains background information for GLA 2081a, 2081b, etc. It is intended for student and tutor use as needed. Author:
Building Equivalent Fractions, the Least Common Denominator, and Ordering Fractions
 Section. PRE-ACTIVITY PREPARATION Building Equivalent Fractions, the Least Common Denominator, and Ordering Fractions You have learned that a fraction might be written in an equivalent form by reducing
Section. PRE-ACTIVITY PREPARATION Building Equivalent Fractions, the Least Common Denominator, and Ordering Fractions You have learned that a fraction might be written in an equivalent form by reducing
Algebra II Chapter 8 Part 2: Rational Functions
 Algebra II Chapter 8 Part 2: Rational Functions Chapter 8 Lesson 4 Multiply and Divide Rational Functions Vocabulary Words to Review: Reciprocal The rules of fractions DO NOT change! *When adding and subtracting,
Algebra II Chapter 8 Part 2: Rational Functions Chapter 8 Lesson 4 Multiply and Divide Rational Functions Vocabulary Words to Review: Reciprocal The rules of fractions DO NOT change! *When adding and subtracting,
ADDING AND SUBTRACTING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
 ADDING AND SUBTRACTING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS To Add or Subtract Two Fractions, 0, 0 Example 1 a) Add b) Subtract a) b) The same principles apply when adding or subtracting rational expressions containing
ADDING AND SUBTRACTING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS To Add or Subtract Two Fractions, 0, 0 Example 1 a) Add b) Subtract a) b) The same principles apply when adding or subtracting rational expressions containing
INDIAN SCHOOL SOHAR FIRST TERM EXAM ( ) INFORMATICS PRACTICES
 INDIAN SCHOOL SOHAR FIRST TERM EXAM (2015-2016) INFORMATICS PRACTICES Page 1 of 5 No. of printed pages: 5 Class: XI Marks: 70 Date: 10-09-15 Time: 3 hours Instructions: a. All the questions are compulsory.
INDIAN SCHOOL SOHAR FIRST TERM EXAM (2015-2016) INFORMATICS PRACTICES Page 1 of 5 No. of printed pages: 5 Class: XI Marks: 70 Date: 10-09-15 Time: 3 hours Instructions: a. All the questions are compulsory.
Solutions for Transformations of Functions
 Solutions for Transformations of Functions I. Souldatos February 20, 209 Answers Problem... Let f(x) = (x + 3) x (x ). Match the following compositions with the functions below. A. f(x + 2) B. f(x 2) C.
Solutions for Transformations of Functions I. Souldatos February 20, 209 Answers Problem... Let f(x) = (x + 3) x (x ). Match the following compositions with the functions below. A. f(x + 2) B. f(x 2) C.
Place Value and Operations with Whole Numbers
 M a t h e m a t i c s Place Value and Operations with Whole Numbers Project: Food in Space.........................2 Developing understanding and fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing
M a t h e m a t i c s Place Value and Operations with Whole Numbers Project: Food in Space.........................2 Developing understanding and fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing
Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.1: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers.
 Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers. (9N3) Procedure: This unit will introduce the concept of rational numbers. This
Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers. (9N3) Procedure: This unit will introduce the concept of rational numbers. This
ALGEBRA I Summer Packet
 ALGEBRA I Summer Packet 2018-2019 Name 7 th Grade Math Teacher: Objectives for Algebra I Summer Packet I. Variables and translating (Problems #1 5) Write Algebraic Expressions Writing Algebraic Equations
ALGEBRA I Summer Packet 2018-2019 Name 7 th Grade Math Teacher: Objectives for Algebra I Summer Packet I. Variables and translating (Problems #1 5) Write Algebraic Expressions Writing Algebraic Equations
Fractions and Decimals
 Chapter Fractions and Decimals FRACTION: A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects. 5 is a fraction with numerator and denominator 5.
Chapter Fractions and Decimals FRACTION: A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects. 5 is a fraction with numerator and denominator 5.
MATHEMATICS HOLIDAY WORK FOR S.1, S.2, S.3 AND S.4 WED, 08 TH JAN 2014.
 MATHEMATICS HOLIDAY WORK FOR S., S., S. AND S. WED, 08 TH JAN 0. INSTRUCTIONS:. Read the notes below on fractions carefully and answer the exercise on pages and.. Note the mistakes pointed out and avoid
MATHEMATICS HOLIDAY WORK FOR S., S., S. AND S. WED, 08 TH JAN 0. INSTRUCTIONS:. Read the notes below on fractions carefully and answer the exercise on pages and.. Note the mistakes pointed out and avoid
3.1 Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts. 3.1 Dividing a Set into Fractional Parts. 3.2 Identifying Parts of Wholes.
 . Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
. Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
Section A Arithmetic ( 5) Exercise A
 Section A Arithmetic In the non-calculator section of the examination there might be times when you need to work with quite awkward numbers quickly and accurately. In particular you must be very familiar
Section A Arithmetic In the non-calculator section of the examination there might be times when you need to work with quite awkward numbers quickly and accurately. In particular you must be very familiar
Lesson 1T ~ Greatest Common Factor
 Lesson T ~ Greatest Common Factor Name Period Date List the factors of each number. Decide whether the number is prime or composite.. 9. 9 9 Is 9 prime or composite? Is prime or composite?.. Is prime or
Lesson T ~ Greatest Common Factor Name Period Date List the factors of each number. Decide whether the number is prime or composite.. 9. 9 9 Is 9 prime or composite? Is prime or composite?.. Is prime or
NF5-21 Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages 13 14
 NF- Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages STANDARDS.NF.B. Goals Students will develop and apply the formula for multiplying unit fractions by unit fractions. Vocabulary denominator numerator of (to mean multiply
NF- Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages STANDARDS.NF.B. Goals Students will develop and apply the formula for multiplying unit fractions by unit fractions. Vocabulary denominator numerator of (to mean multiply
New stage 1 New stage 2
 iv 1 New stage 1 New stage 2 Integers four rules, rounding and ordering 1.1 Face value and place value 1 Using place value diagrams NA2a 1.2 Reading, writing and 2 3 Using place value to read, write NA2a
iv 1 New stage 1 New stage 2 Integers four rules, rounding and ordering 1.1 Face value and place value 1 Using place value diagrams NA2a 1.2 Reading, writing and 2 3 Using place value to read, write NA2a
Gateway Regional School District VERTICAL ALIGNMENT OF MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Grades 3-6
 NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
SWALLOW SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GUIDE. Stage 1: Desired Results
 SWALLOW SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GUIDE Curriculum Area: Math Course Length: Full Year Grade: 5th Date Last Approved: June 2015 Stage 1: Desired Results Course Description and Purpose: 5th grade offers
SWALLOW SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GUIDE Curriculum Area: Math Course Length: Full Year Grade: 5th Date Last Approved: June 2015 Stage 1: Desired Results Course Description and Purpose: 5th grade offers
SCHEME OF WORK Yr 7 DELTA 1 UNIT / LESSON
 SCHEME OF WORK Yr 7 DELTA 1 UNIT / LESSON STEPS FROM STEPS TO OBJECTIVES 1 Analysing and displaying data 2 7 1.1 Two-way tables and bar charts 2 5 Use two-way tables. Interpret and draw dual bar charts
SCHEME OF WORK Yr 7 DELTA 1 UNIT / LESSON STEPS FROM STEPS TO OBJECTIVES 1 Analysing and displaying data 2 7 1.1 Two-way tables and bar charts 2 5 Use two-way tables. Interpret and draw dual bar charts
SWALLOW SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GUIDE. Stage 1: Desired Results
 SWALLOW SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GUIDE Curriculum Area: Math Course Length: Full Year Grade: 6th Date Last Approved: June 2015 Stage 1: Desired Results Course Description and Purpose: In Grade 6, instructional
SWALLOW SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GUIDE Curriculum Area: Math Course Length: Full Year Grade: 6th Date Last Approved: June 2015 Stage 1: Desired Results Course Description and Purpose: In Grade 6, instructional
#1 MATH 6 SOL PRACTICE PACKET #1 Number Sense
 NAME: BLOCK: Due date: #1 MATH 6 SOL PRACTICE PACKET #1 Number Sense do not lose this packet!!! You MUST do EVERY problem. Page 1 of 14 Reporting Category: Number and Number Sense Number of Items: 10 Standards
NAME: BLOCK: Due date: #1 MATH 6 SOL PRACTICE PACKET #1 Number Sense do not lose this packet!!! You MUST do EVERY problem. Page 1 of 14 Reporting Category: Number and Number Sense Number of Items: 10 Standards
25 Live Scheduling System Student Instructions
 25 Live Scheduling System Student Instructions Students will now be able to reserve the small study rooms in the Learning Commons. This guide will give you simple instructions on how to do this. Once at
25 Live Scheduling System Student Instructions Students will now be able to reserve the small study rooms in the Learning Commons. This guide will give you simple instructions on how to do this. Once at
Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10.
 PA Ch 5 Rational Expressions Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 0. Since decimals are special
PA Ch 5 Rational Expressions Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 0. Since decimals are special
FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS
 Mathematics Revision Guides Fractions and Decimals Page of MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS Version: Date: -0-0 Mathematics Revision Guides
Mathematics Revision Guides Fractions and Decimals Page of MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS Version: Date: -0-0 Mathematics Revision Guides
Maths Revision Worksheet: Algebra I Week 1 Revision 5 Problems per night
 2 nd Year Maths Revision Worksheet: Algebra I Maths Revision Worksheet: Algebra I Week 1 Revision 5 Problems per night 1. I know how to add and subtract positive and negative numbers. 2. I know how to
2 nd Year Maths Revision Worksheet: Algebra I Maths Revision Worksheet: Algebra I Week 1 Revision 5 Problems per night 1. I know how to add and subtract positive and negative numbers. 2. I know how to
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 1
 Getting Ready to Teach Unit Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study fractions and mixed numbers They find equivalent fractions, compare fractions, and add and subtract fractions
Getting Ready to Teach Unit Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study fractions and mixed numbers They find equivalent fractions, compare fractions, and add and subtract fractions
INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 INVERSE TRIGNMETRIC FUNCTINS INTRDUCTIN In chapter we learnt that only one-one and onto functions are invertible. If a function f is one-one and onto then its inverse exists and is denoted by f. We shall
INVERSE TRIGNMETRIC FUNCTINS INTRDUCTIN In chapter we learnt that only one-one and onto functions are invertible. If a function f is one-one and onto then its inverse exists and is denoted by f. We shall
Computer Programming C++ (wg) CCOs
 Computer Programming C++ (wg) CCOs I. The student will analyze the different systems, and languages of the computer. (SM 1.4, 3.1, 3.4, 3.6) II. The student will write, compile, link and run a simple C++
Computer Programming C++ (wg) CCOs I. The student will analyze the different systems, and languages of the computer. (SM 1.4, 3.1, 3.4, 3.6) II. The student will write, compile, link and run a simple C++
4th Pui Ching Invitational Mathematics Competition. Heat Event (Secondary 2)
 4th Pui Ching Invitational Mathematics Competition Heat Event (Secondary 2) 1 15 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Instructions to Contestants: 1. 20 100 There are 20 questions in this paper and the total
4th Pui Ching Invitational Mathematics Competition Heat Event (Secondary 2) 1 15 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Instructions to Contestants: 1. 20 100 There are 20 questions in this paper and the total
Roll No. :... Invigilator's Signature : UNIX AND SHELL PROGRAMMING. Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70
 Name : Roll No. :... Invigilator's Signature :. CS/BCA/SEM-5/BCA-502/2011-12 2011 UNIX AND SHELL PROGRAMMING Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates
Name : Roll No. :... Invigilator's Signature :. CS/BCA/SEM-5/BCA-502/2011-12 2011 UNIX AND SHELL PROGRAMMING Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates
50 MATHCOUNTS LECTURES (6) OPERATIONS WITH DECIMALS
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Decimal representation: A decimal is used to represent a portion of whole. It contains three parts: an integer (which indicates the number of wholes), a decimal point (which separates
BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Decimal representation: A decimal is used to represent a portion of whole. It contains three parts: an integer (which indicates the number of wholes), a decimal point (which separates
Accuplacer Arithmetic Review
 Accuplacer Arithmetic Review Hennepin Technical College Placement Testing for Success Page Overview The Arithmetic section of ACCUPLACER contains 7 multiple choice questions that measure your ability to
Accuplacer Arithmetic Review Hennepin Technical College Placement Testing for Success Page Overview The Arithmetic section of ACCUPLACER contains 7 multiple choice questions that measure your ability to
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone Copyright Pearson Australia (a divsion of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd)
 Contents Chapter 1 Whole numbers R1.1 Mathematics in sentences R1.2 Rounding to the first digit R1.3 Operations on whole numbers R1.4 Addition of whole numbers R1.5 Consecutive numbers R1.6 Ordering R1.7
Contents Chapter 1 Whole numbers R1.1 Mathematics in sentences R1.2 Rounding to the first digit R1.3 Operations on whole numbers R1.4 Addition of whole numbers R1.5 Consecutive numbers R1.6 Ordering R1.7
Database Design Lab: MS Access Forms
 Database Design Lab: MS Access Forms 1. Download lab5.accdb and rename it to lab6.accdb. 2. View the Relationship (Database Tools tab) to get an overview of the data model. 3. Create a data entry form
Database Design Lab: MS Access Forms 1. Download lab5.accdb and rename it to lab6.accdb. 2. View the Relationship (Database Tools tab) to get an overview of the data model. 3. Create a data entry form
New stage 1 New stage 2
 iv New stage 1 New stage 2 1 Integers and powers 1.1 Integers and place value 1 2 Reading, writing and ordering NA2a integers and 1.2 Calculating with negative 2 4 The four operations with NA2a/3a numbers
iv New stage 1 New stage 2 1 Integers and powers 1.1 Integers and place value 1 2 Reading, writing and ordering NA2a integers and 1.2 Calculating with negative 2 4 The four operations with NA2a/3a numbers
5.5 Complex Fractions
 5.5 Complex Fractions At this point, right after we cover all the basic operations, we would usually turn our attention to solving equations. However, there is one other type of rational expression that
5.5 Complex Fractions At this point, right after we cover all the basic operations, we would usually turn our attention to solving equations. However, there is one other type of rational expression that
AP Calculus AB Summer Review Packet
 AP Calculus AB Summer Review Packet Mr. Burrows Mrs. Deatherage 1. This packet is to be handed in to your Calculus teacher on the first day of the school year. 2. All work must be shown on separate paper
AP Calculus AB Summer Review Packet Mr. Burrows Mrs. Deatherage 1. This packet is to be handed in to your Calculus teacher on the first day of the school year. 2. All work must be shown on separate paper
Integrated Curriculum for Secondary Schools. MATHEMATICS Form 1
 MINISTRY OF EDUCATION MALAYSIA Integrated Curriculum for Secondary Schools Curriculum Specifications MATHEMATICS Form 1 Curriculum Development Centre Ministry of Education Malaysia 2002 CONTENTS Page WHOLE
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION MALAYSIA Integrated Curriculum for Secondary Schools Curriculum Specifications MATHEMATICS Form 1 Curriculum Development Centre Ministry of Education Malaysia 2002 CONTENTS Page WHOLE
Mathematics. Name: Class: Transforming Life chances
 Mathematics Name: Class: Transforming Life chances Children first- Aspire- Challenge- Achieve Aspire: To be the best I can be in everything that I try to do. To use the adults and resources available both
Mathematics Name: Class: Transforming Life chances Children first- Aspire- Challenge- Achieve Aspire: To be the best I can be in everything that I try to do. To use the adults and resources available both
and denominators of two fractions. For example, you could use
 Learning Goal denominators. Open Question and denominators of two fractions. For example, you could use and 0. Make sure that some of your fractions are improper and some are proper. Make sure that some
Learning Goal denominators. Open Question and denominators of two fractions. For example, you could use and 0. Make sure that some of your fractions are improper and some are proper. Make sure that some
To begin this textbook, we need to start with a refresher of the topics of numbers and numbering systems.
 1.1 Integers To begin this textbook, we need to start with a refresher of the topics of numbers and numbering systems. We will start, here, with a recap of the simplest of numbering systems, the integers.
1.1 Integers To begin this textbook, we need to start with a refresher of the topics of numbers and numbering systems. We will start, here, with a recap of the simplest of numbering systems, the integers.
HOW TO DIVIDE: MCC6.NS.2 Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE
 MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
Section A. 1. is the alignment where the text is aligned from the left edge and ragged from the right edge.
 ICT GRAND WORKSHEET- CLASS-5 2 nd Term - 2014-15 Chapters 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9. Fill in the blanks with the correct answers. Section A 1. is the alignment where the text is aligned from the left edge and ragged
ICT GRAND WORKSHEET- CLASS-5 2 nd Term - 2014-15 Chapters 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9. Fill in the blanks with the correct answers. Section A 1. is the alignment where the text is aligned from the left edge and ragged
DTS PAX (Public Access)
 DTS PAX (Public Access) I. INTRODUCTION... 1 II. Account Registration.....3 III. My Account...5 IV. My Account Profile......6 V. My Account History...7 VI. My Account - Charge Account.8 VII. Account Login..9
DTS PAX (Public Access) I. INTRODUCTION... 1 II. Account Registration.....3 III. My Account...5 IV. My Account Profile......6 V. My Account History...7 VI. My Account - Charge Account.8 VII. Account Login..9
Y7 Learning Stage 1. Y7 Learning Stage 2. Y7 Learning Stage 3
 Y7 Learning Stage 1 Y7 Learning Stage 2 Y7 Learning Stage 3 Understand simple algebraic notation. Collect like terms to simplify algebraic expressions. Use coordinates in the first quadrant. Make a comparative
Y7 Learning Stage 1 Y7 Learning Stage 2 Y7 Learning Stage 3 Understand simple algebraic notation. Collect like terms to simplify algebraic expressions. Use coordinates in the first quadrant. Make a comparative
5.6 Rational Equations
 5.6 Rational Equations Now that we have a good handle on all of the various operations on rational expressions, we want to turn our attention to solving equations that contain rational expressions. The
5.6 Rational Equations Now that we have a good handle on all of the various operations on rational expressions, we want to turn our attention to solving equations that contain rational expressions. The
Introduction to Fractions
 Introduction to Fractions Fractions represent parts of a whole. The top part of a fraction is called the numerator, while the bottom part of a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator states
Introduction to Fractions Fractions represent parts of a whole. The top part of a fraction is called the numerator, while the bottom part of a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator states
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS. Date: Lesson: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers
 Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Chapter 1 Operations With Numbers
 Chapter 1 Operations With Numbers Part I Negative Numbers You may already know what negative numbers are, but even if you don t, then you have probably seen them several times over the past few days. If
Chapter 1 Operations With Numbers Part I Negative Numbers You may already know what negative numbers are, but even if you don t, then you have probably seen them several times over the past few days. If
FUNDAMENTAL ARITHMETIC
 FUNDAMENTAL ARITHMETIC Prime Numbers Prime numbers are any whole numbers greater than that can only be divided by and itself. Below is the list of all prime numbers between and 00: Prime Factorization
FUNDAMENTAL ARITHMETIC Prime Numbers Prime numbers are any whole numbers greater than that can only be divided by and itself. Below is the list of all prime numbers between and 00: Prime Factorization
A triangle that has three acute angles Example:
 1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
Appendix 2 Number Representations
 Appendix 2 Number Representations There are many different ways to represent whole numbers. While we are comfortable counting in decimal (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, ), that is only one set of names
Appendix 2 Number Representations There are many different ways to represent whole numbers. While we are comfortable counting in decimal (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, ), that is only one set of names
TOPIC 2 DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3
 TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
MATH WIZARD USER GUIDE. Page 1 of 15. Created by Landorocks 2007 Teacher Created Resources, Inc. TCR1234 Math Wizard
 MATH WIZARD USER GUIDE Created by Landorocks 2007 Teacher Created Resources, Inc. TCR1234 Math Wizard Page 1 of 15 TABLE OF CONTENTS: I. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 2 II. INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS... 2 III.
MATH WIZARD USER GUIDE Created by Landorocks 2007 Teacher Created Resources, Inc. TCR1234 Math Wizard Page 1 of 15 TABLE OF CONTENTS: I. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 2 II. INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS... 2 III.
Number Sense Workbook 7, Part 1: Unit 3
 Number Sense Workbook, Part : Unit Worksheet NS- page. a),, : 0,,,,, 0, : 0,, 0,, 0,, 0. a) Yes No Yes; Yes; Yes. a) 0 All whole numbers, since any whole number times zero is zero.. is a factor of. is
Number Sense Workbook, Part : Unit Worksheet NS- page. a),, : 0,,,,, 0, : 0,, 0,, 0,, 0. a) Yes No Yes; Yes; Yes. a) 0 All whole numbers, since any whole number times zero is zero.. is a factor of. is
Mathematics Stage 4 Diagnostic Tasks Answers with Common Errors
 Mathematics Stage 4 Diagnostic Tasks Answers with Answers Computation with Integers An integer is a positive or negative whole number, or zero. Not recognising negative numbers as integers. Just writing
Mathematics Stage 4 Diagnostic Tasks Answers with Answers Computation with Integers An integer is a positive or negative whole number, or zero. Not recognising negative numbers as integers. Just writing
Thousands. Hundreds. Tenths. Ones. Tens. Hundredths. Decimal Point. Thousandths. Place Value. 1000s 100s 10s 1s.
 Place Value Thousandths Hundredths Tenths Decimal Point Ones Tens Hundreds Thousands 000s 00s 0s s. 0 00 000 Know the meanings of these column headings is very important. It tells us the value of each
Place Value Thousandths Hundredths Tenths Decimal Point Ones Tens Hundreds Thousands 000s 00s 0s s. 0 00 000 Know the meanings of these column headings is very important. It tells us the value of each
Description Reflect and Review Teasers Answers Recall basics of fractions. Review
 1. Revision Recall basics of fractions. are equivalent fractions of. Since Write five equivalent fractions of. 2. Rational Numbers A number is defined as a number which can be represented in the form of,
1. Revision Recall basics of fractions. are equivalent fractions of. Since Write five equivalent fractions of. 2. Rational Numbers A number is defined as a number which can be represented in the form of,
Scheme of work Elementary 1, the maths pathway
 Objective Code Objective Exemplification Links to prior objectives Resources, enrichment, notes E1.1 Multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 including decimals. 6 x 10, 6.5 x 10, 0.65 10 3 x 100,
Objective Code Objective Exemplification Links to prior objectives Resources, enrichment, notes E1.1 Multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 including decimals. 6 x 10, 6.5 x 10, 0.65 10 3 x 100,
MATH. Finding The Least Common Multiple of a Set of Numbers
 5 Module 11 MATH Finding The Least Common Multiple of a Set of Numbers A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development To the Learner Hi! Dear learner.
5 Module 11 MATH Finding The Least Common Multiple of a Set of Numbers A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development To the Learner Hi! Dear learner.
Math 7 Notes Unit 2B: Rational Numbers
 Math 7 Notes Unit B: Rational Numbers Teachers Before we move to performing operations involving rational numbers, we must be certain our students have some basic understandings and skills. The following
Math 7 Notes Unit B: Rational Numbers Teachers Before we move to performing operations involving rational numbers, we must be certain our students have some basic understandings and skills. The following
( 3) ( 4 ) 1. Exponents and Radicals ( ) ( xy) 1. MATH 102 College Algebra. still holds when m = n, we are led to the result
 Exponents and Radicals ZERO & NEGATIVE EXPONENTS If we assume that the relation still holds when m = n, we are led to the result m m a m n 0 a = a = a. Consequently, = 1, a 0 n n a a a 0 = 1, a 0. Then
Exponents and Radicals ZERO & NEGATIVE EXPONENTS If we assume that the relation still holds when m = n, we are led to the result m m a m n 0 a = a = a. Consequently, = 1, a 0 n n a a a 0 = 1, a 0. Then
C A S I O f x L B UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND. The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit
 C A S I O f x - 8 2 L B UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit MASTERING THE CALCULATOR USING THE CASIO fx-82lb Learning and Teaching Support Unit (LTSU)
C A S I O f x - 8 2 L B UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit MASTERING THE CALCULATOR USING THE CASIO fx-82lb Learning and Teaching Support Unit (LTSU)
Contents. About the Author. Decimals. Acknowledgments. Correlation Chart. Whole Numbers
 Contents iii vi vi xi Preface About the Author Acknowledgments Correlation Chart Whole Numbers 3 Know Your Bowling Score! Addition of Whole Numbers; Mental Math (Activity, page 149) 5 Counting Calories
Contents iii vi vi xi Preface About the Author Acknowledgments Correlation Chart Whole Numbers 3 Know Your Bowling Score! Addition of Whole Numbers; Mental Math (Activity, page 149) 5 Counting Calories
Course Outlines. Elementary Mathematics (Grades K-5) Kids and Numbers (Recommended for K-1 students)
 Course Outlines Elementary Mathematics (Grades K-5) Kids and Numbers (Recommended for K-1 students) Shapes and Patterns. Grouping objects by similar properties. Identifying simple figures within a complex
Course Outlines Elementary Mathematics (Grades K-5) Kids and Numbers (Recommended for K-1 students) Shapes and Patterns. Grouping objects by similar properties. Identifying simple figures within a complex
Grade 6 Math Vocabulary
 Ratio, Rate, Unit Rate, Rate Unit Grade 6 Math Vocabulary Ratio, Rate, Unit Rate, Rate Unit Representing Equivalent Ratios Double Number Line 0 Ratio: An ordered pair of numbers which are not both zero.
Ratio, Rate, Unit Rate, Rate Unit Grade 6 Math Vocabulary Ratio, Rate, Unit Rate, Rate Unit Representing Equivalent Ratios Double Number Line 0 Ratio: An ordered pair of numbers which are not both zero.
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2015 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 7
 ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2015 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 7 INTRODUCTION The 2015 cycle of Annual National Assessment (ANA 2015) will be administered in all public and designated 1 independent
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2015 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 7 INTRODUCTION The 2015 cycle of Annual National Assessment (ANA 2015) will be administered in all public and designated 1 independent
Chapter 13. Curriculum for Grade 6
 TEAM-Math Curriculum Guide DRAFT July 22, 2004 p. 6-1 Part A. Correlation of Objectives with Recommended Textbooks Number Strand Grade 6 Chapter 13. Curriculum for Grade 6 1. Demonstrate computational
TEAM-Math Curriculum Guide DRAFT July 22, 2004 p. 6-1 Part A. Correlation of Objectives with Recommended Textbooks Number Strand Grade 6 Chapter 13. Curriculum for Grade 6 1. Demonstrate computational
Chapter 1 Readme.doc definitions you need to know 1
 Contents Foreword xi Preface to the second edition xv Introduction xvii Chapter 1 Readme.doc definitions you need to know 1 Sample data 1 Italics 1 Introduction 1 Dimensions, measures, members and cells
Contents Foreword xi Preface to the second edition xv Introduction xvii Chapter 1 Readme.doc definitions you need to know 1 Sample data 1 Italics 1 Introduction 1 Dimensions, measures, members and cells
Year 7 Key Performance Indicators Maths (Number)
 Key Performance Indicators Maths (Number) M7.1 N1: I can use the four operations to answer calculations involving decimals. Use correct notation for recurring decimals, know the denominators of simple
Key Performance Indicators Maths (Number) M7.1 N1: I can use the four operations to answer calculations involving decimals. Use correct notation for recurring decimals, know the denominators of simple
X Std. Topic Content Expected Learning Outcomes Mode of Transaction
 X Std COMMON SYLLABUS 2009 - MATHEMATICS I. Theory of Sets ii. Properties of operations on sets iii. De Morgan s lawsverification using example Venn diagram iv. Formula for n( AÈBÈ C) v. Functions To revise
X Std COMMON SYLLABUS 2009 - MATHEMATICS I. Theory of Sets ii. Properties of operations on sets iii. De Morgan s lawsverification using example Venn diagram iv. Formula for n( AÈBÈ C) v. Functions To revise
Converting between Percents, Decimals, and Fractions
 Section. PRE-ACTIVITY PREPARATION Converting between Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Think about how often you have heard, read, or used the term percent (%) in its many everyday applications: The sales
Section. PRE-ACTIVITY PREPARATION Converting between Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Think about how often you have heard, read, or used the term percent (%) in its many everyday applications: The sales
S H A R P E L R H UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND. The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit
 S H A R P E L - 5 3 1 R H UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction 1 A word about starting out 2 1. Addition and subtraction
S H A R P E L - 5 3 1 R H UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction 1 A word about starting out 2 1. Addition and subtraction
Functional Skills Mathematics
 Functional Skills Mathematics Level Learning Resource Fractions N/L. N/L. LEVEL Contents Numerator and Denominator N/L. Page Equivalent Fractions N/L. Pages - Comparing Fractions N/L. Pages - Improper
Functional Skills Mathematics Level Learning Resource Fractions N/L. N/L. LEVEL Contents Numerator and Denominator N/L. Page Equivalent Fractions N/L. Pages - Comparing Fractions N/L. Pages - Improper
Lesson 9: Decimal Expansions of Fractions, Part 1
 Classwork Opening Exercises 1 2 1. a. We know that the fraction can be written as a finite decimal because its denominator is a product of 2 s. Which power of 10 will allow us to easily write the fraction
Classwork Opening Exercises 1 2 1. a. We know that the fraction can be written as a finite decimal because its denominator is a product of 2 s. Which power of 10 will allow us to easily write the fraction
CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK. Creating a New Project in IRBNet. i. After logging in, click Create New Project on left side of the page.
 CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK Creating a New Project in IRBNet i. After logging in, click Create New Project on left side of the page. ii. Enter the title of the project, the principle investigator s (PI)
CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK Creating a New Project in IRBNet i. After logging in, click Create New Project on left side of the page. ii. Enter the title of the project, the principle investigator s (PI)
Certificate Program. Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2013
 Certificate Program We offer online education programs designed to provide the workforce skills necessary to enter a new field or advance your current career. Our Online Career Training Programs in the
Certificate Program We offer online education programs designed to provide the workforce skills necessary to enter a new field or advance your current career. Our Online Career Training Programs in the
Class Book. Anita Straker, Tony Fisher, Rosalyn Hyde, Sue Jennings and Jonathan Longstaffe
 Class Book Anita Straker, Tony Fisher, Rosalyn Hyde, Sue Jennings and Jonathan Longstaffe 5 Contents Tier 5 N5.1 Powers and roots 1 1 Integer powers of numbers 1 Estimating square roots 3 3 Prime factor
Class Book Anita Straker, Tony Fisher, Rosalyn Hyde, Sue Jennings and Jonathan Longstaffe 5 Contents Tier 5 N5.1 Powers and roots 1 1 Integer powers of numbers 1 Estimating square roots 3 3 Prime factor
C A S I O f x S UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND. The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit
 C A S I O f x - 1 0 0 S UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit MASTERING THE CALCULATOR USING THE CASIO fx-100s Learning and Teaching Support Unit (LTSU)
C A S I O f x - 1 0 0 S UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND The Learning Centre Learning and Teaching Support Unit MASTERING THE CALCULATOR USING THE CASIO fx-100s Learning and Teaching Support Unit (LTSU)
