Outline. History of Internet Internet Properties TCP/IP IP Address Domain Name/URL Internet Infrastructure Server and Clients
|
|
|
- Randall Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Outline History of Internet Internet Properties TCP/IP IP Address Domain Name/URL Internet Infrastructure Server and Clients
3 The Internet The Internet is the computer network that connect computers throughout the world. A computer network can be connected by: copper or optical wire (wired network) Through radio-like signal (wireless network) or both
4 History of Internet ARPANET is the first project that tried to connect many different computer networks together The first connection happens in 1969 between University of California, Los Angeles and Stanford Research Institute In 1983, TCP/IP was invented and became a backbone the Internet In 1990, ARPANET underwent a big upgrade which later becomes the Internet
5 Internet Properties Each computer network will select a presentative called host to join the Internet All hosts must speak the same language, TCP/IP protocol. Different parts of the Internet are operated by different entities such as universities, governments, telephone companies No one owns the Internet
6 What does it mean to be on the Internet Run TCP/IP protocol Have an IP Address Can send IP packets to other computers on the Internet
7 TCP/IP Protocol IP or Internet Protocol moves data packets from one host to another. No connection stays so there is no guarantee of successful delivery TCP or Transmission Control Protocol establishes a reliable connection between two hosts. TCP can resend lost packets. Internet uses both protocols because both of them compliments each other
8 Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) On Sender Side: TCP breaks message into packets. TCP then pass packets to IP, sending packets to the sender. Wait for acknowledgement/resend message, resend packets as necessary. On Receiver Side: TCP receive packets from IP. If all packets are received, send acknowledgement message to sender, the reconstruct the message from packets. If some packets are missing, send resend message.
9 Internet Protocol (IP) IP uses IP Address to relay packets across networks IP also decides which datagram (packet) path to take, this process is called Routing.
10 IP Address Each computer on the Internet must have unique IP Address IP Address consists of 4 numbers separated by dots. Each number ranges from 0 to 255 Current version of IP is IPv4 Address For example, is an IP address for
11 Future IP Address Internet users start to reach billion active users but IP Address is limited IP Address that begins with 18 is IP Address of computers at MIT but MIT doesn t have enough computers to use all those IP Address One solution is to increase the size of IP Address IPv6 Address are currently being developed and tested along side IPv4 Address. In the near future, IPv4 Address will be retired. (just like when phone number changes form 9 digits to 10 digits) Example: IPv6 address for is 2001:3C8:5007::98
12 Domain Name IP Address is hard to memorize. For example, if we want to access Facebook, we have to type its IP Address of Domain Name is invented to cover IP Address so we can only need to type instead of Web Browser will connect to Domain Name Server (DNS) to translate to
13 DNS Server Domain Name DNS Server IP address
14 Reading Domain Name To read a domain name, we start from the rightmost part of the domain name, or Top Level Domain (TLD) 3-letter (or more) TLD usually indicates Type of the entity (commercial, governmental organization, etc.) 2-letter TLD usually indicates where the domain is registered (China, Thailand, Myanmar, etc.) More information at
15 Examples of TLD TLD Intended Use (Original) TLD Country.com.net.org.gov.edu.mil.int.biz.info Commercial Network Infrastructure Organization Government (US) Educational Organization Military (US) International Organization (Treaty) Business Informational Site.cm.cn.mm.mn.th.tv.uk.us.vn Cameroon China Myanmar Mongolia Thailand Tuvalu United Kingdom United States Vietnam 15
16 Reading Domain Name (cont.) After the TLD, the next level domain can be: Type of entity (if the TLD is country code) Name of the entity (if the TLD is type of entity) The domain will get more specific the lower (right) level it gets. The leftmost characters indicate service the entity provides. For example, www is web service. Example domain name:
17 Uniform Resource Locator (URL) To get to a specific item (webpage, file, etc) on the Internet, we need a URL, or web address. An example of URL (basic version): A URL consists of: 1. Protocol 2. Domain Name 3. Path 4. Item Name
18 Internet Infrastructure (First Layer) Each computer or computer network will connect to Internet Service Provider (ISP) such as TOT, 3BB, True, AIS Fiber Because ISP needs to provide service to customers all over the country, it has multiple connections in many provinces called Point of Presence (POP) POP LAN
19 Internet Infrastructure (Second Layer) Each POP connects to bigger connection points called Network Access Points (NAPs) NAPs has no owners because it accepts all connection from POP in different ISP POP POP POP NAPs POP
20 Internet Infrastructure (Final Layer) NAPs from different countries communicate via wired and wireless. We call this communication the Internet!!! Internet NAPs NAPs NAPs
21 Cellular Networks For mobile phone (2G, 3G, 4G networks) Devices (phones) connect wirelessly to the network via cellular towers When you move, the phone will switch from one cellular tower to another automatically A cell tower (source: wikipedia)
22 An Example of Cellular Network Source:
23 Internet Servers and Clients Every component in the internet acts as server or client or both Servers are service providers for other computers such as Web servers, servers, FTP servers, etc. Clients are users of those services
24 How Big is The Internet? TCP/IP is the most crucial part of the Internet because we can connect to people in different networks without hassle. If you want to be on the internet, you must obey TCP/IP. No one controls the (entire) Internet so we feel freedom on the Internet There are over 3.3 billions users and 45 billions registered websites. Technology that involves the Internet takes a huge leap in development in the past 10 years.
25 How Fast is Your Internet Connection? There are two ways to measure internet connection speed: Bandwidth and Latency (Lag). Bandwidth Amount of data that can be transfer during a second Usually measure in (kilo, mega)bytes/second Affect how long it takes to download a file Latency Measure delay (seconds) Time it takes for data to reach you Affect real-time communication/ online gaming
26 1 Minute in ,000 Facebook logins 4.1 million YouTube views 3.5 million Google searches 46,200 Instagram posts Image Source: Visual Capitalist
Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science
 Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science Unit 2: Internet and the World Wide Web Lecture 1 This material was developed by Oregon Health & Science University, funded by the Department
Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science Unit 2: Internet and the World Wide Web Lecture 1 This material was developed by Oregon Health & Science University, funded by the Department
and the World Wide Web
 The Internet 1 The Internet and the World Wide Web The Internet is a global collection of interconnected networks Originally ARPNET had only four host computers on the network. Now tens of millions 1 http://computer.howstuffworks.com/internet-infrastructure.htm
The Internet 1 The Internet and the World Wide Web The Internet is a global collection of interconnected networks Originally ARPNET had only four host computers on the network. Now tens of millions 1 http://computer.howstuffworks.com/internet-infrastructure.htm
How does the Internet Work? The Basics: Getting a Web Page. The Basics: Getting a Web Page. Client-Server model. The Internet: Basics
 How does the Internet Work? When you type a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) into a Web Browser and press Return, what do you think happens? That is, what steps do you think are required to obtain a web
How does the Internet Work? When you type a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) into a Web Browser and press Return, what do you think happens? That is, what steps do you think are required to obtain a web
The Internet and the World Wide Web
 Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
Introduction to Networking
 Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
The internet What is it??
 The internet What is it?? The internet is a global system of interconnected computer network that use the standard internet protocol suit (TCP/IP) to serve billions of users word wide. In other word it
The internet What is it?? The internet is a global system of interconnected computer network that use the standard internet protocol suit (TCP/IP) to serve billions of users word wide. In other word it
Typical Network Uses
 Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Introduction to the Internet. September 7, 2005 Lecture 1
 Introduction to the Internet September 7, 2005 Lecture 1 1969 to Present First 4 Nodes in the internet Map of the internet, Young Hyun, from CAIDA ARPANET J. Licklider of MIT first head of ARPA, Advanced
Introduction to the Internet September 7, 2005 Lecture 1 1969 to Present First 4 Nodes in the internet Map of the internet, Young Hyun, from CAIDA ARPANET J. Licklider of MIT first head of ARPA, Advanced
Introduction to Information Science and Technology 2017 Networking I. Sören Schwertfeger 师泽仁
 I Sören Schwertfeger 师泽仁 Outline Internet History of the Internet Internet Structure Internet Protocols Network layer details 1. Physical Layer 2. Data Link Layer 3. Network Layer Internet: Huge network
I Sören Schwertfeger 师泽仁 Outline Internet History of the Internet Internet Structure Internet Protocols Network layer details 1. Physical Layer 2. Data Link Layer 3. Network Layer Internet: Huge network
Scale Yourself. Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology. Computer Technology 3/13/2015
 Computer Technology Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology Learning Goal: Students will be able to understand the elements of a network. Scale Yourself 4 I do understand the elements of a network.
Computer Technology Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology Learning Goal: Students will be able to understand the elements of a network. Scale Yourself 4 I do understand the elements of a network.
Network Connectivity and Mobility
 Network Connectivity and Mobility BSAD 141 Dave Novak Topics Covered Lecture is structured based on the five elements of creating a connected world from the text book (with additional content) 1. Network
Network Connectivity and Mobility BSAD 141 Dave Novak Topics Covered Lecture is structured based on the five elements of creating a connected world from the text book (with additional content) 1. Network
Chapter 15 Networks. Chapter Goals. Networking. Chapter Goals. Networking. Networking. Computer network. Node (host) Any device on a network
 Chapter Goals Chapter 15 Networks Describe the core issues related to computer networks List various types of networks and their characteristics Explain various topologies of local-area networks Explain
Chapter Goals Chapter 15 Networks Describe the core issues related to computer networks List various types of networks and their characteristics Explain various topologies of local-area networks Explain
5/17/2009. Networked Computers Change Our Lives. People Are More Interconnected. Nowhere Is Remote. English Is Becoming a Universal Language
 Chapter 3: Making the Connection: The Basics of Networking Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Networked Computers Change Our Lives The Information Age has brought profound
Chapter 3: Making the Connection: The Basics of Networking Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Networked Computers Change Our Lives The Information Age has brought profound
INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET. Presented by the Benbrook Public Library
 INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET Presented by the Benbrook Public Library INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET What is the Internet? How did it come about? What is the World Wide Web? How does it work? How do I get
INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET Presented by the Benbrook Public Library INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET What is the Internet? How did it come about? What is the World Wide Web? How does it work? How do I get
Internet Routing. Review of Networking Principles. What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view. Communication links
 Internet Routing Review of Networking Principles 1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view Millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems PC s workstations, servers PDA s, phones, toasters
Internet Routing Review of Networking Principles 1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view Millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems PC s workstations, servers PDA s, phones, toasters
Internet Routing. Review of Networking Principles
 Internet Routing Review of Networking Principles 1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view Millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems PC s workstations, servers PDA s, phones, toasters
Internet Routing Review of Networking Principles 1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view Millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems PC s workstations, servers PDA s, phones, toasters
networks List various types of networks and their
 Chapter 15 Networks Chapter Goals Describe the core issues related to computer networks List various types of networks and their characteristics Explain various topologies of local-area networks Explain
Chapter 15 Networks Chapter Goals Describe the core issues related to computer networks List various types of networks and their characteristics Explain various topologies of local-area networks Explain
The Basics of Networking
 c h a p t e r 3 The Basics of Networking Making the Connection lawrence snyder Times are Changing Nowhere Is Remote People are more interconnected Social interactions are changing Freedom of Seach and
c h a p t e r 3 The Basics of Networking Making the Connection lawrence snyder Times are Changing Nowhere Is Remote People are more interconnected Social interactions are changing Freedom of Seach and
Introduction to computer networking
 edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
Chapter 3. The Basics of Networking
 Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking Learning Objectives Tell whether a communication technology (Internet, radio, LAN, etc.) is synchronous or asynchronous; broadcast or point-to-point Explain the roles
Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking Learning Objectives Tell whether a communication technology (Internet, radio, LAN, etc.) is synchronous or asynchronous; broadcast or point-to-point Explain the roles
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies. Networks
 ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
Chapter 16 Networking
 Chapter 16 Networking Outline 16.1 Introduction 16.2 Network Topology 16.3 Network Types 16.4 TCP/IP Protocol Stack 16.5 Application Layer 16.5.1 Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 16.5.2 File Transfer
Chapter 16 Networking Outline 16.1 Introduction 16.2 Network Topology 16.3 Network Types 16.4 TCP/IP Protocol Stack 16.5 Application Layer 16.5.1 Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 16.5.2 File Transfer
6 Computer Networks 6.1. Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning
 6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
LECTURE WK4 NETWORKING
 LECTURE WK4 NETWORKING Workbook and Quiz Workbook o Due in WK5 o Must hand in a hard copy to the tutor as well as an online submission Quiz o In the practical class o 30mins to complete the quiz o Short,
LECTURE WK4 NETWORKING Workbook and Quiz Workbook o Due in WK5 o Must hand in a hard copy to the tutor as well as an online submission Quiz o In the practical class o 30mins to complete the quiz o Short,
Network Protocols and Architectures
 Network Protocols and Architectures Introduction 1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view Millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems PC s workstations, servers PDA s, phones, toasters
Network Protocols and Architectures Introduction 1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view Millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems PC s workstations, servers PDA s, phones, toasters
"The Internet. All the piracy and none of the scurvy." -- Anonymous
 Bridges To Computing General Information: This document was created for use in the "Bridges to Computing" project of Brooklyn College. You are invited and encouraged to use this presentation to promote
Bridges To Computing General Information: This document was created for use in the "Bridges to Computing" project of Brooklyn College. You are invited and encouraged to use this presentation to promote
Chapter 11: Wide-Area Networks and the Internet
 Chapter 11: Wide-Area Networks and the Internet MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. MAN stands for: a. Manchester Access Network c. Metropolitan-Area Network b. Multiple-Area Network d. Multiple Access Network 2. Packet
Chapter 11: Wide-Area Networks and the Internet MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. MAN stands for: a. Manchester Access Network c. Metropolitan-Area Network b. Multiple-Area Network d. Multiple Access Network 2. Packet
Chapter 6 The Internet
 Chapter The Internet Computer Concepts 2014 Chapter Contents Section A: Internet Technology Section B: Fixed Internet Access Section C: Portable and Mobile Internet Access Section D: Internet Services
Chapter The Internet Computer Concepts 2014 Chapter Contents Section A: Internet Technology Section B: Fixed Internet Access Section C: Portable and Mobile Internet Access Section D: Internet Services
Business Data Communications and Networking
 Business Data Communications and Networking 10th Edition Jerry Fitzgerald and Alan Dennis John Wiley & Sons, Inc http://alainmaterials.webs.com/ Copyright 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc 5-1 Chapter 5 TCP/IP
Business Data Communications and Networking 10th Edition Jerry Fitzgerald and Alan Dennis John Wiley & Sons, Inc http://alainmaterials.webs.com/ Copyright 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc 5-1 Chapter 5 TCP/IP
Networking. Networking and Communication Trends Convergence (Accessibility) Speed Stability Simplicity* Embeddedness
 Networking and Communication Trends Convergence (Accessibility) Speed Stability Simplicity* Embeddedness What is a Computer Network General definition Related hardware Network Interface Card Network Operating
Networking and Communication Trends Convergence (Accessibility) Speed Stability Simplicity* Embeddedness What is a Computer Network General definition Related hardware Network Interface Card Network Operating
Part 1: Introduction. Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview
 Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks
 CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences 1403 http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~jiasi/teaching/cs204_spring17/ 1 Why Networks? Supports the applications
CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences 1403 http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~jiasi/teaching/cs204_spring17/ 1 Why Networks? Supports the applications
Overview of the Internet
 Overview of the Internet IVPR 1 Outline Goals and Objectives Topics headlines Introduction Internet and WWW Client/Server Model Diagnostic commands Evolution of Internet Transmission IP Addresses and Domain
Overview of the Internet IVPR 1 Outline Goals and Objectives Topics headlines Introduction Internet and WWW Client/Server Model Diagnostic commands Evolution of Internet Transmission IP Addresses and Domain
AQU Information Systems Fundamentals Spring 2012 Pg. 9.1
 AQU Information Systems Fundamentals Spring 2012 Pg. 9.1 c h a p t e r 9 THE INTERNET & THE NEW INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE 9.1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe features of infrastructure & connectivity
AQU Information Systems Fundamentals Spring 2012 Pg. 9.1 c h a p t e r 9 THE INTERNET & THE NEW INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE 9.1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe features of infrastructure & connectivity
Acknowledgment and Disclaimer:
 What is the Internet Acknowledgment and Disclaimer: This presentation is supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant 1240841. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations
What is the Internet Acknowledgment and Disclaimer: This presentation is supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant 1240841. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations
Özgür ZEYDAN (PhD.)
 Özgür ZEYDAN (PhD.) http://cevre.beun.edu.tr/zeydan/ Computer Network A group of computer systems and other computing hardware devices that are linked together through communication channels. Purpose:
Özgür ZEYDAN (PhD.) http://cevre.beun.edu.tr/zeydan/ Computer Network A group of computer systems and other computing hardware devices that are linked together through communication channels. Purpose:
Web Mechanisms. Draft: 2/23/13 6:54 PM 2013 Christopher Vickery
 Web Mechanisms Draft: 2/23/13 6:54 PM 2013 Christopher Vickery Introduction While it is perfectly possible to create web sites that work without knowing any of their underlying mechanisms, web developers
Web Mechanisms Draft: 2/23/13 6:54 PM 2013 Christopher Vickery Introduction While it is perfectly possible to create web sites that work without knowing any of their underlying mechanisms, web developers
Networking and the Web Reminder: Next Quiz on 4/15
 Networking and the Web Reminder: Next Quiz on 4/15 World-Wide Web Wide use of computers by the general public is directly attributable to the creation of the World Wide Web Key components of the web Computer
Networking and the Web Reminder: Next Quiz on 4/15 World-Wide Web Wide use of computers by the general public is directly attributable to the creation of the World Wide Web Key components of the web Computer
BUSINESS DATA COMMUNICATIONS & NETWORKING
 BUSINESS DATA COMMUNICATIONS & NETWORKING Chapter 1 Introduction to Data Communications FitzGerald Dennis Durcikova Prepared by Taylor M. Wells: College of Business Administration, California State University,
BUSINESS DATA COMMUNICATIONS & NETWORKING Chapter 1 Introduction to Data Communications FitzGerald Dennis Durcikova Prepared by Taylor M. Wells: College of Business Administration, California State University,
PIC 40A. Lecture 1: The Internet. Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 03/31/14
 PIC 40A Lecture 1: The Internet 03/31/14 Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 What is the Internet? For this class we use the following definition: The Internet is a network of networks. Ok. What is a
PIC 40A Lecture 1: The Internet 03/31/14 Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 What is the Internet? For this class we use the following definition: The Internet is a network of networks. Ok. What is a
The Internet. Connecting to the internet. Role of the ISP. Who is online? Internet users by country 2/18/2009. The Internet More than Just WWW
 The Internet What does it mean to be connected to the internet? I.e. What does the internet do?? What do you need to connect your computer to the internet as opposed to any other network? The Internet
The Internet What does it mean to be connected to the internet? I.e. What does the internet do?? What do you need to connect your computer to the internet as opposed to any other network? The Internet
FACTFILE: GCE DIGITAL TECHNOLOGY
 FACTFILE: GCE DIGITAL TECHNOLOGY AS2: FUNDAMENTALS OF DIGITAL TECHNOLOGY WEB TECHNOLOGY AND MULTIMEDIA : KEY TERMS Web Applications 1 Learning Outcomes Students should be able explain the terms: WWW The
FACTFILE: GCE DIGITAL TECHNOLOGY AS2: FUNDAMENTALS OF DIGITAL TECHNOLOGY WEB TECHNOLOGY AND MULTIMEDIA : KEY TERMS Web Applications 1 Learning Outcomes Students should be able explain the terms: WWW The
CN1047 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKING CHAPTER 6 OSI MODEL TRANSPORT LAYER
 CN1047 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKING CHAPTER 6 OSI MODEL TRANSPORT LAYER Transport Layer The Transport layer ensures the reliable arrival of messages and provides error checking mechanisms and data
CN1047 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKING CHAPTER 6 OSI MODEL TRANSPORT LAYER Transport Layer The Transport layer ensures the reliable arrival of messages and provides error checking mechanisms and data
MR AZIZUL ZAMRI BIN MUHAMED AMIN WEB : Your Logo
 MR AZIZUL ZAMRI BIN MUHAMED AMIN WEB : http://fsktm2.uthm.edu.my/azizulzamri Your Logo Chapter 1 Introduction to WWW and the Internet By : Azizulzamri bin Muhamed Amin History of the Internet and WWW COLD
MR AZIZUL ZAMRI BIN MUHAMED AMIN WEB : http://fsktm2.uthm.edu.my/azizulzamri Your Logo Chapter 1 Introduction to WWW and the Internet By : Azizulzamri bin Muhamed Amin History of the Internet and WWW COLD
Networking and Internetworking 1
 Networking and Internetworking 1 Today l Networks and distributed systems l Internet architecture xkcd Networking issues for distributed systems Early networks were designed to meet relatively simple requirements
Networking and Internetworking 1 Today l Networks and distributed systems l Internet architecture xkcd Networking issues for distributed systems Early networks were designed to meet relatively simple requirements
ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18. The Internet. What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback
 ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18 The Internet What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback Python -- Run your code!! Term paper: Start a paragraph with the point of the paragraph, not in modern times
ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18 The Internet What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback Python -- Run your code!! Term paper: Start a paragraph with the point of the paragraph, not in modern times
Connected computers are better! How s it done? Lawrence Snyder University of Washington, Seattle
 Connected computers are better! How s it done? Lawrence Snyder University of Washington, Seattle Lawrence Snyder 2004 Computers are useful alone, but are better when connected (networked) Access more information
Connected computers are better! How s it done? Lawrence Snyder University of Washington, Seattle Lawrence Snyder 2004 Computers are useful alone, but are better when connected (networked) Access more information
Local Area Networks; Ethernet
 Communications and networking history and background telephone system local area networks Internet architecture: what the pieces are and how they fit together names and addresses: what's your name and
Communications and networking history and background telephone system local area networks Internet architecture: what the pieces are and how they fit together names and addresses: what's your name and
2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork. 3. Each machine is connected to a central hub with a point-to-point connection.
 نموذج أسئلة اختبار النهائي عام 2017 الفصل الدراسي الثاني لمقرر شبكات الحاسب CHOSE 1. channel spectrum divided into frequency bands "FDMA" 2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork
نموذج أسئلة اختبار النهائي عام 2017 الفصل الدراسي الثاني لمقرر شبكات الحاسب CHOSE 1. channel spectrum divided into frequency bands "FDMA" 2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork
Component Function Example
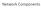 Network Components Component Names Component Function Example Application, or app, user Uses the network Skype, itunes, Amazon Host, or end-system, edge device, node, source, sink Router, or switch, node,
Network Components Component Names Component Function Example Application, or app, user Uses the network Skype, itunes, Amazon Host, or end-system, edge device, node, source, sink Router, or switch, node,
The Internet Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) How the Internet Works Transport Control Protocol (TCP)
 The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets 1 The Internet The Internet is a collection of interconnected network of computers, all freely exchanging information. These computers use specialized software to
The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets 1 The Internet The Internet is a collection of interconnected network of computers, all freely exchanging information. These computers use specialized software to
Session 4 Networks II
 15.561 Information Technology Essentials Session 4 Networks II Copyright 2005 Thomas Malone, Chris Dellarocas Acknowledgments: Slides marked CD are adapted from Chris Dellarocas, U. Md.. Outline Network
15.561 Information Technology Essentials Session 4 Networks II Copyright 2005 Thomas Malone, Chris Dellarocas Acknowledgments: Slides marked CD are adapted from Chris Dellarocas, U. Md.. Outline Network
Switching Networks (Fall 2010) EE 586 Communication and. August 27, Lecture 2. (modified by Cheung for EE586; based on K&R original) 1-1
 EE 586 Communication and Switching Networks (Fall 2010) Lecture 2 August 27, 2010 (modified by Cheung for EE586; based on K&R original) 1-1 Announcements Read Chapter 1 First homework is due 9/3 In Blackboard
EE 586 Communication and Switching Networks (Fall 2010) Lecture 2 August 27, 2010 (modified by Cheung for EE586; based on K&R original) 1-1 Announcements Read Chapter 1 First homework is due 9/3 In Blackboard
DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS
 DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS A/L Guide TERAN SUBASINGHE Data Communication What is data communication? Data Communication is a process of exchanging data or information between two or more devices along
DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS A/L Guide TERAN SUBASINGHE Data Communication What is data communication? Data Communication is a process of exchanging data or information between two or more devices along
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks
 EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 2 Wenbing Zhao wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Misc. Interested in research? Secure
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 2 Wenbing Zhao wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Misc. Interested in research? Secure
Introduction to Computer Networking II. Abdusy Syarif Informatics Department Faculty of Computer Science Universitas Mercu Buana
 Introduction to Computer Networking II Abdusy Syarif Informatics Department Faculty of Computer Science Universitas Mercu Buana Teaching Method E-learning Class Individual assignment Quiz See schedule
Introduction to Computer Networking II Abdusy Syarif Informatics Department Faculty of Computer Science Universitas Mercu Buana Teaching Method E-learning Class Individual assignment Quiz See schedule
Technology in Action. Chapter 13 Behind the Scenes: The Internet: How It Works Prentice-Hall, Inc.
 Technology in Action Chapter 13 Behind the Scenes: The Internet: How It Works 1 Chapter Topics Managing the Internet Interaction between Internet components Internet data transmission and protocols IP
Technology in Action Chapter 13 Behind the Scenes: The Internet: How It Works 1 Chapter Topics Managing the Internet Interaction between Internet components Internet data transmission and protocols IP
Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking
 Fluency with Information Technology 7 th Edition Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking HTML Hypertext Markup Language Layout of document (Margin, font, text, image, ) Jump from point to point (non-linear)
Fluency with Information Technology 7 th Edition Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking HTML Hypertext Markup Language Layout of document (Margin, font, text, image, ) Jump from point to point (non-linear)
CNT 4007 Computer Networks - Chapter 1 : Overview
 CNT 4007 Computer Networks - Chapter 1 : Overview Jonathan Kavalan, Ph.D. Department of Computer, Information Science and Engineering (CISE), University of Florida 1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get
CNT 4007 Computer Networks - Chapter 1 : Overview Jonathan Kavalan, Ph.D. Department of Computer, Information Science and Engineering (CISE), University of Florida 1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get
An internet or interconnected network is formed when two or more networks are connected.
 Computers I 3. The Internet An internet or interconnected network is formed when two or more networks are connected. The most notable internet is called the Internet and is composed of millions of these
Computers I 3. The Internet An internet or interconnected network is formed when two or more networks are connected. The most notable internet is called the Internet and is composed of millions of these
Chapter Topics. The History of the Internet. Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web
 Chapter Topics Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web CS10051: Intro. to Computer Science Kent State University History of the Internet History of the World Wide Web Internet
Chapter Topics Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web CS10051: Intro. to Computer Science Kent State University History of the Internet History of the World Wide Web Internet
Is IPv4 Sufficient for Another 30 Years?
 Is IPv4 Sufficient for Another 30 Years? October 7, 2004 Abstract TCP/IP was developed 30 years ago. It has been successful over the past 30 years, until recently when its limitation started emerging.
Is IPv4 Sufficient for Another 30 Years? October 7, 2004 Abstract TCP/IP was developed 30 years ago. It has been successful over the past 30 years, until recently when its limitation started emerging.
Introduction to Computer Science 2017 Networking. Sören Schwertfeger
 Sören Schwertfeger Outline Internet History of the Internet Internet Structure Internet Protocols Network layer details 1. Physical Layer 2. Data Link Layer 3. Network Layer Internet: Huge network of networks
Sören Schwertfeger Outline Internet History of the Internet Internet Structure Internet Protocols Network layer details 1. Physical Layer 2. Data Link Layer 3. Network Layer Internet: Huge network of networks
Chapter 7. Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology
 Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology LEARNING OBJECTIVES What are the principal components of telecommunications networks and key networking technologies? What are the different
Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology LEARNING OBJECTIVES What are the principal components of telecommunications networks and key networking technologies? What are the different
Introduction to Computer Science. William Hsu Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Taiwan Ocean University
 Introduction to Computer Science William Hsu Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Taiwan Ocean University Chapter 4: Networking and the Internet No one owns the Internet, and only one
Introduction to Computer Science William Hsu Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Taiwan Ocean University Chapter 4: Networking and the Internet No one owns the Internet, and only one
Lecture 10 Internet. ECE 197SA Systems Appreciation. Internet
 Lecture 10 Internet ECE 197SA Systems Appreciation Internet Computer networks Infrastructure for large-scale distributed application Global data exchange between computers Essential for today s society
Lecture 10 Internet ECE 197SA Systems Appreciation Internet Computer networks Infrastructure for large-scale distributed application Global data exchange between computers Essential for today s society
Computer Networks. Computer Networks. Telecommunication Links. CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing - Spring Chapter 12: Computer Networks 1
 Computer Networks Chapter 12 Topics: Communication links LAN / WAN Internet / WWW CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson 1 Computer Networks A computer network is a set of independent computer
Computer Networks Chapter 12 Topics: Communication links LAN / WAN Internet / WWW CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson 1 Computer Networks A computer network is a set of independent computer
Technology in Action. Chapter 13 Behind the Scenes: The Internet: How It Works. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Technology in Action Chapter 13 Behind the Scenes: The Internet: How It Works 1 Management of the Internet Who owns the Internet? No one Individuals Universities Government agencies Private companies Committees
Technology in Action Chapter 13 Behind the Scenes: The Internet: How It Works 1 Management of the Internet Who owns the Internet? No one Individuals Universities Government agencies Private companies Committees
COMPUTER NETWORK. PREPARED BY: DHAVAL R. PATEL Page 1. Q.1 Explain IP address. IP address is unique number of network device in network.
 Q.1 Explain IP address. IP address is unique number of network device in network. Two IP address could not be same. Using this network we can connect the devices with each other. It is separated by dot(.).
Q.1 Explain IP address. IP address is unique number of network device in network. Two IP address could not be same. Using this network we can connect the devices with each other. It is separated by dot(.).
CNPE Communications and Networks Lab Book: Data Transmission Over Digital Networks
 Lab Book: Data Transmission Over Digital Networks Contents Data Transmission Over Digital Networks... 3 Lab Objectives... 3 Lab Resources... 3 Task 1 Build the Home Network... 3 Task 2 Configure IP Addresses...
Lab Book: Data Transmission Over Digital Networks Contents Data Transmission Over Digital Networks... 3 Lab Objectives... 3 Lab Resources... 3 Task 1 Build the Home Network... 3 Task 2 Configure IP Addresses...
Special expressions, phrases, abbreviations and terms of Computer Networks
 access access point adapter Adderssing Realm ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line) algorithm amplify amplitude analog antenna application architecture ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) AS (Autonomous
access access point adapter Adderssing Realm ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line) algorithm amplify amplitude analog antenna application architecture ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) AS (Autonomous
Parts of a Network. app. router. link. host. Computer Networks 2
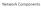 Network Components Parts of a Network app host router link Computer Networks 2 Parts of a Network app host router link Computer Networks 3 Component Names Component Function Example Application, or app,
Network Components Parts of a Network app host router link Computer Networks 2 Parts of a Network app host router link Computer Networks 3 Component Names Component Function Example Application, or app,
Introduction to Internet, Web, and TCP/IP Protocols SEEM
 Introduction to Internet, Web, and TCP/IP Protocols SEEM 3460 1 Local-Area Networks A Local-Area Network (LAN) covers a small distance and a small number of computers LAN A LAN often connects the machines
Introduction to Internet, Web, and TCP/IP Protocols SEEM 3460 1 Local-Area Networks A Local-Area Network (LAN) covers a small distance and a small number of computers LAN A LAN often connects the machines
Computer Networks. More on Standards & Protocols Quality of Service. Week 10. College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University
 Computer Networks More on Standards & Protocols Quality of Service Week 10 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Introduction to Protocols l A protocol is a set of rules
Computer Networks More on Standards & Protocols Quality of Service Week 10 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Introduction to Protocols l A protocol is a set of rules
Chapter 3. E-commerce The Evolution of the Internet 1961 Present. The Internet: Technology Background. The Internet: Key Technology Concepts
 E-commerce 2015 business. technology. society. eleventh edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure: The Internet, Web, and Mobile Platform Copyright 2015 Pearson
E-commerce 2015 business. technology. society. eleventh edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure: The Internet, Web, and Mobile Platform Copyright 2015 Pearson
CSC Introduction to Computers and Their Applications. Background
 CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture 7 The Internet Background The history of the Internet begins in 1957. In a response to the Soviet Union launching Sputnik, the first man-made
CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture 7 The Internet Background The history of the Internet begins in 1957. In a response to the Soviet Union launching Sputnik, the first man-made
Network and Mobile Compu4ng in the 20 th Century and Beyond. COMP 1400 Memorial University Winter 2015
 Network and Mobile Compu4ng in the 20 th Century and Beyond COMP 1400 Memorial University Winter 2015 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view PC server wireless laptop smartphone wireless links wired
Network and Mobile Compu4ng in the 20 th Century and Beyond COMP 1400 Memorial University Winter 2015 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view PC server wireless laptop smartphone wireless links wired
Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network
 Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network Elements of Communication Communicating the Messages Continuous stream of bits 00101010100101010101010101010101010 I have to wait Single communications (e.g. video,
Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network Elements of Communication Communicating the Messages Continuous stream of bits 00101010100101010101010101010101010 I have to wait Single communications (e.g. video,
Due date for pairs programming assignment is next Wednesday before class. 2/16/ Larry Snyder, CSE 1
 Midterm corrections BEFORE Friday LOCATION CHANGE next Tuesday s lab (Feb 22) will be held in CSE 403, where we will hear Richard Ladner on accessibility Due date for pairs programming assignment is next
Midterm corrections BEFORE Friday LOCATION CHANGE next Tuesday s lab (Feb 22) will be held in CSE 403, where we will hear Richard Ladner on accessibility Due date for pairs programming assignment is next
Fig (1) client and Server network
 2.2 How Does the Internet Work? The international network known as the internet consists of hundreds of thousands of smaller networks linking educational, commercial, nonprofit, and military organizations,
2.2 How Does the Internet Work? The international network known as the internet consists of hundreds of thousands of smaller networks linking educational, commercial, nonprofit, and military organizations,
WEBINAR. Web Browsing 101 1/12/2012 WEBINAR TIPS:
 Browsing 101 WEBINAR TIPS: 1. Power off cell phones. 2. If accessing webinar through telephone, turn down volume of computer speakers (or mute them.) 3. Conference attendees will be muted during webinar
Browsing 101 WEBINAR TIPS: 1. Power off cell phones. 2. If accessing webinar through telephone, turn down volume of computer speakers (or mute them.) 3. Conference attendees will be muted during webinar
Chapter 4: Networking and the Internet. Network Classifications. Network topologies. Network topologies (continued) Connecting Networks.
 Chapter 4: Networking and the 4.1 Network Fundamentals 4.2 The 4.3 The World Wide Web 4.4 Protocols 4.5 Security Network Classifications Scope Local area network (LAN) Metropolitan area (MAN) Wide area
Chapter 4: Networking and the 4.1 Network Fundamentals 4.2 The 4.3 The World Wide Web 4.4 Protocols 4.5 Security Network Classifications Scope Local area network (LAN) Metropolitan area (MAN) Wide area
Layering in Networked computing. OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer
 Layering in Networked computing OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer Learning outcomes Understand the need of layering in Networked computing Understand the OSI model and the tcp/ip model Understand
Layering in Networked computing OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer Learning outcomes Understand the need of layering in Networked computing Understand the OSI model and the tcp/ip model Understand
Chapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Instructor Planning Guide
 Chapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Instructor Planning Guide CCNET v6 1 Chapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications CCENT Routing
Chapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Instructor Planning Guide CCNET v6 1 Chapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications CCENT Routing
6 Computer Networks 6.1. Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning
 6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
CHAPTER 2: NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET
 CHAPTER 2: NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET Multiple Choice 1. What type of cable do most networks use? A. Net cable B. Category 3 cable C. Phone cable D. Category 5 cable The answer is D 2. The connector used
CHAPTER 2: NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET Multiple Choice 1. What type of cable do most networks use? A. Net cable B. Category 3 cable C. Phone cable D. Category 5 cable The answer is D 2. The connector used
Session 3 Networks I
 15.561 Information Technology Essentials Session 3 Networks I Copyright 2005 Thomas Malone, Chris Dellarocas, Stuart Madnick Acknowledgments: Slides marked SM are adapted from Stuart Madnick, MIT. Slides
15.561 Information Technology Essentials Session 3 Networks I Copyright 2005 Thomas Malone, Chris Dellarocas, Stuart Madnick Acknowledgments: Slides marked SM are adapted from Stuart Madnick, MIT. Slides
Part I: Introduction. 1: Introduction 1
 Part I: Introduction Chapter goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
Part I: Introduction Chapter goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
Data and Computer Communications
 Data and Computer Communications CHAPTER 1 Tenth Edition by William Stallings Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet Data and Computer Communications, Tenth Edition by William Stallings,
Data and Computer Communications CHAPTER 1 Tenth Edition by William Stallings Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet Data and Computer Communications, Tenth Edition by William Stallings,
Lecture 17 Overview. Last Lecture. Wide Area Networking (2) This Lecture. Internet Protocol (1) Source: chapters 2.2, 2.3,18.4, 19.1, 9.
 Lecture 17 Overview Last Lecture Wide Area Networking (2) This Lecture Internet Protocol (1) Source: chapters 2.2, 2.3,18.4, 19.1, 9.2 Next Lecture Internet Protocol (2) Source: chapters 19.1, 19.2, 22,1
Lecture 17 Overview Last Lecture Wide Area Networking (2) This Lecture Internet Protocol (1) Source: chapters 2.2, 2.3,18.4, 19.1, 9.2 Next Lecture Internet Protocol (2) Source: chapters 19.1, 19.2, 22,1
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet
 Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
ECPE / COMP 177 Fall Some slides from Kurose and Ross, Computer Networking, 5 th Edition
 ECPE / COMP 177 Fall 2014 Some slides from Kurose and Ross, Computer Networking, 5 th Edition Instructor: Dr. Jeff Shafer Email: jshafer at pacific dot edu Office: Anderson 205 Office hours (posted on
ECPE / COMP 177 Fall 2014 Some slides from Kurose and Ross, Computer Networking, 5 th Edition Instructor: Dr. Jeff Shafer Email: jshafer at pacific dot edu Office: Anderson 205 Office hours (posted on
2. Introduction to Internet Applications
 2. Introduction to Internet Applications 1. Representation and Transfer 2. Web Protocols 3. Some Other Application Layer Protocols 4. Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) 5. Uniform Resource Locators (URLs)
2. Introduction to Internet Applications 1. Representation and Transfer 2. Web Protocols 3. Some Other Application Layer Protocols 4. Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) 5. Uniform Resource Locators (URLs)
SJTU 2018 Fall Computer Networking. Wireless Communication
 SJTU 2018 Fall Computer Networking 1 Wireless Communication Internet Protocol Stack 2 Application: supporting network applications - FTP, SMTP, HTTP Transport: data transfer between processes - TCP, UDP
SJTU 2018 Fall Computer Networking 1 Wireless Communication Internet Protocol Stack 2 Application: supporting network applications - FTP, SMTP, HTTP Transport: data transfer between processes - TCP, UDP
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 15: Networking overview Prof. (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) What is a network? 2 What is a network? Wikipedia: A telecommunications network is a network
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 15: Networking overview Prof. (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) What is a network? 2 What is a network? Wikipedia: A telecommunications network is a network
4.2 Virtual Circuit and Datagram Networks
 4.2 VIRTUAL CIRCUIT AND DATAGRAM NETWORKS 313 Available bit rate (ABR) ATM network service. With the Internet offering socalled best-effort service, ATM s ABR might best be characterized as being a slightly-better-than-best-effort
4.2 VIRTUAL CIRCUIT AND DATAGRAM NETWORKS 313 Available bit rate (ABR) ATM network service. With the Internet offering socalled best-effort service, ATM s ABR might best be characterized as being a slightly-better-than-best-effort
Overview of Network Software. CS158a Chris Pollett Jan 31, 2007.
 Overview of Network Software CS158a Chris Pollett Jan 31, 2007. Outline Design Issues for Protocol Hierarchies Reference Models Example Networks Protocol Hierarchies-Review To reduce design complexity
Overview of Network Software CS158a Chris Pollett Jan 31, 2007. Outline Design Issues for Protocol Hierarchies Reference Models Example Networks Protocol Hierarchies-Review To reduce design complexity
Discovering Computers Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web
 Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Just remember It took 38 years for radio to reach 50 million users 13 years for television to reach 50 million users Less than 4 years
Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Just remember It took 38 years for radio to reach 50 million users 13 years for television to reach 50 million users Less than 4 years
Inside vs. Outside. Inside the Box What the computer owner actually has possession of 1/18/2011
 Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Networking Applications
 Networking Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid College of Computing and Information Technology Arab Academy for Science & Technology and Maritime Transport 1 Outline Internet Layers Internet Data Packet transmission
Networking Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid College of Computing and Information Technology Arab Academy for Science & Technology and Maritime Transport 1 Outline Internet Layers Internet Data Packet transmission
