The World Is Not Flat: An Introduction to Modern Geometry
|
|
|
- Paulina Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The World Is Not Flat: An to The University of Iowa September 15, 2015
2 The story of a hunting party
3 The story of a hunting party What color was the bear?
4 The story of a hunting party
5 Overview Gauss and all his friends Riemann s revolution
6 Euclid of Alexandria Active around 300 B.C. Authored several mathematical texts Transformed geometry into a rigorous discipline
7 Elements The five axioms: 1. A straight line segment can be drawn joining any two points. 2. Any straight line segment can be extended indefinitely in a straight line. 3. Given any straight line segment, a circle can be drawn having the segment as radius and one endpoint as center. 4. All right angles are congruent. 5. Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists exactly one line through the point not intersecting the given line.
8 The fathers of non-euclidean Geometry Carl Frederich Gauss ( ) Nikolai Lobachevsky ( ) János Bolyai ( )
9 A family of parallel postulates Given any straight line and a point off the given line, Euclidean: there exists exactly one line through the point not intersecting the given line. Elliptic: there exist no lines through the point not intersecting the given line. Hyperbolic: there exist at least two lines through the point not intersecting the given line. I created a new, different world out of nothing. - Bolyai, in a letter to his father
10 Straight lines What makes a curve in a surface a straight line?
11 Straight lines What makes a curve in a surface a straight line? It will (at least locally) represent the shortest distance between two points. It will have zero acceleration in the surface.
12 Straight lines What makes a curve in a surface a straight line? It will (at least locally) represent the shortest distance between two points. It will have zero acceleration in the surface. The generalization of a straight line in a non-euclidean space is called a geodesic.
13 A family of parallel postulates Euclidean: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists exactly one line through the point not intersecting the given line.
14 A family of parallel postulates Euclidean: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists exactly one line through the point not intersecting the given line.
15 A family of parallel postulates Euclidean: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists exactly one line through the point not intersecting the given line.
16 A family of parallel postulates Elliptic: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists no lines through the point not intersecting the given line.
17 A family of parallel postulates Elliptic: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists no lines through the point not intersecting the given line.
18 A family of parallel postulates Elliptic: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists no lines through the point not intersecting the given line.
19 A family of parallel postulates Hyperbolic: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists at least two lines through the point not intersecting the given line.
20 A family of parallel postulates Hyperbolic: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists at least two lines through the point not intersecting the given line.
21 A family of parallel postulates Hyperbolic: Given any straight line and a point off the given line, there exists at least two lines through the point not intersecting the given line.
22 Curve curvature How can we formally describe curvature?
23 Curve curvature How can we formally describe curvature? To calculate the curvature of a parametric curve, we find its second derivative.
24 Curve curvature How can we formally describe curvature? To calculate the curvature of a parametric curve, we find its second derivative. Curvature is typically represented by the Greek letter κ. zero κ low κ high κ
25 Curve curvature Circles have uniform curvature; specifically, κ = 1 r. κ = 1 2 κ = 1 κ = 3
26 Curve curvature In some sense, the curvature of a curve at a point is the curvature of the largest circle one can make tangent to the curve at that point.
27 Gauss curvature There are several ways to determine the curvature at a point on a surface, but the following process is the most intuitive: 1. Construct the tangent plane to the surface at the point. 2. Consider every plane perpendicular to the tangent plane. 3. Each of these perpendicular planes will intersect the surface in some curve. 4. Select the two curves with the most different curvatures at the point. These are called the principal curvatures. 5. Multiply their curvatures and choose the appropriate sign to obtain the surface s curvature at that point.
28 Gauss curvature R
29 Gauss curvature R
30 Gauss curvature R
31 Gauss curvature K(p) = 0 1 r = 0
32 Gauss curvature R
33 Gauss curvature R
34 Gauss curvature R
35 Gauss curvature K(p) = 1 r 1 r = 1 r 2 > 0
36 Gauss curvature R
37 Gauss curvature R
38 Gauss curvature R
39 Gauss curvature K(p) = k 1 k 2 < 0
40 Gauss curvature Thus, we can separate curvature at a point on a surface into three cases: Zero: the surface can be perfectly flattened. Positive: the surface will rip when flattened. Negative: the surface will fold when flattened.
41 Gauss curvature Thus, we can separate curvature at a point on a surface into three cases: Zero: the surface can be perfectly flattened. Positive: the surface will rip when flattened. Negative: the surface will fold when flattened.
42 Gauss curvature Thus, we can separate curvature at a point on a surface into three cases: Zero: the surface can be perfectly flattened. Positive: the surface will rip when flattened. Negative: the surface will fold when flattened.
43 Gauss curvature Thus, we can separate curvature at a point on a surface into three cases: Zero: the surface can be perfectly flattened. Positive: the surface will rip when flattened. Negative: the surface will fold when flattened.
44 Gauss curvature Thus, we can separate curvature at a point on a surface into three cases: Zero: the surface can be perfectly flattened. Positive: the surface will rip when flattened. Negative: the surface will fold when flattened.
45 Gauss curvature Thus, we can separate curvature at a point on a surface into three cases: Zero: the surface can be perfectly flattened. Positive: the surface will rip when flattened. Negative: the surface will fold when flattened.
46 Gauss curvature Thus, we can separate curvature at a point on a surface into three cases: Zero: the surface can be perfectly flattened. Positive: the surface will rip when flattened. Negative: the surface will fold when flattened.
47 Gauss curvature Thus, we can separate curvature at a point on a surface into three cases: Zero: the surface can be perfectly flattened. Positive: the surface will rip when flattened. Negative: the surface will fold when flattened.
48 The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem illustrates a connection between topological and geometric properties.
49 The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem illustrates a connection between topological and geometric properties. Theorem: If M is a compact, two-dimensional, Riemannian manifold with boundary M, then K da + k g ds = 2πχ(M), M M Where K is the Gauss curvature on M, k g is the geodesic curvature on M, and χ(m) is the Euler characteristic of M.
50 Extensions and applications: Spacetime models Medical imaging Industrial engineering Mathematical bridge-builder
51 References Mlodinow, Leonard (2001). Window. New York, NY: The Free Press. Oprea, John (2007). Differential Geometry and its Applications. Washington, DC: The Mathematical Association of America. Stewart, Ian (2001). Flatterland. Cambridge, MA: Perseus Publishing. Wallace, Edward and West, Stephen (2004). Roads to Geometry. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2007 Hyperbolic Geometry Christina L. Sheets University
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2007 Hyperbolic Geometry Christina L. Sheets University
What makes geometry Euclidean or Non-Euclidean?
 What makes geometry Euclidean or Non-Euclidean? I-1. Each two distinct points determine a line I-2. Three noncollinear points determine a plane The 5 Axioms of I-3. If two points lie in a plane, then any
What makes geometry Euclidean or Non-Euclidean? I-1. Each two distinct points determine a line I-2. Three noncollinear points determine a plane The 5 Axioms of I-3. If two points lie in a plane, then any
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 7 - Slide 1 AND
 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 7 - Slide 1 AND Chapter 9 Geometry Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 7 - Slide 2 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Transformational geometry,
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 7 - Slide 1 AND Chapter 9 Geometry Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 7 - Slide 2 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Transformational geometry,
Impulse Gauss Curvatures 2002 SSHE-MA Conference. Howard Iseri Mansfield University
 Impulse Gauss Curvatures 2002 SSHE-MA Conference Howard Iseri Mansfield University Abstract: In Riemannian (differential) geometry, the differences between Euclidean geometry, elliptic geometry, and hyperbolic
Impulse Gauss Curvatures 2002 SSHE-MA Conference Howard Iseri Mansfield University Abstract: In Riemannian (differential) geometry, the differences between Euclidean geometry, elliptic geometry, and hyperbolic
08. Non-Euclidean Geometry 1. Euclidean Geometry
 08. Non-Euclidean Geometry 1. Euclidean Geometry The Elements. ~300 B.C. ~100 A.D. Earliest existing copy 1570 A.D. First English translation 1956 Dover Edition 13 books of propositions, based on 5 postulates.
08. Non-Euclidean Geometry 1. Euclidean Geometry The Elements. ~300 B.C. ~100 A.D. Earliest existing copy 1570 A.D. First English translation 1956 Dover Edition 13 books of propositions, based on 5 postulates.
A Quick Introduction to Non-Euclidean Geometry. A Tiling of the Poincare Plane From Geometry: Plane and Fancy, David Singer, page 61.
 A Quick Introduction to Non-Euclidean Geometry A Tiling of the Poincare Plane From Geometry: Plane and Fancy, David Singer, page 61. Dr. Robert Gardner Presented at Science Hill High School March 22, 2006
A Quick Introduction to Non-Euclidean Geometry A Tiling of the Poincare Plane From Geometry: Plane and Fancy, David Singer, page 61. Dr. Robert Gardner Presented at Science Hill High School March 22, 2006
Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing
 252-0538-00L, Spring 2018 Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing Discrete Differential Geometry Differential Geometry Motivation Formalize geometric properties of shapes Roi Poranne # 2 Differential Geometry
252-0538-00L, Spring 2018 Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing Discrete Differential Geometry Differential Geometry Motivation Formalize geometric properties of shapes Roi Poranne # 2 Differential Geometry
Mathematics As A Liberal Art
 Math 105 Fall 2015 BY: 2015 Ron Buckmire Mathematics As A Liberal Art Class 26: Friday November 13 Fowler 302 MWF 10:40am- 11:35am http://sites.oxy.edu/ron/math/105/15/ Euclid, Geometry and the Platonic
Math 105 Fall 2015 BY: 2015 Ron Buckmire Mathematics As A Liberal Art Class 26: Friday November 13 Fowler 302 MWF 10:40am- 11:35am http://sites.oxy.edu/ron/math/105/15/ Euclid, Geometry and the Platonic
Curvature Berkeley Math Circle January 08, 2013
 Curvature Berkeley Math Circle January 08, 2013 Linda Green linda@marinmathcircle.org Parts of this handout are taken from Geometry and the Imagination by John Conway, Peter Doyle, Jane Gilman, and Bill
Curvature Berkeley Math Circle January 08, 2013 Linda Green linda@marinmathcircle.org Parts of this handout are taken from Geometry and the Imagination by John Conway, Peter Doyle, Jane Gilman, and Bill
Introduction to geometry
 1 2 Manifolds A topological space in which every point has a neighborhood homeomorphic to (topological disc) is called an n-dimensional (or n-) manifold Introduction to geometry The German way 2-manifold
1 2 Manifolds A topological space in which every point has a neighborhood homeomorphic to (topological disc) is called an n-dimensional (or n-) manifold Introduction to geometry The German way 2-manifold
And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS
 And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS. In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS. In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 5
 274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 5 Dylan Thurston Notes by Qiaochu Yuan Fall 2012 5 Ideal polygons Previously we discussed three models of the hyperbolic plane: the Poincaré disk, the upper half-plane,
274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 5 Dylan Thurston Notes by Qiaochu Yuan Fall 2012 5 Ideal polygons Previously we discussed three models of the hyperbolic plane: the Poincaré disk, the upper half-plane,
Kutztown University Kutztown, Pennsylvania. MAT 550: Foundations of Geometry
 Kutztown University Kutztown, Pennsylvania I. Three semester hours; three clock hours; this is an elective course in the M.Ed. or M.A. degree programs in mathematics. II. Catalog Description: 3 s.h. Foundational
Kutztown University Kutztown, Pennsylvania I. Three semester hours; three clock hours; this is an elective course in the M.Ed. or M.A. degree programs in mathematics. II. Catalog Description: 3 s.h. Foundational
Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
1. A model for spherical/elliptic geometry
 Math 3329-Uniform Geometries Lecture 13 Let s take an overview of what we know. 1. A model for spherical/elliptic geometry Hilbert s axiom system goes with Euclidean geometry. This is the same geometry
Math 3329-Uniform Geometries Lecture 13 Let s take an overview of what we know. 1. A model for spherical/elliptic geometry Hilbert s axiom system goes with Euclidean geometry. This is the same geometry
Euclid s Muse Directions
 Euclid s Muse Directions First: Draw and label three columns on your chart paper as shown below. Name Picture Definition Tape your cards to the chart paper (3 per page) in the appropriate columns. Name
Euclid s Muse Directions First: Draw and label three columns on your chart paper as shown below. Name Picture Definition Tape your cards to the chart paper (3 per page) in the appropriate columns. Name
05 - Surfaces. Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung. CSCI-GA Geometric Modeling - Daniele Panozzo
 05 - Surfaces Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Reminder Curves Turning Number Theorem Continuous world Discrete world k: Curvature is scale dependent is scale-independent Discrete Curvature Integrated
05 - Surfaces Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Reminder Curves Turning Number Theorem Continuous world Discrete world k: Curvature is scale dependent is scale-independent Discrete Curvature Integrated
SMARANDACHE MANIFOLDS. Howard Iseri. American Research Press
 SMARANDACHE MANIFOLDS Howard Iseri American Research Press Smarandache Manifolds Howard Iseri Associate Professor of Mathematics Department of Mathematics and Computer Information Science Mansfield University
SMARANDACHE MANIFOLDS Howard Iseri American Research Press Smarandache Manifolds Howard Iseri Associate Professor of Mathematics Department of Mathematics and Computer Information Science Mansfield University
1 Appendix to notes 2, on Hyperbolic geometry:
 1230, notes 3 1 Appendix to notes 2, on Hyperbolic geometry: The axioms of hyperbolic geometry are axioms 1-4 of Euclid, plus an alternative to axiom 5: Axiom 5-h: Given a line l and a point p not on l,
1230, notes 3 1 Appendix to notes 2, on Hyperbolic geometry: The axioms of hyperbolic geometry are axioms 1-4 of Euclid, plus an alternative to axiom 5: Axiom 5-h: Given a line l and a point p not on l,
(Discrete) Differential Geometry
 (Discrete) Differential Geometry Motivation Understand the structure of the surface Properties: smoothness, curviness, important directions How to modify the surface to change these properties What properties
(Discrete) Differential Geometry Motivation Understand the structure of the surface Properties: smoothness, curviness, important directions How to modify the surface to change these properties What properties
Copyright. Anna Marie Bouboulis
 Copyright by Anna Marie Bouboulis 2013 The Report committee for Anna Marie Bouboulis Certifies that this is the approved version of the following report: Poincaré Disc Models in Hyperbolic Geometry APPROVED
Copyright by Anna Marie Bouboulis 2013 The Report committee for Anna Marie Bouboulis Certifies that this is the approved version of the following report: Poincaré Disc Models in Hyperbolic Geometry APPROVED
The Use of Repeating Patterns to Teach Hyperbolic Geometry Concepts
 The Use of Repeating Patterns to Teach Hyperbolic Geometry Concepts Douglas Dunham Department of Computer Science University of Minnesota, Duluth Duluth, MN 55812-3036, USA E-mail: ddunham@d.umn.edu Web
The Use of Repeating Patterns to Teach Hyperbolic Geometry Concepts Douglas Dunham Department of Computer Science University of Minnesota, Duluth Duluth, MN 55812-3036, USA E-mail: ddunham@d.umn.edu Web
Surfaces: notes on Geometry & Topology
 Surfaces: notes on Geometry & Topology 1 Surfaces A 2-dimensional region of 3D space A portion of space having length and breadth but no thickness 2 Defining Surfaces Analytically... Parametric surfaces
Surfaces: notes on Geometry & Topology 1 Surfaces A 2-dimensional region of 3D space A portion of space having length and breadth but no thickness 2 Defining Surfaces Analytically... Parametric surfaces
EXPERIENCING GEOMETRY
 EXPERIENCING GEOMETRY EUCLIDEAN AND NON-EUCLIDEAN WITH HISTORY THIRD EDITION David W. Henderson Daina Taimina Cornell University, Ithaca, New York PEARSON Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
EXPERIENCING GEOMETRY EUCLIDEAN AND NON-EUCLIDEAN WITH HISTORY THIRD EDITION David W. Henderson Daina Taimina Cornell University, Ithaca, New York PEARSON Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
The Interplay Between Hyperbolic Symmetry and History
 The Interplay Between Hyperbolic Symmetry and History Douglas Dunham Department of Computer Science University of Minnesota, Duluth Duluth, MN 55812-3036, USA E-mail: ddunham@d.umn.edu Web Site: http://www.d.umn.edu/
The Interplay Between Hyperbolic Symmetry and History Douglas Dunham Department of Computer Science University of Minnesota, Duluth Duluth, MN 55812-3036, USA E-mail: ddunham@d.umn.edu Web Site: http://www.d.umn.edu/
Index triangle, 70, theorem, triangle, triangle, triangle, 70
 Index 30-60-90 triangle, 70, 122 360 theorem, 31 45-45-45 triangle, 122 45-45-90 triangle, 70 60-60-60 triangle, 70 AA similarity theorem, 110 AAA congruence theorem, 154 AAASA, 80 AAS theorem, 46 AASAS,
Index 30-60-90 triangle, 70, 122 360 theorem, 31 45-45-45 triangle, 122 45-45-90 triangle, 70 60-60-60 triangle, 70 AA similarity theorem, 110 AAA congruence theorem, 154 AAASA, 80 AAS theorem, 46 AASAS,
Lines That Intersect Circles
 LESSON 11-1 Lines That Intersect Circles Lesson Objectives (p. 746): Vocabulary 1. Interior of a circle (p. 746): 2. Exterior of a circle (p. 746): 3. Chord (p. 746): 4. Secant (p. 746): 5. Tangent of
LESSON 11-1 Lines That Intersect Circles Lesson Objectives (p. 746): Vocabulary 1. Interior of a circle (p. 746): 2. Exterior of a circle (p. 746): 3. Chord (p. 746): 4. Secant (p. 746): 5. Tangent of
Geometry and Gravitation
 Chapter 15 Geometry and Gravitation 15.1 Introduction to Geometry Geometry is one of the oldest branches of mathematics, competing with number theory for historical primacy. Like all good science, its
Chapter 15 Geometry and Gravitation 15.1 Introduction to Geometry Geometry is one of the oldest branches of mathematics, competing with number theory for historical primacy. Like all good science, its
Interpretations and Models. Chapter Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry
 Interpretations and Models Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry Axiomatic Systems in Mathematics The gold standard for rigor in an area of mathematics Not fully achieved in most areas
Interpretations and Models Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry Axiomatic Systems in Mathematics The gold standard for rigor in an area of mathematics Not fully achieved in most areas
Mathematical mysteries: Strange Geometries
 1997 2009, Millennium Mathematics Project, University of Cambridge. Permission is granted to print and copy this page on paper for non commercial use. For other uses, including electronic redistribution,
1997 2009, Millennium Mathematics Project, University of Cambridge. Permission is granted to print and copy this page on paper for non commercial use. For other uses, including electronic redistribution,
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined
 MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
Sonobe Origami for enriching understanding of geometric concepts in three dimensions. DONNA A. DIETZ American University Washington, D.C.
 Sonobe Origami for enriching understanding of geometric concepts in three dimensions DONNA A. DIETZ American University Washington, D.C. Donna Dietz, American University Sonobe Origami for enriching understanding
Sonobe Origami for enriching understanding of geometric concepts in three dimensions DONNA A. DIETZ American University Washington, D.C. Donna Dietz, American University Sonobe Origami for enriching understanding
Course Number: Course Title: Geometry
 Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Geometry. Parallel Lines.
 1 Geometry Parallel Lines 2015 10 21 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Lines: Intersecting, Parallel & Skew Lines & Transversals Parallel Lines & Proofs Properties of Parallel Lines Constructing Parallel
1 Geometry Parallel Lines 2015 10 21 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Lines: Intersecting, Parallel & Skew Lines & Transversals Parallel Lines & Proofs Properties of Parallel Lines Constructing Parallel
A Communications Network???
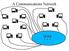 A Communications Network??? A Communications Network What are the desirable properties of the switching box? 1. Every two users must be connected at a switch. 2. Every switch must "look alike". 3. The
A Communications Network??? A Communications Network What are the desirable properties of the switching box? 1. Every two users must be connected at a switch. 2. Every switch must "look alike". 3. The
Lectures 19: The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem I. Table of contents
 Math 348 Fall 07 Lectures 9: The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem I Disclaimer. As we have a textbook, this lecture note is for guidance and supplement only. It should not be relied on when preparing for exams. In
Math 348 Fall 07 Lectures 9: The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem I Disclaimer. As we have a textbook, this lecture note is for guidance and supplement only. It should not be relied on when preparing for exams. In
Greedy Routing with Guaranteed Delivery Using Ricci Flow
 Greedy Routing with Guaranteed Delivery Using Ricci Flow Jie Gao Stony Brook University Joint work with Rik Sarkar, Xiaotian Yin, Wei Zeng, Feng Luo, Xianfeng David Gu Greedy Routing Assign coordinatesto
Greedy Routing with Guaranteed Delivery Using Ricci Flow Jie Gao Stony Brook University Joint work with Rik Sarkar, Xiaotian Yin, Wei Zeng, Feng Luo, Xianfeng David Gu Greedy Routing Assign coordinatesto
Tier 2: GEOMETRY INTRODUCTION TO GEOMETRY Lessons Abbreviation Key Table... 7 G1 LESSON: WHAT IS GEOMETRY?... 8 G1E... 9 G1EA...
 Craig Hane, Ph.D., Founder Tier 2: GEOMETRY INTRODUCTION TO GEOMETRY... 6 1.1 Lessons Abbreviation Key Table... 7 G1 LESSON: WHAT IS GEOMETRY?... 8 G1E... 9 G1EA... 10 G2 LESSON: STRAIGHT LINES AND ANGLES...
Craig Hane, Ph.D., Founder Tier 2: GEOMETRY INTRODUCTION TO GEOMETRY... 6 1.1 Lessons Abbreviation Key Table... 7 G1 LESSON: WHAT IS GEOMETRY?... 8 G1E... 9 G1EA... 10 G2 LESSON: STRAIGHT LINES AND ANGLES...
Hyperbolic Geometry. Thomas Prince. Imperial College London. 21 January 2017
 Hyperbolic Geometry Thomas Prince Imperial College London 21 January 2017 Thomas Prince (Imperial College London) Hyperbolic Planes 21 January 2017 1 / 31 Introducing Geometry What does the word geometry
Hyperbolic Geometry Thomas Prince Imperial College London 21 January 2017 Thomas Prince (Imperial College London) Hyperbolic Planes 21 January 2017 1 / 31 Introducing Geometry What does the word geometry
Euler s Theorem. Brett Chenoweth. February 26, 2013
 Euler s Theorem Brett Chenoweth February 26, 2013 1 Introduction This summer I have spent six weeks of my holidays working on a research project funded by the AMSI. The title of my project was Euler s
Euler s Theorem Brett Chenoweth February 26, 2013 1 Introduction This summer I have spent six weeks of my holidays working on a research project funded by the AMSI. The title of my project was Euler s
The Foundations of Geometry
 The Foundations of Geometry Gerard A. Venema Department of Mathematics and Statistics Calvin College SUB Gottingen 7 219 059 926 2006 A 7409 PEARSON Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 Contents
The Foundations of Geometry Gerard A. Venema Department of Mathematics and Statistics Calvin College SUB Gottingen 7 219 059 926 2006 A 7409 PEARSON Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 Contents
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with
 Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Geometry for Computer Graphics Part 1
 Geometry for Computer Graphics Part 1 MSc Computer Games and Entertainment Maths & Graphics Unit 2012/13 Lecturer(s): Frederic Fol Leymarie (in collaboration with Gareth Edwards) 1 First - For Complete
Geometry for Computer Graphics Part 1 MSc Computer Games and Entertainment Maths & Graphics Unit 2012/13 Lecturer(s): Frederic Fol Leymarie (in collaboration with Gareth Edwards) 1 First - For Complete
Geometry CP. Unit 1 Notes
 Geometry CP Unit 1 Notes 1.1 The Building Blocks of Geometry The three most basic figures of geometry are: Points Shown as dots. No size. Named by capital letters. Are collinear if a single line can contain
Geometry CP Unit 1 Notes 1.1 The Building Blocks of Geometry The three most basic figures of geometry are: Points Shown as dots. No size. Named by capital letters. Are collinear if a single line can contain
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1
 Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1
 Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1 Short Answer 1. Sketch a figure that shows two coplanar lines that do not intersect, but one of the lines is the intersection of two planes. 2. Name two
Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1 Short Answer 1. Sketch a figure that shows two coplanar lines that do not intersect, but one of the lines is the intersection of two planes. 2. Name two
Compactness Theorems for Saddle Surfaces in Metric Spaces of Bounded Curvature. Dimitrios E. Kalikakis
 BULLETIN OF THE GREEK MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 51, 2005 (45 52) Compactness Theorems for Saddle Surfaces in Metric Spaces of Bounded Curvature Dimitrios E. Kalikakis Abstract The notion of a non-regular
BULLETIN OF THE GREEK MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 51, 2005 (45 52) Compactness Theorems for Saddle Surfaces in Metric Spaces of Bounded Curvature Dimitrios E. Kalikakis Abstract The notion of a non-regular
THE UNIFORMIZATION THEOREM AND UNIVERSAL COVERS
 THE UNIFORMIZATION THEOREM AND UNIVERSAL COVERS PETAR YANAKIEV Abstract. This paper will deal with the consequences of the Uniformization Theorem, which is a major result in complex analysis and differential
THE UNIFORMIZATION THEOREM AND UNIVERSAL COVERS PETAR YANAKIEV Abstract. This paper will deal with the consequences of the Uniformization Theorem, which is a major result in complex analysis and differential
GEOMETRY is the study of points in space
 CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
Chapter 6. Sir Migo Mendoza
 Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA AJIT MARATHE. Dr. Douglas Dunham Name of Faculty Adviser. Signature of Faculty Adviser. August 2007 Date GRADUATE SCHOOL
 UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA This is to certify that I have examined this copy of a master s thesis by AJIT MARATHE and have found that it is complete and satisfactory in all respects, and that any and all
UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA This is to certify that I have examined this copy of a master s thesis by AJIT MARATHE and have found that it is complete and satisfactory in all respects, and that any and all
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Supplemental Lecture 4. Surfaces of Zero, Positive and Negative Gaussian Curvature. Euclidean, Spherical and Hyperbolic Geometry.
 Supplemental Lecture 4 Surfaces of Zero, Positive and Negative Gaussian Curvature. Euclidean, Spherical and Hyperbolic Geometry. Abstract This lecture considers two dimensional surfaces embedded in three
Supplemental Lecture 4 Surfaces of Zero, Positive and Negative Gaussian Curvature. Euclidean, Spherical and Hyperbolic Geometry. Abstract This lecture considers two dimensional surfaces embedded in three
1. Right angles. 2. Parallel lines
 Math 3329-Uniform Geometries Lecture 03 Euclid defines a right angle as follows 1. Right angles When a straight line set up on a straight line makes the adjacent angles equal to one another, each of the
Math 3329-Uniform Geometries Lecture 03 Euclid defines a right angle as follows 1. Right angles When a straight line set up on a straight line makes the adjacent angles equal to one another, each of the
The Construction of a Hyperbolic 4-Manifold with a Single Cusp, Following Kolpakov and Martelli. Christopher Abram
 The Construction of a Hyperbolic 4-Manifold with a Single Cusp, Following Kolpakov and Martelli by Christopher Abram A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree Master of
The Construction of a Hyperbolic 4-Manifold with a Single Cusp, Following Kolpakov and Martelli by Christopher Abram A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree Master of
Gaussian and Mean Curvature Planar points: Zero Gaussian curvature and zero mean curvature Tangent plane intersects surface at infinity points Gauss C
 Outline Shape Analysis Basics COS 526, Fall 21 Curvature PCA Distance Features Some slides from Rusinkiewicz Curvature Curvature Curvature κof a curve is reciprocal of radius of circle that best approximates
Outline Shape Analysis Basics COS 526, Fall 21 Curvature PCA Distance Features Some slides from Rusinkiewicz Curvature Curvature Curvature κof a curve is reciprocal of radius of circle that best approximates
pine cone Ratio = 13:8 or 8:5
 Chapter 10: Introducing Geometry 10.1 Basic Ideas of Geometry Geometry is everywhere o Road signs o Carpentry o Architecture o Interior design o Advertising o Art o Science Understanding and appreciating
Chapter 10: Introducing Geometry 10.1 Basic Ideas of Geometry Geometry is everywhere o Road signs o Carpentry o Architecture o Interior design o Advertising o Art o Science Understanding and appreciating
Slope, Distance, Midpoint
 Line segments in a coordinate plane can be analyzed by finding various characteristics of the line including slope, length, and midpoint. These values are useful in applications and coordinate proofs.
Line segments in a coordinate plane can be analyzed by finding various characteristics of the line including slope, length, and midpoint. These values are useful in applications and coordinate proofs.
Geometry Tutor Worksheet 4 Intersecting Lines
 Geometry Tutor Worksheet 4 Intersecting Lines 1 Geometry Tutor - Worksheet 4 Intersecting Lines 1. What is the measure of the angle that is formed when two perpendicular lines intersect? 2. What is the
Geometry Tutor Worksheet 4 Intersecting Lines 1 Geometry Tutor - Worksheet 4 Intersecting Lines 1. What is the measure of the angle that is formed when two perpendicular lines intersect? 2. What is the
Research in Computational Differential Geomet
 Research in Computational Differential Geometry November 5, 2014 Approximations Often we have a series of approximations which we think are getting close to looking like some shape. Approximations Often
Research in Computational Differential Geometry November 5, 2014 Approximations Often we have a series of approximations which we think are getting close to looking like some shape. Approximations Often
<Outline> Mathematical Training Program for Laotian Teachers
 Mathematical Training Program for Laotian Teachers Euclidean Geometry Analytic Geometry Trigonometry Dr Wattana Toutip Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science Khon Kaen University February
Mathematical Training Program for Laotian Teachers Euclidean Geometry Analytic Geometry Trigonometry Dr Wattana Toutip Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science Khon Kaen University February
Preliminary Mathematics of Geometric Modeling (3)
 Preliminary Mathematics of Geometric Modeling (3) Hongxin Zhang and Jieqing Feng 2006-11-27 State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University Differential Geometry of Surfaces Tangent plane and surface normal
Preliminary Mathematics of Geometric Modeling (3) Hongxin Zhang and Jieqing Feng 2006-11-27 State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University Differential Geometry of Surfaces Tangent plane and surface normal
WUSTL Math Circle Sept 27, 2015
 WUSTL Math Circle Sept 7, 015 The K-1 geometry, as we know it, is based on the postulates in Euclid s Elements, which we take for granted in everyday life. Here are a few examples: 1. The distance between
WUSTL Math Circle Sept 7, 015 The K-1 geometry, as we know it, is based on the postulates in Euclid s Elements, which we take for granted in everyday life. Here are a few examples: 1. The distance between
MS2013: Euclidean Geometry. Anca Mustata
 MS2013: Euclidean Geometry Anca Mustata January 10, 2012 Warning: please read this text with a pencil at hand, as you will need to draw your own pictures to illustrate some statements. Euclid s Geometry
MS2013: Euclidean Geometry Anca Mustata January 10, 2012 Warning: please read this text with a pencil at hand, as you will need to draw your own pictures to illustrate some statements. Euclid s Geometry
CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring Differential Geometry of Surfaces
 CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2009 Shape Modeling Differential Geometry of Surfaces Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, 2009 3/4/2009 Recap Differential Geometry of Curves Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, 2009 3/4/2009
CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2009 Shape Modeling Differential Geometry of Surfaces Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, 2009 3/4/2009 Recap Differential Geometry of Curves Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, 2009 3/4/2009
Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term I) 5. InTroduCTIon To EuClId s GEoMETry. l Euclid s five postulates are : ANIL TUTORIALS
 Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term I) 5. InTroduCTIon To EuClId s GEoMETry IMporTAnT TErMs, definitions And results l In geometry, we take a point, a line and a plane as undefined terms. l An axiom
Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term I) 5. InTroduCTIon To EuClId s GEoMETry IMporTAnT TErMs, definitions And results l In geometry, we take a point, a line and a plane as undefined terms. l An axiom
Geodesic and curvature of piecewise flat Finsler surfaces
 Geodesic and curvature of piecewise flat Finsler surfaces Ming Xu Capital Normal University (based on a joint work with S. Deng) in Southwest Jiaotong University, Emei, July 2018 Outline 1 Background Definition
Geodesic and curvature of piecewise flat Finsler surfaces Ming Xu Capital Normal University (based on a joint work with S. Deng) in Southwest Jiaotong University, Emei, July 2018 Outline 1 Background Definition
Arithmetic and Geometry: Uncomfortable Allies? Bill Cherowitzo University of Colorado Denver
 Arithmetic and Geometry: Uncomfortable Allies? Bill Cherowitzo University of Colorado Denver MAA Rocky Mountain Sectional Meeting April 25, 2008 In the beginning... there was Geometry Only ^ Euclid XII.2
Arithmetic and Geometry: Uncomfortable Allies? Bill Cherowitzo University of Colorado Denver MAA Rocky Mountain Sectional Meeting April 25, 2008 In the beginning... there was Geometry Only ^ Euclid XII.2
5. THE ISOPERIMETRIC PROBLEM
 Math 501 - Differential Geometry Herman Gluck March 1, 2012 5. THE ISOPERIMETRIC PROBLEM Theorem. Let C be a simple closed curve in the plane with length L and bounding a region of area A. Then L 2 4 A,
Math 501 - Differential Geometry Herman Gluck March 1, 2012 5. THE ISOPERIMETRIC PROBLEM Theorem. Let C be a simple closed curve in the plane with length L and bounding a region of area A. Then L 2 4 A,
Greedy Routing in Wireless Networks. Jie Gao Stony Brook University
 Greedy Routing in Wireless Networks Jie Gao Stony Brook University A generic sensor node CPU. On-board flash memory or external memory Sensors: thermometer, camera, motion, light sensor, etc. Wireless
Greedy Routing in Wireless Networks Jie Gao Stony Brook University A generic sensor node CPU. On-board flash memory or external memory Sensors: thermometer, camera, motion, light sensor, etc. Wireless
Cambridge University Press Hyperbolic Geometry from a Local Viewpoint Linda Keen and Nikola Lakic Excerpt More information
 Introduction Geometry is the study of spatial relationships, such as the familiar assertion from elementary plane Euclidean geometry that, if two triangles have sides of the same lengths, then they are
Introduction Geometry is the study of spatial relationships, such as the familiar assertion from elementary plane Euclidean geometry that, if two triangles have sides of the same lengths, then they are
Fast marching methods
 1 Fast marching methods Lecture 3 Alexander & Michael Bronstein tosca.cs.technion.ac.il/book Numerical geometry of non-rigid shapes Stanford University, Winter 2009 Metric discretization 2 Approach I:
1 Fast marching methods Lecture 3 Alexander & Michael Bronstein tosca.cs.technion.ac.il/book Numerical geometry of non-rigid shapes Stanford University, Winter 2009 Metric discretization 2 Approach I:
CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring Shape Modeling. Differential Geometry of Surfaces
 CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2011 Shape Modeling Differential Geometry of Surfaces Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, 2011 2/22/2011 Differential Geometry of Surfaces Continuous and Discrete Motivation Smoothness
CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2011 Shape Modeling Differential Geometry of Surfaces Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, 2011 2/22/2011 Differential Geometry of Surfaces Continuous and Discrete Motivation Smoothness
INTRODUCTION TO 3-MANIFOLDS
 INTRODUCTION TO 3-MANIFOLDS NIK AKSAMIT As we know, a topological n-manifold X is a Hausdorff space such that every point contained in it has a neighborhood (is contained in an open set) homeomorphic to
INTRODUCTION TO 3-MANIFOLDS NIK AKSAMIT As we know, a topological n-manifold X is a Hausdorff space such that every point contained in it has a neighborhood (is contained in an open set) homeomorphic to
Shape Modeling. Differential Geometry Primer Smooth Definitions Discrete Theory in a Nutshell. CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2011
 CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2011 Shape Modeling Differential Geometry Primer Smooth Definitions Discrete Theory in a Nutshell 2/15/2011 1 Motivation Geometry processing: understand geometric characteristics,
CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2011 Shape Modeling Differential Geometry Primer Smooth Definitions Discrete Theory in a Nutshell 2/15/2011 1 Motivation Geometry processing: understand geometric characteristics,
Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms
 Unit 1 asics of Geometry Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically looks
Unit 1 asics of Geometry Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically looks
Aspects of Geometry. Finite models of the projective plane and coordinates
 Review Sheet There will be an exam on Thursday, February 14. The exam will cover topics up through material from projective geometry through Day 3 of the DIY Hyperbolic geometry packet. Below are some
Review Sheet There will be an exam on Thursday, February 14. The exam will cover topics up through material from projective geometry through Day 3 of the DIY Hyperbolic geometry packet. Below are some
Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections
 Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
EUCLID S GEOMETRY. Raymond Hoobler. January 27, 2008
 EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
Euclid of Alexandria. Lecture 4 Lines and Geometry. Axioms. Lines
 Euclid of Alexandria Lecture 4 Lines and Geometry 300 BC to 75 B.C. The Father of Geometry Euclid's text Elements is the earliest known systematic discussion of geometry. 1 Axioms In mathematics, an axiom
Euclid of Alexandria Lecture 4 Lines and Geometry 300 BC to 75 B.C. The Father of Geometry Euclid's text Elements is the earliest known systematic discussion of geometry. 1 Axioms In mathematics, an axiom
Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points.
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_spr13t1.tex 1 Solution of Test I Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points. Definition
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_spr13t1.tex 1 Solution of Test I Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points. Definition
Hyplane Polyhedral Models of Hyperbolic Plane
 Original Paper Forma, 21, 5 18, 2006 Hyplane Polyhedral Models of Hyperbolic Plane Kazushi AHARA Department of Mathematics School of Science and Technology, Meiji University, 1-1-1 Higashi-mita, Tama-ku,
Original Paper Forma, 21, 5 18, 2006 Hyplane Polyhedral Models of Hyperbolic Plane Kazushi AHARA Department of Mathematics School of Science and Technology, Meiji University, 1-1-1 Higashi-mita, Tama-ku,
Planes Intersecting Cones: Static Hypertext Version
 Page 1 of 12 Planes Intersecting Cones: Static Hypertext Version On this page, we develop some of the details of the plane-slicing-cone picture discussed in the introduction. The relationship between the
Page 1 of 12 Planes Intersecting Cones: Static Hypertext Version On this page, we develop some of the details of the plane-slicing-cone picture discussed in the introduction. The relationship between the
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units
 Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Basics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes. Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes.
 asics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically
asics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically
Final Exam 1:15-3:15 pm Thursday, December 13, 2018
 Final Exam 1:15-3:15 pm Thursday, December 13, 2018 Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided (or attach additional pages as needed). You are permitted to use pencils/pens, one cheat sheet
Final Exam 1:15-3:15 pm Thursday, December 13, 2018 Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided (or attach additional pages as needed). You are permitted to use pencils/pens, one cheat sheet
A HISTORICAL INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY GEOMETRY
 i MATH 119 A HISTORICAL INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY GEOMETRY Geometry is an word derived from ancient Greek meaning earth measure ( ge = earth or land ) + ( metria = measure ). Euclid wrote the Elements
i MATH 119 A HISTORICAL INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY GEOMETRY Geometry is an word derived from ancient Greek meaning earth measure ( ge = earth or land ) + ( metria = measure ). Euclid wrote the Elements
Hyperbolic Geometry on the Figure-Eight Knot Complement
 Hyperbolic Geometry on the Figure-Eight Knot Complement Alex Gutierrez Arizona State University December 10, 2012 Hyperbolic Space Hyperbolic Space Hyperbolic space H n is the unique complete simply-connected
Hyperbolic Geometry on the Figure-Eight Knot Complement Alex Gutierrez Arizona State University December 10, 2012 Hyperbolic Space Hyperbolic Space Hyperbolic space H n is the unique complete simply-connected
Euclid s Axioms. 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points.
 11.1 Basic Notions Euclid s Axioms 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points. Euclid s Axioms 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points. 2 If two points line in a plane then
11.1 Basic Notions Euclid s Axioms 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points. Euclid s Axioms 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points. 2 If two points line in a plane then
Facilitator Guide. Unit 8
 Facilitator Guide Unit 8 UNIT 08 Facilitator Guide ACTIVITIES NOTE: At many points in the activities for Mathematics Illuminated, workshop participants will be asked to explain, either verbally or in
Facilitator Guide Unit 8 UNIT 08 Facilitator Guide ACTIVITIES NOTE: At many points in the activities for Mathematics Illuminated, workshop participants will be asked to explain, either verbally or in
Hyperbolic Geometry. Chaper Hyperbolic Geometry
 Hyperbolic Geometry Chaper 6.1-6.6 Hyperbolic Geometry Theorems Unique to Hyperbolic Geometry Now we assume Hyperbolic Parallel Postulate (HPP - p21) With the HPP we get for free all the negations of the
Hyperbolic Geometry Chaper 6.1-6.6 Hyperbolic Geometry Theorems Unique to Hyperbolic Geometry Now we assume Hyperbolic Parallel Postulate (HPP - p21) With the HPP we get for free all the negations of the
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
CSE 5559 Computational Topology: Theory, algorithms, and applications to data analysis. Lecture 0: Introduction. Instructor: Yusu Wang
 CSE 5559 Computational Topology: Theory, algorithms, and applications to data analysis Lecture 0: Introduction Instructor: Yusu Wang Lecture 0: Introduction What is topology Why should we be interested
CSE 5559 Computational Topology: Theory, algorithms, and applications to data analysis Lecture 0: Introduction Instructor: Yusu Wang Lecture 0: Introduction What is topology Why should we be interested
September 23,
 1. In many ruler and compass constructions it is important to know that the perpendicular bisector of a secant to a circle is a diameter of that circle. In particular, as a limiting case, this obtains
1. In many ruler and compass constructions it is important to know that the perpendicular bisector of a secant to a circle is a diameter of that circle. In particular, as a limiting case, this obtains
Geometry Definitions, Postulates, and Theorems. Chapter 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Section 3.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles.
 Geometry Definitions, Postulates, and Theorems Chapter : Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Section.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Standards: Prepare for 7.0 Students prove and use theorems involving
Geometry Definitions, Postulates, and Theorems Chapter : Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Section.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Standards: Prepare for 7.0 Students prove and use theorems involving
Pearson Mathematics Geometry
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
Squaring The Circle In The Hyperbolic Disk
 Rose-Hulman Undergraduate Mathematics Journal Volume 15 Issue 1 Article 2 Squaring The Circle In The Hyperbolic Disk Noah Davis Aquinas College, nkd001@aquinas.edu Follow this and additional works at:
Rose-Hulman Undergraduate Mathematics Journal Volume 15 Issue 1 Article 2 Squaring The Circle In The Hyperbolic Disk Noah Davis Aquinas College, nkd001@aquinas.edu Follow this and additional works at:
Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry
 Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Goals: 1) learn to draw conclusions based on patterns 2) learn the building blocks for the structure of geometry 3) learn to measure line segments and angles 4) understand the
Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Goals: 1) learn to draw conclusions based on patterns 2) learn the building blocks for the structure of geometry 3) learn to measure line segments and angles 4) understand the
