V-RAY MATERIAL SETTINGS
|
|
|
- Robyn Quinn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 V-RAY MATERIAL SETTINGS author: Wouter Wynen brought to you by:
2 2006 VisMasters. All rights reserved. VisMasters and the VisMasters logo are trademarks of ArchVision, Inc. All other trademarks belong to their respective owners.
3 V-RAY MATERIAL SETTINGS by: Wouter Wynen February 2006
4
5 INTRODUCTION The basic material settings tutorial explains almost all material parameters of the V-Ray material. If you are new to V-Ray, please read the basic render settings tutorial first, so you can start this tutorial in the correct way. The V-Ray version I used for this tutorial is
6 1. Set render settings Open the render settings dialog and do the following: - set V-Ray as the renderer - output size to 480x360px - global switches: turn off default lights - image sampler to adaptive QMC - antialiasing filter Mitchell-Netravali - indirect illumination ON - Secondary bounces multiplier to 0,85 - Irradiance map settings: - low preset - HSph subdivs = 30 - environment: - skylight pure white color - reflection/refraction pure white, 1,2 multiplier - system: render region division 50x50px 2. Create a test scene Keep it simple. A teapot is a good object for test renders, because of its shape. That s why it was one of the first 3D objects out there! Make two teapots on a larger plane if you want to follow this tutorial as close as possible.. 6
7 3. Open the material editor Open the material editor by pressing m on the keyboard. 4. Load a V-Ray material Press the standard button in the material editor and select VRayMtl from the list. Double click or drag and drop it into one of the material slots. 5. Rename and color Rename the material teapot1. The first parameter in the material is the diffuse slot. This is the main color of the material. The square next to it is a map slot, you can load bitmaps or other kind of maps here to texture the material. For now, simply make the color swatch a light orange color. 7
8 6. Second material I Repeat the previous steps to make a very light grey material. Rename this material ground plane and assign it to the ground plane and small teapot. You should have something like in the image on the left. 7. First render Hit render! Your image should look similar to mine, if you have set all render properties as in step 1. Make sure default lights are turned off. 8
9 8. Reflections Select the orange material in the material editor. Below the diffuse slot are the reflection options of the material. The color swatch next to reflect is the main reflection control. Black means there is no reflection at all, white means the material will become 100% reflective. If you make it red for example, the reflections will be tinted red. First try a medium grey color. 9. Render Hit render. Notice the teapot becomes very reflective. Try a very dark grey, and very light grey too to see the difference. 9
10 10. Max depth Set the reflection color to pure white, and set the max depth parameter to 1 and hit render. You will notice that many areas turn black. The max depth controls how many times a ray can reflect before the calculation stops. Max depth of 1 means only 1 reflection can take place. 2 means a reflection of a reflection can exist and so on... 10
11 11. Exit color Leave max depth at 1 and change the exit color to red. Assign this material also to the small teapot. Render again. Now all reflections of reflections turn red instead of black. The max depth is a way to lower render times in scenes with lots of reflective objects. But by lowering the reflections, the exit color will likely come into play. Sometimes it is therefore useful to change this to another color than black, something more appropriate for the scene for example. 12. Max depth Reset the exit color to black and play with the max depth parameter until most of the black areas disappear. Usually you shouldn t go higher than 10. Higher numbers will only waist valuable render time for no visual improvement. 11
12 13. Fresnel reflections Fresnel reflection is a phenomenon that happens on almost all reflective surfaces. Parts of the surface that point directly at you will reflect less than parts of the surface facing towards you under a greater angle. The amount of the effect is controlled by the IOR of the material. You can find this in the refraction parameters. In real life, the fresnel effect is always linked to this IOR. In V-Ray however, you can unlink them, setting a different IOR for reflection as for refraction. To do this, click the small L next to the fresnel check box. The fresnel IOR box will become available. 14. Fresnel reflections Leave the fresnel IOR at 1.6 and hit render. Notice the middle of the teapot has weaker reflections than the sides. This is the fresnel effect. Lower the fresnel IOR to increase the effect. The lower you go, the less it will reflect in the middle. If you go really high, it will be the same as turning fresnel off (>25). 12
13 15. Teapot 2 Duplicate the orange material, rename it teapot 2 and assign it to the small teapot. Change the diffuse color to a dark red. 16. Reflection glossiness Select the orange material. Change the reflection color back to a medium grey. Turn off fresnel reflections. Change the reflection glossiness from 1.0 to
14 17. Reflection glossiness Hit render. The reflections are very blurry now. This is the effect you get on real objects from very small bumps in the surface. To create this effect in 3D, you could also put a very fine bumpmap in the bumpmap slot. But by using the glossiness parameter instead, rendering will be a lot faster. Play with the glossiness value to see what it does. Glossiness means shininess, so glossiness=1.0 is 100% shiny, lower values are non glossy or blurry reflections. There is much confusion about this, many people will mix up the term glossy with blurry. 18. Smoother blurry reflections The subdivs value beneath the refl glossiness controls the smoothness of the blurry reflections. Change it to 20 and render. The result is much smoother. Note that 8 subdivs means 8x8=64 samples, 20 subdivs means 20x20=400 samples. Doubling the subdivs will take +-4 times longer to render! Make sure you have the AA sampler at adaptive QMC when using high subdivs values! If you want to use adaptive subdivision AA, you can get away with much lower subdivs values (3 to 10). The adaptive AA smooths outs much of the noise from the low subdivs. If you have many blurry reflections in the scene, adaptive QMC will always be faster. 14
15 19. QMC settings: smooth the blurry reflections even more If you want the noise to be even smoother, increasing the subdivs will not always help. Don t go higher than 40 trying to reduce the noise. A better solution can be found in the QMC sampler settings. Open the render settings dialog and go to the QMC sampler rollout. Change the noise threshold to and render again. The noise will be completely gone now, but at the cost of longer render times. The QMC sampler settings give you an easy way to speed up test renders, by simply increasing the noise threshold to 0.05, for example. Note that the QMC sampler settings will also affect irradiance map calculation and DOF, MB, Area shadows, etc... So reducing noise will not only improve glossy effects, but also the GI quality etc... For now, change the noise threshold back to While we re here, go to the system rollout and enable the V-Ray stamp (delete all text except the render time part). You will see speed differences better that way. 20. Highlight glossiness You probably know highlights from the default max materials. Well, these highlights are nothing more than fake blurry reflections. A highlight is actually a reflection of a bright light source. In previous versions of V-Ray, there was no way to render these fake highlights with V-Ray materials. At popular demand, the developers brought fake highlights to the V-Ray material. Note that these highlights will only appear if you use lights in your scene. The skylight will not generate highlights. 15
16 21. Create a spotlight To see the effect of highlight glossiness, create a max spotlight directed at the two teapots. Turn down the skylight multiplier to 0.0 for this test. We don t want any light to come from the sky. In the spotlight settings, turn on shadows and choose V-Ray shadows in the shadow type list. 22. Render Render the scene. The white part on the teapot is the highlight glossiness, the fake blurry reflection. A max spotlight is invisible to the camera and to reflections, but with this highlight glossiness parameter you can make it visible in reflections. 16
17 23. Highlight glossiness linked By default, highlight glossiness setting is linked to the refl glossiness parameter. This means that when you use refl glossiness and you have lights in the scene, the highlight glossiness will appear too. 24. Unlink it! Press the L button next to the highlight glossiness parameter. The highlight glossiness value becomes visible and is set to 1.0 Hit render... the highlight is gone! A value of 1.0 means no highlight glossiness (like 1.0 for blurry reflection means no blurry reflection). 17
18 25. Highlight glossiness only If you want only the highlight glossiness to appear, and not the reflection glossiness, you will have to use a little trick. Logically you would think that 1.0 for refl gloss will turn them off. This is true, but reflections will still appear, only sharp. Mixing sharp reflections with highlight glossiness creates weird unrealistic materials. Just try it. Set highlight gloss to 0.75 and refl gloss to 1.0 and hit render. Although you may like this material, it is not realistic. It is reflecting the light source in a blurry way, and the rest of the environment in a sharp way! That s impossible in real life, as reflections don t make a difference between lights or whatever other objects. 26. Turn off reflections So to be able to render highlight gloss only, you need to turn off reflections for the material. This is possible in V-Ray, but the setting is hidden in the options rollout of the V-Ray material. Deselect trace reflections and render again. Note that now the material has only the fake glossy reflections. This material looks like a standard max material with some highlights on it. 18
19 27. Map slots Next to all reflection parameters is a map slot. This means you can control reflection color, refl glossiness, highlight glossiness and fresnel value by a map. For example the reflection slot. Click it and choose checker from the list. Make it visible in the viewport so you can see if it maps the object correctly. Set all other reflection settings back to default (medium grey, no fresnel, all glossy=1.0, trace reflections on). Delete the spotlight and set skylight back to 1.0. Hit render. You will get something like in my example. All black parts of the map will be non reflective, all white parts are 100% reflective. Try the same map in the other slots too. But take care, white for glossiness means a value of 1.0, so not blurry, and black means very blurry (value 0.0 for glossy). 19
20 28. Use interpolation There is one check box left in the reflection parameters that I didn t explain. The use interpolation check box. This can be used to speed up the calculation of glossy reflections. It works more or less the same way as the Irradiance map for calculating GI. When you check this box, you can adjust interpolation settings in one of the other V-Ray material rollouts. I will not explain these settings, because I don t recommend using the interpolation for glossy reflections. They rarely look good, and when you want quality, they take almost as long as the standard glossy reflections. The next section is about refraction 20
21 1. Start a new scene Open 3D studio max and start a new scene. Open the render settings dialog and do the following: - set V-Ray as the renderer - output size to 480x360px - global switches: turn off default lights - image sampler to adaptive QMC - antialiasing filter Mitchell-Netravali - indirect illumination ON - Secondary bounces multiplier to 0,85 - Irradiance map settings: - low preset - HSph subdivs = 20 - environment: - skylight pure white color - reflection/refraction pure black, 1.0 multiplier - system: - render region division 50*50 px - frame stamp: delete all except the render time part 2. Create the test scene I suggest using the same kind of object as I did. A max teapot is not good now because the mesh has holes in it, it s not watertight and you don t want that on refractive objects. I made this modified torus knot because it will be an interesting shape to test with, because of all the curves and thin/thick areas. If you want, use the exact same settings as I did. 21
22 3. Create materials Make a medium dark blue V-Ray material for the ground plane, and a very light grey V-Ray material for the torus knot and assign them to the corresponding objects. Hit render, you should get something like my example on the left. 4. Refraction parameters Go to the white material and take a look at the refraction parameters. Refraction refers to light rays getting bent when going from one medium to another. For example light travels through air, then hits a glass object and the ray gets bent under a certain angle. Then this ray will travel further through the glass, and eventually will leave it at a certain point, getting bent again. How much a ray gets bent depends on the IOR (index of refraction) of the material. A high IOR means a lot of bending, IOR=1.0 means the rays will not bend. The V-Ray material has all options available to create any kind of refractive material. As you can see, many options are similar to the reflection parameters. First, change the refract color to a medium grey color. 22
23 5. Refraction color Render the image. You will notice the object has a transparent look. The grey refraction color means it s about 50% transparent. 6. Diffuse color Change the diffuse to black and render again. The result is pretty straightforward. 23
24 7. Refraction color Change the refraction color to pure white and render. The result looks weird... Because now the object is 100% transparent, the diffuse color has no effect at all anymore. The black regions are rays that get refracted to the environment color, which is black. 8. Adjust reflections The previous step looks weird, because usually materials with such refractive properties are also reflective. If you set the reflection to pure white, and check fresnel reflections, the material looks a lot better. The material you created now is the basic setup for clear glass in V-Ray. 24
25 9. Create an environment The rendering looks very boring, because the only thing to refract/reflect is the ground plane and the black environment color. Create a large, thin box and position it more or less like I did. 10. VrayLightMtl The goal is to turn this box into a light source. An easy way to do this, is by using the special V- Ray light material. Click the get material button and choose VrayLightMtl from the list. Assign the material to the box and set the multiplier to
26 11. Adjust skylight Hit render. It s way too bright, because our skylight is still active. Set the skylight multiplier to 0.0 and render again. If it s too bright or too dark, you need to play with the V-Ray light material multiplier until it looks okay. You can clearly see the light is coming from our big box now, and the light source also reflects in the torus knot. The contrast between very bright light and black environment is very good for rendering glass or metal like objects. 26
27 12. Refractive GI caustics The light coming from the box is not direct light as with a max spotlight. It is actually treated as first bounce GI (just like the V-Ray skylight). If you would turn off GI and render, there will be no light at all. Because of this, it is important that you leave the refractive GI caustics in the indirect illumination rollout ON. Try rendering this scene without refractive GI caustics. You ll see the shadows are much darker. The GI light is now unable to pass trough the transparent object (there are no GI caustics). Caustics are noting more than refracted/reflected light. To continue, turn refractive GI caustics On again. Also go to the irradiance map rollout and set the preset to custom. Change the min/max rate to -4/-2 to speed up rendering. Note that the GI will be more blurred now, but since we re only testing, it doesn t matter. There will be more on caustics later on in the tutorial. For now remember that you need to enable the GI caustics if you want GI to pass trough transparent objects. 27
28 13. Max depth Increase the max depth parameter in the glass material to 10, both for reflections and refractions. You ll notice a bit more variation in reflection/refraction. In some cases increasing the max depth really helps to make your glass more realistic. It doesn t matter much here because our environment is also black, just like the exit color when max depth is reached. In colored environments the max depth effect will be more noticeable. To continue, reset the max depth to Options: reflect on backside Go to the options rollout of the glass material, and turn on the reflect on backside option. This will allow the inside of the surface to also reflect the environment. When rendering glass, you should leave this option turned on, it generates very nice and realistic inner reflections. This also increases render time of course... To continue the tutorial, turn it OFF again. 28
29 15. Glossiness The glossiness parameter is similar to the one for reflections. It s use is to blur the refractions. This is one of the most time consuming settings, render times will go really high if you use high subdivs... Try a value of 0.8 with 8 subdivs. You ll see that the blurry refractions are very noisy due to the low subdivs. But you get the idea. Turn the glossiness back to
30 16. Index Of Refraction Set the IOR to 1.0 and render. The torus is gone! This is because no rays get bent with this IOR value. Because fresnel IOR is linked to the refraction IOR, this is also set to 1.0, which means the object becomes non reflective too. The refraction color is pure white, so the rays don t become tinted either! All this makes the torus disappear. 17. IOR Unlink the fresnel IOR, so that its value is set to 1.6 again. Hit render. The thing you see now is purely created by reflections. 18. IOR Set the refraction IOR to 1.1 and render again. Each material has its own IOR value. Typical glass values are around 1.6. Do a google search for other common used material IOR s. Render a few tests with different IOR values. Reset the IOR to 1.6 to continue. 30
31 19. Exit color Like with reflection, there s also an exit color for refractions. After a ray has refracted the max depth number of times, this exit color will come in to play. Tick the check box and give it a flashy green color. Hit render. You can clearly see what parts of the image go over the max depth number (5). Make the exit color black again. 20. Fog color The fog color is used to tint the refractions with a certain color. Thicker areas will become darker (more colored) than thinner areas. Try a light red color for fog and render. The material is very dark, but the thinner parts show some transparency. The fog color and fog multiplier are actually an absorption control. The light looses its energy while traveling through the material. The longer it travels, the more energy will be absorbed by the object. That s why thinner parts will remain lighter than the thicker parts. 31
32 21. Fog multiplier Change the fog multiplier to 0.05 and render again. The fog effect is much weaker now, letting more light pass through, resulting in a lighter material. You should experiment with different fog color/multiplier ratios. For example a light but very saturated color with high multiplier, or a dark unsaturated color with a very low multiplier. You can get very different effects by playing with this relationship. 22. Refraction color You probably think, what s the use of the refraction color then? Well, set fog options back to default, and choose a red refract color. Hit render. The glass is colored too, but without the absorption effect. Thin and thick areas are equally colored (the dark areas are refractions of the black environment!). I usually use pure white for refract color and play only with the fog options. But experiment with different refract color/ fog settings to see what they do. Remember, dark refract color means less transparency. The saturation of the color has a huge impact on the look of the refraction. A very dark saturated color will look very similar to a very dark unsaturated color in the color swatch, but it will be completely different when used for refract color or fog color. Just try it! 32
33 23. IOR=1.0 mixed with fog Adjust refraction settings to the ones on the right. By mixing an IOR of 1.0 with fog color, you get a waxy kind of material. 24. Glossiness + IOR=1.0 + fog Adjust the glossiness to 0.75 and the subdivs to 16 and render again. The material looks a bit like reflective wax. Turn glossiness to 1.0 again and IOR to 1.6 before continuing. 33
34 25. Affect shadows An important option we didn t touch yet, it the affect shadows check box. It will have no effect in our test scene because there is no direct light, only GI light. The affect shadows options is only used with direct light rays. Therefore, we will replace the light box with a V-Ray area light. Go to the create panel and choose lights, and from the drop down menu choose V-Ray. 25. V-Ray Light Click and drag in a viewport to create the V-Ray rectangular light. Make the size the same as our box, and position it in the same way. After that, hide the box. Set the V-Ray light settings as in the image on the right (click to enlarge). The multiplier should be equal to the multiplier of the V-Ray light material you used on the light box. We now created a light source exactly the same as the light box, but it will cast raytraced area shadows. 26. Affect shadows In the glass material, turn ON affect shadows and hit render. The image should look like mine. As you can see, it casts green shadows. This is because the affect shadows option and fog color is used. Render time increases because the shadows are raytraced. 34
35 27. Affect shadows OFF Turn affect shadows OFF and render again. Notice the shadows are different now. This is because the GI caustics come back into play. This image is the physically correct one! When you have the affect shadow option turned ON, no refractive GI caustics are computed for that material, they are automatically turned off by V-Ray. The affect shadow option is nothing more than a fake caustics option. So imagine that when using the affect shadow option, refractive caustics would not be turned off automatically, you would get a fake caustic effect AND a real GI caustic effect on top of each other! That s why V-Ray automatically turns off GI caustics for materials that have the affect shadow option turned on. THIS IS VERY IMPORTANT TO UN- DERSTAND! Use the affect shadows option when you want light to pass trough refractive objects, and you don t want to enable refractive GI caustics, or when you don t use GI at all, or when you re using Max lights. Max lights will never produce refractive GI caustics! So if you want the light of max lights to pass trough refractive objects, you MUST use the affect shadow option. 35
36 The top image on the right is rendered with an omni light as the only light source, and the affect shadows option is turned off. Notice the black shadows, no light passes through the material. The bottom image has affect shadows turned on. There is a fake caustic effect but it s nowhere near physically correct. Note that the V-Ray light is a special light. Although it casts direct light just like max lights do, they do produce GI caustics (max lights don t!). Normally only first bounce GI light (like the light coming from skylight and object lights like our light box) produces GI caustics. If you want real caustics when using max lights, you need to enable caustics in the caustics rollout (photon mapped caustics). Don t do this right now, these caustics controls need a tutorial of their own... Just remember that you can get nice caustics effects by using GI and V-Ray lights much easier. That is why I prefer using the light box or V-Ray light over the max lights. You simply check the GI caustics option and you don t have to care about other caustic settings all over the place! Drawback is that you need to have good GI settings for the caustics to be sharp, resulting in longer render times. Another advantage of V-Ray lights or object lights is that they reflect/refract in your objects. Max lights are invisible to camera and reflection/refraction. So to summarize: 1. If you use only object lights and V-Ray lights and you want caustics: - enable GI caustics - use good quality GI settings to make sure the caustics look sharp. 2. If you use max lights and you want the light to pass through refractive materials: - use the affect shadow option for a fake caustic effect - OR enable caustics in the caustics rollout and play with the settings for photon mapped caustics. 3. If you use V-Ray lights and you want photon mapped caustics: - Disable affect shadows - Disable GI caustics - Enable caustics in the caustics rollout and play with the settings. 36
37 28. Final material Use the material settings as in the image on the right. I lowered the fog multiplier a bit, and upped the max depth values both to Final image setup In the irradiance map settings, change everything as in the image on the right. Also go to the QMC sampler rollout and change noise threshold to for maximum quality. 37
38 30. Final image Render the image, it should look something like mine. Notice the nice caustics and area shadows, controlled by the IR map settings. No caustics were enabled in hard to find places, no time consuming raytraced shadows were needed. 31. Comparison with QMC GI As a test, I rendered the image with QMC GI instead of irradiance map for first bounce. QMC GI is not an approximate method like IR map with its undersampling algorithm. QMC GI calculates the GI without compromise, every light sample gets equal attention. So it s a good test to compare how well the GI with IR map is computed. As you can see, in the areas with much lighting detail, the QMC GI image looks better (more physically correct) than the IR map image. But it takes 10 minutes compared to 1 minute 24 seconds for the IR map version... If you want more detailed GI with IR map, you need to edit some of the IR map settings. 38
39 32. Better IR map settings This last image is rendered with optimized IR map settings. As you can see, this comes very close to the QMC GI example, but without any noise on the floor. I will explain how to optimize the IR map settings in an upcoming tutorial. 39
40 This is a new section 1. Translucency Transparent materials like clear glass or water will let light travel through it undistorted (except for the bending due to the IOR). Translucent materials will scatter the light when traveling through it. For example stained glass, wax, grapes, etc... Stained glass can be made with V-Ray by using the refraction glossiness parameter, but wax or grapes for example will need the translucent controls. When to use the translucent controls or not, is a but unclear. Usually translucency is used for really opaque materials in which light can penetrate a certain distance, if it s strong enough. Examples are wax, human skin, orange juice, milk etc... You cannot see through these materials, but light will be able to go through it partially and scatter around. For example when you hold a strong flashlight under your hand, the other side will turn red (blood!) and you can see where your bones are located because they block the light. 40
41 2. Translucency in V-Ray Because the translucency controls are a bit strange in behavior, I will not try to explain them... More technical explanations can be found in the online documents, and I believe the V-Ray team is working on a translucency tutorial... You can get very similar results with extremely different combinations of settings, but when seen under changing lighting conditions, they will react very differently. The translucency controls also depend on the refraction glossiness and fog settings. They work together, and especially the fog color is a very sensitive setting that will have a very drastic effect on the material. One thing you should never do, is using colors that have one of their components set to 255!!! I usually leave the translucency color pure white, the refraction color a grayscale value and then control the material color with the diffuse and fog color. Then with the fog multiplier and translucency light multiplier create various effects of light passing through. 3. Skin Here s a skin material that you can use to study the settings. Play with it and try to understand what effect each parameter has on the final look. Note that because of the use of both reflection and refraction glossiness, this material will render very slowly, especially with these high subdivs values. 41
42 4. Reset all settings from the previous page In the end of the previous page, all settings were changed for the final image. We need to set it back to test render values now. Open the render settings dialog and do the following: - output size to 480x360px - global switches: turn off default lights - image sampler to adaptive QMC - antialiasing filter Mitchell-Netravali - indirect illumination ON - Secondary bounces multiplier to 0,85 - Irradiance map settings: - low preset - HSph subdivs = 20 - environment: - skylight pure white color - reflection/refraction pure black, 1.0 multiplier - system: - render region division 50x50px - frame stamp: delete all except the render time part 5. Create a chrome material Create a new V-Ray material and adjust the settings as in the image on the right. This is a basic chrome material setup. Assign this material to the torus knot object and do a quick test render. It should look like my test image. Now change the reflection glossiness to 0.7 before you continue. 42
43 6. BRDF In this rollout you can choose between Blinn, Phong or Ward shader. The effect of these three types is noticeable the most when using glossy reflections. Render the scene with the three different shaders. The settings affect how the highlights will look like. Ward is commonly used for metallic materials. 7. Anisotropy Anisotropic reflections are reflections stretched in some direction. You see this often on brushed metals, for example the bottom of cooking pans. The anisotropy setting controls the shape of the highlight. The torus knot is not the best example, but you ll get the point. Change the anisotropy setting to -0.6 and render the image. There s also a huge difference between Blinn/Phong/Ward here. Try some other values too (like +0.6 for example). The XYZ axis option allows you to change the direction of the reflections, or you can use a mapping channel instead. The rotation parameter rotates the reflections... 43
44 8. Options rollout First set anisotropy to 0.0 again, and also refl glossiness to Maps rollout The maps rollout sums up all different texture maps. Almost all maps can be accessed in the basic parameters rollout (the small squares next to the parameters), but some will appear only here. Displacement is like bump, but instead of fake rendering it, the actual mesh is deformed to create the irregularities. Refer to the manual for extensive tutorials and examples about displacement. Trace reflections and trace refractions are pretty simple; turn calculation on by checking check box or off by unchecking check box. The cutoff parameter is a threshold value for V-Ray to trace reflections any further or not. Try a value of 0,7 on the current image. Increasing the threshold can speed up rendering when you are using lots of reflections in the scene. Double sided: please refer to the manual. Reflect on backside. We used this option already on page 2 of this tutorial. If turned on, reflections for back facing surfaces will be computed too. Use irradiance map: if you turn this off, the irradiance map will not be used on this material. Instead, the GI on this material will be computed with QMC GI. This can be useful if the irradiance map blurs out small shadow details on certain objects. Treat glossy rays as GI rays: please refer to the manual. Energy preservation mode: please refer These are the last four maps: bump, displace, opacity and environment. Bump allows you to render irregularities in the surface by using a map. Dark areas in the map are low areas, bright areas are high areas. Opacity is the same as you are used to in standard max materials. Environment slot allows you to use different reflect/refract environment for each material. 44
45 10. Reflect/refract interpolation These rollouts contain parameters to control reflect/refract interpolation. These are only needed if you ticked the use interpolation check box in the basic parameters rollout. I don t recommend using interpolation for glossy effects. If you do want to use them, please refer to the manual for more detailed information. 45
46 46
47 About the author Wouter Wynen has studied product development for 5 years at the university in Antwerp, Belgium. During these years, his interest in 3D modeling and visualization grew more and more. In the end, it even overpowered the interest in product design. After graduation, he founded the company Aversis, offering 3D viz & webdesign services. 47
48 share - learn - inspire 2006 VisMasters. All rights reserved. VisMasters and the VisMasters logo are trademarks of ArchVision, Inc. All other trademarks belong to their respective owners.
Caustics - Mental Ray
 Caustics - Mental Ray (Working with real caustic generation) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects. Caustics are the bent reflections
Caustics - Mental Ray (Working with real caustic generation) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects. Caustics are the bent reflections
diffuse diffuse reflection refraction diffuse mapping diffuse reflection reflection filter mapping mapping reflection
 Matières 1 2 3 mapping diffuse reflection diffuse transparency reflection refraction diffuse mapping diffuse reflection diffuse reflection filter mapping bump mapping mapping mapping diffuse reflection
Matières 1 2 3 mapping diffuse reflection diffuse transparency reflection refraction diffuse mapping diffuse reflection diffuse reflection filter mapping bump mapping mapping mapping diffuse reflection
THEA RENDER ADAPTIVE BSD ENGINE
 THEA RENDER ADAPTIVE BSD ENGINE ADAPTIVE (BSD) ENGINE Adaptive (BSD) is the name of the biased engine inside Thea Render. This engine is a biased one (this is why we use the abbreviation "BSD") as it uses
THEA RENDER ADAPTIVE BSD ENGINE ADAPTIVE (BSD) ENGINE Adaptive (BSD) is the name of the biased engine inside Thea Render. This engine is a biased one (this is why we use the abbreviation "BSD") as it uses
Ok, so to get started we will take a look at the settings in the Render setup. If we were to take a render right now this is what we would see...
 Caustics - V-Ray In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects using the V-Ray renderer. Caustics function in V-Ray much like they function
Caustics - V-Ray In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects using the V-Ray renderer. Caustics function in V-Ray much like they function
Caustics - Mental Ray
 Caustics - Mental Ray In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects. Caustics are the focused patterns of light which form after light
Caustics - Mental Ray In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects. Caustics are the focused patterns of light which form after light
Iray Uber Shader Properties. Workshop Reference Guide
 Iray Uber Shader Properties Workshop Reference Guide Sabine Hajostek ( esha ) February 2017 Iray Uber Shader Reference Guide 2 Contents Contents... 3 Basic Information... 4 Shader Modes... 5 PBR Metallicity/Roughness
Iray Uber Shader Properties Workshop Reference Guide Sabine Hajostek ( esha ) February 2017 Iray Uber Shader Reference Guide 2 Contents Contents... 3 Basic Information... 4 Shader Modes... 5 PBR Metallicity/Roughness
Texture Mapping. Images from 3D Creative Magazine
 Texture Mapping Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions Light And Colour Surface Attributes Surface Attributes: Colour Surface Attributes: Shininess Surface Attributes: Specularity
Texture Mapping Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions Light And Colour Surface Attributes Surface Attributes: Colour Surface Attributes: Shininess Surface Attributes: Specularity
8 Human Skin Materials and Faking Sub Surface Scattering in Cycles
 8 Human Skin Materials and Faking Sub Surface Scattering in Cycles In this chapter, we will cover: Simulating SSS in Cycles by using the Translucent shader Simulating SSS in Cycles by using the Vertex
8 Human Skin Materials and Faking Sub Surface Scattering in Cycles In this chapter, we will cover: Simulating SSS in Cycles by using the Translucent shader Simulating SSS in Cycles by using the Vertex
Visualization Insider A Little Background Information
 Visualization Insider A Little Background Information Visualization Insider 2 Creating Backgrounds for 3D Scenes Backgrounds are a critical part of just about every type of 3D scene. Although they are
Visualization Insider A Little Background Information Visualization Insider 2 Creating Backgrounds for 3D Scenes Backgrounds are a critical part of just about every type of 3D scene. Although they are
AWE Surface 1.0 Documentation
 AWE Surface 1.0 Documentation AWE Surface is a new, robust, highly optimized, physically plausible shader for DAZ Studio and 3Delight employing physically based rendering (PBR) metalness / roughness workflow.
AWE Surface 1.0 Documentation AWE Surface is a new, robust, highly optimized, physically plausible shader for DAZ Studio and 3Delight employing physically based rendering (PBR) metalness / roughness workflow.
The V-Ray installer will automatically remove any previous installations. This will allow you to seamlessly upgrade from previous versions.
 Overview This guide is to serve as a reference for installing V-Ray for 3ds Max and 3ds Max Design. Please refer to the Glossary page for specific terms used in this document. If you experience any problems,
Overview This guide is to serve as a reference for installing V-Ray for 3ds Max and 3ds Max Design. Please refer to the Glossary page for specific terms used in this document. If you experience any problems,
A R E N D E R I N G P L U G I N F O R D E S I G N E R S. V-Ray for SketchUp. By Chia Fu Chiang Damien Alomar Jorge Barrero
 A R E N D E R I N G P L U G I N F O R D E S I G N E R S V-Ray for SketchUp By Chia Fu Chiang Damien Alomar Jorge Barrero Table of Contents Install V-Ray for SketchUp... Activating V-Ray for SketchUp...
A R E N D E R I N G P L U G I N F O R D E S I G N E R S V-Ray for SketchUp By Chia Fu Chiang Damien Alomar Jorge Barrero Table of Contents Install V-Ray for SketchUp... Activating V-Ray for SketchUp...
Autodesk Fusion 360: Render. Overview
 Overview Rendering is the process of generating an image by combining geometry, camera, texture, lighting and shading (also called materials) information using a computer program. Before an image can be
Overview Rendering is the process of generating an image by combining geometry, camera, texture, lighting and shading (also called materials) information using a computer program. Before an image can be
Chapter 9- Ray-Tracing
 Ray-tracing is used to produce mirrored and reflective surfaces. It is also being used to create transparency and refraction (bending of images through transparent surfaceslike a magnifying glass or a
Ray-tracing is used to produce mirrored and reflective surfaces. It is also being used to create transparency and refraction (bending of images through transparent surfaceslike a magnifying glass or a
Submerge Camera Shader
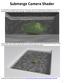 Submerge Camera Shader In this tutorial we are going to take a look at a simple scene with a swimming pool and a teapot and we will use the Mental Ray Camera shader called "Submerge" to change the look
Submerge Camera Shader In this tutorial we are going to take a look at a simple scene with a swimming pool and a teapot and we will use the Mental Ray Camera shader called "Submerge" to change the look
Turn your movie file into the homework folder on the server called Lights, Camera, Action.
 CS32 W11 Homework 3: Due MONDAY, APRIL 18 Now let s put the ball in a world of your making and have some fun. Create a simple AND WE MEAN SIMPLE environment for one of your ball bounces. You will assign
CS32 W11 Homework 3: Due MONDAY, APRIL 18 Now let s put the ball in a world of your making and have some fun. Create a simple AND WE MEAN SIMPLE environment for one of your ball bounces. You will assign
Chapter 11. Caustics and Global Illumination
 11 and Global Illumination Chapter 11 Direct illumination occurs when a light source directly illuminates an object or objects in a scene. Indirect illumination occurs if light illuminates objects by reflection
11 and Global Illumination Chapter 11 Direct illumination occurs when a light source directly illuminates an object or objects in a scene. Indirect illumination occurs if light illuminates objects by reflection
Chapter 4- Blender Render Engines
 Chapter 4- Render Engines What is a Render Engine? As you make your 3D models in, your goal will probably be to generate (render) an image or a movie as a final result. The software that determines how
Chapter 4- Render Engines What is a Render Engine? As you make your 3D models in, your goal will probably be to generate (render) an image or a movie as a final result. The software that determines how
MR Shaders Dielectric Materials Rendering Glass and Simple Caustics
 Dielectric Material This shader is a physically based material shader that can be used to simulate dielectric media such as glass, water, and other liquids. The shader uses Fresnel's formulas for dielectric
Dielectric Material This shader is a physically based material shader that can be used to simulate dielectric media such as glass, water, and other liquids. The shader uses Fresnel's formulas for dielectric
Corona Sky Corona Sun Corona Light Create Camera About
 Plugin menu Corona Sky creates Sky object with attached Corona Sky tag Corona Sun creates Corona Sun object Corona Light creates Corona Light object Create Camera creates Camera with attached Corona Camera
Plugin menu Corona Sky creates Sky object with attached Corona Sky tag Corona Sun creates Corona Sun object Corona Light creates Corona Light object Create Camera creates Camera with attached Corona Camera
Interior space in daylight Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Interior space in daylight Bonus Chapter 1 Day Lighting an Interior Space 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about lighting an interior scene while you work on the lighting for the living
Interior space in daylight Bonus Chapter 1 Day Lighting an Interior Space 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about lighting an interior scene while you work on the lighting for the living
There are many kinds of surface shaders, from those that affect basic surface color, to ones that apply bitmap textures and displacement.
 mental ray Overview Mental ray is a powerful renderer which is based on a scene description language. You can use it as a standalone renderer, or even better, integrated with 3D applications. In 3D applications,
mental ray Overview Mental ray is a powerful renderer which is based on a scene description language. You can use it as a standalone renderer, or even better, integrated with 3D applications. In 3D applications,
Global Illumination. Global Illumination. Direct Illumination vs. Global Illumination. Indirect Illumination. Soft Shadows.
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Angel Ch. 11] 1 Global Illumination
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Angel Ch. 11] 1 Global Illumination
Shadow Casting in World Builder. A step to step tutorial on how to reach decent results on the creation of shadows
 Shadow Casting in World Builder A step to step tutorial on how to reach decent results on the creation of shadows Tutorial on shadow casting in World Builder 3.* Introduction Creating decent shadows in
Shadow Casting in World Builder A step to step tutorial on how to reach decent results on the creation of shadows Tutorial on shadow casting in World Builder 3.* Introduction Creating decent shadows in
Property of: Entrada Interactive. PBR Workflow. Working within a PBR-based environment
 Property of: Entrada Interactive PBR Workflow Working within a PBR-based environment Ryan Manning 8/24/2014 MISCREATED PBR WORKFLOW CryDocs on Physically Based Shading/Rendering: http://docs.cryengine.com/display/sdkdoc4/physically+based+rendering
Property of: Entrada Interactive PBR Workflow Working within a PBR-based environment Ryan Manning 8/24/2014 MISCREATED PBR WORKFLOW CryDocs on Physically Based Shading/Rendering: http://docs.cryengine.com/display/sdkdoc4/physically+based+rendering
Rendering Engines - Specific tools may depend on "Rendering Engine"
 Week 5 3DS Max, Cameras, Lighting and Materials Rendering - Process of turning geometry into pixels Rendering Engines - Specific tools may depend on "Rendering Engine" 1. Internal (3DS MAX) ART (Autodesk
Week 5 3DS Max, Cameras, Lighting and Materials Rendering - Process of turning geometry into pixels Rendering Engines - Specific tools may depend on "Rendering Engine" 1. Internal (3DS MAX) ART (Autodesk
IBL/GI & GLASS. Getting Realistic Results By Yon Resch. The Three Types of GI lighting and Glass
 IBL/GI & GLASS Getting Realistic Results By Yon Resch Glass and other transparent materials are some of the hardest materials to render realistically. This has mainly to do with the number of additional
IBL/GI & GLASS Getting Realistic Results By Yon Resch Glass and other transparent materials are some of the hardest materials to render realistically. This has mainly to do with the number of additional
Mental Ray for BK5100
 for BK5100 Practical guide: Global Illumination Interior and MIA Materials Tweety 1 Technisch Ontwerp en Informatica Lecture overview Final Gather Exterior Lighting and rendering an exterior scene using
for BK5100 Practical guide: Global Illumination Interior and MIA Materials Tweety 1 Technisch Ontwerp en Informatica Lecture overview Final Gather Exterior Lighting and rendering an exterior scene using
Advanced Rendering CHAPTER. Render Window. Learning Objectives. Image Pane
 CHAPTER Advanced Rendering Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Make advanced rendering settings. Set the resolution for a rendering. Save a rendering to an image file.
CHAPTER Advanced Rendering Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Make advanced rendering settings. Set the resolution for a rendering. Save a rendering to an image file.
Global Illumination. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18. BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] 1 Global Illumination
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] 1 Global Illumination
Perfect Hair. Manual Version 1.0
 Perfect Hair Manual Version 1.0 Content Important Information...1 Copyright...1 Disclaimer...1 Usage Rights...1 1. Overview...2 2. User Interface...2 3. Perfect Hair Options...3 3.1. Color...3 3.2. Ambient...4
Perfect Hair Manual Version 1.0 Content Important Information...1 Copyright...1 Disclaimer...1 Usage Rights...1 1. Overview...2 2. User Interface...2 3. Perfect Hair Options...3 3.1. Color...3 3.2. Ambient...4
AR-media TUTORIALS IMPROVING REALISM AMBIENT OCCLUSION. (June, 2011)
 AR-media TUTORIALS IMPROVING REALISM AMBIENT OCCLUSION (June, 2011) Copyright Copyright 2008/2011 Inglobe Technologies S.r.l. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted,
AR-media TUTORIALS IMPROVING REALISM AMBIENT OCCLUSION (June, 2011) Copyright Copyright 2008/2011 Inglobe Technologies S.r.l. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted,
3ds Max certification prep
 3ds Max certification prep Study online at quizlet.com/_25oorz 1. 24 Frames per second 2. 25 Frames per second, Europe 3. 30 Frames per second, Americas and Japan 4. Absolute mode, off set mode 5. How
3ds Max certification prep Study online at quizlet.com/_25oorz 1. 24 Frames per second 2. 25 Frames per second, Europe 3. 30 Frames per second, Americas and Japan 4. Absolute mode, off set mode 5. How
Max scene used to generate the image from the second pdf in this tutorial.
 Tutorial covers creating vector drawings from a 3ds max scene and methods for compositing these drawings back into a rendering. Rendering set up is based of the lighting set up from the mental ray/skylight/mr
Tutorial covers creating vector drawings from a 3ds max scene and methods for compositing these drawings back into a rendering. Rendering set up is based of the lighting set up from the mental ray/skylight/mr
Chapter 5- Materials & Textures
 Chapter 5- Materials & Textures As mentioned in the past chapter, materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent
Chapter 5- Materials & Textures As mentioned in the past chapter, materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent
Global Illumination. Global Illumination. Direct Illumination vs. Global Illumination. Indirect Illumination. Soft Shadows.
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] March 28, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] March 28, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California
3D Space is one of the most rewarding areas
 Lesson 8 206 3D Space Add a new dimension to your animations. In This Lesson 207 enabling layers for 3D 208 moving and rotating layers in 3D space 210 multiplaning effects 212 3D motion paths 213 multiple
Lesson 8 206 3D Space Add a new dimension to your animations. In This Lesson 207 enabling layers for 3D 208 moving and rotating layers in 3D space 210 multiplaning effects 212 3D motion paths 213 multiple
Chapter 12- NURBS & Meta Shape Basics
 Chapter 12- NURBS & Meta Shape Basics When you press Shift-A for Add, you will notice other object types beside meshes, cameras and lights that can be created. Two types of objects that can be created
Chapter 12- NURBS & Meta Shape Basics When you press Shift-A for Add, you will notice other object types beside meshes, cameras and lights that can be created. Two types of objects that can be created
Ambient Occlusion Pass
 Ambient Occlusion Pass (Soft Shadows in the Nooks and Crannies to Replicate Photorealistic Lighting) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for an Ambient Occlusion
Ambient Occlusion Pass (Soft Shadows in the Nooks and Crannies to Replicate Photorealistic Lighting) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for an Ambient Occlusion
Lecture 18: Primer on Ray Tracing Techniques
 Lecture 18: Primer on Ray Tracing Techniques 6.172: Performance Engineering of Software Systems Joshua Slocum November 16, 2010 A Little Background Image rendering technique Simulate rays of light - ray
Lecture 18: Primer on Ray Tracing Techniques 6.172: Performance Engineering of Software Systems Joshua Slocum November 16, 2010 A Little Background Image rendering technique Simulate rays of light - ray
FreeForm 3D Displacer User Manual. freeform created by mettle.com
 FreeForm 3D Displacer User Manual freeform created by mettle.com Contents 3 Installation 4 Controls 6 Controls - cont d 8 Support 9 Application FreeForm 3D Displacer The FreeForm 3D Displacer plugin for
FreeForm 3D Displacer User Manual freeform created by mettle.com Contents 3 Installation 4 Controls 6 Controls - cont d 8 Support 9 Application FreeForm 3D Displacer The FreeForm 3D Displacer plugin for
LEVEL 1 ANIMATION ACADEMY2010
 1 Textures add more realism to an environment and characters. There are many 2D painting programs that can be used to create textures, such as Adobe Photoshop and Corel Painter. Many artists use photographs
1 Textures add more realism to an environment and characters. There are many 2D painting programs that can be used to create textures, such as Adobe Photoshop and Corel Painter. Many artists use photographs
ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering. Texture Mapping
 ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering Texture Mapping Is the way in which a material is wrapped around an object. The default method is UVW mapping (see below). When you drag a material
ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering Texture Mapping Is the way in which a material is wrapped around an object. The default method is UVW mapping (see below). When you drag a material
Pen Tool, Fill Layers, Color Range, Levels Adjustments, Magic Wand tool, and shadowing techniques
 Creating a superhero using the pen tool Topics covered: Pen Tool, Fill Layers, Color Range, Levels Adjustments, Magic Wand tool, and shadowing techniques Getting Started 1. Reset your work environment
Creating a superhero using the pen tool Topics covered: Pen Tool, Fill Layers, Color Range, Levels Adjustments, Magic Wand tool, and shadowing techniques Getting Started 1. Reset your work environment
Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio
 Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio This product includes a beautiful glass chess set, 70 faceted glass shader presets and a 360 degree prop with 5 material files. Some people find
Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio This product includes a beautiful glass chess set, 70 faceted glass shader presets and a 360 degree prop with 5 material files. Some people find
MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for
MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for
Materials in Kerkythea ~ a beginners guide
 Materials in Kerkythea ~ a beginners guide I started using Kerkythea as a way of rendering SketchUP models. I quickly found that I needed to be able to create and work with materials. I read Patrick Nieborg
Materials in Kerkythea ~ a beginners guide I started using Kerkythea as a way of rendering SketchUP models. I quickly found that I needed to be able to create and work with materials. I read Patrick Nieborg
ULTIMATE IRAY SKIN MANAGER
 ULTIMATE IRAY SKIN MANAGER V3Digitimes, January 2018 1 Ultimage Iray Skin Manager is a product made to help you to configure, modify, adapt Iray Skin Settings in the most efficient, easy, and comfortable
ULTIMATE IRAY SKIN MANAGER V3Digitimes, January 2018 1 Ultimage Iray Skin Manager is a product made to help you to configure, modify, adapt Iray Skin Settings in the most efficient, easy, and comfortable
3 Interactions of Light Waves
 CHAPTER 22 3 Interactions of Light Waves SECTION The Nature of Light BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does reflection affect the way we see
CHAPTER 22 3 Interactions of Light Waves SECTION The Nature of Light BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does reflection affect the way we see
Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018
 Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Theoretical foundations Ray Tracing from the Ground Up Chapters 13-15 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF
Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Theoretical foundations Ray Tracing from the Ground Up Chapters 13-15 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF
MATERIAL TYPES CLO VIRTUAL FASHION
 M A T E R I A L T Y P E S CONTENTS GENERAL SETTINGS 3 PRESET 9 NEW MATERIALS (CLO 4.2) 16 GENERAL SETTINGS Changing Material Type Set the appropriate Type for the material. Select the fabric and apply
M A T E R I A L T Y P E S CONTENTS GENERAL SETTINGS 3 PRESET 9 NEW MATERIALS (CLO 4.2) 16 GENERAL SETTINGS Changing Material Type Set the appropriate Type for the material. Select the fabric and apply
UV Mapping to avoid texture flaws and enable proper shading
 UV Mapping to avoid texture flaws and enable proper shading Foreword: Throughout this tutorial I am going to be using Maya s built in UV Mapping utility, which I am going to base my projections on individual
UV Mapping to avoid texture flaws and enable proper shading Foreword: Throughout this tutorial I am going to be using Maya s built in UV Mapping utility, which I am going to base my projections on individual
Textures and UV Mapping in Blender
 Textures and UV Mapping in Blender Categories : Uncategorised Date : 21st November 2017 1 / 25 (See below for an introduction to UV maps and unwrapping) Jim s Notes regarding Blender objects, the UV Editor
Textures and UV Mapping in Blender Categories : Uncategorised Date : 21st November 2017 1 / 25 (See below for an introduction to UV maps and unwrapping) Jim s Notes regarding Blender objects, the UV Editor
Tangents. In this tutorial we are going to take a look at how tangents can affect an animation.
 Tangents In this tutorial we are going to take a look at how tangents can affect an animation. One of the 12 Principles of Animation is called Slow In and Slow Out. This refers to the spacing of the in
Tangents In this tutorial we are going to take a look at how tangents can affect an animation. One of the 12 Principles of Animation is called Slow In and Slow Out. This refers to the spacing of the in
Lighting & 3D Graphics. Images from 3D Creative Magazine
 Lighting & 3D Graphics Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions 3D Lighting Basics 3D Light Sources Lighting Controls & Effects Brightness & Colour Shadows Hotspot And Falloff
Lighting & 3D Graphics Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions 3D Lighting Basics 3D Light Sources Lighting Controls & Effects Brightness & Colour Shadows Hotspot And Falloff
TUTORIAL 7: Global Illumination & Ambient Occlusion
 TUTORIAL 7: Global Illumination & Ambient Occlusion The goal of this short tutorial is to introduce a few select aspects of mental ray so that you may consider incorporating them in your projects if appropriate.
TUTORIAL 7: Global Illumination & Ambient Occlusion The goal of this short tutorial is to introduce a few select aspects of mental ray so that you may consider incorporating them in your projects if appropriate.
02 Shading and Frames. Steve Marschner CS5625 Spring 2016
 02 Shading and Frames Steve Marschner CS5625 Spring 2016 Light reflection physics Radiometry redux Power Intensity power per unit solid angle Irradiance power per unit area Radiance power per unit (solid
02 Shading and Frames Steve Marschner CS5625 Spring 2016 Light reflection physics Radiometry redux Power Intensity power per unit solid angle Irradiance power per unit area Radiance power per unit (solid
Advanced Maya Texturing and Lighting
 Advanced Maya Texturing and Lighting Lanier, Lee ISBN-13: 9780470292730 Table of Contents Introduction. Chapter 1 Understanding Lighting, Color, and Composition. Understanding the Art of Lighting. Using
Advanced Maya Texturing and Lighting Lanier, Lee ISBN-13: 9780470292730 Table of Contents Introduction. Chapter 1 Understanding Lighting, Color, and Composition. Understanding the Art of Lighting. Using
Photo Studio Optimizer
 CATIA V5 Training Foils Photo Studio Optimizer Version 5 Release 19 September 008 EDU_CAT_EN_PSO_FF_V5R19 Photo Studio Optimizer Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course you will be able
CATIA V5 Training Foils Photo Studio Optimizer Version 5 Release 19 September 008 EDU_CAT_EN_PSO_FF_V5R19 Photo Studio Optimizer Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course you will be able
I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob Cosgrove on Wednesday to discuss the future of the cluster. Computer Graphics
 Announcements Assignment 4 will be out later today Problem Set 3 is due today or tomorrow by 9am in my mail box (4 th floor NSH) How are the machines working out? I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob
Announcements Assignment 4 will be out later today Problem Set 3 is due today or tomorrow by 9am in my mail box (4 th floor NSH) How are the machines working out? I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob
Oso Toon Shader. Step 1: Flat Color
 Oso Toon Shader By default the Oso Toon Shader has most of the same elements of standard Iray Uber Shader, that it is based on. However, there are some additional functions that allow OTS to do some dramatic
Oso Toon Shader By default the Oso Toon Shader has most of the same elements of standard Iray Uber Shader, that it is based on. However, there are some additional functions that allow OTS to do some dramatic
Chapter 5 Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
SNC2D PHYSICS 4/27/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P ) Light Rays & Reflection. The Ray Model of Light
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P.402-409) Light Rays & Reflection A driver adjusts her rearview mirror. The mirror allows her to see the cars behind her. Mirrors help
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P.402-409) Light Rays & Reflection A driver adjusts her rearview mirror. The mirror allows her to see the cars behind her. Mirrors help
Chapter 6- Lighting and Cameras
 Lighting Types and Settings When you create a scene in Blender, you start with a few basic elements that will include a camera, but may or may not include a light. Remember that what the camera sees is
Lighting Types and Settings When you create a scene in Blender, you start with a few basic elements that will include a camera, but may or may not include a light. Remember that what the camera sees is
UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS
 1 UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS Science 8 2 LIGHT BEHAVES IN PREDICTABLE WAYS. Section 2.0 1 3 LIGHT TRAVELS IN RAYS AND INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS Topic 2.1 RAY DIAGRAMS Scientists use ray diagrams
1 UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS Science 8 2 LIGHT BEHAVES IN PREDICTABLE WAYS. Section 2.0 1 3 LIGHT TRAVELS IN RAYS AND INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS Topic 2.1 RAY DIAGRAMS Scientists use ray diagrams
Soft shadows. Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February
 Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Dissolving Models with Particle Flow and Animated Opacity Map
 Dissolving Models with Particle Flow and Animated Opacity Map In this tutorial we are going to start taking a look at Particle Flow, and one of its uses in digital effects of making a model look as though
Dissolving Models with Particle Flow and Animated Opacity Map In this tutorial we are going to start taking a look at Particle Flow, and one of its uses in digital effects of making a model look as though
THE SAMPLING TAB. Pixel Samples. Ray Variance Antialiasing. H16 Mantra User Guide
 THE SAMPLING TAB The Sampling Tab can be found under the Rendering Tab on the Mantra Node. The parameters found on this tab control the amount of sampling performed by Mantra while generating an image.
THE SAMPLING TAB The Sampling Tab can be found under the Rendering Tab on the Mantra Node. The parameters found on this tab control the amount of sampling performed by Mantra while generating an image.
Radeon ProRender plug-in for 3ds Max. User Guide v1.0
 Radeon ProRender plug-in for 3ds Max User Guide v1.0 This document is a user and setup guide with tips and tricks on how to render photorealistic images in real-time, set materials and lighting. DISCLAIMER
Radeon ProRender plug-in for 3ds Max User Guide v1.0 This document is a user and setup guide with tips and tricks on how to render photorealistic images in real-time, set materials and lighting. DISCLAIMER
4) Finish the spline here. To complete the spline, double click the last point or select the spline tool again.
 1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural
 1 Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural to consider using it in video games too. 2 I hope that
1 Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural to consider using it in video games too. 2 I hope that
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
FLAMINGO CHEAT SHEET FOR ES 305 CLASS 5 Pages of Fresh Flamingo Goodness
 FLAMINGO CHEAT SHEET FOR ES 305 CLASS 5 Pages of Fresh Flamingo Goodness *Keep this PDF with you at all times it will help you to maneuver the vast and confusing ocean that is the Flamingo Materials Editor!
FLAMINGO CHEAT SHEET FOR ES 305 CLASS 5 Pages of Fresh Flamingo Goodness *Keep this PDF with you at all times it will help you to maneuver the vast and confusing ocean that is the Flamingo Materials Editor!
SAMPLING AND NOISE. Increasing the number of samples per pixel gives an anti-aliased image which better represents the actual scene.
 SAMPLING AND NOISE When generating an image, Mantra must determine a color value for each pixel by examining the scene behind the image plane. Mantra achieves this by sending out a number of rays from
SAMPLING AND NOISE When generating an image, Mantra must determine a color value for each pixel by examining the scene behind the image plane. Mantra achieves this by sending out a number of rays from
Burning Laser. In this tutorial we are going to use particle flow to create a laser beam that shoots off sparks and leaves a burn mark on a surface!
 Burning Laser In this tutorial we are going to use particle flow to create a laser beam that shoots off sparks and leaves a burn mark on a surface! In order to save time on things you should already know
Burning Laser In this tutorial we are going to use particle flow to create a laser beam that shoots off sparks and leaves a burn mark on a surface! In order to save time on things you should already know
Introduction to 3dsMax TNM061/TNGD25 Lab 3: Lighting and rendering
 Introduction to 3dsMax TNM061/TNGD25 Lab 3: Lighting and rendering Contents 1 Light sources 2 1.1 Simple light sources.............................. 2 1.2 A directional light...............................
Introduction to 3dsMax TNM061/TNGD25 Lab 3: Lighting and rendering Contents 1 Light sources 2 1.1 Simple light sources.............................. 2 1.2 A directional light...............................
Basic Rendering Techniques Part B
 Basic Rendering Techniques Part B Using Materials in 3d Max The simplest method for changing g the default gray color of a 3d object is to apply hue to the object using the diffuse color feature. The physical
Basic Rendering Techniques Part B Using Materials in 3d Max The simplest method for changing g the default gray color of a 3d object is to apply hue to the object using the diffuse color feature. The physical
MAYA; AN INTRODUCTION TO MAYA; EndOfLine.info;
 MAYA; AN INTRODUCTION TO MAYA; EndOfLine.info; Maya is an intuitive modelling and animation software that relies on a different set of techniques and strategies than Rhinoceros. It is important to note
MAYA; AN INTRODUCTION TO MAYA; EndOfLine.info; Maya is an intuitive modelling and animation software that relies on a different set of techniques and strategies than Rhinoceros. It is important to note
Lighting affects appearance
 Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
Advanced Maya e Texturing. and Lighting. Second Edition WILEY PUBLISHING, INC.
 Advanced Maya e Texturing and Lighting Second Edition Lee Lanier WILEY PUBLISHING, INC. Contents Introduction xvi Chapter 1 Understanding Lighting, Color, and Composition 1 Understanding the Art of Lighting
Advanced Maya e Texturing and Lighting Second Edition Lee Lanier WILEY PUBLISHING, INC. Contents Introduction xvi Chapter 1 Understanding Lighting, Color, and Composition 1 Understanding the Art of Lighting
MASY Easy Caustics. A Manual
 MASY Easy Caustics A Manual Table of Contents Introduction...3 Chapter 1: The Base Rig...4 Chapter 2: The Props and Scenes...8 Introduction Thank you for purchasing the Easy Caustics lighting pack for
MASY Easy Caustics A Manual Table of Contents Introduction...3 Chapter 1: The Base Rig...4 Chapter 2: The Props and Scenes...8 Introduction Thank you for purchasing the Easy Caustics lighting pack for
Planets Earth, Mars and Moon Shaders Asset V Documentation (Unity 5 version)
 Planets Earth, Mars and Moon Shaders Asset V0.4.4 Documentation (Unity 5 version) Charles Pérois - 2015 Introduction 2 Table des matières 1. Introduction...3 2. Release Notes...4 3. How to Use...6 1. Set
Planets Earth, Mars and Moon Shaders Asset V0.4.4 Documentation (Unity 5 version) Charles Pérois - 2015 Introduction 2 Table des matières 1. Introduction...3 2. Release Notes...4 3. How to Use...6 1. Set
Advanced Distant Light for DAZ Studio
 Contents Advanced Distant Light for DAZ Studio Introduction Important Concepts Quick Start Quick Tips Parameter Settings Light Group Shadow Group Lighting Control Group Known Issues Introduction The Advanced
Contents Advanced Distant Light for DAZ Studio Introduction Important Concepts Quick Start Quick Tips Parameter Settings Light Group Shadow Group Lighting Control Group Known Issues Introduction The Advanced
How-To Guide SAP 3D Visual Enterprise Author 8.0 Document Version: How To Work with Textures
 How-To Guide SAP 3D Visual Enterprise Author 8.0 Document Version: 1.0-2014-07-04 Document History Document Version Description 1.0 First version Document History 2014 SAP AG or an SAP affiliate company.
How-To Guide SAP 3D Visual Enterprise Author 8.0 Document Version: 1.0-2014-07-04 Document History Document Version Description 1.0 First version Document History 2014 SAP AG or an SAP affiliate company.
Distributed Ray Tracing
 CT5510: Computer Graphics Distributed Ray Tracing BOCHANG MOON Distributed Ray Tracing Motivation The classical ray tracing produces very clean images (look fake) Perfect focus Perfect reflections Sharp
CT5510: Computer Graphics Distributed Ray Tracing BOCHANG MOON Distributed Ray Tracing Motivation The classical ray tracing produces very clean images (look fake) Perfect focus Perfect reflections Sharp
Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ]
![Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ] Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ]](/thumbs/78/78594982.jpg) CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15 Ray Tracing Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch. 13.2-13.3] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Local Illumination Object illuminations
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15 Ray Tracing Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch. 13.2-13.3] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Local Illumination Object illuminations
EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics
 Ray Tracing EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 29: Distributed Ray Tracing Introduction and context ray casting Recursive ray tracing shadows reflection refraction Ray tracing implementation
Ray Tracing EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 29: Distributed Ray Tracing Introduction and context ray casting Recursive ray tracing shadows reflection refraction Ray tracing implementation
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Quick Training Guide: Renderworks Migration Design Software Solutions Ltd, Quick Training Guide: Renderworks Migration
 Quick Training Guide: Renderworks Migration 2010-2012 Page 1 of 9 Copyright Notices 2007-2011 Tamsin Slatter. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form by any
Quick Training Guide: Renderworks Migration 2010-2012 Page 1 of 9 Copyright Notices 2007-2011 Tamsin Slatter. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form by any
Lesson 11. Polygonal Spaceship
 11 Polygonal Spaceship In this lesson, you will build and texture map a polygonal spaceship. Starting with a polygonal cube, you will extrude facets until you have a completed ship. You will then be able
11 Polygonal Spaceship In this lesson, you will build and texture map a polygonal spaceship. Starting with a polygonal cube, you will extrude facets until you have a completed ship. You will then be able
Lecture 15: Shading-I. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
WET AND TANNED SKINS
 WET AND TANNED SKINS This file is provided to help you adjusting your wet gloss effect and tan. This water gloss effect will depend mainly on gloss properties (base and top coat) and bump properties (base
WET AND TANNED SKINS This file is provided to help you adjusting your wet gloss effect and tan. This water gloss effect will depend mainly on gloss properties (base and top coat) and bump properties (base
Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment. Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment
 Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment Screen-space techniques Deferred rendering Screen-space ambient occlusion Depth of Field
Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment Screen-space techniques Deferred rendering Screen-space ambient occlusion Depth of Field
Chapter 5- Materials & Textures
 Chapter 5- Materials & Textures As mentioned in the past chapter, materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent
Chapter 5- Materials & Textures As mentioned in the past chapter, materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent
O Hailey: Chapter 3 Bonus Materials
 O Hailey: Chapter 3 Bonus Materials Maya s Toon Line For those familiar with toon lines in Maya, you may skip ahead past this section. Those not familiar might find it useful to understand the basics of
O Hailey: Chapter 3 Bonus Materials Maya s Toon Line For those familiar with toon lines in Maya, you may skip ahead past this section. Those not familiar might find it useful to understand the basics of
Announcements. Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) Computer Graphics
 Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
critical theory Computer Science
 Art/Science Shading, Materials, Collaboration Textures Example title Artists In the recommend real world, two the main following: factors determine the appearance of a surface: basic understanding what
Art/Science Shading, Materials, Collaboration Textures Example title Artists In the recommend real world, two the main following: factors determine the appearance of a surface: basic understanding what
Shading. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017
 Shading Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Shading Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Creating a Snowman Scene
 Creating a Snowman Scene By: Shane Trautsch Blender 2.72 What you will learn Basic Modeling Particle systems sculpting Materials and Textures Lighting Creating a Snow By now, you have created a snowman.
Creating a Snowman Scene By: Shane Trautsch Blender 2.72 What you will learn Basic Modeling Particle systems sculpting Materials and Textures Lighting Creating a Snow By now, you have created a snowman.
Cast Shadows Maya 2013
 2000-2012 Michael O'Rourke Cast Shadows Maya 2013 Concept Cast shadows are defined on a per-light basis, because shadow-casting computations can be time-consuming Cast shadows are off by default in Maya,
2000-2012 Michael O'Rourke Cast Shadows Maya 2013 Concept Cast shadows are defined on a per-light basis, because shadow-casting computations can be time-consuming Cast shadows are off by default in Maya,
