MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots Fall Depth First Search A* and Dijkstra s Algorithm
|
|
|
- Buddy Allison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots Fall Breadth First Search Depth First Search A* and Dijkstra s Algorithm
2 Admin Stuff Course Website: Instructor: M. Ani Hsieh 159 Curtis Hall Teaching Assistants: Bill Mather Location: PISB 109 Pre-requisites: Linear Algebra Linear Differential Equations 2
3 Admin Stuff Cont. Main Text & Software: Principles of Robot Motion: Theory, Algorithms, and Implementations Computer Unreal Tournament 2004 (UT3 At your own discrection) USARSim (Freeware) Supplemental Texts: Introduction to Mobile Autonomous Robots Probabilistic Robotics Grading: Assignments 40% Final 40% Participation 10% Teamwork 10% Misc: Assignments must be ed to Assignments are due on 11:59 pm unless otherwise specified. Assignments, w/ exception of code, must be submitted in electronically via in PDF format. The file MUST BE a single PDF file and must NOT exceed 5MBs. All Matlab code submission must conform to the guidelines outlined in each assignment. If we cannot run your code, it WILL NOT be graded. Late submissions WILL NOT be accepted 3
4 Assignments & Office Hours Assignments are individual assignments You may work together, BUT everyone MUST submit their own work. Time & Location of Office Hours Prof. Hsieh Mon 4:00-5:00pm, 159 Curtis Hall w/ exception of Week 2, Week 2 Wed 4:30-5:30pm in Hess 10F Bill Mather Thurs 3:00-5:00pm, Hess 10F Equipment Personal Laptop w/ Wireless capabilities 4
5 Basic Goals of Programming Coding with a purpose Utility Usability Maintainability 5
6 Compiled vs Interpreted Compiled Modified into binary and permanently stored Machine-readable only Interpreted Human-readable form At run-time, an interpreter modifies the content into binary as it is run 6
7 Common Problems Common mistakes programmers make Utility Program does not work as it is suppose to Program does not do a job better than an alternative program Usability Too complicated or too simple to be useful Maintainability You or other people cannot understand the programming behind your program 7
8 Motion Planning What is Motion Planning? Determining where to go 8
9 Historical Perspective Searched-based AI Courtesy of Howie Choset 9
10 Historical Searched-based AI STRIPS Action Planning (1960) Motion Planning -> More than a search Courtesy of Howie Choset 10
11 Live Motion Planning Experiments Person 1 walks through some obstacles Person 1, looking at Person 2, directs Person 2 through obstacles Person 1, looking at Person 2 with eyes closed, directs Person 2 through obstacles Person 1, looking at a map and not Person 2, whose eyes are still closed, directs Person 2 through obstacles Person 1, looking at an object and Person 2, whose eyes are closed, directs Person 2 to grab an obstacle How do we do the last experiment with a map? Courtesy of Howie Choset 11
12 What Did We Assume? Perfect sensors? What information Uncertainty Perfect control? What controls? Uncertainty Perfect thinking? Knowledge of the world? Complete? Processing the world? Everything? What Else? Courtesy of Howie Choset 12
13 Robots Courtesy of Howie Choset 13
14 Robots Courtesy of Howie Choset 14
15 Trends in Robotics/Motion Planning Classical Robotics (mid-70 s) exact models no sensing necessary Hybrids (since 90 s) models based at higher levels reactive at lower levels Reactive Paradigm (mid-80 s) no models relies heavily on good sensing Probabilistic Robotics (since mid-90 s) seamless integration of models and sensing inaccurate models, inaccurate sensing Courtesy of Howie Choset 15
16 Example of a World and a Robot Courtesy of Howie Choset 16
17 Basic Path Planning Problem Statement: Compute a continuous sequence of collision-free robot configurations connecting the initial and goal configurations Geometry of environment Geometry and kinematics of Robot Path Planner Collision Free Path Initial and goal configurations Courtesy of Howie Choset 17
18 Topics Graph Search (BFS, DFS, A*, D*) Bug Algorithms Curve Following Roadmaps Potential Functions Obstacle Avoidance 18
19 Preliminaries Completeness of a motion planning algorithm An algorithm is complete if, in finite time, it finds a path if such a path exists or terminates with failure if it does not. Computational efficiency of an algorithm Scalability when consider multi-robot apps 19
20 Motion Planning as Graph Searches Abstraction representation of a collection of items A collection of vertices & edges V 1 V 2 e 45 V 5 V 3 V 4 e 13 e 34 e 23 e 46 V 6 V e 1 45 V 5 V 3 V 4 e 13 e 34 e 46 V e 23 e 46 V 6 2 V 2 Terminology Adjacency Paths and Cycles Degree of a vertex Fully connected graphs 20
21 Types of Graphs Directed vs. Undirected Weighted vs. Unweighted w 13 w 23 w 34 w 45 w 46 21
22 Types of Graphs Cyclic vs. Acyclic Trees Root Child/Leaf 22
23 Graph Representation: Example A F Objective: We want to represent all possible ways to get from configuration A to B using a graph HOW? 23
24 Graph Representation: Example A B C D E F 24
25 Search in Path Planning Find a path between two locations in an unknown, partially known, or known environment Search Performance Completeness Optimality Operating Costs Space Complexity Time Complexity 25
26 Search Uninformed Search Use no information obtained from the environment Blind search: BFS (Wavefront), DFS Informed Search Use evaluation function More efficient Heuristic Searchers: A*, D*, etc. 26
27 Uninformed Search: BFS Graph search from A to N Queue A B C D E F G H I J K Pop here Push here BFS L M N 27
28 Uninformed Search: DFS Graph search from A to N Stack A B C D E F G Push and Pop here DFS H I J K L M N 28
29 Informed Search: A* Notation n node/state c(n 1, n 2 ) the length of an edge connecting n 1 and n 2 b(n 1 ) = n 2 backpointer of a node n 1 to a node n 2 29
30 Informed Search: A* Evaluation/Cost Function f(n) = g(n) + h(n) Operating Cost Function g(n) Actual operating cost of having been traversed Heuristic Function h(n) Information used to find promising nodes to traverse Admissible never overestimate the actual path cost Cost on Grid 30
31 N Start O is empty? N Pick n best frm O s.t. f(n best ) f(n) Remove n best frm O & add it to C n best = goal? Expand all nodes x who are nbrs of n best & not in C Y Y End End A*: Algorithm The search requires 2 lists to store information about nodes 1. Open list (O) stores nodes for expansion 2. Closed list (C) stores nodes which we have explored N x is not in O? Y Update b(x)=n best if g(n best )+c(n best ) < g(x) Add x to O 31
32 Two Examples of Running A* 32
33 Example (1/5) 33
34 Example (2/5) 34
35 Example 3/5 35
36 Example 4/5 36
37 Example 5/5 37
38 A*: Example (1/6) 38
39 A*: Example (2/6) 39
40 A*: Example (3/6) 40
41 A*: Example (4/6) 41
42 A*: Example (5/6) 42
43 A*: Example (6/6) 43
44 A*: Example Result 44
45 Dijkstra s Search: f(n) = g(n) 1. O = {S} 2. O = {1,2,4,5}; C = {S} (1,2,4,5) all point back to S 3. O = {1,4,5}; C = {S,2} (there are no adjacent nodes not in C) 4. O = {1,5,3}; C = {S,2,4} (1,2,4, point to S; 5 points to 4) 5. O = {5,3}; C = {S,2,4,1} 6. O = {3,G}; C = {S, 2, 4, 1} (goal points to 5 which points to 4 which points to S) 45
Motion Planning, Part III Graph Search, Part I. Howie Choset
 Motion Planning, Part III Graph Search, Part I Howie Choset Happy President s Day The Configuration Space What it is A set of reachable areas constructed from knowledge of both the robot and the world
Motion Planning, Part III Graph Search, Part I Howie Choset Happy President s Day The Configuration Space What it is A set of reachable areas constructed from knowledge of both the robot and the world
Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS DASL Summer Program Path Planning References: http://robotics.mem.drexel.edu/mhsieh/courses/mem380i/index.html http://dasl.mem.drexel.edu/hing/bfsdfstutorial.htm
Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS DASL Summer Program Path Planning References: http://robotics.mem.drexel.edu/mhsieh/courses/mem380i/index.html http://dasl.mem.drexel.edu/hing/bfsdfstutorial.htm
Motion Planning, Part IV Graph Search Part II. Howie Choset
 Motion Planning, Part IV Graph Search Part II Howie Choset Map-Based Approaches: Properties of a roadmap: Roadmap Theory Accessibility: there exists a collision-free path from the start to the road map
Motion Planning, Part IV Graph Search Part II Howie Choset Map-Based Approaches: Properties of a roadmap: Roadmap Theory Accessibility: there exists a collision-free path from the start to the road map
Robotic Motion Planning: A* and D* Search
 Robotic Motion Planning: A* and D* Search Robotics Institute 6-75 http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~motion Howie Choset http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~choset 6-75, Howie Choset with slides from G. Ayorker
Robotic Motion Planning: A* and D* Search Robotics Institute 6-75 http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~motion Howie Choset http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~choset 6-75, Howie Choset with slides from G. Ayorker
Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 )
 Path Planning for Point Robots Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/mpa Class Objectives Motion planning framework Classic motion planning approaches 2 3 Configuration Space:
Path Planning for Point Robots Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/mpa Class Objectives Motion planning framework Classic motion planning approaches 2 3 Configuration Space:
Week 4 Lecture Notes Part 1 Blind Search cont. and Informed Search
 Week 4 Lecture Notes Part 1 Blind Search cont. and Informed Search Created by Nicholas Collins (s4291997) and Nicholas Mayer (s4289230) Admin Assignment 1 is due 9 September, not 4 September as it says
Week 4 Lecture Notes Part 1 Blind Search cont. and Informed Search Created by Nicholas Collins (s4291997) and Nicholas Mayer (s4289230) Admin Assignment 1 is due 9 September, not 4 September as it says
Can work in a group of at most 3 students.! Can work individually! If you work in a group of 2 or 3 students,!
 Assignment 1 is out! Due: 26 Aug 23:59! Submit in turnitin! Code + report! Can work in a group of at most 3 students.! Can work individually! If you work in a group of 2 or 3 students,! Each member must
Assignment 1 is out! Due: 26 Aug 23:59! Submit in turnitin! Code + report! Can work in a group of at most 3 students.! Can work individually! If you work in a group of 2 or 3 students,! Each member must
Notes. Video Game AI: Lecture 5 Planning for Pathfinding. Lecture Overview. Knowledge vs Search. Jonathan Schaeffer this Friday
 Notes Video Game AI: Lecture 5 Planning for Pathfinding Nathan Sturtevant COMP 3705 Jonathan Schaeffer this Friday Planning vs localization We cover planning today Localization is just mapping a real-valued
Notes Video Game AI: Lecture 5 Planning for Pathfinding Nathan Sturtevant COMP 3705 Jonathan Schaeffer this Friday Planning vs localization We cover planning today Localization is just mapping a real-valued
Assignment 1 is out! Due: 9 Sep 23:59! Can work in a group of 2-3 students.! NO cheating!!!! Submit in turnitin! Code + report!
 Assignment 1 is out! Due: 9 Sep 23:59! Submit in turnitin! Code + report! Can work in a group of 2-3 students.! Please register your group in the website linked from the assignment description before tomorrow
Assignment 1 is out! Due: 9 Sep 23:59! Submit in turnitin! Code + report! Can work in a group of 2-3 students.! Please register your group in the website linked from the assignment description before tomorrow
ME512: Mobile Robotics Path Planning Algorithms. Atul Thakur, Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department IIT Patna
 ME512: Mobile Robotics Path Planning Algorithms Atul Thakur, Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department IIT Patna Path Planning Problem Given Robot state Obstacle positions Robot capabilities
ME512: Mobile Robotics Path Planning Algorithms Atul Thakur, Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department IIT Patna Path Planning Problem Given Robot state Obstacle positions Robot capabilities
Route planning / Search Movement Group behavior Decision making
 Game AI Where is the AI Route planning / Search Movement Group behavior Decision making General Search Algorithm Design Keep a pair of set of states: One, the set of states to explore, called the open
Game AI Where is the AI Route planning / Search Movement Group behavior Decision making General Search Algorithm Design Keep a pair of set of states: One, the set of states to explore, called the open
Spring 2010: Lecture 9. Ashutosh Saxena. Ashutosh Saxena
 CS 4758/6758: Robot Learning Spring 2010: Lecture 9 Why planning and control? Video Typical Architecture Planning 0.1 Hz Control 50 Hz Does it apply to all robots and all scenarios? Previous Lecture: Potential
CS 4758/6758: Robot Learning Spring 2010: Lecture 9 Why planning and control? Video Typical Architecture Planning 0.1 Hz Control 50 Hz Does it apply to all robots and all scenarios? Previous Lecture: Potential
Best-First Search: The A* Algorithm
 August, 07 Search is.. A (preferably methodical) process for finding something. Searching for: pre-existing entities (information, objects, etc.) strategies for creating/designing entities. Examples: Web
August, 07 Search is.. A (preferably methodical) process for finding something. Searching for: pre-existing entities (information, objects, etc.) strategies for creating/designing entities. Examples: Web
Discrete Motion Planning
 RBE MOTION PLANNING Discrete Motion Planning Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Announcement Homework 1 is out Due Date - Feb 1 Updated
RBE MOTION PLANNING Discrete Motion Planning Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Announcement Homework 1 is out Due Date - Feb 1 Updated
Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation
 Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation 1 Agenda Motivation Basic Definitions Configuration Space Global Planning Local Planning Obstacle Avoidance ROS Navigation Stack 2 Literature Choset, Lynch,
Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation 1 Agenda Motivation Basic Definitions Configuration Space Global Planning Local Planning Obstacle Avoidance ROS Navigation Stack 2 Literature Choset, Lynch,
Problem Solving and Search
 Artificial Intelligence Problem Solving and Search Dae-Won Kim School of Computer Science & Engineering Chung-Ang University Outline Problem-solving agents Problem types Problem formulation Example problems
Artificial Intelligence Problem Solving and Search Dae-Won Kim School of Computer Science & Engineering Chung-Ang University Outline Problem-solving agents Problem types Problem formulation Example problems
The big picture: from Perception to Planning to Control
 The big picture: from Perception to Planning to Control Perception Location, Map Signals: video, inertial, range Sensors Real World 1 Planning vs Control 0. In control we go from to A to B in free space
The big picture: from Perception to Planning to Control Perception Location, Map Signals: video, inertial, range Sensors Real World 1 Planning vs Control 0. In control we go from to A to B in free space
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Search Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Outline Problem formulation & examples Basic search algorithms 2/100 Example:
Artificial Intelligence Search Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Outline Problem formulation & examples Basic search algorithms 2/100 Example:
The goal of this assignment is to implement and test Breadth-first search (BFS) on a simple navigation problem (path-finding).
 CSCE 420 Programing Assignment #1 due: Thurs, Sept 18 (by start of class) Objective The goal of this assignment is to implement and test Breadth-first search (BFS) on a simple navigation problem (path-finding).
CSCE 420 Programing Assignment #1 due: Thurs, Sept 18 (by start of class) Objective The goal of this assignment is to implement and test Breadth-first search (BFS) on a simple navigation problem (path-finding).
Path Planning. CMPS 146, Fall Josh McCoy
 Path Planning CMPS 46, Fall 203 Josh McCoy Readings Reading Path Planning: 97-255 Dijkstra and graphs early. CMPS 46, Fall 203 Pathfinding Why search? Consider this problem given a set of integers, we
Path Planning CMPS 46, Fall 203 Josh McCoy Readings Reading Path Planning: 97-255 Dijkstra and graphs early. CMPS 46, Fall 203 Pathfinding Why search? Consider this problem given a set of integers, we
Informed search strategies (Section ) Source: Fotolia
 Informed search strategies (Section 3.5-3.6) Source: Fotolia Review: Tree search Initialize the frontier using the starting state While the frontier is not empty Choose a frontier node to expand according
Informed search strategies (Section 3.5-3.6) Source: Fotolia Review: Tree search Initialize the frontier using the starting state While the frontier is not empty Choose a frontier node to expand according
CSC263 Week 8. Larry Zhang.
 CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
CS 460/560 Introduction to Computational Robotics Fall 2017, Rutgers University. Course Logistics. Instructor: Jingjin Yu
 CS 460/560 Introduction to Computational Robotics Fall 2017, Rutgers University Course Logistics Instructor: Jingjin Yu Logistics, etc. General Lectures: Noon-1:20pm Tuesdays and Fridays, SEC 118 Instructor:
CS 460/560 Introduction to Computational Robotics Fall 2017, Rutgers University Course Logistics Instructor: Jingjin Yu Logistics, etc. General Lectures: Noon-1:20pm Tuesdays and Fridays, SEC 118 Instructor:
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up. Nicki Dell Spring 2014
 CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up Nicki Dell Spring 2014 Final Exam As also indicated on the web page: Next Tuesday, 2:30-4:20 in this room Cumulative but
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up Nicki Dell Spring 2014 Final Exam As also indicated on the web page: Next Tuesday, 2:30-4:20 in this room Cumulative but
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Lesson 1 1 About Lecturer: Prof. Sarit Kraus TA: Galit Haim: haimga@cs.biu.ac.il (almost) All you need can be found on the course website: http://u.cs.biu.ac.il/~haimga/teaching/ai/
Artificial Intelligence Lesson 1 1 About Lecturer: Prof. Sarit Kraus TA: Galit Haim: haimga@cs.biu.ac.il (almost) All you need can be found on the course website: http://u.cs.biu.ac.il/~haimga/teaching/ai/
DFS. Depth-limited Search
 DFS Completeness? No, fails in infinite depth spaces or spaces with loops Yes, assuming state space finite. Time complexity? O(b m ), terrible if m is much bigger than d. can do well if lots of goals Space
DFS Completeness? No, fails in infinite depth spaces or spaces with loops Yes, assuming state space finite. Time complexity? O(b m ), terrible if m is much bigger than d. can do well if lots of goals Space
A* optimality proof, cycle checking
 A* optimality proof, cycle checking CPSC 322 Search 5 Textbook 3.6 and 3.7.1 January 21, 2011 Taught by Mike Chiang Lecture Overview Recap Admissibility of A* Cycle checking and multiple path pruning Slide
A* optimality proof, cycle checking CPSC 322 Search 5 Textbook 3.6 and 3.7.1 January 21, 2011 Taught by Mike Chiang Lecture Overview Recap Admissibility of A* Cycle checking and multiple path pruning Slide
COS Lecture 13 Autonomous Robot Navigation
 COS 495 - Lecture 13 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Fall 2011 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structure Prior Knowledge Operator Commands Localization
COS 495 - Lecture 13 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Fall 2011 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structure Prior Knowledge Operator Commands Localization
A* and 3D Configuration Space
 Homework #4 A* and 3D Configuration Space Part I: Star Algorithm to build 3D Configuration Space I have implemented again the Star Algorithm to compute the 3-dimensional configuration space Q starting
Homework #4 A* and 3D Configuration Space Part I: Star Algorithm to build 3D Configuration Space I have implemented again the Star Algorithm to compute the 3-dimensional configuration space Q starting
PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL
 PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL Path finding refers to determining the shortest path between two vertices in a graph. We discussed the Floyd Warshall algorithm previously,
PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL Path finding refers to determining the shortest path between two vertices in a graph. We discussed the Floyd Warshall algorithm previously,
Motion Planning. Howie CHoset
 Motion Planning Howie CHoset Questions Where are we? Where do we go? Which is more important? Encoders Encoders Incremental Photodetector Encoder disk LED Photoemitter Encoders - Incremental Encoders -
Motion Planning Howie CHoset Questions Where are we? Where do we go? Which is more important? Encoders Encoders Incremental Photodetector Encoder disk LED Photoemitter Encoders - Incremental Encoders -
ME/CS 132: Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Vision
 ME/CS 132: Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Vision Lecture #5: Search Algorithm 1 Yoshiaki Kuwata 4/12/2011 Lecture Overview Introduction Label Correcting Algorithm Core idea Depth-first search Breadth-first
ME/CS 132: Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Vision Lecture #5: Search Algorithm 1 Yoshiaki Kuwata 4/12/2011 Lecture Overview Introduction Label Correcting Algorithm Core idea Depth-first search Breadth-first
Algorithms and Path Planning
 Algorithms and Path Planning Topics Simple Search Depth First Search Breadth First Search Dijkstra s Search Greedy Search A* Search Classes of interest ECE400: Computer Systems Programming CS4700: Foundations
Algorithms and Path Planning Topics Simple Search Depth First Search Breadth First Search Dijkstra s Search Greedy Search A* Search Classes of interest ECE400: Computer Systems Programming CS4700: Foundations
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Graphs. Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale Room - Faner 3131
 Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Informed Search CS457 David Kauchak Fall 2011
 Admin Informed Search CS57 David Kauchak Fall 011 Some material used from : Sara Owsley Sood and others Q3 mean: 6. median: 7 Final projects proposals looked pretty good start working plan out exactly
Admin Informed Search CS57 David Kauchak Fall 011 Some material used from : Sara Owsley Sood and others Q3 mean: 6. median: 7 Final projects proposals looked pretty good start working plan out exactly
Motion Planning for a Point Robot (2/2) Point Robot on a Grid. Planning requires models. Point Robot on a Grid 1/18/2012.
 Motion Planning for a Point Robot (/) Class scribing Position paper 1 Planning requires models Point Robot on a Grid The Bug algorithms are reactive motion strategies ; they are not motion planners To
Motion Planning for a Point Robot (/) Class scribing Position paper 1 Planning requires models Point Robot on a Grid The Bug algorithms are reactive motion strategies ; they are not motion planners To
CISC 3130 Data Structures Spring 2018
 CISC 3130 Data Structures Spring 2018 Instructor: Ari Mermelstein Email address for questions: mermelstein AT sci DOT brooklyn DOT cuny DOT edu Email address for homework submissions: mermelstein DOT homework
CISC 3130 Data Structures Spring 2018 Instructor: Ari Mermelstein Email address for questions: mermelstein AT sci DOT brooklyn DOT cuny DOT edu Email address for homework submissions: mermelstein DOT homework
CS61BL. Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting
 CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
Outline for today s lecture. Informed Search I. One issue: How to search backwards? Very briefly: Bidirectional search. Outline for today s lecture
 Outline for today s lecture Informed Search I Uninformed Search Briefly: Bidirectional Search (AIMA 3.4.6) Uniform Cost Search (UCS) Informed Search Introduction to Informed search Heuristics 1 st attempt:
Outline for today s lecture Informed Search I Uninformed Search Briefly: Bidirectional Search (AIMA 3.4.6) Uniform Cost Search (UCS) Informed Search Introduction to Informed search Heuristics 1 st attempt:
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Search and Games. Adi Botea. ANU Summer Schools in Logic and Learning February, 2009
 Search and Games Adi Botea ANU Summer Schools in Logic and Learning February, 2009 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Problem Representation 3 Uninformed Search 4 Informed Search 5 Hierarchical Abstraction Outline
Search and Games Adi Botea ANU Summer Schools in Logic and Learning February, 2009 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Problem Representation 3 Uninformed Search 4 Informed Search 5 Hierarchical Abstraction Outline
University of Waterloo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 457A: Cooperative and Adaptive Algorithms Midterm Examination
 University of Waterloo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 457A: Cooperative and Adaptive Algorithms Midterm Examination Exam Date/Time: Tuesday, June 13, 2017, 8:30-9:50 pm Exam Hall:
University of Waterloo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 457A: Cooperative and Adaptive Algorithms Midterm Examination Exam Date/Time: Tuesday, June 13, 2017, 8:30-9:50 pm Exam Hall:
HW#1 due today. HW#2 due Monday, 9/09/13, in class Continue reading Chapter 3
 9-04-2013 Uninformed (blind) search algorithms Breadth-First Search (BFS) Uniform-Cost Search Depth-First Search (DFS) Depth-Limited Search Iterative Deepening Best-First Search HW#1 due today HW#2 due
9-04-2013 Uninformed (blind) search algorithms Breadth-First Search (BFS) Uniform-Cost Search Depth-First Search (DFS) Depth-Limited Search Iterative Deepening Best-First Search HW#1 due today HW#2 due
Path Planning. Marcello Restelli. Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano tel:
 Marcello Restelli Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano email: restelli@elet.polimi.it tel: 02 2399 3470 Path Planning Robotica for Computer Engineering students A.A. 2006/2007
Marcello Restelli Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano email: restelli@elet.polimi.it tel: 02 2399 3470 Path Planning Robotica for Computer Engineering students A.A. 2006/2007
Selection, Bubble, Insertion, Merge, Heap, Quick Bucket, Radix
 Spring 2010 Review Topics Big O Notation Heaps Sorting Selection, Bubble, Insertion, Merge, Heap, Quick Bucket, Radix Hashtables Tree Balancing: AVL trees and DSW algorithm Graphs: Basic terminology and
Spring 2010 Review Topics Big O Notation Heaps Sorting Selection, Bubble, Insertion, Merge, Heap, Quick Bucket, Radix Hashtables Tree Balancing: AVL trees and DSW algorithm Graphs: Basic terminology and
Road Map Methods. Including material from Howie Choset / G.D. Hager S. Leonard
 Road Map Methods Including material from Howie Choset The Basic Idea Capture the connectivity of Q free by a graph or network of paths. 16-735, Howie Choset, with significant copying from who loosely based
Road Map Methods Including material from Howie Choset The Basic Idea Capture the connectivity of Q free by a graph or network of paths. 16-735, Howie Choset, with significant copying from who loosely based
Problem Solving: Informed Search
 Problem Solving: Informed Search References Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 (Chapters 1,2, and 4) Nilsson, Artificial intelligence: A New synthesis.
Problem Solving: Informed Search References Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 (Chapters 1,2, and 4) Nilsson, Artificial intelligence: A New synthesis.
Announcements Problem Set 4 is out!
 CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 13 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Depth First Search (DFS) Shortest path Shortest weight path (Dijkstra's
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 13 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Depth First Search (DFS) Shortest path Shortest weight path (Dijkstra's
Search EECS 348 Intro to Artificial Intelligence
 Search EECS 348 Intro to Artificial Intelligence (slides from Oren Etzioni, based on Stuart Russell, Dan Weld, Henry Kautz, and others) What is Search? Search is a class of techniques for systematically
Search EECS 348 Intro to Artificial Intelligence (slides from Oren Etzioni, based on Stuart Russell, Dan Weld, Henry Kautz, and others) What is Search? Search is a class of techniques for systematically
Search EECS 395/495 Intro to Artificial Intelligence
 Search EECS 395/495 Intro to Artificial Intelligence Doug Downey (slides from Oren Etzioni, based on Stuart Russell, Dan Weld, Henry Kautz, and others) What is Search? Search is a class of techniques for
Search EECS 395/495 Intro to Artificial Intelligence Doug Downey (slides from Oren Etzioni, based on Stuart Russell, Dan Weld, Henry Kautz, and others) What is Search? Search is a class of techniques for
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
CS106X Final Review. Rachel Gardner and Jared Bitz. slides adapted from Ashley Taylor, Anton Apostolatos, Nolan Handali, and Zachary Birnholz
 CS106X Final Review Rachel Gardner and Jared Bitz slides adapted from Ashley Taylor, Anton Apostolatos, Nolan Handali, and Zachary Birnholz Final Review Session Overview Logistics Pointers and Dynamic
CS106X Final Review Rachel Gardner and Jared Bitz slides adapted from Ashley Taylor, Anton Apostolatos, Nolan Handali, and Zachary Birnholz Final Review Session Overview Logistics Pointers and Dynamic
Motion Planning. Howie CHoset
 Motion Planning Howie CHoset What is Motion Planning? What is Motion Planning? Determining where to go Overview The Basics Motion Planning Statement The World and Robot Configuration Space Metrics Algorithms
Motion Planning Howie CHoset What is Motion Planning? What is Motion Planning? Determining where to go Overview The Basics Motion Planning Statement The World and Robot Configuration Space Metrics Algorithms
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications
 Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Path Planning. Jacky Baltes Dept. of Computer Science University of Manitoba 11/21/10
 Path Planning Jacky Baltes Autonomous Agents Lab Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Email: jacky@cs.umanitoba.ca http://www.cs.umanitoba.ca/~jacky Path Planning Jacky Baltes Dept. of
Path Planning Jacky Baltes Autonomous Agents Lab Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Email: jacky@cs.umanitoba.ca http://www.cs.umanitoba.ca/~jacky Path Planning Jacky Baltes Dept. of
Informed (Heuristic) Search. Idea: be smart about what paths to try.
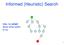 Informed (Heuristic) Search Idea: be smart about what paths to try. 1 Blind Search vs. Informed Search What s the difference? How do we formally specify this? A node is selected for expansion based on
Informed (Heuristic) Search Idea: be smart about what paths to try. 1 Blind Search vs. Informed Search What s the difference? How do we formally specify this? A node is selected for expansion based on
Path Planning for Point Robots. NUS CS 5247 David Hsu
 Path Planning for Point Robots NUS CS 5247 David Hsu Problem Input Robot represented as a point in the plane Obstacles represented as polygons Initial and goal positions Output A collision-free path between
Path Planning for Point Robots NUS CS 5247 David Hsu Problem Input Robot represented as a point in the plane Obstacles represented as polygons Initial and goal positions Output A collision-free path between
mywbut.com Informed Search Strategies-I
 Informed Search Strategies-I 1 3.1 Introduction We have outlined the different types of search strategies. In the earlier chapter we have looked at different blind search strategies. Uninformed search
Informed Search Strategies-I 1 3.1 Introduction We have outlined the different types of search strategies. In the earlier chapter we have looked at different blind search strategies. Uninformed search
Uninformed Search. Day 1 & 2 of Search. Russel & Norvig Chap. 3. Material in part from
 Uninformed Day & 2 of Russel & Norvig Chap. 3 Material in part from http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials Examples of problems? The Oak Tree Informed versus Uninformed Heuristic versus Blind A Problem a
Uninformed Day & 2 of Russel & Norvig Chap. 3 Material in part from http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials Examples of problems? The Oak Tree Informed versus Uninformed Heuristic versus Blind A Problem a
Today s s lecture. Lecture 3: Search - 2. Problem Solving by Search. Agent vs. Conventional AI View. Victor R. Lesser. CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004
 Today s s lecture Search and Agents Material at the end of last lecture Lecture 3: Search - 2 Victor R. Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 Continuation of Simple Search The use of background knowledge to accelerate
Today s s lecture Search and Agents Material at the end of last lecture Lecture 3: Search - 2 Victor R. Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 Continuation of Simple Search The use of background knowledge to accelerate
CPS 170: Artificial Intelligence Search
 CPS 170: Artificial Intelligence http://www.cs.duke.edu/courses/spring09/cps170/ Search Instructor: Vincent Conitzer Search We have some actions that can change the state of the world Change resulting
CPS 170: Artificial Intelligence http://www.cs.duke.edu/courses/spring09/cps170/ Search Instructor: Vincent Conitzer Search We have some actions that can change the state of the world Change resulting
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
Principles of Autonomy and Decision Making
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.410-13 Principles of Autonomy and Decision Making Problem Set #7 Part 2 Problem 3: Search (20 points) You are trying to find a path from vertex 0 to vertex 7 in
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.410-13 Principles of Autonomy and Decision Making Problem Set #7 Part 2 Problem 3: Search (20 points) You are trying to find a path from vertex 0 to vertex 7 in
Geometric Path Planning McGill COMP 765 Oct 12 th, 2017
 Geometric Path Planning McGill COMP 765 Oct 12 th, 2017 The Motion Planning Problem Intuition: Find a safe path/trajectory from start to goal More precisely: A path is a series of robot configurations
Geometric Path Planning McGill COMP 765 Oct 12 th, 2017 The Motion Planning Problem Intuition: Find a safe path/trajectory from start to goal More precisely: A path is a series of robot configurations
21# 33# 90# 91# 34# # 39# # # 31# 98# 0# 1# 2# 3# 4# 5# 6# 7# 8# 9# 10# #
 1. Prove that n log n n is Ω(n). York University EECS 11Z Winter 1 Problem Set 3 Instructor: James Elder Solutions log n n. Thus n log n n n n n log n n Ω(n).. Show that n is Ω (n log n). We seek a c >,
1. Prove that n log n n is Ω(n). York University EECS 11Z Winter 1 Problem Set 3 Instructor: James Elder Solutions log n n. Thus n log n n n n n log n n Ω(n).. Show that n is Ω (n log n). We seek a c >,
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12. Questions? Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first Search. (Introduce permutation and subset generation)
 MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence. Peter Ljunglöf. 19 January, 2018
 DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 3: Classical search algorithms CHAPTER 3: CLASSICAL SEARCH ALGORITHMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 19 January, 2018 1 DEADLINE FOR
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 3: Classical search algorithms CHAPTER 3: CLASSICAL SEARCH ALGORITHMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 19 January, 2018 1 DEADLINE FOR
Visibility Graph. How does a Mobile Robot get from A to B?
 Robot Path Planning Things to Consider: Spatial reasoning/understanding: robots can have many dimensions in space, obstacles can be complicated Global Planning: Do we know the environment apriori? Online
Robot Path Planning Things to Consider: Spatial reasoning/understanding: robots can have many dimensions in space, obstacles can be complicated Global Planning: Do we know the environment apriori? Online
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals
 csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals 1 Depth-first search (DFS) G can be directed or undirected DFS(v) mark v visited for all adjacent edges (v,w) of v do if w is not visited parent(w) = v (v,w)
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals 1 Depth-first search (DFS) G can be directed or undirected DFS(v) mark v visited for all adjacent edges (v,w) of v do if w is not visited parent(w) = v (v,w)
CS 1114: Implementing Search. Last time. ! Graph traversal. ! Two types of todo lists: ! Prof. Graeme Bailey.
 CS 1114: Implementing Search! Prof. Graeme Bailey http://cs1114.cs.cornell.edu (notes modified from Noah Snavely, Spring 2009) Last time! Graph traversal 1 1 2 10 9 2 3 6 3 5 6 8 5 4 7 9 4 7 8 10! Two
CS 1114: Implementing Search! Prof. Graeme Bailey http://cs1114.cs.cornell.edu (notes modified from Noah Snavely, Spring 2009) Last time! Graph traversal 1 1 2 10 9 2 3 6 3 5 6 8 5 4 7 9 4 7 8 10! Two
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
COMP251: Algorithms and Data Structures. Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University
 COMP251: Algorithms and Data Structures Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University About Me Jérôme Waldispühl Associate Professor of Computer Science I am conducting research in Bioinformatics
COMP251: Algorithms and Data Structures Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University About Me Jérôme Waldispühl Associate Professor of Computer Science I am conducting research in Bioinformatics
Pathfinding. Advaith Siddharthan
 Pathfinding Advaith Siddharthan Context What is Intelligence? Rational? Search Optimisation Reasoning Impulsive? Quicker response Less predictable Personality/Emotions: Angry/Bored/Curious Overview The
Pathfinding Advaith Siddharthan Context What is Intelligence? Rational? Search Optimisation Reasoning Impulsive? Quicker response Less predictable Personality/Emotions: Angry/Bored/Curious Overview The
Navigation and Metric Path Planning
 Navigation and Metric Path Planning October 4, 2011 Minerva tour guide robot (CMU): Gave tours in Smithsonian s National Museum of History Example of Minerva s occupancy map used for navigation Objectives
Navigation and Metric Path Planning October 4, 2011 Minerva tour guide robot (CMU): Gave tours in Smithsonian s National Museum of History Example of Minerva s occupancy map used for navigation Objectives
Robotic Motion Planning: Cell Decompositions (with some discussion on coverage and pursuer/evader)
 Robotic Motion Planning: Cell Decompositions (with some discussion on coverage and pursuer/evader) Robotics Institute 16-735 http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~motion Howie Choset http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~choset
Robotic Motion Planning: Cell Decompositions (with some discussion on coverage and pursuer/evader) Robotics Institute 16-735 http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~motion Howie Choset http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~choset
17/05/2018. Outline. Outline. Divide and Conquer. Control Abstraction for Divide &Conquer. Outline. Module 2: Divide and Conquer
 Module 2: Divide and Conquer Divide and Conquer Control Abstraction for Divide &Conquer 1 Recurrence equation for Divide and Conquer: If the size of problem p is n and the sizes of the k sub problems are
Module 2: Divide and Conquer Divide and Conquer Control Abstraction for Divide &Conquer 1 Recurrence equation for Divide and Conquer: If the size of problem p is n and the sizes of the k sub problems are
Discrete search algorithms
 Robot Autonomy (16-662, S13) Lecture#08 (Monday February 11) Discrete search algorithms Lecturer: Siddhartha Srinivasa Scribes: Kavya Suresh & David Matten I. INTRODUCTION These notes contain a detailed
Robot Autonomy (16-662, S13) Lecture#08 (Monday February 11) Discrete search algorithms Lecturer: Siddhartha Srinivasa Scribes: Kavya Suresh & David Matten I. INTRODUCTION These notes contain a detailed
Algorithms and Theory of Computation. Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms
 Algorithms and Theory of Computation Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms Xiaohui Bei MAS 714 August 20, 2018 Nanyang Technological University MAS 714 August 20, 2018 1 / 18 Connectivity In a undirected graph G
Algorithms and Theory of Computation Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms Xiaohui Bei MAS 714 August 20, 2018 Nanyang Technological University MAS 714 August 20, 2018 1 / 18 Connectivity In a undirected graph G
Robot Motion Planning
 Robot Motion Planning James Bruce Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University April 7, 2004 Agent Planning An agent is a situated entity which can choose and execute actions within in an environment.
Robot Motion Planning James Bruce Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University April 7, 2004 Agent Planning An agent is a situated entity which can choose and execute actions within in an environment.
CS 106X, Lecture 23 Dijkstra and A* Search
 CS 106X, Lecture 23 Dijkstra and A* Search reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, Chapter 18 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Nick Troccoli, licensed under Creative Commons
CS 106X, Lecture 23 Dijkstra and A* Search reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, Chapter 18 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Nick Troccoli, licensed under Creative Commons
Chapter 3. A problem-solving agent is a kind of goal-based agent. It decide what to do by finding sequences of actions that lead to desirable states.
 Chapter 3 A problem-solving agent is a kind of goal-based agent. It decide what to do by finding sequences of actions that lead to desirable states. A problem can be defined by four components : 1. The
Chapter 3 A problem-solving agent is a kind of goal-based agent. It decide what to do by finding sequences of actions that lead to desirable states. A problem can be defined by four components : 1. The
Announcements. CSEP 521 Applied Algorithms. Announcements. Polynomial time efficiency. Definitions of efficiency 1/14/2013
 Announcements CSEP 51 Applied Algorithms Richard Anderson Winter 013 Lecture Reading Chapter.1,. Chapter 3 Chapter Homework Guidelines Prove that your algorithm works A proof is a convincing argument Give
Announcements CSEP 51 Applied Algorithms Richard Anderson Winter 013 Lecture Reading Chapter.1,. Chapter 3 Chapter Homework Guidelines Prove that your algorithm works A proof is a convincing argument Give
9/17/2015 7:56 AM. CSCE 625 Programing Assignment #1 due: Tues, Sep 22 (by start of class) Objective
 CSCE 625 Programing Assignment #1 due: Tues, Sep 22 (by start of class) Objective The goal of this assignment is to implement and compare the performance of Breadth-first search (BFS), Depth-First Search
CSCE 625 Programing Assignment #1 due: Tues, Sep 22 (by start of class) Objective The goal of this assignment is to implement and compare the performance of Breadth-first search (BFS), Depth-First Search
A.I.: Informed Search Algorithms. Chapter III: Part Deux
 A.I.: Informed Search Algorithms Chapter III: Part Deux Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Outline Overview Informed Search: uses problem-specific knowledge. General approach:
A.I.: Informed Search Algorithms Chapter III: Part Deux Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Outline Overview Informed Search: uses problem-specific knowledge. General approach:
Topic 1 Uninformed Search
 Topic 1 Uninformed Search [George F Luger. 2008. Artificial Intelligence Structures and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving. 6 th Ed. Pearson. ISBN: 0321545893.] 1 Contents 1. Depth-First Search (DFS)
Topic 1 Uninformed Search [George F Luger. 2008. Artificial Intelligence Structures and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving. 6 th Ed. Pearson. ISBN: 0321545893.] 1 Contents 1. Depth-First Search (DFS)
Branch & Bound (B&B) and Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 Branch & Bound (B&B) and Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 CSP 1 January 25, 2013 P&M textbook 3.7.4 & 4.0-4.2 Lecture Overview Recap Branch & Bound Wrap up of search module
Branch & Bound (B&B) and Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 CSP 1 January 25, 2013 P&M textbook 3.7.4 & 4.0-4.2 Lecture Overview Recap Branch & Bound Wrap up of search module
Uninformed Search Methods
 Uninformed Search Methods Search Algorithms Uninformed Blind search Breadth-first uniform first depth-first Iterative deepening depth-first Bidirectional Branch and Bound Informed Heuristic search Greedy
Uninformed Search Methods Search Algorithms Uninformed Blind search Breadth-first uniform first depth-first Iterative deepening depth-first Bidirectional Branch and Bound Informed Heuristic search Greedy
Search. (Textbook Chpt ) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 2. May, 10, CPSC 322, Lecture 2 Slide 1
 Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 2 (Textbook Chpt 3.0-3.4) May, 10, 2012 CPSC 322, Lecture 2 Slide 1 Colored Cards You need to have 4 colored index cards Come and get them from me if you still
Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 2 (Textbook Chpt 3.0-3.4) May, 10, 2012 CPSC 322, Lecture 2 Slide 1 Colored Cards You need to have 4 colored index cards Come and get them from me if you still
Basic Motion Planning Algorithms
 Basic Motion Planning Algorithms Sohaib Younis Intelligent Robotics 7 January, 2013 1 Outline Introduction Environment Map Dijkstra's algorithm A* algorithm Summary 2 Introduction Definition: Motion Planning
Basic Motion Planning Algorithms Sohaib Younis Intelligent Robotics 7 January, 2013 1 Outline Introduction Environment Map Dijkstra's algorithm A* algorithm Summary 2 Introduction Definition: Motion Planning
EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots
 EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots Lecture 3: Path Planning Algorithm Prof. Yi Guo ECE Dept. Plan Representing the Space Path Planning Methods A* Search Algorithm D* Search Algorithm Representing
EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots Lecture 3: Path Planning Algorithm Prof. Yi Guo ECE Dept. Plan Representing the Space Path Planning Methods A* Search Algorithm D* Search Algorithm Representing
CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction
 CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Outline Motivation Importance of graphs for algorithm design applications
CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Outline Motivation Importance of graphs for algorithm design applications
Robot Programming with Lisp
 6. Search Algorithms Gayane Kazhoyan (Stuart Russell, Peter Norvig) Institute for University of Bremen Contents Problem Definition Uninformed search strategies BFS Uniform-Cost DFS Depth-Limited Iterative
6. Search Algorithms Gayane Kazhoyan (Stuart Russell, Peter Norvig) Institute for University of Bremen Contents Problem Definition Uninformed search strategies BFS Uniform-Cost DFS Depth-Limited Iterative
2. True or false: even though BFS and DFS have the same space complexity, they do not always have the same worst case asymptotic time complexity.
 1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
Graphs and Algorithms
 Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
CMU-Q Lecture 2: Search problems Uninformed search. Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro
 CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 2: Search problems Uninformed search Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro RECAP: ACT RATIONALLY Think like people Think rationally Agent Sensors? Actuators Percepts Actions Environment Act like
CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 2: Search problems Uninformed search Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro RECAP: ACT RATIONALLY Think like people Think rationally Agent Sensors? Actuators Percepts Actions Environment Act like
COMP3702/7702 Artificial Intelligence Week2: Search (Russell & Norvig ch. 3)" Hanna Kurniawati"
 COMP3702/7702 Artificial Intelligence Week2: Search (Russell & Norvig ch. 3)" Hanna Kurniawati" Last week" What is Artificial Intelligence?" Some history" Agent defined" The agent design problem" Search:
COMP3702/7702 Artificial Intelligence Week2: Search (Russell & Norvig ch. 3)" Hanna Kurniawati" Last week" What is Artificial Intelligence?" Some history" Agent defined" The agent design problem" Search:
Efficient memory-bounded search methods
 Efficient memory-bounded search methods Mikhail Simin Arjang Fahim CSCE 580: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Dr. Marco Voltorta Outline of The Presentation Motivations and Objectives Background - BFS
Efficient memory-bounded search methods Mikhail Simin Arjang Fahim CSCE 580: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Dr. Marco Voltorta Outline of The Presentation Motivations and Objectives Background - BFS
