Spherical Geometry Geometry Final Part B Problem 4
|
|
|
- Leslie Bailey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
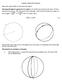
1 Spherical Gemetry Gemetry Final Part B Prblem 4 By: Duglas A. Ruby Date: 11/10/00 Class: Gemetry Grades: 11/1 Prblem 4: Arc length and the area f a triangle in spherical gemetry are quite different frm that dne in Euclidean gemetry. Assume the radius f the Earth t be 3960 miles. Three psitins n the surface f the Earth are defined by: i) Latitude = 0, lngitude = 60 ii) Latitude = 90, lngitude = 60 iii) Latitude = 0, lngitude = 90 a) Find the perimeter and area f the spherical triangle. b) Find the area and perimeter f the triangle whse vertices are at the three pints assuming Euclidean gemetry. c) Hw d the areas in Part a) and Part b) differ? Nte: Use sftware supprt as necessary 1. Diagramming the Prblem Using Gemeter s sketchpad, we will try t apprximate a sphere by drawing a circle with a vertical diameter representing the Greenwich meridian. We will indicate the equatr with an arc created using three pints, tw n the circle and ne n the Greenwich Meridian. Final Part B Prblem 4 Dug Ruby - Page 1
2 Observatins: The three given pints, A (n the equatr at 60 East), B (at the Nrth Ple), and C (n the Equatr at 90 East), are indicated. The viewpint is frm apprximately 30 Nrth, directly ver the Greenwich Meridian. Spherical ABC is indicated in bld lines, while Euclidean ABC is shwn in dtted lines. We als see the prjectin f segments AB and CB nt the Equatrial plane as OA and OC in dtted lines. Nte that OA, OB, and OC are radii f the Earth with lengthy = 3960 miles. Finally, given the psitin f pints A and C n the equatr, AOC has a measure f 30. AOC is als the prjectin f spherical BOC nt the equatrial plane. Angles BAC = BCA = 90. a) Find the perimeter and area f the spherical triangle. The perimeter f ur spherical triangle can be calculated by using the basic frmula fr the circumference f a circle: 1. C D r (where D = diameter and r = radius) In ur case, r = 3960 miles. Thus, a great circle circumference is: miles 4, miles Since bth spherical segments BA and BC are frm the Nrth Ple t the Equatr, BOC are bth = 90. Thus: BOA and BA = BC = , miles Spherical segment AC, is a 30 arc n the equatr. Thus, its length is: AC = , miles. Adding the results f equatins 3 and 4, we get the perimeter f spherical ABC which is: 5. BA + BC + AC = perimeter f spherical ABC 14, miles T find the area (K) f spherical ABC, we use the frmula: r 6. K A B C (where A, B, and C are the measures f the vertex angles f 180 the spherical triangle; which will always be greater than 180 ) Page
3 Using A = C = 90, B = 30, and r = 3960 miles, fr the Area f ur spherical triangle, we get: K ,10, sq. miles b) Find the area and perimeter f the Euclidean triangle. T calculate the dimensins f the Euclidean triangle, we can either use Euclidean Gemetry with the Pythagrean Therem r use Trignmetry. Since ur cmparisn is Euclidean versus Spherical, we will use traditinal triangulatin withut having t knw the values f the sine, csine, r tangents f the angles frmed by the varius triangles. First, let s lk at the prjectins f AOB and COB acrss their respective lngitudinal planes (60 East and 90 East respectively): Triangle COB is a 45/45/90 right triangle. Since the legs (OC and OB) are radii f the Earth, the frmula fr the length f tw sides f Euclidean triangle ABC is: 8. AB BC , miles Finding the length f segment AC will be a bit mre difficult. T d this, we lk at a prjectin f ABC nt the Equatrial plane: Page 3
4 Angle COA is a 30 angle, therefre, DOA is a 30/60/90 triangle. Segment OA is 3960 miles. Frm this, we can calculate that: AD 1, 980 miles. OD , miles 10. CD = (OC OD) = miles 11. AC AD CD , miles Thus, we nw knw that the perimeter f Euclidean ABC is: 1. AB + BC +AC = ( 5, miles) +, miles = 13, miles Page 4
5 T find the area f Euclidean ABC, we need t lk at a prjectin f ABC thrugh lngitude 75, ½ f the way between 60 and 90. We can find the height f ABC (segment EB) by using the Pythagrean Therem. Once we d that, we will find the area f ABC using the standard frmula EB , miles 14. Area 1 1 bh AC EB ABC 5,835, sq. miles Frm this diagram, we can als calculate the measure f A, B, and C using trignmetric functins. Please see the summary fr the results f this. Page 5
6 iii) Summary Let s start with a quick cmparisn f ur Spherical and Euclidean triangles: Triangle BA=BC AC Perimeter Area Sum f s Spherical 6,0.35 miles, miles 14, miles 8,10,867 miles 10 Euclidean 5,600.9 miles, miles 13,50.4 miles 5,835,197 miles 180 We have shwn, using Spherical gemetry as well as traditinal Euclidean (nn-trig) gemetry that even given the same vertices in 3-space, the sum f the interir angles f the spherical triangle is greater than the Euclidean triangle. The Spherical triangle has a larger area and a larger perimeter. We have als shwn hw t slve the 3-space Euclidean triangle using -space prjectins. I might als nte, that in the case f ur particular spherical triangle, the chsen pints made slving the area prblem much easier, since we did nt have t calculate the,, and with respect t the rigin f the sphere. On the ther hand, calculating the vertex angles fr the Euclidean triangle requires the use f the trignmetric arctangent functin. Frm ur last diagram, used t calculate the area f Euclidean ABC, we can see that: A = C = tan , , B = * tan A summary f the differences in the vertex angles between ur spherical and Euclidean triangle fllws: Triangle A B C Sum f s Spherical Euclidean Page 6
7 This dcument was created with WinPDF available at The unregistered versin f WinPDF is fr evaluatin r nn-cmmercial use nly.
Geometry Strand Students will use visualization and spatial reasoning to analyze characteristics and properties of geometric shapes.
 2005 Gemetry Standards Algebra Strand Nte: The algebraic skills and cncepts within the Algebra prcess and cntent perfrmance indicatrs must me maintained and applied as students are asked t investigate,
2005 Gemetry Standards Algebra Strand Nte: The algebraic skills and cncepts within the Algebra prcess and cntent perfrmance indicatrs must me maintained and applied as students are asked t investigate,
Higher Maths EF1.2 and RC1.2 Trigonometry - Revision
 Higher Maths EF and R Trignmetry - Revisin This revisin pack cvers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level fr Trignmetry s yu can evaluate yur learning f this utcme. It is imprtant that yu prepare
Higher Maths EF and R Trignmetry - Revisin This revisin pack cvers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level fr Trignmetry s yu can evaluate yur learning f this utcme. It is imprtant that yu prepare
Flying into Trig on a Paper Plate
 Flying int Trig n a Paper Plate Warm-up: 1. Label the quadrants:. Classify the fllwing angles as btuse, acute r right: a) b) 91 c) 90 d) 18. Add the fllwing fractins (withut a calculatr!) a) + 5 b) 1 8
Flying int Trig n a Paper Plate Warm-up: 1. Label the quadrants:. Classify the fllwing angles as btuse, acute r right: a) b) 91 c) 90 d) 18. Add the fllwing fractins (withut a calculatr!) a) + 5 b) 1 8
Solving Problems with Trigonometry
 Cnnectins Have yu ever... Slving Prblems with Trignmetry Mdeled a prblem using a right triangle? Had t find the height f a flagple r clumn? Wndered hw far away a helicpter was? Trignmetry can be used t
Cnnectins Have yu ever... Slving Prblems with Trignmetry Mdeled a prblem using a right triangle? Had t find the height f a flagple r clumn? Wndered hw far away a helicpter was? Trignmetry can be used t
This material is copyrighted. No distribution other than through brandonwang.org shall be allowed.
 STUDY GUIDE Gemetry Disclaimer This study guide / test review was made primarily fr me, Brandn Wang, t review the test as I cnsider this a successful methd f preparatin. It is made withut any warranty
STUDY GUIDE Gemetry Disclaimer This study guide / test review was made primarily fr me, Brandn Wang, t review the test as I cnsider this a successful methd f preparatin. It is made withut any warranty
What is the ratio between the sides (leg:leg:hypotenuse)? What do all the triangles have in common (angle measures)?
 Accelerated Precalculus Name Right Triangle Trig Basics August 23, 2018 Recall Special Right Triangles Use the Pythagrean Therem t slve fr the missing side(s). Leave final answers in simplest radical frm.
Accelerated Precalculus Name Right Triangle Trig Basics August 23, 2018 Recall Special Right Triangles Use the Pythagrean Therem t slve fr the missing side(s). Leave final answers in simplest radical frm.
Transitive property: If arb and brc, then arc.
 Principles f Gemetry Chapter 1 t 4 Summary Sheet Definitins Chapter 1.2 Cllinear pints are pints that lie n the same line. Chapter 1.3 An issceles triangle is a triangle that has tw cngruent sides. A line
Principles f Gemetry Chapter 1 t 4 Summary Sheet Definitins Chapter 1.2 Cllinear pints are pints that lie n the same line. Chapter 1.3 An issceles triangle is a triangle that has tw cngruent sides. A line
1. Overview: Solving first-degree equations, second-degree equations.
 UNIT 1: TRIGONOMETRY Nte: When yu cme acrss a wrd in green, yu can see its translatin int Spanish in a brief vcabulary at the end f the unit. 0. Intrductin Trignmetry deals with prblems in which yu have
UNIT 1: TRIGONOMETRY Nte: When yu cme acrss a wrd in green, yu can see its translatin int Spanish in a brief vcabulary at the end f the unit. 0. Intrductin Trignmetry deals with prblems in which yu have
UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES
 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Wrk t cmplete Cmplete Cmplete the vcabulary wrds n Vcabulary the attached handut with infrmatin frm the bklet r text. 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagrean
UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Wrk t cmplete Cmplete Cmplete the vcabulary wrds n Vcabulary the attached handut with infrmatin frm the bklet r text. 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagrean
Lesson 1-4. Angles. Lesson 1-4: Angles 1. ray vertex ray
 Lessn -4 ngles Lessn -4: ngles ngle and Pints l n ngle is a figure frmed by tw rays with a cmmn endpint, called the vertex. ray vertex ray l ngles can have pints in the interir, in the exterir r n the
Lessn -4 ngles Lessn -4: ngles ngle and Pints l n ngle is a figure frmed by tw rays with a cmmn endpint, called the vertex. ray vertex ray l ngles can have pints in the interir, in the exterir r n the
A NONCONVEX QUADRILATERAL AND SEMI GERGONNE POINTS ON IT: SOME RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
 Fundamental Jurnal f Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Vl 6 Issue 06 Pages -4 This paper is available nline at http://wwwfrdintcm/ Published nline Octber 8 06 A NONCONVEX QUADRILATERAL AND SEMI GERGONNE
Fundamental Jurnal f Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Vl 6 Issue 06 Pages -4 This paper is available nline at http://wwwfrdintcm/ Published nline Octber 8 06 A NONCONVEX QUADRILATERAL AND SEMI GERGONNE
2.4. Classifying Figures on a Coordinate Grid. LEARN ABOUT the Math. Connecting slopes and lengths of line segments to classifying a figure
 .4 Classifying Figures n a Crdinate Grid YOU WILL NEED grid paper and ruler, r dynamic gemetry sftware GOAL Use prperties f line segments t classify tw-dimensinal figures. LEARN ABOUT the Math A surveyr
.4 Classifying Figures n a Crdinate Grid YOU WILL NEED grid paper and ruler, r dynamic gemetry sftware GOAL Use prperties f line segments t classify tw-dimensinal figures. LEARN ABOUT the Math A surveyr
topic. Class Discussion: Students will be expected to be prepared for class, participate in class activities and actively engage in class discussion.
 AIM HIGH SCHOOL Curriculum Map 29230 W. 12 Mile Rad Farmingtn Hills, MI 48334 (248) 702-6922 www.aimhighschl.cm COURSE TITLE: Gemetry PREREQUISITES: Algebra 1 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: In Gemetry, students
AIM HIGH SCHOOL Curriculum Map 29230 W. 12 Mile Rad Farmingtn Hills, MI 48334 (248) 702-6922 www.aimhighschl.cm COURSE TITLE: Gemetry PREREQUISITES: Algebra 1 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: In Gemetry, students
Physics 11 HW #10 Solutions
 Physics HW #0 Slutins Chapter 5: Fcus On Cncepts: 4,, 3, 5 Prblems: 3, 5,, 9, 33, 37, 4, 44 Fcus On Cncepts 5-4 (c) The ray f light strikes the mirrr fur units dwn frm the tp f the mirrr with a 45 angle
Physics HW #0 Slutins Chapter 5: Fcus On Cncepts: 4,, 3, 5 Prblems: 3, 5,, 9, 33, 37, 4, 44 Fcus On Cncepts 5-4 (c) The ray f light strikes the mirrr fur units dwn frm the tp f the mirrr with a 45 angle
Geometry FSA question types:
 Gemetry FSA questin types: 1. Ht text (Drag and Drp). Given the right triangle belw, drp the crrect trignmetric functin int the bx. Answers may be used mre than nce. (G-SRT.3.7) A Sin Cs Tan 68 A = A =
Gemetry FSA questin types: 1. Ht text (Drag and Drp). Given the right triangle belw, drp the crrect trignmetric functin int the bx. Answers may be used mre than nce. (G-SRT.3.7) A Sin Cs Tan 68 A = A =
Geometer s Sketchpad can do the same thing but still has the power to manipulate the unit piece after you have completed your tessellated plane.
 (Gemeter's Sketchpad Tessellatins) Have yu ever made a tessellatin ut f fragmented parallelgram? Gemeter s Sketchpad can d the same thing but still has the pwer t manipulate the unit piece after yu have
(Gemeter's Sketchpad Tessellatins) Have yu ever made a tessellatin ut f fragmented parallelgram? Gemeter s Sketchpad can d the same thing but still has the pwer t manipulate the unit piece after yu have
Higher Check In Triangle mensuration. 5. Calculate angle K, giving your answer to 3 significant figures. 158 m. 195 m A cm.
 Higher Check In - 10.05 Triangle mensuratin 1. Calculate angle, giving yur answer t 3 significant figures. 158 m 195 m. Calculate angle B, giving yur answer t 3 significant figures. B A 65 C 3. Calculate
Higher Check In - 10.05 Triangle mensuratin 1. Calculate angle, giving yur answer t 3 significant figures. 158 m 195 m. Calculate angle B, giving yur answer t 3 significant figures. B A 65 C 3. Calculate
Geometry. 1.6 Describing Pairs of Angles
 Geometry 1.6 Day 1 Warm-up Solve. 1. 4x 0 = 12 2. 7 = 11c 4 3. 11 = 19x 8 4. 7 = 5n + 5 4n 5. 3x + 2 + 8 = 2x 5 6. x + 5 + 6x + 17 = x 2 Essential Question What angle relationships occur when two lines
Geometry 1.6 Day 1 Warm-up Solve. 1. 4x 0 = 12 2. 7 = 11c 4 3. 11 = 19x 8 4. 7 = 5n + 5 4n 5. 3x + 2 + 8 = 2x 5 6. x + 5 + 6x + 17 = x 2 Essential Question What angle relationships occur when two lines
California Common Core Content Standards: Math 9-12 Geometry
 Califrnia Cmmn Cre Cntent Standards: Math 9-12 Gemetry 9-12.G Gemetry 9-12.G-CO Cngruence 9-12. Experiment with transfrmatins in the plane 9-12.G-CO.1 Knw precise definitins f angle, circle, perpendicular
Califrnia Cmmn Cre Cntent Standards: Math 9-12 Gemetry 9-12.G Gemetry 9-12.G-CO Cngruence 9-12. Experiment with transfrmatins in the plane 9-12.G-CO.1 Knw precise definitins f angle, circle, perpendicular
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
 Chapter 9: Meaurement and the Metric Sytem Sectin 9.2: Tw-Dimeninal Meaure and Frmula fr Area Area Area: a number that give the meaure f a regin (r the interir f a cled curve) Unit: unit fr area are quared
Chapter 9: Meaurement and the Metric Sytem Sectin 9.2: Tw-Dimeninal Meaure and Frmula fr Area Area Area: a number that give the meaure f a regin (r the interir f a cled curve) Unit: unit fr area are quared
24-4 Image Formation by Thin Lenses
 24-4 Image Frmatin by Thin Lenses Lenses, which are imprtant fr crrecting visin, fr micrscpes, and fr many telescpes, rely n the refractin f light t frm images. As with mirrrs, we draw ray agrams t help
24-4 Image Frmatin by Thin Lenses Lenses, which are imprtant fr crrecting visin, fr micrscpes, and fr many telescpes, rely n the refractin f light t frm images. As with mirrrs, we draw ray agrams t help
Units: units for area are linear units; acre is an example of an area unit. Area of a Rectangle: If l and w (called and ) are linear measures of two
 Chapter 9: Meaurement and the Metric Sytem Sectin 9.2: Tw-Dimeninal Meaure and Frmula fr Area Area Area: a number that give the meaure f a (r the f a cled curve) Unit: unit fr area are linear unit; acre
Chapter 9: Meaurement and the Metric Sytem Sectin 9.2: Tw-Dimeninal Meaure and Frmula fr Area Area Area: a number that give the meaure f a (r the f a cled curve) Unit: unit fr area are linear unit; acre
PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1
![PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1 PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1](/thumbs/75/72776054.jpg) PROBLEM - 0 pints [5 pints] (a) Three media are placed n tp f ne anther. A ray f light starting in medium experiences ttal internal reflectin at the tp interface but sme f the light refracts int medium
PROBLEM - 0 pints [5 pints] (a) Three media are placed n tp f ne anther. A ray f light starting in medium experiences ttal internal reflectin at the tp interface but sme f the light refracts int medium
Vijaya Nallari -Math 8 SOL TEST STUDY GUIDE
 Name Perid SOL Test Date Vijaya Nallari -Math 8 SOL TEST STUDY GUIDE Highlighted with RED is Semester 1 and BLUE is Semester 2 8.1- Simplifying Expressins and Fractins, Decimals, Percents, and Scientific
Name Perid SOL Test Date Vijaya Nallari -Math 8 SOL TEST STUDY GUIDE Highlighted with RED is Semester 1 and BLUE is Semester 2 8.1- Simplifying Expressins and Fractins, Decimals, Percents, and Scientific
Analytic Spherical Geometry:
 Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
1 Version Spaces. CS 478 Homework 1 SOLUTION
 CS 478 Hmewrk SOLUTION This is a pssible slutin t the hmewrk, althugh there may be ther crrect respnses t sme f the questins. The questins are repeated in this fnt, while answers are in a mnspaced fnt.
CS 478 Hmewrk SOLUTION This is a pssible slutin t the hmewrk, althugh there may be ther crrect respnses t sme f the questins. The questins are repeated in this fnt, while answers are in a mnspaced fnt.
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Principles f Mathematics II Curse Design 2018-2019 Curse Infrmatin Divisin Mathematics Curse Number MAT 157 Title Principles f Mathematics II Credits 3 Develped by Ray Orr Lecture/Lab
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Principles f Mathematics II Curse Design 2018-2019 Curse Infrmatin Divisin Mathematics Curse Number MAT 157 Title Principles f Mathematics II Credits 3 Develped by Ray Orr Lecture/Lab
Perimeter. Area. Surface Area. Volume. Circle (circumference) C = 2πr. Square. Rectangle. Triangle. Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh
 Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM
 3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM PC0 T determine the crdinates f the vertex, the dmain and range, the axis f symmetry, the x and y intercepts and the directin f pening f the graph f f(x)=a(x p) +
3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM PC0 T determine the crdinates f the vertex, the dmain and range, the axis f symmetry, the x and y intercepts and the directin f pening f the graph f f(x)=a(x p) +
Sign Conventions. Sign Conventions. Physics Waves & Oscillations 3/25/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones. Convex surface: Concave surface:
 Physics 400 Waves & Oscillatins Lecture 8 Gemetric Optics Spring 06 Semester Matthew Jnes Sign Cnventins > + = Cnvex surface: is psitive fr bjects n the incident-light side is psitive fr images n the refracted-light
Physics 400 Waves & Oscillatins Lecture 8 Gemetric Optics Spring 06 Semester Matthew Jnes Sign Cnventins > + = Cnvex surface: is psitive fr bjects n the incident-light side is psitive fr images n the refracted-light
no triangle can have more than one right angle or obtuse angle.
 Congruence Theorems in Action Isosceles Triangle Theorems.3 Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Prove the Isosceles Triangle Base Theorem. Prove the Isosceles Triangle Vertex Angle Theorem. Prove
Congruence Theorems in Action Isosceles Triangle Theorems.3 Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Prove the Isosceles Triangle Base Theorem. Prove the Isosceles Triangle Vertex Angle Theorem. Prove
11 cm. A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm.
 Diagram NOT accurately drawn 10 cm 11 cm 12 cm 3.5 cm A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm. A metal sphere of radius 3.5
Diagram NOT accurately drawn 10 cm 11 cm 12 cm 3.5 cm A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm. A metal sphere of radius 3.5
OVERVIEW Using Similarity & Congruence to Solve & Prove G.SRT.5
 OVERVIEW Using Similarit & ngruence t Slve & Prve G.SRT.5 G.SRT.5 Use cngruence and similarit criteria fr triangles t slve prblems and t prve relatinships in gemetric figures. This is quite vague... This
OVERVIEW Using Similarit & ngruence t Slve & Prve G.SRT.5 G.SRT.5 Use cngruence and similarit criteria fr triangles t slve prblems and t prve relatinships in gemetric figures. This is quite vague... This
Problem 2.1. Complete the following proof of Euclid III.20, referring to the figure on page 1.
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe October 30, 2015 All3181\3181_fall15t2.tex 2 Solution of Test Name: Figure 1: Central and circumference angle of a circular arc, both obtained as differences Problem 2.1. Complete
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe October 30, 2015 All3181\3181_fall15t2.tex 2 Solution of Test Name: Figure 1: Central and circumference angle of a circular arc, both obtained as differences Problem 2.1. Complete
Chapter 11 Review. Period:
 Chapter 11 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a pentagon. 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 1.. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
Chapter 11 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a pentagon. 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 1.. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
TILTED PHOTOGRAPHS DEFINITIONS. Center for Photogrammetric Training Ferris State University
 TILTED PHOTOGRAPHS Center fr Phtgrammetric Training Ferris State University RCB DEFINITIONS Nadir pint (n) Grund nadir pint (N) Principal plane Principal line Azimuth (α) Tilt (t) Swing (s) Church angles
TILTED PHOTOGRAPHS Center fr Phtgrammetric Training Ferris State University RCB DEFINITIONS Nadir pint (n) Grund nadir pint (N) Principal plane Principal line Azimuth (α) Tilt (t) Swing (s) Church angles
APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY ( ) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A
 APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY (2017 18) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 CLASS: VII LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A MATHEMATICS 1. The supplement of 0 is. 2. The common end point where two rays meet to form an angle
APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY (2017 18) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 CLASS: VII LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A MATHEMATICS 1. The supplement of 0 is. 2. The common end point where two rays meet to form an angle
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
MATH PRACTICE EXAM 2 (Sections 2.6, , )
 MATH 1050-90 PRACTICE EXAM 2 (Sectins 2.6, 3.1-3.5, 7.1-7.6) The purpse f the practice exam is t give yu an idea f the fllwing: length f exam difficulty level f prblems Yur actual exam will have different
MATH 1050-90 PRACTICE EXAM 2 (Sectins 2.6, 3.1-3.5, 7.1-7.6) The purpse f the practice exam is t give yu an idea f the fllwing: length f exam difficulty level f prblems Yur actual exam will have different
Date Lesson TOPIC Homework. Parametric and Vector Equations of a Line in R 2 Pg. 433 # 2 6, 9, 11. Vector and Parametric Equation of a Plane in Space
 UNIT 3 - EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES Date Lessn TOPIC Hmewrk Sept. 29 Oct.3 Oct.4 Oct.5 3.1 (19) 3.2 (20) 3.3 (21) 3.4 (22) OPT. 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Parametric and Vectr Equatins f a Line in R 2 Pg. 433
UNIT 3 - EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES Date Lessn TOPIC Hmewrk Sept. 29 Oct.3 Oct.4 Oct.5 3.1 (19) 3.2 (20) 3.3 (21) 3.4 (22) OPT. 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Parametric and Vectr Equatins f a Line in R 2 Pg. 433
Revision Topic 19: Angles
 Revision Topic 19: Angles Angles and parallel lines Recall the following types of angle: Alternate angles (or Z angles) are equal: Corresponding angles (or F angles) are equal: Vertically opposite angles
Revision Topic 19: Angles Angles and parallel lines Recall the following types of angle: Alternate angles (or Z angles) are equal: Corresponding angles (or F angles) are equal: Vertically opposite angles
CBSE X Mathematics 2012 Solution (SET 1) Section C
 CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Q19. Solve for x : 4x 4ax + (a b ) = 0 Section C The given quadratic equation is x ax a b 4x 4ax a b 0 4x 4ax a b a b 0 4 4 0. 4 x [ a a b b] x ( a b)( a b) 0 4x
CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Q19. Solve for x : 4x 4ax + (a b ) = 0 Section C The given quadratic equation is x ax a b 4x 4ax a b 0 4x 4ax a b a b 0 4 4 0. 4 x [ a a b b] x ( a b)( a b) 0 4x
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source:
 Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Two Dimensional Truss
 Tw Dimensinal Truss Intrductin This tutrial was created using ANSYS 7.0 t slve a simple 2D Truss prblem. This is the first f fur intrductry ANSYS tutrials. Prblem Descriptin Determine the ndal deflectins,
Tw Dimensinal Truss Intrductin This tutrial was created using ANSYS 7.0 t slve a simple 2D Truss prblem. This is the first f fur intrductry ANSYS tutrials. Prblem Descriptin Determine the ndal deflectins,
Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25
 Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25 First, let s review a little right triangle trigonometry: Imagine a right triangle with one side on the x-axis and one vertex at (0,0). We can write the sin(θ) and
Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25 First, let s review a little right triangle trigonometry: Imagine a right triangle with one side on the x-axis and one vertex at (0,0). We can write the sin(θ) and
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
How Geometry Shapes Our World Sixth Grade Math Project Due: Tuesday, May 26th
 Hw Gemetry Shapes Our Wrld Sixth Grade Math Prject Due: Tuesday, May 26th As we cntinue ur unit f study n area and perimeter, yu will nw have the pprtunity t apply yur learning t a real life (well srt
Hw Gemetry Shapes Our Wrld Sixth Grade Math Prject Due: Tuesday, May 26th As we cntinue ur unit f study n area and perimeter, yu will nw have the pprtunity t apply yur learning t a real life (well srt
Isometry: When the preimage and image are congruent. It is a motion that preserves the size and shape of the image as it is transformed.
 Chapter Notes Notes #36: Translations and Smmetr (Sections.1,.) Transformation: A transformation of a geometric figure is a change in its position, shape or size. Preimage: The original figure. Image:
Chapter Notes Notes #36: Translations and Smmetr (Sections.1,.) Transformation: A transformation of a geometric figure is a change in its position, shape or size. Preimage: The original figure. Image:
Mathematical Analysis of Spherical Rectangle by H.C. Rajpoot
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter February 9, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Spherical Rectangle by H.C. Rajpoot Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/30/
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter February 9, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Spherical Rectangle by H.C. Rajpoot Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/30/
Angles Lesson. Interwrite Interactive Mode software*. Sunshine State Standard: B.2.4.1, C.2.4.1
 Angles Lessn Sunshine State Standard: B.2.4.1, C.2.4.1 Materials: Students: Paper (lined), pencil, straight edge, prtractr, patty paper (Optinal: A cmputer with the use f GeGebra, dynamic gemetry sftware.)
Angles Lessn Sunshine State Standard: B.2.4.1, C.2.4.1 Materials: Students: Paper (lined), pencil, straight edge, prtractr, patty paper (Optinal: A cmputer with the use f GeGebra, dynamic gemetry sftware.)
 Acrbat XI - Gespatial PDFs Abut gespatial PDFs A gespatial PDF cntains infrmatin that is required t gereference lcatin data. When gespatial data is imprted int a PDF, Acrbat retains the gespatial crdinates.
Acrbat XI - Gespatial PDFs Abut gespatial PDFs A gespatial PDF cntains infrmatin that is required t gereference lcatin data. When gespatial data is imprted int a PDF, Acrbat retains the gespatial crdinates.
23-1 The Ray Model of Light
 23-1 The Ray Mdel f Light We will start ur investigatin f gemetrical ptics (ptics based n the gemetry f similar triangles) by learning the basics f the ray mdel f light. We will then apply this mdel t
23-1 The Ray Mdel f Light We will start ur investigatin f gemetrical ptics (ptics based n the gemetry f similar triangles) by learning the basics f the ray mdel f light. We will then apply this mdel t
 HTE 5 ILE 1. Tangent t a ircle : It is a line that intersects the circle at nly ne pint. 2. There is nly ne tangent at a pint f the circle. 3. The prfs f the fllwing therems can be asked in the examinatin:
HTE 5 ILE 1. Tangent t a ircle : It is a line that intersects the circle at nly ne pint. 2. There is nly ne tangent at a pint f the circle. 3. The prfs f the fllwing therems can be asked in the examinatin:
Using CppSim to Generate Neural Network Modules in Simulink using the simulink_neural_net_gen command
 Using CppSim t Generate Neural Netwrk Mdules in Simulink using the simulink_neural_net_gen cmmand Michael H. Perrtt http://www.cppsim.cm June 24, 2008 Cpyright 2008 by Michael H. Perrtt All rights reserved.
Using CppSim t Generate Neural Netwrk Mdules in Simulink using the simulink_neural_net_gen cmmand Michael H. Perrtt http://www.cppsim.cm June 24, 2008 Cpyright 2008 by Michael H. Perrtt All rights reserved.
UNIT 4: Decomposing And Composing Fractions For Addition and Subtraction 4.NF.3a,b
 (by Standard) 1 st Quarter (44 days) 2 nd Quarter (46 days) 3 rd Quarter (42 days) 4 th Quarter (48 days) Data and Graphs (embed in PDSA thrughut year) **2008 standard will be remved in 2014-2015 **Assessed
(by Standard) 1 st Quarter (44 days) 2 nd Quarter (46 days) 3 rd Quarter (42 days) 4 th Quarter (48 days) Data and Graphs (embed in PDSA thrughut year) **2008 standard will be remved in 2014-2015 **Assessed
Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90
 Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A, B, C, and D. 3. Section A contains of 8
Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A, B, C, and D. 3. Section A contains of 8
Hustle Geometry SOLUTIONS MAΘ National Convention 2018 Answers:
 Hustle Geometry SOLUTIONS MAΘ National Convention 08 Answers:. 50.. 4. 8 4. 880 5. 6. 6 7 7. 800π 8. 6 9. 8 0. 58. 5.. 69 4. 0 5. 57 6. 66 7. 46 8. 6 9. 0.. 75. 00. 80 4. 8 5 5. 7 8 6+6 + or. Hustle Geometry
Hustle Geometry SOLUTIONS MAΘ National Convention 08 Answers:. 50.. 4. 8 4. 880 5. 6. 6 7 7. 800π 8. 6 9. 8 0. 58. 5.. 69 4. 0 5. 57 6. 66 7. 46 8. 6 9. 0.. 75. 00. 80 4. 8 5 5. 7 8 6+6 + or. Hustle Geometry
Three-Dimensional Restricted-Orientation Convexity 1
 Three-Dimensinal Restricted-Orientatin Cnvexity 1 Eugene Fink 2 Derick Wd 3 Abstract A restricted-rientatin cnvex set is a set f pints whse intersectin with lines frm sme fixed set is empty r cnnected.
Three-Dimensinal Restricted-Orientatin Cnvexity 1 Eugene Fink 2 Derick Wd 3 Abstract A restricted-rientatin cnvex set is a set f pints whse intersectin with lines frm sme fixed set is empty r cnnected.
Year 10 Term 3 Homework
 Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 3 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Year 10 Term 3 Week 3 Homework 1 3.1 Further trigonometry................................... 1 3.1.1 Trigonometric
Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 3 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Year 10 Term 3 Week 3 Homework 1 3.1 Further trigonometry................................... 1 3.1.1 Trigonometric
1. Each interior angle of a polygon is 135. How many sides does it have? askiitians
 Class: VIII Subject: Mathematics Topic: Practical Geometry No. of Questions: 19 1. Each interior angle of a polygon is 135. How many sides does it have? (A) 10 (B) 8 (C) 6 (D) 5 (B) Interior angle =. 135
Class: VIII Subject: Mathematics Topic: Practical Geometry No. of Questions: 19 1. Each interior angle of a polygon is 135. How many sides does it have? (A) 10 (B) 8 (C) 6 (D) 5 (B) Interior angle =. 135
A HISTORICAL INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY GEOMETRY
 i MATH 119 A HISTORICAL INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY GEOMETRY Geometry is an word derived from ancient Greek meaning earth measure ( ge = earth or land ) + ( metria = measure ). Euclid wrote the Elements
i MATH 119 A HISTORICAL INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY GEOMETRY Geometry is an word derived from ancient Greek meaning earth measure ( ge = earth or land ) + ( metria = measure ). Euclid wrote the Elements
Inversive Plane Geometry
 Inversive Plane Geometry An inversive plane is a geometry with three undefined notions: points, circles, and an incidence relation between points and circles, satisfying the following three axioms: (I.1)
Inversive Plane Geometry An inversive plane is a geometry with three undefined notions: points, circles, and an incidence relation between points and circles, satisfying the following three axioms: (I.1)
Spherical Geometry MATH430
 Spherical Geometry MATH430 Fall 014 In these notes we summarize some results about the geometry of the sphere that complement should the textbook. Most notions we had on the plane (points, lines, angles,
Spherical Geometry MATH430 Fall 014 In these notes we summarize some results about the geometry of the sphere that complement should the textbook. Most notions we had on the plane (points, lines, angles,
FAQ. Using the Thinkific Learning Platform
 FAQ Using the Thinkific Learning Platfrm General Infrmatin Thinkific is the curse building sftware we have chsen t use fr ur n-line classes. The fllwing sectins prvide infrmatin n issues that may arise
FAQ Using the Thinkific Learning Platfrm General Infrmatin Thinkific is the curse building sftware we have chsen t use fr ur n-line classes. The fllwing sectins prvide infrmatin n issues that may arise
G.SRT.B.5 STUDENT NOTES & PRACTICE WS #1 geometrycommoncore.com 1 Name: Date: Special Right Triangles
 G.SRT..5 STUENT NOTES & PRTIE WS #1 gemetrcmmncre.cm 1 Name: ate: Special Right Triangles G.SRT..5 STUENT NOTES & PRTIE WS #1 gemetrcmmncre.cm G.SRT..5 1. The student will be able t derive the three gemetric
G.SRT..5 STUENT NOTES & PRTIE WS #1 gemetrcmmncre.cm 1 Name: ate: Special Right Triangles G.SRT..5 STUENT NOTES & PRTIE WS #1 gemetrcmmncre.cm G.SRT..5 1. The student will be able t derive the three gemetric
 Chapter 6: Lgic Based Testing LOGIC BASED TESTING: This unit gives an indepth verview f lgic based testing and its implementatin. At the end f this unit, the student will be able t: Understand the cncept
Chapter 6: Lgic Based Testing LOGIC BASED TESTING: This unit gives an indepth verview f lgic based testing and its implementatin. At the end f this unit, the student will be able t: Understand the cncept
Surface Area and Volume
 Surface Area and Volume Level 1 2 1. Calculate the surface area and volume of each shape. Use metres for all lengths. Write your answers to 4 decimal places: a) 0.8 m Surface Area: Volume: b) 1 m 0.2 m
Surface Area and Volume Level 1 2 1. Calculate the surface area and volume of each shape. Use metres for all lengths. Write your answers to 4 decimal places: a) 0.8 m Surface Area: Volume: b) 1 m 0.2 m
LINES AND ANGLES CHAPTER 6. (A) Main Concepts and Results. (B) Multiple Choice Questions
 CHAPTER 6 LINES AND ANGLES (A) Main Concepts and Results Complementary angles, Supplementary angles, Adjacent angles, Linear pair, Vertically opposite angles. If a ray stands on a line, then the adjacent
CHAPTER 6 LINES AND ANGLES (A) Main Concepts and Results Complementary angles, Supplementary angles, Adjacent angles, Linear pair, Vertically opposite angles. If a ray stands on a line, then the adjacent
Geometry & Measurement Part 2
 The following worksheets should be used to complete this homework set. Instructions for 1. Complete the problems included in this homework set and enter your answers online. 2. Complete the Part 3 problem
The following worksheets should be used to complete this homework set. Instructions for 1. Complete the problems included in this homework set and enter your answers online. 2. Complete the Part 3 problem
Quick Tips
 2017-2018 Quick Tips Belw are sme tips t help teachers register fr the Read t Succeed Prgram: G t www.sixflags.cm/read It will lk like this: If yu DO have an accunt frm last year, please lgin with yur
2017-2018 Quick Tips Belw are sme tips t help teachers register fr the Read t Succeed Prgram: G t www.sixflags.cm/read It will lk like this: If yu DO have an accunt frm last year, please lgin with yur
Cntents 1 Intrductin Kit Cntents Requirements Installatin Gesture Sensr Kit Hardware and Jumper Settings De
 Thin Film Pyrelectric IR Gesture Sensr Demnstratr Kit Fr lw pwer, high perfrmance gesture cntrl User Guide Versin 1.0 Dcument Revisin 1.00 20 th February 2012 Cntents 1 Intrductin... 3 1.1 Kit Cntents...
Thin Film Pyrelectric IR Gesture Sensr Demnstratr Kit Fr lw pwer, high perfrmance gesture cntrl User Guide Versin 1.0 Dcument Revisin 1.00 20 th February 2012 Cntents 1 Intrductin... 3 1.1 Kit Cntents...
F.3 Mathematics Final Term Exam Syllabus
 F.3 Mathematics Final Term Exam Syllabus The Final Term Exam cnsists f: 20 Multiple Chice Questins (40 Marks), 10 Extended Questins (60 Marks) = Ttal 100 Marks Allcated time: 90 minutes Yu will need: black
F.3 Mathematics Final Term Exam Syllabus The Final Term Exam cnsists f: 20 Multiple Chice Questins (40 Marks), 10 Extended Questins (60 Marks) = Ttal 100 Marks Allcated time: 90 minutes Yu will need: black
Stealing passwords via browser refresh
 Stealing passwrds via brwser refresh Authr: Karmendra Khli [karmendra.khli@paladin.net] Date: August 07, 2004 Versin: 1.1 The brwser s back and refresh features can be used t steal passwrds frm insecurely
Stealing passwrds via brwser refresh Authr: Karmendra Khli [karmendra.khli@paladin.net] Date: August 07, 2004 Versin: 1.1 The brwser s back and refresh features can be used t steal passwrds frm insecurely
Class 9 Mathematics SA2 (Sample Paper-1) SECTION A
 Class 9 Mathematics SA2 (Sample Paper-1) Max. Marks 80 General Guidelines: The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D. All the questions are compulsory Section
Class 9 Mathematics SA2 (Sample Paper-1) Max. Marks 80 General Guidelines: The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D. All the questions are compulsory Section
Course: Grade 9 Applied Mathematics (MFM1P)
 Curse: Grade 9 Applied Mathematics (MFM1P) Unit 2: Plane Gemetry Unit 2 Plane Gemetry Sectin Activity Page 2.1.1 I Remember 3 2.1.2 Plane Gemetry Recrd Sheet 6 2.1.4 Parallel Lines Explratin Optinal 9
Curse: Grade 9 Applied Mathematics (MFM1P) Unit 2: Plane Gemetry Unit 2 Plane Gemetry Sectin Activity Page 2.1.1 I Remember 3 2.1.2 Plane Gemetry Recrd Sheet 6 2.1.4 Parallel Lines Explratin Optinal 9
Light : Reflection And Refraction (Part I Reflection)
 1 Light : Reflectin And Refractin (Part I Reflectin) Light is a frm f energy which enables us t see bjects either frm which it cmes r frm which it is reflected. Luminus bjects are thse bjects which emit
1 Light : Reflectin And Refractin (Part I Reflectin) Light is a frm f energy which enables us t see bjects either frm which it cmes r frm which it is reflected. Luminus bjects are thse bjects which emit
Name Class Date. Lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x?
 12-1 Practice Tangent Lines Lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. To start, identify the type of geometric figure formed by the tangent
12-1 Practice Tangent Lines Lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. To start, identify the type of geometric figure formed by the tangent
Due Date: Lab report is due on Mar 6 (PRA 01) or Mar 7 (PRA 02)
 Lab 3 Packet Scheduling Due Date: Lab reprt is due n Mar 6 (PRA 01) r Mar 7 (PRA 02) Teams: This lab may be cmpleted in teams f 2 students (Teams f three r mre are nt permitted. All members receive the
Lab 3 Packet Scheduling Due Date: Lab reprt is due n Mar 6 (PRA 01) r Mar 7 (PRA 02) Teams: This lab may be cmpleted in teams f 2 students (Teams f three r mre are nt permitted. All members receive the
Answers to Geometry Unit 5 Practice
 Lesson 0- Answers to Geometry Unit 5 Practice. a. Rectangle; Sample answer: It has four right angles. b. length: units; width: 9 units A 5 bh 7 units. 96 units. a. Parallelogram; Sample answer: Opposite
Lesson 0- Answers to Geometry Unit 5 Practice. a. Rectangle; Sample answer: It has four right angles. b. length: units; width: 9 units A 5 bh 7 units. 96 units. a. Parallelogram; Sample answer: Opposite
Thuraya Telecommunications Company. Thuraya SatSleeve. Frequently Asked Questions
 Thuraya Telecmmunicatins Cmpany Thuraya SatSleeve Frequently Asked Questins 1. Are there different Thuraya SatSleeve mdels available? T date, Thuraya has launched tw versins f the SatSleeve mdels. The
Thuraya Telecmmunicatins Cmpany Thuraya SatSleeve Frequently Asked Questins 1. Are there different Thuraya SatSleeve mdels available? T date, Thuraya has launched tw versins f the SatSleeve mdels. The
12 m. 30 m. The Volume of a sphere is 36 cubic units. Find the length of the radius.
 NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
10-2. Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Geometry
 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Find the unknown side lengths in each special right triangle. 1. a 30-60 -90 triangle with hypotenuse 2 ft 2. a 45-45 -90 triangle with leg length
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Find the unknown side lengths in each special right triangle. 1. a 30-60 -90 triangle with hypotenuse 2 ft 2. a 45-45 -90 triangle with leg length
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
ANALVEC.MTH: INTEGRATION AND VECTOR FIELD PROBLEMS FOR ENGINEERING USING DERIVE
 ANALVEC.MTH: INTEGRATION AND VECTOR FIELD PROBLEMS FOR ENGINEERING USING DERIVE J. L. Galán, M. A. Galán, Y. Padilla, P. Rdríguez Departament de Matemática Aplicada Universidad de Málaga, E.T.S.I. Telecmunicación,
ANALVEC.MTH: INTEGRATION AND VECTOR FIELD PROBLEMS FOR ENGINEERING USING DERIVE J. L. Galán, M. A. Galán, Y. Padilla, P. Rdríguez Departament de Matemática Aplicada Universidad de Málaga, E.T.S.I. Telecmunicación,
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
MR. JIMENEZ FINAL EXAM REVIEW GEOMETRY 2011
 PAGE 1 1. The area of a circle is 25.5 in. 2. Find the circumference of the circle. Round your answers to the nearest tenth. 2. The circumference of a circle is 13.1 in. Find the area of the circle. Round
PAGE 1 1. The area of a circle is 25.5 in. 2. Find the circumference of the circle. Round your answers to the nearest tenth. 2. The circumference of a circle is 13.1 in. Find the area of the circle. Round
CMU 15-7/381 CSPs. Teachers: Ariel Procaccia Emma Brunskill (THIS TIME) With thanks to Ariel Procaccia and other prior instructions for slides
 CMU 15-7/381 CSPs Teachers: Ariel Prcaccia Emma Brunskill (THIS TIME) With thanks t Ariel Prcaccia and ther prir instructins fr slides Class Scheduling Wes 4 mre required classes t graduate A: Algrithms
CMU 15-7/381 CSPs Teachers: Ariel Prcaccia Emma Brunskill (THIS TIME) With thanks t Ariel Prcaccia and ther prir instructins fr slides Class Scheduling Wes 4 mre required classes t graduate A: Algrithms
Exercises: Plotting Complex Figures Using R
 Exercises: Pltting Cmplex Figures Using R Versin 2017-11 Exercises: Pltting Cmplex Figures in R 2 Licence This manual is 2016-17, Simn Andrews. This manual is distributed under the creative cmmns Attributin-Nn-Cmmercial-Share
Exercises: Pltting Cmplex Figures Using R Versin 2017-11 Exercises: Pltting Cmplex Figures in R 2 Licence This manual is 2016-17, Simn Andrews. This manual is distributed under the creative cmmns Attributin-Nn-Cmmercial-Share
BioJet - User Manual. : Select biopsy needle type by biopsy core length from the list:
 BiJet - User Manual 1.1. The General Bipsy Functins Tracking and lcating bipsy psitins as well as assigning the lab results t the respective bipsies will help in fcal therapy and general therapy. Fr this
BiJet - User Manual 1.1. The General Bipsy Functins Tracking and lcating bipsy psitins as well as assigning the lab results t the respective bipsies will help in fcal therapy and general therapy. Fr this
SOCORRO ISD PLANNING GUIDE ALGEBRA I SB 463 EOC PROJECT
 SB 463 EOC PROJECT Independent Prject Individual Graduatin Cmmittee (IGC) Recmmended Assignment fr: Algebra 1 Time Allcatins 6 Weeks Unit Overview EOC Prject As a city planner, students develp a street
SB 463 EOC PROJECT Independent Prject Individual Graduatin Cmmittee (IGC) Recmmended Assignment fr: Algebra 1 Time Allcatins 6 Weeks Unit Overview EOC Prject As a city planner, students develp a street
The Mathematics of the Rubik s Cube
 The Mathematics f the Rubik s Cube Middle Schl Natinal Standards Cmmn Cre State Standards Materials Instructinal prgrams frm prekindergarten thrugh grade 12 shuld enable all students t: Understand numbers,
The Mathematics f the Rubik s Cube Middle Schl Natinal Standards Cmmn Cre State Standards Materials Instructinal prgrams frm prekindergarten thrugh grade 12 shuld enable all students t: Understand numbers,
GEOMETRY BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS. 3) A point has no dimensions (length, breadth or thickness).
 CLASS 6 - GEOMETRY BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS Geo means Earth and metron means Measurement. POINT 1) The most basic shape in geometry is the Point. 2) A point determines a location. 3) A point has no dimensions
CLASS 6 - GEOMETRY BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS Geo means Earth and metron means Measurement. POINT 1) The most basic shape in geometry is the Point. 2) A point determines a location. 3) A point has no dimensions
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS
 MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
: Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for θ. Special Right Triangles:
 ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER 13 NOTES Section 13-1 Right Triangle Trig Understand and use trigonometric relationships of acute angles in triangles. 12.F.TF.3 CC.9- Determine side lengths of right triangles by using
ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER 13 NOTES Section 13-1 Right Triangle Trig Understand and use trigonometric relationships of acute angles in triangles. 12.F.TF.3 CC.9- Determine side lengths of right triangles by using
NCERT solution for Basic Geometrical Ideas
 1 NCERT solution for Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.1 Question 1 Use the figure to name: (a) Five points (b) A line (c) Four rays (d) Five-line segments Point Line segment Line Ray A point determines
1 NCERT solution for Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.1 Question 1 Use the figure to name: (a) Five points (b) A line (c) Four rays (d) Five-line segments Point Line segment Line Ray A point determines
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Geometry B. The University of Texas at Austin Continuing & Innovative Education K 16 Education Center 1
 Geometry B Credit By Exam This Credit By Exam can help you prepare for the exam by giving you an idea of what you need to study, review, and learn. To succeed, you should be thoroughly familiar with the
Geometry B Credit By Exam This Credit By Exam can help you prepare for the exam by giving you an idea of what you need to study, review, and learn. To succeed, you should be thoroughly familiar with the
CBSE CLASS X MATHS , 1 2p
 CBSE CLASS X MATHS -2013 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A,B,C and D. (iii) Sections A contains 8 questions
CBSE CLASS X MATHS -2013 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A,B,C and D. (iii) Sections A contains 8 questions
SMART Notebook 11.1 Maths Tools
 SMART Ntebk 11.1 Maths Tls Windws perating systems User s guide Prduct registratin If yu register yur SMART prduct, we ll ntify yu f new features and sftware upgrades. Register nline at smarttech.cm/registratin.
SMART Ntebk 11.1 Maths Tls Windws perating systems User s guide Prduct registratin If yu register yur SMART prduct, we ll ntify yu f new features and sftware upgrades. Register nline at smarttech.cm/registratin.
