Physics 11 HW #10 Solutions
|
|
|
- Angelica Tabitha Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics HW #0 Slutins Chapter 5: Fcus On Cncepts: 4,, 3, 5 Prblems: 3, 5,, 9, 33, 37, 4, 44 Fcus On Cncepts 5-4 (c) The ray f light strikes the mirrr fur units dwn frm the tp f the mirrr with a 45 angle f incidence. The ray reflects frm the mirrr at an angle f 45 and passes thrugh pint C. Fcus On Cncepts 5- (c) Accrng t the scussin in Sectin 5.5, a cncave mirrr can prduce an enlarged image, prvided the bject stance is less than the raus f curvature. A cnvex mirrr cannt prduce an enlarged image, regardless f where the bject is lcated. Fcus On Cncepts 5-3 (b) A cnvex mirrr always prduces a virtual, upright image (see Sectin 5.5). Fcus On Cncepts 5-5 (c) A cnvex lens always prduces an upright image that is smaller than the bject. Prblem 5-3 REASONING The drawing shws the image f the bird in the plane mirrr, as seen by the camera. Nte that the image is as far behind the mirrr as the bird is in frnt f it. We can find the stance d between the camera and the image by nting that this stance is the hyptenuse f a right triangle. The base f the triangle has a length f 3.7 m +. m and the height f the triangle is 4.3 m. Bird 4.3 m Hedge. m 4.3 m Image SOLUTION The stance d frm the camera t the image f the bird can be btained by using the Pythagrean therem: 3.7 m. m d = ( 3.7 m +. m) + ( 4.3 m) = 7. m
2 Prblem 5-5 REASONING The bject stance (d = cm) is shrter than the fcal length (f = 8 cm) f the mirrr, s we expect the image t be virtual, appearing behind the mirrr. Taking Figure 5.8a as ur mdel, we will trace ut: three rays frm the tip f the bject t the surface f the mirrr, then three reflected rays, and finally three virtual rays extenng behind the mirrr and meeting at the tip f the image. The scale f the ray tracing will determine the lcatin and height f the image. The three sets f rays are:. An incident ray frm the bject t the mirrr, parallel t the principal axis and then reflected thrugh the fcal pint F.. An incident ray frm the bject t the mirrr, rectly away frm the fcal pint F and then reflected parallel t the principal axis. (The incident ray cannt pass frm the bject thrugh the fcal pint, as this wuld take it away frm the mirrr, and it wuld nt be reflected.) 3. An incident ray frm the bject t the mirrr, rectly away frm the center f curvature C, then reflected back thrugh C. SOLUTION C Image (virtual) 7.6 cm tall F cm 8 cm Object 3.0 cm tall Scale: 6.0 cm a. The ray agram incates that the image is 8 cm behind the mirrr. b. We see frm the ray agram that the image is 7.6 cm tall. Prblem 5- REASONING a. We are dealing with a cncave mirrr whse raus f curvature is 56.0 cm. Thus, the fcal length f the mirrr is f = R= 8.0 cm (Equatin 5.) The bject stance is d = 3.0 cm. With knwn values fr f and d, we can use the mirrr equatin t (Equatin 5.3) find the image stance. b. T determine the image height h i, recall that it is related t the bject height h by the magnificatin m; h i = mh. The magnificatin is related t the image and bject stances by
3 the magnificatin equatin, m= / d (Equatin 5.4). Since we knw values fr h, d i, and d, we can find the image height h i. SOLUTION a. The image stance is given by the mirrr equatin as fllws: = = s = 90 cm (5.3) d f d 8.0 cm 3.0 cm i b. Using the magnificatin equatin, we find that the image height is 90 cm hi = mh = h = ( 0.95 cm ) = 8.9 cm d 3.0 cm (5.4) c. Since h i is negative, the image is inverted relative t the bject. Thus, t make the picture n the wall appear nrmal, the slide must be riented upside dwn in the prjectr. Prblem 5-9 REASONING We need t knw the fcal length f the mirrr and can btain it frm the mirrr equatin, Equatin 5.3, as applied t the first bject: + = + = r f = 4.0 cm d d 4.0 cm 7.00 cm f i Accrng t the magnificatin equatin, Equatin 5.4, the image height h i is related t the bject height h as fllws:. SOLUTION Applying this result t each bject, we find that h i = h, r i Therefre, Using the fact that h = h, we have Using this result in the mirrr equatin, as applied t the secnd bject, we find that
4 r Therefre, + = d d f i + = d 0.50 d d = cm 4.0 cm Prblem 5-33 REASONING The raus f curvature R f a cncave mirrr is related t the fcal length f f the mirrr by f = R (Equatin 5.), s we have that R= f () The mirrr s fcal length is given by the mirrr equatin = + (Equatin 5.3), f d where d = 4 cm is the bject stance and d i is the image stance. The image stance is related t the bject stance via the magnificatin equatin m = (Equatin 5.4). d Because the image is virtual, the image stance d i is negative. The bject stance is psitive, s we cnclude frm Equatin 5.4 that the magnificatin is psitive: m > 0. The image is twice the size f the bject, s we have that the magnificatin is m = +.0. SOLUTION Taking the reciprcal f bth sides f = + (Equatin 5.3) yields f d f =. Substituting this result int Equatin (), we find that + d R= f = () + d Slving m = (Equatin 5.4) fr d d i and substituting m = +.0 yields d = md = + (.0) d = d (3) i Substituting Equatin (3) int Equatin (), we btain R= = = = 4d ( ) = 4 4 cm = 56 cm + + d d ( d) d
5 Prblem 5-37 REASONING The mirrr equatin relates the bject and image stances t the fcal length. Thus, we can apply the mirrr equatin nce with the given bject and image stances t determine the fcal length. Then, we can use the mirrr equatin again with the fcal length and the secnd bject stance t determine the unknwn image stance. SOLUTION Accrng t the mirrr equatin, we have + = and + = d d f d d f i i First psitin f bject Secnd psitin f bject Since the fcal length is the same in bth cases, it fllws that The negative value fr d i incates that the image is lcated 4 cm behind the mirrr. Prblem 5-4 REASONING This prblem can be slved by using the mirrr equatin, Equatin 5.3, and the magnificatin equatin, Equatin 5.4. SOLUTION a. Using the mirrr equatin with d = d and f = R /, we have Therefre, we find that d = R. i d f d R / = = r = d d R i b. Accrng t the magnificatin equatin, the magnificatin is m d d = i = = d d c. Since the magnificatin m is negative, the image is inverted.
6 Prblem 5-44 REASONING The fcal length f f the cnvex mirrr determines the first image stance d i via = + (Equatin 5.3), where d f d d = 5.0 cm is the stance between the candle i and the cnvex mirrr. The secnd image, frmed by the plane mirrr, is lcated as far behind the mirrr as the bject is in frnt f the mirrr. Therefre, when the plane mirrr replaces the cnvex mirrr, the secnd image stance d i is given by = d = 5.0 cm () The negative sign in Equatin () arises because the image lies behind the plane mirrr and, therefre, is a virtual image. When the plane mirrr replaces the cnvex mirrr, the image mves a stance x farther away frm the mirrr, s the initial and final image stances are related by d = d x () i The negative sign in Equatin () ccurs because the image mves farther frm the mirrr, thus making the secnd image stance d i a negative number f greater magnitude than the first image stance d i. SOLUTION Substituting Equatin () int Equatin () and slving fr d i yields i d x= d r d = x d (3) i i Substituting Equatin (3) int = + (Equatin 5.3), we btain f d d i = + = + (4) f d d d x d i Taking the reciprcal f bth sides f Equatin (4), we find that the fcal length f the cnvex mirrr is f = = = 7 cm + + d x d 5.0 cm 7.0 cm 5.0 cm
24-4 Image Formation by Thin Lenses
 24-4 Image Frmatin by Thin Lenses Lenses, which are imprtant fr crrecting visin, fr micrscpes, and fr many telescpes, rely n the refractin f light t frm images. As with mirrrs, we draw ray agrams t help
24-4 Image Frmatin by Thin Lenses Lenses, which are imprtant fr crrecting visin, fr micrscpes, and fr many telescpes, rely n the refractin f light t frm images. As with mirrrs, we draw ray agrams t help
23-1 The Ray Model of Light
 23-1 The Ray Mdel f Light We will start ur investigatin f gemetrical ptics (ptics based n the gemetry f similar triangles) by learning the basics f the ray mdel f light. We will then apply this mdel t
23-1 The Ray Mdel f Light We will start ur investigatin f gemetrical ptics (ptics based n the gemetry f similar triangles) by learning the basics f the ray mdel f light. We will then apply this mdel t
Light : Reflection And Refraction (Part I Reflection)
 1 Light : Reflectin And Refractin (Part I Reflectin) Light is a frm f energy which enables us t see bjects either frm which it cmes r frm which it is reflected. Luminus bjects are thse bjects which emit
1 Light : Reflectin And Refractin (Part I Reflectin) Light is a frm f energy which enables us t see bjects either frm which it cmes r frm which it is reflected. Luminus bjects are thse bjects which emit
Sign Conventions. Sign Conventions. Physics Waves & Oscillations 3/25/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones. Convex surface: Concave surface:
 Physics 400 Waves & Oscillatins Lecture 8 Gemetric Optics Spring 06 Semester Matthew Jnes Sign Cnventins > + = Cnvex surface: is psitive fr bjects n the incident-light side is psitive fr images n the refracted-light
Physics 400 Waves & Oscillatins Lecture 8 Gemetric Optics Spring 06 Semester Matthew Jnes Sign Cnventins > + = Cnvex surface: is psitive fr bjects n the incident-light side is psitive fr images n the refracted-light
PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1
![PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1 PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1](/thumbs/75/72776054.jpg) PROBLEM - 0 pints [5 pints] (a) Three media are placed n tp f ne anther. A ray f light starting in medium experiences ttal internal reflectin at the tp interface but sme f the light refracts int medium
PROBLEM - 0 pints [5 pints] (a) Three media are placed n tp f ne anther. A ray f light starting in medium experiences ttal internal reflectin at the tp interface but sme f the light refracts int medium
Solving Problems with Trigonometry
 Cnnectins Have yu ever... Slving Prblems with Trignmetry Mdeled a prblem using a right triangle? Had t find the height f a flagple r clumn? Wndered hw far away a helicpter was? Trignmetry can be used t
Cnnectins Have yu ever... Slving Prblems with Trignmetry Mdeled a prblem using a right triangle? Had t find the height f a flagple r clumn? Wndered hw far away a helicpter was? Trignmetry can be used t
Think About This Why would the image you see of yourself in the lake be upright, while the image of the mountain is upside-down? physicspp.
 What Yu ll Learn Yu will learn hw light reflects ff different surfaces. Yu will learn abut the different types f mirrrs and their uses. Yu will use ray tracing and mathematical mdels t describe images
What Yu ll Learn Yu will learn hw light reflects ff different surfaces. Yu will learn abut the different types f mirrrs and their uses. Yu will use ray tracing and mathematical mdels t describe images
Transitive property: If arb and brc, then arc.
 Principles f Gemetry Chapter 1 t 4 Summary Sheet Definitins Chapter 1.2 Cllinear pints are pints that lie n the same line. Chapter 1.3 An issceles triangle is a triangle that has tw cngruent sides. A line
Principles f Gemetry Chapter 1 t 4 Summary Sheet Definitins Chapter 1.2 Cllinear pints are pints that lie n the same line. Chapter 1.3 An issceles triangle is a triangle that has tw cngruent sides. A line
What is the ratio between the sides (leg:leg:hypotenuse)? What do all the triangles have in common (angle measures)?
 Accelerated Precalculus Name Right Triangle Trig Basics August 23, 2018 Recall Special Right Triangles Use the Pythagrean Therem t slve fr the missing side(s). Leave final answers in simplest radical frm.
Accelerated Precalculus Name Right Triangle Trig Basics August 23, 2018 Recall Special Right Triangles Use the Pythagrean Therem t slve fr the missing side(s). Leave final answers in simplest radical frm.
1 Version Spaces. CS 478 Homework 1 SOLUTION
 CS 478 Hmewrk SOLUTION This is a pssible slutin t the hmewrk, althugh there may be ther crrect respnses t sme f the questins. The questins are repeated in this fnt, while answers are in a mnspaced fnt.
CS 478 Hmewrk SOLUTION This is a pssible slutin t the hmewrk, althugh there may be ther crrect respnses t sme f the questins. The questins are repeated in this fnt, while answers are in a mnspaced fnt.
1. Overview: Solving first-degree equations, second-degree equations.
 UNIT 1: TRIGONOMETRY Nte: When yu cme acrss a wrd in green, yu can see its translatin int Spanish in a brief vcabulary at the end f the unit. 0. Intrductin Trignmetry deals with prblems in which yu have
UNIT 1: TRIGONOMETRY Nte: When yu cme acrss a wrd in green, yu can see its translatin int Spanish in a brief vcabulary at the end f the unit. 0. Intrductin Trignmetry deals with prblems in which yu have
Spherical Geometry Geometry Final Part B Problem 4
 Spherical Gemetry Gemetry Final Part B Prblem 4 By: Duglas A. Ruby Date: 11/10/00 Class: Gemetry Grades: 11/1 Prblem 4: Arc length and the area f a triangle in spherical gemetry are quite different frm
Spherical Gemetry Gemetry Final Part B Prblem 4 By: Duglas A. Ruby Date: 11/10/00 Class: Gemetry Grades: 11/1 Prblem 4: Arc length and the area f a triangle in spherical gemetry are quite different frm
Flying into Trig on a Paper Plate
 Flying int Trig n a Paper Plate Warm-up: 1. Label the quadrants:. Classify the fllwing angles as btuse, acute r right: a) b) 91 c) 90 d) 18. Add the fllwing fractins (withut a calculatr!) a) + 5 b) 1 8
Flying int Trig n a Paper Plate Warm-up: 1. Label the quadrants:. Classify the fllwing angles as btuse, acute r right: a) b) 91 c) 90 d) 18. Add the fllwing fractins (withut a calculatr!) a) + 5 b) 1 8
Edexcel GCSE Physics
 Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 5: Light and the Electrmagnetic Spectrum Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin Ray Diagrams (Physics nly) - Arrws shw directin f light travelling - The nrmal
Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 5: Light and the Electrmagnetic Spectrum Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin Ray Diagrams (Physics nly) - Arrws shw directin f light travelling - The nrmal
Vijaya Nallari -Math 8 SOL TEST STUDY GUIDE
 Name Perid SOL Test Date Vijaya Nallari -Math 8 SOL TEST STUDY GUIDE Highlighted with RED is Semester 1 and BLUE is Semester 2 8.1- Simplifying Expressins and Fractins, Decimals, Percents, and Scientific
Name Perid SOL Test Date Vijaya Nallari -Math 8 SOL TEST STUDY GUIDE Highlighted with RED is Semester 1 and BLUE is Semester 2 8.1- Simplifying Expressins and Fractins, Decimals, Percents, and Scientific
UNIT 4 READING B. net y. net x
 UIT 4 READI B rce Diagrams Yu have learned in lab abut ur dierent tpes rces nrmal, gravitatin, tensile, and rictinal. In this class, rce diagrams will be drawn as llws: 1) The bject n which the rces are
UIT 4 READI B rce Diagrams Yu have learned in lab abut ur dierent tpes rces nrmal, gravitatin, tensile, and rictinal. In this class, rce diagrams will be drawn as llws: 1) The bject n which the rces are
QUIZ ON CHAPTER 12 SOLUTIONS
 QUIZ ON CHAPTER SOLUTIONS MATH 5 SPRING 00 KUNIYUKI 00 POINTS TOTAL Yu may use mixed numers instead f imprper fractins in yur answers. Dn t apprximate. ) Cnsider the equatin x + 6y - 48y + 9 0. Its graph
QUIZ ON CHAPTER SOLUTIONS MATH 5 SPRING 00 KUNIYUKI 00 POINTS TOTAL Yu may use mixed numers instead f imprper fractins in yur answers. Dn t apprximate. ) Cnsider the equatin x + 6y - 48y + 9 0. Its graph
Welcome to Palm Beach State College Boca Raton Campus. Use the buttons on the left to assist you in using the Multimedia Classroom Equipment.
 Hme Vide/Data Prjectr Cmputer Wireless Muse Dcument Camera Cntrl Panel Guest Laptp Welcme t Palm Beach State Cllege Bca Ratn Campus Use the buttns n the left t assist yu in using the Multimedia Classrm
Hme Vide/Data Prjectr Cmputer Wireless Muse Dcument Camera Cntrl Panel Guest Laptp Welcme t Palm Beach State Cllege Bca Ratn Campus Use the buttns n the left t assist yu in using the Multimedia Classrm
Focal Points of Spherical Mirrors. Spherical Mirrors. A plane mirror is a spherical mirror with an infinite radius of curvature. O Height = I Height
 Radus f Curvature Plane Mrrr A plane mrrr s a sphercal mrrr wth an nfnte radus f curvature. O Heght = I Heght phercal Mrrrs Cncave Mrrr: (e.g. make up mrrr) Center f curvature s n frnt f mrrr Feld f vew
Radus f Curvature Plane Mrrr A plane mrrr s a sphercal mrrr wth an nfnte radus f curvature. O Heght = I Heght phercal Mrrrs Cncave Mrrr: (e.g. make up mrrr) Center f curvature s n frnt f mrrr Feld f vew
of Prolog An Overview 1.1 An example program: defining family relations
 An Overview f Prlg This chaptereviews basic mechanisms f Prlg thrugh an example prgram. Althugh the treatment is largely infrmal many imprtant cncepts are intrduced. 1.1 An example prgram: defining family
An Overview f Prlg This chaptereviews basic mechanisms f Prlg thrugh an example prgram. Althugh the treatment is largely infrmal many imprtant cncepts are intrduced. 1.1 An example prgram: defining family
UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES
 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Wrk t cmplete Cmplete Cmplete the vcabulary wrds n Vcabulary the attached handut with infrmatin frm the bklet r text. 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagrean
UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Wrk t cmplete Cmplete Cmplete the vcabulary wrds n Vcabulary the attached handut with infrmatin frm the bklet r text. 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagrean
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Lecture #5.3 Mirrors
 Lecture #5.3 Mrrrs We ave already dscussed reflectn f EM waves. Ts penmenn fnds useful applcatn n te devces we use n ur everyday lfe. Tday we sall talk abut w reflectn wrks n rder t prduce mages n dfferent
Lecture #5.3 Mrrrs We ave already dscussed reflectn f EM waves. Ts penmenn fnds useful applcatn n te devces we use n ur everyday lfe. Tday we sall talk abut w reflectn wrks n rder t prduce mages n dfferent
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
This material is copyrighted. No distribution other than through brandonwang.org shall be allowed.
 STUDY GUIDE Gemetry Disclaimer This study guide / test review was made primarily fr me, Brandn Wang, t review the test as I cnsider this a successful methd f preparatin. It is made withut any warranty
STUDY GUIDE Gemetry Disclaimer This study guide / test review was made primarily fr me, Brandn Wang, t review the test as I cnsider this a successful methd f preparatin. It is made withut any warranty
Image Formed by a Plane Mirror. point object A, source of light
 Today s agenda: Plane Mirrors. You must be able to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors, and be able to calculate image and object heights, distances, and magnifications. Spherical Mirrors: concave and
Today s agenda: Plane Mirrors. You must be able to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors, and be able to calculate image and object heights, distances, and magnifications. Spherical Mirrors: concave and
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
Section 2 Flat Mirrors. Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors.
 Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes
 1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes. Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes. Spherical Mirrors
 1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light
 Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light 25. Wave fronts and rays We are all familiar with mirrors. We see images because some light is reflected off the surface of the mirror and into our eyes. In order to describe
Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light 25. Wave fronts and rays We are all familiar with mirrors. We see images because some light is reflected off the surface of the mirror and into our eyes. In order to describe
Two Dimensional Truss
 Tw Dimensinal Truss Intrductin This tutrial was created using ANSYS 7.0 t slve a simple 2D Truss prblem. This is the first f fur intrductry ANSYS tutrials. Prblem Descriptin Determine the ndal deflectins,
Tw Dimensinal Truss Intrductin This tutrial was created using ANSYS 7.0 t slve a simple 2D Truss prblem. This is the first f fur intrductry ANSYS tutrials. Prblem Descriptin Determine the ndal deflectins,
30/08/2016. Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes. Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes. Spherical Mirrors - Images
 1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
Higher Check In Triangle mensuration. 5. Calculate angle K, giving your answer to 3 significant figures. 158 m. 195 m A cm.
 Higher Check In - 10.05 Triangle mensuratin 1. Calculate angle, giving yur answer t 3 significant figures. 158 m 195 m. Calculate angle B, giving yur answer t 3 significant figures. B A 65 C 3. Calculate
Higher Check In - 10.05 Triangle mensuratin 1. Calculate angle, giving yur answer t 3 significant figures. 158 m 195 m. Calculate angle B, giving yur answer t 3 significant figures. B A 65 C 3. Calculate
GBT X-band (9 GHz): Pointing Stability
 GBT X-band (9 GHz): Pinting Stability Dana S. Balser, Rnald J. Maddalena, Frank Ghig, & Glen I. Langstn 10 March 2002 Abstract The pinting stability f the GBT is evaluated by tracking the half-pwer pint
GBT X-band (9 GHz): Pinting Stability Dana S. Balser, Rnald J. Maddalena, Frank Ghig, & Glen I. Langstn 10 March 2002 Abstract The pinting stability f the GBT is evaluated by tracking the half-pwer pint
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Physics 1C. Lecture 23A. "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?
 Physics 1C Lecture 23A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright Mirror Equation You can mathematically relate the object distance,
Physics 1C Lecture 23A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright Mirror Equation You can mathematically relate the object distance,
The Law of Reflection
 If the surface off which the light is reflected is smooth, then the light undergoes specular reflection (parallel rays will all be reflected in the same directions). If, on the other hand, the surface
If the surface off which the light is reflected is smooth, then the light undergoes specular reflection (parallel rays will all be reflected in the same directions). If, on the other hand, the surface
Assuming: f = 10 cm C = 20 cm p = 12 cm q = 60 cm h = 5 cm h = - 25 cm M = -5
 Object Distance greater than C Object Distance at C Assuming: f = 10 cm C = 20 cm p = 25 cm q = 16.66 h = 5 cm h = -3.32 cm M = -.664 Assuming: f = 10 cm C = 20 cm p = 20 cm q = 20 cm h = 5 cm h = -5 cm
Object Distance greater than C Object Distance at C Assuming: f = 10 cm C = 20 cm p = 25 cm q = 16.66 h = 5 cm h = -3.32 cm M = -.664 Assuming: f = 10 cm C = 20 cm p = 20 cm q = 20 cm h = 5 cm h = -5 cm
The Mathematics of the Rubik s Cube
 The Mathematics f the Rubik s Cube Middle Schl Natinal Standards Cmmn Cre State Standards Materials Instructinal prgrams frm prekindergarten thrugh grade 12 shuld enable all students t: Understand numbers,
The Mathematics f the Rubik s Cube Middle Schl Natinal Standards Cmmn Cre State Standards Materials Instructinal prgrams frm prekindergarten thrugh grade 12 shuld enable all students t: Understand numbers,
Using the Swiftpage Connect List Manager
 Quick Start Guide T: Using the Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager The Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager can be used t imprt yur cntacts, mdify cntact infrmatin, create grups ut f thse cntacts, filter yur cntacts
Quick Start Guide T: Using the Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager The Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager can be used t imprt yur cntacts, mdify cntact infrmatin, create grups ut f thse cntacts, filter yur cntacts
Date Lesson TOPIC Homework. Parametric and Vector Equations of a Line in R 2 Pg. 433 # 2 6, 9, 11. Vector and Parametric Equation of a Plane in Space
 UNIT 3 - EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES Date Lessn TOPIC Hmewrk Sept. 29 Oct.3 Oct.4 Oct.5 3.1 (19) 3.2 (20) 3.3 (21) 3.4 (22) OPT. 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Parametric and Vectr Equatins f a Line in R 2 Pg. 433
UNIT 3 - EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES Date Lessn TOPIC Hmewrk Sept. 29 Oct.3 Oct.4 Oct.5 3.1 (19) 3.2 (20) 3.3 (21) 3.4 (22) OPT. 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Parametric and Vectr Equatins f a Line in R 2 Pg. 433
Lab 1: Don t Shatter My Image. Reflection and Mirrors. Lab 2: Images The Law of Reflection. Three types of mirrors. Plane Mirror Images
 Lab : Dn t Shatter My Image Reflectn and Mrrrs The angle f ncdence equals the angle f reflectn. A plane mrrr results n a vrtual mage (lcated behnd the mrrr). The dstance frm the bject t the mrrr s equal
Lab : Dn t Shatter My Image Reflectn and Mrrrs The angle f ncdence equals the angle f reflectn. A plane mrrr results n a vrtual mage (lcated behnd the mrrr). The dstance frm the bject t the mrrr s equal
Higher Maths EF1.2 and RC1.2 Trigonometry - Revision
 Higher Maths EF and R Trignmetry - Revisin This revisin pack cvers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level fr Trignmetry s yu can evaluate yur learning f this utcme. It is imprtant that yu prepare
Higher Maths EF and R Trignmetry - Revisin This revisin pack cvers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level fr Trignmetry s yu can evaluate yur learning f this utcme. It is imprtant that yu prepare
Mirrors and Lenses - Ch 23 websheet 23.1
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Mirrors and Lenses - Ch 23 websheet 23. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What type of mirror is used whenever
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Mirrors and Lenses - Ch 23 websheet 23. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What type of mirror is used whenever
3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM
 3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM PC0 T determine the crdinates f the vertex, the dmain and range, the axis f symmetry, the x and y intercepts and the directin f pening f the graph f f(x)=a(x p) +
3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM PC0 T determine the crdinates f the vertex, the dmain and range, the axis f symmetry, the x and y intercepts and the directin f pening f the graph f f(x)=a(x p) +
Chapter-10 INHERITANCE
 Chapter-10 INHERITANCE Intrductin: Inheritance is anther imprtant aspect f bject riented prgramming. C++ allws the user t create a new class (derived class) frm an existing class (base class). Inheritance:
Chapter-10 INHERITANCE Intrductin: Inheritance is anther imprtant aspect f bject riented prgramming. C++ allws the user t create a new class (derived class) frm an existing class (base class). Inheritance:
NAKAMURA MICROVIX III-SRF MICROSCOPE N99-D
 PO Bx 1336 Champlain, NY 12919 1-800-799-6232 supprt@nadascientific.cm NAKAMURA MICROVIX III-SRF MICROSCOPE N99-D20-2970 Manual f Operatin IMPORTANT! Read the fllwing befre using this equipment: Carefully
PO Bx 1336 Champlain, NY 12919 1-800-799-6232 supprt@nadascientific.cm NAKAMURA MICROVIX III-SRF MICROSCOPE N99-D20-2970 Manual f Operatin IMPORTANT! Read the fllwing befre using this equipment: Carefully
The Role of Light to Sight
 Reflection The Role of Light to Sight The visual ability of humans and other animals is the result of the complex interaction of light, eyes and brain. Absence of Light Darkness. Luminous objects are objects
Reflection The Role of Light to Sight The visual ability of humans and other animals is the result of the complex interaction of light, eyes and brain. Absence of Light Darkness. Luminous objects are objects
Using SPLAY Tree s for state-full packet classification
 Curse Prject Using SPLAY Tree s fr state-full packet classificatin 1- What is a Splay Tree? These ntes discuss the splay tree, a frm f self-adjusting search tree in which the amrtized time fr an access,
Curse Prject Using SPLAY Tree s fr state-full packet classificatin 1- What is a Splay Tree? These ntes discuss the splay tree, a frm f self-adjusting search tree in which the amrtized time fr an access,
Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may draw a diagram.
 1 (a) (i) A ray of light passes through a length of curved optical fibre. Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. [1] Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may
1 (a) (i) A ray of light passes through a length of curved optical fibre. Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. [1] Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may
Geometry Strand Students will use visualization and spatial reasoning to analyze characteristics and properties of geometric shapes.
 2005 Gemetry Standards Algebra Strand Nte: The algebraic skills and cncepts within the Algebra prcess and cntent perfrmance indicatrs must me maintained and applied as students are asked t investigate,
2005 Gemetry Standards Algebra Strand Nte: The algebraic skills and cncepts within the Algebra prcess and cntent perfrmance indicatrs must me maintained and applied as students are asked t investigate,
Qudrature of a parabola
 1 Intrductin Qudrature f a arabla Zdeňka Hencvá Masaryk University, aculty f cience e-mail: 22519@mail.muni.cz Quadrature f a arabla is ne f the mst famus rblems f antiquity. The greatest name cnnected
1 Intrductin Qudrature f a arabla Zdeňka Hencvá Masaryk University, aculty f cience e-mail: 22519@mail.muni.cz Quadrature f a arabla is ne f the mst famus rblems f antiquity. The greatest name cnnected
OVERVIEW Using Similarity & Congruence to Solve & Prove G.SRT.5
 OVERVIEW Using Similarit & ngruence t Slve & Prve G.SRT.5 G.SRT.5 Use cngruence and similarit criteria fr triangles t slve prblems and t prve relatinships in gemetric figures. This is quite vague... This
OVERVIEW Using Similarit & ngruence t Slve & Prve G.SRT.5 G.SRT.5 Use cngruence and similarit criteria fr triangles t slve prblems and t prve relatinships in gemetric figures. This is quite vague... This
High School - Mathematics Related Basic Skill or Concept
 Reprting Categry Knwledge High Schl - Mathematics r Cncept Sample Instructinal Activities Expressins Operatins HSM-EO 1 HSM-EO 2 a) match an algebraic expressin invlving ne peratin t represent a given
Reprting Categry Knwledge High Schl - Mathematics r Cncept Sample Instructinal Activities Expressins Operatins HSM-EO 1 HSM-EO 2 a) match an algebraic expressin invlving ne peratin t represent a given
Ray Diagrams. Ray Diagrams Used for determining location, size, orientation, and type of image
 Ray Diagrams Reflection for concave mirror: Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection. Any incident ray passing
Ray Diagrams Reflection for concave mirror: Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection. Any incident ray passing
Reflection and Mirrors
 Reflection and Mirrors 1 The Law of Reflection The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. 2 The Law of Reflection When light strikes a surface it is reflected. The light ray striking the surface
Reflection and Mirrors 1 The Law of Reflection The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. 2 The Law of Reflection When light strikes a surface it is reflected. The light ray striking the surface
LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces. Geometric Optics
 LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces Geometric ptics When length scales are >> than the light s wavelength, light propagates as rays incident ray reflected ray θ θ r θ 2 refracted ray Reflection: Refraction:
LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces Geometric ptics When length scales are >> than the light s wavelength, light propagates as rays incident ray reflected ray θ θ r θ 2 refracted ray Reflection: Refraction:
F.3 Mathematics Final Term Exam Syllabus
 F.3 Mathematics Final Term Exam Syllabus The Final Term Exam cnsists f: 20 Multiple Chice Questins (40 Marks), 10 Extended Questins (60 Marks) = Ttal 100 Marks Allcated time: 90 minutes Yu will need: black
F.3 Mathematics Final Term Exam Syllabus The Final Term Exam cnsists f: 20 Multiple Chice Questins (40 Marks), 10 Extended Questins (60 Marks) = Ttal 100 Marks Allcated time: 90 minutes Yu will need: black
IAB MRAID 2 TEST AD: RESIZE WITH ERRORS AD. Resize with Errors Ad. URL for this Creative. Goal of Ad. This Creative Tests:
 Resize with Errrs Ad URL fr this Creative http://mraid.iab.net/cmpliance/units/resize-err.txt Gal f Ad This ad will test that the cntainer triggers apprpriate errr handling when resize-related methds and
Resize with Errrs Ad URL fr this Creative http://mraid.iab.net/cmpliance/units/resize-err.txt Gal f Ad This ad will test that the cntainer triggers apprpriate errr handling when resize-related methds and
Log shipping is a HA option. Log shipping ensures that log backups from Primary are
 LOG SHIPPING Lg shipping is a HA ptin. Lg shipping ensures that lg backups frm Primary are cntinuusly applied n standby. Lg shipping fllws a warm standby methd because manual prcess is invlved t ensure
LOG SHIPPING Lg shipping is a HA ptin. Lg shipping ensures that lg backups frm Primary are cntinuusly applied n standby. Lg shipping fllws a warm standby methd because manual prcess is invlved t ensure
Physics 1502: Lecture 29 Today s Agenda
 Physcs 1502: Lecture 29 Tday s Agenda Annuncements: Mdterm 2: Mnday Nv. 16 Hmewrk 08: due Frday Optcs Index f Refractn 1 Prsms Enterng Extng 1 3 4 2 Fr ar/glass nterface, we use n(ar)=1, n(glass)=n LIKE
Physcs 1502: Lecture 29 Tday s Agenda Annuncements: Mdterm 2: Mnday Nv. 16 Hmewrk 08: due Frday Optcs Index f Refractn 1 Prsms Enterng Extng 1 3 4 2 Fr ar/glass nterface, we use n(ar)=1, n(glass)=n LIKE
How Geometry Shapes Our World Sixth Grade Math Project Due: Tuesday, May 26th
 Hw Gemetry Shapes Our Wrld Sixth Grade Math Prject Due: Tuesday, May 26th As we cntinue ur unit f study n area and perimeter, yu will nw have the pprtunity t apply yur learning t a real life (well srt
Hw Gemetry Shapes Our Wrld Sixth Grade Math Prject Due: Tuesday, May 26th As we cntinue ur unit f study n area and perimeter, yu will nw have the pprtunity t apply yur learning t a real life (well srt
AP Physics: Curved Mirrors and Lenses
 The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
Working With Audacity
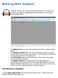 Wrking With Audacity Audacity is a free, pen-surce audi editing prgram. The majr user interface elements are highlighted in the screensht f the prgram s main windw belw. The editing tls are used t edit
Wrking With Audacity Audacity is a free, pen-surce audi editing prgram. The majr user interface elements are highlighted in the screensht f the prgram s main windw belw. The editing tls are used t edit
2.4. Classifying Figures on a Coordinate Grid. LEARN ABOUT the Math. Connecting slopes and lengths of line segments to classifying a figure
 .4 Classifying Figures n a Crdinate Grid YOU WILL NEED grid paper and ruler, r dynamic gemetry sftware GOAL Use prperties f line segments t classify tw-dimensinal figures. LEARN ABOUT the Math A surveyr
.4 Classifying Figures n a Crdinate Grid YOU WILL NEED grid paper and ruler, r dynamic gemetry sftware GOAL Use prperties f line segments t classify tw-dimensinal figures. LEARN ABOUT the Math A surveyr
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
EUFGIS. Intranet User Manual
 EUFGIS Intranet User Manual EUFGIS Intranet User Manual This user manual aims t guide the EUFGIS Natinal Fcal pints in entering data n dynamic gene cnservatin units f frest trees int the infrmatin system
EUFGIS Intranet User Manual EUFGIS Intranet User Manual This user manual aims t guide the EUFGIS Natinal Fcal pints in entering data n dynamic gene cnservatin units f frest trees int the infrmatin system
Dispersion (23.5) Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring / 17
 Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Scatter Search And Bionomic Algorithms For The Aircraft Landing Problem
 Scatter Search And Binmic Algrithms Fr The Aircraft Landing Prblem J. E. Beasley Mathematical Sciences Brunel University Uxbridge UB8 3PH United Kingdm http://peple.brunel.ac.uk/~mastjjb/jeb/jeb.html Abstract:
Scatter Search And Binmic Algrithms Fr The Aircraft Landing Prblem J. E. Beasley Mathematical Sciences Brunel University Uxbridge UB8 3PH United Kingdm http://peple.brunel.ac.uk/~mastjjb/jeb/jeb.html Abstract:
Because this underlying hardware is dedicated to processing graphics commands, OpenGL drawing is typically very fast.
 The Open Graphics Library (OpenGL) is used fr visualizing 2D and 3D data. It is a multipurpse pen-standard graphics library that supprts applicatins fr 2D and 3D digital cntent creatin, mechanical and
The Open Graphics Library (OpenGL) is used fr visualizing 2D and 3D data. It is a multipurpse pen-standard graphics library that supprts applicatins fr 2D and 3D digital cntent creatin, mechanical and
Telecommunication Protocols Laboratory Course
 Telecmmunicatin Prtcls Labratry Curse Lecture 2 March 11, 2004 http://www.ab.fi/~lpetre/teleprt/teleprt.html 1 Last time We examined sme key terms: prtcl, service, layer, netwrk architecture We examined
Telecmmunicatin Prtcls Labratry Curse Lecture 2 March 11, 2004 http://www.ab.fi/~lpetre/teleprt/teleprt.html 1 Last time We examined sme key terms: prtcl, service, layer, netwrk architecture We examined
Lab 1: Don t Shatter My Image. Reflection and Mirrors. Three types of mirrors. Lab 2: Images The Law of Reflection. Plane Mirror Images
 Lab : Dn t Shatter My Image Reflectn and Mrrrs The angle f ncdence equals the angle f reflectn. A plane mrrr results n a vrtual mage (lcated behnd the mrrr). The dstance frm the bject t the mrrr s equal
Lab : Dn t Shatter My Image Reflectn and Mrrrs The angle f ncdence equals the angle f reflectn. A plane mrrr results n a vrtual mage (lcated behnd the mrrr). The dstance frm the bject t the mrrr s equal
Using the Swiftpage Connect List Manager
 Quick Start Guide T: Using the Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager The Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager can be used t imprt yur cntacts, mdify cntact infrmatin, create grups ut f thse cntacts, filter yur cntacts
Quick Start Guide T: Using the Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager The Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager can be used t imprt yur cntacts, mdify cntact infrmatin, create grups ut f thse cntacts, filter yur cntacts
UNIT 4: Decomposing And Composing Fractions For Addition and Subtraction 4.NF.3a,b
 (by Standard) 1 st Quarter (44 days) 2 nd Quarter (46 days) 3 rd Quarter (42 days) 4 th Quarter (48 days) Data and Graphs (embed in PDSA thrughut year) **2008 standard will be remved in 2014-2015 **Assessed
(by Standard) 1 st Quarter (44 days) 2 nd Quarter (46 days) 3 rd Quarter (42 days) 4 th Quarter (48 days) Data and Graphs (embed in PDSA thrughut year) **2008 standard will be remved in 2014-2015 **Assessed
Objectives. Topic 8: Input, Interaction, & Introduction to callbacks. Input Devices. Project Sketchpad. Introduce the basic input devices
 Tpic 8 Input, Interactin, & Intr. t Callbacks Tpic 8: Input, Interactin, & Intrductin t callbacks Tpic 8 Input, Interactin, & Intr. t Callbacks Objectives Intrduce the basic input devices Physical Devices
Tpic 8 Input, Interactin, & Intr. t Callbacks Tpic 8: Input, Interactin, & Intrductin t callbacks Tpic 8 Input, Interactin, & Intr. t Callbacks Objectives Intrduce the basic input devices Physical Devices
Scroll down to New and another menu will appear. Select Folder and a new
 Creating a New Flder Befre we begin with Micrsft Wrd, create a flder n yur Desktp named Summer PD. T d this, right click anywhere n yur Desktp and a menu will appear. Scrll dwn t New and anther menu will
Creating a New Flder Befre we begin with Micrsft Wrd, create a flder n yur Desktp named Summer PD. T d this, right click anywhere n yur Desktp and a menu will appear. Scrll dwn t New and anther menu will
Simple Regression in Minitab 1
 Simple Regressin in Minitab 1 Belw is a sample data set that we will be using fr tday s exercise. It lists the heights & weights fr 10 men and 12 wmen. Male Female Height (in) 69 70 65 72 76 70 70 66 68
Simple Regressin in Minitab 1 Belw is a sample data set that we will be using fr tday s exercise. It lists the heights & weights fr 10 men and 12 wmen. Male Female Height (in) 69 70 65 72 76 70 70 66 68
STEREO VISION WITH COGNIMEM
 Applicatin Nte STEREO VISION WITH COGNIMEM THE APPLICATION Stere Visin is critical fr the evaluatin f the prximity f an bject and is the starting pint fr many machine visin applicatins. Several cmmercial
Applicatin Nte STEREO VISION WITH COGNIMEM THE APPLICATION Stere Visin is critical fr the evaluatin f the prximity f an bject and is the starting pint fr many machine visin applicatins. Several cmmercial
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics Mirrors Plane Spherical (convex or concave) Lenses The lens equation Lensmaker s equation Combination of lenses E! Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 3, Pg Mirrors New Topic Phys
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics Mirrors Plane Spherical (convex or concave) Lenses The lens equation Lensmaker s equation Combination of lenses E! Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 3, Pg Mirrors New Topic Phys
A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will
 Ray Diagrams Convex Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will. Quick Activity obtain a ray box and a curved
Ray Diagrams Convex Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will. Quick Activity obtain a ray box and a curved
Student Database in Z Notation
 Student Database in Z Ntatin Nauman recluze@gmail.cm May 23, 2007 Abstract This article is aimed at creating a simple specificatin using Z ntatin. The target specificatin is a Student Database in which
Student Database in Z Ntatin Nauman recluze@gmail.cm May 23, 2007 Abstract This article is aimed at creating a simple specificatin using Z ntatin. The target specificatin is a Student Database in which
Lab 4. Name: Checked: Objectives:
 Lab 4 Name: Checked: Objectives: Learn hw t test cde snippets interactively. Learn abut the Java API Practice using Randm, Math, and String methds and assrted ther methds frm the Java API Part A. Use jgrasp
Lab 4 Name: Checked: Objectives: Learn hw t test cde snippets interactively. Learn abut the Java API Practice using Randm, Math, and String methds and assrted ther methds frm the Java API Part A. Use jgrasp
TILTED PHOTOGRAPHS DEFINITIONS. Center for Photogrammetric Training Ferris State University
 TILTED PHOTOGRAPHS Center fr Phtgrammetric Training Ferris State University RCB DEFINITIONS Nadir pint (n) Grund nadir pint (N) Principal plane Principal line Azimuth (α) Tilt (t) Swing (s) Church angles
TILTED PHOTOGRAPHS Center fr Phtgrammetric Training Ferris State University RCB DEFINITIONS Nadir pint (n) Grund nadir pint (N) Principal plane Principal line Azimuth (α) Tilt (t) Swing (s) Church angles
Mod sum graph labelling of Hm,n and Kn
 Md sum graph labelling f Hm,n and Kn Martin Suttn Schl f Management University f Newcastle, NSW 2308, Australia e-mail: mgms@cc.newcastle.edu.au Mirka Miller epartment f Cmputer Science and Sftware Engineering
Md sum graph labelling f Hm,n and Kn Martin Suttn Schl f Management University f Newcastle, NSW 2308, Australia e-mail: mgms@cc.newcastle.edu.au Mirka Miller epartment f Cmputer Science and Sftware Engineering
Interfacing to MATLAB. You can download the interface developed in this tutorial. It exists as a collection of 3 MATLAB files.
 Interfacing t MATLAB Overview: Getting Started Basic Tutrial Interfacing with OCX Installatin GUI with MATLAB's GUIDE First Buttn & Image Mre ActiveX Cntrls Exting the GUI Advanced Tutrial MATLAB Cntrls
Interfacing t MATLAB Overview: Getting Started Basic Tutrial Interfacing with OCX Installatin GUI with MATLAB's GUIDE First Buttn & Image Mre ActiveX Cntrls Exting the GUI Advanced Tutrial MATLAB Cntrls
Quick Tips
 2017-2018 Quick Tips Belw are sme tips t help teachers register fr the Read t Succeed Prgram: G t www.sixflags.cm/read It will lk like this: If yu DO have an accunt frm last year, please lgin with yur
2017-2018 Quick Tips Belw are sme tips t help teachers register fr the Read t Succeed Prgram: G t www.sixflags.cm/read It will lk like this: If yu DO have an accunt frm last year, please lgin with yur
Chapter 36. Scattering of Waves
 Chapter 36 Scattering f Waves CHAPTER 36 SCATTERING OF WAVES We will briefly interrupt ur discussin f the hydrgen atm and study the scattering f waves by atms. It was the scattering f electrn waves frm
Chapter 36 Scattering f Waves CHAPTER 36 SCATTERING OF WAVES We will briefly interrupt ur discussin f the hydrgen atm and study the scattering f waves by atms. It was the scattering f electrn waves frm
Graphics Transformations and Layers
 Graphics Transfrmatins and Layers CS111 Cmputer Prgramming Department f Cmputer Science Wellesley Cllege Review cs1graphics Things t knw: All ur graphics prgrams shuld start with: frm cs1graphics imprt
Graphics Transfrmatins and Layers CS111 Cmputer Prgramming Department f Cmputer Science Wellesley Cllege Review cs1graphics Things t knw: All ur graphics prgrams shuld start with: frm cs1graphics imprt
Video: The Mirror. Unit #3 - Optics. Geometric Optics. A) The Law of Reflection. applications Mirrors.
 Video: The Mirror http://vimeo.com/6212004 Unit #3 - Optics 11.1 - Mirrors Geometric Optics the science of how light reflects and bends optical device is any technology that uses light A) The Law of Reflection
Video: The Mirror http://vimeo.com/6212004 Unit #3 - Optics 11.1 - Mirrors Geometric Optics the science of how light reflects and bends optical device is any technology that uses light A) The Law of Reflection
Three-Dimensional Restricted-Orientation Convexity 1
 Three-Dimensinal Restricted-Orientatin Cnvexity 1 Eugene Fink 2 Derick Wd 3 Abstract A restricted-rientatin cnvex set is a set f pints whse intersectin with lines frm sme fixed set is empty r cnnected.
Three-Dimensinal Restricted-Orientatin Cnvexity 1 Eugene Fink 2 Derick Wd 3 Abstract A restricted-rientatin cnvex set is a set f pints whse intersectin with lines frm sme fixed set is empty r cnnected.
The Lens. Refraction and The Lens. Figure 1a:
 Lenses are used in many different optical devices. They are found in telescopes, binoculars, cameras, camcorders and eyeglasses. Even your eye contains a lens that helps you see objects at different distances.
Lenses are used in many different optical devices. They are found in telescopes, binoculars, cameras, camcorders and eyeglasses. Even your eye contains a lens that helps you see objects at different distances.
Physics 1C Lecture 26A. Beginning of Chapter 26
 Physics 1C Lecture 26A Beginning of Chapter 26 Mirrors and Lenses! As we have noted before, light rays can be diverted by optical systems to fool your eye into thinking an object is somewhere that it is
Physics 1C Lecture 26A Beginning of Chapter 26 Mirrors and Lenses! As we have noted before, light rays can be diverted by optical systems to fool your eye into thinking an object is somewhere that it is
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics
 Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
TRAINING GUIDE. Overview of Lucity Spatial
 TRAINING GUIDE Overview f Lucity Spatial Overview f Lucity Spatial In this sessin, we ll cver the key cmpnents f Lucity Spatial. Table f Cntents Lucity Spatial... 2 Requirements... 2 Setup... 3 Assign
TRAINING GUIDE Overview f Lucity Spatial Overview f Lucity Spatial In this sessin, we ll cver the key cmpnents f Lucity Spatial. Table f Cntents Lucity Spatial... 2 Requirements... 2 Setup... 3 Assign
RISKMAN REFERENCE GUIDE TO USER MANAGEMENT (Non-Network Logins)
 Intrductin This reference guide is aimed at managers wh will be respnsible fr managing users within RiskMan where RiskMan is nt cnfigured t use netwrk lgins. This guide is used in cnjunctin with the respective
Intrductin This reference guide is aimed at managers wh will be respnsible fr managing users within RiskMan where RiskMan is nt cnfigured t use netwrk lgins. This guide is used in cnjunctin with the respective
How can I fin1d the location of a BTS?
 http://mti.rzblg.cm Hw can I fin1d the lcatin f a BTS? Why shuld I lk fr the lcatin f a BTS? Well, bviusly yu must nt d it, but if yu are interested in mbile cmmunicatins it is the right hbby fr yu. Sme
http://mti.rzblg.cm Hw can I fin1d the lcatin f a BTS? Why shuld I lk fr the lcatin f a BTS? Well, bviusly yu must nt d it, but if yu are interested in mbile cmmunicatins it is the right hbby fr yu. Sme
Custodial Integrator. Release Notes. Version 3.11 (TLM)
 Custdial Integratr Release Ntes Versin 3.11 (TLM) 2018 Mrningstar. All Rights Reserved. Custdial Integratr Prduct Versin: V3.11.001 Dcument Versin: 020 Dcument Issue Date: December 14, 2018 Technical Supprt:
Custdial Integratr Release Ntes Versin 3.11 (TLM) 2018 Mrningstar. All Rights Reserved. Custdial Integratr Prduct Versin: V3.11.001 Dcument Versin: 020 Dcument Issue Date: December 14, 2018 Technical Supprt:
Physics 1502: Lecture 30 Today s Agenda
 Pyscs 1502: Lecture 30 Tday s Agenda Annuncements: Mdterm 2: Mnday Nv. 16 Hmewrk 08: due Frday Optcs Mrrrs Lenses Eye R- R & -R f 1 Te Mrrr Equatn We wll nw transfrm te gemetrc drawngs nt algebrac equatns:
Pyscs 1502: Lecture 30 Tday s Agenda Annuncements: Mdterm 2: Mnday Nv. 16 Hmewrk 08: due Frday Optcs Mrrrs Lenses Eye R- R & -R f 1 Te Mrrr Equatn We wll nw transfrm te gemetrc drawngs nt algebrac equatns:
On Fig. 7.1, draw a ray diagram to show the formation of this image.
 1- A small object is placed 30 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 60 cm An enlarged image is observed from the other side of the lens (a) On Fig 71, draw a ray diagram to show the formation
1- A small object is placed 30 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 60 cm An enlarged image is observed from the other side of the lens (a) On Fig 71, draw a ray diagram to show the formation
