What is an edge? Paint. Depth discontinuity. Material change. Texture boundary
|
|
|
- Jonah Goodwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EDGES AND TEXTURES The slides are from several sources through James Hays (Brown); Srinivasa Narasimhan (CMU); Silvio Savarese (U. of Michigan); Bill Freeman and Antonio Torralba (MIT), including their own slides.
2 What is an edge?
3 What is an edge? Paint Depth discontinuity Material change Texture boundary 32
4 Characterizing edges An edge is a place of rapid change in the image intensity function image intensity function (along horizontal scanline) first derivative edges correspond to extrema of derivative
5 Partial derivatives of an image f ( x, y ) f ( x, y ) x y -1 1 or or 1-1
6 Image gradient The gradient of an image: T T T T The gradient points in the direction of most rapid increase in intensity How does this direction relate to the direction of the edge? The gradient direction is given by The edge strength is given by the gradient magnitude Source: Steve Seitz
7 Effects of noise Consider a single row or column of the image Plotting intensity as a function of position gives a signal Where is the edge? Source: S. Seitz
8 Solution: smooth first f g f* g d ( f g) dx To find edges, look for peaks in ( f g) d dx Source: S. Seitz
9 Derivative theorem of convolution Differentiation is convolution, and convolution is associative: d d ( f g) = f g dx dx This saves us one operation: f d dx g f d dx g Source: S. Seitz
10 Derivative of Gaussian filter x-direction y-direction These filters are separable.
11 Derivative of Gaussian filter x-direction y-direction Which one finds horizontal/vertical edges? vertical edges horizontal edges
12 Scale of Gaussian derivative filter 1 pixel 3 pixels 7 pixels Smoothed derivative removes noise, but blurs edge. Also finds edges at different scales Source: D. Forsyth
13 Review: Smoothing vs. derivative filters Smoothing filters Gaussian: remove high-frequency components; l filt low-pass filter. Can the values of a smoothing filter be negative? Gaussian = No. What should the values sum to of the filter? One: constant regions are not affected by the filter. Derivative filters Derivatives of Gaussian. Can the values of a derivative filter be negative? Yes. What should the values sum to of the filter? Zero: no response in constant regions. High absolute value at points of high contrast.
14 Canny Edge Detection Most widely used edge detector in computer vision. First derivative of the Gaussian closely approximates the operator that optimizes the product of signal-tonoise ratio and localization. Analysis based on "step-edges" corrupted by "additive Gaussian noise". Least squares with binomial weights ~~~ edge detector. J. Canny, A Computational Approach To Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 8: , 1986.
15 Edge Detection Criteria Criteria for optimal edge detection (Canny 86): Good detection accuracy: minimize the probability of false positives (detecting spurious edges caused by noise), false negatives (missing real edges) Good localization: edges must be detected as close as possible to the true edges. Single response constraint: minimize the number of local maxima around the true edge (i.e. detector must return single point for each true edge point)
16 Examples... valid mostly for straight edges... True edge Poor robustness to noise Poor localization Too many responses
17 Steps: Canny Edge Detection 1+2. Gaussian smoothing together with derivative of Gaussian (~discrete) 3. Find magnitude and orientation of gradient 4. Extract edge points: Non-maximum suppression 5. Linking and thresholding: Hysteresis MATLAB: edge(i, canny )
18 First Two Steps Smoothing I y) g(x, ' I ), ( y x e y x g I g I g S y x g g y g x g g I g g y x I g I g y x Derivative Can be done with two one-dimensional filters. 2
19 two dimensional Gaussian h = g h x (x, y) = h(x, y) x = x x 2 +y 2 2πσ 4 e 2σ 2 h y (x, y) = h(x, y) y x 2 +y y 2 2πσ 4 e 2σ 2 = Scale
20 Example: I S x S y S g I g I S S x S y = gradient vector
21 sigma 1 pixel 2 pixels Increased smoothing: Eliminates noise edges. Makes edges smoother and thicker. Removes fine detail.
22 Third Step magnitude and direction of S S x S y magnitude direction (S 2 x tan S 1 2 y S S y x ) image gradient magnitude
23 Non-maximum suppression along the direction of gradient Fourth Step At q, we have a maximum if the value is larger than those at both p and at r. Interpolate to get these values. Source: D. Forsyth
24 Example: Non-Maximum Suppression Original image Gradient magnitude Non-maxima suppressed courtesy of G. Loy Slide credit: Christopher Rasmussen
25 high threshold strong edges only low threshold weak edges too
26 Fifth Step: Hysteresis Thresholding Hysteresis: no LOW maybe HIGH sure. Maintain two thresholds k high and k low Use k high to find strong edges to start edge chain. Use k low to find weak edges along the edge chain. Typical ratio of thresholds is roughly k high / k low = 2-2.5
27 Closing edge gaps Gradient magnitude Check that maximum value of gradient value is sufficiently large and... t 1 t 2... use hysteresis. use a high threshold to start edge curves and a low threshold to continue them. Not an edge Pixel number in linked list along gradient maxima Labeled as edge maybe a line
28 Example gap is gone Original image Strong + connected weak edges Strong edges only Weak edges too courtesy of G. Loy
29 Effect of (Gaussian kernel spread/size) original Canny with Canny with The choice of depends on desired behavior large detects large scale edges small detects fine features Source: S. Seitz
30 Example of Canny edge detection original image (Lena)
31 Compute Gradients (DoG) X-Derivative of Gaussian Y-Derivative of Gaussian Gradient Magnitude and orientation
32 Before non-max suppression...
33 ...after non-max suppression
34 Before the hysteresis thresholding Threshold at low/high levels to get weak/strong edge pixels Do connected components, starting from strong edge pixels
35 Final Canny Edges
36 A hidden advantage for the human observer. She/he first see the original image and only after the edges detected. What happens if she/he cannot see the original image first and therefore can rely on it? This is how all the computer vision algorithms has to work... all the time!
37
38
39 Learning to detect boundaries image human segmentation gradient magnitude Berkeley segmentation database:
40 - All are 3D objects in 2D projections! - The top-down recognition is very ad-hoc now. Edge detection is only the very beginning. - Edges are based on local, low-level pixel information. Much more is needed to detect boundaries or to recognize objects.
41 Representing Texture 3D is "present" and the textures are therefore more complex Source: Forsyth
42 Texture and Material ~2D
43 Texture and Orientation ~2D
44 Texture and Scale ~2D 3D
45 Representation of sets 3D ~2D
46 What is texture? Regular or stochastic patterns caused by orderly markings of a small unit. 3D textures are much more complicated in 2D representation. Will highlight only 2D textures. Even there the representations are far from perfect....an example:
47 Overcomplete representation: filter banks Leung and Malik (2001); 48 anisotropic and isotropic filters Gaussian and first derivative, Laplacian sensitive to texture rotation LM Filter Bank x sigma y 3 sigma 36 elongated filters: 3 scales; 6 orientations; first/second derivative Gaussian 8 Laplacian (difference of Gaussian); 4 low-pass Gaussian Code for filter banks:
48 Can you match the texture to the response? Filters Record simple statistics (e.g., mean, std.) of absolute filter responses. A 1 B 2 C 3 Mean abs responses
49 Filters Record simple statistics (e.g., mean, std.) of absolute filter responses A 1 B B 2 C C 3 A Mean abs responses
50 Another representation of textures Take absolute values of the output at each pixel. Lighter pixels, stronger response. 0 middle lighter + how coarse is the scale is important
51 Low-level edges and perceived contours Background Texture Shadows Kristen Grauman, UT-Austin...the reality is more complicated...
Edge detection. Goal: Identify sudden. an image. Ideal: artist s line drawing. object-level knowledge)
 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels Ideal: artist
Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels Ideal: artist
Edge and Texture. CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University
 Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
Edge Detection CSC 767
 Edge Detection CSC 767 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels
Edge Detection CSC 767 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels
Review of Filtering. Filtering in frequency domain
 Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
Edge Detection. CSE 576 Ali Farhadi. Many slides from Steve Seitz and Larry Zitnick
 Edge Detection CSE 576 Ali Farhadi Many slides from Steve Seitz and Larry Zitnick Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity
Edge Detection CSE 576 Ali Farhadi Many slides from Steve Seitz and Larry Zitnick Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity
Edge detection. Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek
 Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image
Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
 The image part with relationship ID rid2 was not found in the file. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture 6 Wavelets (cont), Lines and edges Tammy Riklin Raviv Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion
The image part with relationship ID rid2 was not found in the file. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture 6 Wavelets (cont), Lines and edges Tammy Riklin Raviv Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion
Edge Detection. CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy. René Magritte, Decalcomania. Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins
 Edge Detection René Magritte, Decalcomania Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy Discontinuities in Intensity Source: Robert Collins Origin
Edge Detection René Magritte, Decalcomania Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy Discontinuities in Intensity Source: Robert Collins Origin
Edge detection. Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek
 Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, edges carry most of the semantic and shape information
Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, edges carry most of the semantic and shape information
Prof. Feng Liu. Winter /15/2019
 Prof. Feng Liu Winter 2019 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~fliu/courses/cs410/ 01/15/2019 Last Time Filter 2 Today More on Filter Feature Detection 3 Filter Re-cap noisy image naïve denoising Gaussian blur better
Prof. Feng Liu Winter 2019 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~fliu/courses/cs410/ 01/15/2019 Last Time Filter 2 Today More on Filter Feature Detection 3 Filter Re-cap noisy image naïve denoising Gaussian blur better
Edge Detection. Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City
 Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
Edge and corner detection
 Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Edges and Binary Images
 CS 699: Intro to Computer Vision Edges and Binary Images Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 5, 205 Plan for today Edge detection Binary image analysis Homework Due on 9/22, :59pm
CS 699: Intro to Computer Vision Edges and Binary Images Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 5, 205 Plan for today Edge detection Binary image analysis Homework Due on 9/22, :59pm
Solution: filter the image, then subsample F 1 F 2. subsample blur subsample. blur
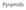 Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors
 #1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
#1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
CS 4495 Computer Vision. Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges. Aaron Bobick. School of Interactive Computing. Templates/Edges
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
CS5670: Computer Vision
 CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 2: Edge detection From Sandlot Science Announcements Project 1 (Hybrid Images) is now on the course webpage (see Projects link) Due Wednesday, Feb 15, by 11:59pm
CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 2: Edge detection From Sandlot Science Announcements Project 1 (Hybrid Images) is now on the course webpage (see Projects link) Due Wednesday, Feb 15, by 11:59pm
Edge Detection. Today s reading. Cipolla & Gee on edge detection (available online) From Sandlot Science
 Edge Detection From Sandlot Science Today s reading Cipolla & Gee on edge detection (available online) Project 1a assigned last Friday due this Friday Last time: Cross-correlation Let be the image, be
Edge Detection From Sandlot Science Today s reading Cipolla & Gee on edge detection (available online) Project 1a assigned last Friday due this Friday Last time: Cross-correlation Let be the image, be
Edge Detection. Announcements. Edge detection. Origin of Edges. Mailing list: you should have received messages
 Announcements Mailing list: csep576@cs.washington.edu you should have received messages Project 1 out today (due in two weeks) Carpools Edge Detection From Sandlot Science Today s reading Forsyth, chapters
Announcements Mailing list: csep576@cs.washington.edu you should have received messages Project 1 out today (due in two weeks) Carpools Edge Detection From Sandlot Science Today s reading Forsyth, chapters
Image Analysis. Edge Detection
 Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Image gradients and edges April 11 th, 2017
 4//27 Image gradients and edges April th, 27 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
4//27 Image gradients and edges April th, 27 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April 10 th, 2018
 Image gradients and edges April th, 28 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April th, 28 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image Analysis. Edge Detection
 Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Edge Detection. EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro
 Edge Detection EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) 2 Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity illumination discontinuity Edges are caused
Edge Detection EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) 2 Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity illumination discontinuity Edges are caused
Lecture 6: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
#1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement - Filtering
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement - Filtering Derivative Derivative is defined as a rate of change. Discrete Derivative Finite Distance Example Derivatives in 2-dimension Derivatives of Images
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement - Filtering Derivative Derivative is defined as a rate of change. Discrete Derivative Finite Distance Example Derivatives in 2-dimension Derivatives of Images
CS 2770: Computer Vision. Edges and Segments. Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017
 CS 2770: Computer Vision Edges and Segments Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017 Edges vs Segments Figure adapted from J. Hays Edges vs Segments Edges More low-level Don t
CS 2770: Computer Vision Edges and Segments Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017 Edges vs Segments Figure adapted from J. Hays Edges vs Segments Edges More low-level Don t
Other Linear Filters CS 211A
 Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours. Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators Laplacian
CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators Laplacian
Does everyone have an override code?
 Does everyone have an override code? Project 1 due Friday 9pm Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect
Does everyone have an override code? Project 1 due Friday 9pm Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect
Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to linear, associative operators). Images
 Images (we will, eventually, come back to imaging geometry. But, now that we know how images come from the world, we will examine operations on images). Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to
Images (we will, eventually, come back to imaging geometry. But, now that we know how images come from the world, we will examine operations on images). Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to
Local Image preprocessing (cont d)
 Local Image preprocessing (cont d) 1 Outline - Edge detectors - Corner detectors - Reading: textbook 5.3.1-5.3.5 and 5.3.10 2 What are edges? Edges correspond to relevant features in the image. An edge
Local Image preprocessing (cont d) 1 Outline - Edge detectors - Corner detectors - Reading: textbook 5.3.1-5.3.5 and 5.3.10 2 What are edges? Edges correspond to relevant features in the image. An edge
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks
 Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Reminder Project due Friday Fourier Bases Teases away fast vs. slow changes in the image. This change
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Reminder Project due Friday Fourier Bases Teases away fast vs. slow changes in the image. This change
Image gradients and edges
 Image gradients and edges April 7 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS0 due this Friday Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April 7 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS0 due this Friday Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours. Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators From Edges
CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators From Edges
Image gradients and edges
 Image gradients and edges Thurs Sept 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Last time Various models for image noise Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, remov ing noise Box filter Gaussian
Image gradients and edges Thurs Sept 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Last time Various models for image noise Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, remov ing noise Box filter Gaussian
Edge Detection Lecture 03 Computer Vision
 Edge Detection Lecture 3 Computer Vision Suggested readings Chapter 5 Linda G. Shapiro and George Stockman, Computer Vision, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall,. Chapter David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Edge Detection Lecture 3 Computer Vision Suggested readings Chapter 5 Linda G. Shapiro and George Stockman, Computer Vision, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall,. Chapter David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely
 CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 2: Edge detection From Sandlot Science Announcements Project 1 released, due Friday, September 7 1 Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts
CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 2: Edge detection From Sandlot Science Announcements Project 1 released, due Friday, September 7 1 Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts
Lecture 4: Finding lines: from detection to model fitting
 Lecture 4: Finding lines: from detection to model fitting Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today Edge detection Canny edge detector Line fitting Hough Transform RANSAC (Problem
Lecture 4: Finding lines: from detection to model fitting Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today Edge detection Canny edge detector Line fitting Hough Transform RANSAC (Problem
Edge detection. Convert a 2D image into a set of curves. Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels
 Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
2%34 #5 +,,% ! # %& ()% #% +,,%. & /%0%)( 1 ! # %& % %()# +(& ,.+/ +&0%//#/ &
 ! # %& ()% #% +,,%. & /%0%)( 1 2%34 #5 +,,%! # %& % %()# +(&,.+/ +&0%//#/ & & Many slides in this lecture are due to other authors; they are credited on the bottom right Topics of This Lecture Problem
! # %& ()% #% +,,%. & /%0%)( 1 2%34 #5 +,,%! # %& % %()# +(&,.+/ +&0%//#/ & & Many slides in this lecture are due to other authors; they are credited on the bottom right Topics of This Lecture Problem
Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami
 Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami Adaptive Systems Lab The University of Aizu Overview Introduction What is Vision Processing? Basic Knowledge
Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami Adaptive Systems Lab The University of Aizu Overview Introduction What is Vision Processing? Basic Knowledge
Straight Lines and Hough
 09/30/11 Straight Lines and Hough Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Lana Lazebnik, Steve Seitz, David Forsyth, David Lowe, Fei-Fei Li Project 1 A few project highlights
09/30/11 Straight Lines and Hough Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Lana Lazebnik, Steve Seitz, David Forsyth, David Lowe, Fei-Fei Li Project 1 A few project highlights
Computer Vision I. Announcement. Corners. Edges. Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 11
 Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Biomedical Image Analysis. Point, Edge and Line Detection
 Biomedical Image Analysis Point, Edge and Line Detection Contents: Point and line detection Advanced edge detection: Canny Local/regional edge processing Global processing: Hough transform BMIA 15 V. Roth
Biomedical Image Analysis Point, Edge and Line Detection Contents: Point and line detection Advanced edge detection: Canny Local/regional edge processing Global processing: Hough transform BMIA 15 V. Roth
Filtering Images. Contents
 Image Processing and Data Visualization with MATLAB Filtering Images Hansrudi Noser June 8-9, 010 UZH, Multimedia and Robotics Summer School Noise Smoothing Filters Sigmoid Filters Gradient Filters Contents
Image Processing and Data Visualization with MATLAB Filtering Images Hansrudi Noser June 8-9, 010 UZH, Multimedia and Robotics Summer School Noise Smoothing Filters Sigmoid Filters Gradient Filters Contents
Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection
 Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection By Dr. Yu Cao Department of Computer Science The University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, MA 01854, USA Part of the slides
Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection By Dr. Yu Cao Department of Computer Science The University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, MA 01854, USA Part of the slides
Edge detection. Gradient-based edge operators
 Edge detection Gradient-based edge operators Prewitt Sobel Roberts Laplacian zero-crossings Canny edge detector Hough transform for detection of straight lines Circle Hough Transform Digital Image Processing:
Edge detection Gradient-based edge operators Prewitt Sobel Roberts Laplacian zero-crossings Canny edge detector Hough transform for detection of straight lines Circle Hough Transform Digital Image Processing:
[ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16
![[ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16 [ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16](/thumbs/89/98496315.jpg) Review Edges and Binary Images Tuesday, Sept 6 Thought question: how could we compute a temporal gradient from video data? What filter is likely to have produced this image output? original filtered output
Review Edges and Binary Images Tuesday, Sept 6 Thought question: how could we compute a temporal gradient from video data? What filter is likely to have produced this image output? original filtered output
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014
 SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
Segmentation and Grouping
 Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Image Processing
 Image Processing 159.731 Canny Edge Detection Report Syed Irfanullah, Azeezullah 00297844 Danh Anh Huynh 02136047 1 Canny Edge Detection INTRODUCTION Edges Edges characterize boundaries and are therefore
Image Processing 159.731 Canny Edge Detection Report Syed Irfanullah, Azeezullah 00297844 Danh Anh Huynh 02136047 1 Canny Edge Detection INTRODUCTION Edges Edges characterize boundaries and are therefore
Lecture 10 Detectors and descriptors
 Lecture 10 Detectors and descriptors Properties of detectors Edge detectors Harris DoG Properties of detectors SIFT Shape context Silvio Savarese Lecture 10-26-Feb-14 From the 3D to 2D & vice versa P =
Lecture 10 Detectors and descriptors Properties of detectors Edge detectors Harris DoG Properties of detectors SIFT Shape context Silvio Savarese Lecture 10-26-Feb-14 From the 3D to 2D & vice versa P =
Filtering in frequency domain
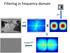 Filtering in frequency domain FFT FFT = Inverse FFT Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert
Filtering in frequency domain FFT FFT = Inverse FFT Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert
Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image
 Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image H.S. Bhadauria 1, Annapurna Singh 2, Anuj Kumar 3 Govind Ballabh Pant Engineering College ( Pauri garhwal),computer Science and Engineering
Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image H.S. Bhadauria 1, Annapurna Singh 2, Anuj Kumar 3 Govind Ballabh Pant Engineering College ( Pauri garhwal),computer Science and Engineering
Edge Detection. CS664 Computer Vision. 3. Edges. Several Causes of Edges. Detecting Edges. Finite Differences. The Gradient
 Edge Detection CS664 Computer Vision. Edges Convert a gray or color image into set of curves Represented as binary image Capture properties of shapes Dan Huttenlocher Several Causes of Edges Sudden changes
Edge Detection CS664 Computer Vision. Edges Convert a gray or color image into set of curves Represented as binary image Capture properties of shapes Dan Huttenlocher Several Causes of Edges Sudden changes
Neighborhood operations
 Neighborhood operations Generate an output pixel on the basis of the pixel and its neighbors Often involve the convolution of an image with a filter kernel or mask g ( i, j) = f h = f ( i m, j n) h( m,
Neighborhood operations Generate an output pixel on the basis of the pixel and its neighbors Often involve the convolution of an image with a filter kernel or mask g ( i, j) = f h = f ( i m, j n) h( m,
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Applications of Image Filters
 02/04/0 Applications of Image Filters Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Review: Image filtering g[, ] f [.,.] h[.,.] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 90
02/04/0 Applications of Image Filters Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Review: Image filtering g[, ] f [.,.] h[.,.] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 90
Edge detection. Stefano Ferrari. Università degli Studi di Milano Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I)
 Edge detection Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I) academic year 2011 2012 Image segmentation Several image processing
Edge detection Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I) academic year 2011 2012 Image segmentation Several image processing
Image features. Image Features
 Image features Image features, such as edges and interest points, provide rich information on the image content. They correspond to local regions in the image and are fundamental in many applications in
Image features Image features, such as edges and interest points, provide rich information on the image content. They correspond to local regions in the image and are fundamental in many applications in
Announcements. Edge Detection. An Isotropic Gaussian. Filters are templates. Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3.
 Announcements Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 9 Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3. Reading from textbook An Isotropic Gaussian The picture
Announcements Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 9 Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3. Reading from textbook An Isotropic Gaussian The picture
Edge and local feature detection - 2. Importance of edge detection in computer vision
 Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 3: Edges
 EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 3: Edges The goal of this fourth lab is to ˆ Understanding what are edges, and different ways to detect them ˆ Understand different types of edge detectors - intensity,
EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 3: Edges The goal of this fourth lab is to ˆ Understanding what are edges, and different ways to detect them ˆ Understand different types of edge detectors - intensity,
Computer Vision Course Lecture 04. Template Matching Image Pyramids. Ceyhun Burak Akgül, PhD cba-research.com. Spring 2015 Last updated 11/03/2015
 Computer Vision Course Lecture 04 Template Matching Image Pyramids Ceyhun Burak Akgül, PhD cba-research.com Spring 2015 Last updated 11/03/2015 Photo credit: Olivier Teboul vision.mas.ecp.fr/personnel/teboul
Computer Vision Course Lecture 04 Template Matching Image Pyramids Ceyhun Burak Akgül, PhD cba-research.com Spring 2015 Last updated 11/03/2015 Photo credit: Olivier Teboul vision.mas.ecp.fr/personnel/teboul
Filtering and Edge Detection. Computer Vision I. CSE252A Lecture 10. Announcement
 Filtering and Edge Detection CSE252A Lecture 10 Announcement HW1graded, will be released later today HW2 assigned, due Wed. Nov. 7 1 Image formation: Color Channel k " $ $ # $ I r I g I b % " ' $ ' = (
Filtering and Edge Detection CSE252A Lecture 10 Announcement HW1graded, will be released later today HW2 assigned, due Wed. Nov. 7 1 Image formation: Color Channel k " $ $ # $ I r I g I b % " ' $ ' = (
Concepts in. Edge Detection
 Concepts in Edge Detection Dr. Sukhendu Das Deptt. of Computer Science and Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Chennai 600036, India. http://www.cs.iitm.ernet.in/~sdas Email: sdas@iitm.ac.in
Concepts in Edge Detection Dr. Sukhendu Das Deptt. of Computer Science and Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Chennai 600036, India. http://www.cs.iitm.ernet.in/~sdas Email: sdas@iitm.ac.in
Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching
 Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching Lecture 08 Computer Vision Material Citations Dr George Stockman Professor Emeritus, Michigan State University Dr David Lowe Professor, University of British
Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching Lecture 08 Computer Vision Material Citations Dr George Stockman Professor Emeritus, Michigan State University Dr David Lowe Professor, University of British
A Robust Method for Circle / Ellipse Extraction Based Canny Edge Detection
 International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2015, PP 49-57 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) A Robust Method for Circle / Ellipse
International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2015, PP 49-57 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) A Robust Method for Circle / Ellipse
Announcements. Edges. Last Lecture. Gradients: Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge Detection, Lines. Intro Computer Vision. CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Previously. Edge detection. Today. Thresholding. Gradients -> edges 2/1/2011. Edges and Binary Image Analysis
 2//20 Previously Edges and Binary Image Analysis Mon, Jan 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
2//20 Previously Edges and Binary Image Analysis Mon, Jan 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
Edges, interpolation, templates. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth)
 Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Gradients and edges edges are points of large gradient magnitude edge detection strategy 1. determine
Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Gradients and edges edges are points of large gradient magnitude edge detection strategy 1. determine
Boundaries and Sketches
 Boundaries and Sketches Szeliski 4.2 Computer Vision James Hays Many slides from Michael Maire, Jitendra Malek Today s lecture Segmentation vs Boundary Detection Why boundaries / Grouping? Recap: Canny
Boundaries and Sketches Szeliski 4.2 Computer Vision James Hays Many slides from Michael Maire, Jitendra Malek Today s lecture Segmentation vs Boundary Detection Why boundaries / Grouping? Recap: Canny
Feature descriptors. Alain Pagani Prof. Didier Stricker. Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking
 Feature descriptors Alain Pagani Prof. Didier Stricker Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking 1 Overview Previous lectures: Feature extraction Today: Gradiant/edge Points (Kanade-Tomasi + Harris)
Feature descriptors Alain Pagani Prof. Didier Stricker Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking 1 Overview Previous lectures: Feature extraction Today: Gradiant/edge Points (Kanade-Tomasi + Harris)
Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 12 th, 2018
 4/2/208 Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 2 th, 208 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Previously Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
4/2/208 Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 2 th, 208 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Previously Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 2012
 CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 01 Dr. Mubarak Shah Univ. of Central Florida Office 47-F HEC Lecture-5 SIFT: David Lowe, UBC SIFT - Key Point Extraction Stands for scale invariant feature transform Patented
CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 01 Dr. Mubarak Shah Univ. of Central Florida Office 47-F HEC Lecture-5 SIFT: David Lowe, UBC SIFT - Key Point Extraction Stands for scale invariant feature transform Patented
Edges and Binary Image Analysis. Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin. Today. Edge detection and matching
 /25/207 Edges and Binary Image Analysis Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Today Edge detection and matching process the image gradient to find curves/contours comparing contours Binary image analysis
/25/207 Edges and Binary Image Analysis Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Today Edge detection and matching process the image gradient to find curves/contours comparing contours Binary image analysis
Filtering Applications & Edge Detection. GV12/3072 Image Processing.
 Filtering Applications & Edge Detection GV12/3072 1 Outline Sampling & Reconstruction Revisited Anti-Aliasing Edges Edge detection Simple edge detector Canny edge detector Performance analysis Hough Transform
Filtering Applications & Edge Detection GV12/3072 1 Outline Sampling & Reconstruction Revisited Anti-Aliasing Edges Edge detection Simple edge detector Canny edge detector Performance analysis Hough Transform
Types of Edges. Why Edge Detection? Types of Edges. Edge Detection. Gradient. Edge Detection
 Why Edge Detection? How can an algorithm extract relevant information from an image that is enables the algorithm to recognize objects? The most important information for the interpretation of an image
Why Edge Detection? How can an algorithm extract relevant information from an image that is enables the algorithm to recognize objects? The most important information for the interpretation of an image
Ulrik Söderström 16 Feb Image Processing. Segmentation
 Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09. Image enhancement. Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters
 EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Image enhancement Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Image enhancement Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image
Line, edge, blob and corner detection
 Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 1 / 92 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Jim Little little@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2016/2017 Term 2 2 / 92 Menu February 14, 2017 Topics:
1 / 92 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Jim Little little@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2016/2017 Term 2 2 / 92 Menu February 14, 2017 Topics:
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB
 Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Image Credit: https://docs.adaptive-vision.com/4.7/studio/machine_vision_guide/templatematching.html Lecture 9: Template Matching (cont.) and Scaled Representations ( unless otherwise
CPSC 425: Computer Vision Image Credit: https://docs.adaptive-vision.com/4.7/studio/machine_vision_guide/templatematching.html Lecture 9: Template Matching (cont.) and Scaled Representations ( unless otherwise
SURVEY ON IMAGE PROCESSING IN THE FIELD OF DE-NOISING TECHNIQUES AND EDGE DETECTION TECHNIQUES ON RADIOGRAPHIC IMAGES
 SURVEY ON IMAGE PROCESSING IN THE FIELD OF DE-NOISING TECHNIQUES AND EDGE DETECTION TECHNIQUES ON RADIOGRAPHIC IMAGES 1 B.THAMOTHARAN, 2 M.MENAKA, 3 SANDHYA VAIDYANATHAN, 3 SOWMYA RAVIKUMAR 1 Asst. Prof.,
SURVEY ON IMAGE PROCESSING IN THE FIELD OF DE-NOISING TECHNIQUES AND EDGE DETECTION TECHNIQUES ON RADIOGRAPHIC IMAGES 1 B.THAMOTHARAN, 2 M.MENAKA, 3 SANDHYA VAIDYANATHAN, 3 SOWMYA RAVIKUMAR 1 Asst. Prof.,
Topic 4 Image Segmentation
 Topic 4 Image Segmentation What is Segmentation? Why? Segmentation important contributing factor to the success of an automated image analysis process What is Image Analysis: Processing images to derive
Topic 4 Image Segmentation What is Segmentation? Why? Segmentation important contributing factor to the success of an automated image analysis process What is Image Analysis: Processing images to derive
An Algorithm for Blurred Thermal image edge enhancement for security by image processing technique
 An Algorithm for Blurred Thermal image edge enhancement for security by image processing technique Vinay Negi 1, Dr.K.P.Mishra 2 1 ECE (PhD Research scholar), Monad University, India, Hapur 2 ECE, KIET,
An Algorithm for Blurred Thermal image edge enhancement for security by image processing technique Vinay Negi 1, Dr.K.P.Mishra 2 1 ECE (PhD Research scholar), Monad University, India, Hapur 2 ECE, KIET,
2D Image Processing Feature Descriptors
 2D Image Processing Feature Descriptors Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Overview
2D Image Processing Feature Descriptors Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Overview
School of Computing University of Utah
 School of Computing University of Utah Presentation Outline 1 2 3 4 Main paper to be discussed David G. Lowe, Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints, IJCV, 2004. How to find useful keypoints?
School of Computing University of Utah Presentation Outline 1 2 3 4 Main paper to be discussed David G. Lowe, Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints, IJCV, 2004. How to find useful keypoints?
EECS490: Digital Image Processing. Lecture #19
 Lecture #19 Shading and texture analysis using morphology Gray scale reconstruction Basic image segmentation: edges v. regions Point and line locators, edge types and noise Edge operators: LoG, DoG, Canny
Lecture #19 Shading and texture analysis using morphology Gray scale reconstruction Basic image segmentation: edges v. regions Point and line locators, edge types and noise Edge operators: LoG, DoG, Canny
What Are Edges? Lecture 5: Gradients and Edge Detection. Boundaries of objects. Boundaries of Lighting. Types of Edges (1D Profiles)
 What Are Edges? Simple answer: discontinuities in intensity. Lecture 5: Gradients and Edge Detection Reading: T&V Section 4.1 and 4. Boundaries of objects Boundaries of Material Properties D.Jacobs, U.Maryland
What Are Edges? Simple answer: discontinuities in intensity. Lecture 5: Gradients and Edge Detection Reading: T&V Section 4.1 and 4. Boundaries of objects Boundaries of Material Properties D.Jacobs, U.Maryland
Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation
 #1 Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Hough Transform Robust method to find a shape in an image Shape can be described in parametric form A voting
#1 Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Hough Transform Robust method to find a shape in an image Shape can be described in parametric form A voting
Image Processing. Traitement d images. Yuliya Tarabalka Tel.
 Traitement d images Yuliya Tarabalka yuliya.tarabalka@hyperinet.eu yuliya.tarabalka@gipsa-lab.grenoble-inp.fr Tel. 04 76 82 62 68 Noise reduction Image restoration Restoration attempts to reconstruct an
Traitement d images Yuliya Tarabalka yuliya.tarabalka@hyperinet.eu yuliya.tarabalka@gipsa-lab.grenoble-inp.fr Tel. 04 76 82 62 68 Noise reduction Image restoration Restoration attempts to reconstruct an
Edges, interpolation, templates. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth)
 Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Edge detection edge detection has many applications in image processing an edge detector implements
Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Edge detection edge detection has many applications in image processing an edge detector implements
Introduction. Introduction. Related Research. SIFT method. SIFT method. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant. Scale.
 Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints David G. Lowe presented by, Sudheendra Invariance Intensity Scale Rotation Affine View point Introduction Introduction SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature
Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints David G. Lowe presented by, Sudheendra Invariance Intensity Scale Rotation Affine View point Introduction Introduction SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature
Algorithms for Edge Detection and Enhancement for Real Time Images: A Comparative Study
 Algorithms for Edge Detection and Enhancement for Real Time Images: A Comparative Study Ashita Vermani, Akshyata Ojha Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics & Telecommunication., College of Engineering
Algorithms for Edge Detection and Enhancement for Real Time Images: A Comparative Study Ashita Vermani, Akshyata Ojha Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics & Telecommunication., College of Engineering
