Introduction to Mobile Robotics
|
|
|
- Claud Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble olivier. 1/22
2 What is a robot? Robot = mechatronic system with perception, decision and action skills, capable of carrying out different tasks in the real world, in an autonomous way. Sensors Perception Decision Action Actuators 2/22
3 The robot of the day sensors sensors actuators actuators 1 raspberry pi3 Ubuntu + ROS Sensors 2 laserscanners Actuators 2 wheels driven by 2 motors + encoders 1 PC Ubuntu + ROS In charge of sensor data acquisition, processing & visualization; In charge of controlling actuators. 3/22
4 Sensor (1/2) A sensor is an instrument measuring a physical property of the environment; Sensors are imprecise and limited; The environment of a robot is generally complex, changing, unpredictable and uncertain; Understanding the world in which a robot evolves remains a challenge. Courtesy of sick 4/22
5 Sensor (2/2) Robair is equipped with a 2D laser scanner; The laser scanner has: a range of about 5.5 meters; a field of view of 240 degrees; an angular resolution of 1/3 degrees. The laser scanner costs about 1200 euros. Output: a table with 720 elements (r, Ɵ) Quality of data depends on distance, angle Polar to cartesian: X = r cos (Ɵ); Y = r sin (Ɵ). 5/22
6 Actuators of a mobile robot An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving or controlling a mechanism or system; An actuator controls a degree of freedom (rotation, translation); Actuators could be complex. 6/22
7 Actuators of robair (1/3) Robair has 2 wheels controlled by 2 motors; Robair is a differential drive robot; Simplest and most used kinematic model of robot. ω V R A monocycle describes a virtual circle of radius R; We have V = R ω 7/22
8 Actuators of robair (2/3) Robair has 2 wheels controlled by 2 motors; ω V r V w V l R We have V = R ω We have V r = (R + w/2) ω We have V l = (R w/2) ω We find: R= W 2 V l +V r V r V l 8/22
9 Actuators of robair (3/3) Finally, we have the direct kinematic model: ω = V r V l w (1) V= V l +V r 2 (2) Controlling (V l, V r ), we can determine (V, ω) But it is easier and more intuitive to control (V, ω) and determine (V l, V r ) (inverse kinematic model) V r = V + w 2 ω V l = V w 2 ω To simplify the control (at the beginning), we will perform translation OR rotation in place 9/22
10 y Estimation of motion: encoder While Robair is moving in its environment, we would like to know its position in this environment; Its position is determined by its position (x, y) in the environment + its orientation θ: (x, y, θ) θ x On each wheel, there is a system (named encoder) able to estimate the distance traveled by each wheel over a short time Δt 10/22
11 Estimation of position: odometry We call d l and d r the distance traveled by each wheel over Δt; d = d r +d l 2 using (2) Where d is the distance traveled and θ is the angle traveled x t = x t 1 + d cos θ y t = y t 1 + d sin(θ) θ t = θ t 1 + θ θ = d r d l w using (1) This is an estimation: with time the error associated to this estimation increases Drift problem 11/22
12 What is a robot? Robot = mechatronic system with perception, decision and action skills, capable of carrying out different tasks in the real world, in an autonomous way. Robot = artificial machine Body Robot Perception: Sensors Sensors Décision: Brain Computer Action: Members Actuators Autonomy: capacity to understand the current situation and to react in an approprious way taking into account the tasks to carry out. Sensors Perception Decision Action Actuators 12/22
13 Perception Perception Measurements Z X Vehicle State PERCEPTION M Static Objects Vehicle Motion Measurements U O Moving Objects Present Focus: interpretation of raw and noisy sensor data Identify static and dynamic part of sensor data Modeling static part of the environment Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) Modeling dynamic part of the environment Detection And Tracking of Moving Objects (DATMO) 13/22
14 Decision/Plan of future actions Most of the time, a mobile robot has to move in its environment: It needs to plan its future actions The mobile robot has a map and it knows where it is in the map (position A for instance); It should reach an other position in the map (position B for instance) Question: How to get there? Answer: sequence of actions to go from A to B that is feasible and without collision. north West, South, East (12 times), North (6 times), West (twice) 14/22
15 Action/control/navigation The mobile robot has a sequence of actions to execute, to reach its goal: it has to execute this sequence of actions (session 3); Monitoring of execution: we monitor what happen and react if needed. We need to be able to estimate actions/motions of the mobile robot; Collision detection/avoidance: the mobile robot should be able to detect and avoid collision. 15/22
16 Organization of the course 11 sessions: 1. 4 sessions to introduce basic concepts: 1. Introduction to mobile robotics and IoT + introduction to perception (DATMO); 2. Lab on ROS + perception(datmo); 3. Lab on perception (DATMO) + introduction to decision and action; 4. Lab on decision and action + tests. Design and develop a follow me behavior 5. Tutorial on perception (Localization) + Tutorial on IoT 2. 7 sessions to apply and «get in depth» these basic concepts on a practical project. 16/22
17 Projects Design, develop and test software(/middleware) for a mobile robot application; Customization of projects and robots is possible Projects will be done by groups of 4 students MAX Have your own laptop, install ROS (under ubuntu) and do the tutorial on ROS Evaluation: 2 intermediate evaluations (week 5 and week 8-9) 1 final defense + demo 17/22
18 Examples of applications(1/3) Advanced driver assistant system (ADAS) or autonomous vehicles Darpa Urban Challenge 2007 Google car 2010 IP Prevent 2008 Google car /22
19 Examples of applications(2/3) Service robotics Roomba Robomow Dyia One Baxter Staubli 19/22
20 Examples of applications(3/3) Companion robots Paro Aibo Buddy Nao Pepper 20/22
21 Summary (1/2) A mobile robot is equipped with 2 kind of sensors: Exteroceptive sensors that give information about the environment (ie, laser scanner); Proprioceptive sensors that give information about the internal state of the robot (ie, odometer); A mobile robot is equipped with some actuators characterized by their degree of freedom; Robair is a differential drive robot; Sensors and actuators are imprecise and limited; The environment of a robot is generally complex, changing, unpredictable and uncertain. 21/22
22 Summary (2/2) The link between sensors and actuators is done in 3 steps: Sensors Perception Decision Action Actuators A mobile robot control architecture is: a Finite State Automaton; An instantiation of the «perception-decision-action» architecture Sensors Perception Decision Action Actuators Sensors Detect (and track) a moving person Decide actions to move to the moving person Move to the moving person Actuators 22/22
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard 1/29 Some examples of mobile robots
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard 1/29 Some examples of mobile robots
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors
 CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016 2 REVIEW TRANSFORMS Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016 2 REVIEW TRANSFORMS Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016
W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making
 W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline & DP-Grids concept Dynamic Probabilistic Grids Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept Dynamic Probabilistic
W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline & DP-Grids concept Dynamic Probabilistic Grids Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept Dynamic Probabilistic
Localization, Where am I?
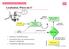 5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
Robotics. Haslum COMP3620/6320
 Robotics P@trik Haslum COMP3620/6320 Introduction Robotics Industrial Automation * Repetitive manipulation tasks (assembly, etc). * Well-known, controlled environment. * High-power, high-precision, very
Robotics P@trik Haslum COMP3620/6320 Introduction Robotics Industrial Automation * Repetitive manipulation tasks (assembly, etc). * Well-known, controlled environment. * High-power, high-precision, very
Practical Robotics (PRAC)
 Practical Robotics (PRAC) A Mobile Robot Navigation System (1) - Sensor and Kinematic Modelling Nick Pears University of York, Department of Computer Science December 17, 2014 nep (UoY CS) PRAC Practical
Practical Robotics (PRAC) A Mobile Robot Navigation System (1) - Sensor and Kinematic Modelling Nick Pears University of York, Department of Computer Science December 17, 2014 nep (UoY CS) PRAC Practical
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Kinematics of Wheeled Robots
 CSE 390/MEAM 40 Kinematics of Wheeled Robots Professor Vijay Kumar Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics University of Pennsylvania September 16, 006 1 Introduction In this chapter,
CSE 390/MEAM 40 Kinematics of Wheeled Robots Professor Vijay Kumar Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics University of Pennsylvania September 16, 006 1 Introduction In this chapter,
Task Level Hierarchical System for BCI-enabled Shared Autonomy Iretiayo Akinola, Boyuan Chen, Jonathan Koss, Aalhad Patankar, Jake Varley & Peter
 Task Level Hierarchical System for BCI-enabled Shared Autonomy Iretiayo Akinola, Boyuan Chen, Jonathan Koss, Aalhad Patankar, Jake Varley & Peter Allen Columbia University Shared Autonomy Agent 1 Agent
Task Level Hierarchical System for BCI-enabled Shared Autonomy Iretiayo Akinola, Boyuan Chen, Jonathan Koss, Aalhad Patankar, Jake Varley & Peter Allen Columbia University Shared Autonomy Agent 1 Agent
Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012
 COS 495 - Autonomous Robot Navigation Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012 Duration: Total Marks: 70 Closed Book 2 hours Start Time: End Time: By signing this exam, I agree to the honor code Name: Signature:
COS 495 - Autonomous Robot Navigation Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012 Duration: Total Marks: 70 Closed Book 2 hours Start Time: End Time: By signing this exam, I agree to the honor code Name: Signature:
Motion Models (cont) 1 3/15/2018
 Motion Models (cont) 1 3/15/018 Computing the Density to compute,, and use the appropriate probability density function; i.e., for zeromean Gaussian noise: 3/15/018 Sampling from the Velocity Motion Model
Motion Models (cont) 1 3/15/018 Computing the Density to compute,, and use the appropriate probability density function; i.e., for zeromean Gaussian noise: 3/15/018 Sampling from the Velocity Motion Model
Localization and Map Building
 Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
1 Differential Drive Kinematics
 CS W4733 NOTES - Differential Drive Robots Note: these notes were compiled from Dudek and Jenkin, Computational Principles of Mobile Robotics. 1 Differential Drive Kinematics Many mobile robots use a drive
CS W4733 NOTES - Differential Drive Robots Note: these notes were compiled from Dudek and Jenkin, Computational Principles of Mobile Robotics. 1 Differential Drive Kinematics Many mobile robots use a drive
Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685
 Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685 Previously Representation of rigid body motion Two different interpretations - as transformations between different coord. frames - as operators acting on a rigid body
Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685 Previously Representation of rigid body motion Two different interpretations - as transformations between different coord. frames - as operators acting on a rigid body
Zürich. Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza. ETH Master Course: L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary
 Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza ETH Master Course: 151-0854-00L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary 2 Lecture Overview Mobile Robot Control Scheme knowledge, data base mission
Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza ETH Master Course: 151-0854-00L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary 2 Lecture Overview Mobile Robot Control Scheme knowledge, data base mission
ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots. Mid Term Exam. Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100
 ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots Mid Term Exam Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100 Instructions: Read the exam carefully before starting. Equations are at the back, but they are NOT necessarily valid
ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots Mid Term Exam Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100 Instructions: Read the exam carefully before starting. Equations are at the back, but they are NOT necessarily valid
Cinematica dei Robot Mobili su Ruote. Corso di Robotica Prof. Davide Brugali Università degli Studi di Bergamo
 Cinematica dei Robot Mobili su Ruote Corso di Robotica Prof. Davide Brugali Università degli Studi di Bergamo Riferimenti bibliografici Roland SIEGWART, Illah R. NOURBAKHSH Introduction to Autonomous Mobile
Cinematica dei Robot Mobili su Ruote Corso di Robotica Prof. Davide Brugali Università degli Studi di Bergamo Riferimenti bibliografici Roland SIEGWART, Illah R. NOURBAKHSH Introduction to Autonomous Mobile
Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots. Dr. Daisy Tang
 Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots Dr. Daisy Tang Two Presentations A real-time algorithm for mobile robot mapping with applications to multi-robot and 3D mapping, by Thrun, Burgard
Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots Dr. Daisy Tang Two Presentations A real-time algorithm for mobile robot mapping with applications to multi-robot and 3D mapping, by Thrun, Burgard
Localization and Map Building
 Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
EMC 2015 Tooling and Infrastructure
 EMC 2015 Tooling and Infrastructure Sjoerd van den Dries Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering April 29, 2015 Introducing PICO Telepresence Robot from Aldebaran Robot
EMC 2015 Tooling and Infrastructure Sjoerd van den Dries Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering April 29, 2015 Introducing PICO Telepresence Robot from Aldebaran Robot
Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar
 The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar Naveed Muhammad 1,2 and Simon Lacroix 1,2 Abstract
The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar Naveed Muhammad 1,2 and Simon Lacroix 1,2 Abstract
Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3
 Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3 Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland January 28, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) Kinematics of
Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3 Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland January 28, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) Kinematics of
Autonomous Vehicles:
 Autonomous Vehicles: Research, Design and Implementation of Autonomous Vehicles Research Group - GPVA http://www.eletrica.unisinos.br/~autonom Tutorial page: http://inf.unisinos.br/~osorio/palestras/cerma07.html
Autonomous Vehicles: Research, Design and Implementation of Autonomous Vehicles Research Group - GPVA http://www.eletrica.unisinos.br/~autonom Tutorial page: http://inf.unisinos.br/~osorio/palestras/cerma07.html
Autonomous Vehicles:
 Autonomous Vehicles: Research, Design and Implementation of Autonomous Vehicles Research Group - GPVA http://www.eletrica.unisinos.br/~autonom Tutorial page: http://inf.unisinos.br/~osorio/palestras/cerma07.html
Autonomous Vehicles: Research, Design and Implementation of Autonomous Vehicles Research Group - GPVA http://www.eletrica.unisinos.br/~autonom Tutorial page: http://inf.unisinos.br/~osorio/palestras/cerma07.html
Spring Localization II. Roland Siegwart, Margarita Chli, Martin Rufli. ASL Autonomous Systems Lab. Autonomous Mobile Robots
 Spring 2016 Localization II Localization I 25.04.2016 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
Spring 2016 Localization II Localization I 25.04.2016 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
ME132 February 3, 2011
 ME132 February 3, 2011 Outline: - active sensors - introduction to lab setup (Player/Stage) - lab assignment - brief overview of OpenCV ME132 February 3, 2011 Outline: - active sensors - introduction to
ME132 February 3, 2011 Outline: - active sensors - introduction to lab setup (Player/Stage) - lab assignment - brief overview of OpenCV ME132 February 3, 2011 Outline: - active sensors - introduction to
Robotics Tasks. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Manipulator Robots. Mobile Robots. Degrees of Freedom. Sensors and Effectors
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 5: Robot Motion Planning 1/31/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Motion planning (today) How to move from
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 5: Robot Motion Planning 1/31/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Motion planning (today) How to move from
Introduction to Robotics
 Introduction to Robotics Ph.D. Antonio Marin-Hernandez Artificial Intelligence Department Universidad Veracruzana Sebastian Camacho # 5 Xalapa, Veracruz Robotics Action and Perception LAAS-CNRS 7, av du
Introduction to Robotics Ph.D. Antonio Marin-Hernandez Artificial Intelligence Department Universidad Veracruzana Sebastian Camacho # 5 Xalapa, Veracruz Robotics Action and Perception LAAS-CNRS 7, av du
MTRX4700 Experimental Robotics
 MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
Robotics (Kinematics) Winter 1393 Bonab University
 Robotics () Winter 1393 Bonab University : most basic study of how mechanical systems behave Introduction Need to understand the mechanical behavior for: Design Control Both: Manipulators, Mobile Robots
Robotics () Winter 1393 Bonab University : most basic study of how mechanical systems behave Introduction Need to understand the mechanical behavior for: Design Control Both: Manipulators, Mobile Robots
Sensor technology for mobile robots
 Laser application, vision application, sonar application and sensor fusion (6wasserf@informatik.uni-hamburg.de) Outline Introduction Mobile robots perception Definitions Sensor classification Sensor Performance
Laser application, vision application, sonar application and sensor fusion (6wasserf@informatik.uni-hamburg.de) Outline Introduction Mobile robots perception Definitions Sensor classification Sensor Performance
Simultaneous Localization
 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed
EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 2
 EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 2 Welcome Dr. Ing. Ahmad Kamal Nasir Organization Lab Course Lab grading policy (40%) Attendance = 10 % In-Lab tasks = 30 % Lab assignment + viva = 60 % Make a group Either
EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 2 Welcome Dr. Ing. Ahmad Kamal Nasir Organization Lab Course Lab grading policy (40%) Attendance = 10 % In-Lab tasks = 30 % Lab assignment + viva = 60 % Make a group Either
Robot Programming with Lisp
 7. Coordinate Transformations, TF, ActionLib Institute for Artificial University of Bremen Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 2 Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 3 Poses in 3D
7. Coordinate Transformations, TF, ActionLib Institute for Artificial University of Bremen Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 2 Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 3 Poses in 3D
Fundamental problems in mobile robotics
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Kinematics Fundamental problems in mobile robotics Locomotion: how the robot moves in the environment Perception: how
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Kinematics Fundamental problems in mobile robotics Locomotion: how the robot moves in the environment Perception: how
Motion Models (cont) 1 2/17/2017
 Motion Models (cont) 1 /17/017 Sampling from the Velocity Motion Model suppose that a robot has a map of its enironment and it needs to find its pose in the enironment this is the robot localization problem
Motion Models (cont) 1 /17/017 Sampling from the Velocity Motion Model suppose that a robot has a map of its enironment and it needs to find its pose in the enironment this is the robot localization problem
Robot For Assistance. Master Project ME-GY 996. Presented By: Karim Chamaa. Presented To: Dr. Vikram Kapila
 Robot For Assistance Master Project ME-GY 996 Presented By: Karim Chamaa Presented To: Dr. Vikram Kapila Project Description Building a robot with an assistance duty. Goals: Build a cheap and independent
Robot For Assistance Master Project ME-GY 996 Presented By: Karim Chamaa Presented To: Dr. Vikram Kapila Project Description Building a robot with an assistance duty. Goals: Build a cheap and independent
Grid-based Localization and Online Mapping with Moving Objects Detection and Tracking: new results
 Grid-based Localization and Online Mapping with Moving Objects Detection and Tracking: new results Trung-Dung Vu, Julien Burlet and Olivier Aycard Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble, France firstname.lastname@inrialpes.fr
Grid-based Localization and Online Mapping with Moving Objects Detection and Tracking: new results Trung-Dung Vu, Julien Burlet and Olivier Aycard Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble, France firstname.lastname@inrialpes.fr
S-SHAPED ONE TRAIL PARALLEL PARKING OF A CAR-LIKE MOBILE ROBOT
 S-SHAPED ONE TRAIL PARALLEL PARKING OF A CAR-LIKE MOBILE ROBOT 1 SOE YU MAUNG MAUNG, 2 NU NU WIN, 3 MYINT HTAY 1,2,3 Mechatronic Engineering Department, Mandalay Technological University, The Republic
S-SHAPED ONE TRAIL PARALLEL PARKING OF A CAR-LIKE MOBILE ROBOT 1 SOE YU MAUNG MAUNG, 2 NU NU WIN, 3 MYINT HTAY 1,2,3 Mechatronic Engineering Department, Mandalay Technological University, The Republic
ME 597: AUTONOMOUS MOBILE ROBOTICS SECTION 2 COORDINATE TRANSFORMS. Prof. Steven Waslander
 ME 597: AUTONOMOUS MOILE ROOTICS SECTION 2 COORDINATE TRANSFORMS Prof. Steven Waslander OUTLINE Coordinate Frames and Transforms Rotation Matrices Euler Angles Quaternions Homogeneous Transforms 2 COORDINATE
ME 597: AUTONOMOUS MOILE ROOTICS SECTION 2 COORDINATE TRANSFORMS Prof. Steven Waslander OUTLINE Coordinate Frames and Transforms Rotation Matrices Euler Angles Quaternions Homogeneous Transforms 2 COORDINATE
E80. Experimental Engineering. Lecture 9 Inertial Measurement
 Lecture 9 Inertial Measurement http://www.volker-doormann.org/physics.htm Feb. 19, 2013 Christopher M. Clark Where is the rocket? Outline Sensors People Accelerometers Gyroscopes Representations State
Lecture 9 Inertial Measurement http://www.volker-doormann.org/physics.htm Feb. 19, 2013 Christopher M. Clark Where is the rocket? Outline Sensors People Accelerometers Gyroscopes Representations State
Robotics. SAAST Robotics Robot Arms
 SAAST Robotics 008 Robot Arms Vijay Kumar Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Professor of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Topics Types of robot arms
SAAST Robotics 008 Robot Arms Vijay Kumar Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Professor of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Topics Types of robot arms
Motion Control (wheeled robots)
 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning
 Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 10.05.2017
Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 10.05.2017
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)
 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Lecture 16 April 8, 2013 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time series of
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Lecture 16 April 8, 2013 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time series of
Final Exam : Introduction to Robotics. Last Updated: 9 May You will have 1 hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam
 Final Exam 16-311: Introduction to Robotics Last Updated: 9 May 2017 Name: Andrew ID: Team Number: You will have 1 hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam There are 6 sections on 20 pages. Make sure
Final Exam 16-311: Introduction to Robotics Last Updated: 9 May 2017 Name: Andrew ID: Team Number: You will have 1 hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam There are 6 sections on 20 pages. Make sure
Sensor Modalities. Sensor modality: Different modalities:
 Sensor Modalities Sensor modality: Sensors which measure same form of energy and process it in similar ways Modality refers to the raw input used by the sensors Different modalities: Sound Pressure Temperature
Sensor Modalities Sensor modality: Sensors which measure same form of energy and process it in similar ways Modality refers to the raw input used by the sensors Different modalities: Sound Pressure Temperature
MTRX4700: Experimental Robotics
 Stefan B. Williams April, 2013 MTR4700: Experimental Robotics Assignment 3 Note: This assignment contributes 10% towards your final mark. This assignment is due on Friday, May 10 th during Week 9 before
Stefan B. Williams April, 2013 MTR4700: Experimental Robotics Assignment 3 Note: This assignment contributes 10% towards your final mark. This assignment is due on Friday, May 10 th during Week 9 before
CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots. Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta
 CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta 1 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements Kinematic/dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel
CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta 1 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements Kinematic/dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel
Chapter 4 Dynamics. Part Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics. Mobile Robotics - Prof Alonzo Kelly, CMU RI
 Chapter 4 Dynamics Part 2 4.3 Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics 1 Outline 4.3 Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics 4.3.1 Constraints of Disallowed Direction 4.3.2 Constraints of Rolling without Slipping
Chapter 4 Dynamics Part 2 4.3 Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics 1 Outline 4.3 Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics 4.3.1 Constraints of Disallowed Direction 4.3.2 Constraints of Rolling without Slipping
Mobile Robots: An Introduction.
 Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots Winter Robot Kinematics
 MEM38 Applied Autonomous obots Winter obot Kinematics Coordinate Transformations Motivation Ultimatel, we are interested in the motion of the robot with respect to a global or inertial navigation frame
MEM38 Applied Autonomous obots Winter obot Kinematics Coordinate Transformations Motivation Ultimatel, we are interested in the motion of the robot with respect to a global or inertial navigation frame
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 Name Code Class Branch Page 1 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : ROBOTICS (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 0 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : A7055 : IV B. Tech I Semester : MECHANICAL
Name Code Class Branch Page 1 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : ROBOTICS (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 0 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : A7055 : IV B. Tech I Semester : MECHANICAL
Actuated Sensor Networks: a 40-minute rant on convergence of vision, robotics, and sensor networks
 1 Actuated Sensor Networks: a 40-minute rant on convergence of vision, robotics, and sensor networks Chad Jenkins Assistant Professor Computer Science Department Brown University Women in Computer Science
1 Actuated Sensor Networks: a 40-minute rant on convergence of vision, robotics, and sensor networks Chad Jenkins Assistant Professor Computer Science Department Brown University Women in Computer Science
Robotics: Science and Systems II
 Robotics: Science and Systems II 6.189/2.994/16.401 September 7th, 2005 Last Semester Motor Control Visual Servoing Range Processing Planning Manipulation Lab Progression 1. Schematics: Layout and Components
Robotics: Science and Systems II 6.189/2.994/16.401 September 7th, 2005 Last Semester Motor Control Visual Servoing Range Processing Planning Manipulation Lab Progression 1. Schematics: Layout and Components
10/11/07 1. Motion Control (wheeled robots) Representing Robot Position ( ) ( ) [ ] T
![10/11/07 1. Motion Control (wheeled robots) Representing Robot Position ( ) ( ) [ ] T 10/11/07 1. Motion Control (wheeled robots) Representing Robot Position ( ) ( ) [ ] T](/thumbs/79/79288754.jpg) 3 3 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Introduction: Mobile Robot Kinematics Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground
3 3 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Introduction: Mobile Robot Kinematics Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground
Spring Localization II. Roland Siegwart, Margarita Chli, Juan Nieto, Nick Lawrance. ASL Autonomous Systems Lab. Autonomous Mobile Robots
 Spring 2018 Localization II Localization I 16.04.2018 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
Spring 2018 Localization II Localization I 16.04.2018 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
Developing Algorithms for Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Developing Algorithms for Robotics and Autonomous Systems Jorik Caljouw 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Key Takeaway of this Talk Success in developing an autonomous robotics system requires: 1. Multi-domain
Developing Algorithms for Robotics and Autonomous Systems Jorik Caljouw 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Key Takeaway of this Talk Success in developing an autonomous robotics system requires: 1. Multi-domain
Rigid Body Transformations
 F1/10 th Racing Rigid Body Transformations (Or How Different sensors see the same world) By, Paritosh Kelkar Mapping the surroundings Specify destination and generate path to goal The colored cells represent
F1/10 th Racing Rigid Body Transformations (Or How Different sensors see the same world) By, Paritosh Kelkar Mapping the surroundings Specify destination and generate path to goal The colored cells represent
Practical Course WS 2010 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
 Practical Course WS 2010 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Cyrill Stachniss University of Freiburg, Germany Topics of this Course SLAM - simultaneous localization and mapping What does the world look
Practical Course WS 2010 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Cyrill Stachniss University of Freiburg, Germany Topics of this Course SLAM - simultaneous localization and mapping What does the world look
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Robot motion planning! Today. Robotics Tasks. Mobile Robots
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture 6: Robot Motion Planning 9/13/2007 Announcements Project 1 due (yesterday)! Project 2 (Pacman with ghosts) up in a few days Reminder: you are allowed to
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture 6: Robot Motion Planning 9/13/2007 Announcements Project 1 due (yesterday)! Project 2 (Pacman with ghosts) up in a few days Reminder: you are allowed to
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Announcements
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture 6: Robot Motion Planning 9/13/2007 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Project
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture 6: Robot Motion Planning 9/13/2007 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Project
From Personal Computers to Personal Robots
 From Personal Computers to Personal Robots Challenges in Computer Science Education Nikolaus Correll Department of Computer Science University of Colorado at Boulder Mechanism vs. Computer Unimate (1961)
From Personal Computers to Personal Robots Challenges in Computer Science Education Nikolaus Correll Department of Computer Science University of Colorado at Boulder Mechanism vs. Computer Unimate (1961)
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 6: Perception/Odometry Terry Payne Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 47 Today We ll talk about perception and motor control. 2 / 47 Perception
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 6: Perception/Odometry Terry Payne Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 47 Today We ll talk about perception and motor control. 2 / 47 Perception
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 6: Perception/Odometry Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 47 Today We ll talk about perception and motor control. 2 / 47 Perception
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 6: Perception/Odometry Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 47 Today We ll talk about perception and motor control. 2 / 47 Perception
Manipulator trajectory planning
 Manipulator trajectory planning Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Department of Cybernetics Czech Republic http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~hlavac Courtesy to
Manipulator trajectory planning Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Department of Cybernetics Czech Republic http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~hlavac Courtesy to
Advanced path planning. ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012
 Advanced path planning ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012 Simon Lacroix Toulouse, France Where do I come from? Robotics at LAAS/CNRS, Toulouse, France Research topics Perception, planning and decision-making,
Advanced path planning ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012 Simon Lacroix Toulouse, France Where do I come from? Robotics at LAAS/CNRS, Toulouse, France Research topics Perception, planning and decision-making,
Towards Optimal 3D Point Clouds
 By Andreas Nüchter, Jan Elseberg and Dorit Borrmann, Germany feature Automation in 3D Mobile Laser Scanning Towards Optimal 3D Point Clouds Motivated by the increasing need for rapid characterisation of
By Andreas Nüchter, Jan Elseberg and Dorit Borrmann, Germany feature Automation in 3D Mobile Laser Scanning Towards Optimal 3D Point Clouds Motivated by the increasing need for rapid characterisation of
Robotic Perception and Action: Vehicle SLAM Assignment
 Robotic Perception and Action: Vehicle SLAM Assignment Mariolino De Cecco Mariolino De Cecco, Mattia Tavernini 1 CONTENTS Vehicle SLAM Assignment Contents Assignment Scenario 3 Odometry Localization...........................................
Robotic Perception and Action: Vehicle SLAM Assignment Mariolino De Cecco Mariolino De Cecco, Mattia Tavernini 1 CONTENTS Vehicle SLAM Assignment Contents Assignment Scenario 3 Odometry Localization...........................................
Designing a Pick and Place Robotics Application Using MATLAB and Simulink
 Designing a Pick and Place Robotics Application Using MATLAB and Simulink Carlos Santacruz-Rosero, PhD Sr Application Engineer Robotics Pulkit Kapur Sr Industry Marketing Manager Robotics 2017 The MathWorks,
Designing a Pick and Place Robotics Application Using MATLAB and Simulink Carlos Santacruz-Rosero, PhD Sr Application Engineer Robotics Pulkit Kapur Sr Industry Marketing Manager Robotics 2017 The MathWorks,
A Constructive Approach to Teaching with Robotino
 7 th International Scientific Conference Technics and Informatics in Education Faculty of Technical Sciences, Čačak, Serbia, 25-27 th May 218 Session 3 Engineering Education and Practice UDC 37 7.52 A
7 th International Scientific Conference Technics and Informatics in Education Faculty of Technical Sciences, Čačak, Serbia, 25-27 th May 218 Session 3 Engineering Education and Practice UDC 37 7.52 A
Robot Mapping. A Short Introduction to the Bayes Filter and Related Models. Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard
 Robot Mapping A Short Introduction to the Bayes Filter and Related Models Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Recursive
Robot Mapping A Short Introduction to the Bayes Filter and Related Models Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Recursive
Spring 2016, Robot Autonomy, Final Report (Team 7) Motion Planning for Autonomous All-Terrain Vehicle
 Spring 2016, 16662 Robot Autonomy, Final Report (Team 7) Motion Planning for Autonomous All-Terrain Vehicle Guan-Horng Liu 1, Samuel Wang 1, Shu-Kai Lin 1, Chris Wang 2, and Tiffany May 1 Advisors: Mr.
Spring 2016, 16662 Robot Autonomy, Final Report (Team 7) Motion Planning for Autonomous All-Terrain Vehicle Guan-Horng Liu 1, Samuel Wang 1, Shu-Kai Lin 1, Chris Wang 2, and Tiffany May 1 Advisors: Mr.
A Modular Software Framework for Eye-Hand Coordination in Humanoid Robots
 A Modular Software Framework for Eye-Hand Coordination in Humanoid Robots Jurgen Leitner, Simon Harding, Alexander Forster and Peter Corke Presentation: Hana Fusman Introduction/ Overview The goal of their
A Modular Software Framework for Eye-Hand Coordination in Humanoid Robots Jurgen Leitner, Simon Harding, Alexander Forster and Peter Corke Presentation: Hana Fusman Introduction/ Overview The goal of their
Obstacles Avoidance for Car-Like Robots Integration And Experimentation on Two Robots
 Obstacles Avoidance for Car-Like Robots Integration And Experimentation on Two Robots Olivier Lefebvre Florent Lamiraux Cédric Pradalier Thierry Fraichard firstname.lastname@laas.fr firstname.lastname@inrialpes.fr
Obstacles Avoidance for Car-Like Robots Integration And Experimentation on Two Robots Olivier Lefebvre Florent Lamiraux Cédric Pradalier Thierry Fraichard firstname.lastname@laas.fr firstname.lastname@inrialpes.fr
Team Description Paper Team AutonOHM
 Team Description Paper Team AutonOHM Jon Martin, Daniel Ammon, Helmut Engelhardt, Tobias Fink, Tobias Scholz, and Marco Masannek University of Applied Science Nueremberg Georg-Simon-Ohm, Kesslerplatz 12,
Team Description Paper Team AutonOHM Jon Martin, Daniel Ammon, Helmut Engelhardt, Tobias Fink, Tobias Scholz, and Marco Masannek University of Applied Science Nueremberg Georg-Simon-Ohm, Kesslerplatz 12,
MASTER'S THESIS. Development of a mobile robot platform. Rickard Nyberg Master of Science in Engineering Technology Mechanical Engineering
 MASTER'S THESIS Development of a mobile robot platform Rickard Nyberg 2014 Master of Science in Engineering Technology Mechanical Engineering Luleå University of Technology Institutionen för teknikvetenskap
MASTER'S THESIS Development of a mobile robot platform Rickard Nyberg 2014 Master of Science in Engineering Technology Mechanical Engineering Luleå University of Technology Institutionen för teknikvetenskap
Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ x + 5y + 7z 9x + 3y + 11z
 Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
6D SLAM with Kurt3D. Andreas Nüchter, Kai Lingemann, Joachim Hertzberg
 6D SLAM with Kurt3D Andreas Nüchter, Kai Lingemann, Joachim Hertzberg University of Osnabrück, Institute of Computer Science Knowledge Based Systems Research Group Albrechtstr. 28, D-4969 Osnabrück, Germany
6D SLAM with Kurt3D Andreas Nüchter, Kai Lingemann, Joachim Hertzberg University of Osnabrück, Institute of Computer Science Knowledge Based Systems Research Group Albrechtstr. 28, D-4969 Osnabrück, Germany
Omni-Directional Drive and Mecanum: Team 1675 Style. Jon Anderson FRC Mentor
 Omni-Directional Drive and Mecanum: Team 1675 Style Jon Anderson jon.c.anderson@gmail.com FRC Mentor Omni-Directional Drive Omni-Directional Drive is Holonomic The controllable degrees of freedom is equal
Omni-Directional Drive and Mecanum: Team 1675 Style Jon Anderson jon.c.anderson@gmail.com FRC Mentor Omni-Directional Drive Omni-Directional Drive is Holonomic The controllable degrees of freedom is equal
Servosila Robotic Heads
 Servosila Robotic Heads www.servosila.com TABLE OF CONTENTS SERVOSILA ROBOTIC HEADS 2 SOFTWARE-DEFINED FUNCTIONS OF THE ROBOTIC HEADS 2 SPECIFICATIONS: ROBOTIC HEADS 4 DIMENSIONS OF ROBOTIC HEAD 5 DIMENSIONS
Servosila Robotic Heads www.servosila.com TABLE OF CONTENTS SERVOSILA ROBOTIC HEADS 2 SOFTWARE-DEFINED FUNCTIONS OF THE ROBOTIC HEADS 2 SPECIFICATIONS: ROBOTIC HEADS 4 DIMENSIONS OF ROBOTIC HEAD 5 DIMENSIONS
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 10: Mobile Robots, Control, and Coordination in Robot Teams Dr. Amanda Prorok Robots and Mobile Systems smart infrastructure / mobility-on-demand connected vehicles /
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 10: Mobile Robots, Control, and Coordination in Robot Teams Dr. Amanda Prorok Robots and Mobile Systems smart infrastructure / mobility-on-demand connected vehicles /
Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations
 Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations 1 Definition of polar coordinates Let us first recall the definition of Cartesian coordinates: to each point in the plane we can
Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations 1 Definition of polar coordinates Let us first recall the definition of Cartesian coordinates: to each point in the plane we can
Mobile Robotics. Marcello Restelli. Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano tel:
 Marcello Restelli Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano email: restelli@elet.polimi.it tel: 02-2399-3470 Mobile Robotics Robotica for Computer Engineering students A.A. 2006/2007
Marcello Restelli Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano email: restelli@elet.polimi.it tel: 02-2399-3470 Mobile Robotics Robotica for Computer Engineering students A.A. 2006/2007
Section 9.1 Angles, Arcs, & Their Measures (Part I)
 Week 1 Handout MAC 1114 Professor Niraj Wagh J Section 9.1 Angles, Arcs, & Their Measures (Part I) Basic Terminology Line: Two distinct points A and B determine a line called line AB. Segment: The portion
Week 1 Handout MAC 1114 Professor Niraj Wagh J Section 9.1 Angles, Arcs, & Their Measures (Part I) Basic Terminology Line: Two distinct points A and B determine a line called line AB. Segment: The portion
EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2
 1 EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2 09/05/2017 Robotic system components A robotic system has three major components: Actuators: the muscles of the robot Sensors: provide information about the environment and
1 EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2 09/05/2017 Robotic system components A robotic system has three major components: Actuators: the muscles of the robot Sensors: provide information about the environment and
Mobile Robots Summery. Autonomous Mobile Robots
 Mobile Robots Summery Roland Siegwart Mike Bosse, Marco Hutter, Martin Rufli, Davide Scaramuzza, (Margarita Chli, Paul Furgale) Mobile Robots Summery 1 Introduction probabilistic map-based localization
Mobile Robots Summery Roland Siegwart Mike Bosse, Marco Hutter, Martin Rufli, Davide Scaramuzza, (Margarita Chli, Paul Furgale) Mobile Robots Summery 1 Introduction probabilistic map-based localization
Mobile Robotics. Mathematics, Models, and Methods. HI Cambridge. Alonzo Kelly. Carnegie Mellon University UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM
 NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM Jorma Selkäinaho, Aarne Halme and Janne Paanajärvi Automation Technology Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo,
NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM Jorma Selkäinaho, Aarne Halme and Janne Paanajärvi Automation Technology Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo,
Non-holonomic Planning
 Non-holonomic Planning Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We have learned about RRTs. q new q init q near q rand But the standard
Non-holonomic Planning Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We have learned about RRTs. q new q init q near q rand But the standard
OFERTA O120410PA CURRENT DATE 10/04//2012 VALID UNTIL 10/05/2012 SUMMIT XL
 OFERTA O120410PA CURRENT DATE 10/04//2012 VALID UNTIL 10/05/2012 SUMMIT XL CLIENT CLIENT: Gaitech REPRESENTANT: Andrew Pether MAIL: andyroojp@hotmail.com PRODUCT Introduction The SUMMIT XL has skid-steering
OFERTA O120410PA CURRENT DATE 10/04//2012 VALID UNTIL 10/05/2012 SUMMIT XL CLIENT CLIENT: Gaitech REPRESENTANT: Andrew Pether MAIL: andyroojp@hotmail.com PRODUCT Introduction The SUMMIT XL has skid-steering
Robot Motion Control Matteo Matteucci
 Robot Motion Control Open loop control A mobile robot is meant to move from one place to another Pre-compute a smooth trajectory based on motion segments (e.g., line and circle segments) from start to
Robot Motion Control Open loop control A mobile robot is meant to move from one place to another Pre-compute a smooth trajectory based on motion segments (e.g., line and circle segments) from start to
Southern Illinois University Edwardsville
 Southern Illinois University Edwardsville 2014-2015 I certify that the design and engineering of the vehicle Roadrunner by the SIUE Team Roadrunner has been significant and equivalent to what might be
Southern Illinois University Edwardsville 2014-2015 I certify that the design and engineering of the vehicle Roadrunner by the SIUE Team Roadrunner has been significant and equivalent to what might be
Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar
 Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar Naveed Muhammad 1,2 and Simon Lacroix 1,2 Abstract This paper presents a technique for the calibration of multi-beam laser scanners. The technique is based on
Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar Naveed Muhammad 1,2 and Simon Lacroix 1,2 Abstract This paper presents a technique for the calibration of multi-beam laser scanners. The technique is based on
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 6 PERCEPTION/ODOMETRY comp329-2013-parsons-lect06 2/43 Today We ll talk about perception and
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 6 PERCEPTION/ODOMETRY comp329-2013-parsons-lect06 2/43 Today We ll talk about perception and
Robotics Project. Final Report. Computer Science University of Minnesota. December 17, 2007
 Robotics Project Final Report Computer Science 5551 University of Minnesota December 17, 2007 Peter Bailey, Matt Beckler, Thomas Bishop, and John Saxton Abstract: A solution of the parallel-parking problem
Robotics Project Final Report Computer Science 5551 University of Minnesota December 17, 2007 Peter Bailey, Matt Beckler, Thomas Bishop, and John Saxton Abstract: A solution of the parallel-parking problem
Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM. Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology
 Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology Content Introduction to Problem (s) Localization A few basic equations Dead Reckoning
Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology Content Introduction to Problem (s) Localization A few basic equations Dead Reckoning
Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018
 Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018 Asaf Moses Systematics Ltd., Technical Product Manager aviasafm@systematics.co.il 1 Autonomous
Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018 Asaf Moses Systematics Ltd., Technical Product Manager aviasafm@systematics.co.il 1 Autonomous
AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS. LOCALIZATION, MAPPING & SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Part V Mapping & Occupancy Grid Mapping
 AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS LOCALIZATION, MAPPING & SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Part V Mapping & Occupancy Grid Mapping Maria Isabel Ribeiro Pedro Lima with revisions introduced by Rodrigo Ventura Instituto
AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS LOCALIZATION, MAPPING & SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Part V Mapping & Occupancy Grid Mapping Maria Isabel Ribeiro Pedro Lima with revisions introduced by Rodrigo Ventura Instituto
MEAM 520. Mobile Robots
 MEAM 520 Mobile Robots Katherine J. Kuchenbecker, Ph.D. General Robotics, Automation, Sensing, and Perception Lab (GRASP) MEAM Department, SEAS, Universit of Pennslvania Lecture 22: December 6, 2012 T
MEAM 520 Mobile Robots Katherine J. Kuchenbecker, Ph.D. General Robotics, Automation, Sensing, and Perception Lab (GRASP) MEAM Department, SEAS, Universit of Pennslvania Lecture 22: December 6, 2012 T
