Autonomous Vehicles:
|
|
|
- Marion Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Autonomous Vehicles: Research, Design and Implementation of Autonomous Vehicles Research Group - GPVA Tutorial page: html Dr. Fernando S. Osório - Applied Computing Post Dr. Christian R. Kelber PIPCA Post-Grad. Program PIPCA - Electrical Engineering / Computer Eng. Dr. Cláudio R. Jung - Applied Computing M.Sc.. Program PIPCA M.Sc. Farlei Heinen - Computer Engineering B.Sc. (Director) Grupo de Pesquisas em Veículos Autônomos Autonomous Vehicles Research Group - Unisinos 1 Veículos Autônomos Inteligentes Introduction Robotic: Automatons, Mobile Robots and Autonomous Robots Perception, Action, Locomotion e Communication and Intelligence Intelligent Vehicles Technologies for Vehicle Automation pyramid Intelligent of Autonomous Vehicles : Computational Architectures Simulation of Autonomous Vehicles Computer Vision Practical Applications Agenda 2 1
2 CONTROL: : Computational Architectures => From where do I start? Modeling and Simulation Models: - Sensorial Models - Actuator Models - Kinematics Models - Environment Models - A.I. Models (Path Planning, Agents,...) Simulation: - Validate models - Test robustness - Improve design : Computational Architectures 17 CONTROL: : Computational Architectures => From where do I start? Modeling and Simulation Scientific American January 2007 : Computational Architectures 17 2
3 CONTROL: : Computational Architectures Sensorial Models Kinematics Models C2 C1 C0 M1 C3 C4 C5 M2 Sensorial Model: Sonar Infrared Radar, Compass, Odometer Kinematics Model: Differential Aeckerman C7 C6 φ Y Aeckerman θ X θ = V / L * Sin (Φ) X = V * Cos (Φ) * Cos (θ) Y = V * Cos (Φ) * Cos (θ) : Computational Architectures 18 CONTROL: : Computational Architectures Sensorial Models Kinematics Models Robotic : * Reactive * Deliberative * Hierarchical * Hybrid Environment Maps * Building Maps * Path Planning * SMPA - Sense Model Plan Act Problems: * Complex tasks * Avoid Obstacles: Static / Mobile - Unexpected obstacles * Robot actual position estimation - Where am I? : Computational Architectures 17 3
4 CONTROL: : Computational Architectures Complexity... P.Bessièrre * Action Planning * Ability to Perceive the Environment * Ability to Decide * Ability to Act * High Level Tasks Planning * Reaction: Sensorial-Motor * Estimate Actual and Future States * Adaptation and Learning * Robustness * Unexpected Situations => From where do I start??? : Computational Architectures 20 CONTROL: : Computational Architectures Complexity... : Computational Architectures 21 4
5 CONTROL: : Computational Architectures Complexity... Simplify! How? : Computational Architectures 22 CONTROL: REACTIVE Architecture Complexity... Simplify! How? MIT - OCW Reactive: Sensorial-Motor Integration Able to Act Able to Perceive the Environment Able to React Reactive Architecture 23 5
6 CONTROL: REACTIVE Architecture Reactive: Sensorial-Motor Integration Reactive S2 S1 S0 M1 S7 S3 S4 S5 M2 S6 IF S1 < Threshold and S2 < Threshold and S3 < Threshold and S4 < Threshold THEN Action (Go_Forward) IF S1 < Threshold and S2 < Threshold and S3 > Threshold and S4 > Threshold THEN Action (Turn_Left) IF S2 > Threshold and S3 > Threshold and S2 > S3 and S1 > S4 THEN Action (Turn_Right) Sensorial-Motor: Perceive => Act Reactive 24 CONTROL: REACTIVE Architecture Reactive: Sensorial-Motor Integration Reactive Robotic Lawn Mowers - Toro imow - Husqvarna Auto Mower - Automower Electrolux Sensorial-Motor: Avoid Obstacles, Wall Following, Wander Electrolux Trilobite Robotic Vacuum Cleaner ZA1 Reactive 25 6
7 CONTROL: REACTIVE Architecture Reactive: Sensorial-Motor Integration Reactive Sensorial-Motor: - Avoid Obstacles - Wall Following - Wander Simple behaviors Robustness? Complex tasks? Reactive 26 CONTROL: DELIBERATIVE Architectures Deliberative: Planning + Action Deliberative SIMROB (2D) - Map - Configuration Space - Visibility Graph - Optimized Path (Dijkstra) Robotic Arm: Pre-defined paths Deliberative Architecture 27 7
8 CONTROL: DELIBERATIVE Architectures Deliberative: Planning + Action Deliberative Tarefas Complexas... Robustez? Imprevistos? Ambiente pouco conhecido? Deliberative Geometric Map based Navigation: Planning: Graph+Dijkstra, A* Grid based Navigation: Planning: A* 28 CONTROL: HIERARCHICAL and HYBRID Architectures Combining: Deliberative + Reactive Hierarchical and Hybrid Hierarchical and Hybrid Hierarchical : - Layers - Priorities - Information Exchange Figures From: Brooks, R. A. MIT A.I. Memo 864 Sept Brooks - Subsumption Architecture 29 8
9 CONTROL: HIERARCHICAL and HYBRID Architectures Building the Environment Map: SMPA - SENSE / MODEL / PLAN / ACT Hierarchical and Hybrid MODEL S E N S E PLAN: AStar Dijkstra ACT! Hierarchical and Hybrid Sebastian Thrun / CMU 30 CONTROL: Simple HYBRID Architectures Hybrid Farlei Heinen PLAN: Dijkstra ACT & ReACT Hybrid 31 9
10 CONTROL: Simple HYBRID Architectures Hybrid Farlei Heinen References: SEVA2D / SEVA3D Autonomous Vehicle Parking TASK PLANNING & CONTROL: Finite State Automata (FSA) Artificial Neural Net (ANN) ACTION: Sense, Act React (change state) SEVA-A (Automaton) Farlei Heinen SEVA-N (Neural) Farlei Heinen Fernando Osório Luciane Fortes Milton Heinen Publications: SBRN 2002 WCCI 2006 Hybrid 32 CONTROL: Simple HYBRID Architectures Hybrid SimRob3D Simulation SEVA3D 3D World Kinematics: Estimation of Position and Orientation Robot Model Perception: Sensor Simulation Motor Actions Sensorial Information Commands Sensors : SEVA3D-A (FSA) SEVA3D-N (Neural) Visualization Hybrid 32 10
11 CONTROL: : Computational Architectures Sensorial Models Kinematics Models Robotic : * Reactive * Deliberative * Hierarchical * Hybrid Environment Maps * Building Maps * Path Planning * SMPA - Sense Model Plan Act Problems: * Complex tasks * Avoid Obstacles: Static / Mobile - Unexpected obstacles * Robot actual position estimation - Where am I? 33 PROBLEMS: System Task Execution * Avoid Obstacles - Known Obstacles - Unknown Obstacles (static / no movement) - Unknown Obstacles (dynamic / moving objects) * Positioning - How to determine the exact actual position of the robot? - How to maintain the control of exact position after displacement? - Error and Imprecision: Move forward / Rotate 34 11
12 PROBLEMS: * Avoid Obstacles System Task Execution - Known Obstacles - Unknown Obstacles (static / no movement) - Unknown Obstacles (dynamic / moving objects) 35 PROBLEMS: * Positioning System Task Execution - How to determine the exact actual position of the robot? - How to maintain the control of exact position after displacement? - Error and Imprecision: Move forward / Rotate 36 12
13 COHBRA / HyCAR Robot [SimRob3D] Sensors Actuators Layers Behaviors Environment Representation Maps Positioning Estimator (Monte Carlo) Sequencer Polygonal Modules Path Planning Grid Topological and Semantic Shared Memory COHBRA e Híbrido de Robôs Autônomos HyCAR - Hybrid for Autonomous Robots 37 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] Simulation using SimRob3D 38 13
14 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] Simulation using a static environment Position estimation based on Monte Carlo Localization Method 39 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] Simulation using a static environment Position estimation based on Monte Carlo Localization Method 40 14
15 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] Simulation using a static environment Environment was changed related to the original map Internal robot representation is different from actual world configuration 41 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] Simulation using a dynamic environment (mobile obstacles) 42 15
16 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] Position estimation based on Monte Carlo Method: Robot was moved, starting in a new and unknown position 43 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] Virtual Environment: 3D Realistic Environment SimRob3D Simulation Tool 44 16
17 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] Virtual Environment: 3D Realistic Environment SimRob3D Simulation Tool 45 COHBRA / HyCAR [SimRob3D] SEVA 3D SimRob3D Simulation Tool 46 17
18 Intelligent Autonomous Robots and Vehicles << Intelligence >> * Task and Actions Planning * Ability to Perceive the Environment * Ability to Decide * Ability to Act * High Level Tasks Planning * Reaction: Sensorial-Motor Integration * Estimate Actual and Future States: Environment + Behavior = Interaction * Adaptation and Learning * Robustness: Unexpected Situations Next steps... GPVA 47 Intelligent Autonomous Robots and Vehicles << Intelligence >> * Task and Actions Planning * Ability to Perceive the Environment * Ability to Decide * Ability to Act * High Level Tasks Planning * Reaction: Sensorial-Motor Integration * Estimate Actual and Future States: Environment + Behavior = Interaction * Adaptation and Learning * Robustness: Unexpected Situations Next steps... DARPA Challenge - Desert (2004, 2005) DARPA Challenge - Urban (2007) GPVA 47 18
19 Intelligent Autonomous Robots and Vehicles << Intelligence >> * Task and Actions Planning * Ability to Perceive the Environment * Ability to Decide * Ability to Act * High Level Tasks Planning * Reaction: Sensorial-Motor Integration * Estimate Actual and Future States: Environment + Behavior = Interaction * Adaptation and Learning * Robustness: Unexpected Situations Next steps... Computational Vision Computational Vision 48 Intelligent Autonomous Robots and Vehicles << Intelligence >> Computational Vision Path following: - Follow Me, Lane Follow Avoid danger situations: going out of the track - Lane Detection Obstacle detection: pedestrians, cars, etc Traffic signs detection and recognition Visual Navigation (Based on Images) Computational Vision 49 19
20 Intelligent Autonomous Robots and Vehicles << Intelligence >> Computational Vision Lane Follow Lane Departure Detection Follow Me Computational Vision 50 Image Database: Path defined by a sequence of image Visual Navigation Reference ImagemAtual NCC (match) PróximaImagem Next Imagemcapturada Robot acquired image pelorobô Navigation based on Monochromatic Images [Jones et al. 1997] Algorithm: NCC Normalized Cross-Correlation Correlation Visual Navigation 51 20
21 Visual Navigation [Matsumoto et al. 1996] Matlab Code IR: Reference Image ICR: Image Captured by the robot [Righes 2004, 2005] Visual Navigation 52 Visual Navigation [Righes 04] Visual Navigation 53 21
22 Visual Navigation Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping with Uncertainty using Scale-Invariant Visual Landmarks Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little (UBC, CA) Algorithm: SIFT Reference Int. Journal of Robotics Research Vol. 21, No. 8, August 2002, pp , Visual Navigation 54 Visual Navigation Omnidirectional Cameras Visual Navigation 55 22
23 Aerial Visual Navigation Vision System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Correlation: Satellite image and Helicopter Results... Not good at all! Visual Navigation 55 Aerial Visual Navigation Vision System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Referential Correlation in the Crossing Point Using helicopter only images Very Good Match! Visual Navigation 23
24 Vehicle Visual System Vision system used to identify traffic signs [F.Alves 2003] [H]SI RGB Color HSV Color Color based sign segmentation Artificial Neural Network Recognition Visual Systems Multiple Vehicles: Fire fighting squad Planning, Navigation, + Strategy, Cooperation Visual Systems 24
25 Google: Veículos Autônomos 25
Autonomous Vehicles:
 Autonomous Vehicles: Research, Design and Implementation of Autonomous Vehicles Research Group - GPVA http://www.eletrica.unisinos.br/~autonom Tutorial page: http://inf.unisinos.br/~osorio/palestras/cerma07.html
Autonomous Vehicles: Research, Design and Implementation of Autonomous Vehicles Research Group - GPVA http://www.eletrica.unisinos.br/~autonom Tutorial page: http://inf.unisinos.br/~osorio/palestras/cerma07.html
Mobile Robots: An Introduction.
 Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Robotics. Haslum COMP3620/6320
 Robotics P@trik Haslum COMP3620/6320 Introduction Robotics Industrial Automation * Repetitive manipulation tasks (assembly, etc). * Well-known, controlled environment. * High-power, high-precision, very
Robotics P@trik Haslum COMP3620/6320 Introduction Robotics Industrial Automation * Repetitive manipulation tasks (assembly, etc). * Well-known, controlled environment. * High-power, high-precision, very
Last update: May 6, Robotics. CMSC 421: Chapter 25. CMSC 421: Chapter 25 1
 Last update: May 6, 2010 Robotics CMSC 421: Chapter 25 CMSC 421: Chapter 25 1 A machine to perform tasks What is a robot? Some level of autonomy and flexibility, in some type of environment Sensory-motor
Last update: May 6, 2010 Robotics CMSC 421: Chapter 25 CMSC 421: Chapter 25 1 A machine to perform tasks What is a robot? Some level of autonomy and flexibility, in some type of environment Sensory-motor
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard olivier. 1/22 What is a robot? Robot
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard olivier. 1/22 What is a robot? Robot
An Architecture for Automated Driving in Urban Environments
 An Architecture for Automated Driving in Urban Environments Gang Chen and Thierry Fraichard Inria Rhône-Alpes & LIG-CNRS Lab., Grenoble (FR) firstname.lastname@inrialpes.fr Summary. This paper presents
An Architecture for Automated Driving in Urban Environments Gang Chen and Thierry Fraichard Inria Rhône-Alpes & LIG-CNRS Lab., Grenoble (FR) firstname.lastname@inrialpes.fr Summary. This paper presents
Mobile robots control architectures
 1 Mobile robots control architectures Dimitri Popov Universität Hamburg Fakultät für Mathematik, Informatik und Naturwissenschaften Department Informatik Integriertes Seminar Intelligent Robotics 10 1.
1 Mobile robots control architectures Dimitri Popov Universität Hamburg Fakultät für Mathematik, Informatik und Naturwissenschaften Department Informatik Integriertes Seminar Intelligent Robotics 10 1.
Lecture 18: Planning and plan execution, applications
 Lecture 18: Planning and plan execution, applications Planning, plan execution, replanning Planner as a part of an autonomous robot: robot architectures The subsumption architecture The 3-tier architecture:
Lecture 18: Planning and plan execution, applications Planning, plan execution, replanning Planner as a part of an autonomous robot: robot architectures The subsumption architecture The 3-tier architecture:
The area processing unit of Caroline
 2nd Workshop Robot Vision RobVis '08 February 18-20, 2008 Auckland, New Zealand The area processing unit of Caroline Finding the way through DARPA's urban challenge February 18th, 2008 Kai Berger Christian
2nd Workshop Robot Vision RobVis '08 February 18-20, 2008 Auckland, New Zealand The area processing unit of Caroline Finding the way through DARPA's urban challenge February 18th, 2008 Kai Berger Christian
Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
 Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots second edition Roland Siegwart, Illah R. Nourbakhsh, and Davide Scaramuzza The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Contents Acknowledgments xiii
Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots second edition Roland Siegwart, Illah R. Nourbakhsh, and Davide Scaramuzza The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Contents Acknowledgments xiii
Robot Localization: Historical Context
 Robot Localization: Historical Context Initially, roboticists thought the world could be modeled exactly Path planning and control assumed perfect, exact, deterministic world Reactive robotics (behavior
Robot Localization: Historical Context Initially, roboticists thought the world could be modeled exactly Path planning and control assumed perfect, exact, deterministic world Reactive robotics (behavior
Reactive and Hybrid Agents. Based on An Introduction to MultiAgent Systems and slides by Michael Wooldridge
 Reactive and Hybrid Agents Based on An Introduction to MultiAgent Systems and slides by Michael Wooldridge Reactive Architectures Problems with symbolic/logical approaches (transduction, computational
Reactive and Hybrid Agents Based on An Introduction to MultiAgent Systems and slides by Michael Wooldridge Reactive Architectures Problems with symbolic/logical approaches (transduction, computational
Visually Augmented POMDP for Indoor Robot Navigation
 Visually Augmented POMDP for Indoor obot Navigation LÓPEZ M.E., BAEA., BEGASA L.M., ESCUDEO M.S. Electronics Department University of Alcalá Campus Universitario. 28871 Alcalá de Henares (Madrid) SPAIN
Visually Augmented POMDP for Indoor obot Navigation LÓPEZ M.E., BAEA., BEGASA L.M., ESCUDEO M.S. Electronics Department University of Alcalá Campus Universitario. 28871 Alcalá de Henares (Madrid) SPAIN
Localization of Multiple Robots with Simple Sensors
 Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation Niagara Falls, Canada July 2005 Localization of Multiple Robots with Simple Sensors Mike Peasgood and Christopher Clark Lab
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation Niagara Falls, Canada July 2005 Localization of Multiple Robots with Simple Sensors Mike Peasgood and Christopher Clark Lab
Mobile Robotics. Mathematics, Models, and Methods. HI Cambridge. Alonzo Kelly. Carnegie Mellon University UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Sensor Modalities. Sensor modality: Different modalities:
 Sensor Modalities Sensor modality: Sensors which measure same form of energy and process it in similar ways Modality refers to the raw input used by the sensors Different modalities: Sound Pressure Temperature
Sensor Modalities Sensor modality: Sensors which measure same form of energy and process it in similar ways Modality refers to the raw input used by the sensors Different modalities: Sound Pressure Temperature
Vol. 21 No. 6, pp ,
 Vol. 21 No. 6, pp.69 696, 23 69 3 3 3 Map Generation of a Mobile Robot by Integrating Omnidirectional Stereo and Laser Range Finder Yoshiro Negishi 3, Jun Miura 3 and Yoshiaki Shirai 3 This paper describes
Vol. 21 No. 6, pp.69 696, 23 69 3 3 3 Map Generation of a Mobile Robot by Integrating Omnidirectional Stereo and Laser Range Finder Yoshiro Negishi 3, Jun Miura 3 and Yoshiaki Shirai 3 This paper describes
Vehicle Localization. Hannah Rae Kerner 21 April 2015
 Vehicle Localization Hannah Rae Kerner 21 April 2015 Spotted in Mtn View: Google Car Why precision localization? in order for a robot to follow a road, it needs to know where the road is to stay in a particular
Vehicle Localization Hannah Rae Kerner 21 April 2015 Spotted in Mtn View: Google Car Why precision localization? in order for a robot to follow a road, it needs to know where the road is to stay in a particular
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 10: Mobile Robots, Control, and Coordination in Robot Teams Dr. Amanda Prorok Robots and Mobile Systems smart infrastructure / mobility-on-demand connected vehicles /
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 10: Mobile Robots, Control, and Coordination in Robot Teams Dr. Amanda Prorok Robots and Mobile Systems smart infrastructure / mobility-on-demand connected vehicles /
Anibal Ollero Professor and head of GRVC University of Seville (Spain)
 Aerial Manipulation Anibal Ollero Professor and head of GRVC University of Seville (Spain) aollero@us.es Scientific Advisor of the Center for Advanced Aerospace Technologies (Seville, Spain) aollero@catec.aero
Aerial Manipulation Anibal Ollero Professor and head of GRVC University of Seville (Spain) aollero@us.es Scientific Advisor of the Center for Advanced Aerospace Technologies (Seville, Spain) aollero@catec.aero
Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features
 Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Presented by Adam Bickett
Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Presented by Adam Bickett
Advanced path planning. ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012
 Advanced path planning ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012 Simon Lacroix Toulouse, France Where do I come from? Robotics at LAAS/CNRS, Toulouse, France Research topics Perception, planning and decision-making,
Advanced path planning ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012 Simon Lacroix Toulouse, France Where do I come from? Robotics at LAAS/CNRS, Toulouse, France Research topics Perception, planning and decision-making,
Mapping Contoured Terrain Using SLAM with a Radio- Controlled Helicopter Platform. Project Proposal. Cognitive Robotics, Spring 2005
 Mapping Contoured Terrain Using SLAM with a Radio- Controlled Helicopter Platform Project Proposal Cognitive Robotics, Spring 2005 Kaijen Hsiao Henry de Plinval Jason Miller Introduction In the context
Mapping Contoured Terrain Using SLAM with a Radio- Controlled Helicopter Platform Project Proposal Cognitive Robotics, Spring 2005 Kaijen Hsiao Henry de Plinval Jason Miller Introduction In the context
Efficient Route Finding and Sensors for Collision Detection in Google s Driverless Car
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 12, December 2014,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 12, December 2014,
Localization and Map Building
 Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Advanced Applications. Robot folds towels. Robotic Control Tasks
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2011 Advanced Applications: Robotics Announcements Practice Final Out (optional) Similar extra credit system as practice midterm Contest (optional): Tomorrow night
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2011 Advanced Applications: Robotics Announcements Practice Final Out (optional) Similar extra credit system as practice midterm Contest (optional): Tomorrow night
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Announcements
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2011 Advanced Applications: Robotics Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley A few slides from Sebastian Thrun, Dan Klein 1 Announcements Practice Final Out (optional) Similar
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2011 Advanced Applications: Robotics Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley A few slides from Sebastian Thrun, Dan Klein 1 Announcements Practice Final Out (optional) Similar
Robotic Behaviors. Potential Field Methods
 Robotic Behaviors Potential field techniques - trajectory generation - closed feedback-loop control Design of variety of behaviors - motivated by potential field based approach steering behaviors Closed
Robotic Behaviors Potential field techniques - trajectory generation - closed feedback-loop control Design of variety of behaviors - motivated by potential field based approach steering behaviors Closed
Robotics. CSPP Artificial Intelligence March 10, 2004
 Robotics CSPP 56553 Artificial Intelligence March 10, 2004 Roadmap Robotics is AI-complete Integration of many AI techniques Classic AI Search in configuration space (Ultra) Modern AI Subsumption architecture
Robotics CSPP 56553 Artificial Intelligence March 10, 2004 Roadmap Robotics is AI-complete Integration of many AI techniques Classic AI Search in configuration space (Ultra) Modern AI Subsumption architecture
Mini Survey Paper (Robotic Mapping) Ryan Hamor CPRE 583 September 2011
 Mini Survey Paper (Robotic Mapping) Ryan Hamor CPRE 583 September 2011 Introduction The goal of this survey paper is to examine the field of robotic mapping and the use of FPGAs in various implementations.
Mini Survey Paper (Robotic Mapping) Ryan Hamor CPRE 583 September 2011 Introduction The goal of this survey paper is to examine the field of robotic mapping and the use of FPGAs in various implementations.
Towards Fully-automated Driving. tue-mps.org. Challenges and Potential Solutions. Dr. Gijs Dubbelman Mobile Perception Systems EE-SPS/VCA
 Towards Fully-automated Driving Challenges and Potential Solutions Dr. Gijs Dubbelman Mobile Perception Systems EE-SPS/VCA Mobile Perception Systems 6 PhDs, 1 postdoc, 1 project manager, 2 software engineers
Towards Fully-automated Driving Challenges and Potential Solutions Dr. Gijs Dubbelman Mobile Perception Systems EE-SPS/VCA Mobile Perception Systems 6 PhDs, 1 postdoc, 1 project manager, 2 software engineers
Complex behavior emergent from simpler ones
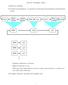 Reactive Paradigm: Basics Based on ethology Vertical decomposition, as opposed to horizontal decomposition of hierarchical model Primitive behaviors at bottom Higher behaviors at top Each layer has independent
Reactive Paradigm: Basics Based on ethology Vertical decomposition, as opposed to horizontal decomposition of hierarchical model Primitive behaviors at bottom Higher behaviors at top Each layer has independent
Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018
 Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018 Asaf Moses Systematics Ltd., Technical Product Manager aviasafm@systematics.co.il 1 Autonomous
Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018 Asaf Moses Systematics Ltd., Technical Product Manager aviasafm@systematics.co.il 1 Autonomous
Software Architecture--Continued. Another Software Architecture Example
 Software Architecture--Continued References for Software Architecture examples: Software Architecture, Perspectives on an Emerging Discipline, by Mary Shaw and David Garlin, Prentice Hall, 1996. B. Hayes-Roth,
Software Architecture--Continued References for Software Architecture examples: Software Architecture, Perspectives on an Emerging Discipline, by Mary Shaw and David Garlin, Prentice Hall, 1996. B. Hayes-Roth,
ROBOTICS (5 cfu) 09/02/2016. Last and first name Matricola Graduating
 ROBOTICS (5 cfu) 09/02/2016 Last and first name Matricola Graduating PART 1 - QUIZ (8 marks) 1. For a 3x3 matrix to be a rotation matrix, it should hold - each row vector has module 1 T F - the product
ROBOTICS (5 cfu) 09/02/2016 Last and first name Matricola Graduating PART 1 - QUIZ (8 marks) 1. For a 3x3 matrix to be a rotation matrix, it should hold - each row vector has module 1 T F - the product
Title: Survey navigation for a mobile robot by using a hierarchical cognitive map
 Title: Survey navigation for a mobile robot by using a hierarchical cognitive map Authors: Eduardo J. Pérez Alberto Poncela Cristina Urdiales Antonio Bandera Francisco Sandoval Contact Author: Affiliations:
Title: Survey navigation for a mobile robot by using a hierarchical cognitive map Authors: Eduardo J. Pérez Alberto Poncela Cristina Urdiales Antonio Bandera Francisco Sandoval Contact Author: Affiliations:
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard 1/29 Some examples of mobile robots
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard 1/29 Some examples of mobile robots
Cognitive Robotics. Robot Cognitive Architectures. Matteo Matteucci
 based on Gianni A. Di Caro lecture on ROBOT CONTROL RCHITECTURES SINGLE AND MULTI-ROBOT SYSTEMS: A CASE STUDY IN SWARM ROBOTICS Cognitive Robotics Robot Cognitive Architectures Matteo Matteucci matteo.matteucci@polimi.it
based on Gianni A. Di Caro lecture on ROBOT CONTROL RCHITECTURES SINGLE AND MULTI-ROBOT SYSTEMS: A CASE STUDY IN SWARM ROBOTICS Cognitive Robotics Robot Cognitive Architectures Matteo Matteucci matteo.matteucci@polimi.it
Zürich. Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza. ETH Master Course: L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary
 Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza ETH Master Course: 151-0854-00L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary 2 Lecture Overview Mobile Robot Control Scheme knowledge, data base mission
Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza ETH Master Course: 151-0854-00L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary 2 Lecture Overview Mobile Robot Control Scheme knowledge, data base mission
Human Detection. A state-of-the-art survey. Mohammad Dorgham. University of Hamburg
 Human Detection A state-of-the-art survey Mohammad Dorgham University of Hamburg Presentation outline Motivation Applications Overview of approaches (categorized) Approaches details References Motivation
Human Detection A state-of-the-art survey Mohammad Dorgham University of Hamburg Presentation outline Motivation Applications Overview of approaches (categorized) Approaches details References Motivation
Distributed Intelligent Systems W3 An Introduction to Sensing, Action, and Control in Mobile Robotics
 Distributed Intelligent Systems W3 An Introduction to Sensing, Action, and Control in Mobile Robotics 1 Outline General concepts Autonomy Perception-to-action loop Sensing, actuating, computing e-puck
Distributed Intelligent Systems W3 An Introduction to Sensing, Action, and Control in Mobile Robotics 1 Outline General concepts Autonomy Perception-to-action loop Sensing, actuating, computing e-puck
Matching Evaluation of 2D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment
 Matching Evaluation of D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment Taichi Yamada, and Akihisa Ohya Abstract In the real environment such as urban areas sidewalk,
Matching Evaluation of D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment Taichi Yamada, and Akihisa Ohya Abstract In the real environment such as urban areas sidewalk,
An Experimental Study of the Autonomous Helicopter Landing Problem
 An Experimental Study of the Autonomous Helicopter Landing Problem Srikanth Saripalli 1, Gaurav S. Sukhatme 1, and James F. Montgomery 2 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Southern California,
An Experimental Study of the Autonomous Helicopter Landing Problem Srikanth Saripalli 1, Gaurav S. Sukhatme 1, and James F. Montgomery 2 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Southern California,
Survey navigation for a mobile robot by using a hierarchical cognitive map
 Survey navigation for a mobile robot by using a hierarchical cognitive map E.J. Pérez, A. Poncela, C. Urdiales, A. Bandera and F. Sandoval Departamento de Tecnología Electrónica, E.T.S.I. Telecomunicación
Survey navigation for a mobile robot by using a hierarchical cognitive map E.J. Pérez, A. Poncela, C. Urdiales, A. Bandera and F. Sandoval Departamento de Tecnología Electrónica, E.T.S.I. Telecomunicación
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
A Vision and Differential Steering System for a Mobile Robot Platform Abujawad Rafid Siddiqui
 Master Thesis Computer Science Thesis no: MCS-2010-22 May 2010 A Vision and Differential Steering System for a Mobile Robot Platform Abujawad Rafid Siddiqui School School of Computing of Blekinge Institute
Master Thesis Computer Science Thesis no: MCS-2010-22 May 2010 A Vision and Differential Steering System for a Mobile Robot Platform Abujawad Rafid Siddiqui School School of Computing of Blekinge Institute
Monte Carlo Localization using Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids. Karan M. Gupta
 1 Monte Carlo Localization using Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids Karan M. Gupta Agenda Introduction Occupancy Grids Sonar Sensor Model Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids Monte Carlo Localization
1 Monte Carlo Localization using Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids Karan M. Gupta Agenda Introduction Occupancy Grids Sonar Sensor Model Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids Monte Carlo Localization
Path Planning with Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance for a Jumping-Enabled Robot
 Path Planning with Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance for a Jumping-Enabled Robot Peggy (Yuchun) Wang and Caitlin Hogan Department of Computer Science, Stanford University Robotic navigation is an important concern
Path Planning with Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance for a Jumping-Enabled Robot Peggy (Yuchun) Wang and Caitlin Hogan Department of Computer Science, Stanford University Robotic navigation is an important concern
Mobile Robots Locomotion
 Mobile Robots Locomotion Institute for Software Technology 1 Course Outline 1. Introduction to Mobile Robots 2. Locomotion 3. Sensors 4. Localization 5. Environment Modelling 6. Reactive Navigation 2 Today
Mobile Robots Locomotion Institute for Software Technology 1 Course Outline 1. Introduction to Mobile Robots 2. Locomotion 3. Sensors 4. Localization 5. Environment Modelling 6. Reactive Navigation 2 Today
Locality through Modular Network Topology
 Locality through Modular Network Topology Oliver Lipton and Harry Huchra December 18, 2017 Abstract Our experiment concerns designing a robot to accomplish the task of locality grounding. Through a dataset
Locality through Modular Network Topology Oliver Lipton and Harry Huchra December 18, 2017 Abstract Our experiment concerns designing a robot to accomplish the task of locality grounding. Through a dataset
Gregory Bock, Brittany Dhall, Ryan Hendrickson, & Jared Lamkin Project Advisors: Dr. Jing Wang & Dr. In Soo Ahn Department of Electrical and Computer
 Gregory Bock, Brittany Dhall, Ryan Hendrickson, & Jared Lamkin Project Advisors: Dr. Jing Wang & Dr. In Soo Ahn Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering April 26 th, 2016 Outline 2 I. Introduction
Gregory Bock, Brittany Dhall, Ryan Hendrickson, & Jared Lamkin Project Advisors: Dr. Jing Wang & Dr. In Soo Ahn Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering April 26 th, 2016 Outline 2 I. Introduction
Fundamental problems in mobile robotics
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Kinematics Fundamental problems in mobile robotics Locomotion: how the robot moves in the environment Perception: how
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Kinematics Fundamental problems in mobile robotics Locomotion: how the robot moves in the environment Perception: how
Path planning for autonomous vehicles
 Path planning for autonomous vehicles Solveig Bruvoll, FFI May 19 2016 Mobile robots/autonomous vehicles vs. manipulators Manipulators Fixed position Limited workspace Mobile robots Position changes Environment
Path planning for autonomous vehicles Solveig Bruvoll, FFI May 19 2016 Mobile robots/autonomous vehicles vs. manipulators Manipulators Fixed position Limited workspace Mobile robots Position changes Environment
An Angle Estimation to Landmarks for Autonomous Satellite Navigation
 5th International Conference on Environment, Materials, Chemistry and Power Electronics (EMCPE 2016) An Angle Estimation to Landmarks for Autonomous Satellite Navigation Qing XUE a, Hongwen YANG, Jian
5th International Conference on Environment, Materials, Chemistry and Power Electronics (EMCPE 2016) An Angle Estimation to Landmarks for Autonomous Satellite Navigation Qing XUE a, Hongwen YANG, Jian
On Road Vehicle Detection using Shadows
 On Road Vehicle Detection using Shadows Gilad Buchman Grasp Lab, Department of Computer and Information Science School of Engineering University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA buchmag@seas.upenn.edu
On Road Vehicle Detection using Shadows Gilad Buchman Grasp Lab, Department of Computer and Information Science School of Engineering University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA buchmag@seas.upenn.edu
W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making
 W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline & DP-Grids concept Dynamic Probabilistic Grids Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept Dynamic Probabilistic
W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline & DP-Grids concept Dynamic Probabilistic Grids Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept Dynamic Probabilistic
CSE-571 Robotics. Sensors for Mobile Robots. Beam-based Sensor Model. Proximity Sensors. Probabilistic Sensor Models. Beam-based Scan-based Landmarks
 Sensors for Mobile Robots CSE-57 Robotics Probabilistic Sensor Models Beam-based Scan-based Landmarks Contact sensors: Bumpers Internal sensors Accelerometers (spring-mounted masses) Gyroscopes (spinning
Sensors for Mobile Robots CSE-57 Robotics Probabilistic Sensor Models Beam-based Scan-based Landmarks Contact sensors: Bumpers Internal sensors Accelerometers (spring-mounted masses) Gyroscopes (spinning
Vision based autonomous driving - A survey of recent methods. -Tejus Gupta
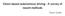 Vision based autonomous driving - A survey of recent methods -Tejus Gupta Presently, there are three major paradigms for vision based autonomous driving: Directly map input image to driving action using
Vision based autonomous driving - A survey of recent methods -Tejus Gupta Presently, there are three major paradigms for vision based autonomous driving: Directly map input image to driving action using
OCCUPANCY GRID MODELING FOR MOBILE ROBOT USING ULTRASONIC RANGE FINDER
 OCCUPANCY GRID MODELING FOR MOBILE ROBOT USING ULTRASONIC RANGE FINDER Jyoshita, Priti 2, Tejal Sangwan 3,2,3,4 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Hindu College of Engineering Sonepat,
OCCUPANCY GRID MODELING FOR MOBILE ROBOT USING ULTRASONIC RANGE FINDER Jyoshita, Priti 2, Tejal Sangwan 3,2,3,4 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Hindu College of Engineering Sonepat,
Vision for Mobile Robot Navigation
 Vision for Mobile Robot Navigation Ranga Rodrigo November 20, 2009 Outline Contents 1 Indoor Navigation 1 1.1 Map-Based Approaches............................ 2 1.2 Map-Building Approaches...........................
Vision for Mobile Robot Navigation Ranga Rodrigo November 20, 2009 Outline Contents 1 Indoor Navigation 1 1.1 Map-Based Approaches............................ 2 1.2 Map-Building Approaches...........................
Presentation Outline
 Autonomous Vehicle Navigation Using Stereoscopic Imaging Senior Capstone Project Progress Report Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Bradley University Presented by: Beach, Wlaznik Advisors:
Autonomous Vehicle Navigation Using Stereoscopic Imaging Senior Capstone Project Progress Report Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Bradley University Presented by: Beach, Wlaznik Advisors:
Traffic Sign Recognition for Autonomous Driving Robot
 Volume-7, Issue-4, July-August 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 385-392 Traffic Sign Recognition for Autonomous Driving Robot K.Pavani 1, A. Prasanna Lakshmi
Volume-7, Issue-4, July-August 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 385-392 Traffic Sign Recognition for Autonomous Driving Robot K.Pavani 1, A. Prasanna Lakshmi
Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning
 Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 10.05.2017
Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 10.05.2017
Wall-Follower. Xiaodong Fang. EEL5666 Intelligent Machines Design Laboratory University of Florida School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 Wall-Follower Xiaodong Fang EEL5666 Intelligent Machines Design Laboratory University of Florida School of Electrical and Computer Engineering TAs: Tim Martin Josh Weaver Instructors: Dr. A. Antonio Arroyo
Wall-Follower Xiaodong Fang EEL5666 Intelligent Machines Design Laboratory University of Florida School of Electrical and Computer Engineering TAs: Tim Martin Josh Weaver Instructors: Dr. A. Antonio Arroyo
A Fuzzy Local Path Planning and Obstacle Avoidance for Mobile Robots
 A Fuzzy Local Path Planning and Obstacle Avoidance for Mobile Robots H.Aminaiee Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran Abstract This paper presents a local
A Fuzzy Local Path Planning and Obstacle Avoidance for Mobile Robots H.Aminaiee Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran Abstract This paper presents a local
Robotics/Perception II
 Robotics/Perception II Artificial Intelligence and Integrated Computer Systems Division (AIICS) Outline Sensors - summary Computer systems Robotic architectures Mapping and Localization Motion planning
Robotics/Perception II Artificial Intelligence and Integrated Computer Systems Division (AIICS) Outline Sensors - summary Computer systems Robotic architectures Mapping and Localization Motion planning
Attack Resilient State Estimation for Vehicular Systems
 December 15 th 2013. T-SET Final Report Attack Resilient State Estimation for Vehicular Systems Nicola Bezzo (nicbezzo@seas.upenn.edu) Prof. Insup Lee (lee@cis.upenn.edu) PRECISE Center University of Pennsylvania
December 15 th 2013. T-SET Final Report Attack Resilient State Estimation for Vehicular Systems Nicola Bezzo (nicbezzo@seas.upenn.edu) Prof. Insup Lee (lee@cis.upenn.edu) PRECISE Center University of Pennsylvania
Big Picture: Overview of Issues and Challenges in Autonomous Robotics + Impact on Practical Implementation Details
 Big Picture: Overview of Issues and Challenges in Autonomous Robotics + Impact on Practical Implementation Details August 27, 2002 Class Meeting 2 Announcements/Questions Course mailing list set up: cs594-sir@cs.utk.edu
Big Picture: Overview of Issues and Challenges in Autonomous Robotics + Impact on Practical Implementation Details August 27, 2002 Class Meeting 2 Announcements/Questions Course mailing list set up: cs594-sir@cs.utk.edu
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Software
 CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Software Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Mobile Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 18.09.2016 2 Review Definition Robot: A machine capable of performing
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Software Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Mobile Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 18.09.2016 2 Review Definition Robot: A machine capable of performing
Topological Localization Based on Visual Features in Manufacturing Environment
 , Issue (28) 33-4 Journal of Advanced Research in Industrial Automation and Cyber-Physical System Journal homepage: www.akademiabaru.com/ard.html ISSN: XXXX-XXXX Topological Localization Based on Visual
, Issue (28) 33-4 Journal of Advanced Research in Industrial Automation and Cyber-Physical System Journal homepage: www.akademiabaru.com/ard.html ISSN: XXXX-XXXX Topological Localization Based on Visual
Remote Sensing Image Analysis via a Texture Classification Neural Network
 Remote Sensing Image Analysis via a Texture Classification Neural Network Hayit K. Greenspan and Rodney Goodman Department of Electrical Engineering California Institute of Technology, 116-81 Pasadena,
Remote Sensing Image Analysis via a Texture Classification Neural Network Hayit K. Greenspan and Rodney Goodman Department of Electrical Engineering California Institute of Technology, 116-81 Pasadena,
Online Simultaneous Localization and Mapping in Dynamic Environments
 To appear in Proceedings of the Intl. Conf. on Robotics and Automation ICRA New Orleans, Louisiana, Apr, 2004 Online Simultaneous Localization and Mapping in Dynamic Environments Denis Wolf and Gaurav
To appear in Proceedings of the Intl. Conf. on Robotics and Automation ICRA New Orleans, Louisiana, Apr, 2004 Online Simultaneous Localization and Mapping in Dynamic Environments Denis Wolf and Gaurav
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (4) (2016) Research Article
 Jestr Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (4) (2016) 102-106 Research Article Design, Construction and Programming of a Mobile Robot Controlled by Artificial Vision Claudio Urrea* and
Jestr Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 9 (4) (2016) 102-106 Research Article Design, Construction and Programming of a Mobile Robot Controlled by Artificial Vision Claudio Urrea* and
Robotics Tasks. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Manipulator Robots. Mobile Robots. Degrees of Freedom. Sensors and Effectors
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 5: Robot Motion Planning 1/31/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Motion planning (today) How to move from
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 5: Robot Motion Planning 1/31/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Motion planning (today) How to move from
Sensory Augmentation for Increased Awareness of Driving Environment
 Sensory Augmentation for Increased Awareness of Driving Environment Pranay Agrawal John M. Dolan Dec. 12, 2014 Technologies for Safe and Efficient Transportation (T-SET) UTC The Robotics Institute Carnegie
Sensory Augmentation for Increased Awareness of Driving Environment Pranay Agrawal John M. Dolan Dec. 12, 2014 Technologies for Safe and Efficient Transportation (T-SET) UTC The Robotics Institute Carnegie
Appearance-based Visual Localisation in Outdoor Environments with an Omnidirectional Camera
 52. Internationales Wissenschaftliches Kolloquium Technische Universität Ilmenau 10. - 13. September 2007 M. Schenderlein / K. Debes / A. Koenig / H.-M. Gross Appearance-based Visual Localisation in Outdoor
52. Internationales Wissenschaftliches Kolloquium Technische Universität Ilmenau 10. - 13. September 2007 M. Schenderlein / K. Debes / A. Koenig / H.-M. Gross Appearance-based Visual Localisation in Outdoor
Collecting outdoor datasets for benchmarking vision based robot localization
 Collecting outdoor datasets for benchmarking vision based robot localization Emanuele Frontoni*, Andrea Ascani, Adriano Mancini, Primo Zingaretti Department of Ingegneria Infromatica, Gestionale e dell
Collecting outdoor datasets for benchmarking vision based robot localization Emanuele Frontoni*, Andrea Ascani, Adriano Mancini, Primo Zingaretti Department of Ingegneria Infromatica, Gestionale e dell
LAIR. UNDERWATER ROBOTICS Field Explorations in Marine Biology, Oceanography, and Archeology
 UNDERWATER ROBOTICS Field Explorations in Marine Biology, Oceanography, and Archeology COS 402: Artificial Intelligence - Sept. 2011 Christopher M. Clark Outline! Past Projects! Maltese Cistern Mapping!
UNDERWATER ROBOTICS Field Explorations in Marine Biology, Oceanography, and Archeology COS 402: Artificial Intelligence - Sept. 2011 Christopher M. Clark Outline! Past Projects! Maltese Cistern Mapping!
NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM
 NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM Jorma Selkäinaho, Aarne Halme and Janne Paanajärvi Automation Technology Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo,
NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM Jorma Selkäinaho, Aarne Halme and Janne Paanajärvi Automation Technology Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo,
URBAN STRUCTURE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL AND ORTHOGONAL LINES
 URBAN STRUCTURE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL AND ORTHOGONAL LINES An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by RUI LIU Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
URBAN STRUCTURE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL AND ORTHOGONAL LINES An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by RUI LIU Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Topological Mapping. Discrete Bayes Filter
 Topological Mapping Discrete Bayes Filter Vision Based Localization Given a image(s) acquired by moving camera determine the robot s location and pose? Towards localization without odometry What can be
Topological Mapping Discrete Bayes Filter Vision Based Localization Given a image(s) acquired by moving camera determine the robot s location and pose? Towards localization without odometry What can be
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
 Sebastian Lembcke SLAM 1 / 29 MIN Faculty Department of Informatics Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Visual Loop-Closure Detection University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural
Sebastian Lembcke SLAM 1 / 29 MIN Faculty Department of Informatics Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Visual Loop-Closure Detection University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural
Agent Based Intersection Traffic Simulation
 Agent Based Intersection Traffic Simulation David Wilkie May 7, 2009 Abstract This project focuses on simulating the traffic at an intersection using agent-based planning and behavioral methods. The motivation
Agent Based Intersection Traffic Simulation David Wilkie May 7, 2009 Abstract This project focuses on simulating the traffic at an intersection using agent-based planning and behavioral methods. The motivation
A Path Tracking Method For Autonomous Mobile Robots Based On Grid Decomposition
 A Path Tracking Method For Autonomous Mobile Robots Based On Grid Decomposition A. Pozo-Ruz*, C. Urdiales, A. Bandera, E. J. Pérez and F. Sandoval Dpto. Tecnología Electrónica. E.T.S.I. Telecomunicación,
A Path Tracking Method For Autonomous Mobile Robots Based On Grid Decomposition A. Pozo-Ruz*, C. Urdiales, A. Bandera, E. J. Pérez and F. Sandoval Dpto. Tecnología Electrónica. E.T.S.I. Telecomunicación,
Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots. Dr. Daisy Tang
 Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots Dr. Daisy Tang Two Presentations A real-time algorithm for mobile robot mapping with applications to multi-robot and 3D mapping, by Thrun, Burgard
Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots Dr. Daisy Tang Two Presentations A real-time algorithm for mobile robot mapping with applications to multi-robot and 3D mapping, by Thrun, Burgard
A Modular, Hybrid System Architecture for Autonomous, Urban Driving
 A Modular, Hybrid System Architecture for Autonomous, Urban Driving Dave Wooden, Matt Powers, Magnus Egerstedt, Henrik Christensen, and Tucker Balch Robotics and Intelligent Machines Georgia Institute
A Modular, Hybrid System Architecture for Autonomous, Urban Driving Dave Wooden, Matt Powers, Magnus Egerstedt, Henrik Christensen, and Tucker Balch Robotics and Intelligent Machines Georgia Institute
Fast Local Planner for Autonomous Helicopter
 Fast Local Planner for Autonomous Helicopter Alexander Washburn talexan@seas.upenn.edu Faculty advisor: Maxim Likhachev April 22, 2008 Abstract: One challenge of autonomous flight is creating a system
Fast Local Planner for Autonomous Helicopter Alexander Washburn talexan@seas.upenn.edu Faculty advisor: Maxim Likhachev April 22, 2008 Abstract: One challenge of autonomous flight is creating a system
Elastic Correction of Dead-Reckoning Errors in Map Building
 Elastic Correction of Dead-Reckoning Errors in Map Building Matteo Golfarelli Dario Maio Stefano Rizzi DEIS, Università di Bologna Bologna, Italy Abstract A major problem in map building is due to the
Elastic Correction of Dead-Reckoning Errors in Map Building Matteo Golfarelli Dario Maio Stefano Rizzi DEIS, Università di Bologna Bologna, Italy Abstract A major problem in map building is due to the
i. baturone 1, a. gersnoviez 2 and a. barriga 1 contents list of figures
 N E U R O - F U Z Z Y T E C H N I Q U E S TO O P T I M I Z E A N F P G A E M B E D D E D C O N T R O L L E R F O R R O B OT N A V I G AT I O N i. baturone 1, a. gersnoviez 2 and a. barriga 1 contents 1
N E U R O - F U Z Z Y T E C H N I Q U E S TO O P T I M I Z E A N F P G A E M B E D D E D C O N T R O L L E R F O R R O B OT N A V I G AT I O N i. baturone 1, a. gersnoviez 2 and a. barriga 1 contents 1
Offline Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) using Miniature Robots
 Offline Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) using Miniature Robots Objectives SLAM approaches SLAM for ALICE EKF for Navigation Mapping and Network Modeling Test results Philipp Schaer and Adrian
Offline Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) using Miniature Robots Objectives SLAM approaches SLAM for ALICE EKF for Navigation Mapping and Network Modeling Test results Philipp Schaer and Adrian
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors
 CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016 2 REVIEW TRANSFORMS Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016 2 REVIEW TRANSFORMS Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016
Learning Fuzzy Rules by Evolution for Mobile Agent Control
 Learning Fuzzy Rules by Evolution for Mobile Agent Control George Chronis, James Keller and Marjorie Skubic Dept. of Computer Engineering and Computer Science, University of Missouri-Columbia, email: gchronis@ece.missouri.edu
Learning Fuzzy Rules by Evolution for Mobile Agent Control George Chronis, James Keller and Marjorie Skubic Dept. of Computer Engineering and Computer Science, University of Missouri-Columbia, email: gchronis@ece.missouri.edu
KNOWLEDGE ARCHITECTURE FOR ENVIRONMENT REPRESENTATION IN AUTONOMOUS AGENTS
 KNOWLEDGE ARCHITECTURE FOR ENVIRONMENT REPRESENTATION IN AUTONOMOUS AGENTS Dario Maio, Stefano Rizzi DEIS - Facoltà di Ingegneria, Università di Bologna, Italy dmaio@deis.unibo.it, srizzi@deis.unibo.it
KNOWLEDGE ARCHITECTURE FOR ENVIRONMENT REPRESENTATION IN AUTONOMOUS AGENTS Dario Maio, Stefano Rizzi DEIS - Facoltà di Ingegneria, Università di Bologna, Italy dmaio@deis.unibo.it, srizzi@deis.unibo.it
Laserscanner Based Cooperative Pre-Data-Fusion
 Laserscanner Based Cooperative Pre-Data-Fusion 63 Laserscanner Based Cooperative Pre-Data-Fusion F. Ahlers, Ch. Stimming, Ibeo Automobile Sensor GmbH Abstract The Cooperative Pre-Data-Fusion is a novel
Laserscanner Based Cooperative Pre-Data-Fusion 63 Laserscanner Based Cooperative Pre-Data-Fusion F. Ahlers, Ch. Stimming, Ibeo Automobile Sensor GmbH Abstract The Cooperative Pre-Data-Fusion is a novel
Simultaneous Localization
 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed
Learning how to combine sensory-motor functions into a robust behavior
 Artificial Intelligence 172 (2008) 392 412 www.elsevier.com/locate/artint Learning how to combine sensory-motor functions into a robust behavior Benoit Morisset a,, Malik Ghallab b a SRI International,
Artificial Intelligence 172 (2008) 392 412 www.elsevier.com/locate/artint Learning how to combine sensory-motor functions into a robust behavior Benoit Morisset a,, Malik Ghallab b a SRI International,
Signals, Instruments, and Systems W9. An Introduction to Mobile Robotics and the e-puck Robot
 Signals, Instruments, and Systems W9 An Introduction to Mobile Robotics and the e-puck Robot 1 Outline Motivation and general concepts for robotics: autonomy, controllers, control loop The e-puck miniature
Signals, Instruments, and Systems W9 An Introduction to Mobile Robotics and the e-puck Robot 1 Outline Motivation and general concepts for robotics: autonomy, controllers, control loop The e-puck miniature
Measuring the World: Designing Robust Vehicle Localization for Autonomous Driving. Frank Schuster, Dr. Martin Haueis
 Measuring the World: Designing Robust Vehicle Localization for Autonomous Driving Frank Schuster, Dr. Martin Haueis Agenda Motivation: Why measure the world for autonomous driving? Map Content: What do
Measuring the World: Designing Robust Vehicle Localization for Autonomous Driving Frank Schuster, Dr. Martin Haueis Agenda Motivation: Why measure the world for autonomous driving? Map Content: What do
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 WRI C225 Lecture 02 130124 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Basics Image Formation Image Processing 3 Intelligent
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 WRI C225 Lecture 02 130124 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Basics Image Formation Image Processing 3 Intelligent
DISTANCE MEASUREMENT USING STEREO VISION
 DISTANCE MEASUREMENT USING STEREO VISION Sheetal Nagar 1, Jitendra Verma 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, IIMT, Greater Noida (India) 2 Department of computer science Engineering,
DISTANCE MEASUREMENT USING STEREO VISION Sheetal Nagar 1, Jitendra Verma 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, IIMT, Greater Noida (India) 2 Department of computer science Engineering,
