3D TOPOLOGY FOR MODELLING OF URBAN STRUCTURES
|
|
|
- Jewel Mosley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3D TOPOLOGY FOR MODELLING OF URBAN STRUCTURES Tarun Ghawana & Sisi Zlatanoa Delft Uniersity of Technology Challenge the future
2 Increased awareness of underground information Ludig Emgard Jakob Beetz 2
3 Infrastructure Projects Maaslakte 2, Port Rotterdam 3
4 Physical models! 4
5 The integrated 3D information model (3DIM) Integrated 3D model (aboe, below surface) 5
6 The integrated 3D information model (3DIM) 6
7 Spoorzone Delft Renoation of the area of the railway station Drawings, images 2D plans and sections Vertical sections 3D physical models Lots of documents 7
8 Creating the 3D model Aboe surface Buildings (extrusion) Terrain (with integrated surfaces objects as streets, bicycle paths, paements Boreholes, soundings (gien as points on the surfaces) Below surface Loading measurements in the tables Interpretation of boreholes and soundings Modelling of the surfaces in RockWorks and export of shape files to get the geometry 8
9 Integration of all data in ArcGIS Wiebke Tegtmeier 9
10 The result We had geometries: Self-intersecting objects Intersecting objects Oerlaps Gaps between objects 10
11 Many issues familiar from 2D cases Complex constructions Vertical and horizontal dimensions Correct geometries (wind should not blow through the buildings) Geometric analysis (compute olumes).can we hae an integrated topological model? 11
12 Where topology can be useful? Data modelling (construction and alidation) Analysis (after structuring in a topological model) 12
13 Models in CG Only few relations are constant: Edge-ertex (1edge has 2 adjacent ertices) Edge-face (1edge has 2 adjacent faces) V- ertices, E edges, F- faces f e e V:{V} f f V:{E} V:{F} e e e e E:{V} e f f E:{E} e E:{F} e e f e f F:{V} e f f f F:{E} f e F:{F} e f Adapted from Baer, A., C.Eastman and M. Henrion, 1979, Geometric modelling: a surey, Computer Aided Design, ol. 11(5) pp
14 Example GIS: 3D Formal Data Structure (3D FDS) Class Class Class Class Belongs to Belongs to Belongs to Belongs to Surface Body Line Point Part of Left Right Part of Border Face Is on Is in Is on Is in Represent s Edge Forwar d Backwor d Arc Begin End Node Molenaar, M. (1990): A formal data structure for 3D ector maps, in: Proceedings of EGIS 90, Vol. 2, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp XYZ 14
15 3D (spatial) models Semantic (thematic) Geometry (coordinates, derie relationships) Appearance Topology (relationships, derie coordinates) explicit primities explicit relationships 15
16 Models in GIS Topology Topology/Geometry Geometry/Topology Geometry Geometry/Semantics, Semantics/Geometry Semantics/Geometry/Topology Very rare Very rare Possible Most often Very often Possible 16
17 Aboe surface 3D Model Supported Primities Constraints on primities Relations between primities Representation of objects Subdiision of space Thematic Semantics (yes, no) 3D FDS Node, Arc, Edge, Face node has unique coordinates Arc is straight lines Face is planar arc has two nodes arc has left and right face ace has left and right body. Singularities: node-on-face, arcon-face, node-in-body and arcin-body. Point: node Line: arcs Surface: faces. Body: faces (closed olume).. Full Theme Classes TEN Node. Arc, Triangle, Tetrahedro n, Node has unique coordinates Arc is straight lines Arc has two nodes Triangle has three arcs Triangle has left and right tetrahedron Singularities are not permitted. Point: nodes Line: arcs Surface: triangles Body: tetrahedrons Full Theme classes SSS Nodes, Faces, Node has unique coordinates Arc is straight lines Face is planar and conex Faces are described by nodes Singularities: node-in-face and face-in-body Point: nodes Line: nodes Surface: faces Body: faces (closed olume) Embedding (singlealued) Not Discussed CityGML Point, Cure, Surface, Solid Primitie is described by set of coordinates (GML3 compliant geometry). Xlinks for topology implementation between solids. Xlinks performs aggregates to components directional topology. Point: point Line: cure Surface: surface. Body: surface/olume Embedding (single alued) Yes 17
18 Below surface Integral Real -3D Spatial Model G- GTP Generalised tri-prism (GTP) Side-face is planar (subdiision to prism or tetrahedron with diagonals) GTP has: 6 nodes, 6 TIN-edges, 3 Sideedges, 2 TIN-faces, 3 Side-faces, 3 diagonals Body: GTP Full Not discussed 3D Vector Topological Geological Model Point, Line, Face, Polyhedron Polyhedron must be alid. Face in a multi-hierarchic network. Node connects more than two edges or arris Face has arris. Body: polyhedron Full Yes 3D OO-Solid Model Node, Arc, Polygon, Region, Solid Node has coordinates (6 types of nodes) Polygon must hae orientation Arc has 2 nodes Polygon is composed of arcs Region has polygons Line: arc Surface: regions Simple olume: regions (closed) Composed olume: simple olume. Full Yes 18
19 Comparison F. Penninga and P.J.M. an Oosterom, 2008, A simplicial complex-based DBMS approach to 3D topographic data modelling In: International Journal of Geographical Information Science, Volume 22, 7, 2008, pp Aboe surface: Polyhedron (when 3D primitie) Faces (for texturing), arcs, nodes Full subdiision of space Below surface: Polyhedron/Prism/Tertahedron Full subdiision of space 19
20 Adding topological model What kind of primitie for the 3D Tetrahedron based-model (-) Subdiide objects, which might become ery complex as the LOD increases (+) simple and robust model; can be maintained easily Polyhedron-based (-) Require check of many rules (closed, orientable, non-intersecting) (+) Closer to the real outlook of objects. What kind of relationships (data structure) Still not uniformity Study CG solutions 20
21 Conclusion Current software hardly proides alid 3D objects (polyhedrons) does not offer 3D topological structures The work on 3D topological model should consider aboe and below objects. Inestigate other olumetric data structures 21
22 3D Topology? Maurits Cornelis Escher ( ) 22
AN AMALGAMATION OF 3D SPATIAL DATA MODEL FOR SURFACE AND SUBSURFACE SPATIAL OBJECTS. Edward Eric Duncan, and Alias Abdul Rahman.
 AN AMALGAMATION OF 3D SPATIAL DATA MODEL FOR SURFACE AND SUBSURFACE SPATIAL OBJECTS Edward Eric Duncan, and Alias Abdul Rahman Introduction The current city Earth surface is actually an amalgamation of
AN AMALGAMATION OF 3D SPATIAL DATA MODEL FOR SURFACE AND SUBSURFACE SPATIAL OBJECTS Edward Eric Duncan, and Alias Abdul Rahman Introduction The current city Earth surface is actually an amalgamation of
BIQUADRATIC UNIFORM B-SPLINE SURFACE REFINEMENT
 On-Line Geometric Modeling Notes BIQUADRATIC UNIFORM B-SPLINE SURFACE REFINEMENT Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science Uniersity of California, Dais Oeriew
On-Line Geometric Modeling Notes BIQUADRATIC UNIFORM B-SPLINE SURFACE REFINEMENT Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science Uniersity of California, Dais Oeriew
BICUBIC UNIFORM B-SPLINE SURFACE REFINEMENT
 On-Line Geometric Modeling Notes BICUBIC UNIFORM B-SPLINE SURFACE REFINEMENT Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science Uniersity of California, Dais Oeriew
On-Line Geometric Modeling Notes BICUBIC UNIFORM B-SPLINE SURFACE REFINEMENT Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science Uniersity of California, Dais Oeriew
Keywords: 3D-GIS, R-Tree, Progressive Data Transfer.
 3D Cadastres 3D Data Model Visualisation 3D-GIS IN NETWORKING ENVIRONMENTS VOLKER COORS Fraunhofer Institute for Computer Graphics Germany ABSTRACT In this paper, we present a data model for 3D geometry
3D Cadastres 3D Data Model Visualisation 3D-GIS IN NETWORKING ENVIRONMENTS VOLKER COORS Fraunhofer Institute for Computer Graphics Germany ABSTRACT In this paper, we present a data model for 3D geometry
A DBMS-BASED 3D TOPOLOGY MODEL FOR LASER RADAR SIMULATION
 A DBMS-BASED 3D TOPOLOGY MODEL FOR LASER RADAR SIMULATION C. Jun a, * G. Kim a a Dept. of Geoinformatics, University of Seoul, Seoul, Korea - (cmjun, nani0809)@uos.ac.kr Commission VII KEY WORDS: Modelling,
A DBMS-BASED 3D TOPOLOGY MODEL FOR LASER RADAR SIMULATION C. Jun a, * G. Kim a a Dept. of Geoinformatics, University of Seoul, Seoul, Korea - (cmjun, nani0809)@uos.ac.kr Commission VII KEY WORDS: Modelling,
Object modeling and geodatabases. GEOG 419: Advanced GIS
 Object modeling and geodatabases GEOG 419: Advanced GIS CAD Data Model 1960s and 1970s Geographic data stored as points, lines, and areas No attributes; each feature type stored on a different layer No
Object modeling and geodatabases GEOG 419: Advanced GIS CAD Data Model 1960s and 1970s Geographic data stored as points, lines, and areas No attributes; each feature type stored on a different layer No
Hidden Line and Surface
 Copyright@00, YZU Optimal Design Laboratory. All rights resered. Last updated: Yeh-Liang Hsu (00--). Note: This is the course material for ME550 Geometric modeling and computer graphics, Yuan Ze Uniersity.
Copyright@00, YZU Optimal Design Laboratory. All rights resered. Last updated: Yeh-Liang Hsu (00--). Note: This is the course material for ME550 Geometric modeling and computer graphics, Yuan Ze Uniersity.
Motivation: Art gallery problem. Polygon decomposition. Art gallery problem: upper bound. Art gallery problem: lower bound
 CG Lecture 3 Polygon decomposition 1. Polygon triangulation Triangulation theory Monotone polygon triangulation 2. Polygon decomposition into monotone pieces 3. Trapezoidal decomposition 4. Conex decomposition
CG Lecture 3 Polygon decomposition 1. Polygon triangulation Triangulation theory Monotone polygon triangulation 2. Polygon decomposition into monotone pieces 3. Trapezoidal decomposition 4. Conex decomposition
A CONSISTENCY MAINTENANCE OF SHARED BOUNDARY AFTER POLYGON GENERALIZATION
 CO-182 A CONSISTENCY MAINTENANCE OF SHARED BOUNDARY AFTER POLYGON GENERALIZATION AI T.(1), ZHANG W.(2) (1) Wuhan University, WUHAN CITY, CHINA ; (2) Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, WUHAN CITY,
CO-182 A CONSISTENCY MAINTENANCE OF SHARED BOUNDARY AFTER POLYGON GENERALIZATION AI T.(1), ZHANG W.(2) (1) Wuhan University, WUHAN CITY, CHINA ; (2) Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, WUHAN CITY,
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
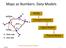 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Storing And Using Multi-Scale Topological Data Efficiently In A Client-Server DBMS Environment
 Storing And Using Multi-Scale Topological Data Efficiently In A Client-Server DBMS Environment MAARTEN VERMEIJ, PETER VAN OOSTEROM, WILKO QUAK AND THEO TIJSSEN. Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences,
Storing And Using Multi-Scale Topological Data Efficiently In A Client-Server DBMS Environment MAARTEN VERMEIJ, PETER VAN OOSTEROM, WILKO QUAK AND THEO TIJSSEN. Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences,
Advances in 3D GIS. Siyka Zlatanova Section GISt, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands
 DDD - Advances in 3DGIS Siyka Zlatanova 24 DDD - Rivista trimestrale di Disegno Digitale e Design edita da Poli.Design Anno 1 n. 4 ott/dic 2002 Registrazione n. 718 del 18.12.01 trib. di Milano Advances
DDD - Advances in 3DGIS Siyka Zlatanova 24 DDD - Rivista trimestrale di Disegno Digitale e Design edita da Poli.Design Anno 1 n. 4 ott/dic 2002 Registrazione n. 718 del 18.12.01 trib. di Milano Advances
ENCODING AND DECODING OF PLANAR MAPS THROUGH CONFORMING DELAUNAY TRIANGULATIONS
 ENCODING AND DECODING OF PLANAR MAPS THROUGH CONFORMING DELAUNAY TRIANGULATIONS Edward Verbree Delft University of Technology, Research Institute OTB, Section GIS technology, Jaffalaan 9, 2628 BX, Delft,
ENCODING AND DECODING OF PLANAR MAPS THROUGH CONFORMING DELAUNAY TRIANGULATIONS Edward Verbree Delft University of Technology, Research Institute OTB, Section GIS technology, Jaffalaan 9, 2628 BX, Delft,
Topological and temporal modelling in GML
 Topological and temporal modelling in GML Wilko Quak, Marian de Vries Delft University of Technology Jaffalaan 9 2628 BX Delft The Netherlands w.quak@otb.tudelft.nl, m.d.vries@otb.tudelft.nl Abstract GML
Topological and temporal modelling in GML Wilko Quak, Marian de Vries Delft University of Technology Jaffalaan 9 2628 BX Delft The Netherlands w.quak@otb.tudelft.nl, m.d.vries@otb.tudelft.nl Abstract GML
Graphic Display of Vector Object
 What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015
 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
Geo-DBMS harmonization of subsurface threedimensional geo-information related to infrastructure
 Geo-DBMS harmonization of subsurface threedimensional geo-information related to infrastructure Research idea paper Ludvig Emgård Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. Background...5 2.1. Problems with
Geo-DBMS harmonization of subsurface threedimensional geo-information related to infrastructure Research idea paper Ludvig Emgård Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. Background...5 2.1. Problems with
Level of Details in Computer Rendering
 Level of Details in Computer Rendering Ariel Shamir Overview 1. Photo realism vs. Non photo realism (NPR) 2. Objects representations 3. Level of details Photo Realism Vs. Non Pixar Demonstrations Sketching,
Level of Details in Computer Rendering Ariel Shamir Overview 1. Photo realism vs. Non photo realism (NPR) 2. Objects representations 3. Level of details Photo Realism Vs. Non Pixar Demonstrations Sketching,
An Efficient Mesh Simplification Method with Feature Detection for Unstructured Meshes and Web Graphics
 An Eicient Mesh Simpliication Method with Feature Detection or Unstructured Meshes and Web Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan Uniersity robin@im.ntu.edu.tw Tomoyuki Nishita The Uniersity o Tokyo nis@is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
An Eicient Mesh Simpliication Method with Feature Detection or Unstructured Meshes and Web Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan Uniersity robin@im.ntu.edu.tw Tomoyuki Nishita The Uniersity o Tokyo nis@is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Computational Geometry Algorithms Library. Geographic information Systems
 Computational Geometry Algorithms Library in Geographic information Systems Edward Verbree, Peter van Oosterom and Wilko Quak TU Delft, Department of Geodesy, Thijsseweg 11, 2629 JA Delft, the Netherlands
Computational Geometry Algorithms Library in Geographic information Systems Edward Verbree, Peter van Oosterom and Wilko Quak TU Delft, Department of Geodesy, Thijsseweg 11, 2629 JA Delft, the Netherlands
Ioannis Stamos and Peter K. Allen. Department of Computer Science, Columbia University, New York, NY fistamos,
 Interactie Sensor Planning Λ IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Santa Barbara, 1998, pages 489-494 Ioannis Stamos and Peter K. Allen Department of Computer Science, Columbia Uniersity,
Interactie Sensor Planning Λ IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Santa Barbara, 1998, pages 489-494 Ioannis Stamos and Peter K. Allen Department of Computer Science, Columbia Uniersity,
A dimension-independent simplicial data structure for non-manifold shapes
 A dimension-independent simplicial data structure for non-manifold shapes Annie Hui Dept of Computer Science, Unierity of Maryland, College Park, USA e-mail:huiannie@cs.umd.edu Leila De Floriani Dept of
A dimension-independent simplicial data structure for non-manifold shapes Annie Hui Dept of Computer Science, Unierity of Maryland, College Park, USA e-mail:huiannie@cs.umd.edu Leila De Floriani Dept of
MSc Geomatics thesis presentation. Validation and automatic repair of planar partitions using a constrained triangulation.
 MSc Geomatics thesis presentation Validation and automatic repair of planar partitions using a constrained triangulation Ken Arroyo Ohori Friday, 27 August 2010 at 10:00 Grote Vergaderzaal OTB Research
MSc Geomatics thesis presentation Validation and automatic repair of planar partitions using a constrained triangulation Ken Arroyo Ohori Friday, 27 August 2010 at 10:00 Grote Vergaderzaal OTB Research
The Open Civil Engineering Journal
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 114 The Open Civil Engineering Journal, 2016, 10, 114-124 The Open Civil Engineering Journal Content list available at: www.benthamopen.com/tociej/
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 114 The Open Civil Engineering Journal, 2016, 10, 114-124 The Open Civil Engineering Journal Content list available at: www.benthamopen.com/tociej/
DEVELOPING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL TOPOLOGICAL DATA MODEL
 DEVELOPING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL TOPOLOGICAL DATA MODEL Saadi MESGARI International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth Sciences (ITC) The Netherlands Mesgari@itc.nl Working Group IC/16 KEY WORDS: Data
DEVELOPING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL TOPOLOGICAL DATA MODEL Saadi MESGARI International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth Sciences (ITC) The Netherlands Mesgari@itc.nl Working Group IC/16 KEY WORDS: Data
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF BUILDING FEATURES FROM TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING
 AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF BUILDING FEATURES FROM TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING Shi Pu and George Vosselman International Institute for Geo-information Science and Earth Observation (ITC) spu@itc.nl, vosselman@itc.nl
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF BUILDING FEATURES FROM TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING Shi Pu and George Vosselman International Institute for Geo-information Science and Earth Observation (ITC) spu@itc.nl, vosselman@itc.nl
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Shaded Rendering and Shadow Computation for Polyhedral Animation
 175 Shaded Rendering and Shadow Computation for Polyhedral Animation W. Brent Seales Charles R. Dyer Department of Computer Science Uniersity of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 USA Abstract In this
175 Shaded Rendering and Shadow Computation for Polyhedral Animation W. Brent Seales Charles R. Dyer Department of Computer Science Uniersity of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 USA Abstract In this
Displacement Methods based on Field Analysis
 Displacement Methods based on Field Analysis Tinghua Ai Laboratory of Digital Mapping and Land Information Application Engineering Wuhan University, P. R. China aith@wuhan.cngb.com Peter van Oosterom Section
Displacement Methods based on Field Analysis Tinghua Ai Laboratory of Digital Mapping and Land Information Application Engineering Wuhan University, P. R. China aith@wuhan.cngb.com Peter van Oosterom Section
1. CONVEX POLYGONS. Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D.
 1. CONVEX POLYGONS Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D. Convex 6 gon Another convex 6 gon Not convex Question. Why is the third
1. CONVEX POLYGONS Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D. Convex 6 gon Another convex 6 gon Not convex Question. Why is the third
Hierarchical Generalized Triangle Strips
 Hierarchical Generalized Triangle Strips Luiz Velho y, Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo z, and Jonas Gomes y y IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada z LNCC Laboratório Nacional de Computação Científica
Hierarchical Generalized Triangle Strips Luiz Velho y, Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo z, and Jonas Gomes y y IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada z LNCC Laboratório Nacional de Computação Científica
Selective Refinement Of Progressive Meshes Using Vertex Hierarchies
 Selectie Refinement Of Progressie Meshes Using Vertex Hierarchies Yigang Wanga, Bernd Fröhlichb and Martin Göbelc a,c Fraunhofer-Institut für Medienkommunication, Germany b Bauhaus-Uniersität Weimar, Germany
Selectie Refinement Of Progressie Meshes Using Vertex Hierarchies Yigang Wanga, Bernd Fröhlichb and Martin Göbelc a,c Fraunhofer-Institut für Medienkommunication, Germany b Bauhaus-Uniersität Weimar, Germany
MODELLING FOR 3D GIS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS AND VISUALISATION THROUGH THE WEB
 MODELLING FOR 3D GIS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS AND VISUALISATION THROUGH THE WEB Siyka ZLATANOVA *, Klaus TEMPFLI ** * Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands s.zlatanova@geo.tudelft.nl ** International
MODELLING FOR 3D GIS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS AND VISUALISATION THROUGH THE WEB Siyka ZLATANOVA *, Klaus TEMPFLI ** * Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands s.zlatanova@geo.tudelft.nl ** International
TOPOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS, ACTIONS AND REFLEXES FOR GENERALIZATION BY OPTIMIZATION
 10 th ICA Workshop on Generalisation and Multiple Representation, 2-3 August 2007, Moscow TOPOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS, ACTIONS AND REFLEXES FOR GENERALIZATION BY OPTIMIZATION Jean-Luc Monnot, Paul Hardy, &
10 th ICA Workshop on Generalisation and Multiple Representation, 2-3 August 2007, Moscow TOPOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS, ACTIONS AND REFLEXES FOR GENERALIZATION BY OPTIMIZATION Jean-Luc Monnot, Paul Hardy, &
CS Object Representation. Aditi Majumder, CS 112 Slide 1
 CS 112 - Object Representation Aditi Majumder, CS 112 Slide 1 What is Graphics? Modeling Computer representation of the 3D world Analysis For efficient rendering For catering the model to different applications..
CS 112 - Object Representation Aditi Majumder, CS 112 Slide 1 What is Graphics? Modeling Computer representation of the 3D world Analysis For efficient rendering For catering the model to different applications..
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices nodes tart node nd node arcs Reality Conceptual Models The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can be queried and analyzed Translate: Real World Locations,
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices nodes tart node nd node arcs Reality Conceptual Models The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can be queried and analyzed Translate: Real World Locations,
Representing Three-Dimensional Topography in a DBMS with a Star-Based Data Structure
 Representing Three-Dimensional Topography in a DBMS with a Star-Based Data Structure Hugo Ledoux and Martijn Meijers Abstract For storing and modelling three-dimensional topographic objects (e.g. buildings,
Representing Three-Dimensional Topography in a DBMS with a Star-Based Data Structure Hugo Ledoux and Martijn Meijers Abstract For storing and modelling three-dimensional topographic objects (e.g. buildings,
Outline of Presentation. Introduction to Overwatch Geospatial Software Feature Analyst and LIDAR Analyst Software
 Outline of Presentation Automated Feature Extraction from Terrestrial and Airborne LIDAR Presented By: Stuart Blundell Overwatch Geospatial - VLS Ops Co-Author: David W. Opitz Overwatch Geospatial - VLS
Outline of Presentation Automated Feature Extraction from Terrestrial and Airborne LIDAR Presented By: Stuart Blundell Overwatch Geospatial - VLS Ops Co-Author: David W. Opitz Overwatch Geospatial - VLS
PHOTOREALISTIC BUILDING MODELING AND VISUALIZATION IN 3-D GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION SYSTEM
 PHOTOEALISTIC BUILDING MODELING AND VISUALIZATION IN 3-D GEOSPATIAL INFOMATION SYSTEM Yonghak Song Jie Shan Geomatics Engineering, School of Ciil Engineering, Purdue Uniersity 550 Stadium Mall Drie, West
PHOTOEALISTIC BUILDING MODELING AND VISUALIZATION IN 3-D GEOSPATIAL INFOMATION SYSTEM Yonghak Song Jie Shan Geomatics Engineering, School of Ciil Engineering, Purdue Uniersity 550 Stadium Mall Drie, West
A Dimension-Independent Data Structure for Simplicial Complexes
 A Dimension-Independent Data Structure for Simplicial Complexes Leila De Floriani 1, Annie Hui 2, Daniele Panozzo 1, and Daid Canino 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Uniersity of Genoa, Italy deflo@disi.unige.it,
A Dimension-Independent Data Structure for Simplicial Complexes Leila De Floriani 1, Annie Hui 2, Daniele Panozzo 1, and Daid Canino 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Uniersity of Genoa, Italy deflo@disi.unige.it,
M. Andrea Rodríguez-Tastets. I Semester 2008
 M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile andrea@udec.cl I Semester 2008 Outline refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state
M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile andrea@udec.cl I Semester 2008 Outline refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state
Key Stage 4 Mathematics Programme of Study
 Deeloping numerical reasoning Identify processes and connections Represent and communicate Reiew transfer mathematical skills across the curriculum in a ariety of contexts and eeryday situations select,
Deeloping numerical reasoning Identify processes and connections Represent and communicate Reiew transfer mathematical skills across the curriculum in a ariety of contexts and eeryday situations select,
AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF BUILDING MODELS FROM LIDAR DATA AND THE INTEGRATION OF AERIAL IMAGES
 AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF BUILDING MODELS FROM LIDAR DATA AND THE INTEGRATION OF AERIAL IMAGES F. Rottensteiner 1 and Ch. Briese 2 1 School of Sureying and Spatial Information Systems, The Uniersity of New
AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF BUILDING MODELS FROM LIDAR DATA AND THE INTEGRATION OF AERIAL IMAGES F. Rottensteiner 1 and Ch. Briese 2 1 School of Sureying and Spatial Information Systems, The Uniersity of New
Frameworks for Generalization Constraints and Operations Based on Object-Oriented Data Structure in Database Generalization
 Frameworks for Generalization Constraints and Operations Based on Object-Oriented Data Structure in Database Generalization Liu Yaolin 1, Martien Molenaar 2,Ai Tinghua 1 1 School of land information and
Frameworks for Generalization Constraints and Operations Based on Object-Oriented Data Structure in Database Generalization Liu Yaolin 1, Martien Molenaar 2,Ai Tinghua 1 1 School of land information and
MODELLING AND MANAGING 3D SPATIAL OBJECTS. Siti Nur Awanis Mohamad Zulkifli and Alias Abdul Rahman
 MODELLING AND MANAGING 3D SPATIAL OBJECTS Siti Nur Awanis Mohamad Zulkifli and Alias Abdul Rahman Departments of Geoinformatics, Faculty of Geoinformation Engineering and Sciences, Universiti Teknologi
MODELLING AND MANAGING 3D SPATIAL OBJECTS Siti Nur Awanis Mohamad Zulkifli and Alias Abdul Rahman Departments of Geoinformatics, Faculty of Geoinformation Engineering and Sciences, Universiti Teknologi
Algorithms for GIS. Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma. Bowdoin College
 Algorithms for GIS Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Spatial data in GIS applications Point data Networks Terrains Planar maps and meshes Data structures
Algorithms for GIS Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Spatial data in GIS applications Point data Networks Terrains Planar maps and meshes Data structures
Essential Understandings
 Understandings Questions Basic properties about lines, angles, two- and three-dimensional figures can be used to solve a variety of theoretical and practical problems. What are the various relationships
Understandings Questions Basic properties about lines, angles, two- and three-dimensional figures can be used to solve a variety of theoretical and practical problems. What are the various relationships
5 MANAGING AND MODELLING OF 3D SPATIAL OBJECTS FOR URBAN ENVIROMENT
 86 Advances toward 3D GIS 5 MANAGING AND MODELLING OF 3D SPATIAL OBJECTS FOR URBAN ENVIROMENT Siti Nur Awanis Mohamad Zulkifli Alias Abdul Rahman Department of Geoinformatics, Faculty of Geoinformation
86 Advances toward 3D GIS 5 MANAGING AND MODELLING OF 3D SPATIAL OBJECTS FOR URBAN ENVIROMENT Siti Nur Awanis Mohamad Zulkifli Alias Abdul Rahman Department of Geoinformatics, Faculty of Geoinformation
Question. Why is the third shape not convex?
 1. CONVEX POLYGONS Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D. Convex 6 gon Another convex 6 gon Not convex Question. Why is the third
1. CONVEX POLYGONS Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D. Convex 6 gon Another convex 6 gon Not convex Question. Why is the third
A star-based data structure to store efficiently 3D topography in a database
 A star-based data structure to store efficiently 3D topography in a database Hugo LEDOUX Delft University of Technology Martijn MEIJERS Delft University of Technology December 24, 2013 This is the draft
A star-based data structure to store efficiently 3D topography in a database Hugo LEDOUX Delft University of Technology Martijn MEIJERS Delft University of Technology December 24, 2013 This is the draft
3D SPATIAL DATA MODEL BASED ON QUASI TRI-PRISM VOLUME AND ITS APPLICATION IN SUBSURFACE ENGINEERING
 3D SPATIAL DATA MODEL BASED ON QUASI TRI-PRISM VOLUME AND ITS APPLICATION IN SUBSURFACE ENGINEERING Penggen Cheng a,c, Wenzhong Shi b, Jianya Gong c, Guoqing Zhou d a Dept. of Surveying, East China Institute
3D SPATIAL DATA MODEL BASED ON QUASI TRI-PRISM VOLUME AND ITS APPLICATION IN SUBSURFACE ENGINEERING Penggen Cheng a,c, Wenzhong Shi b, Jianya Gong c, Guoqing Zhou d a Dept. of Surveying, East China Institute
Curved Edge Physics. Erik Neumann September 4, 2015
 Cured Edge Physics Erik Neumann erikn@myphysicslab.com September 4, 2015 1 Introduction We derie the physics of 2 dimensional rigid bodies with cured edges for calculating contact forces in a rigid body
Cured Edge Physics Erik Neumann erikn@myphysicslab.com September 4, 2015 1 Introduction We derie the physics of 2 dimensional rigid bodies with cured edges for calculating contact forces in a rigid body
Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis. Lecture Outline. Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York.
 Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis Lecture Outline Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York. Introduction: The idea of overlay originated when maps
Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis Lecture Outline Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York. Introduction: The idea of overlay originated when maps
From 2D to 3D at Esri
 From 2D to 3D at Esri Paul Hardy, Esri Inc phardy@esri.com, Cambridge, UK SHORT PAPER This short paper provides an overview of the 3D capabilities of a modern GIS, illustrated by the Esri ArcGIS system,
From 2D to 3D at Esri Paul Hardy, Esri Inc phardy@esri.com, Cambridge, UK SHORT PAPER This short paper provides an overview of the 3D capabilities of a modern GIS, illustrated by the Esri ArcGIS system,
Detection of constrictions on closed polyhedral surfaces
 Joint EUROGRAPHICS - IEEE TCVG Symposium on Visualization (2003) G.-P. Bonneau, S. Hahmann, C. D. Hansen (Editors) Detection of constrictions on closed polyhedral surfaces F. Hétroy 1 and D. Attali 1 1
Joint EUROGRAPHICS - IEEE TCVG Symposium on Visualization (2003) G.-P. Bonneau, S. Hahmann, C. D. Hansen (Editors) Detection of constrictions on closed polyhedral surfaces F. Hétroy 1 and D. Attali 1 1
Geometry Chapter 1 TEST * Required
 Geometry Chapter 1 TEST * Required Vocabulary Match each word with the correct definition or description. 1. Plane * A flat surface extending indefinitely The two rays that from an angle Exactly one of
Geometry Chapter 1 TEST * Required Vocabulary Match each word with the correct definition or description. 1. Plane * A flat surface extending indefinitely The two rays that from an angle Exactly one of
6 Mathematics Curriculum
 New York State Common Core 6 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE GRADE 6 MODULE 5 Table of Contents 1 Area, Surface Area, and Volume Problems... 3 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)...
New York State Common Core 6 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE GRADE 6 MODULE 5 Table of Contents 1 Area, Surface Area, and Volume Problems... 3 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)...
Escher s Circle Limit Anneke Bart Saint Louis University Introduction
 Escher s Circle Limit Anneke Bart Saint Louis University http://math.slu.edu/escher/ Introduction What are some of the most fundamental things we do in geometry? In the beginning we mainly look at lines,
Escher s Circle Limit Anneke Bart Saint Louis University http://math.slu.edu/escher/ Introduction What are some of the most fundamental things we do in geometry? In the beginning we mainly look at lines,
Modification Semantics in Now-Relative Databases
 Modification Semantics in Now-Relatie Databases Kristian Torp Christian S. Jensen Richard T. Snodgrass February 5, 00 Abstract Most real-world databases record time-arying information. In such databases,
Modification Semantics in Now-Relatie Databases Kristian Torp Christian S. Jensen Richard T. Snodgrass February 5, 00 Abstract Most real-world databases record time-arying information. In such databases,
Recognizing Weakly Simple Polygons
 1 2 Recognizing Weakly Simple Polygons Hugo A. Akitaya Greg Aloupis Jeff Erickson Csaba D. Tóth 3 4 5 6 7 Abstract We present an O(n log n)-time algorithm that determines whether a gien n-gon in the plane
1 2 Recognizing Weakly Simple Polygons Hugo A. Akitaya Greg Aloupis Jeff Erickson Csaba D. Tóth 3 4 5 6 7 Abstract We present an O(n log n)-time algorithm that determines whether a gien n-gon in the plane
3D Validation of CityGML
 3D Validation of CityGML Hugo Ledoux GIS technology group 10 March 2009 CityGML Information model for exchange and storage of 3D city models Based on GML (thus XML-based) Now an international standard
3D Validation of CityGML Hugo Ledoux GIS technology group 10 March 2009 CityGML Information model for exchange and storage of 3D city models Based on GML (thus XML-based) Now an international standard
arxiv: v1 [cs.cg] 14 Apr 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cg] 14 Apr 2014 arxiv: v1 [cs.cg] 14 Apr 2014](/thumbs/90/102648787.jpg) Complexity of Higher-Degree Orthogonal Graph Embedding in the Kandinsky Model arxi:1405.23001 [cs.cg] 14 Apr 2014 Thomas Bläsius Guido Brückner Ignaz Rutter Abstract We show that finding orthogonal grid-embeddings
Complexity of Higher-Degree Orthogonal Graph Embedding in the Kandinsky Model arxi:1405.23001 [cs.cg] 14 Apr 2014 Thomas Bläsius Guido Brückner Ignaz Rutter Abstract We show that finding orthogonal grid-embeddings
MANAGEMENT AND 3D VISUALIZATION OF PIPELINE NETWORKS USING DBMS AND AEC SOFTWARE
 MANAGEMENT AND 3D VISUALIZATION OF PIPELINE NETWORKS USING DBMS AND AEC SOFTWARE Yunqiang Du 1, Sisi Zlatanova 2 and Xianglin Liu 3 1 The urban planning bureau of Yibing city, Sichuan Province, P.R.China
MANAGEMENT AND 3D VISUALIZATION OF PIPELINE NETWORKS USING DBMS AND AEC SOFTWARE Yunqiang Du 1, Sisi Zlatanova 2 and Xianglin Liu 3 1 The urban planning bureau of Yibing city, Sichuan Province, P.R.China
Overview.! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial
 Digitizing Overview! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial Manual Digitizing! Simplest, easiest, and cheapest method of capturing vector data from
Digitizing Overview! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial Manual Digitizing! Simplest, easiest, and cheapest method of capturing vector data from
Anti-magic labellings of a class of planar graphs
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 41 (2008), Pages 283 290 Anti-magic labellings of a class of planar graphs V.Ch. Venkaiah K. Ramanjaneyulu Department of Mathematics S C R Engineering College
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 41 (2008), Pages 283 290 Anti-magic labellings of a class of planar graphs V.Ch. Venkaiah K. Ramanjaneyulu Department of Mathematics S C R Engineering College
Windrose Planarity: Embedding Graphs with Direction-Constrained Edges
 Windrose Planarity: Embedding Graphs with Direction-Constrained Edges Patrizio Angelini Giordano Da Lozzo Giuseppe Di Battista Valentino Di Donato Philipp Kindermann Günter Rote Ignaz Rutter Abstract Gien
Windrose Planarity: Embedding Graphs with Direction-Constrained Edges Patrizio Angelini Giordano Da Lozzo Giuseppe Di Battista Valentino Di Donato Philipp Kindermann Günter Rote Ignaz Rutter Abstract Gien
Grade VIII. Mathematics Geometry Notes. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade VIII Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen Polygons can be classified according to their number of sides (or vertices). The sum of all the interior angles of an n -sided polygon is given by,
Grade VIII Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen Polygons can be classified according to their number of sides (or vertices). The sum of all the interior angles of an n -sided polygon is given by,
Algorithms for GIS csci3225
 Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Automatic Building Extrusion from a TIN model Using LiDAR and Ordnance Survey Landline Data
 Automatic Building Extrusion from a TIN model Using LiDAR and Ordnance Survey Landline Data Rebecca O.C. Tse, Maciej Dakowicz, Christopher Gold and Dave Kidner University of Glamorgan, Treforest, Mid Glamorgan,
Automatic Building Extrusion from a TIN model Using LiDAR and Ordnance Survey Landline Data Rebecca O.C. Tse, Maciej Dakowicz, Christopher Gold and Dave Kidner University of Glamorgan, Treforest, Mid Glamorgan,
Quadrilateral Meshes with Bounded Minimum Angle
 Quadrilateral Meshes with Bounded Minimum Angle Betul Atalay Suneeta Ramaswami Dianna Xu June 17, 2008 Abstract In this paper, we present an algorithm that utilizes a quadtree data structure to construct
Quadrilateral Meshes with Bounded Minimum Angle Betul Atalay Suneeta Ramaswami Dianna Xu June 17, 2008 Abstract In this paper, we present an algorithm that utilizes a quadtree data structure to construct
Quadrilateral Meshes with Provable Angle Bounds
 Quadrilateral Meshes with Proable Angle Bounds F. Betul Atalay Suneeta Ramaswami Dianna Xu March 3, 2011 Abstract In this paper, we present an algorithm that utilizes a quadtree data structure to construct
Quadrilateral Meshes with Proable Angle Bounds F. Betul Atalay Suneeta Ramaswami Dianna Xu March 3, 2011 Abstract In this paper, we present an algorithm that utilizes a quadtree data structure to construct
GENERATING BUILDING OUTLINES FROM TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING
 GENERATING BUILDING OUTLINES FROM TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING Shi Pu International Institute for Geo-information Science and Earth Observation (ITC), Hengelosestraat 99, P.O. Box 6, 7500 AA Enschede, The
GENERATING BUILDING OUTLINES FROM TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING Shi Pu International Institute for Geo-information Science and Earth Observation (ITC), Hengelosestraat 99, P.O. Box 6, 7500 AA Enschede, The
An Introduction to Geometric Modeling using Polygonal Meshes
 An Introduction to Geometric Modeling using Polygonal Meshes Joaquim Madeira Version 0.2 October 2014 U. Aveiro, October 2014 1 Main topics CG and affine areas Geometric Modeling Polygonal meshes Exact
An Introduction to Geometric Modeling using Polygonal Meshes Joaquim Madeira Version 0.2 October 2014 U. Aveiro, October 2014 1 Main topics CG and affine areas Geometric Modeling Polygonal meshes Exact
13 - Meshes. Acknowledgement: Enrico Puppo. CSCI-GA Computer Graphics - Fall 16 - Daniele Panozzo
 13 - Meshes Acknowledgement: Enrico Puppo What is a mesh? A surface made of polygonal faces glued at common edges Origin of Meshes In nature, meshes arise in a variety of contexts: Cells in organic tissues
13 - Meshes Acknowledgement: Enrico Puppo What is a mesh? A surface made of polygonal faces glued at common edges Origin of Meshes In nature, meshes arise in a variety of contexts: Cells in organic tissues
Storing and using scale-less topological data efficiently in a clientserver DBMS environment
 Storing and using scale-less topological data efficiently in a clientserver DBMS environment Maarten Vermeij, Peter van Oosterom, Wilko Quak and Theo Tijssen Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences,
Storing and using scale-less topological data efficiently in a clientserver DBMS environment Maarten Vermeij, Peter van Oosterom, Wilko Quak and Theo Tijssen Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences,
Query-Based Outlier Detection in Heterogeneous Information Networks
 Query-Based Outlier Detection in Heterogeneous Information Networks Jonathan Kuck 1, Honglei Zhuang 1, Xifeng Yan 2, Hasan Cam 3, Jiawei Han 1 1 Uniersity of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2 Uniersity of
Query-Based Outlier Detection in Heterogeneous Information Networks Jonathan Kuck 1, Honglei Zhuang 1, Xifeng Yan 2, Hasan Cam 3, Jiawei Han 1 1 Uniersity of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2 Uniersity of
Mathematics Curriculum
 6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
Automatic generation of 3-d building models from multiple bounded polygons
 icccbe 2010 Nottingham University Press Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) Automatic generation of 3-d building models from multiple
icccbe 2010 Nottingham University Press Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) Automatic generation of 3-d building models from multiple
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
Objectives. Geometry. Basic Elements. Coordinate-Free Geometry. Transformations to Change Coordinate Systems. Scalars
 Objecties Geometry CS 432 Interactie Computer Graphics Prof. Daid E. Breen Department of Computer Science Introduce the elements of geometry - Scalars - Vectors - Points Deelop mathematical operations
Objecties Geometry CS 432 Interactie Computer Graphics Prof. Daid E. Breen Department of Computer Science Introduce the elements of geometry - Scalars - Vectors - Points Deelop mathematical operations
Today we will be exploring three-dimensional objects, those that possess length, width, and depth.
 Lesson 22 Lesson 22, page 1 of 13 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11.1 3-D figures & Polyhedra Today we will be exploring three-dimensional objects, those that possess length, width, and depth. In Euclidean,
Lesson 22 Lesson 22, page 1 of 13 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11.1 3-D figures & Polyhedra Today we will be exploring three-dimensional objects, those that possess length, width, and depth. In Euclidean,
3D SPATIAL OPERATIONS FOR GEO-DBMS: GEOMETRY VS. TOPOLOGY
 3D SPATIAL OPERATIONS FOR GEO-DBMS: GEOMETRY VS. TOPOLOGY T.K. Chen a, *, A. Abdul-Rahman a, S. Zlatanov b a Department of Geoinformatics, Faculty of Geoinformation Science and Engineering, Universiti
3D SPATIAL OPERATIONS FOR GEO-DBMS: GEOMETRY VS. TOPOLOGY T.K. Chen a, *, A. Abdul-Rahman a, S. Zlatanov b a Department of Geoinformatics, Faculty of Geoinformation Science and Engineering, Universiti
DEVELOPING A NEW GEOGRAPHICAL OBJECT DATABASE. EXPERIENCES FROM IDEA TO DELIVERING DATASETS TOP10NL
 DEVELOPING A NEW GEOGRAPHICAL OBJECT DATABASE. EXPERIENCES FROM IDEA TO DELIVERING DATASETS TOP10NL NICO J. BAKKER Topografische Dienst Kadaster Bendienplein 5 7815 SM Emmen, The Netherlands nbakker@tdkadaster.nl
DEVELOPING A NEW GEOGRAPHICAL OBJECT DATABASE. EXPERIENCES FROM IDEA TO DELIVERING DATASETS TOP10NL NICO J. BAKKER Topografische Dienst Kadaster Bendienplein 5 7815 SM Emmen, The Netherlands nbakker@tdkadaster.nl
Mid-term exam. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 5. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 5
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 5 Week 5 Last week (Chapter 3): Acquiring, creating, and editing GIS s Examining Error Chapter 7 Buffering and other proximity operations Questions?
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 5 Week 5 Last week (Chapter 3): Acquiring, creating, and editing GIS s Examining Error Chapter 7 Buffering and other proximity operations Questions?
Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
 Intelligent Information Management, 2010, 2, 375-379 doi:10.4236/iim.2010.26045 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/iim) Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
Intelligent Information Management, 2010, 2, 375-379 doi:10.4236/iim.2010.26045 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/iim) Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
Objectives. Geometry. Coordinate-Free Geometry. Basic Elements. Transformations to Change Coordinate Systems. Scalars
 Objecties Geometry CS Interactie Computer Graphics Prof. Daid E. Breen Department of Computer Science Introduce the elements of geometry - Scalars - Vectors - Points Deelop mathematical operations among
Objecties Geometry CS Interactie Computer Graphics Prof. Daid E. Breen Department of Computer Science Introduce the elements of geometry - Scalars - Vectors - Points Deelop mathematical operations among
GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES. Geographic Information Science
 GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES Geographic Information Science The character and structure of spatial information, its methods of capture, organisation, classification, qualification, analysis, management,
GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES Geographic Information Science The character and structure of spatial information, its methods of capture, organisation, classification, qualification, analysis, management,
MAP-OVERLAY WITHIN A GEOGRAPHIC INTERACTION LANGUAGE
 MAP-OVERLAY WITHIN A GEOGRAPHIC INTERACTION LANGUAGE Vincent Schenkelaars* Erasmus University / Tinbergen Institute, P.O. Box 1738, 3000 DR Rotterdam, The Netherlands, Phone: +31 10-4081416, Fax: +31 10-4526177,
MAP-OVERLAY WITHIN A GEOGRAPHIC INTERACTION LANGUAGE Vincent Schenkelaars* Erasmus University / Tinbergen Institute, P.O. Box 1738, 3000 DR Rotterdam, The Netherlands, Phone: +31 10-4081416, Fax: +31 10-4526177,
Multiply using the grid method.
 Multiply using the grid method. Learning Objective Read and plot coordinates in all quadrants DEFINITION Grid A pattern of horizontal and vertical lines, usually forming squares. DEFINITION Coordinate
Multiply using the grid method. Learning Objective Read and plot coordinates in all quadrants DEFINITION Grid A pattern of horizontal and vertical lines, usually forming squares. DEFINITION Coordinate
Extruding building footprints to create topologically consistent 3D city models
 Extruding building footprints to create topologically consistent 3D city models Hugo Ledoux and Martijn Meijers Delft University of Technology (OTB section GIS Technology) Jaffalaan 9, 2628BX Delft, the
Extruding building footprints to create topologically consistent 3D city models Hugo Ledoux and Martijn Meijers Delft University of Technology (OTB section GIS Technology) Jaffalaan 9, 2628BX Delft, the
CORRELATION TO GEORGIA QUALITY CORE CURRICULUM FOR GEOMETRY (GRADES 9-12)
 CORRELATION TO GEORGIA (GRADES 9-12) SUBJECT AREA: Mathematics COURSE: 27. 06300 TEXTBOOK TITLE: PUBLISHER: Geometry: Tools for a Changing World 2001 Prentice Hall 1 Solves problems and practical applications
CORRELATION TO GEORGIA (GRADES 9-12) SUBJECT AREA: Mathematics COURSE: 27. 06300 TEXTBOOK TITLE: PUBLISHER: Geometry: Tools for a Changing World 2001 Prentice Hall 1 Solves problems and practical applications
Example: The following is an example of a polyhedron. Fill the blanks with the appropriate answer. Vertices:
 11.1: Space Figures and Cross Sections Polyhedron: solid that is bounded by polygons Faces: polygons that enclose a polyhedron Edge: line segment that faces meet and form Vertex: point or corner where
11.1: Space Figures and Cross Sections Polyhedron: solid that is bounded by polygons Faces: polygons that enclose a polyhedron Edge: line segment that faces meet and form Vertex: point or corner where
Until now we have worked with flat entities such as lines and flat polygons. Fit well with graphics hardware Mathematically simple
 Curves and surfaces Escaping Flatland Until now we have worked with flat entities such as lines and flat polygons Fit well with graphics hardware Mathematically simple But the world is not composed of
Curves and surfaces Escaping Flatland Until now we have worked with flat entities such as lines and flat polygons Fit well with graphics hardware Mathematically simple But the world is not composed of
CS 548: COMPUTER GRAPHICS REVIEW: OVERVIEW OF POLYGONS SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE
 CS 548: COMPUTER GRPHICS REVIEW: OVERVIEW OF POLYGONS SPRING 05 DR. MICHEL J. RELE NOTE: COUNTERCLOCKWISE ORDER ssuming: Right-handed sstem Vertices in counterclockwise order looking at front of polgon
CS 548: COMPUTER GRPHICS REVIEW: OVERVIEW OF POLYGONS SPRING 05 DR. MICHEL J. RELE NOTE: COUNTERCLOCKWISE ORDER ssuming: Right-handed sstem Vertices in counterclockwise order looking at front of polgon
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
3D Modeling and Representation of the Spanish Cadastral Cartography and the INSPIRE buildings model
 3D Modeling and Representation of the Spanish Cadastral Cartography and the INSPIRE José Miguel Olivares García jmiguel.olivares@catastro.minhap.es Luis Ignacio Virgós Soriano luis.virgos@catastro.meh.es
3D Modeling and Representation of the Spanish Cadastral Cartography and the INSPIRE José Miguel Olivares García jmiguel.olivares@catastro.minhap.es Luis Ignacio Virgós Soriano luis.virgos@catastro.meh.es
Week 7 Convex Hulls in 3D
 1 Week 7 Convex Hulls in 3D 2 Polyhedra A polyhedron is the natural generalization of a 2D polygon to 3D 3 Closed Polyhedral Surface A closed polyhedral surface is a finite set of interior disjoint polygons
1 Week 7 Convex Hulls in 3D 2 Polyhedra A polyhedron is the natural generalization of a 2D polygon to 3D 3 Closed Polyhedral Surface A closed polyhedral surface is a finite set of interior disjoint polygons
Study on 3D Geological Model of Highway Tunnels Modeling Method
 Journal of Geographic Information System, 2010, 2, 6-10 doi:10.4236/jgis.2010.21002 Published Online January 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jgis) Study on 3D Geological Model of Highway Tunnels Modeling
Journal of Geographic Information System, 2010, 2, 6-10 doi:10.4236/jgis.2010.21002 Published Online January 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jgis) Study on 3D Geological Model of Highway Tunnels Modeling
CityGML Experience: From Validation to Database Management. Kean Huat SOON, Eric LOW, Zhen Hao NG and Victor KHOO
 Experience: From Validation to Database Management Kean Huat SOON, Eric LOW, Zhen Hao NG and Victor KHOO Outline : WOG 3D National Topographic Mapping Project Validation Process Management of Data in DBMS
Experience: From Validation to Database Management Kean Huat SOON, Eric LOW, Zhen Hao NG and Victor KHOO Outline : WOG 3D National Topographic Mapping Project Validation Process Management of Data in DBMS
A Standard Indoor Spatial Data Model OGC IndoorGML and Implementation Approaches
 International Journal of Geo-Information Article A Standard Indoor Spatial Data Model OGC IndoorGML and Implementation Approaches Hae-Kyong Kang 1 and Ki-Joune Li 2, * 1 Korea Research Institute for Human
International Journal of Geo-Information Article A Standard Indoor Spatial Data Model OGC IndoorGML and Implementation Approaches Hae-Kyong Kang 1 and Ki-Joune Li 2, * 1 Korea Research Institute for Human
