Mid-term exam. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 5. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 5
|
|
|
- Godfrey Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 5 Week 5 Last week (Chapter 3): Acquiring, creating, and editing GIS s Examining Error Chapter 7 Buffering and other proximity operations Questions? Next week- read: Chapter 2: pp Mid-term exam Wednesday of next week All lecture and lab material through this week Bring calculator Book: Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11 Book questions Labs: Processes (import, clip) Software (licensing and modules) Data (coverages, shapefiles, DOQ, DRG) Questions with short answers Matching, True / False 1
2 This week s topics Chapter 11 Overlay processes Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS s Geographic Information Systems Applications in Natural Resource Management Chapter 11 Overlay Processes Michael G. Wing & Pete Bettinger Objectives: Overlay Processes The outcomes from using an overlay process to accomplish one or more analytical tasks within GIS; The circumstances that help you decide when each of the three overlay processes might be used to support an analysis or research objective; and The differences among the three overlay processes, and between them and other similar GIS processes. 2
3 Overlay strength One of the most powerful capabilities of GIS is its ability to integrate landscape and attribute information from multiple s into a single layer Design with Nature (Ian McHarg 1969) demonstrated a manual overlay process that caught the attention of many and started some critical thinking among people who would later create the first GIS software programs Overlay process mechanics (1) Typically, we are working with two s A point, line, or polygon contains features of interest A polygon is used to define the union, intersect, or identity area to be considered in processing Can also intersect two line s A third is created that contains the results Overlay process mechanics (2) Unlike a merge process, which also integrates two s to produce a third, a overlay process Creates new features when intersections occur Depending on the type of overlay and input s, the results of some overlay processes will be identical or very similar to the results of other GIS processes Example: A clip process and an identity or intersect process may lead to the same resulting, depending on the inputs 3
4 Overlay s Fire Stands day, month, year basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age Union overlay process Fire Stands Resulting day, month, year basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age, day, month, year All polygons from both s will be split at their intersections and preserved in the output Union output Resulting : fire and stands, defined along original fire boundaries and along the boundaries of the stands Stand attributes present, fire attributes absent Stand attributes present, fire attributes present Stand attributes absent, fire attributes present Attributes: basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age, day, month, year 4
5 Database #1 Database #2 Database # In #1 and #2 In #1, outside of #2 An example of the processing of features during an union operation. Database #2 In #2, outside of #1 In #1 and #2 Output GIS Database a b a 2 4b 2 6a 2 6b 2 7a 2 7b 1 2 Intersect overlay process Fire Stands Resulting day, month, year basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age, day, month, year Only those features in the area common to both s will be preserved in the output. Intersect output Resulting : stands, defined along original stand boundaries yet only within the boundary of the fire Should have a full set of attributes in the output. Attributes: basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age, day, month, year 5
6 Database #1 Database #2 Database # In #1 and #2 In #1, outside of #2 An example of the processing of features during an intersect operation Database #2 In #2, outside of #1 In #1 and #2 Output GIS Database A portion of arc 1 1 A portion of arc 2 6 A portion of arc 1 1 A portion A portion of arc 2 4 of arc 2 7 Identity overlay process Fire Stands Resulting day, month, year basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age, day, month, year All features of the input, as well as those features of the identity that overlap the input, are preserved in the output. Identity output Resulting : fire, defined along original fire boundaries and along the boundaries of the stands Attributes: basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age, day, month, year 6
7 A closer look at the results of the identity operation of fire and stands Stand L Fire area outside of Daniel Pickett forest Fire area inside of Daniel Pickett forest Stand M Stand U Stand X Stand N Stand VegType Basal Area Age MBF Month Day Year L C M N C U A X B Identity overlay process II Stands Fire Resulting basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age day, month, year basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age, day, month, year All features of the input, as well as those features of the identity that overlap the input, are preserved in the output. Identity output II Resulting : stands, defined along original stand boundaries and along the boundaries of the fire Attributes: basal area, volume per acre, vegetation type, age, day, month, year 7
8 A closer look at the results of the identity II operation of stands and fire Stand boundaries Fire area Stand T Stand VegType Basal Area Age MBF Month Day Year T C U A V A W C X B Y B Stand U Stand X Stand V Stand Y Stand W 1 1 Database #1 Database #2 Database # In #1 and #2 In #1, outside of #2 An example of the processing of features during an identity operation. Database #2 In #2, outside of #1 In #1 and #2 Output GIS Database 1 1b 1 1a 2 4b 2 6b 2 7a Overlay Considerations Usually requires a polygon layer as the overlay Two line layers can be intersected ArcGIS allows, depending on your license level, more than two layers Potential users should clearly understand the differences among the overlay processes before selecting one May require significant processing time depending on size of inputs 8
9 Database #1 Database # Figure An example of the manipulation of landscape features during an intersect overlay of line and polygon s Overlay of Database #2 On Database # Output GIS Database Point overlay application Research plots (57) on the Brown Tract What is the land allocation? An intersect overlay process could help you answer # ## # ## # # # # # # # ## # # # # # # # # # # # ## # ## # # # # ## # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # Research Plots # # Forest Stands Research plot land allocations Land allocation Research plot ID Even-aged 48 Research 6 Uneven-aged 3 9
10 Line overlay application Stream records: 398 What is the land allocation for streams? An intersect overlay process could help you answer Streams Forest Stands Stream record land allocations Land allocation Stream record count Even-aged 281 Meadow 2 Oak Woodland 3 Research 7 Uneven-aged 65 <No Value> 40 Spurious or sliver polygons Can be detected by looking at area measurements in tabular Very small areas will help identify their presence Deciding whether these very small areas are meaningful will depend On your organization s policies about minimum mapping units The goals of your analysis project 10
11 Spurious polygon Height at this end: about 5 feet Width: about 66 feet Can be combined/dissolved into an adjacent polygon but which one? Figure A spurious polygon that was created during the intersect process. Overlay summary 1 2 Output GIS Union Output Figure Summary of results for union, intersect, identity, and identity reverse order for the stands and _fire GIS s. Intersect Output Identity Output Identity Reverse Order Output Geographic Information Systems Applications in Natural Resource Management Chapter 8 Combining and Splitting Landscape Features, and Merging GIS Databases Michael G. Wing & Pete Bettinger 11
12 Chapter 8 Objectives Objectives: Why, when, and how you might want to combine landscape features; The reasons for splitting landscape features, and the situations where this process might be appropriate; and Why two or more GIS s might be merged, and what you would expect to find within a merged. The combine process These changes are saved in a new The combine process is also known as a dissolve Figure 8.1. Combining two polygons, by eliminating a shared edge, to produce a single polygon. Shared edge Polygon 2 Polygon 1 Polygon 1 Prior to combining the polygons After combining the polygons 12
13 Combine/Dissolve Input Combine/Dissolve Output Why combine features? May help remove some of the smaller features that are the products of digitizing or other GIS process Spurious or erroneous polygons Landscape delineations in data acquired from elsewhere does not match existing data Remove redundant features in a No need for boundaries between features that have the same attribute values Changes in a landscape Supporting a spatial analysis Using ROS classes to aggregate landscape features 13
14 A combine example Forest boundary Even-aged stands between the ages of 40 and Figure 8.2. Stands on the Brown Tract that are even-aged, and between the ages of 40 and Figure 8.3. Two similar-aged stands on the Brown Tract that share a common border. Both are even-aged, and between the ages of 40 and Attributes may need attention following a combine Table 8.1. Results of combining two stands. Site Trees per Height Board feet Stand Acres Hectares Age index hectare (m) per hectare Both stands before using a "combine features" process First stand selected ,325 Second stand selected ,388 Combined stand after using a "combine features" process if age is used as the combine field 44 Combined stand after using a "union features" process ,325 14
15 Multiple spatial features, one record Options: Leave as is Spit into two Combine with help of land separating the two stands Figure 8.4. Two polygons (regions) represented by a single record in the Brown Tract stands GIS (stand 283). Overlapping polygons Why? Editing spatial locations Merging (discussed later) Possible fix Combine Overlap Gap Figure 8.5. Overlap and gap remaining after editing polygon boundaries. Another combine application Overlapping areas of the buffer are removed Combine can be used to remove overlapping buffer results Overlapping areas of the buffer remain Figure 8.6. The results of two buffering operations, one where the overlapping areas of the buffer around each stream are removed, and the other where the overlapping areas remain. 15
16 Splitting landscape features Used to redefine a portion of a landscape and is typically in reference to polygons or lines We use an existing GIS or can create a graphic with the shape we want to use as a splitter Example: splitting a stand into two parts to reflect an intersecting stream Figure 8.7. A 160-acre (64.8 ha) polygon split along a stream, forming two smaller forest management units. Node of line defining the polygon Stream line used to split the polygon Polygon 1 Polygon to be split Polygon 2 a. 160-acre (64.8 ha) polygon and a stream that will be used to split it into two smaller polygons b. Resulting two smaller forest management units after splitting the 160-acre (64.8 ha) polygon Reasons for splitting a landscape feature A road that has had part of its length resurfaced with a different material or obliterated through a restoration process A stream that has been surveyed and now has attribute data available for part of its length 16
17 The split process Varies among GIS programs Within ArcMap, we can draw a graphic shape (line or polygon) through the feature we want to split Splitting lines is typically straight-forward In the case of polygons the graphic shape must cross the border of the polygon twice Make sure you have a back-up copy of the feature that you split Splitting a large management unit along a line created by a user of desktop GIS software. Unit being split Line along which the unit will be split Merge A merge process creates a new GIS from a set or subset of one or more previously developed GIS s Point, line, and polygon s can be merged but different feature types are generally not mixed While several polygon s might be merged, a line or point would not typically be included in this process A merge process is also called an append process in some software When merged features overlap, no new features are created 17
18 Why merge s? Example: identify forest areas that have no management restrictions (all silvicultural practices appropriate for the resources affected are allowed) Identify restricted areas: Within a certain distance of streams (buffer) Within a certain distance of roads (buffer) Near sensitive habitat areas (buffer) Merge the restricted areas into a single Use the single as an erase and to remove these layers any s that will be used to guide management activities This should make the delineation of restricted areas more efficient Streams GIS Roads GIS Owl nest location GIS Buffer 100 feet Buffer 100 feet Buffer 1000 feet Buffered streams GIS Buffered roads GIS Owl nest location GIS Merge Merged GIS Stands GIS Erase Unrestricted areas GIS Figure 8.9. A process that can be used to delineate unrestricted areas in a forested landscape. Unrestricted areas Restricted areas Figure A description of the restricted and unrestricted areas on the Daniel Pickett forest. 18
19 Another use for a merge The merge process can also be used to stitch together spatial s that share common borders Examples: Merging adjacent USGS topographic maps together Connecting data from two adjoining counties Roads, streams, and other features Merge example Merge example 19
GIS and Forest Engineering Applications
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 3 This week s topics Clip and erase processes Chapter 6 Selecting landscape features in a GIS Chapter 5 GIS Lab3: Determining land use and ownership
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 3 This week s topics Clip and erase processes Chapter 6 Selecting landscape features in a GIS Chapter 5 GIS Lab3: Determining land use and ownership
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 17: Geoprocessing and Spatial Analysis
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 17: and Spatial Analysis tools are commonly used tools that we normally use to prepare data for further analysis. In ArcMap, the most commonly used tools appear in
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 17: and Spatial Analysis tools are commonly used tools that we normally use to prepare data for further analysis. In ArcMap, the most commonly used tools appear in
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 CHAPTER 11 VECTOR DATA ANALYSIS 11.1 Buffering 11.1.1 Variations in Buffering Box 11.1 Riparian Buffer Width 11.1.2 Applications of Buffering 11.2 Overlay 11.2.1 Feature Type and Overlay 11.2.2 Overlay
CHAPTER 11 VECTOR DATA ANALYSIS 11.1 Buffering 11.1.1 Variations in Buffering Box 11.1 Riparian Buffer Width 11.1.2 Applications of Buffering 11.2 Overlay 11.2.1 Feature Type and Overlay 11.2.2 Overlay
Announcements. Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for:
 Data Announcements Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for: Source Map of Bangor MEGIS NG911 road file for Bangor MEGIS Tax maps for Bangor City Hall, may
Data Announcements Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for: Source Map of Bangor MEGIS NG911 road file for Bangor MEGIS Tax maps for Bangor City Hall, may
Lecture 8. Vector Data Analyses. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 8 Vector Data Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Vector Data Analysis Vector data analysis involves one or a combination of: Measuring
Lecture 8 Vector Data Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Vector Data Analysis Vector data analysis involves one or a combination of: Measuring
Spatial Analysis (Vector) I
 Spatial Analysis (Vector) I GEOG 300, Lecture 8 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Spatial Analysis In a GIS, Data are usually grouped into layers (or themes). The analysis functions of a GIS use the spatial and non-spatial
Spatial Analysis (Vector) I GEOG 300, Lecture 8 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Spatial Analysis In a GIS, Data are usually grouped into layers (or themes). The analysis functions of a GIS use the spatial and non-spatial
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
GIS LAB 8. Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation
 GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
layers in a raster model
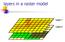 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS
 Slides by Wheaton et al. (2009-2014) are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton
Slides by Wheaton et al. (2009-2014) are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton
Vector Data. James Frew ESM 263 Winter
 Vector Data 1 Why Vector Data? Recall: features vs fields features: discrete enffes with specific locafons fields: confnuous funcfons of (x, y) Vector is GIS-speak for feature representafons dimensionality:
Vector Data 1 Why Vector Data? Recall: features vs fields features: discrete enffes with specific locafons fields: confnuous funcfons of (x, y) Vector is GIS-speak for feature representafons dimensionality:
Chapter 17 Creating a New Suit from Old Cloth: Manipulating Vector Mode Cartographic Data
 Chapter 17 Creating a New Suit from Old Cloth: Manipulating Vector Mode Cartographic Data Imagine for a moment that digital cartographic databases were a perfect analog of the paper map. Once you digitized
Chapter 17 Creating a New Suit from Old Cloth: Manipulating Vector Mode Cartographic Data Imagine for a moment that digital cartographic databases were a perfect analog of the paper map. Once you digitized
Making ArcGIS Work for You. Elizabeth Cook USDA-NRCS GIS Specialist Columbia, MO
 Making ArcGIS Work for You Elizabeth Cook USDA-NRCS GIS Specialist Columbia, MO 1 Topics Using ArcMap beyond the Toolkit buttons GIS data formats Attributes and what you can do with them Calculating Acres
Making ArcGIS Work for You Elizabeth Cook USDA-NRCS GIS Specialist Columbia, MO 1 Topics Using ArcMap beyond the Toolkit buttons GIS data formats Attributes and what you can do with them Calculating Acres
GIS in the Social and Natural Sciences. Last Lecture. Today s Outline 5/14/2017. GEOG 4110/5100 Special Topics in Geography
 GEOG 4110/5100 Special Topics in Geography GIS in the Social and Natural Sciences Working with Vector Data in a GIS Last Lecture We talked about the main types of vector data models (CDS, TDS, TIN, Networks)
GEOG 4110/5100 Special Topics in Geography GIS in the Social and Natural Sciences Working with Vector Data in a GIS Last Lecture We talked about the main types of vector data models (CDS, TDS, TIN, Networks)
VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS
 VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Spatial Analysis Operations performed on spatial data that add value Can reveal things that might otherwise be invisible
VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Spatial Analysis Operations performed on spatial data that add value Can reveal things that might otherwise be invisible
Notes: Notes: Notes: Notes:
 NR406 GIS Applications in Fire Ecology & Management Lesson 2 - Overlay Analysis in GIS Gathering Information from Multiple Data Layers One of the many strengths of a GIS is that you can stack several data
NR406 GIS Applications in Fire Ecology & Management Lesson 2 - Overlay Analysis in GIS Gathering Information from Multiple Data Layers One of the many strengths of a GIS is that you can stack several data
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3
 Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Vector-Based GIS Data Processing. Chapter 6
 Vector-Based GIS Data Processing Chapter 6 Vector Data Model Feature Classes points lines polygons Layers limited to one class of data Figure p. 186 Vector Data Model Shapefiles ArcView non-topological
Vector-Based GIS Data Processing Chapter 6 Vector Data Model Feature Classes points lines polygons Layers limited to one class of data Figure p. 186 Vector Data Model Shapefiles ArcView non-topological
GIS Virtual Workshop: Buffering
 This workshop will teach the different methods of buffering data. They will include: Basic buffering of data Merging buffering zones Clipping the buffer Concentric rings around the object You will find
This workshop will teach the different methods of buffering data. They will include: Basic buffering of data Merging buffering zones Clipping the buffer Concentric rings around the object You will find
Remote Sensing and GIS. GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Geology Remote Sensing and GIS GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis RS & GIS XXXI Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Geology Remote Sensing and GIS GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis RS & GIS XXXI Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator
Minnesota Department of Natural Resources ArcView Utilities Extension User s Guide
 Introduction This document describes the functionality and use of the ArcView Utilities extension for the ArcView desktop GIS software. These tools were developed out of the need for additional geoprocessing
Introduction This document describes the functionality and use of the ArcView Utilities extension for the ArcView desktop GIS software. These tools were developed out of the need for additional geoprocessing
Protocol for Riparian Buffer Restoration Prioritization in Centre County and Clinton County
 Protocol for Riparian Buffer Restoration Prioritization in Centre County and Clinton County Chesapeake Conservancy has developed this methodology to prioritize riparian buffer restoration in Centre County
Protocol for Riparian Buffer Restoration Prioritization in Centre County and Clinton County Chesapeake Conservancy has developed this methodology to prioritize riparian buffer restoration in Centre County
Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis. Lecture Outline. Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York.
 Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis Lecture Outline Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York. Introduction: The idea of overlay originated when maps
Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis Lecture Outline Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York. Introduction: The idea of overlay originated when maps
Overview.! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial
 Digitizing Overview! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial Manual Digitizing! Simplest, easiest, and cheapest method of capturing vector data from
Digitizing Overview! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial Manual Digitizing! Simplest, easiest, and cheapest method of capturing vector data from
Digitizing and Editing Polygons in the STS Gypsy Moth Project. M. Dodd 2/10/04
 Digitizing and Editing Polygons in the STS Gypsy Moth Project M. Dodd 2/10/04 Digitizing and Editing Polygons in the STS Gypsy Moth Project OVERVIEW OF DIGITIZING IN STS 3 THE DIGITIZING WINDOW 4 DIGITIZING
Digitizing and Editing Polygons in the STS Gypsy Moth Project M. Dodd 2/10/04 Digitizing and Editing Polygons in the STS Gypsy Moth Project OVERVIEW OF DIGITIZING IN STS 3 THE DIGITIZING WINDOW 4 DIGITIZING
Coverage data model. Vector-Based Spatial Analysis: Tools Processes. Topological Data Model. Polygons Files. Geographic Information Systems.
 GEOG4340 Geographic Information Systems Lecture Four 2013winter Vector-Based Spatial Analysis: Tools Processes Reading materials: Chapter 6 of Intro GIS by J. R. Jensen and R.R. Jensen Cheng. Q., Earth
GEOG4340 Geographic Information Systems Lecture Four 2013winter Vector-Based Spatial Analysis: Tools Processes Reading materials: Chapter 6 of Intro GIS by J. R. Jensen and R.R. Jensen Cheng. Q., Earth
Basic Geospatial Analysis Techniques: This presentation introduces you to basic geospatial analysis techniques, such as spatial and aspatial
 Basic Geospatial Analysis Techniques: This presentation introduces you to basic geospatial analysis techniques, such as spatial and aspatial selections, buffering and dissolving, overly operations, table
Basic Geospatial Analysis Techniques: This presentation introduces you to basic geospatial analysis techniques, such as spatial and aspatial selections, buffering and dissolving, overly operations, table
Model Builder Tutorial (Automating Suitability Analysis)
 Model Builder Tutorial (Automating Suitability Analysis) Model Builder in ArcGIS 10.x Part I: Introduction Part II: Suitability Analysis: A discussion Part III: Launching a Model Window Part IV: A Simple
Model Builder Tutorial (Automating Suitability Analysis) Model Builder in ArcGIS 10.x Part I: Introduction Part II: Suitability Analysis: A discussion Part III: Launching a Model Window Part IV: A Simple
Lab Exercise 6: Vector Spatial Analysis
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Urban Studies and Planning 11.520: A Workshop on Geographic Information Systems 11.188: Urban Planning and Social Science Laboratory Lab Exercise 6:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Urban Studies and Planning 11.520: A Workshop on Geographic Information Systems 11.188: Urban Planning and Social Science Laboratory Lab Exercise 6:
Digging Into Autodesk Map 3D 2007 Level 1 Training Rick Ellis Michael Carris Russell Martin
 Digging Into Autodesk Map 3D 2007 Level 1 Training Rick Ellis Michael Carris Russell Martin PO Box 344 Canby Oregon 97013 www.cadapult-software.com training@cadapult-software.com (503) 829-8929 Table of
Digging Into Autodesk Map 3D 2007 Level 1 Training Rick Ellis Michael Carris Russell Martin PO Box 344 Canby Oregon 97013 www.cadapult-software.com training@cadapult-software.com (503) 829-8929 Table of
Georeferencing and Digitizing
 INTRODUCTION There is a great deal of geographic data available in formats that cannot be immediately integrated with other GIS data. In order to use these types of data in GIS it is necessary to align
INTRODUCTION There is a great deal of geographic data available in formats that cannot be immediately integrated with other GIS data. In order to use these types of data in GIS it is necessary to align
3D Cadastral System Functionalities for 5D Multi- Purpose LIS
 3D Cadastral System Functionalities for 5D Multi- Purpose LIS ΕΣΠΑ 2007-2013, Δράση«Διμερής Ε&Τ Συνεργασία Ελλάδας- Ισραήλ 2013-2015» YΠOYPΓEIO ΠAΙΔΕΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΘΡΗΣΚΕΥΜΑΤΩΝ Γ.Γ.Ε.Τ. ΕΥΔΕ - ΕΤΑΚ Outline 5DMuPLIS
3D Cadastral System Functionalities for 5D Multi- Purpose LIS ΕΣΠΑ 2007-2013, Δράση«Διμερής Ε&Τ Συνεργασία Ελλάδας- Ισραήλ 2013-2015» YΠOYPΓEIO ΠAΙΔΕΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΘΡΗΣΚΕΥΜΑΤΩΝ Γ.Γ.Ε.Τ. ΕΥΔΕ - ΕΤΑΚ Outline 5DMuPLIS
Lab.4 & Assignment 2. Lab4. Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map
 EATS4400 GIS Lab.4 & Assignment 2 Lab4 Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map In this lab exercise you will have chance to go through the steps to convert hardcopy map into digital map for ArcGIS. Digitizing
EATS4400 GIS Lab.4 & Assignment 2 Lab4 Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map In this lab exercise you will have chance to go through the steps to convert hardcopy map into digital map for ArcGIS. Digitizing
MODULE 1 BASIC LIDAR TECHNIQUES
 MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
NRM435 Spring 2017 Accuracy Assessment of GIS Data
 Accuracy Assessment Lab Page 1 of 18 NRM435 Spring 2017 Accuracy Assessment of GIS Data GIS data always contains errors hopefully the errors are so small that will do not significantly affect the results
Accuracy Assessment Lab Page 1 of 18 NRM435 Spring 2017 Accuracy Assessment of GIS Data GIS data always contains errors hopefully the errors are so small that will do not significantly affect the results
Spatial Analysis 2. Basic operations Béla Márkus
 Spatial Analysis 2. Basic operations Béla Márkus Spatial Analysis 2.: Basic operations Béla Márkus Lector: János Tamás This module was created within TÁMOP - 4.1.2-08/1/A-2009-0027 "Tananyagfejlesztéssel
Spatial Analysis 2. Basic operations Béla Márkus Spatial Analysis 2.: Basic operations Béla Márkus Lector: János Tamás This module was created within TÁMOP - 4.1.2-08/1/A-2009-0027 "Tananyagfejlesztéssel
GIS Basics for Urban Studies
 GIS Basics for Urban Studies Date: March 21, 2018 Contacts: Mehdi Aminipouri, Graduate Peer GIS Faciliator, SFU Library (maminipo@sfu.ca) Keshav Mukunda, GIS & Map Librarian Librarian for Geography (kmukunda@sfu.ca)
GIS Basics for Urban Studies Date: March 21, 2018 Contacts: Mehdi Aminipouri, Graduate Peer GIS Faciliator, SFU Library (maminipo@sfu.ca) Keshav Mukunda, GIS & Map Librarian Librarian for Geography (kmukunda@sfu.ca)
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Data Assembling Topics:
 Topics: 1. GPX to Shape file 2. Data conversion with FME 3. Create a polygon feature 4. Merging /Appending data into a new dataset 5. Reproject data from one coordinate system to another 6. Data clipping
Topics: 1. GPX to Shape file 2. Data conversion with FME 3. Create a polygon feature 4. Merging /Appending data into a new dataset 5. Reproject data from one coordinate system to another 6. Data clipping
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8
 LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling
 Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
GIS LAB 1. Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas.
 GIS LAB 1 Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas. ArcGIS offers some advantages for novice users. The graphical user interface is similar to many Windows packages
GIS LAB 1 Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas. ArcGIS offers some advantages for novice users. The graphical user interface is similar to many Windows packages
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS
 Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
Data Models and Data processing in GIS
 PDHonline Course L155G (5 PDH) Data Models and Data processing in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
PDHonline Course L155G (5 PDH) Data Models and Data processing in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
1. NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Interface
 Using the Landscape Project through NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox are recommended for the use of this app. Navigate to the NJDEP-DFW s Landscape Project web page at www.njfishandwildlife.com/ensp/landscape/
Using the Landscape Project through NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox are recommended for the use of this app. Navigate to the NJDEP-DFW s Landscape Project web page at www.njfishandwildlife.com/ensp/landscape/
Polygon Analysis. Download and unzip the personal geodatabase polygon_analysis_lab.mdb from.
 NRM435 Spring 2019 Page 1 of 11 Polygon Analysis Download and unzip the personal geodatabase polygon_analysis_lab.mdb from /data/ The personal geodatabase contains five feature datasets.create an Arcmap
NRM435 Spring 2019 Page 1 of 11 Polygon Analysis Download and unzip the personal geodatabase polygon_analysis_lab.mdb from /data/ The personal geodatabase contains five feature datasets.create an Arcmap
Appendix 2: Random Plots Workbook: Unstratified Sample
 Appendix 2: Random Plots Workbook: Unstratified Sample These instructions will help users of all skill levels create a random sample of i-tree Eco plot centers, plot areas, and the associated i-tree Eco-required
Appendix 2: Random Plots Workbook: Unstratified Sample These instructions will help users of all skill levels create a random sample of i-tree Eco plot centers, plot areas, and the associated i-tree Eco-required
Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams.
 GIS LAB 3 Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams. One of the primary goals of this course is to give you some hands-on
GIS LAB 3 Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams. One of the primary goals of this course is to give you some hands-on
ENGRG 59910: Introduction to GIS
 ENGRG 59910: Introduction to GIS Lecture 05: GIS and Databases Basics Acknowledgment: Michael Piasecki Where are we now? Basic geographic concepts Introduction to GIS, coordinate system, projection, datum
ENGRG 59910: Introduction to GIS Lecture 05: GIS and Databases Basics Acknowledgment: Michael Piasecki Where are we now? Basic geographic concepts Introduction to GIS, coordinate system, projection, datum
FE 257 Week 4 Topics. Final project. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications.
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 4 FE 257 Week 4 Topics Final project discussion Chapter 7 Buffering landscape features Chapter 3 Acquiring, creating, and editing GIS databases and
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 4 FE 257 Week 4 Topics Final project discussion Chapter 7 Buffering landscape features Chapter 3 Acquiring, creating, and editing GIS databases and
Prioritizing Land with GIS for Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) Funding Derya Özgöç Çağlar and Richard L.
 Page 1 of 13 Prioritizing Land with GIS for Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) Funding Derya Özgöç Çağlar and Richard L. Farnsworth APPENDIX: GIS Application This exercise will guide you through
Page 1 of 13 Prioritizing Land with GIS for Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) Funding Derya Özgöç Çağlar and Richard L. Farnsworth APPENDIX: GIS Application This exercise will guide you through
Watershed Modeling Maricopa Predictive HEC-1 Model. Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models
 Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor
 Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor Written by Rick Guritz Alaska Satellite Facility Nov. 24, 2015 Contents
Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor Written by Rick Guritz Alaska Satellite Facility Nov. 24, 2015 Contents
Suitability Modeling with GIS
 Developed and Presented by Juniper GIS 1/33 Course Objectives What is Suitability Modeling? The Suitability Modeling Process Cartographic Modeling GIS Tools for Suitability Modeling Demonstrations of Models
Developed and Presented by Juniper GIS 1/33 Course Objectives What is Suitability Modeling? The Suitability Modeling Process Cartographic Modeling GIS Tools for Suitability Modeling Demonstrations of Models
Spec2Harv. Converting Spectrum output to HARVEST input. Version 1.0a. User s Guide. Written by: Eric J. Gustafson Luke V.
 Spec2Harv Converting Spectrum output to HARVEST input Version 1.0a User s Guide Written by: Eric J. Gustafson Luke V. Rasmussen North Central Research Station USDA Forest Service Larry A. Leefers Department
Spec2Harv Converting Spectrum output to HARVEST input Version 1.0a User s Guide Written by: Eric J. Gustafson Luke V. Rasmussen North Central Research Station USDA Forest Service Larry A. Leefers Department
Extracting RESULTs Information from the Land & Resource Data Warehouse (LRDW)
 Extracting RESULTs Information from the Land & Resource Data Warehouse (LRDW) The following instructions will illustrate how to extract inventory Results information from the Land & Resource data Warehouse
Extracting RESULTs Information from the Land & Resource Data Warehouse (LRDW) The following instructions will illustrate how to extract inventory Results information from the Land & Resource data Warehouse
3.2 TIPS FOR USING MATLAB
 3.2 TIPS FOR USING MATLAB 3.2.1 Exporting Graphics from MATLAB to WORD and Editing Details Given a graphical plot in MATLAB, say graph.fig, the following procedure allows this graph to be imported into
3.2 TIPS FOR USING MATLAB 3.2.1 Exporting Graphics from MATLAB to WORD and Editing Details Given a graphical plot in MATLAB, say graph.fig, the following procedure allows this graph to be imported into
Southern Ontario Interim Landcover (SIL) Data Compilation Documentation
 Southern Ontario Interim Landcover (SIL) Data Compilation Documentation Introductory Datasets: Goal: To utilize all relevant corporate MNR datasets as well as external datasets that hold ecological value.
Southern Ontario Interim Landcover (SIL) Data Compilation Documentation Introductory Datasets: Goal: To utilize all relevant corporate MNR datasets as well as external datasets that hold ecological value.
Introduction to GIS & Mapping: ArcGIS Desktop
 Introduction to GIS & Mapping: ArcGIS Desktop Your task in this exercise is to determine the best place to build a mixed use facility in Hudson County, NJ. In order to revitalize the community and take
Introduction to GIS & Mapping: ArcGIS Desktop Your task in this exercise is to determine the best place to build a mixed use facility in Hudson County, NJ. In order to revitalize the community and take
Exercise 4 Compiling a Spatial Database: Adding and Linking Attribute Data
 Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 4 Page: 1/9 GEOG 377/CEE 357: An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Exercise 4 Compiling a Spatial Database: Adding and Linking Attribute Data 1. Introduction
Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 4 Page: 1/9 GEOG 377/CEE 357: An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Exercise 4 Compiling a Spatial Database: Adding and Linking Attribute Data 1. Introduction
In this lab, you will create two maps. One map will show two different projections of the same data.
 Projection Exercise Part 2 of 1.963 Lab for 9/27/04 Introduction In this exercise, you will work with projections, by re-projecting a grid dataset from one projection into another. You will create a map
Projection Exercise Part 2 of 1.963 Lab for 9/27/04 Introduction In this exercise, you will work with projections, by re-projecting a grid dataset from one projection into another. You will create a map
GIS Workshop Spring 2016
 1/ 14 GIS Geographic Information System. An integrated collection of computer software and data used to view and manage information about geographic places, analyze spatial relationships, and model spatial
1/ 14 GIS Geographic Information System. An integrated collection of computer software and data used to view and manage information about geographic places, analyze spatial relationships, and model spatial
Tutorial: Using SAGA for Least Cost Path Analysis
 Tutorial: Using SAGA for Least Cost Path Analysis Developed by Kim Cimmery (Kapcimmery at hot mail dot com) March 2013 1. Introduction The shortest path between two points is a straight line (unless you
Tutorial: Using SAGA for Least Cost Path Analysis Developed by Kim Cimmery (Kapcimmery at hot mail dot com) March 2013 1. Introduction The shortest path between two points is a straight line (unless you
Data Assembly, Part II. GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4
 Data Assembly, Part II GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4 Objectives Continuation of effective troubleshooting Create shapefiles for analysis with buffers, union, and dissolve functions Calculate polygon
Data Assembly, Part II GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4 Objectives Continuation of effective troubleshooting Create shapefiles for analysis with buffers, union, and dissolve functions Calculate polygon
Instruction Manual for SilvAssist for ArcGIS
 Instruction Manual for SilvAssist for ArcGIS Version 2.0 Table of Contents Introduction..II Preparing to use SilvAssist..1-3 Plot Allocator Menu Definitions and Use.....4 General Use and Setup....5-7 Auto
Instruction Manual for SilvAssist for ArcGIS Version 2.0 Table of Contents Introduction..II Preparing to use SilvAssist..1-3 Plot Allocator Menu Definitions and Use.....4 General Use and Setup....5-7 Auto
Tips for a Good Meshing Experience
 Tips for a Good Meshing Experience Meshes are very powerful and flexible for modeling 2D overland flows in a complex urban environment. However, complex geometries can be frustrating for many modelers
Tips for a Good Meshing Experience Meshes are very powerful and flexible for modeling 2D overland flows in a complex urban environment. However, complex geometries can be frustrating for many modelers
TABLES, ANATOMY OF A TABLE
 week 6 TABLES, ANATOMY OF A TABLE topics of the week Table structure Working with tables Table relationships Cardinality, Joins and Relates Table Jargon What is a Database? What is a Table? What is a Record/Row?
week 6 TABLES, ANATOMY OF A TABLE topics of the week Table structure Working with tables Table relationships Cardinality, Joins and Relates Table Jargon What is a Database? What is a Table? What is a Record/Row?
Introduction to Geospatial Technology Lab Series. Lab: Basic Geospatial Analysis Techniques
 Introduction to Geospatial Technology Lab Series Lab: Basic Geospatial Analysis Techniques Document Version: 2012-08-24 Lab Author: Richard Smith Organization: Copyright 2003-2012 Center for Systems Security
Introduction to Geospatial Technology Lab Series Lab: Basic Geospatial Analysis Techniques Document Version: 2012-08-24 Lab Author: Richard Smith Organization: Copyright 2003-2012 Center for Systems Security
SilvAssist 3.5 Instruction Manual Instruction Manual for the SilvAssist Toolbar For ArcGIS. Version 3.5
 Instruction Manual for the SilvAssist Toolbar For ArcGIS Version 3.5 1 2 Contents Introduction... 5 Preparing to Use SilvAssist... 6 Polygon Selection... 6 Plot Allocator... 7 Requirements:... 7 Operation...
Instruction Manual for the SilvAssist Toolbar For ArcGIS Version 3.5 1 2 Contents Introduction... 5 Preparing to Use SilvAssist... 6 Polygon Selection... 6 Plot Allocator... 7 Requirements:... 7 Operation...
Lecture 7 Digitizing. Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017
 Lecture 7 Digitizing Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
Lecture 7 Digitizing Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
Introduction to LiDAR
 Introduction to LiDAR Our goals here are to introduce you to LiDAR data. LiDAR data is becoming common, provides ground, building, and vegetation heights at high accuracy and detail, and is available statewide.
Introduction to LiDAR Our goals here are to introduce you to LiDAR data. LiDAR data is becoming common, provides ground, building, and vegetation heights at high accuracy and detail, and is available statewide.
To the GeoView System Overview Online Training Course
 Welcome! To the GeoView System Overview Online Training Course The Alberta Department of Energy provides GeoView as a mapping system to enable users to find geographic information in Alberta. GeoView retrieves
Welcome! To the GeoView System Overview Online Training Course The Alberta Department of Energy provides GeoView as a mapping system to enable users to find geographic information in Alberta. GeoView retrieves
LAB 9: Buffering and Overlay in ArcGIS - ArcMAP
 LAB 9: Buffering and Overlay in ArcGIS - ArcMAP What You ll Learn: to apply the concepts of buffering and overlay, two common cartographic operations. You should read chapter 9 in the GIS Fundamentals
LAB 9: Buffering and Overlay in ArcGIS - ArcMAP What You ll Learn: to apply the concepts of buffering and overlay, two common cartographic operations. You should read chapter 9 in the GIS Fundamentals
v SMS 11.1 Tutorial GIS Requirements GIS Module Map Module ArcGis (Optional) Time minutes Prerequisites None Objectives
 v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial GIS Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how you can read in GIS data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. We will
v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial GIS Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how you can read in GIS data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. We will
ArcMap - EXPLORING THE DATABASE Part I. SPATIAL DATA FORMATS Part II
 Week 5 ArcMap - EXPLORING THE DATABASE Part I SPATIAL DATA FORMATS Part II topics of the week Exploring the Database More on the Table of Contents Exploration tools Identify, Find, Measure, Map tips, Hyperlink,
Week 5 ArcMap - EXPLORING THE DATABASE Part I SPATIAL DATA FORMATS Part II topics of the week Exploring the Database More on the Table of Contents Exploration tools Identify, Find, Measure, Map tips, Hyperlink,
Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x
 Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x This guide provides instructions for performing a few basic tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.1, such as adding data to a map document, viewing and changing coordinate system information,
Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x This guide provides instructions for performing a few basic tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.1, such as adding data to a map document, viewing and changing coordinate system information,
Mapping Wildlife Habitat. using ArcView 3.2 and NH GRANIT Data
 Mapping Wildlife Habitat using ArcView 3.2 and NH GRANIT Data Mapping Wildlife Habitat ORIGINAL DRAFT: June 2002 Revised: June 2004 Complex Systems Research Center All exercises and desktop publishing
Mapping Wildlife Habitat using ArcView 3.2 and NH GRANIT Data Mapping Wildlife Habitat ORIGINAL DRAFT: June 2002 Revised: June 2004 Complex Systems Research Center All exercises and desktop publishing
Building and Analyzing Topology in Autodesk Map GI21-1
 December 2-5, 2003 MGM Grand Hotel Las Vegas Building and Analyzing Topology in Autodesk Map GI21-1 Alex Penney ISD Training Content Manager, Autodesk Professional Services, Autodesk Inc. Topology is one
December 2-5, 2003 MGM Grand Hotel Las Vegas Building and Analyzing Topology in Autodesk Map GI21-1 Alex Penney ISD Training Content Manager, Autodesk Professional Services, Autodesk Inc. Topology is one
Lab 5: Georeferencing, Digitization, and Processing
 Lab 5: Georeferencing, Digitization, and Processing Purpose: An introduction to georeferencing images, practice digitizing, and combine lesson up to this point. To Do: Register a scanned image, digitize
Lab 5: Georeferencing, Digitization, and Processing Purpose: An introduction to georeferencing images, practice digitizing, and combine lesson up to this point. To Do: Register a scanned image, digitize
Extracting Inventory History Information from the Land & Resource Data Warehouse (LRDW)
 Extracting Inventory History Information from the Land & Resource Data Warehouse (LRDW) The following instructions will illustrate how to extract inventory history information from the Land & Resource
Extracting Inventory History Information from the Land & Resource Data Warehouse (LRDW) The following instructions will illustrate how to extract inventory history information from the Land & Resource
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
Making Topographic Maps
 T O P O Applications N Making Topographic Maps M A P S Making Topographic Maps with TNTmips page 1 Before Getting Started TNTmips provides a variety of tools for working with map data and making topographic
T O P O Applications N Making Topographic Maps M A P S Making Topographic Maps with TNTmips page 1 Before Getting Started TNTmips provides a variety of tools for working with map data and making topographic
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF LAND SURVEYING & GEO-INFORMATICS LSGI521 PRINCIPLES OF GIS
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF LAND SURVEYING & GEO-INFORMATICS LSGI521 PRINCIPLES OF GIS Student name: Student ID: Table of Content Working with files, folders, various software and
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF LAND SURVEYING & GEO-INFORMATICS LSGI521 PRINCIPLES OF GIS Student name: Student ID: Table of Content Working with files, folders, various software and
YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS
 YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS Presenter Name Presenter Title Duty Location Date of Presentation US Army Corps of Engineers YRERFS Downy Woodpecker Riparian Forest (RF) Habitat Determination
YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS Presenter Name Presenter Title Duty Location Date of Presentation US Army Corps of Engineers YRERFS Downy Woodpecker Riparian Forest (RF) Habitat Determination
Soil texture: based on percentage of sand in the soil, partially determines the rate of percolation of water into the groundwater.
 Overview: In this week's lab you will identify areas within Webster Township that are most vulnerable to surface and groundwater contamination by conducting a risk analysis with raster data. You will create
Overview: In this week's lab you will identify areas within Webster Township that are most vulnerable to surface and groundwater contamination by conducting a risk analysis with raster data. You will create
A Second Look at DEM s
 A Second Look at DEM s Overview Detailed topographic data is available for the U.S. from several sources and in several formats. Perhaps the most readily available and easy to use is the National Elevation
A Second Look at DEM s Overview Detailed topographic data is available for the U.S. from several sources and in several formats. Perhaps the most readily available and easy to use is the National Elevation
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Longley Chapter 3. Representations
 Longley Chapter 3 Digital Geographic Data Representation Geographic Data Type Data Models Representing Spatial and Temporal Data Attributes The Nature of Geographic Data Representations Are needed to convey
Longley Chapter 3 Digital Geographic Data Representation Geographic Data Type Data Models Representing Spatial and Temporal Data Attributes The Nature of Geographic Data Representations Are needed to convey
Appendix Z Basic ArcMap and GDSE Tools
 Appendix Z Basic ArcMap and GDSE Tools Introduction IFMAP has been developed within ESRI s ArcMap interface. As such, the application is inherently map-based. Although a user can enter tabular data through
Appendix Z Basic ArcMap and GDSE Tools Introduction IFMAP has been developed within ESRI s ArcMap interface. As such, the application is inherently map-based. Although a user can enter tabular data through
4. If you are prompted to enable hardware acceleration to improve performance, click
 Exercise 1a: Creating new points ArcGIS 10 Complexity: Beginner Data Requirement: ArcGIS Tutorial Data Setup About creating new points In this exercise, you will use an aerial photograph to create a new
Exercise 1a: Creating new points ArcGIS 10 Complexity: Beginner Data Requirement: ArcGIS Tutorial Data Setup About creating new points In this exercise, you will use an aerial photograph to create a new
ESRI User Conference 2016 WITH
 ESRI User Conference 2016 WITH INTRODUCTION Currently Planning Analyst Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest GIS Program Manager Bighorn National Forest Systems Analyst Georgia-Pacific and Olympic Resource
ESRI User Conference 2016 WITH INTRODUCTION Currently Planning Analyst Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest GIS Program Manager Bighorn National Forest Systems Analyst Georgia-Pacific and Olympic Resource
Key Terms. Attribute join Target table Join table Spatial join
 Key Terms Attribute join Target table Join table Spatial join Lect 10A Building Geodatabase Create a new file geodatabase Map x,y data Convert shape files to geodatabase feature classes Spatial Data Formats
Key Terms Attribute join Target table Join table Spatial join Lect 10A Building Geodatabase Create a new file geodatabase Map x,y data Convert shape files to geodatabase feature classes Spatial Data Formats
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONTOURS! Self-Paced Lab Due Friday! WEEK SIX Lecture RASTER ANALYSES Joe Wheaton YOUR EXCERCISE Integer Elevations Rounded up
HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONTOURS! Self-Paced Lab Due Friday! WEEK SIX Lecture RASTER ANALYSES Joe Wheaton YOUR EXCERCISE Integer Elevations Rounded up
GISCI GEOSPATIAL CORE TECHNICAL KNOWLEDGE EXAM CANDIDATE MANUAL AUGUST 2017
 GISCI GEOSPATIAL CORE TECHNICAL KNOWLEDGE EXAM CANDIDATE MANUAL AUGUST 2017 This document provides information about the GISCI Geospatial Core Technical Knowledge Exam, now a requirement for GISCI GISP
GISCI GEOSPATIAL CORE TECHNICAL KNOWLEDGE EXAM CANDIDATE MANUAL AUGUST 2017 This document provides information about the GISCI Geospatial Core Technical Knowledge Exam, now a requirement for GISCI GISP
GIS IN ECOLOGY: ANALYZING VECTOR DATA
 GIS IN ECOLOGY: ANALYZING VECTOR DATA Contents Introduction... 3 Tools and Functionality for Vector Data... 3 Course Data Sources... 4 Instructions for Copying the Course Dataset... 4 Tasks... 4 Getting
GIS IN ECOLOGY: ANALYZING VECTOR DATA Contents Introduction... 3 Tools and Functionality for Vector Data... 3 Course Data Sources... 4 Instructions for Copying the Course Dataset... 4 Tasks... 4 Getting
Alternate Animal Movement Routes v. 2.1
 Alternate Animal Movement Routes v. 2.1 Aka: altroutes.avx Last modified: April 12, 2005 TOPICS: ArcView 3.x, Animal Movement, Alternate, Route, Path, Proportion, Distance, Bearing, Azimuth, Angle, Point,
Alternate Animal Movement Routes v. 2.1 Aka: altroutes.avx Last modified: April 12, 2005 TOPICS: ArcView 3.x, Animal Movement, Alternate, Route, Path, Proportion, Distance, Bearing, Azimuth, Angle, Point,
Pond Distance and Habitat for use in Wildlife Modeling
 Pond Distance and Habitat for use in Wildlife Modeling These instructions enable you to aggregate layers within a study area, calculate new fields, and create new data out of existing data, for use in
Pond Distance and Habitat for use in Wildlife Modeling These instructions enable you to aggregate layers within a study area, calculate new fields, and create new data out of existing data, for use in
