Markov Random Fields and Segmentation with Graph Cuts
|
|
|
- Clement Ball
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Markov Random Fields and Segmentation with Graph Cuts Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Many slides from D. Hoiem
2 Administrative stuffs Final project Proposal due Oct 27 (Thursday) HW 4 is out Due 11:59pm on Wed, November 2nd, 2016
3 Today s class Review EM and GMM i Markov Random Fields j w ij Segmentation with Graph Cuts HW 4
4 Missing Data Problems: Segmentation Challenge: Segment the image into figure and ground without knowing what the foreground looks like in advance. Three sub-problems: 1. If we had labels, how could we model the appearance of foreground and background? MLE: maximum likelihood estimation 2. Once we have modeled the fg/bg appearance, how do we compute the likelihood that a pixel is foreground? Probabilistic inference 3. How can we get both labels and appearance models at once? Hidden data problem: Expectation Maximization Foreground Background
5 EM: Mixture of Gaussians 1. Initialize parameters 2. Compute likelihood of hidden variables for current parameters 3. Estimate new parameters for each component, weighted by likelihood ),,, ( ) ( ) 2 ( ) ( t t t n n nm x m z p π σ μ n n nm n nm t m x 1 ˆ 1) ( n m n nm n nm t m x 2 1) 2 ( ˆ 1 ˆ N n nm t m 1) ( ˆ k k n k n n m n m n n k z p k z x p m z p m z x p,, Given by normal distribution
6 Gaussian Mixture Models: Practical Tips Number of components Select by hand based on knowledge of problem Select using cross-validation or sample data Usually, not too sensitive and safer to use more components Covariance matrix Spherical covariance: dimensions within each component are independent with equal variance (1 parameter but usually too restrictive) Spherical Diagonal covariance: dimensions within each component are not independent with difference variances (N parameters for N-D data) Full covariance: no assumptions (N*(N+1)/2 parameters); for high N might be expensive to do EM, to evaluate, and may overfit Typically use Full if lots of data, few dimensions; Use Diagonal otherwise Can get stuck in local minima Use multiple restarts Choose solution with greatest data likelihood σ σ 2 σ x σ y 2 a c c b Spherical Diagonal Full
7 Hard EM Same as EM except compute z* as most likely values for hidden variables K-means is an example Advantages Simpler: can be applied when cannot derive EM Sometimes works better if you want to make hard predictions at the end But Generally, pdf parameters are not as accurate as EM
8 EM Demo GMM with images demos
9 function EM_segmentation(im, K) x = im(:); N = numel(x); minsigma = std(x)/numel(x); % prevent component from getting 0 variance % Initialize GMM parameters prior = zeros(k, 1); mu = zeros(k, 1); sigma = zeros(k, 1); prior(:) = 1/K; minx = min(x); maxx = max(x); for k = 1:K mu(k) = ( *rand(1))*(maxx-minx) + minx; sigma(k) = (1/K)*std(x); end % Initialize P(component_i x_i) (initial values not important) pm = ones(n, K); oldpm = zeros(n, K);
10 maxiter = 200; niter = 0; % EM algorithm: loop until convergence while (mean(abs(pm(:)-oldpm(:)))>0.001) && (niter < maxiter) niter = niter+1; oldpm = pm; % estimate probability that each data point belongs to each component for k = 1:K pm(:, k) = prior(k)*normpdf(x, mu(k), sigma(k)); end pm = pm./ repmat(sum(pm, 2), [1 K]); % compute maximum likelihood parameters for expected components for k = 1:K prior(k) = sum(pm(:, k))/n; mu(k) = sum(pm(:, k).*x) / sum(pm(:, k)); sigma(k) = sqrt( sum(pm(:, k).*(x - mu(k)).^2) / sum(pm(:, k))); sigma(k) = max(sigma(k), minsigma); % prevent variance from going to 0 end end
11 What s wrong with this prediction? P(foreground image)
12 Solution: Encode dependencies between pixels P(foreground image) Normalizing constant called partition function 1 P( y;, data) f ( y ;, data) f ( y, y ;, data Z i1.. N 1 i 2 i j ) i, jedges Labels to be predicted Individual predictions Pairwise predictions
13 Writing Likelihood as an Energy 1 P( y;, data) p ( y ;, data) p ( y, y ;, data Z i1.. N 1 i 2 i j ) i, jedges -log Energy( y;, data) ( y ;, data) ( y, y ;, data i 1 i 2 i j ) i, jedges Cost of assignment y i Cost of pairwise assignment y i,y j
14 Notes on energy-based formulation Energy( y;, data) ( y ;, data) ( y, y ;, data i Primarily used when you only care about the most likely solution (not the confidences) 1 i 2 i j ) i, jedges Can think of it as a general cost function Can have larger cliques than 2 Clique is the set of variables that go into a potential function
15 Markov Random Fields Node y i : pixel label Edge: constrained pairs Cost to assign a label to each pixel Energy( y;, data) i Cost to assign a pair of labels to connected pixels 1 ( yi;, data) 2( yi, y j;, data) i, jedges
16 Markov Random Fields Example: label smoothing grid Unary potential 0: -logp(y i = 0 data) 1: -logp(y i = 1 data) Pairwise Potential K 1 K 0 K>0 Energy( y;, data) i 1 ( yi;, data) 2( yi, y j;, data) i, jedges
17 Solving MRFs with graph cuts Source (Label 0) Cost to assign to 1 Cost to split nodes Cost to assign to 0 Sink (Label 1) Energy( y;, data) i 1 ( yi;, data) 2( yi, y j;, data) i, jedges
18 Solving MRFs with graph cuts Source (Label 0) Cost to assign to 1 Cost to split nodes Cost to assign to 0 Sink (Label 1) Energy( y;, data) i 1 ( yi;, data) 2( yi, y j;, data) i, jedges
19 GrabCut segmentation User provides rough indication of foreground region. Goal: Automatically provide a pixel-level segmentation.
20 Colour Model R Foreground & Background Background G Gaussian Mixture Model (typically 5-8 components) Source: Rother
21 Graph cuts Boykov and Jolly (2001) Image Foreground (source) Min Cut Background (sink) Cut: separating source and sink; Energy: collection of edges Min Cut: Global minimal energy in polynomial time Source: Rother
22 Colour Model R Foreground & Background Iterated graph cut R Foreground Background G Background G Gaussian Mixture Model (typically 5-8 components) Source: Rother
23 GrabCut segmentation 1. Define graph usually 4-connected or 8-connected Divide diagonal potentials by sqrt(2) 2. Define unary potentials Color histogram or mixture of Gaussians for background and foreground unary _ 3. Define pairwise potentials edge _ potential( x) log P( c( x); P( c( x); c( x) c( y) potential( x, y) k1 k2 exp Apply graph cuts 5. Return to 2, using current labels to compute foreground, background models foreground background 2 ) )
24 What is easy or hard about these cases for graphcutbased segmentation?
25 Easier examples GrabCut Interactive Foreground Extraction 10
26 More difficult Examples Fine structure Harder Case Initial Rectangle Camouflage & Low Contrast Initial Result GrabCut Interactive Foreground Extraction 11
27 Lazy Snapping (Li et al. SG 2004)
28 Graph cuts with multiple labels Alpha expansion Repeat until no change For α = 1.. M Assign each pixel to current label or α (2-class graphcut) Achieves strong local minimum Alpha-beta swap Repeat until no change For α = 1.. M, β = 1.. M (except α) Re-assign all pixels currently labeled as α or β to one of those two labels while keeping all other pixels fixed
29 Using graph cuts for recognition TextonBoost (Shotton et al IJCV)
30 Using graph cuts for recognition Unary Potentials from classifier (note: edge potentials are from input image also; this is illustration from paper) Alpha Expansion Graph Cuts TextonBoost (Shotton et al IJCV)
31 Limitations of graph cuts Associative: edge potentials penalize different labels Must satisfy If not associative, can sometimes clip potentials Graph cut algorithm applies to only 2-label problems Multi-label extensions are not globally optimal (but still usually provide very good solutions)
32 Graph cuts: Pros and Cons Pros Very fast inference Can incorporate data likelihoods and priors Applies to a wide range of problems (stereo, image labeling, recognition) stereo stitching recognition Cons Not always applicable (associative only) Need unary terms (not used for bottom-up segmentation, for example) Use whenever applicable
33 More about MRFs/CRFs Other common uses Graph structure on regions Encoding relations between multiple scene elements Inference methods Loopy BP or BP-TRW Exact for tree-shaped structures Approximate solutions for general graphs More widely applicable and can produce marginals but often slower
34 Further reading and resources Graph cuts Classic paper: What Energy Functions can be Minimized via Graph Cuts? (Kolmogorov and Zabih, ECCV '02/PAMI '04) Belief propagation Yedidia, J.S.; Freeman, W.T.; Weiss, Y., "Understanding Belief Propagation and Its Generalizations, Technical Report, 2001: Comparative study Szeliski et al. A comparative study of energy minimization methods for markov random fields with smoothness-based priors, PAMI 2008 Kappes et al. A comparative study of modern inference techniques for discrete energy minimization problems, CVPR 2013
35 HW 4 Part 1: SLIC (Achanta et al. PAMI 2012) 1. Initialize cluster centers on pixel grid in steps S - Features: Lab color, x-y position 2. Move centers to position in 3x3 window with smallest gradient 3. Compare each pixel to cluster center within 2S pixel distance and assign to nearest 4. Recompute cluster centers as mean color/position of pixels belonging to each cluster 5. Stop when residual error is small
36 HW 4 Part 1: SLIC Graduate credits (up to 15 points) Improve your results on SLIC Color space, gradient features, edges (up to 15 points) Implement Adaptive-SLIC d c : Color difference d s : Spatial difference maximum observed spatial and color distances (m s, m c )
37 HW 4 Part 2: EM algorithm The false scores come from a uniform distribution The true scores for each image have a Gaussian distribution Annotators are always bad or always good The good/bad label of each annotator is the missing data
38 HW 4 Part 3: GraphCut Define unary potential Define pairwise potential Contrastive term Solve segementation using graph-cut Read GraphCut.m
39 HW 4 Part 3: GraphCut Graduate credits (up to 15 points) try two more images (up to 10 points) image composition
40 Things to remember Markov Random Fields Encode dependencies between pixels w ij i Likelihood as energy j Segmentation with Graph Cuts
41 Next module: Object Recognition Face recognition Image categorization Machine learning Object category detection Tracking objects
Markov Random Fields and Segmentation with Graph Cuts
 Markov Random Fields and Segmentation with Graph Cuts Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Many slides from D. Hoiem Administrative stuffs Final project Proposal due Oct 30 (Monday) HW 4 is out
Markov Random Fields and Segmentation with Graph Cuts Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Many slides from D. Hoiem Administrative stuffs Final project Proposal due Oct 30 (Monday) HW 4 is out
MRFs and Segmentation with Graph Cuts
 02/24/10 MRFs and Segmentation with Graph Cuts Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Today s class Finish up EM MRFs w ij i Segmentation with Graph Cuts j EM Algorithm: Recap
02/24/10 MRFs and Segmentation with Graph Cuts Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Today s class Finish up EM MRFs w ij i Segmentation with Graph Cuts j EM Algorithm: Recap
Markov/Conditional Random Fields, Graph Cut, and applications in Computer Vision
 Markov/Conditional Random Fields, Graph Cut, and applications in Computer Vision Fuxin Li Slides and materials from Le Song, Tucker Hermans, Pawan Kumar, Carsten Rother, Peter Orchard, and others Recap:
Markov/Conditional Random Fields, Graph Cut, and applications in Computer Vision Fuxin Li Slides and materials from Le Song, Tucker Hermans, Pawan Kumar, Carsten Rother, Peter Orchard, and others Recap:
ECE 6504: Advanced Topics in Machine Learning Probabilistic Graphical Models and Large-Scale Learning
 ECE 6504: Advanced Topics in Machine Learning Probabilistic Graphical Models and Large-Scale Learning Topics Markov Random Fields: Inference Exact: VE Exact+Approximate: BP Readings: Barber 5 Dhruv Batra
ECE 6504: Advanced Topics in Machine Learning Probabilistic Graphical Models and Large-Scale Learning Topics Markov Random Fields: Inference Exact: VE Exact+Approximate: BP Readings: Barber 5 Dhruv Batra
Segmentation with non-linear constraints on appearance, complexity, and geometry
 IPAM February 2013 Western Univesity Segmentation with non-linear constraints on appearance, complexity, and geometry Yuri Boykov Andrew Delong Lena Gorelick Hossam Isack Anton Osokin Frank Schmidt Olga
IPAM February 2013 Western Univesity Segmentation with non-linear constraints on appearance, complexity, and geometry Yuri Boykov Andrew Delong Lena Gorelick Hossam Isack Anton Osokin Frank Schmidt Olga
Segmentation in electron microscopy images
 Segmentation in electron microscopy images Aurelien Lucchi, Kevin Smith, Yunpeng Li Bohumil Maco, Graham Knott, Pascal Fua. http://cvlab.epfl.ch/research/medical/neurons/ Outline Automated Approach to
Segmentation in electron microscopy images Aurelien Lucchi, Kevin Smith, Yunpeng Li Bohumil Maco, Graham Knott, Pascal Fua. http://cvlab.epfl.ch/research/medical/neurons/ Outline Automated Approach to
10708 Graphical Models: Homework 4
 10708 Graphical Models: Homework 4 Due November 12th, beginning of class October 29, 2008 Instructions: There are six questions on this assignment. Each question has the name of one of the TAs beside it,
10708 Graphical Models: Homework 4 Due November 12th, beginning of class October 29, 2008 Instructions: There are six questions on this assignment. Each question has the name of one of the TAs beside it,
Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests. Daniel Munoz Februrary 9, 2009
 Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests Daniel Munoz 16-721 Februrary 9, 2009 Papers [shotton-eccv-06] J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi, TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context
Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests Daniel Munoz 16-721 Februrary 9, 2009 Papers [shotton-eccv-06] J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi, TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context
Prof. Feng Liu. Spring /17/2017. With slides by F. Durand, Y.Y. Chuang, R. Raskar, and C.
 Prof. Feng Liu Spring 2017 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~fliu/courses/cs510/ 05/17/2017 With slides by F. Durand, Y.Y. Chuang, R. Raskar, and C. Rother Last Time Image segmentation Normalized cut and segmentation
Prof. Feng Liu Spring 2017 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~fliu/courses/cs510/ 05/17/2017 With slides by F. Durand, Y.Y. Chuang, R. Raskar, and C. Rother Last Time Image segmentation Normalized cut and segmentation
Clustering web search results
 Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSE546 Emily Fox University of Washington November 4, 2013 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] 2 1 Clustering web search results 3 Some Data 4 2 K-means
Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSE546 Emily Fox University of Washington November 4, 2013 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] 2 1 Clustering web search results 3 Some Data 4 2 K-means
Image Segmentation Using Iterated Graph Cuts Based on Multi-scale Smoothing
 Image Segmentation Using Iterated Graph Cuts Based on Multi-scale Smoothing Tomoyuki Nagahashi 1, Hironobu Fujiyoshi 1, and Takeo Kanade 2 1 Dept. of Computer Science, Chubu University. Matsumoto 1200,
Image Segmentation Using Iterated Graph Cuts Based on Multi-scale Smoothing Tomoyuki Nagahashi 1, Hironobu Fujiyoshi 1, and Takeo Kanade 2 1 Dept. of Computer Science, Chubu University. Matsumoto 1200,
intro, applications MRF, labeling... how it can be computed at all? Applications in segmentation: GraphCut, GrabCut, demos
 Image as Markov Random Field and Applications 1 Tomáš Svoboda, svoboda@cmp.felk.cvut.cz Czech Technical University in Prague, Center for Machine Perception http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz Talk Outline Last update:
Image as Markov Random Field and Applications 1 Tomáš Svoboda, svoboda@cmp.felk.cvut.cz Czech Technical University in Prague, Center for Machine Perception http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz Talk Outline Last update:
Grouping and Segmentation
 03/17/15 Grouping and Segmentation Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Today s class Segmentation and grouping Gestalt cues By clustering (mean-shift) By boundaries (watershed)
03/17/15 Grouping and Segmentation Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Today s class Segmentation and grouping Gestalt cues By clustering (mean-shift) By boundaries (watershed)
Segmentation. Separate image into coherent regions
 Segmentation II Segmentation Separate image into coherent regions Berkeley segmentation database: http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/research/projects/cs/vision/grouping/segbench/ Slide by L. Lazebnik Interactive
Segmentation II Segmentation Separate image into coherent regions Berkeley segmentation database: http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/research/projects/cs/vision/grouping/segbench/ Slide by L. Lazebnik Interactive
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Unsupervised Learning: Kmeans, GMM, EM Readings: Barber 20.1-20.3 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Tasks Supervised Learning x Classification y Discrete x Regression
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Unsupervised Learning: Kmeans, GMM, EM Readings: Barber 20.1-20.3 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Tasks Supervised Learning x Classification y Discrete x Regression
Segmentation. Bottom up Segmentation Semantic Segmentation
 Segmentation Bottom up Segmentation Semantic Segmentation Semantic Labeling of Street Scenes Ground Truth Labels 11 classes, almost all occur simultaneously, large changes in viewpoint, scale sky, road,
Segmentation Bottom up Segmentation Semantic Segmentation Semantic Labeling of Street Scenes Ground Truth Labels 11 classes, almost all occur simultaneously, large changes in viewpoint, scale sky, road,
Announcements. Image Segmentation. From images to objects. Extracting objects. Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class
 Image Segmentation Announcements Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class Project voting From Sandlot Science Today s Readings Forsyth & Ponce, Chapter 1 (plus lots of optional references
Image Segmentation Announcements Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class Project voting From Sandlot Science Today s Readings Forsyth & Ponce, Chapter 1 (plus lots of optional references
Energy Minimization for Segmentation in Computer Vision
 S * = arg S min E(S) Energy Minimization for Segmentation in Computer Vision Meng Tang, Dmitrii Marin, Ismail Ben Ayed, Yuri Boykov Outline Clustering/segmentation methods K-means, GrabCut, Normalized
S * = arg S min E(S) Energy Minimization for Segmentation in Computer Vision Meng Tang, Dmitrii Marin, Ismail Ben Ayed, Yuri Boykov Outline Clustering/segmentation methods K-means, GrabCut, Normalized
Measuring Uncertainty in Graph Cut Solutions - Efficiently Computing Min-marginal Energies using Dynamic Graph Cuts
 Measuring Uncertainty in Graph Cut Solutions - Efficiently Computing Min-marginal Energies using Dynamic Graph Cuts Pushmeet Kohli Philip H.S. Torr Department of Computing, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford.
Measuring Uncertainty in Graph Cut Solutions - Efficiently Computing Min-marginal Energies using Dynamic Graph Cuts Pushmeet Kohli Philip H.S. Torr Department of Computing, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford.
Regularization and Markov Random Fields (MRF) CS 664 Spring 2008
 Regularization and Markov Random Fields (MRF) CS 664 Spring 2008 Regularization in Low Level Vision Low level vision problems concerned with estimating some quantity at each pixel Visual motion (u(x,y),v(x,y))
Regularization and Markov Random Fields (MRF) CS 664 Spring 2008 Regularization in Low Level Vision Low level vision problems concerned with estimating some quantity at each pixel Visual motion (u(x,y),v(x,y))
Discrete Optimization Methods in Computer Vision CSE 6389 Slides by: Boykov Modified and Presented by: Mostafa Parchami Basic overview of graph cuts
 Discrete Optimization Methods in Computer Vision CSE 6389 Slides by: Boykov Modified and Presented by: Mostafa Parchami Basic overview of graph cuts [Yuri Boykov, Olga Veksler, Ramin Zabih, Fast Approximation
Discrete Optimization Methods in Computer Vision CSE 6389 Slides by: Boykov Modified and Presented by: Mostafa Parchami Basic overview of graph cuts [Yuri Boykov, Olga Veksler, Ramin Zabih, Fast Approximation
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701
 Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Clustering and EM Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Clustering K-means Mixture of Gaussians Expectation Maximization Variational Methods 2 Clustering 3 K-
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Clustering and EM Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Clustering K-means Mixture of Gaussians Expectation Maximization Variational Methods 2 Clustering 3 K-
Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model
 Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Outline Basics Motivation, definition, evaluation Methods Partitional Hierarchical Density-based Mixture model Spectral methods Advanced topics
Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Outline Basics Motivation, definition, evaluation Methods Partitional Hierarchical Density-based Mixture model Spectral methods Advanced topics
Clustering K-means. Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, Carlos Guestrin
 Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, 2014 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014
Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, 2014 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014
Generative and discriminative classification techniques
 Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 2014-2015 Jakob Verbeek, November 28, 2014 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.14.15
Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 2014-2015 Jakob Verbeek, November 28, 2014 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.14.15
Models for grids. Computer vision: models, learning and inference. Multi label Denoising. Binary Denoising. Denoising Goal.
 Models for grids Computer vision: models, learning and inference Chapter 9 Graphical Models Consider models where one unknown world state at each pixel in the image takes the form of a grid. Loops in the
Models for grids Computer vision: models, learning and inference Chapter 9 Graphical Models Consider models where one unknown world state at each pixel in the image takes the form of a grid. Loops in the
Image Segmentation Using Iterated Graph Cuts BasedonMulti-scaleSmoothing
 Image Segmentation Using Iterated Graph Cuts BasedonMulti-scaleSmoothing Tomoyuki Nagahashi 1, Hironobu Fujiyoshi 1, and Takeo Kanade 2 1 Dept. of Computer Science, Chubu University. Matsumoto 1200, Kasugai,
Image Segmentation Using Iterated Graph Cuts BasedonMulti-scaleSmoothing Tomoyuki Nagahashi 1, Hironobu Fujiyoshi 1, and Takeo Kanade 2 1 Dept. of Computer Science, Chubu University. Matsumoto 1200, Kasugai,
Approximate decoding: ICM, block methods, alpha-beta swap & alpha-expansion
 Approximate decoding: ICM, block methods, alpha-beta swap & alpha-expansion Julieta Martinez University of British Columbia August 25, 2015 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kp3ik5f3-2c&t=18m36s Outline
Approximate decoding: ICM, block methods, alpha-beta swap & alpha-expansion Julieta Martinez University of British Columbia August 25, 2015 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kp3ik5f3-2c&t=18m36s Outline
Content-based image and video analysis. Machine learning
 Content-based image and video analysis Machine learning for multimedia retrieval 04.05.2009 What is machine learning? Some problems are very hard to solve by writing a computer program by hand Almost all
Content-based image and video analysis Machine learning for multimedia retrieval 04.05.2009 What is machine learning? Some problems are very hard to solve by writing a computer program by hand Almost all
Fall 09, Homework 5
 5-38 Fall 09, Homework 5 Due: Wednesday, November 8th, beginning of the class You can work in a group of up to two people. This group does not need to be the same group as for the other homeworks. You
5-38 Fall 09, Homework 5 Due: Wednesday, November 8th, beginning of the class You can work in a group of up to two people. This group does not need to be the same group as for the other homeworks. You
Colorado School of Mines. Computer Vision. Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science.
 Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Image Segmentation Some material for these slides comes from https://www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs4487a/
Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Image Segmentation Some material for these slides comes from https://www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs4487a/
Learning CRFs using Graph Cuts
 Appears in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2008 Learning CRFs using Graph Cuts Martin Szummer 1, Pushmeet Kohli 1, and Derek Hoiem 2 1 Microsoft Research, Cambridge CB3 0FB, United Kingdom
Appears in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2008 Learning CRFs using Graph Cuts Martin Szummer 1, Pushmeet Kohli 1, and Derek Hoiem 2 1 Microsoft Research, Cambridge CB3 0FB, United Kingdom
Chapter 8 of Bishop's Book: Graphical Models
 Chapter 8 of Bishop's Book: Graphical Models Review of Probability Probability density over possible values of x Used to find probability of x falling in some range For continuous variables, the probability
Chapter 8 of Bishop's Book: Graphical Models Review of Probability Probability density over possible values of x Used to find probability of x falling in some range For continuous variables, the probability
Expectation Maximization: Inferring model parameters and class labels
 Expectation Maximization: Inferring model parameters and class labels Emily Fox University of Washington February 27, 2017 Mixture of Gaussian recap 1 2/26/17 Jumble of unlabeled images HISTOGRAM blue
Expectation Maximization: Inferring model parameters and class labels Emily Fox University of Washington February 27, 2017 Mixture of Gaussian recap 1 2/26/17 Jumble of unlabeled images HISTOGRAM blue
Lecture 7: Segmentation. Thursday, Sept 20
 Lecture 7: Segmentation Thursday, Sept 20 Outline Why segmentation? Gestalt properties, fun illusions and/or revealing examples Clustering Hierarchical K-means Mean Shift Graph-theoretic Normalized cuts
Lecture 7: Segmentation Thursday, Sept 20 Outline Why segmentation? Gestalt properties, fun illusions and/or revealing examples Clustering Hierarchical K-means Mean Shift Graph-theoretic Normalized cuts
IMPROVED FINE STRUCTURE MODELING VIA GUIDED STOCHASTIC CLIQUE FORMATION IN FULLY CONNECTED CONDITIONAL RANDOM FIELDS
 IMPROVED FINE STRUCTURE MODELING VIA GUIDED STOCHASTIC CLIQUE FORMATION IN FULLY CONNECTED CONDITIONAL RANDOM FIELDS M. J. Shafiee, A. G. Chung, A. Wong, and P. Fieguth Vision & Image Processing Lab, Systems
IMPROVED FINE STRUCTURE MODELING VIA GUIDED STOCHASTIC CLIQUE FORMATION IN FULLY CONNECTED CONDITIONAL RANDOM FIELDS M. J. Shafiee, A. G. Chung, A. Wong, and P. Fieguth Vision & Image Processing Lab, Systems
Markov Networks in Computer Vision
 Markov Networks in Computer Vision Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Markov Networks for Computer Vision Some applications: 1. Image segmentation 2. Removal of blur/noise 3. Stereo reconstruction
Markov Networks in Computer Vision Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Markov Networks for Computer Vision Some applications: 1. Image segmentation 2. Removal of blur/noise 3. Stereo reconstruction
Applied Bayesian Nonparametrics 5. Spatial Models via Gaussian Processes, not MRFs Tutorial at CVPR 2012 Erik Sudderth Brown University
 Applied Bayesian Nonparametrics 5. Spatial Models via Gaussian Processes, not MRFs Tutorial at CVPR 2012 Erik Sudderth Brown University NIPS 2008: E. Sudderth & M. Jordan, Shared Segmentation of Natural
Applied Bayesian Nonparametrics 5. Spatial Models via Gaussian Processes, not MRFs Tutorial at CVPR 2012 Erik Sudderth Brown University NIPS 2008: E. Sudderth & M. Jordan, Shared Segmentation of Natural
Image Segmentation. April 24, Stanford University. Philipp Krähenbühl (Stanford University) Segmentation April 24, / 63
 Image Segmentation Philipp Krähenbühl Stanford University April 24, 2013 Philipp Krähenbühl (Stanford University) Segmentation April 24, 2013 1 / 63 Image Segmentation Goal: identify groups of pixels that
Image Segmentation Philipp Krähenbühl Stanford University April 24, 2013 Philipp Krähenbühl (Stanford University) Segmentation April 24, 2013 1 / 63 Image Segmentation Goal: identify groups of pixels that
Markov Networks in Computer Vision. Sargur Srihari
 Markov Networks in Computer Vision Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Markov Networks for Computer Vision Important application area for MNs 1. Image segmentation 2. Removal of blur/noise 3. Stereo reconstruction
Markov Networks in Computer Vision Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Markov Networks for Computer Vision Important application area for MNs 1. Image segmentation 2. Removal of blur/noise 3. Stereo reconstruction
Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift. CAP 5415 Fall 2007
 Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift CAP 5415 Fall 2007 Review on Segmentation by Clustering Each Pixel Data Vector Example (From Comanciu and Meer) Review of k-means Let's find three clusters in this data These
Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift CAP 5415 Fall 2007 Review on Segmentation by Clustering Each Pixel Data Vector Example (From Comanciu and Meer) Review of k-means Let's find three clusters in this data These
CS448f: Image Processing For Photography and Vision. Graph Cuts
 CS448f: Image Processing For Photography and Vision Graph Cuts Seam Carving Video Make images smaller by removing seams Seam = connected path of pixels from top to bottom or left edge to right edge Don
CS448f: Image Processing For Photography and Vision Graph Cuts Seam Carving Video Make images smaller by removing seams Seam = connected path of pixels from top to bottom or left edge to right edge Don
Algorithms for Markov Random Fields in Computer Vision
 Algorithms for Markov Random Fields in Computer Vision Dan Huttenlocher November, 2003 (Joint work with Pedro Felzenszwalb) Random Field Broadly applicable stochastic model Collection of n sites S Hidden
Algorithms for Markov Random Fields in Computer Vision Dan Huttenlocher November, 2003 (Joint work with Pedro Felzenszwalb) Random Field Broadly applicable stochastic model Collection of n sites S Hidden
Problem Set 4. Assigned: March 23, 2006 Due: April 17, (6.882) Belief Propagation for Segmentation
 6.098/6.882 Computational Photography 1 Problem Set 4 Assigned: March 23, 2006 Due: April 17, 2006 Problem 1 (6.882) Belief Propagation for Segmentation In this problem you will set-up a Markov Random
6.098/6.882 Computational Photography 1 Problem Set 4 Assigned: March 23, 2006 Due: April 17, 2006 Problem 1 (6.882) Belief Propagation for Segmentation In this problem you will set-up a Markov Random
Multi-Label Moves for Multi-Label Energies
 Multi-Label Moves for Multi-Label Energies Olga Veksler University of Western Ontario some work is joint with Olivier Juan, Xiaoqing Liu, Yu Liu Outline Review multi-label optimization with graph cuts
Multi-Label Moves for Multi-Label Energies Olga Veksler University of Western Ontario some work is joint with Olivier Juan, Xiaoqing Liu, Yu Liu Outline Review multi-label optimization with graph cuts
Clustering K-means. Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, Carlos Guestrin
 Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, 2014 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014
Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, 2014 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014
Simultaneous Multi-class Pixel Labeling over Coherent Image Sets
 Simultaneous Multi-class Pixel Labeling over Coherent Image Sets Paul Rivera Research School of Computer Science Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Stephen Gould Research School of Computer
Simultaneous Multi-class Pixel Labeling over Coherent Image Sets Paul Rivera Research School of Computer Science Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Stephen Gould Research School of Computer
Detection of Man-made Structures in Natural Images
 Detection of Man-made Structures in Natural Images Tim Rees December 17, 2004 Abstract Object detection in images is a very active research topic in many disciplines. Probabilistic methods have been applied
Detection of Man-made Structures in Natural Images Tim Rees December 17, 2004 Abstract Object detection in images is a very active research topic in many disciplines. Probabilistic methods have been applied
Computer Vision : Exercise 4 Labelling Problems
 Computer Vision Exercise 4 Labelling Problems 13/01/2014 Computer Vision : Exercise 4 Labelling Problems Outline 1. Energy Minimization (example segmentation) 2. Iterated Conditional Modes 3. Dynamic Programming
Computer Vision Exercise 4 Labelling Problems 13/01/2014 Computer Vision : Exercise 4 Labelling Problems Outline 1. Energy Minimization (example segmentation) 2. Iterated Conditional Modes 3. Dynamic Programming
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images. Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009
 Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Reduce, Reuse & Recycle: Efficiently Solving Multi-Label MRFs
 Reduce, Reuse & Recycle: Efficiently Solving Multi-Label MRFs Karteek Alahari 1 Pushmeet Kohli 2 Philip H. S. Torr 1 1 Oxford Brookes University 2 Microsoft Research, Cambridge Abstract In this paper,
Reduce, Reuse & Recycle: Efficiently Solving Multi-Label MRFs Karteek Alahari 1 Pushmeet Kohli 2 Philip H. S. Torr 1 1 Oxford Brookes University 2 Microsoft Research, Cambridge Abstract In this paper,
Mathematics in Image Processing
 Mathematics in Image Processing Michal Šorel Department of Image Processing Institute of Information Theory and Automation (ÚTIA) Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic http://zoi.utia.cas.cz/ Mathematics
Mathematics in Image Processing Michal Šorel Department of Image Processing Institute of Information Theory and Automation (ÚTIA) Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic http://zoi.utia.cas.cz/ Mathematics
Image Segmentation. Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech. Many slides from D. Hoiem
 Image Segmentation Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Many slides from D. Hoiem Administrative stuffs HW 3 due 11:59 PM, Oct 25 (Wed) Final project proposal due Oct 30 (Mon) Title Problem Tentative
Image Segmentation Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Many slides from D. Hoiem Administrative stuffs HW 3 due 11:59 PM, Oct 25 (Wed) Final project proposal due Oct 30 (Mon) Title Problem Tentative
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 17 EM CS/CNS/EE 155 Andreas Krause Announcements Project poster session on Thursday Dec 3, 4-6pm in Annenberg 2 nd floor atrium! Easels, poster boards and cookies
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 17 EM CS/CNS/EE 155 Andreas Krause Announcements Project poster session on Thursday Dec 3, 4-6pm in Annenberg 2 nd floor atrium! Easels, poster boards and cookies
ECE521: Week 11, Lecture March 2017: HMM learning/inference. With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov
 ECE521: Week 11, Lecture 20 27 March 2017: HMM learning/inference With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov Examples of other perspectives Murphy 17.4 End of Russell & Norvig 15.2 (Artificial Intelligence: A Modern
ECE521: Week 11, Lecture 20 27 March 2017: HMM learning/inference With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov Examples of other perspectives Murphy 17.4 End of Russell & Norvig 15.2 (Artificial Intelligence: A Modern
K-Means and Gaussian Mixture Models
 K-Means and Gaussian Mixture Models David Rosenberg New York University June 15, 2015 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 June 15, 2015 1 / 43 K-Means Clustering Example: Old Faithful Geyser
K-Means and Gaussian Mixture Models David Rosenberg New York University June 15, 2015 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 June 15, 2015 1 / 43 K-Means Clustering Example: Old Faithful Geyser
Segmentation Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 27
 Segmentation http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 218, Lecture 27 Course announcements Homework 7 is due on Sunday 6 th. - Any questions about homework 7? - How many of you have
Segmentation http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 218, Lecture 27 Course announcements Homework 7 is due on Sunday 6 th. - Any questions about homework 7? - How many of you have
Supervised texture detection in images
 Supervised texture detection in images Branislav Mičušík and Allan Hanbury Pattern Recognition and Image Processing Group, Institute of Computer Aided Automation, Vienna University of Technology Favoritenstraße
Supervised texture detection in images Branislav Mičušík and Allan Hanbury Pattern Recognition and Image Processing Group, Institute of Computer Aided Automation, Vienna University of Technology Favoritenstraße
CS6670: Computer Vision
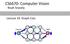 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 19: Graph Cuts source S sink T Readings Szeliski, Chapter 11.2 11.5 Stereo results with window search problems in areas of uniform texture Window-based matching
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 19: Graph Cuts source S sink T Readings Szeliski, Chapter 11.2 11.5 Stereo results with window search problems in areas of uniform texture Window-based matching
Comparison of Graph Cuts with Belief Propagation for Stereo, using Identical MRF Parameters
 Comparison of Graph Cuts with Belief Propagation for Stereo, using Identical MRF Parameters Marshall F. Tappen William T. Freeman Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute
Comparison of Graph Cuts with Belief Propagation for Stereo, using Identical MRF Parameters Marshall F. Tappen William T. Freeman Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute
CAP5415-Computer Vision Lecture 13-Image/Video Segmentation Part II. Dr. Ulas Bagci
 CAP-Computer Vision Lecture -Image/Video Segmentation Part II Dr. Ulas Bagci bagci@ucf.edu Labeling & Segmentation Labeling is a common way for modeling various computer vision problems (e.g. optical flow,
CAP-Computer Vision Lecture -Image/Video Segmentation Part II Dr. Ulas Bagci bagci@ucf.edu Labeling & Segmentation Labeling is a common way for modeling various computer vision problems (e.g. optical flow,
A Feature Point Matching Based Approach for Video Objects Segmentation
 A Feature Point Matching Based Approach for Video Objects Segmentation Yan Zhang, Zhong Zhou, Wei Wu State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems, Beijing, P.R. China School of Computer
A Feature Point Matching Based Approach for Video Objects Segmentation Yan Zhang, Zhong Zhou, Wei Wu State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems, Beijing, P.R. China School of Computer
Belief propagation and MRF s
 Belief propagation and MRF s Bill Freeman 6.869 March 7, 2011 1 1 Undirected graphical models A set of nodes joined by undirected edges. The graph makes conditional independencies explicit: If two nodes
Belief propagation and MRF s Bill Freeman 6.869 March 7, 2011 1 1 Undirected graphical models A set of nodes joined by undirected edges. The graph makes conditional independencies explicit: If two nodes
Image Pyramids and Applications
 Image Pyramids and Applications Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Golconda, René Magritte, 1953 Administrative stuffs HW 1 will be posted tonight, due 11:59 PM Sept 25 Anonymous feedback Previous
Image Pyramids and Applications Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Golconda, René Magritte, 1953 Administrative stuffs HW 1 will be posted tonight, due 11:59 PM Sept 25 Anonymous feedback Previous
Machine Learning. Topic 5: Linear Discriminants. Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013
 Machine Learning Topic 5: Linear Discriminants Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013 Thanks to Mark Cartwright for his extensive contributions to these slides Thanks to Alpaydin, Bishop, and Duda/Hart/Stork
Machine Learning Topic 5: Linear Discriminants Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013 Thanks to Mark Cartwright for his extensive contributions to these slides Thanks to Alpaydin, Bishop, and Duda/Hart/Stork
18 October, 2013 MVA ENS Cachan. Lecture 6: Introduction to graphical models Iasonas Kokkinos
 Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 18 October, 2013 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 6: Introduction to graphical models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 18 October, 2013 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 6: Introduction to graphical models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
SPM-BP: Sped-up PatchMatch Belief Propagation for Continuous MRFs. Yu Li, Dongbo Min, Michael S. Brown, Minh N. Do, Jiangbo Lu
 SPM-BP: Sped-up PatchMatch Belief Propagation for Continuous MRFs Yu Li, Dongbo Min, Michael S. Brown, Minh N. Do, Jiangbo Lu Discrete Pixel-Labeling Optimization on MRF 2/37 Many computer vision tasks
SPM-BP: Sped-up PatchMatch Belief Propagation for Continuous MRFs Yu Li, Dongbo Min, Michael S. Brown, Minh N. Do, Jiangbo Lu Discrete Pixel-Labeling Optimization on MRF 2/37 Many computer vision tasks
CS 229 Midterm Review
 CS 229 Midterm Review Course Staff Fall 2018 11/2/2018 Outline Today: SVMs Kernels Tree Ensembles EM Algorithm / Mixture Models [ Focus on building intuition, less so on solving specific problems. Ask
CS 229 Midterm Review Course Staff Fall 2018 11/2/2018 Outline Today: SVMs Kernels Tree Ensembles EM Algorithm / Mixture Models [ Focus on building intuition, less so on solving specific problems. Ask
Overview Citation. ML Introduction. Overview Schedule. ML Intro Dataset. Introduction to Semi-Supervised Learning Review 10/4/2010
 INFORMATICS SEMINAR SEPT. 27 & OCT. 4, 2010 Introduction to Semi-Supervised Learning Review 2 Overview Citation X. Zhu and A.B. Goldberg, Introduction to Semi- Supervised Learning, Morgan & Claypool Publishers,
INFORMATICS SEMINAR SEPT. 27 & OCT. 4, 2010 Introduction to Semi-Supervised Learning Review 2 Overview Citation X. Zhu and A.B. Goldberg, Introduction to Semi- Supervised Learning, Morgan & Claypool Publishers,
Part-based and local feature models for generic object recognition
 Part-based and local feature models for generic object recognition May 28 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS2 grades up on SmartSite PS2 stats: Mean: 80.15 Standard Dev: 22.77 Vote on piazza
Part-based and local feature models for generic object recognition May 28 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS2 grades up on SmartSite PS2 stats: Mean: 80.15 Standard Dev: 22.77 Vote on piazza
Undirected Graphical Models. Raul Queiroz Feitosa
 Undirected Graphical Models Raul Queiroz Feitosa Pros and Cons Advantages of UGMs over DGMs UGMs are more natural for some domains (e.g. context-dependent entities) Discriminative UGMs (CRF) are better
Undirected Graphical Models Raul Queiroz Feitosa Pros and Cons Advantages of UGMs over DGMs UGMs are more natural for some domains (e.g. context-dependent entities) Discriminative UGMs (CRF) are better
Discrete Optimization of Ray Potentials for Semantic 3D Reconstruction
 Discrete Optimization of Ray Potentials for Semantic 3D Reconstruction Marc Pollefeys Joined work with Nikolay Savinov, Christian Haene, Lubor Ladicky 2 Comparison to Volumetric Fusion Higher-order ray
Discrete Optimization of Ray Potentials for Semantic 3D Reconstruction Marc Pollefeys Joined work with Nikolay Savinov, Christian Haene, Lubor Ladicky 2 Comparison to Volumetric Fusion Higher-order ray
Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 3.3 Advanced Global Matching
 Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 3.3 Advanced Global Matching Correlated Correspondences [ASP*04] A Complete Registration System [HAW*08] In this session Advanced Global Matching Some practical
Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 3.3 Advanced Global Matching Correlated Correspondences [ASP*04] A Complete Registration System [HAW*08] In this session Advanced Global Matching Some practical
Image Segmentation with a Bounding Box Prior Victor Lempitsky, Pushmeet Kohli, Carsten Rother, Toby Sharp Microsoft Research Cambridge
 Image Segmentation with a Bounding Box Prior Victor Lempitsky, Pushmeet Kohli, Carsten Rother, Toby Sharp Microsoft Research Cambridge Dylan Rhodes and Jasper Lin 1 Presentation Overview Segmentation problem
Image Segmentation with a Bounding Box Prior Victor Lempitsky, Pushmeet Kohli, Carsten Rother, Toby Sharp Microsoft Research Cambridge Dylan Rhodes and Jasper Lin 1 Presentation Overview Segmentation problem
Principal-channels for One-sided Object Cutout
 Principal-channels for One-sided Object Cutout Lior Gavish, Lior Wolf, Lior Shapira, and Daniel Cohen-Or Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel Abstract We introduce principal-channels for cutting out objects
Principal-channels for One-sided Object Cutout Lior Gavish, Lior Wolf, Lior Shapira, and Daniel Cohen-Or Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel Abstract We introduce principal-channels for cutting out objects
CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models. Lecture 10: Learning with Partially Observed Data. Theo Rekatsinas
 CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 10: Learning with Partially Observed Data Theo Rekatsinas 1 Partially Observed GMs Speech recognition 2 Partially Observed GMs Evolution 3 Partially Observed
CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 10: Learning with Partially Observed Data Theo Rekatsinas 1 Partially Observed GMs Speech recognition 2 Partially Observed GMs Evolution 3 Partially Observed
human vision: grouping k-means clustering graph-theoretic clustering Hough transform line fitting RANSAC
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Segmentation human vision: grouping k-means clustering graph-theoretic clustering Hough transform line fitting RANSAC Reading: Chapters 14, 15 Some of the slides are credited to:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Segmentation human vision: grouping k-means clustering graph-theoretic clustering Hough transform line fitting RANSAC Reading: Chapters 14, 15 Some of the slides are credited to:
Multiple cosegmentation
 Armand Joulin, Francis Bach and Jean Ponce. INRIA -Ecole Normale Supérieure April 25, 2012 Segmentation Introduction Segmentation Supervised and weakly-supervised segmentation Cosegmentation Segmentation
Armand Joulin, Francis Bach and Jean Ponce. INRIA -Ecole Normale Supérieure April 25, 2012 Segmentation Introduction Segmentation Supervised and weakly-supervised segmentation Cosegmentation Segmentation
Lecture 13 Segmentation and Scene Understanding Chris Choy, Ph.D. candidate Stanford Vision and Learning Lab (SVL)
 Lecture 13 Segmentation and Scene Understanding Chris Choy, Ph.D. candidate Stanford Vision and Learning Lab (SVL) http://chrischoy.org Stanford CS231A 1 Understanding a Scene Objects Chairs, Cups, Tables,
Lecture 13 Segmentation and Scene Understanding Chris Choy, Ph.D. candidate Stanford Vision and Learning Lab (SVL) http://chrischoy.org Stanford CS231A 1 Understanding a Scene Objects Chairs, Cups, Tables,
Generative and discriminative classification techniques
 Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 013-014 Jakob Verbeek, December 13+0, 013 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.13.14
Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 013-014 Jakob Verbeek, December 13+0, 013 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.13.14
A discriminative view of MRF pre-processing algorithms supplementary material
 A discriminative view of MRF pre-processing algorithms supplementary material Chen Wang 1,2 Charles Herrmann 2 Ramin Zabih 1,2 1 Google Research 2 Cornell University {chenwang, cih, rdz}@cs.cornell.edu
A discriminative view of MRF pre-processing algorithms supplementary material Chen Wang 1,2 Charles Herrmann 2 Ramin Zabih 1,2 1 Google Research 2 Cornell University {chenwang, cih, rdz}@cs.cornell.edu
Unsupervised Learning
 Unsupervised Learning Learning without Class Labels (or correct outputs) Density Estimation Learn P(X) given training data for X Clustering Partition data into clusters Dimensionality Reduction Discover
Unsupervised Learning Learning without Class Labels (or correct outputs) Density Estimation Learn P(X) given training data for X Clustering Partition data into clusters Dimensionality Reduction Discover
Structured Models in. Dan Huttenlocher. June 2010
 Structured Models in Computer Vision i Dan Huttenlocher June 2010 Structured Models Problems where output variables are mutually dependent or constrained E.g., spatial or temporal relations Such dependencies
Structured Models in Computer Vision i Dan Huttenlocher June 2010 Structured Models Problems where output variables are mutually dependent or constrained E.g., spatial or temporal relations Such dependencies
CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu. Lectures 21 & 22 Segmentation and clustering
 CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu Lectures 21 & 22 Segmentation and clustering 1 Schedule Last class We started on segmentation Today Segmentation continued Readings
CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu Lectures 21 & 22 Segmentation and clustering 1 Schedule Last class We started on segmentation Today Segmentation continued Readings
Extracting Smooth and Transparent Layers from a Single Image
 Extracting Smooth and Transparent Layers from a Single Image Sai-Kit Yeung Tai-Pang Wu Chi-Keung Tang saikit@ust.hk pang@ust.hk cktang@cse.ust.hk Vision and Graphics Group The Hong Kong University of Science
Extracting Smooth and Transparent Layers from a Single Image Sai-Kit Yeung Tai-Pang Wu Chi-Keung Tang saikit@ust.hk pang@ust.hk cktang@cse.ust.hk Vision and Graphics Group The Hong Kong University of Science
CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, :59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points]
![CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, :59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points] CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, :59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points]](/thumbs/89/100746783.jpg) CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, 2015. 11:59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points] Instructions. Please write up your responses to the following problems clearly and concisely.
CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, 2015. 11:59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points] Instructions. Please write up your responses to the following problems clearly and concisely.
Unsupervised Learning. Clustering and the EM Algorithm. Unsupervised Learning is Model Learning
 Unsupervised Learning Clustering and the EM Algorithm Susanna Ricco Supervised Learning Given data in the form < x, y >, y is the target to learn. Good news: Easy to tell if our algorithm is giving the
Unsupervised Learning Clustering and the EM Algorithm Susanna Ricco Supervised Learning Given data in the form < x, y >, y is the target to learn. Good news: Easy to tell if our algorithm is giving the
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Clustering (1): Basics. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Clustering (1): Basics Kalev Kask Unsupervised learning Supervised learning Predict target value ( y ) given features ( x ) Unsupervised learning Understand patterns of
Machine Learning and Data Mining Clustering (1): Basics Kalev Kask Unsupervised learning Supervised learning Predict target value ( y ) given features ( x ) Unsupervised learning Understand patterns of
Machine Learning. Unsupervised Learning. Manfred Huber
 Machine Learning Unsupervised Learning Manfred Huber 2015 1 Unsupervised Learning In supervised learning the training data provides desired target output for learning In unsupervised learning the training
Machine Learning Unsupervised Learning Manfred Huber 2015 1 Unsupervised Learning In supervised learning the training data provides desired target output for learning In unsupervised learning the training
10-701/15-781, Fall 2006, Final
 -7/-78, Fall 6, Final Dec, :pm-8:pm There are 9 questions in this exam ( pages including this cover sheet). If you need more room to work out your answer to a question, use the back of the page and clearly
-7/-78, Fall 6, Final Dec, :pm-8:pm There are 9 questions in this exam ( pages including this cover sheet). If you need more room to work out your answer to a question, use the back of the page and clearly
Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm
 Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm Padhraic Smyth, Department of Computer Science University of California, Irvine Finite Mixture Models A finite mixture model with K components, for
Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm Padhraic Smyth, Department of Computer Science University of California, Irvine Finite Mixture Models A finite mixture model with K components, for
Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
 Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz Unsupervised learning Daniel Hennes 29.01.2018 (WS 2017/18) University Stuttgart - IPVS - Machine Learning & Robotics 1 Today Supervised learning Regression (linear
Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz Unsupervised learning Daniel Hennes 29.01.2018 (WS 2017/18) University Stuttgart - IPVS - Machine Learning & Robotics 1 Today Supervised learning Regression (linear
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 4a. Inference in Graphical Models
 Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 4a. Inference in Graphical Models Inference on a Chain (Rep.) The first values of µ α and µ β are: The partition function can be computed at any node: Overall, we have O(NK 2
Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 4a. Inference in Graphical Models Inference on a Chain (Rep.) The first values of µ α and µ β are: The partition function can be computed at any node: Overall, we have O(NK 2
Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods. Some slides: courtesy of O. Capms, Penn State, J.Ponce and D. Fortsyth, Computer Vision Book
 Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods Some slides: courtesy of O. Capms, Penn State, J.Ponce and D. Fortsyth, Computer Vision Book Previously Binary segmentation Segmentation by thresholding
Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods Some slides: courtesy of O. Capms, Penn State, J.Ponce and D. Fortsyth, Computer Vision Book Previously Binary segmentation Segmentation by thresholding
Inference and Representation
 Inference and Representation Rachel Hodos New York University Lecture 5, October 6, 2015 Rachel Hodos Lecture 5: Inference and Representation Today: Learning with hidden variables Outline: Unsupervised
Inference and Representation Rachel Hodos New York University Lecture 5, October 6, 2015 Rachel Hodos Lecture 5: Inference and Representation Today: Learning with hidden variables Outline: Unsupervised
Introduction to object recognition. Slides adapted from Fei-Fei Li, Rob Fergus, Antonio Torralba, and others
 Introduction to object recognition Slides adapted from Fei-Fei Li, Rob Fergus, Antonio Torralba, and others Overview Basic recognition tasks A statistical learning approach Traditional or shallow recognition
Introduction to object recognition Slides adapted from Fei-Fei Li, Rob Fergus, Antonio Torralba, and others Overview Basic recognition tasks A statistical learning approach Traditional or shallow recognition
Segmentation and Grouping
 CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Segmentation and Grouping Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 24, 2015 Goals: Grouping in vision Gather features that belong together Obtain an intermediate
CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Segmentation and Grouping Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 24, 2015 Goals: Grouping in vision Gather features that belong together Obtain an intermediate
Robust Higher Order Potentials for Enforcing Label Consistency
 Int J Comput Vis (2009) 82: 302 324 DOI 10.1007/s11263-008-0202-0 Robust Higher Order Potentials for Enforcing Label Consistency Pushmeet Kohli L ubor Ladický Philip H.S. Torr Received: 17 August 2008
Int J Comput Vis (2009) 82: 302 324 DOI 10.1007/s11263-008-0202-0 Robust Higher Order Potentials for Enforcing Label Consistency Pushmeet Kohli L ubor Ladický Philip H.S. Torr Received: 17 August 2008
What have we leaned so far?
 What have we leaned so far? Camera structure Eye structure Project 1: High Dynamic Range Imaging What have we learned so far? Image Filtering Image Warping Camera Projection Model Project 2: Panoramic
What have we leaned so far? Camera structure Eye structure Project 1: High Dynamic Range Imaging What have we learned so far? Image Filtering Image Warping Camera Projection Model Project 2: Panoramic
Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM
 Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM Ying Wu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 yingwu@northwestern.edu http://www.eecs.northwestern.edu/~yingwu
Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM Ying Wu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 yingwu@northwestern.edu http://www.eecs.northwestern.edu/~yingwu
