arxiv: v1 [math.co] 15 Jun 2011
|
|
|
- Jack Cox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 O the extremal properties of the average eccetricity arxiv: v1 [math.co] 15 Ju 011 Aleksadar Ilić Faculty of Scieces ad Mathematics, Višegradska 33, Niš Uiversity of Niš, Serbia Jauary 1, 018 Abstract The eccetricity of a vertex is the maximum distace from it to aother vertex ad the average eccetricity ecc(g) of a graph G is the mea value of eccetricities of all vertices of G. The average eccetricity is deeply coected with a topological descriptor called the eccetric coectivity idex, defied as a sum of products of vertex degrees ad eccetricities. I this paper we aalyze extremal properties of the average eccetricity, itroducig two graph trasformatios that icrease or decrease ecc(g). Furthermore, we resolve four cojectures, obtaied by the system AutoGraphiX, about the average eccetricity ad other graph parameters (the clique umber, the Radić idex ad the idepedece umber), refute oe AutoGraphiX cojecture about the average eccetricity ad the miimum vertex degree ad correct oe AutoGraphiX cojecture about the domiatio umber. Key words: distaces; average eccetricity; vertex degree; Radić idex; Auto- GraphiX; extremal graph. AMS Classificatios: 05C1, 05C35, 9E10. 1 Itroductio Let G = (V,E) be a coected simple graph with = V vertices ad m = E edges. Let deg(v) deotes the degree of the vertex v. Let δ = δ(g) be the miimum vertex degree, ad = (G) be the maximum vertex degree of a graph G. For vertices u,v V, the distace d(u,v) is defied as the legth of the shortest path betwee u ad v i G. The eccetricity of a vertex is the maximum distace from it to ay other vertex, ε(v) = max u V d(u,v). The radius of a graph r(g) is the miimum eccetricity of ay vertex. The diameter of a graph d(g) is the maximum eccetricity of ay vertex i the graph, or the greatest distace betwee ay pair of vertices. For a arbitrary vertex v V it holds that r(g) ε(v) d(g). A vertex c of G is called cetral if ε(c) = r(g). The ceter C(G) is the set of all cetral vertices i G. A eccetric vertex of a vertex v is a vertex farthest away from v. Every tree has exactly oe or two ceter vertices [8]. 1
2 The average eccetricity of a graph G is the mea value of eccetricities of vertices of G, ecc(g) = 1 ε(v). For example, we have the followig formulas for the average eccetricity of the complete graph K, complete bipartite graph K,m, hypercube H, path P, cycle C ad star S, ecc(k ) = 1 ecc(k,m ) = ecc(q ) = ecc(p ) = ecc(c ) = ecc(s ) = 1. Dakelma, Goddard ad Swart [11] preseted some upper bouds ad formulas for the average eccetricity regardig the diameter ad the miimum vertex degree. Furthermore, they examie the chage i the average eccetricity whe a graph is replaced by a spaig subgraph, i particular the two extreme cases: takig a spaig tree ad removig oe edge. Dakelma ad Etriger [1] studied the average distace of G withi various classes of graphs. I theoretical chemistry molecular structure descriptors(also called topological idices) are used for modelig physico-chemical, pharmacologic, toxicologic, biological ad other properties of chemical compouds[17]. There exist several types of such idices, especially those based o vertex ad edge distaces [3, 6]. Arguably the best kow of these idices is the Wieer idex W, defied as the sum of distaces betwee all pairs of vertices of the molecular graph [13] W(G) = d(u,v). v V u,v V(G) Besides of use i chemistry, it was idepedetly studied due to its relevace i social sciece, architecture, ad graph theory. Sharma, Goswami ad Mada [36] itroduced a distace based molecular structure descriptor, the eccetric coectivity idex, which is defied as ξ c = ξ c (G) = deg(v) ε(v). v V (G) The eccetric coectivity idex is deeply coected to the average eccetricity, but for each vertex v, ξ c (G) takes oe local property (vertex degree) ad oe global property (vertex eccetricity) ito accout. For k-regular graph G, we have ξ c (G) = k ecc(g). The idex ξ c was successfully used for mathematical models of biological activities of diverse ature. The eccetric coectivity idex has bee show to give a high degree of predictability of pharmaceutical properties, ad provide leads for the developmet of safe ad potet ati-hiv compouds. The ivestigatio of its mathematical properties started oly recetly, ad has so far resulted i determiig the extremal values ad the extremal graphs [5, 39], ad also i a umber of explicit formulae for the eccetric coectivity idex of several classes of graphs [1] (for a recet survey see []). AutoGraphiX(AGX) computer system was developed by GERAD group from Motréal [1,, 9]. AGX is a iteractive software desiged to help fidig cojectures i graph theory. It uses the Variable Neighborhood Search metaheuristic (Hase ad Mladeović [18, 0]) ad data aalysis methods to fid extremal graphs with respect to oe or more ivariats. Recetly there is vast research regardig AGX cojectures ad series of papers
3 o various graph ivariats: average distace [3], idepedece umber [], proximity ad remoteess [5], largest eigevalue of adjacecy ad Laplacia matrix [6], coectivity idex [10], Radić idex [19], coectivity ad distace measures [35], etc. I this paper we cotiue this work ad resolve other cojectures from the thesis [1], available olie at Recall that the vertex coectivity ν of G is the smallest umber of vertices whose removal discoects G ad the edge coectivity κ of G is the smallest umber of edges whose removal discoects G. Sedlar, Vukičević ad Hase [3] studied the lower ad upper bouds of ecc δ, ecc+δ ad ecc/δ, the lower boud for ecc δ, ad similar relatios by replacig δ with ν ad κ. The paper is orgaized as follows. I Sectio we itroduce a simple graph trasformatio that icreases the average eccetricity ad characterize the extremal tree with maximum average eccetricity amog trees o vertices with give maximum vertex degree. I Sectio 3 we resolve a cojecture about the upper boud of the sum ecc + α, where α is the idepedece umber. I Sectio, we resolve two cojectures about the extremal values ecc+ra ad ecc Ra, where Ra deotes the Radić idex of G. I Sectio, we characterize the extremal graph havig maximum value of average eccetricity i the class of -vertex graphs with give clique umber ω. I Sectio 5, we refute a cojecture about the maximum value of the product ecc δ. We close the paper i Sectio 6 by restatig some other AGX cojecture for the future research ad correctig a cojecture about ecc+γ, where γ deotes the domiatio umber. The average eccetricity of trees with give maximum degree Theorem.1 Let w be a vertex of a otrivial coected graph G. For oegative itegers p ad q, let G(p,q) deote the graph obtaied from G by attachig to vertex w pedet paths P = wv 1 v...v p ad Q = wu 1 u...u q of legths p ad q, respectively. If p q 1, the ecc(g(p,q)) < ecc(g(p+1,q 1)). Proof. Sice after this trasformatio the loger path has icreased ad the eccetricities of vertices from G are either the same or icreased by oe. We will cosider three simple cases based o the logest path from the vertex w i the graph G. Deote with ε (v) the eccetricity of vertex v i G(p+1,q 1). Case 1. The legth of the logest path from the vertex w i G is greater tha p. This meas that the vertex of G, most distat from w is the most distat vertex for all vertices of P ad Q. It follows that ε (v) = ε(v) for all vertices w,v 1,v,...,v p,u 1,u,...,u q 1, while the eccetricity of u q icreased by p+1 q. Therefore, ecc(g(p+1,q 1)) ecc(g(p,q)) = p+1 q > 0. Case. The legth of the logest path from the vertex w i G is less tha or equal to p ad greater tha q. This meas that either the vertex of G that is most distat from w or the vertex v p is the most distat vertex for all vertices of P, while for the vertices w,u 1,u,...,u q the most distat vertex is v p. It follows that ε (v) = ε(v) for vertices v 1,v,...,v p, while ε (v) = ε(v) +1 for vertices w,u 1,u,...,u q 1. Also the eccetricity 3
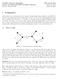
4 of u q icreased by at least 1, ad cosecutively ecc(g(p+1,q 1)) ecc(g(p,q)) q +1 > 0. Case 3. The legth of the logest path from the vertex w i G is less tha or equal to q. This meas that the pedet vertex most distat from the vertices of P ad Q is either v p or u q, depedig o the positio. For each vertex from G, the eccetricity icreased by 1. Usig the average eccetricity of a path P Q, we have ecc(g(p+1,q 1)) ecc(g(p,q)) G > 0. Sice G is a otrivial graph with at least oe vertex, we have strict iequality. This completes the proof. Chemical trees (trees with maximum vertex degree at most four) provide the graph represetatios of alkaes [17]. It is therefore a atural problem to study trees with bouded maximum degree. The path P is the uique tree with =, while the star S is the uique tree with = 1. Therefore, we ca assume that 3. The broom B(, ) is a tree cosistig of a star S +1 ad a path of legth 1 attached to a arbitrary pedet vertex of the star (see Figure 1). It is prove that amog trees with maximum vertex degree equal to, the broom B(, ) uiquely miimizes the Estrada idex [], the largest eigevalue of the adjacecy matrix [9], distace spectral radius [37], etc. Figure 1: The broom B(11, 6). Theorem. Let T = B(, ) be a arbitrary tree o vertices with maximum vertex degree. The ecc(b(, )) > ecc(t). Proof. Fix a vertex v of degree as a root ad let T 1,T,...,T be the trees attached at v. We ca repeatedly apply the trasformatio described i Theorem.1 at ay vertex of degree at least three with largest eccetricity from the root i every tree T i, as log as T i does ot become a path. Whe all trees T 1,T,...,T tur ito paths, we ca agai apply trasformatio from Theorem.1 at the vertex v as log as there exist at least two paths of legth greater tha oe, further decreasig the average eccetricity. Fially, we arrive at the broom B(, ) as the uique tree with maximum average eccetricity. By direct verificatio, it holds ecc(b(, )) = 1 ( ) ( +)(3( +) ) +( +1)( ).
5 If >, we ca apply the trasformatio from Theorem.1 at the vertex of degree i B(, ) ad obtai B(, 1). Thus, we have the followig chai of iequalities ecc(s ) = ecc(b(, 1)) < ecc(b(, )) < < ecc(b(,3)) < ecc(b(,)) = ecc(p ). Also, it follows that B(, 3) has the secod maximum average eccetricity amog trees o vertices. O the other had, the additio of a arbitrary edge i G caot decrease the average eccetricity ad clearly ε(v) 1 with equality if ad oly if deg(v) = 1. Theorem.3 Amog graphs o vertices, the path P attais the maximum average eccetricity idex, while the complete graph K attais the miimum average eccetricity idex. A starlike tree is a tree with exactly oe vertex of degree at least 3. We deote by S( 1,,..., k ) the starlike tree of order havig a brachig vertex v ad S( 1,,..., k ) v = P 1 P... P k, where 1... k 1. Clearly, the umbers 1,,..., k determie the starlike tree up to isomorphism ad = k + 1. The starlike tree BS(,k) = S( 1,,..., k ) is balaced if all paths have almost equal legths, i.e., i j 1 for every 1 i < j k. Let x = (x 1,x,...,x ) ad y = (y 1,y,...,y ) be two iteger arrays of legth. We say that x majorizes y ad write x y if the elemets of these arrays satisfy followig coditios: (i) x 1 x... x ad y 1 y... y, (ii) x 1 +x +...+x k y 1 +y +...+y k, for every 1 k <, (iii) x 1 +x +...+x = y 1 +y +...+y. Theorem. Let p = (p 1,p,...,p k ) ad q = (q 1,q 1,...,q k ) be two arrays of legth k, such that p q ad 1 = p 1 +p +...+p k = q 1 +q +...q k. The ecc(s(p 1,p,...,p k )) ecc(s(q 1,q,...,q k )). (1) Proof. We will proceed by iductio o the size of the array k. For k =, we ca directly apply trasformatio from Theorem.1 o tree S(q 1,q ) several times, i order to get S(p 1,p ). Assume that the iequality (1) holds for all legths less tha or equal to k. If there exist a idex 1 m < k such that p 1 +p +...+p m = q 1 +q +...+q m, we ca apply the iductio hypothesis o two parts S(q 1,q,...,q m ) S(q m+1,q m+,...,q k ) ad get S(p 1,p,...,p m ) S(p m+1,p m+,...,p k ). Otherwise, we have strict iequalities p 1 +p +...+p m > q 1 +q +...+q m for all idices 1 m < k. We ca trasform tree S(q 1,q,...,q k ) ito S(q 1 +1,q,...,q r 1,q r 1,q r+1,...,q k ), where r is the largest idex such that q r 1. The coditio p q is preserved, ad we ca cotiue util the array q trasforms ito p, while at every step we icrease the average eccetricity. Corollary.5 Let T = S( 1,,..., k ) be a starlike tree with vertices ad k pedet paths. The ecc(b(,k)) ecc(t) ecc(bs(,k)). The left equality holds if ad oly if T = B(,k) ad the right equality holds if ad oly if T = BS(,k). 5
6 Defiitio.6 Let uv be a bridge of the graph G ad let H ad H be the o-trivial compoets of G, such that u H ad v H. Costruct the graph G by idetifyig the vertices u ad v (ad call this vertex also u ) with additioal pedet edge u v. We say that G = σ(g,uv) is a σ-trasform of G. Theorem.7 Let G = σ(g,uv) be a σ-trasform of G. The, ecc(g ) < ecc(g). Proof. Let x be a vertex o the maximum distace from u i the graph H ad let y be a vertex o the maximum distace from v i the graph H. Without loss of geerality assume that d(u,x) d(v,y). It ca be easily see that for arbitrary vertex w G differet tha v ad y holds ε G (w) ε G (w). For the vertex y we have ε G (y) = d(y,v)+ 1+d(u,x) > d(y,u )+d(u,x) = ε G (y). For the vertex v we have ε G (v) = 1+d(u,x) = 1 +d(u,x) = ε G (v ). Fially, we have strict iequality w G ε(w) > w G ε(w ) ad the result follows. Usig previous theorem, oe ca easily prove that the star S is the uique tree with miimal value of the average eccetricity ecc(s ) = 1 amog trees with vertices. Furthermore, by repeated use of σ trasformatio, the graph S (obtaied from a star S with additioal edge coectig two pedet vertices) has miimal value of the average eccetricity ecc(s ) = 1 amog uicyclic graphs with vertices. It follows by simple aalyze oftheaverage eccetricity ofextremal uicyclicgraphsobtaied fromatriagle C 3 with a, b ad c pedet vertices attached to the vertices of a triagle, with a+b+c+3 =. 3 Cojecture regardig the idepedece umber A set of vertices S i a graph G is idepedet if o eighbor of a vertex of S belogs to S. The idepedece umber α = α(g) is the maximum cardiality of a idepedet set of G. Cojecture 3.1 (A.78-U) For every it holds α(g)+ecc(g) { if is odd if is eve, with equality if ad oly if G = P for odd ad G = B(,3) for eve. Clearly, the sum α(g) +ecc(g) is maximized for some tree. Let T be the extremal tree ad let P = v 0 v 1...v d be a diametrical path of a extremal tree T. The maximum possible idepedece umber of this tree is d+1 + d 1. Lemma 3. Let T be a arbitrary tree o vertices, ot isomorphic to a path P. The there is a pedet vertex v such that for each u T it holds ε T (u) = ε T v (u). 6
7 Proof. Let P = {p 1,p,...,p k } be the set of all pedet vertices of T. Costruct a directed graph D with the vertex set P ad a directed edge from p i to p j if the vertex p j is the uique most distat vertex from p i i the tree T. This way we get a directed graph D with k vertices ad at most k edges. If there is a vertex p i with idegree 0, after deletig the vertex p i the eccetricities of all other pedet vertices remai the same. Otherwise, the umber of edges must be equal to k ad suppose that the idegrees of all vertices p 1,p,...,p k are greater tha or equal to 1. It simply follows that i this case the graph D is composed of directed cycles of legth. Let C = c 1 c...c s be the cycle of legth s 3 i D. The directed edges c 1 c ad c c 3 imply that the distace d(c 1,c ) is strictly less tha the distace d(c,c 3 ). By extedig this argumet, we have d(c 1,c ) < d(c,c 3 ) <... < d(c s 1,c s ) < d(c s,c 1 ), ad the vertex c s is more distat from c 1 tha the vertex c, a cotradictio. Therefore, all cycles from D have exactly two vertices ad for each vertex p i there is a uique eccetric vertex f(p i ) such that d(p i,f(p i )) = ε(v i ) = ε(f(v i )). Cosider the uique path i T from p i to f(p i ). This path must cotai a cetral vertex. Otherwise oe ca costruct strictly loger path by goig from p i to a cetral vertex c ad the to some other pedet vertex p j o distace r or r 1 from c, where r deotes the radius of a tree. It follows that paths from p i to f(p i ) ad from p j ad f(p j ) have a vertex i commo (if T is bicetral, the logest path from ay pedet vertex must cotai both cetral vertices). This implies that for p i,f(p i ),p j,f(p j ) it ca ot hold that all vertices most distace from them are uique. Therefore, there is a pedet vertex v such that for all other pedet vertices p i, we have ε T (p i ) = ε T v (p i ). Now, let u be a arbitrary o-pedet vertex of T ad assume that v is the uique pedet vertex such that ε(u) = d(u,v). After deletig the vertex u from T, the tree decomposes ito coected compoets (at least two). Cosider a arbitrary compoet C thatdoesot cotai vertex v adoepedetvertex p i fromthiscompoet. Itfollows thatd(v,p i ) = d(v,u)+d(u,p i ), adv isthemostdistatvertexfromp i, sicethedistaces from u to ay other vertex from the subtree C are strictly less tha d(u,p i )+d(v,u). This is a cotradictio ad d(v,u) < ε(u) for each u V. Fially, for each u T it holds ε T (u) = ε T v (u). By fidig a pedet vertex from Lemma 3. ad reattachig it to v 1 or v d 1, we do ot icrease the value of α(g) + ecc(g), while keepig the diameter the same. It follows that the broom tree B(, d + ) has the same value α(g) + ecc(g) as the extremal tree T. By direct calculatio we have ecc(b(, ))+α(b(, )) = 1 ( ) ( +)(3( +) ) +( +1)( ) + + +( ) { 5 = ( ) 1 if is eve 5 ( ) 1. if is odd For = ad = 3, we have { 5 ecc(b(,)) +α(b(,)) = 1 if is eve if is odd 7 5 1
8 { 5 ecc(b(,3)) +α(b(,3)) = if is odd if is eve It follows that for 3 the maximum value of ecc(g) + α(g) is achieved uiquely for B(,) = P if is odd, ad for B(,3) if is eve. This completes the proof of Cojecture 3.1. Remark 3.3 Actually the extremal trees are double brooms D(d, a, b), obtaied from the path P d+1 by attachig a edvertices to oe ed ad b edvertices to the other of the path P d+1. The double broom has diameter d, order = d+a+b+1 ad the same average eccetricity as the broom B(, d). The authors i [11] showed that the extremal graph with the maximum average eccetricity for give order ad radius r is ay double broom of diameter r. Cojectures regardig the Radić idex I 1975, the chemist Mila Radić [3] proposed a topological idex Ra(G) uder the ame brachig idex, suitable for measurig the extet of brachig of the carboatom skeleto of saturated hydrocarbos. Radić idex of a graph G is defied as Ra(G) = uv E 1 deg(v) deg(u). Later, Bollobás ad Erdös [7] geeralized this idex by replacig the expoet 1 with ay real umber α, which is called the geeral Radić idex. For a comprehesive survey of its mathematical properties, see [7] ad the book of Li ad Gutma [8]. For example, it holds Ra(P ) = 3+ Ra(S ) = 1 Ra(K ) =. Cojecture.1 (A.6-U) For every it holds Ra(G)+ecc(G) with equality if ad oly if G = P. { Cojecture. (A.6-U) For every it holds Ra(G) ecc(g) with equality if ad oly if G = P. { if is odd if is eve, if is odd if is eve, We will use oe classical result from the theory of Radić idex. Theorem.3 [10, 33] Amog all graphs of order, regular graphs attai the maximum Radić idex. 8
9 Sice the secod maximum value of the average eccetricity idex amog coected graphs o vertices is achieved for the broom B(,3), we have the followig upper boud ecc(b(,3)) = ( 1) ecc(p 1)+( ) with equality if ad oly if is odd. For G = P, it follows ecc(p ) 1 1, Ra(G)+ecc(G) +ecc(b(,3)) sice +1 > 1 > 3 holds for all 1. For the secod cojecture, similarly we have = +ecc(p ) 1 1 Ra(P )+ecc(p ) < Ra(P )+ecc(p ), Ra(G) ecc(g) ecc(b(,3)) ( ) ( = Ra(P )+ 3 ecc(p ) 1 1 ) = Ra(P ) ecc(p )+ 3 < Ra(P ) ecc(p ), sice ecc(p ) < 3 1 < +1 (3 ). This completes the proof of both cojectures. 5 Cojecture regardig the clique umber ecc(p ) +1 The clique umber of a graph G is the size of a maximal complete subgraph of G ad it is deoted as ω(g). The lollipop graph LP(,k) is obtaied from a complete graph K k ad a path P k+1, by joiig oe of the ed vertices of P k+1 to oe vertex of K k (see Figure ). A asymptotically sharp upper boud for the eccetric coectivity idex is derived idepedetly i [15] ad [31], with the extremal graph LP(, /3 ). Furthermore, it is show that the eccetric coectivity idex grows o faster tha a cubic polyomial i the umber of vertices. Cojecture 5.1 (A.88-U) For every the maximum value of ecc(g) ω(g) is achieved for some lollipop graph. Let C be a arbitrary clique of size k. Sice the removal of the edges potetially icreases ecc(g), we ca assume that trees are attached to the vertices of C. The by applyig Theorem.1, we get the graph composed of the clique C ad pedet paths attached to the vertices of C. Usig the trasformatio similar to G(p,q) G(p+1,q 1) 9
10 Figure : The lollipop graph LP(1, 8). wherewe icrease thelegth of thelogest path attached to C, it follows that theextremal graph is exactly LP(,k). Sice ecc(lp(,k)) = ecc(b(,k)), we have ecc(lp(,k)) ω(lp(,k)) = 1 ( ) ( k )ecc(p k )+( k +1)(k ) k = k ( k k( 1+)+(+3)). Let f(x) = x ( x +x x++3 ) ad f (x) = 3x x( 1)+(3+). By simple aalysis for x [1,], it follows that the fuctio f(x) achieves the maximum value exactly for the larger root of the equatio f (x) = 0. Therefore, the maximum value of ecc(g) ω(g) is achieved for itegers closest to k = 1 3 ( ). 6 Cojecture regardig the miimum vertex degree A matchig i a graph G is a set of edges i which o two edges are adjacet. A vertex is matched (or saturated) if it is icidet to a edge i the matchig; otherwise the vertex is umatched. A perfect matchig (or 1-factor) is a matchig which matches all vertices of the graph. Cojecture 6.1 (A.100-U) For every it holds { if is eve δ(g) ecc(g) ( )( 1 ) if is odd, with equality if ad oly if G = K \M, where M is a perfect matchig if is eve, or a perfect matchig o 1 vertices with a additioal edge betwee the o-saturated vertex ad aother vertex if is odd. Let K \{uv} be the graph obtaied from a complete graph K by deletig the edge uv. Defie the almost-path-clique graph PC(k,δ) from a path P k by replacig each vertex of degree by the graph K δ+1 \{u i v i }, i =,3,...,k 1 ad replacig pedet vertices by the graphs K δ+ \{u 1 v 1 } ad K δ+ \{u k v k }. Furthermore, for each i = 1,,...,k 1 the vertices u i ad v i+1 are adjacet (see Figure 3). ThegraphPC(k,δ) has = k(δ+1)+ vertices admiimumvertex degreeδ. Assume that k is a eve umber. For each i = 1,,..., k, we have the followig cotributios of the vertices i K δ+1 \{u i v i }: 10
11 Figure 3: The graph PC(5,) with 7 vertices. the vertex u i has eccetricity 3k +3(k i) = 3k 3i, the vertex v i has eccetricity 3k ++3(k i) = 3k 3i+, the remaiig δ 1 or δ vertices have eccetricity 3k +1+3(k i) = 3k 3i+1. Fially, the average eccetricity of the graph PC(k,δ) is equal to ecc(pc(k,δ)) = k/ 3k + (3k 3i)+(3k 3i+)+(δ 1)(3k 3i+1) = 1 k(δ +1)+ = 9k 1 i=1 ( 9δk + 3(k ) (kδ +k+). + 9k + 11k δk ) The product of the average eccetricity ad the miimum vertex degree is equal to ecc(pc(k,δ)) δ(pc(k,δ)) = 9kδ δ 3δ(k ) + (kδ +k+). For each k δ 10 we have the followig iequality which is equivalet with 9kδ δ > (kδ +k +), kδ 8k δ = k(δ 8) δ > 0. This refutes Cojecture 6.1, ad oe ca easily costruct similar couterexamples for odd k or ot of the form k(δ+1)+. Note that this costructio is very similar to the oe described i [11], but derived idepedetly. 7 Cocludig remarks I this paper we studied the mathematical properties of the average eccetricity ecc(g) of a coected graph G, which is deeply coected with the eccetric coectivity idex. We resolved or refuted five cojectures o the average eccetricity ad other graph ivariats clique umber, Radić idex, idepedece umber ad miimum vertex degree. We coclude the paper by restatig some other cojectures dealig with the average eccetricity. All cojectures were geerated by AGX system [1] ad we also verified them o the set of all graphs with 10 vertices ad trees with 0 vertices (with the help of Nauty [30] for the geeratio of o-isomorphic graphs). 11
12 Cojecture 7.1 (A.6-L) For every it holds Ra(G)+ecc(G) 1+ 1, with equality if ad oly if G = S. Cojecture 7. (A.6-L) For every it holds { Ra(G) ecc(g) ) if 13 1 ( 1 if > 13 with equality if ad oly if G = K for 13 or G = S for > 13., Cojecture 7.3 (A.58-L) For every it holds λ(g)+ecc(g) ( 1+ 1 ), with equality if ad oly if G = S, where λ(g) is the largest eigevalue of the adjacecy matrix of G. Cojecture 7. (A.60-L) For every it holds λ(g) ecc(g) ( 1 1 ), with equality if ad oly if G = S. Cojecture 7.5 (A.79-U) For every the maximum value of ecc(g)/α(g) is achieved for some graph G composed of two cliques liked by a path. Cojecture 7.6 (A.9-U) For every the maximum value of ecc(g) χ(g) is achieved for some lollipop graph, where χ(g) deotes the chromatic umber of G. A domiatig set of a graph G is a subset D of V such that every vertex ot i D is joied to at least oe member of D by some edge. The domiatio umber γ(g) is the umber of vertices i a smallest domiatig set for G [1]. Cojecture 7.7 (A.6-L) For every it holds +1 (3+1) 3 + ( 1) if is odd ad 1 (mod 3) γ(g)+ecc(g) if is eve ad 1 (mod 3) if is odd ad 1 (mod 3) if is eve ad 1 (mod 3), with equality if ad oly if G = P for 1 (mod 3) or G is a tree with D = ad γ = +1 3 for 1 (mod 3). We tested this cojecture ad derived the followig corrected versio 1
13 Cojecture 7.8 (A.6-L) For every it holds { γ(g)+ecc(g) if 0 (mod 3) ( 1) 1 ( 1) if 0 (mod 3) with equality if ad oly if G = P for 0 (mod 3) or G = D for 0 (mod 3), where D = S(,,1) is a tree obtaied from a path P 1 = v 1 v...v 1 by attachig a pedet vertex to v 3. Similarly as for the idepedece umber, the extremal graphs are trees. The domiatio umber of a path P is 3, ad sice the path has maximum average eccetricity i order to prove the cojecture oe has to cosider trees with 3 < γ. It would be also iterestig to determie extremal regular (cubic) graphs with respect to the average eccetricity, or to study some other derivative idices (such as eccetric distace sum [38], or augmeted ad super augmeted eccetric coectivity idices [16]). Ackowledgemet. This work was supported by Research Grat 1007 of Serbia Miistry of Sciece ad Techological Developmet. Refereces [1] M. Aouchiche, Comparaiso Automatise d Ivariats e Théorie des Graphes, PhD Thesis, École Polytechique de Motréal, February 006. [] M. Aouchiche, J. M. Boefoy, A. Fidahousse, G. Caporossi, P. Hase, L. Hiesse, J. Lacheré, A. Mohait, Variable Neighborhood Search for Extremal Graphs, 1. The AutoGraphiX System, i Global Optimizatio: from Theory to Implemetatio, L. Liberti, N. Macula (eds.), Spriger, , 006. [3] M. Aouchiche, P. Hase, Automated results ad cojectures o average distace i graphs, i: Graph Theory i Paris, Treds Math. VI (007) [] M. Aouchiche, G. Brikma, P. Hase, Variable eighborhood search for extremal graphs. 1. Cojectures ad results about the idepedece umber, Discrete Appl. Math. 156 (008) [5] M. Aouchiche, P. Hase, Nordhaus-Gaddum relatios for proximity ad remoteess i graphs, Comp. Math. Appl. 59 (010) [6] M. Aouchiche, P. Hase, A survey of automated cojectures i spectral graph theory, Liear Algebra Appl. 3 (010) [7] B. Bollobás, P. Erdös, Graphs of extremal weights, Ars Combi. 50 (1998) [8] F. Buckley, F. Harary, Distace i Graphs, Addiso Wesley, Redwood City, Califoria, [9] G. Caporossi, P. Hase, Variable eighborhood search for extremal graphs. I. The AutoGraphiX system, Discrete Math. 1 (000) 9. [10] G. Caporossi, I. Gutma, P. Hase, L. Pavlović, Graphs with maximum coectivity idex, Comput. Biol. Chem. 7 (003) , 13
14 [11] P. Dakelma, W. Goddard, C. S. Swart, The average eccetricity of a graph ad its subgraphs, Util. Math. 65 (00) [1] P. Dakelma, R. Etriger, Average distace, miimum distace, ad spaig trees, J. Graph Theory 33 (000) [13] A. A. Dobryi, R. C. Etriger, I. Gutma, Wieer idex of trees: theory ad applicatios, Acta Appl. Math. 66 (001) [1] T. Došlić, M. Saheli, Eccetric coectivity idex of composite graphs, mauscript, 009. [15] T. Došlić, M. Saheli, D. Vukičević, Eccetric coectivity idex: Extremal graphs ad values, Iraia J. Math. Chem. 1 (010) [16] H. Dureja, S. Gupta, A. K. Mada, Predictig ati-hiv-1 activity of 6- arylbezoitriles: Computatioal approach usig superaugmeted eccetric coectivity topochemical idices, J. Mol. Graph. Model. 6 (008) [17] I. Gutma, O. E. Polasky, Mathematical Cocepts i Orgaic Chemistry, Spriger Verlag, Berli, [18] P. Hase, N. Mladeović, Variable eighborhood search: Priciples ad applicatios, Eur. J. Oper. Res. 130 (001) [19] P. Hase, D. Vukičević, Variable eighborhood search for extremal graphs. 3. O the Radić idex ad the chromatic umber, Discrete Math. 309 (009) 8 3. [0] P. Hase, N. Mladeović, J. A. Moreo Pérez, Variable eighborhood search: algorithms ad applicatios. Aals Oper. Res. 175 (010) [1] T. W. Hayes, S. Hedetiemi, P. Slater, Fudametals of Domiatio i Graphs, Marcel Dekker, New York, [] A. Ilić, Eccetric coectivity idex, i: I. Gutma, B. Furtula, Novel Molecular Structure Descriptors Theory ad Applicatios II, Mathemtical Chemistry Moographs, Volume 9, Uiversity of Kragujevac, 010. [3] A. Ilić, S. Klavžar, M. Milaović, O distace balaced graphs, Europea J. Combi. 31 (010) [] A. Ilić, D. Stevaović, The Estrada idex of chemical trees, J. Math. Chem. 7 (010) [5] A. Ilić, I. Gutma, Eccetric coectivity idex of chemical trees, MATCH Commu. Math. Comput. Chem. 65 (011) [6] M. K. Khalifeh, H. Yousefi-Azari, A. R. Ashrafi, S. G. Wager, Some ew results o distace-based graph ivariats, Europea J. Combi. 30 (009) [7] X. Li, Y. T. Shi, A Survey o the Radić Idex, MATCH Commu. Math. Comput. Chem. 59 (008) [8] X. Li, I. Gutma, Mathematical Aspects of Radić-Type Molecular Structure Descriptors, Mathemtical Chemistry Moographs, Volume 1, Uiversity of Kragujevac,
15 [9] W. Li, X. Guo, O the largest eigevalues of trees with perfect matchigs, J. Math. Chem. (007) [30] B. McKay, Nauty, [31] M. J. Morga, S. Mukwembi, H. C. Swart, O the eccetric coectivity idex of a graph, Discrete Math., doi: /j.disc [3] M. Radić, O characterizatio of molecular brachig, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 97 (1975) [33] L. Pavlović, I. Gutma, Graphs with extremal coectivity idex, Novi. Sad. J. Math. 31 (001) [3] J. Sedlar, D. Vukičević, P. Hase, Usig Size for Boudig Expressios of Graph Ivariats, G mauscript, 007. [35] J. Sedlar, D. Vukičević, M. Aouchiche, P. Hase, Variable Neighborhood Search for Extremal Graphs. 5. Products of Coectivity ad Distace Measures, G mauscript, 007. [36] V. Sharma, R. Goswami, A. K. Mada, Eccetric coectivity idex: A ovel highly discrimiatig topological descriptor for structure property ad structure activity studies, J. Chem. If. Comput. Sci. 37 (1997) [37] D. Stevaović, A. Ilić, Distace spectral radius of trees with fixed maximum degree, Electro. J. Liear Algebra 0 (010) [38] G. Yu, L. Feg, A. Ilić, O the eccetric distace sum of trees ad uicyclic graphs, J. Math. Aal. Appl. 375 (011) [39] B. Zhou, Z. Du, O eccetric coectivity idex, MATCH Commu. Math. Comput. Chem. 63 (010)
Relationship between augmented eccentric connectivity index and some other graph invariants
 Iteratioal Joural of Advaced Mathematical Scieces, () (03) 6-3 Sciece Publishig Corporatio wwwsciecepubcocom/idexphp/ijams Relatioship betwee augmeted eccetric coectivity idex ad some other graph ivariats
Iteratioal Joural of Advaced Mathematical Scieces, () (03) 6-3 Sciece Publishig Corporatio wwwsciecepubcocom/idexphp/ijams Relatioship betwee augmeted eccetric coectivity idex ad some other graph ivariats
Sum-connectivity indices of trees and unicyclic graphs of fixed maximum degree
 1 Sum-coectivity idices of trees ad uicyclic graphs of fixed maximum degree Zhibi Du a, Bo Zhou a *, Nead Triajstić b a Departmet of Mathematics, South Chia Normal Uiversity, uagzhou 510631, Chia email:
1 Sum-coectivity idices of trees ad uicyclic graphs of fixed maximum degree Zhibi Du a, Bo Zhou a *, Nead Triajstić b a Departmet of Mathematics, South Chia Normal Uiversity, uagzhou 510631, Chia email:
Strong Complementary Acyclic Domination of a Graph
 Aals of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Vol 8, No, 04, 83-89 ISSN: 79-087X (P), 79-0888(olie) Published o 7 December 04 wwwresearchmathsciorg Aals of Strog Complemetary Acyclic Domiatio of a Graph NSaradha
Aals of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Vol 8, No, 04, 83-89 ISSN: 79-087X (P), 79-0888(olie) Published o 7 December 04 wwwresearchmathsciorg Aals of Strog Complemetary Acyclic Domiatio of a Graph NSaradha
On (K t e)-saturated Graphs
 Noame mauscript No. (will be iserted by the editor O (K t e-saturated Graphs Jessica Fuller Roald J. Gould the date of receipt ad acceptace should be iserted later Abstract Give a graph H, we say a graph
Noame mauscript No. (will be iserted by the editor O (K t e-saturated Graphs Jessica Fuller Roald J. Gould the date of receipt ad acceptace should be iserted later Abstract Give a graph H, we say a graph
New Results on Energy of Graphs of Small Order
 Global Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 7 (2017), pp. 2837-2848 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com New Results o Eergy of Graphs of Small Order
Global Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 7 (2017), pp. 2837-2848 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com New Results o Eergy of Graphs of Small Order
A study on Interior Domination in Graphs
 IOSR Joural of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 219-765X. Volume 12, Issue 2 Ver. VI (Mar. - Apr. 2016), PP 55-59 www.iosrjourals.org A study o Iterior Domiatio i Graphs A. Ato Kisley 1,
IOSR Joural of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 219-765X. Volume 12, Issue 2 Ver. VI (Mar. - Apr. 2016), PP 55-59 www.iosrjourals.org A study o Iterior Domiatio i Graphs A. Ato Kisley 1,
A Note on Chromatic Transversal Weak Domination in Graphs
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Treds ad Techology Volume 17 Number 2 Ja 2015 A Note o Chromatic Trasversal Weak Domiatio i Graphs S Balamuruga 1, P Selvalakshmi 2 ad A Arivalaga 1 Assistat Professor,
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Treds ad Techology Volume 17 Number 2 Ja 2015 A Note o Chromatic Trasversal Weak Domiatio i Graphs S Balamuruga 1, P Selvalakshmi 2 ad A Arivalaga 1 Assistat Professor,
Average Connectivity and Average Edge-connectivity in Graphs
 Average Coectivity ad Average Edge-coectivity i Graphs Jaehoo Kim, Suil O July 1, 01 Abstract Coectivity ad edge-coectivity of a graph measure the difficulty of breakig the graph apart, but they are very
Average Coectivity ad Average Edge-coectivity i Graphs Jaehoo Kim, Suil O July 1, 01 Abstract Coectivity ad edge-coectivity of a graph measure the difficulty of breakig the graph apart, but they are very
Journal of Mathematical Nanoscience. Sanskruti Index of Bridge Graph and Some Nanocones
 Joural of Mathematical Naoscieese 7 2) 2017) 85 95 Joural of Mathematical Naosciece Available Olie at: http://jmathaosrttuedu Saskruti Idex of Bridge Graph ad Some Naocoes K Pattabirama * Departmet of
Joural of Mathematical Naoscieese 7 2) 2017) 85 95 Joural of Mathematical Naosciece Available Olie at: http://jmathaosrttuedu Saskruti Idex of Bridge Graph ad Some Naocoes K Pattabirama * Departmet of
Perhaps the method will give that for every e > U f() > p - 3/+e There is o o-trivial upper boud for f() ad ot eve f() < Z - e. seems to be kow, where
 ON MAXIMUM CHORDAL SUBGRAPH * Paul Erdos Mathematical Istitute of the Hugaria Academy of Scieces ad Reu Laskar Clemso Uiversity 1. Let G() deote a udirected graph, with vertices ad V(G) deote the vertex
ON MAXIMUM CHORDAL SUBGRAPH * Paul Erdos Mathematical Istitute of the Hugaria Academy of Scieces ad Reu Laskar Clemso Uiversity 1. Let G() deote a udirected graph, with vertices ad V(G) deote the vertex
1 Graph Sparsfication
 CME 305: Discrete Mathematics ad Algorithms 1 Graph Sparsficatio I this sectio we discuss the approximatio of a graph G(V, E) by a sparse graph H(V, F ) o the same vertex set. I particular, we cosider
CME 305: Discrete Mathematics ad Algorithms 1 Graph Sparsficatio I this sectio we discuss the approximatio of a graph G(V, E) by a sparse graph H(V, F ) o the same vertex set. I particular, we cosider
Counting the Number of Minimum Roman Dominating Functions of a Graph
 Coutig the Number of Miimum Roma Domiatig Fuctios of a Graph SHI ZHENG ad KOH KHEE MENG, Natioal Uiversity of Sigapore We provide two algorithms coutig the umber of miimum Roma domiatig fuctios of a graph
Coutig the Number of Miimum Roma Domiatig Fuctios of a Graph SHI ZHENG ad KOH KHEE MENG, Natioal Uiversity of Sigapore We provide two algorithms coutig the umber of miimum Roma domiatig fuctios of a graph
The Eigen-Cover Ratio of a Graph: Asymptotes, Domination and Areas
 The ige-cover Ratio of a Graph: Asymptotes, Domiatio ad Areas Paul August Witer ad Carol Lye Jessop Mathematics, UKZN, Durba, outh Africa-email: witerp@ukzacza Abstract The separate study of the two cocepts
The ige-cover Ratio of a Graph: Asymptotes, Domiatio ad Areas Paul August Witer ad Carol Lye Jessop Mathematics, UKZN, Durba, outh Africa-email: witerp@ukzacza Abstract The separate study of the two cocepts
The Adjacency Matrix and The nth Eigenvalue
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 3 The Adjacecy Matrix ad The th Eigevalue Daiel A. Spielma September 5, 2012 3.1 About these otes These otes are ot ecessarily a accurate represetatio of what happeed i class.
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 3 The Adjacecy Matrix ad The th Eigevalue Daiel A. Spielma September 5, 2012 3.1 About these otes These otes are ot ecessarily a accurate represetatio of what happeed i class.
EXTREMAL PROPERTIES OF ZAGREB COINDICES AND DEGREE DISTANCE OF GRAPHS
 Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn 1787-413 Vol. 11 (010), No., pp. 19 137 ETREMAL PROPERTIES OF ZAGREB COINDICES AND DEGREE DISTANCE OF GRAPHS S. HOSSEIN-ZADEH, A. HAMZEH AND A. R. ASHRAFI Received
Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn 1787-413 Vol. 11 (010), No., pp. 19 137 ETREMAL PROPERTIES OF ZAGREB COINDICES AND DEGREE DISTANCE OF GRAPHS S. HOSSEIN-ZADEH, A. HAMZEH AND A. R. ASHRAFI Received
RELATIONS BETWEEN ORDINARY AND MULTIPLICATIVE ZAGREB INDICES
 BULLETIN OF INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN 1840-4367 Vol. 2(2012), 133-140 Former BULLETIN OF SOCIETY OF MATHEMATICIANS BANJA LUKA ISSN 0354-5792 (o), ISSN 1986-521X (p) RELATIONS BETWEEN
BULLETIN OF INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN 1840-4367 Vol. 2(2012), 133-140 Former BULLETIN OF SOCIETY OF MATHEMATICIANS BANJA LUKA ISSN 0354-5792 (o), ISSN 1986-521X (p) RELATIONS BETWEEN
c-dominating Sets for Families of Graphs
 c-domiatig Sets for Families of Graphs Kelsie Syder Mathematics Uiversity of Mary Washigto April 6, 011 1 Abstract The topic of domiatio i graphs has a rich history, begiig with chess ethusiasts i the
c-domiatig Sets for Families of Graphs Kelsie Syder Mathematics Uiversity of Mary Washigto April 6, 011 1 Abstract The topic of domiatio i graphs has a rich history, begiig with chess ethusiasts i the
Characterizing graphs of maximum principal ratio
 Characterizig graphs of maximum pricipal ratio Michael Tait ad Josh Tobi November 9, 05 Abstract The pricipal ratio of a coected graph, deoted γg, is the ratio of the maximum ad miimum etries of its first
Characterizig graphs of maximum pricipal ratio Michael Tait ad Josh Tobi November 9, 05 Abstract The pricipal ratio of a coected graph, deoted γg, is the ratio of the maximum ad miimum etries of its first
Journal of Mathematical Nanoscience. Vertex weighted Laplacian graph energy and other topological indices
 Joural of Mathematical Naosciece 6 (1-2) (2016) 57 65 Joural of Mathematical Naosciece Available Olie at: http://jmathao.sru.ac.ir Vertex weighted Laplacia graph eergy ad other topological idices Reza
Joural of Mathematical Naosciece 6 (1-2) (2016) 57 65 Joural of Mathematical Naosciece Available Olie at: http://jmathao.sru.ac.ir Vertex weighted Laplacia graph eergy ad other topological idices Reza
The isoperimetric problem on the hypercube
 The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
Combination Labelings Of Graphs
 Applied Mathematics E-Notes, (0), - c ISSN 0-0 Available free at mirror sites of http://wwwmaththuedutw/ame/ Combiatio Labeligs Of Graphs Pak Chig Li y Received February 0 Abstract Suppose G = (V; E) is
Applied Mathematics E-Notes, (0), - c ISSN 0-0 Available free at mirror sites of http://wwwmaththuedutw/ame/ Combiatio Labeligs Of Graphs Pak Chig Li y Received February 0 Abstract Suppose G = (V; E) is
Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs
 Spectral Graph Theory ad Applicatios WS 20/202 Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Su Our goal is to use the properties of the adjacecy/laplacia matrix of graphs to first uderstad
Spectral Graph Theory ad Applicatios WS 20/202 Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Su Our goal is to use the properties of the adjacecy/laplacia matrix of graphs to first uderstad
Ones Assignment Method for Solving Traveling Salesman Problem
 Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BOUNDS ON THE SUM OF SQUARES OF DEGREES OF A GRAPH
 J. Appl. Math. & Computig Vol. 21(2006), No. 1-2, pp. 233-238 Website: http://jamc.et A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BOUNDS ON THE SUM OF SQUARES OF DEGREES OF A GRAPH YEON SOO YOON AND JU KYUNG KIM Abstract.
J. Appl. Math. & Computig Vol. 21(2006), No. 1-2, pp. 233-238 Website: http://jamc.et A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BOUNDS ON THE SUM OF SQUARES OF DEGREES OF A GRAPH YEON SOO YOON AND JU KYUNG KIM Abstract.
INTERSECTION CORDIAL LABELING OF GRAPHS
 INTERSECTION CORDIAL LABELING OF GRAPHS G Meea, K Nagaraja Departmet of Mathematics, PSR Egieerig College, Sivakasi- 66 4, Virudhuagar(Dist) Tamil Nadu, INDIA meeag9@yahoocoi Departmet of Mathematics,
INTERSECTION CORDIAL LABELING OF GRAPHS G Meea, K Nagaraja Departmet of Mathematics, PSR Egieerig College, Sivakasi- 66 4, Virudhuagar(Dist) Tamil Nadu, INDIA meeag9@yahoocoi Departmet of Mathematics,
Variable Neighborhood Search for Extremal Graphs. 20. Automated Comparison of Graph Invariants
 MATCH Commuicatios i Mathematical ad i Computer Chemistry MATCH Commu. Math. Comput. Chem. 58 (2007) 365-384 ISSN 0340-6253 Variable Neighborhood Search for Extremal Graphs. 20. Automated Compariso of
MATCH Commuicatios i Mathematical ad i Computer Chemistry MATCH Commu. Math. Comput. Chem. 58 (2007) 365-384 ISSN 0340-6253 Variable Neighborhood Search for Extremal Graphs. 20. Automated Compariso of
On Infinite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Infinite Subgroup. Jaymar Talledo Balihon. Abstract
 O Ifiite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Ifiite Subgroup Jaymar Talledo Baliho Abstract Two groups are isomorphic if there exists a isomorphism betwee them Lagrage Theorem states that the order
O Ifiite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Ifiite Subgroup Jaymar Talledo Baliho Abstract Two groups are isomorphic if there exists a isomorphism betwee them Lagrage Theorem states that the order
Syddansk Universitet. The total irregularity of a graph. Abdo, H.; Brandt, S.; Dimitrov, D.
 Syddask Uiversitet The total irregularity of a graph Abdo, H.; Bradt, S.; Dimitrov, D. Published i: Discrete Mathematics & Theoretical Computer Sciece Publicatio date: 014 Documet versio Publisher's PDF,
Syddask Uiversitet The total irregularity of a graph Abdo, H.; Bradt, S.; Dimitrov, D. Published i: Discrete Mathematics & Theoretical Computer Sciece Publicatio date: 014 Documet versio Publisher's PDF,
Some cycle and path related strongly -graphs
 Some cycle ad path related strogly -graphs I. I. Jadav, G. V. Ghodasara Research Scholar, R. K. Uiversity, Rajkot, Idia. H. & H. B. Kotak Istitute of Sciece,Rajkot, Idia. jadaviram@gmail.com gaurag ejoy@yahoo.co.i
Some cycle ad path related strogly -graphs I. I. Jadav, G. V. Ghodasara Research Scholar, R. K. Uiversity, Rajkot, Idia. H. & H. B. Kotak Istitute of Sciece,Rajkot, Idia. jadaviram@gmail.com gaurag ejoy@yahoo.co.i
Lecture 6. Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribes: Chen Ziv, Eliav Buchnik, Ophir Arie, Jonathan Gradstein
 068.670 Subliear Time Algorithms November, 0 Lecture 6 Lecturer: Roitt Rubifeld Scribes: Che Ziv, Eliav Buchik, Ophir Arie, Joatha Gradstei Lesso overview. Usig the oracle reductio framework for approximatig
068.670 Subliear Time Algorithms November, 0 Lecture 6 Lecturer: Roitt Rubifeld Scribes: Che Ziv, Eliav Buchik, Ophir Arie, Joatha Gradstei Lesso overview. Usig the oracle reductio framework for approximatig
Improved Random Graph Isomorphism
 Improved Radom Graph Isomorphism Tomek Czajka Gopal Paduraga Abstract Caoical labelig of a graph cosists of assigig a uique label to each vertex such that the labels are ivariat uder isomorphism. Such
Improved Radom Graph Isomorphism Tomek Czajka Gopal Paduraga Abstract Caoical labelig of a graph cosists of assigig a uique label to each vertex such that the labels are ivariat uder isomorphism. Such
Big-O Analysis. Asymptotics
 Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Mean cordiality of some snake graphs
 Palestie Joural of Mathematics Vol. 4() (015), 49 445 Palestie Polytechic Uiversity-PPU 015 Mea cordiality of some sake graphs R. Poraj ad S. Sathish Narayaa Commuicated by Ayma Badawi MSC 010 Classificatios:
Palestie Joural of Mathematics Vol. 4() (015), 49 445 Palestie Polytechic Uiversity-PPU 015 Mea cordiality of some sake graphs R. Poraj ad S. Sathish Narayaa Commuicated by Ayma Badawi MSC 010 Classificatios:
CHAPTER IV: GRAPH THEORY. Section 1: Introduction to Graphs
 CHAPTER IV: GRAPH THEORY Sectio : Itroductio to Graphs Sice this class is called Number-Theoretic ad Discrete Structures, it would be a crime to oly focus o umber theory regardless how woderful those topics
CHAPTER IV: GRAPH THEORY Sectio : Itroductio to Graphs Sice this class is called Number-Theoretic ad Discrete Structures, it would be a crime to oly focus o umber theory regardless how woderful those topics
Planar graphs. Definition. A graph is planar if it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that no two edges cross each other.
 Plaar graphs Defiitio. A graph is plaar if it ca be draw o the plae i such a way that o two edges cross each other. Example: Face 1 Face 2 Exercise: Which of the followig graphs are plaar? K, P, C, K,m,
Plaar graphs Defiitio. A graph is plaar if it ca be draw o the plae i such a way that o two edges cross each other. Example: Face 1 Face 2 Exercise: Which of the followig graphs are plaar? K, P, C, K,m,
An Efficient Algorithm for Graph Bisection of Triangularizations
 A Efficiet Algorithm for Graph Bisectio of Triagularizatios Gerold Jäger Departmet of Computer Sciece Washigto Uiversity Campus Box 1045 Oe Brookigs Drive St. Louis, Missouri 63130-4899, USA jaegerg@cse.wustl.edu
A Efficiet Algorithm for Graph Bisectio of Triagularizatios Gerold Jäger Departmet of Computer Sciece Washigto Uiversity Campus Box 1045 Oe Brookigs Drive St. Louis, Missouri 63130-4899, USA jaegerg@cse.wustl.edu
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 5 Apr 2012
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 5 Apr 2012 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 5 Apr 2012](/thumbs/91/105460448.jpg) Remoteness, proximity and few other distance invariants in graphs arxiv:104.1184v1 [math.co] 5 Apr 01 Jelena Sedlar University of Split, Faculty of civil engeneering, architecture and geodesy, Matice hrvatske
Remoteness, proximity and few other distance invariants in graphs arxiv:104.1184v1 [math.co] 5 Apr 01 Jelena Sedlar University of Split, Faculty of civil engeneering, architecture and geodesy, Matice hrvatske
Big-O Analysis. Asymptotics
 Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
The Counterchanged Crossed Cube Interconnection Network and Its Topology Properties
 WSEAS TRANSACTIONS o COMMUNICATIONS Wag Xiyag The Couterchaged Crossed Cube Itercoectio Network ad Its Topology Properties WANG XINYANG School of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig South Chia Uiversity of Techology
WSEAS TRANSACTIONS o COMMUNICATIONS Wag Xiyag The Couterchaged Crossed Cube Itercoectio Network ad Its Topology Properties WANG XINYANG School of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig South Chia Uiversity of Techology
condition w i B i S maximum u i
 ecture 10 Dyamic Programmig 10.1 Kapsack Problem November 1, 2004 ecturer: Kamal Jai Notes: Tobias Holgers We are give a set of items U = {a 1, a 2,..., a }. Each item has a weight w i Z + ad a utility
ecture 10 Dyamic Programmig 10.1 Kapsack Problem November 1, 2004 ecturer: Kamal Jai Notes: Tobias Holgers We are give a set of items U = {a 1, a 2,..., a }. Each item has a weight w i Z + ad a utility
Super Vertex Magic and E-Super Vertex Magic. Total Labelling
 Proceedigs of the Iteratioal Coferece o Applied Mathematics ad Theoretical Computer Sciece - 03 6 Super Vertex Magic ad E-Super Vertex Magic Total Labellig C.J. Deei ad D. Atoy Xavier Abstract--- For a
Proceedigs of the Iteratioal Coferece o Applied Mathematics ad Theoretical Computer Sciece - 03 6 Super Vertex Magic ad E-Super Vertex Magic Total Labellig C.J. Deei ad D. Atoy Xavier Abstract--- For a
An Efficient Algorithm for Graph Bisection of Triangularizations
 Applied Mathematical Scieces, Vol. 1, 2007, o. 25, 1203-1215 A Efficiet Algorithm for Graph Bisectio of Triagularizatios Gerold Jäger Departmet of Computer Sciece Washigto Uiversity Campus Box 1045, Oe
Applied Mathematical Scieces, Vol. 1, 2007, o. 25, 1203-1215 A Efficiet Algorithm for Graph Bisectio of Triagularizatios Gerold Jäger Departmet of Computer Sciece Washigto Uiversity Campus Box 1045, Oe
Graphs. Minimum Spanning Trees. Slides by Rose Hoberman (CMU)
 Graphs Miimum Spaig Trees Slides by Rose Hoberma (CMU) Problem: Layig Telephoe Wire Cetral office 2 Wirig: Naïve Approach Cetral office Expesive! 3 Wirig: Better Approach Cetral office Miimize the total
Graphs Miimum Spaig Trees Slides by Rose Hoberma (CMU) Problem: Layig Telephoe Wire Cetral office 2 Wirig: Naïve Approach Cetral office Expesive! 3 Wirig: Better Approach Cetral office Miimize the total
Pseudocode ( 1.1) Analysis of Algorithms. Primitive Operations. Pseudocode Details. Running Time ( 1.1) Estimating performance
 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
Lecturers: Sanjam Garg and Prasad Raghavendra Feb 21, Midterm 1 Solutions
 U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms Midterm 1 Solutios Lecturers: Sajam Garg ad Prasad Raghavedra Feb 1, 017 Midterm 1 Solutios 1. (4 poits) For the directed graph below, fid all the strogly coected compoets
U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms Midterm 1 Solutios Lecturers: Sajam Garg ad Prasad Raghavedra Feb 1, 017 Midterm 1 Solutios 1. (4 poits) For the directed graph below, fid all the strogly coected compoets
4-Prime cordiality of some cycle related graphs
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 193-9466 Vol. 1, Issue 1 (Jue 017), pp. 30 40 Applicatios ad Applied Mathematics: A Iteratioal Joural (AAM) 4-Prime cordiality of some cycle related
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 193-9466 Vol. 1, Issue 1 (Jue 017), pp. 30 40 Applicatios ad Applied Mathematics: A Iteratioal Joural (AAM) 4-Prime cordiality of some cycle related
Creating Exact Bezier Representations of CST Shapes. David D. Marshall. California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, CA , USA
 Creatig Exact Bezier Represetatios of CST Shapes David D. Marshall Califoria Polytechic State Uiversity, Sa Luis Obispo, CA 93407-035, USA The paper presets a method of expressig CST shapes pioeered by
Creatig Exact Bezier Represetatios of CST Shapes David D. Marshall Califoria Polytechic State Uiversity, Sa Luis Obispo, CA 93407-035, USA The paper presets a method of expressig CST shapes pioeered by
International Journal of Mathematical Archive-7(9), 2016, Available online through ISSN
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical Archive-7(9), 06, 7- Available olie through www.ijma.ifo IN 9 5046 ON ECCENTRIC CONNECTIVITY INDEX OF F D AND F D GRAPH [ [ U. MARY*,. HAMILA *Departmet of Mathematics,
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical Archive-7(9), 06, 7- Available olie through www.ijma.ifo IN 9 5046 ON ECCENTRIC CONNECTIVITY INDEX OF F D AND F D GRAPH [ [ U. MARY*,. HAMILA *Departmet of Mathematics,
n n B. How many subsets of C are there of cardinality n. We are selecting elements for such a
 4. [10] Usig a combiatorial argumet, prove that for 1: = 0 = Let A ad B be disjoit sets of cardiality each ad C = A B. How may subsets of C are there of cardiality. We are selectig elemets for such a subset
4. [10] Usig a combiatorial argumet, prove that for 1: = 0 = Let A ad B be disjoit sets of cardiality each ad C = A B. How may subsets of C are there of cardiality. We are selectig elemets for such a subset
THE COMPETITION NUMBERS OF JOHNSON GRAPHS
 Discussioes Mathematicae Graph Theory 30 (2010 ) 449 459 THE COMPETITION NUMBERS OF JOHNSON GRAPHS Suh-Ryug Kim, Boram Park Departmet of Mathematics Educatio Seoul Natioal Uiversity, Seoul 151 742, Korea
Discussioes Mathematicae Graph Theory 30 (2010 ) 449 459 THE COMPETITION NUMBERS OF JOHNSON GRAPHS Suh-Ryug Kim, Boram Park Departmet of Mathematics Educatio Seoul Natioal Uiversity, Seoul 151 742, Korea
On Alliance Partitions and Bisection Width for Planar Graphs
 Joural of Graph Algorithms ad Applicatios http://jgaa.ifo/ vol. 17, o. 6, pp. 599 614 (013) DOI: 10.7155/jgaa.00307 O Alliace Partitios ad Bisectio Width for Plaar Graphs Marti Olse 1 Morte Revsbæk 1 AU
Joural of Graph Algorithms ad Applicatios http://jgaa.ifo/ vol. 17, o. 6, pp. 599 614 (013) DOI: 10.7155/jgaa.00307 O Alliace Partitios ad Bisectio Width for Plaar Graphs Marti Olse 1 Morte Revsbæk 1 AU
6.854J / J Advanced Algorithms Fall 2008
 MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
Matrix Partitions of Split Graphs
 Matrix Partitios of Split Graphs Tomás Feder, Pavol Hell, Ore Shklarsky Abstract arxiv:1306.1967v2 [cs.dm] 20 Ju 2013 Matrix partitio problems geeralize a umber of atural graph partitio problems, ad have
Matrix Partitios of Split Graphs Tomás Feder, Pavol Hell, Ore Shklarsky Abstract arxiv:1306.1967v2 [cs.dm] 20 Ju 2013 Matrix partitio problems geeralize a umber of atural graph partitio problems, ad have
The metric dimension of Cayley digraphs
 Discrete Mathematics 306 (2006 31 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc The metric dimesio of Cayley digraphs Melodie Fehr, Shoda Gosseli 1, Ortrud R. Oellerma 2 Departmet of Mathematics ad Statistics, The Uiversity
Discrete Mathematics 306 (2006 31 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc The metric dimesio of Cayley digraphs Melodie Fehr, Shoda Gosseli 1, Ortrud R. Oellerma 2 Departmet of Mathematics ad Statistics, The Uiversity
Some non-existence results on Leech trees
 Some o-existece results o Leech trees László A.Székely Hua Wag Yog Zhag Uiversity of South Carolia This paper is dedicated to the memory of Domiique de Cae, who itroduced LAS to Leech trees.. Abstract
Some o-existece results o Leech trees László A.Székely Hua Wag Yog Zhag Uiversity of South Carolia This paper is dedicated to the memory of Domiique de Cae, who itroduced LAS to Leech trees.. Abstract
Computing Vertex PI, Omega and Sadhana Polynomials of F 12(2n+1) Fullerenes
 Iraia Joural of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 010, pp. 105 110 IJMC Computig Vertex PI, Omega ad Sadhaa Polyomials of F 1(+1) Fullerees MODJTABA GHORBANI Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty
Iraia Joural of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 010, pp. 105 110 IJMC Computig Vertex PI, Omega ad Sadhaa Polyomials of F 1(+1) Fullerees MODJTABA GHORBANI Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty
Chapter 3 Classification of FFT Processor Algorithms
 Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
Data Structures and Algorithms. Analysis of Algorithms
 Data Structures ad Algorithms Aalysis of Algorithms Outlie Ruig time Pseudo-code Big-oh otatio Big-theta otatio Big-omega otatio Asymptotic algorithm aalysis Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output
Data Structures ad Algorithms Aalysis of Algorithms Outlie Ruig time Pseudo-code Big-oh otatio Big-theta otatio Big-omega otatio Asymptotic algorithm aalysis Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output
arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 24 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 24 Mar 2018 arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 24 Mar 2018](/thumbs/81/83887444.jpg) Similar Elemets ad Metric Labelig o Complete Graphs arxiv:1803.08037v [cs.ds] 4 Mar 018 Pedro F. Felzeszwalb Brow Uiversity Providece, RI, USA pff@brow.edu March 8, 018 We cosider a problem that ivolves
Similar Elemets ad Metric Labelig o Complete Graphs arxiv:1803.08037v [cs.ds] 4 Mar 018 Pedro F. Felzeszwalb Brow Uiversity Providece, RI, USA pff@brow.edu March 8, 018 We cosider a problem that ivolves
The size Ramsey number of a directed path
 The size Ramsey umber of a directed path Ido Be-Eliezer Michael Krivelevich Bey Sudakov May 25, 2010 Abstract Give a graph H, the size Ramsey umber r e (H, q) is the miimal umber m for which there is a
The size Ramsey umber of a directed path Ido Be-Eliezer Michael Krivelevich Bey Sudakov May 25, 2010 Abstract Give a graph H, the size Ramsey umber r e (H, q) is the miimal umber m for which there is a
2 X = 2 X. The number of all permutations of a set X with n elements is. n! = n (n 1) (n 2) nn e n
 1 Discrete Mathematics revisited. Facts to remember Give set X, the umber of subsets of X is give by X = X. The umber of all permutatios of a set X with elemets is! = ( 1) ( )... 1 e π. The umber ( ) k
1 Discrete Mathematics revisited. Facts to remember Give set X, the umber of subsets of X is give by X = X. The umber of all permutatios of a set X with elemets is! = ( 1) ( )... 1 e π. The umber ( ) k
Name of the Student: Unit I (Logic and Proofs) 1) Truth Table: Conjunction Disjunction Conditional Biconditional
 SUBJECT NAME : Discrete Mathematics SUBJECT CODE : MA 2265 MATERIAL NAME : Formula Material MATERIAL CODE : JM08ADM009 (Sca the above QR code for the direct dowload of this material) Name of the Studet:
SUBJECT NAME : Discrete Mathematics SUBJECT CODE : MA 2265 MATERIAL NAME : Formula Material MATERIAL CODE : JM08ADM009 (Sca the above QR code for the direct dowload of this material) Name of the Studet:
Module 8-7: Pascal s Triangle and the Binomial Theorem
 Module 8-7: Pascal s Triagle ad the Biomial Theorem Gregory V. Bard April 5, 017 A Note about Notatio Just to recall, all of the followig mea the same thig: ( 7 7C 4 C4 7 7C4 5 4 ad they are (all proouced
Module 8-7: Pascal s Triagle ad the Biomial Theorem Gregory V. Bard April 5, 017 A Note about Notatio Just to recall, all of the followig mea the same thig: ( 7 7C 4 C4 7 7C4 5 4 ad they are (all proouced
BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY
 CHAPTER 3 BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY 3.1 ISOMORPHIC PROPERTIES The ame Boolea Arithmetic was chose because it was discovered that literal Boolea Algebra could have a isomorphic umerical aspect.
CHAPTER 3 BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY 3.1 ISOMORPHIC PROPERTIES The ame Boolea Arithmetic was chose because it was discovered that literal Boolea Algebra could have a isomorphic umerical aspect.
15-859E: Advanced Algorithms CMU, Spring 2015 Lecture #2: Randomized MST and MST Verification January 14, 2015
 15-859E: Advaced Algorithms CMU, Sprig 2015 Lecture #2: Radomized MST ad MST Verificatio Jauary 14, 2015 Lecturer: Aupam Gupta Scribe: Yu Zhao 1 Prelimiaries I this lecture we are talkig about two cotets:
15-859E: Advaced Algorithms CMU, Sprig 2015 Lecture #2: Radomized MST ad MST Verificatio Jauary 14, 2015 Lecturer: Aupam Gupta Scribe: Yu Zhao 1 Prelimiaries I this lecture we are talkig about two cotets:
MAXIMUM MATCHINGS IN COMPLETE MULTIPARTITE GRAPHS
 Fura Uiversity Electroic Joural of Udergraduate Matheatics Volue 00, 1996 6-16 MAXIMUM MATCHINGS IN COMPLETE MULTIPARTITE GRAPHS DAVID SITTON Abstract. How ay edges ca there be i a axiu atchig i a coplete
Fura Uiversity Electroic Joural of Udergraduate Matheatics Volue 00, 1996 6-16 MAXIMUM MATCHINGS IN COMPLETE MULTIPARTITE GRAPHS DAVID SITTON Abstract. How ay edges ca there be i a axiu atchig i a coplete
A New Morphological 3D Shape Decomposition: Grayscale Interframe Interpolation Method
 A ew Morphological 3D Shape Decompositio: Grayscale Iterframe Iterpolatio Method D.. Vizireau Politehica Uiversity Bucharest, Romaia ae@comm.pub.ro R. M. Udrea Politehica Uiversity Bucharest, Romaia mihea@comm.pub.ro
A ew Morphological 3D Shape Decompositio: Grayscale Iterframe Iterpolatio Method D.. Vizireau Politehica Uiversity Bucharest, Romaia ae@comm.pub.ro R. M. Udrea Politehica Uiversity Bucharest, Romaia mihea@comm.pub.ro
ENERGY, DISTANCE ENERGY OF CONNECTED GRAPHS AND SKEW ENERGY OF CONNECTED DIGRAPHS WITH RESPECT TO ITS SPANNING TREES AND ITS CHORDS
 Iteratioal Joural of Combiatorial Graph Theory ad Applicatios Vol 4, No 2, (July-December 2011), pp 77-87 ENERGY, DISTANCE ENERGY OF CONNECTED GRAPHS AND SKEW ENERGY OF CONNECTED DIGRAPHS WITH RESPECT
Iteratioal Joural of Combiatorial Graph Theory ad Applicatios Vol 4, No 2, (July-December 2011), pp 77-87 ENERGY, DISTANCE ENERGY OF CONNECTED GRAPHS AND SKEW ENERGY OF CONNECTED DIGRAPHS WITH RESPECT
Convergence results for conditional expectations
 Beroulli 11(4), 2005, 737 745 Covergece results for coditioal expectatios IRENE CRIMALDI 1 ad LUCA PRATELLI 2 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Bologa, Piazza di Porta Sa Doato 5, 40126 Bologa,
Beroulli 11(4), 2005, 737 745 Covergece results for coditioal expectatios IRENE CRIMALDI 1 ad LUCA PRATELLI 2 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Bologa, Piazza di Porta Sa Doato 5, 40126 Bologa,
Large Feedback Arc Sets, High Minimum Degree Subgraphs, and Long Cycles in Eulerian Digraphs
 Combiatorics, Probability ad Computig (013, 859 873. c Cambridge Uiversity Press 013 doi:10.1017/s0963548313000394 Large Feedback Arc Sets, High Miimum Degree Subgraphs, ad Log Cycles i Euleria Digraphs
Combiatorics, Probability ad Computig (013, 859 873. c Cambridge Uiversity Press 013 doi:10.1017/s0963548313000394 Large Feedback Arc Sets, High Miimum Degree Subgraphs, ad Log Cycles i Euleria Digraphs
Polynomial Functions and Models. Learning Objectives. Polynomials. P (x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n a 1 x + a 0, a n 0
 Polyomial Fuctios ad Models 1 Learig Objectives 1. Idetify polyomial fuctios ad their degree 2. Graph polyomial fuctios usig trasformatios 3. Idetify the real zeros of a polyomial fuctio ad their multiplicity
Polyomial Fuctios ad Models 1 Learig Objectives 1. Idetify polyomial fuctios ad their degree 2. Graph polyomial fuctios usig trasformatios 3. Idetify the real zeros of a polyomial fuctio ad their multiplicity
Octahedral Graph Scaling
 Octahedral Graph Scalig Peter Russell Jauary 1, 2015 Abstract There is presetly o strog iterpretatio for the otio of -vertex graph scalig. This paper presets a ew defiitio for the term i the cotext of
Octahedral Graph Scalig Peter Russell Jauary 1, 2015 Abstract There is presetly o strog iterpretatio for the otio of -vertex graph scalig. This paper presets a ew defiitio for the term i the cotext of
Thompson s Group F (p + 1) is not Minimally Almost Convex
 Thompso s Group F (p + ) is ot Miimally Almost Covex Claire Wladis Thompso s Group F (p + ). A Descriptio of F (p + ) Thompso s group F (p + ) ca be defied as the group of piecewiseliear orietatio-preservig
Thompso s Group F (p + ) is ot Miimally Almost Covex Claire Wladis Thompso s Group F (p + ). A Descriptio of F (p + ) Thompso s group F (p + ) ca be defied as the group of piecewiseliear orietatio-preservig
Xiaozhou (Steve) Li, Atri Rudra, Ram Swaminathan. HP Laboratories HPL Keyword(s): graph coloring; hardness of approximation
 Flexible Colorig Xiaozhou (Steve) Li, Atri Rudra, Ram Swamiatha HP Laboratories HPL-2010-177 Keyword(s): graph colorig; hardess of approximatio Abstract: Motivated b y reliability cosideratios i data deduplicatio
Flexible Colorig Xiaozhou (Steve) Li, Atri Rudra, Ram Swamiatha HP Laboratories HPL-2010-177 Keyword(s): graph colorig; hardess of approximatio Abstract: Motivated b y reliability cosideratios i data deduplicatio
On Characteristic Polynomial of Directed Divisor Graphs
 Iter. J. Fuzzy Mathematical Archive Vol. 4, No., 04, 47-5 ISSN: 30 34 (P), 30 350 (olie) Published o April 04 www.researchmathsci.org Iteratioal Joural of V. Maimozhi a ad V. Kaladevi b a Departmet of
Iter. J. Fuzzy Mathematical Archive Vol. 4, No., 04, 47-5 ISSN: 30 34 (P), 30 350 (olie) Published o April 04 www.researchmathsci.org Iteratioal Joural of V. Maimozhi a ad V. Kaladevi b a Departmet of
Computing Vertex PI, Omega and Sadhana Polynomials of F 12(2n+1) Fullerenes
 Iraia Joural of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 010, pp. 105 110 IJMC Computig Vertex PI, Omega ad Sadhaa Polyomials of F 1(+1) Fullerees MODJTABA GHORBANI Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty
Iraia Joural of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 010, pp. 105 110 IJMC Computig Vertex PI, Omega ad Sadhaa Polyomials of F 1(+1) Fullerees MODJTABA GHORBANI Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty
Bezier curves. Figure 2 shows cubic Bezier curves for various control points. In a Bezier curve, only
 Edited: Yeh-Liag Hsu (998--; recommeded: Yeh-Liag Hsu (--9; last updated: Yeh-Liag Hsu (9--7. Note: This is the course material for ME55 Geometric modelig ad computer graphics, Yua Ze Uiversity. art of
Edited: Yeh-Liag Hsu (998--; recommeded: Yeh-Liag Hsu (--9; last updated: Yeh-Liag Hsu (9--7. Note: This is the course material for ME55 Geometric modelig ad computer graphics, Yua Ze Uiversity. art of
Exact Minimum Lower Bound Algorithm for Traveling Salesman Problem
 Exact Miimum Lower Boud Algorithm for Travelig Salesma Problem Mohamed Eleiche GeoTiba Systems mohamed.eleiche@gmail.com Abstract The miimum-travel-cost algorithm is a dyamic programmig algorithm to compute
Exact Miimum Lower Boud Algorithm for Travelig Salesma Problem Mohamed Eleiche GeoTiba Systems mohamed.eleiche@gmail.com Abstract The miimum-travel-cost algorithm is a dyamic programmig algorithm to compute
MINIMUM CROSSINGS IN JOIN OF GRAPHS WITH PATHS AND CYCLES
 3 Acta Electrotechica et Iformatica, Vol. 1, No. 3, 01, 3 37, DOI: 10.478/v10198-01-008-0 MINIMUM CROSSINGS IN JOIN OF GRAPHS WITH PATHS AND CYCLES Mariá KLEŠČ, Matúš VALO Departmet of Mathematics ad Theoretical
3 Acta Electrotechica et Iformatica, Vol. 1, No. 3, 01, 3 37, DOI: 10.478/v10198-01-008-0 MINIMUM CROSSINGS IN JOIN OF GRAPHS WITH PATHS AND CYCLES Mariá KLEŠČ, Matúš VALO Departmet of Mathematics ad Theoretical
Running Time ( 3.1) Analysis of Algorithms. Experimental Studies. Limitations of Experiments
 Ruig Time ( 3.1) Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step- by- step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects.
Ruig Time ( 3.1) Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step- by- step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects.
Monochromatic Structures in Edge-coloured Graphs and Hypergraphs - A survey
 Moochromatic Structures i Edge-coloured Graphs ad Hypergraphs - A survey Shiya Fujita 1, Hery Liu 2, ad Colto Magat 3 1 Iteratioal College of Arts ad Scieces Yokohama City Uiversity 22-2, Seto, Kaazawa-ku
Moochromatic Structures i Edge-coloured Graphs ad Hypergraphs - A survey Shiya Fujita 1, Hery Liu 2, ad Colto Magat 3 1 Iteratioal College of Arts ad Scieces Yokohama City Uiversity 22-2, Seto, Kaazawa-ku
Analysis of Algorithms
 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Ruig Time Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects. The
Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Ruig Time Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects. The
Some New Results on Prime Graphs
 Ope Joural of Discrete Mathematics, 202, 2, 99-04 http://dxdoiorg/0426/ojdm202209 Published Olie July 202 (http://wwwscirporg/joural/ojdm) Some New Results o Prime Graphs Samir Vaidya, Udaya M Prajapati
Ope Joural of Discrete Mathematics, 202, 2, 99-04 http://dxdoiorg/0426/ojdm202209 Published Olie July 202 (http://wwwscirporg/joural/ojdm) Some New Results o Prime Graphs Samir Vaidya, Udaya M Prajapati
Pattern Recognition Systems Lab 1 Least Mean Squares
 Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Prime Cordial Labeling on Graphs
 World Academy of Sciece, Egieerig ad Techology Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical ad Computatioal Scieces Vol:7, No:5, 013 Prime Cordial Labelig o Graphs S. Babitha ad J. Baskar Babujee, Iteratioal Sciece
World Academy of Sciece, Egieerig ad Techology Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical ad Computatioal Scieces Vol:7, No:5, 013 Prime Cordial Labelig o Graphs S. Babitha ad J. Baskar Babujee, Iteratioal Sciece
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks, Queues, and Heaps Monday, February 18 / Tuesday, February 19
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
Analysis of Algorithms
 Aalysis of Algorithms Ruig Time of a algorithm Ruig Time Upper Bouds Lower Bouds Examples Mathematical facts Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite
Aalysis of Algorithms Ruig Time of a algorithm Ruig Time Upper Bouds Lower Bouds Examples Mathematical facts Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Miimum Spaig Trees 0 Goodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig a Network Suppose
Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Miimum Spaig Trees 0 Goodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig a Network Suppose
Analysis Metrics. Intro to Algorithm Analysis. Slides. 12. Alg Analysis. 12. Alg Analysis
 Itro to Algorithm Aalysis Aalysis Metrics Slides. Table of Cotets. Aalysis Metrics 3. Exact Aalysis Rules 4. Simple Summatio 5. Summatio Formulas 6. Order of Magitude 7. Big-O otatio 8. Big-O Theorems
Itro to Algorithm Aalysis Aalysis Metrics Slides. Table of Cotets. Aalysis Metrics 3. Exact Aalysis Rules 4. Simple Summatio 5. Summatio Formulas 6. Order of Magitude 7. Big-O otatio 8. Big-O Theorems
EVEN VERTEX EQUITABLE EVEN LABELING FOR CYCLE RELATED GRAPHS
 Kragujevac Joural of Matheatics Volue 43(3) (019), Pages 47 441. EVEN VERTEX EQUITABLE EVEN LABELING FOR CYCLE RELATED GRAPHS A. LOURDUSAMY 1 AND F. PATRICK 1 Abstract. Let G be a graph with p vertices
Kragujevac Joural of Matheatics Volue 43(3) (019), Pages 47 441. EVEN VERTEX EQUITABLE EVEN LABELING FOR CYCLE RELATED GRAPHS A. LOURDUSAMY 1 AND F. PATRICK 1 Abstract. Let G be a graph with p vertices
On Ryser s conjecture for t-intersecting and degree-bounded hypergraphs arxiv: v2 [math.co] 9 Dec 2017
![On Ryser s conjecture for t-intersecting and degree-bounded hypergraphs arxiv: v2 [math.co] 9 Dec 2017 On Ryser s conjecture for t-intersecting and degree-bounded hypergraphs arxiv: v2 [math.co] 9 Dec 2017](/thumbs/74/70358759.jpg) O Ryser s cojecture for t-itersectig ad degree-bouded hypergraphs arxiv:1705.1004v [math.co] 9 Dec 017 Zoltá Király Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egerváry Research Group (MTA-ELTE) Eötvös Uiversity Pázmáy
O Ryser s cojecture for t-itersectig ad degree-bouded hypergraphs arxiv:1705.1004v [math.co] 9 Dec 017 Zoltá Király Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egerváry Research Group (MTA-ELTE) Eötvös Uiversity Pázmáy
Symmetric Class 0 subgraphs of complete graphs
 DIMACS Techical Report 0-0 November 0 Symmetric Class 0 subgraphs of complete graphs Vi de Silva Departmet of Mathematics Pomoa College Claremot, CA, USA Chaig Verbec, Jr. Becer Friedma Istitute Booth
DIMACS Techical Report 0-0 November 0 Symmetric Class 0 subgraphs of complete graphs Vi de Silva Departmet of Mathematics Pomoa College Claremot, CA, USA Chaig Verbec, Jr. Becer Friedma Istitute Booth
Sorting in Linear Time. Data Structures and Algorithms Andrei Bulatov
 Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Cubic Polynomial Curves with a Shape Parameter
 roceedigs of the th WSEAS Iteratioal Coferece o Robotics Cotrol ad Maufacturig Techology Hagzhou Chia April -8 00 (pp5-70) Cubic olyomial Curves with a Shape arameter MO GUOLIANG ZHAO YANAN Iformatio ad
roceedigs of the th WSEAS Iteratioal Coferece o Robotics Cotrol ad Maufacturig Techology Hagzhou Chia April -8 00 (pp5-70) Cubic olyomial Curves with a Shape arameter MO GUOLIANG ZHAO YANAN Iformatio ad
Random Graphs and Complex Networks T
 Radom Graphs ad Complex Networks T-79.7003 Charalampos E. Tsourakakis Aalto Uiversity Lecture 3 7 September 013 Aoucemet Homework 1 is out, due i two weeks from ow. Exercises: Probabilistic iequalities
Radom Graphs ad Complex Networks T-79.7003 Charalampos E. Tsourakakis Aalto Uiversity Lecture 3 7 September 013 Aoucemet Homework 1 is out, due i two weeks from ow. Exercises: Probabilistic iequalities
MINIMUM COVERING SEIDEL ENERGY OF A GRAPH
 J. Idoes. Math. Soc. Vol., No. 1 (016, pp. 71 8. MINIMUM COVERING SEIDEL ENERGY OF A GRAPH M. R. Rajesh Kaa 1, R. Jagadeesh, Mohammad Reza Farahai 3 1 Post Graduate Departmet of Mathematics, Maharai s
J. Idoes. Math. Soc. Vol., No. 1 (016, pp. 71 8. MINIMUM COVERING SEIDEL ENERGY OF A GRAPH M. R. Rajesh Kaa 1, R. Jagadeesh, Mohammad Reza Farahai 3 1 Post Graduate Departmet of Mathematics, Maharai s
Minimum Spanning Trees. Application: Connecting a Network
 Miimum Spaig Tree // : Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. oodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, Miimum Spaig Trees oodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig
Miimum Spaig Tree // : Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. oodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, Miimum Spaig Trees oodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig
4-PRIME CORDIAL LABELING OF SOME DEGREE SPLITTING GRAPHS
 Iteratioal Joural of Maagemet, IT & Egieerig Vol. 8 Issue 7, July 018, ISSN: 49-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Joural Homepage: Double-Blid Peer Reviewed Refereed Ope Access Iteratioal Joural - Icluded i the
Iteratioal Joural of Maagemet, IT & Egieerig Vol. 8 Issue 7, July 018, ISSN: 49-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Joural Homepage: Double-Blid Peer Reviewed Refereed Ope Access Iteratioal Joural - Icluded i the
3D Model Retrieval Method Based on Sample Prediction
 20 Iteratioal Coferece o Computer Commuicatio ad Maagemet Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (20) (20) IACSIT Press, Sigapore 3D Model Retrieval Method Based o Sample Predictio Qigche Zhag, Ya Tag* School of Computer
20 Iteratioal Coferece o Computer Commuicatio ad Maagemet Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (20) (20) IACSIT Press, Sigapore 3D Model Retrieval Method Based o Sample Predictio Qigche Zhag, Ya Tag* School of Computer
Outline and Reading. Analysis of Algorithms. Running Time. Experimental Studies. Limitations of Experiments. Theoretical Analysis
 Outlie ad Readig Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output Ruig time ( 3.) Pseudo-code ( 3.2) Coutig primitive operatios ( 3.3-3.) Asymptotic otatio ( 3.6) Asymptotic aalysis ( 3.7) Case study Aalysis
Outlie ad Readig Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output Ruig time ( 3.) Pseudo-code ( 3.2) Coutig primitive operatios ( 3.3-3.) Asymptotic otatio ( 3.6) Asymptotic aalysis ( 3.7) Case study Aalysis
