Gradient Descent - Problem of Hiking Down a Mountain
|
|
|
- Julian Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gradient Descent - Problem of Hiking Down a Mountain Udacity Have you ever climbed a mountain? I am sure you had to hike down at some point? Hiking down is a great exercise and it is going to help us understand gradient descent. Whats the goal when you are hiking down a mountain? reach the bottom. Let s focus on reaching the bottom for now. - To have fun and to What is the red dot doing when it s hiking down? It s always going in the downward direction, until it hits the bottom. Let s call our friend calculus and see what she has to say about this. Derivatives Before we hop in, let me remind you a little bit about derivatives. There are different ways to look at derivatives, two of the most common ones are Slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function Rate of change of the function 1
2 Following are some of the common derivatives: d(x2 ) dx = 2x d( 2y5 ) dy = 10y 4 d(5 θ)2 dθ = 2(5 θ) (negative sign coming from θ) Sounds great! What if, we have more than one variable in our function? Well, we will talk about partial derivatives then! Let s look at some examples: x (x2 y 2 ) = 2xy 2 y ( 2y5 + z 2 ) = 10y 4 θ 2 (5θ 1 + 2θ 2 12θ 3 ) = 2 θ 2 (0.55 (5θ 1 + 2θ 2 12θ 3 )) = 2 (Can you convince yourself where the is coming from?) Now that we have familiarized ourselves with derivatives, let s start walking towards gradient descent algorithm. Wait, we are not there yet! Some more calculus! What is Gradient? Gradient is the generalization of derivatives in several variables. variables in the following function J(θ 1, θ 2, θ 3 ) J(Θ) = 0.55 (5θ 1 + 2θ 2 12θ 3 ) J J(Θ) =, J, J θ 1 θ 2 θ 3 = 5, 2, 12 Let s use θ s as our Here, is just a symbolic way of indicating that we are taking gradient of the function, and the gradient is inside < and > to denote that gradient is a vector. Let s look at a slightly more complicated example. Make sure you really understand this, we will use this type of expression in Linear Regression with Gradient Descent. J(Θ) = 1 2 (0.55 (5θ 1 + 2θ 2 12θ 3 )) 2 J J(Θ) =, J, J θ 1 θ 2 θ 3 = 5 (0.55 (5θ 1 + 2θ 2 12θ 3 )), 2 (0.55 (5θ 1 + 2θ 2 12θ 3 )), 12 (0.55 (5θ 1 + 2θ 2 12θ 3 )) 2
3 Why do we care about gradient? Gradient is a pretty powerful tool in calculus. Remember, in one variable, derivative gives us the slope of the tangent line. In several variables, Gradient points towards direction of the fastest increase of the function. This is extensively used in Gradient Descent Algorithm. Let s see how. What is the idea behind Gradient Descent Algorithm? Gradient descent algorithm is an iterative process that takes us to the minimum of a function (This will not happen always, there are some caveats!). Let s look at the red dot example again: If you want to reach the bottom, in which direction would you walk? In the downward direction, right? How do we find the downward direction? That s the direction opposite of the fastest increase. This means, if we are at point Θ 0 and want to move to lowest nearby point (this is why we say local minimum ) our next step should be at: Θ 1 = Θ 0 α J(Θ) evaluated at Θ 0 This needs some more clarification. 3
4 What s the deal with α? α is called the Learning Rate or step size. Which means, we want to take baby steps so that we don t overshoot the bottom. This is particularly important when we are very close to the minimum. A smart choice of α is crucial. When α is too small, it will take our algorithm forever to reach the lowest point and if α is too big we might overshoot and miss the bottom. Why sign? sign indicates that we are stepping in the direction opposite to that of J i.e. we are stepping in the direction opposite to that of fastest increase. 4
5 Example in one variable Let s see what this looks like in one variable. Suppose J(θ) = θ 2, then derivative J (θ) = 2θ. Our initial choices are θ 0 = 1 and α = 0.4 Then, θ 0 = 1 θ 1 = θ 0 α J (θ 0 ) = = 0.2 θ 2 = θ 1 α J (θ 1 ) = 0.04 θ 3 = θ 4 = θ θ 3 θ 2 θ
6 Example in two variables Suppose J(Θ) = θ1 2 + θ2 2. By simple, observation we can see that (0, 0) gives the minimum value for J. Let s see, if that s what we get by our gradient descent method. Let s choose Θ 0 = (1, 3) and α = 0.1. J(Θ) = 2θ 1, 2θ 2 Evaluated at (1, 3) this gradient vector is < 2, 6 > Θ 0 = (1, 3) Θ 1 = Θ 0 α J(Θ) = (1, 3) 0.1(2, 6) = (0.8, 2.4) Θ 2 = (0.8, 2.4) 0.1(1.6, 4.8) = (0.64, 1.92) Θ 3 = (0.512, 1.536) Θ 4 = (0.4096, ). Θ 10 = ( , ). Θ 50 = ( e 05, e 05 ). Θ 100 = ( e 10, e 10 ) 6
7 50 40 z θ 1 θ 2 θ 0 10 min θ θ 2 Yay! we see that we are indeed approaching the minimum, which we know is (0, 0). Caution Following are few of the most important things to keep in mind: Function must be differentiable. Learning rate should not be too small or too large. 7
8 Application in Linear Regression Gradient Descent algorithm is one of the methods used in linear regression to find the minimum of the error or cost function. Remember that your error or cost function must be differentiable to be able to use gradient descent. This is one of the reasons behind squaring the differences. Using absolute values to calculate errors may lead to corners as illustrated in the picture above. 8
Hey there, I m (name) and today I m gonna talk to you about rate of change and slope.
 Rate and Change of Slope A1711 Activity Introduction Hey there, I m (name) and today I m gonna talk to you about rate of change and slope. Slope is the steepness of a line and is represented by the letter
Rate and Change of Slope A1711 Activity Introduction Hey there, I m (name) and today I m gonna talk to you about rate of change and slope. Slope is the steepness of a line and is represented by the letter
Exam in Calculus. Wednesday June 1st First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty
 Exam in Calculus Wednesday June 1st 211 First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty The present exam consists of 7 numbered pages with a total of 12 exercises. It is allowed to use books, notes,
Exam in Calculus Wednesday June 1st 211 First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty The present exam consists of 7 numbered pages with a total of 12 exercises. It is allowed to use books, notes,
MTH 122 Calculus II Essex County College Division of Mathematics and Physics 1 Lecture Notes #11 Sakai Web Project Material
 MTH Calculus II Essex County College Division of Mathematics and Physics Lecture Notes # Sakai Web Project Material Introduction - - 0 - Figure : Graph of y sin ( x y ) = x cos (x + y) with red tangent
MTH Calculus II Essex County College Division of Mathematics and Physics Lecture Notes # Sakai Web Project Material Introduction - - 0 - Figure : Graph of y sin ( x y ) = x cos (x + y) with red tangent
Surfaces and Partial Derivatives
 Surfaces and James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 15, 2017 Outline 1 2 Tangent Planes Let s go back to our simple surface
Surfaces and James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 15, 2017 Outline 1 2 Tangent Planes Let s go back to our simple surface
Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry
 Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry Review of Triangles Recall that the sum of all angles in any triangle is 180. Let s look at what this means for a right triangle: A right angle is an angle which
Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry Review of Triangles Recall that the sum of all angles in any triangle is 180. Let s look at what this means for a right triangle: A right angle is an angle which
Polar Coordinates. 2, π and ( )
 Polar Coordinates Up to this point we ve dealt exclusively with the Cartesian (or Rectangular, or x-y) coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is not always the easiest coordinate system to work
Polar Coordinates Up to this point we ve dealt exclusively with the Cartesian (or Rectangular, or x-y) coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is not always the easiest coordinate system to work
AP Calculus. Extreme Values: Graphically. Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163. Slide 4 / 163. Slide 3 / 163. Slide 5 / 163. Slide 6 / 163
 Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163 AP Calculus Analyzing Functions Using Derivatives 2015-11-04 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 163 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 4 / 163 Extreme Values
Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163 AP Calculus Analyzing Functions Using Derivatives 2015-11-04 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 163 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 4 / 163 Extreme Values
Gradient and Directional Derivatives
 Gradient and Directional Derivatives MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Given z = f (x, y) we understand that f : gives the rate of change of z in
Gradient and Directional Derivatives MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Given z = f (x, y) we understand that f : gives the rate of change of z in
Background for Surface Integration
 Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials
 2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials 2.9.1 Linear Approximation Consider the following graph, Recall that this is the tangent line at x = a. We had the following definition, f (a) = lim x a f(x)
2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials 2.9.1 Linear Approximation Consider the following graph, Recall that this is the tangent line at x = a. We had the following definition, f (a) = lim x a f(x)
Parallel Transport on the Torus
 MLI Home Mathematics The Torus Parallel Transport Parallel Transport on the Torus Because it really is all about the torus, baby After reading about the torus s curvature, shape operator, and geodesics,
MLI Home Mathematics The Torus Parallel Transport Parallel Transport on the Torus Because it really is all about the torus, baby After reading about the torus s curvature, shape operator, and geodesics,
Lecture Transcript While and Do While Statements in C++
 Lecture Transcript While and Do While Statements in C++ Hello and welcome back. In this lecture we are going to look at the while and do...while iteration statements in C++. Here is a quick recap of some
Lecture Transcript While and Do While Statements in C++ Hello and welcome back. In this lecture we are going to look at the while and do...while iteration statements in C++. Here is a quick recap of some
Surfaces and Partial Derivatives
 Surfaces and Partial Derivatives James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 9, 2016 Outline Partial Derivatives Tangent Planes
Surfaces and Partial Derivatives James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 9, 2016 Outline Partial Derivatives Tangent Planes
Basics of Computational Geometry
 Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
DS Machine Learning and Data Mining I. Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University
 DS 4400 Machine Learning and Data Mining I Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University September 20 2018 Review Solution for multiple linear regression can be computed in closed form
DS 4400 Machine Learning and Data Mining I Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University September 20 2018 Review Solution for multiple linear regression can be computed in closed form
CALCULUS II. Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS II Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... ii Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates... 3 Introduction... 3 Parametric Equations and Curves...
CALCULUS II Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... ii Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates... 3 Introduction... 3 Parametric Equations and Curves...
Partial Derivatives (Online)
 7in x 10in Felder c04_online.tex V3 - January 21, 2015 9:44 A.M. Page 1 CHAPTER 4 Partial Derivatives (Online) 4.7 Tangent Plane Approximations and Power Series It is often helpful to use a linear approximation
7in x 10in Felder c04_online.tex V3 - January 21, 2015 9:44 A.M. Page 1 CHAPTER 4 Partial Derivatives (Online) 4.7 Tangent Plane Approximations and Power Series It is often helpful to use a linear approximation
AB Calculus: Extreme Values of a Function
 AB Calculus: Extreme Values of a Function Name: Extrema (plural for extremum) are the maximum and minimum values of a function. In the past, you have used your calculator to calculate the maximum and minimum
AB Calculus: Extreme Values of a Function Name: Extrema (plural for extremum) are the maximum and minimum values of a function. In the past, you have used your calculator to calculate the maximum and minimum
DS Machine Learning and Data Mining I. Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University
 DS 4400 Machine Learning and Data Mining I Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University January 22 2019 Outline Practical issues in Linear Regression Outliers Categorical variables Lab
DS 4400 Machine Learning and Data Mining I Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University January 22 2019 Outline Practical issues in Linear Regression Outliers Categorical variables Lab
Machine Learning Lecture-1
 Machine Learning Lecture-1 Programming Club Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur pclubiitk@gmail.com February 25, 2016 Programming Club (IIT Kanpur) ML-1 February 25, 2016 1 / 18 Acknowledgement This
Machine Learning Lecture-1 Programming Club Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur pclubiitk@gmail.com February 25, 2016 Programming Club (IIT Kanpur) ML-1 February 25, 2016 1 / 18 Acknowledgement This
Euler s Method for Approximating Solution Curves
 Euler s Method for Approximating Solution Curves As you may have begun to suspect at this point, time constraints will allow us to learn only a few of the many known methods for solving differential equations.
Euler s Method for Approximating Solution Curves As you may have begun to suspect at this point, time constraints will allow us to learn only a few of the many known methods for solving differential equations.
Linear and quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables.
 ams/econ 11b supplementary notes ucsc Linear quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables. c 016, Yonatan Katznelson Finding the extreme (minimum or maximum) values of a function, is
ams/econ 11b supplementary notes ucsc Linear quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables. c 016, Yonatan Katznelson Finding the extreme (minimum or maximum) values of a function, is
Exam 3 SCORE. MA 114 Exam 3 Spring Section and/or TA:
 MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross Product
 University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
Functions of Several Variables
 Functions of Several Variables Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Philippe B Laval KSU April 7, 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) Functions of Several Variables April 7, 2012 1 / 19 Introduction
Functions of Several Variables Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Philippe B Laval KSU April 7, 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) Functions of Several Variables April 7, 2012 1 / 19 Introduction
REGRESSION ANALYSIS : LINEAR BY MAUAJAMA FIRDAUS & TULIKA SAHA
 REGRESSION ANALYSIS : LINEAR BY MAUAJAMA FIRDAUS & TULIKA SAHA MACHINE LEARNING It is the science of getting computer to learn without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning is an area of artificial
REGRESSION ANALYSIS : LINEAR BY MAUAJAMA FIRDAUS & TULIKA SAHA MACHINE LEARNING It is the science of getting computer to learn without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning is an area of artificial
Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( ) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent
 Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
1 extrema notebook. November 25, 2012
 Do now as a warm up: Suppose this graph is a function f, defined on [a,b]. What would you say about the value of f at each of these x values: a, x 1, x 2, x 3, x 4, x 5, x 6, and b? What would you say
Do now as a warm up: Suppose this graph is a function f, defined on [a,b]. What would you say about the value of f at each of these x values: a, x 1, x 2, x 3, x 4, x 5, x 6, and b? What would you say
Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables
 Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April 4, 2014 Outline 1 Continuity
Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April 4, 2014 Outline 1 Continuity
CSC 4510 Machine Learning
 4: Regression (con.nued) CSC 4510 Machine Learning Dr. Mary Angela Papalaskari Department of CompuBng Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/4510/ The slides in this presentabon
4: Regression (con.nued) CSC 4510 Machine Learning Dr. Mary Angela Papalaskari Department of CompuBng Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/4510/ The slides in this presentabon
Tangent line problems
 You will find lots of practice problems and homework problems that simply ask you to differentiate. The following examples are to illustrate some of the types of tangent line problems that you may come
You will find lots of practice problems and homework problems that simply ask you to differentiate. The following examples are to illustrate some of the types of tangent line problems that you may come
Directional Derivatives as Vectors
 Directional Derivatives as Vectors John Ganci 1 Al Lehnen 2 1 Richland College Dallas, TX jganci@dcccd.edu 2 Madison Area Technical College Madison, WI alehnen@matcmadison.edu Statement of problem We are
Directional Derivatives as Vectors John Ganci 1 Al Lehnen 2 1 Richland College Dallas, TX jganci@dcccd.edu 2 Madison Area Technical College Madison, WI alehnen@matcmadison.edu Statement of problem We are
We can conclude that if f is differentiable in an interval containing a, then. f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f (a)(x a).
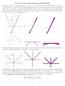 = sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
= sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
Triple Integrals. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Triple Integrals
 Triple Integrals MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 211 Riemann Sum Approach Suppose we wish to integrate w f (x, y, z), a continuous function, on the box-shaped region
Triple Integrals MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 211 Riemann Sum Approach Suppose we wish to integrate w f (x, y, z), a continuous function, on the box-shaped region
Linear Regression & Gradient Descent
 Linear Regression & Gradient Descent These slides were assembled by Byron Boots, with grateful acknowledgement to Eric Eaton and the many others who made their course materials freely available online.
Linear Regression & Gradient Descent These slides were assembled by Byron Boots, with grateful acknowledgement to Eric Eaton and the many others who made their course materials freely available online.
Chapter 2: Android Device Basics
 Chapter 2: Android Device Basics 1 Chapter 2: Android Device Basics Android devices have a ton of cool features and are really fun to play with, but they have a very practical side as well. We ll touch
Chapter 2: Android Device Basics 1 Chapter 2: Android Device Basics Android devices have a ton of cool features and are really fun to play with, but they have a very practical side as well. We ll touch
AP CALCULUS BC 2013 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP CALCULUS BC 2013 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 The figure above shows the graph of f, the derivative of a twice-differentiable function f, on the closed interval 0 x 8. The graph of f has horizontal
AP CALCULUS BC 2013 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 The figure above shows the graph of f, the derivative of a twice-differentiable function f, on the closed interval 0 x 8. The graph of f has horizontal
Supplemental 1.5. Objectives Interval Notation Increasing & Decreasing Functions Average Rate of Change Difference Quotient
 Supplemental 1.5 Objectives Interval Notation Increasing & Decreasing Functions Average Rate of Change Difference Quotient Interval Notation Many times in this class we will only want to talk about what
Supplemental 1.5 Objectives Interval Notation Increasing & Decreasing Functions Average Rate of Change Difference Quotient Interval Notation Many times in this class we will only want to talk about what
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
3.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 288 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector 3.6.1 Functions of two Variables Directional Derivatives Let us first quickly review, one more time, te
288 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector 3.6.1 Functions of two Variables Directional Derivatives Let us first quickly review, one more time, te
6.001 Notes: Section 6.1
 6.001 Notes: Section 6.1 Slide 6.1.1 When we first starting talking about Scheme expressions, you may recall we said that (almost) every Scheme expression had three components, a syntax (legal ways of
6.001 Notes: Section 6.1 Slide 6.1.1 When we first starting talking about Scheme expressions, you may recall we said that (almost) every Scheme expression had three components, a syntax (legal ways of
Lecture 2 September 3
 EE 381V: Large Scale Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 2 September 3 Lecturer: Caramanis & Sanghavi Scribe: Hongbo Si, Qiaoyang Ye 2.1 Overview of the last Lecture The focus of the last lecture was to give
EE 381V: Large Scale Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 2 September 3 Lecturer: Caramanis & Sanghavi Scribe: Hongbo Si, Qiaoyang Ye 2.1 Overview of the last Lecture The focus of the last lecture was to give
Note that ALL of these points are Intercepts(along an axis), something you should see often in later work.
 SECTION 1.1: Plotting Coordinate Points on the X-Y Graph This should be a review subject, as it was covered in the prerequisite coursework. But as a reminder, and for practice, plot each of the following
SECTION 1.1: Plotting Coordinate Points on the X-Y Graph This should be a review subject, as it was covered in the prerequisite coursework. But as a reminder, and for practice, plot each of the following
3 Types of Gradient Descent Algorithms for Small & Large Data Sets
 3 Types of Gradient Descent Algorithms for Small & Large Data Sets Introduction Gradient Descent Algorithm (GD) is an iterative algorithm to find a Global Minimum of an objective function (cost function)
3 Types of Gradient Descent Algorithms for Small & Large Data Sets Introduction Gradient Descent Algorithm (GD) is an iterative algorithm to find a Global Minimum of an objective function (cost function)
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
HMC CS 158, Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Programming: Regularized Polynomial Regression
 HMC CS 158, Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Programming: Regularized Polynomial Regression Goals: To open up the black-box of scikit-learn and implement regression models. To investigate how adding polynomial
HMC CS 158, Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Programming: Regularized Polynomial Regression Goals: To open up the black-box of scikit-learn and implement regression models. To investigate how adding polynomial
Today. Gradient descent for minimization of functions of real variables. Multi-dimensional scaling. Self-organizing maps
 Today Gradient descent for minimization of functions of real variables. Multi-dimensional scaling Self-organizing maps Gradient Descent Derivatives Consider function f(x) : R R. The derivative w.r.t. x
Today Gradient descent for minimization of functions of real variables. Multi-dimensional scaling Self-organizing maps Gradient Descent Derivatives Consider function f(x) : R R. The derivative w.r.t. x
30. Constrained Optimization
 30. Constrained Optimization The graph of z = f(x, y) is represented by a surface in R 3. Normally, x and y are chosen independently of one another so that one may roam over the entire surface of f (within
30. Constrained Optimization The graph of z = f(x, y) is represented by a surface in R 3. Normally, x and y are chosen independently of one another so that one may roam over the entire surface of f (within
while its direction is given by the right hand rule: point fingers of the right hand in a 1 a 2 a 3 b 1 b 2 b 3 A B = det i j k
 I.f Tangent Planes and Normal Lines Again we begin by: Recall: (1) Given two vectors A = a 1 i + a 2 j + a 3 k, B = b 1 i + b 2 j + b 3 k then A B is a vector perpendicular to both A and B. Then length
I.f Tangent Planes and Normal Lines Again we begin by: Recall: (1) Given two vectors A = a 1 i + a 2 j + a 3 k, B = b 1 i + b 2 j + b 3 k then A B is a vector perpendicular to both A and B. Then length
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
lecture 10 - depth from blur, binocular stereo
 This lecture carries forward some of the topics from early in the course, namely defocus blur and binocular disparity. The main emphasis here will be on the information these cues carry about depth, rather
This lecture carries forward some of the topics from early in the course, namely defocus blur and binocular disparity. The main emphasis here will be on the information these cues carry about depth, rather
First of all, we need to know what it means for a parameterize curve to be differentiable. FACT:
 CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
d f(g(t), h(t)) = x dt + f ( y dt = 0. Notice that we can rewrite the relationship on the left hand side of the equality using the dot product: ( f
 Gradients and the Directional Derivative In 14.3, we discussed the partial derivatives f f and, which tell us the rate of change of the x y height of the surface defined by f in the x direction and the
Gradients and the Directional Derivative In 14.3, we discussed the partial derivatives f f and, which tell us the rate of change of the x y height of the surface defined by f in the x direction and the
10 Polar Coordinates, Parametric Equations
 Polar Coordinates, Parametric Equations ½¼º½ ÈÓÐ Ö ÓÓÖ Ò Ø Coordinate systems are tools that let us use algebraic methods to understand geometry While the rectangular (also called Cartesian) coordinates
Polar Coordinates, Parametric Equations ½¼º½ ÈÓÐ Ö ÓÓÖ Ò Ø Coordinate systems are tools that let us use algebraic methods to understand geometry While the rectangular (also called Cartesian) coordinates
MA 243 Calculus III Fall Assignment 1. Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals)
 MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
Implicit Function Explorations
 Activities with Implicit Functions and Implicit Differentiation on the TI-89/Voyage 00 Dennis Pence Western Michigan University Kalamazoo, Michigan USA Abstract: Unfortunately the topic of implicit differentiation
Activities with Implicit Functions and Implicit Differentiation on the TI-89/Voyage 00 Dennis Pence Western Michigan University Kalamazoo, Michigan USA Abstract: Unfortunately the topic of implicit differentiation
Advanced Curve Fitting. Eric Haller, Secondary Occasional Teacher, Peel District School Board
 Advanced Curve Fitting Eric Haller, Secondary Occasional Teacher, Peel District School Board rickyhaller@hotmail.com In many experiments students collect two-variable data, make scatter plots, and then
Advanced Curve Fitting Eric Haller, Secondary Occasional Teacher, Peel District School Board rickyhaller@hotmail.com In many experiments students collect two-variable data, make scatter plots, and then
12 Polar Coordinates, Parametric Equations
 54 Chapter Polar Coordinates, Parametric Equations Polar Coordinates, Parametric Equations Just as we describe curves in the plane using equations involving x and y, so can we describe curves using equations
54 Chapter Polar Coordinates, Parametric Equations Polar Coordinates, Parametric Equations Just as we describe curves in the plane using equations involving x and y, so can we describe curves using equations
Increasing/Decreasing Behavior
 Derivatives and the Shapes of Graphs In this section, we will specifically discuss the information that f (x) and f (x) give us about the graph of f(x); it turns out understanding the first and second
Derivatives and the Shapes of Graphs In this section, we will specifically discuss the information that f (x) and f (x) give us about the graph of f(x); it turns out understanding the first and second
Backpropagation + Deep Learning
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Backpropagation + Deep Learning Matt Gormley Lecture 13 Mar 1, 2018 1 Reminders
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Backpropagation + Deep Learning Matt Gormley Lecture 13 Mar 1, 2018 1 Reminders
The big picture and a math review
 The big picture and a math review Intermediate Micro Topic 1 Mathematical appendix of Varian The big picture Microeconomics Study of decision-making under scarcity Individuals households firms investors
The big picture and a math review Intermediate Micro Topic 1 Mathematical appendix of Varian The big picture Microeconomics Study of decision-making under scarcity Individuals households firms investors
f xx (x, y) = 6 + 6x f xy (x, y) = 0 f yy (x, y) = y In general, the quantity that we re interested in is
 1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
Programming Exercise 1: Linear Regression
 Programming Exercise 1: Linear Regression Machine Learning Introduction In this exercise, you will implement linear regression and get to see it work on data. Before starting on this programming exercise,
Programming Exercise 1: Linear Regression Machine Learning Introduction In this exercise, you will implement linear regression and get to see it work on data. Before starting on this programming exercise,
MATH 19520/51 Class 15
 MATH 19520/51 Class 15 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-11-01 1 Change of variables in two dimensions. 2 Double integrals via change of variables. Change of Variables Slogan: An n-variable substitution
MATH 19520/51 Class 15 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-11-01 1 Change of variables in two dimensions. 2 Double integrals via change of variables. Change of Variables Slogan: An n-variable substitution
. The differential of y f (x)
 Calculus I - Prof D Yuen Exam Review version 11/14/01 Please report any typos Derivative Rules Of course you have to remember all your derivative rules Implicit Differentiation Differentiate both sides
Calculus I - Prof D Yuen Exam Review version 11/14/01 Please report any typos Derivative Rules Of course you have to remember all your derivative rules Implicit Differentiation Differentiate both sides
Here are some of the more basic curves that we ll need to know how to do as well as limits on the parameter if they are required.
 1 of 10 23/07/2016 05:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Line Integrals / Line Integrals - Part I Problems] [Notes] [Practice Problems] [Assignment Calculus III - Notes Line Integrals Part
1 of 10 23/07/2016 05:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Line Integrals / Line Integrals - Part I Problems] [Notes] [Practice Problems] [Assignment Calculus III - Notes Line Integrals Part
Logistic Regression and Gradient Ascent
 Logistic Regression and Gradient Ascent CS 349-02 (Machine Learning) April 0, 207 The perceptron algorithm has a couple of issues: () the predictions have no probabilistic interpretation or confidence
Logistic Regression and Gradient Ascent CS 349-02 (Machine Learning) April 0, 207 The perceptron algorithm has a couple of issues: () the predictions have no probabilistic interpretation or confidence
MAC2313 Final A. a. The vector r u r v lies in the tangent plane of S at a given point. b. S f(x, y, z) ds = R f(r(u, v)) r u r v du dv.
 MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. Let f(x, y, z) be a function continuous in R 3 and let S be a surface parameterized by r(u, v) with the domain of the parameterization given by R; how many of the following are
MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. Let f(x, y, z) be a function continuous in R 3 and let S be a surface parameterized by r(u, v) with the domain of the parameterization given by R; how many of the following are
Cost Functions in Machine Learning
 Cost Functions in Machine Learning Kevin Swingler Motivation Given some data that reflects measurements from the environment We want to build a model that reflects certain statistics about that data Something
Cost Functions in Machine Learning Kevin Swingler Motivation Given some data that reflects measurements from the environment We want to build a model that reflects certain statistics about that data Something
R f da (where da denotes the differential of area dxdy (or dydx)
 Math 28H Topics for the second exam (Technically, everything covered on the first exam, plus) Constrained Optimization: Lagrange Multipliers Most optimization problems that arise naturally are not unconstrained;
Math 28H Topics for the second exam (Technically, everything covered on the first exam, plus) Constrained Optimization: Lagrange Multipliers Most optimization problems that arise naturally are not unconstrained;
Engineering Mechanics Prof. Siva Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Statics - 4.3
 Engineering Mechanics Prof. Siva Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Statics - 4.3 In this case let s say delta B and delta C are the kinematically consistent displacements.
Engineering Mechanics Prof. Siva Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Statics - 4.3 In this case let s say delta B and delta C are the kinematically consistent displacements.
Lagrange Multipliers
 Lagrange Multipliers Introduction and Goals: The goal of this lab is to become more familiar with the process and workings of Lagrange multipliers. This lab is designed more to help you understand the
Lagrange Multipliers Introduction and Goals: The goal of this lab is to become more familiar with the process and workings of Lagrange multipliers. This lab is designed more to help you understand the
Introduction to Algorithms / Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Shortest Paths Date: 10/13/15
 600.363 Introduction to Algorithms / 600.463 Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Shortest Paths Date: 10/13/15 14.1 Introduction Today we re going to talk about algorithms for computing shortest
600.363 Introduction to Algorithms / 600.463 Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Shortest Paths Date: 10/13/15 14.1 Introduction Today we re going to talk about algorithms for computing shortest
Solution 2. ((3)(1) (2)(1), (4 3), (4)(2) (3)(3)) = (1, 1, 1) D u (f) = (6x + 2yz, 2y + 2xz, 2xy) (0,1,1) = = 4 14
 Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Intro. Scheme Basics. scm> 5 5. scm>
 Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Lecture 4: Optimization
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Lecture 4: Optimization 13 Sep 2015 Instructor: Bhiksha Raj (slides largely by Najim Dehak, JHU) 11-755/18-797 1 Index 1. The problem of optimization 2. Direct optimization
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Lecture 4: Optimization 13 Sep 2015 Instructor: Bhiksha Raj (slides largely by Najim Dehak, JHU) 11-755/18-797 1 Index 1. The problem of optimization 2. Direct optimization
The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), Goals. Warm-up: Differentiability. Notes. Notes.
 The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), 14.5 10 March 2014 Goals. We will: Define the differential df and use it to approximate changes in a function s value.
The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), 14.5 10 March 2014 Goals. We will: Define the differential df and use it to approximate changes in a function s value.
International Conference Las Vegas, NV, USA March 7-9, 2014
 International Conference Las Vegas, NV, USA March 7-9, 2014 Overview About ETS (engineering school) Why Nspire CAS? Why Computer Algebra? Examples in pre-calculus Examples in single variable calculus Examples
International Conference Las Vegas, NV, USA March 7-9, 2014 Overview About ETS (engineering school) Why Nspire CAS? Why Computer Algebra? Examples in pre-calculus Examples in single variable calculus Examples
A small review, Second Midterm, Calculus 3, Prof. Montero 3450: , Fall 2008
 A small review, Second Midterm, Calculus, Prof. Montero 45:-4, Fall 8 Maxima and minima Let us recall first, that for a function f(x, y), the gradient is the vector ( f)(x, y) = ( ) f f (x, y); (x, y).
A small review, Second Midterm, Calculus, Prof. Montero 45:-4, Fall 8 Maxima and minima Let us recall first, that for a function f(x, y), the gradient is the vector ( f)(x, y) = ( ) f f (x, y); (x, y).
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS. Date: Lesson: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers
 Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION
 LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we ll describe extend the optimization techniques you learned in your first semester calculus class to optimize functions of multiple variables.
LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we ll describe extend the optimization techniques you learned in your first semester calculus class to optimize functions of multiple variables.
MA 220 Lesson 28 Notes Section 3.3 (p. 191, 2 nd half of text)
 MA 220 Lesson 28 Notes Section 3.3 (p. 191, 2 nd half of tet) The property of the graph of a function curving upward or downward is defined as the concavity of the graph of a function. Concavity if how
MA 220 Lesson 28 Notes Section 3.3 (p. 191, 2 nd half of tet) The property of the graph of a function curving upward or downward is defined as the concavity of the graph of a function. Concavity if how
Week 5: Geometry and Applications
 Week 5: Geometry and Applications Introduction Now that we have some tools from differentiation, we can study geometry, motion, and few other issues associated with functions of several variables. Much
Week 5: Geometry and Applications Introduction Now that we have some tools from differentiation, we can study geometry, motion, and few other issues associated with functions of several variables. Much
The Bisection Method versus Newton s Method in Maple (Classic Version for Windows)
 The Bisection Method versus (Classic Version for Windows) Author: Barbara Forrest Contact: baforres@uwaterloo.ca Copyrighted/NOT FOR RESALE version 1.1 Contents 1 Objectives for this Lab i 2 Approximate
The Bisection Method versus (Classic Version for Windows) Author: Barbara Forrest Contact: baforres@uwaterloo.ca Copyrighted/NOT FOR RESALE version 1.1 Contents 1 Objectives for this Lab i 2 Approximate
An Introduction to the Directional Derivative and the Gradient Math Insight
 An Introduction to the Directional Derivative and the Gradient Math Insight The directional derivative Let the function f(x,y) be the height of a mountain range at each point x=(x,y). If you stand at some
An Introduction to the Directional Derivative and the Gradient Math Insight The directional derivative Let the function f(x,y) be the height of a mountain range at each point x=(x,y). If you stand at some
Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ x + 5y + 7z 9x + 3y + 11z
 Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6. ) is graphed below:
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Math 213 Calculus III Practice Exam 2 Solutions Fall 2002
 Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Catalan Numbers. Table 1: Balanced Parentheses
 Catalan Numbers Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles November, 00 We begin with a set of problems that will be shown to be completely equivalent. The solution to each problem
Catalan Numbers Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles November, 00 We begin with a set of problems that will be shown to be completely equivalent. The solution to each problem
Chapter 7. Polygons, Circles, Stars and Stuff
 Chapter 7. Polygons, Circles, Stars and Stuff Now it s time for the magic! Magic? asked Morf. What do you mean, magic? You ve never talked about Logo magic before. We ve talked about shapes, and how you
Chapter 7. Polygons, Circles, Stars and Stuff Now it s time for the magic! Magic? asked Morf. What do you mean, magic? You ve never talked about Logo magic before. We ve talked about shapes, and how you
BDD and Testing. User requirements and testing are tightly coupled
 BDD and Testing User requirements and testing are tightly coupled 1 New Concept: Acceptance Tests Customer criteria for accepting a milestone Get paid if pass! Black-box tests specified with the customer
BDD and Testing User requirements and testing are tightly coupled 1 New Concept: Acceptance Tests Customer criteria for accepting a milestone Get paid if pass! Black-box tests specified with the customer
How does light energy travel? transparent transmit mediums media medium
 Have you ever observed a solar eclipse like the one in this photograph? During a solar eclipse, it can become very dark in the middle of a sunny day. This may seem amazing to us, but it was terrifying
Have you ever observed a solar eclipse like the one in this photograph? During a solar eclipse, it can become very dark in the middle of a sunny day. This may seem amazing to us, but it was terrifying
AP Calculus. Slide 1 / 213 Slide 2 / 213. Slide 3 / 213. Slide 4 / 213. Slide 4 (Answer) / 213 Slide 5 / 213. Derivatives. Derivatives Exploration
 Slide 1 / 213 Slide 2 / 213 AP Calculus Derivatives 2015-11-03 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 213 Table of Contents Slide 4 / 213 Rate of Change Slope of a Curve (Instantaneous ROC) Derivative Rules: Power, Constant,
Slide 1 / 213 Slide 2 / 213 AP Calculus Derivatives 2015-11-03 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 213 Table of Contents Slide 4 / 213 Rate of Change Slope of a Curve (Instantaneous ROC) Derivative Rules: Power, Constant,
Now each of you should be familiar with inverses from your previous mathematical
 5. Inverse Functions TOOTLIFTST: Knowledge of derivatives of basic functions, including power, eponential, logarithmic, trigonometric, and inverse trigonometric functions. Now each of you should be familiar
5. Inverse Functions TOOTLIFTST: Knowledge of derivatives of basic functions, including power, eponential, logarithmic, trigonometric, and inverse trigonometric functions. Now each of you should be familiar
Section 4.4: Parabolas
 Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
Learning via Optimization
 Lecture 7 1 Outline 1. Optimization Convexity 2. Linear regression in depth Locally weighted linear regression 3. Brief dips Logistic Regression [Stochastic] gradient ascent/descent Support Vector Machines
Lecture 7 1 Outline 1. Optimization Convexity 2. Linear regression in depth Locally weighted linear regression 3. Brief dips Logistic Regression [Stochastic] gradient ascent/descent Support Vector Machines
Exam 2 Preparation Math 2080 (Spring 2011) Exam 2: Thursday, May 12.
 Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14 Scan Converting Lines, Circles and Ellipses Hello everybody, welcome again
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14 Scan Converting Lines, Circles and Ellipses Hello everybody, welcome again
Calculus III Meets the Final
 Calculus III Meets the Final Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky December 7, 2018 Homework Review for Final Exam on Thursday, December 13, 6:00-8:00 PM Be sure you know which room to go to for the final!
Calculus III Meets the Final Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky December 7, 2018 Homework Review for Final Exam on Thursday, December 13, 6:00-8:00 PM Be sure you know which room to go to for the final!
CARTESIAN OVOIDS. A. Cartesian Ovoids in the case n o < n i
 CARTESIAN OVOIDS The Cartesian ovoids are plane curves that have been first described by Rene Descartes (in 1637 AD) and represent the geometric locus of points that have the same linear combination of
CARTESIAN OVOIDS The Cartesian ovoids are plane curves that have been first described by Rene Descartes (in 1637 AD) and represent the geometric locus of points that have the same linear combination of
