while its direction is given by the right hand rule: point fingers of the right hand in a 1 a 2 a 3 b 1 b 2 b 3 A B = det i j k
|
|
|
- Joy Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 I.f Tangent Planes and Normal Lines Again we begin by: Recall: (1) Given two vectors A = a 1 i + a 2 j + a 3 k, B = b 1 i + b 2 j + b 3 k then A B is a vector perpendicular to both A and B. Then length of A B is A B sin θ, while its direction is given by the right hand rule: point fingers of the right hand in the direction of A, curl them in the direction of B. Then the thumb points in the direction of A B. To compute A B, it is convenient to use the formula: A B = det i j k a 1 a 2 a 3. b 1 b 2 b 3 A B B A Observe that A B = (B A), while if A and B are parallel, A B = 0. (2) A plane is determined by a vector N = αi + βj + γk (called the normal vector), and a point P 0 = (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) on the plane. Any other point P = (x, y, z) of space is then on the plane iff the vector P 0 P is perpendicular to N, i.e., P 0 P N = 0, or (x x 0 )α + (y y 0 )β + (z z 0 )γ = 0. 50
2 N P0 P (3) Instead of a vector N and a point P 0, we may specify three points of the plane P 0, P 1, P 2 (not collinear). N P 2 P 0 P 1 We then construct the vectors P 0 P 1, P 0 P 2 and set N = P 0 P 1 P 0 P 2. For planes it does matter whether we choose N or N as the normal! (4) Curves in space are given in parametric form as: x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t) a t b. This is a very convenient way for us! Remember, once again, that z = f(x, y) gives a surface, not a curve. Suppose the curve C is given in the above form. Then 51
3 r(t 0 ) = x(t 0 )i + y(t 0 )j + z(t 0 )k is the vector from the origin (0, 0, 0) to the point on C at t = t 0. We recall that dr/dt = (dx/dt)i + (dy/dt)j + (dz/dt)k gives a tangent vector to the curve C. z d r d t C r ( t ) y x Suppose now we are given a surface in (x, y, z) space. It is convenient for us to write the surface S in the form F (x, y, z) = 0, so if we had the equation z = f(x, y), then we would get F (x, y, z) = z f(x, y). Let P 0 = (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) be a point of S. Then the Tangent Plane T of S at P 0 is the plane which: (1) contains P 0 and (2) if C is any curve on S through P 0, then the tangent vector to C at P 0 is on the plane. S P 0 C 1 C3 C 2 The tangent plane plays the same role for surfaces that the tangent line played for y = f(x) in the (x, y) plane. We obtain the equation of the tangent plane T at P 0 as follows: We know one point of T (namely P 0 ), so we need only find the normal vector N. To do this, let C be any given curve through P 0 such that C lies on S. 52
4 Then C is given by x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t) a t b for some functions x(t), y(t), z(t). On the other hand, since C is on the surface S, we must have F (x(t), y(t), z(t)) = 0 for all t! I.e., differentiating both sides with respect to t, we obtain F x dx dt + F y dy dt + F z dz dt = 0. F P 0 d r d t C We know that dr/dt = (dx/dt)i + (dy/dt)j + (dz/dt)k is tangent to C at P 0, and thus F = ( F/ x)i + ( F/ y)j + ( F/ z)k is perpendicular to dr/dt! But C was not specified! So F is perpendicular to the tangent of any curve, and we conclude that we may take F as the normal to the tangent plane! In summary the equation of the tangent plane to F (x, y, z) = 0 at P 0 = (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is F x (x 0, y 0, z 0 )(x x 0 ) + F y (x 0, y 0, z 0 )(y y 0 ) + F z (x 0, y 0, z 0 )(z z 0 ) = 0. By definition, the line through P 0 in the direction of F (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is called 53
5 the Normal Line. Its equation is x = x 0 + t F x (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) y = y 0 + t F y (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) z = z 0 + t F z (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) < t <. Finally, two surfaces are perpendicular (or orthogonal) at a point of intersection iff the normal vectors N 1, N 2 of their respective tangent planes are perpendicular: N 1 N 2 = 0. Remark. Observe that F is also perpendicular to the equipotential surfaces F (x, y, z) = c, with c = constant, by exactly the same calculations. Earlier we showed that F gave the direction of maximal rate of increase for the function F (x, y, z). We now also know that F is perpendicular to the surface F (x, y, z) = 0. F F = c We thus have that the maximal rate of increase of F (x, y, z) can be obtained by going in a perpendicular direction to the equipotential surfaces: F (x, y, z) = c. We illustrate the above results with the following examples. Example 1. Find the directional derivative of f = x sin(e z ) + ye x at the point (0, 1, 1) 54
6 in the direction of the vector v = i j + k. Answer. f = (sin(e z ) + ye x )i + e x j + x cos(e z )e z k, so f = (sin e + 1)i + j + 0k (0,1,1) while a unit vector u in the direction of v is u = i j + k Finally, df dx = f u = v (sin e + 1) 1 3 = sin(e) 3. Example 2. Let the electrical potential V be given by V = 5x 2 + 3y 3 z + xz 4. You are at the point (1, 1, 0). (a) In which direction should you head for the maximal rate of change of V with respect to distance? What is the maximal rate? (b) Do the same for the minimal (i.e., most negative) rate. Answer. V = (10x + z 4 )i + 9y 2 zj + (3y 3 + 4z 3 x)k. Therefore at (1, 1, 0), V = 10i + 0j + 3k. (1,1,0) (a) We have the direction of maximal rate of change = direction of V = 10i+3k. The rate = V = 109. (b) The direction of the most negative rate of change = direction of V = 10i 3k. This rate = V =
7 Example 3. Let (u, v) be differentiable functions. Show: (uv) = v u + u v. Answer. (uv) = x (uv)i + y (uv)j + z (uv)k [ u = x v + u v ] [ u i + x y v + u v y [ u = v x i + u y j + u ] z k + u = v u + u v. ] [ u j + z v + u v z ] [ v x i + v y j + v z k ] i Example 4. Find the tangent plane and normal line to the surface z = x 2 + y 2 at the point x = 1, y = 1. Answer. Write the surface as F (x, y, z) = 0. Here F (x, y, z) = x 2 + y 2 z. Then the normal vector to the tangent plane is F = 2xi + 2yj k = 2i 2j k. (1, 1,2) So the equation of the tangent plane is (2i 2j k) ((x 1)i + (y ( 1))j + (z 2)k) = 0 or 2(x 1) 2(y + 1) (z 2) = 0, while the normal line is: x = 1 + 2t y = 1 2t < t <. z = 2 t 56
8 Example 5. Find the point(s) on the sphere z 2 + x 2 + y 2 = 1 where the tangent plane is parallel to the plane x + y + z = 17. Answer. The normal vector N 1, to the given plane is N 1 = i + j + k. We now calculate the normal N 2 to the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1. Here F (x, y, z) = x 2 + y 2 + z 2 1 and so N 2 = F = 2xi + 2yj + 2zk. We wish N 2 and N 1 to be parallel, i.e., N 1 N 2 = 0 or det i j k = 0. 2x 2y 2z Equivalently, i[2z 2y] j[2z 2x] + k[2y 2x] = 0. We have z = y, z = x, y = x. Note that only two of these three equations are useful, since they imply the third. We choose: y = z and x = z. Then, we keep in mind that (x, y, z) is on the sphere! I.e., x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1, and so we must have z 2 + z 2 + z 2 = 1 or z 2 = 1 3. We thus find z = 1/ 3, z = 1/ 3 and the two points on the sphere are (1/ 3, 1/ 3, 1/ 3) and ( 1/ 3, 1/ 3, 1/ 3). 57
9 Example 6. Find parametric equations for the tangent line to the curve of intersection of the paraboloid z = 4(x 2 + y 2 ) and the ellipsoid x 2 + 4y 2 + z 2 = 21 at the point (1, 1, 4). Answer. Note that the intersection curve(s) satisfy x 2 + (z 4x 2 ) + z 2 = 21 or 3x 2 + z 2 + z = 21 and 4y 2 = 21 z 2 x 2 = 21 z z2 z. 3 These last two equations give x and y as functions of z by taking square roots. Clearly these equations imply that the intersection is complicated! Proceeding directly does not seem too wise. Instead, note that the curve of intersection must lie on both surfaces simultaneously. It follows that its tangent line must have a direction vector V which is perpendicular to the normals N 1 and N 2 of the two surfaces. We may therefore take V = N 1 N 2. Now z = 4(x 2 + y 2 ) can be written as 4(x 2 + y 2 ) z = 0. Its normal N 1 is thus N 1 = 8xi + 8yj 1k and N 1 (1,1,4) = 8i + 8j k. 58
10 In the same way, the ellipsoid x 2 + 4y 2 + z 2 = 21 has normal N 2 given by N 2 = 2xi + 8yj + 2zk and N 2 (1,1,4) = 2i + 8j + 8k. We then have V = det i j k = 72i 66j + 48k and the equation of the tangent line becomes: x = t y = 1 66t < t <. z = t 59
11 Further Exercises: 1) Find the tangent plane and normal line to z 2 = x 2 + y 2 at (1, 0, 1). 2) Find the tangent plane and normal line to x 2 + y2 4 + z2 9 = 1 at (1, 0, 0). 3) Find the tangent plane and normal line to the cylinder x 2 +y 2 = 8 at (2, 2, 1). 4) Find all points of the surface x = y 2 + z 2 where the normal line intersects the plane x + y + z = 1 at right angles. Find the points of the plane where the normal lines intersect the plane. 5) Find all points of the surface z = 4x 2 +9y 2 where the tangent plane is parallel to the plane 16x + 18y + 2z = 1. 6) Find a tangent vector at the point (1, 0, 1) to the curve of intersection of the surfaces z 2 = x 2 + y 2 and z = x + 4y. 7) Show that the normal line at any point on the surface (x 1) 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1 passes through the point (1, 0, 0). 8) Show that the normal line to the surface z = x 2 + y 2 at the point (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) must contain the point (0, 0, 1 + z 0 ). 60
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2
 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2 Lecture 25 February 28, 2007 Recall Fact Recall Fact If f is a dierentiable function of x and y, then f has a directional derivative in the direction
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2 Lecture 25 February 28, 2007 Recall Fact Recall Fact If f is a dierentiable function of x and y, then f has a directional derivative in the direction
Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9
 Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9 Some surfaces are defined implicitly, such as the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1. In general an implicitly defined surface has the equation
Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9 Some surfaces are defined implicitly, such as the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1. In general an implicitly defined surface has the equation
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2
 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2 Marius Ionescu October 26, 2012 Marius Ionescu () Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part October 2 26, 2012 1 / 12 Recall Fact Marius
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2 Marius Ionescu October 26, 2012 Marius Ionescu () Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part October 2 26, 2012 1 / 12 Recall Fact Marius
Parametric Surfaces. Substitution
 Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives
 Recall that if z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as and represent the rates of change of z in the x- and y-directions, that is, in the directions of the unit vectors i and
Recall that if z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as and represent the rates of change of z in the x- and y-directions, that is, in the directions of the unit vectors i and
Background for Surface Integration
 Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Math Exam III Review
 Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Kevin James. MTHSC 206 Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gra
 MTHSC 206 Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Definition We define the directional derivative of the function f (x, y) at the point (x 0, y 0 ) in the direction of the unit vector
MTHSC 206 Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Definition We define the directional derivative of the function f (x, y) at the point (x 0, y 0 ) in the direction of the unit vector
f xx (x, y) = 6 + 6x f xy (x, y) = 0 f yy (x, y) = y In general, the quantity that we re interested in is
 1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers
 In this section we present Lagrange s method for maximizing or minimizing a general function f(x, y, z) subject to a constraint (or side condition) of the form g(x, y, z) = k. Figure 1 shows this curve
In this section we present Lagrange s method for maximizing or minimizing a general function f(x, y, z) subject to a constraint (or side condition) of the form g(x, y, z) = k. Figure 1 shows this curve
14.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 14 Partial Derivatives 14.6 and the Gradient Vector Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and the Gradient Vector In this section we introduce
14 Partial Derivatives 14.6 and the Gradient Vector Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and the Gradient Vector In this section we introduce
Grad operator, triple and line integrals. Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures
 Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
Surfaces and Integral Curves
 MODULE 1: MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 16 Lecture 3 Surfaces and Integral Curves In Lecture 3, we recall some geometrical concepts that are essential for understanding the nature of solutions of partial
MODULE 1: MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 16 Lecture 3 Surfaces and Integral Curves In Lecture 3, we recall some geometrical concepts that are essential for understanding the nature of solutions of partial
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Directional Derivatives as Vectors
 Directional Derivatives as Vectors John Ganci 1 Al Lehnen 2 1 Richland College Dallas, TX jganci@dcccd.edu 2 Madison Area Technical College Madison, WI alehnen@matcmadison.edu Statement of problem We are
Directional Derivatives as Vectors John Ganci 1 Al Lehnen 2 1 Richland College Dallas, TX jganci@dcccd.edu 2 Madison Area Technical College Madison, WI alehnen@matcmadison.edu Statement of problem We are
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule
 Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule April 5, 2010 A Functions of two variables Suppose that γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)) is a differentiable parametrized curve in R 3 which lies on the surface S defined
Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule April 5, 2010 A Functions of two variables Suppose that γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)) is a differentiable parametrized curve in R 3 which lies on the surface S defined
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus
 Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
The Divergence Theorem
 The Divergence Theorem MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2011 Green s Theorem Revisited Green s Theorem: M(x, y) dx + N(x, y) dy = C R ( N x M ) da y y x Green
The Divergence Theorem MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2011 Green s Theorem Revisited Green s Theorem: M(x, y) dx + N(x, y) dy = C R ( N x M ) da y y x Green
This exam will be cumulative. Consult the review sheets for the midterms for reviews of Chapters
 Final exam review Math 265 Fall 2007 This exam will be cumulative. onsult the review sheets for the midterms for reviews of hapters 12 15. 16.1. Vector Fields. A vector field on R 2 is a function F from
Final exam review Math 265 Fall 2007 This exam will be cumulative. onsult the review sheets for the midterms for reviews of hapters 12 15. 16.1. Vector Fields. A vector field on R 2 is a function F from
Functions of Several Variables
 Functions of Several Variables Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Philippe B Laval KSU April 7, 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) Functions of Several Variables April 7, 2012 1 / 19 Introduction
Functions of Several Variables Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Philippe B Laval KSU April 7, 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) Functions of Several Variables April 7, 2012 1 / 19 Introduction
MATH 200 (Fall 2016) Exam 1 Solutions (a) (10 points) Find an equation of the sphere with center ( 2, 1, 4).
 MATH 00 (Fall 016) Exam 1 Solutions 1 1. (a) (10 points) Find an equation of the sphere with center (, 1, 4). (x ( )) + (y 1) + (z ( 4)) 3 (x + ) + (y 1) + (z + 4) 9 (b) (10 points) Find an equation of
MATH 00 (Fall 016) Exam 1 Solutions 1 1. (a) (10 points) Find an equation of the sphere with center (, 1, 4). (x ( )) + (y 1) + (z ( 4)) 3 (x + ) + (y 1) + (z + 4) 9 (b) (10 points) Find an equation of
First of all, we need to know what it means for a parameterize curve to be differentiable. FACT:
 CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV. Exam I (Friday, April 29) will cover sections
 REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
Math 209, Fall 2009 Homework 3
 Math 209, Fall 2009 Homework 3 () Find equations of the tangent plane and the normal line to the given surface at the specified point: x 2 + 2y 2 3z 2 = 3, P (2,, ). Solution Using implicit differentiation
Math 209, Fall 2009 Homework 3 () Find equations of the tangent plane and the normal line to the given surface at the specified point: x 2 + 2y 2 3z 2 = 3, P (2,, ). Solution Using implicit differentiation
MA 243 Calculus III Fall Assignment 1. Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals)
 MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
MATH 261 FALL 2000 FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS. 1. This test booklet has 14 pages including this one. There are 25 questions, each worth 8 points.
 MATH 261 FALL 2 FINAL EXAM STUDENT NAME - STUDENT ID - RECITATION HOUR - RECITATION INSTRUCTOR INSTRUCTOR - INSTRUCTIONS 1. This test booklet has 14 pages including this one. There are 25 questions, each
MATH 261 FALL 2 FINAL EXAM STUDENT NAME - STUDENT ID - RECITATION HOUR - RECITATION INSTRUCTOR INSTRUCTOR - INSTRUCTIONS 1. This test booklet has 14 pages including this one. There are 25 questions, each
12.7 Tangent Planes and Normal Lines
 .7 Tangent Planes and Normal Lines Tangent Plane and Normal Line to a Surface Suppose we have a surface S generated by z f(x,y). We can represent it as f(x,y)-z 0 or F(x,y,z) 0 if we wish. Hence we can
.7 Tangent Planes and Normal Lines Tangent Plane and Normal Line to a Surface Suppose we have a surface S generated by z f(x,y). We can represent it as f(x,y)-z 0 or F(x,y,z) 0 if we wish. Hence we can
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations
 27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6. ) is graphed below:
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Solution of final examination
 of final examination Math 20, pring 201 December 9, 201 Problem 1 Let v(t) (2t e t ) i j + π cos(πt) k be the velocity of a particle with initial position r(0) ( 1, 0, 2). Find the accelaration at the
of final examination Math 20, pring 201 December 9, 201 Problem 1 Let v(t) (2t e t ) i j + π cos(πt) k be the velocity of a particle with initial position r(0) ( 1, 0, 2). Find the accelaration at the
18.02 Final Exam. y = 0
 No books, notes or calculators. 5 problems, 50 points. 8.0 Final Exam Useful formula: cos (θ) = ( + cos(θ)) Problem. (0 points) a) (5 pts.) Find the equation in the form Ax + By + z = D of the plane P
No books, notes or calculators. 5 problems, 50 points. 8.0 Final Exam Useful formula: cos (θ) = ( + cos(θ)) Problem. (0 points) a) (5 pts.) Find the equation in the form Ax + By + z = D of the plane P
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Review 1. Richard Koch. April 23, 2005
 Review Richard Koch April 3, 5 Curves From the chapter on curves, you should know. the formula for arc length in section.;. the definition of T (s), κ(s), N(s), B(s) in section.4. 3. the fact that κ =
Review Richard Koch April 3, 5 Curves From the chapter on curves, you should know. the formula for arc length in section.;. the definition of T (s), κ(s), N(s), B(s) in section.4. 3. the fact that κ =
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS. Page. 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary Assignments...2
 PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring In-term exam April 11th. Suggested solutions
 Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form
 Differential Geometry Lia Vas Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form Patching up the Coordinate Patches. Recall that a proper coordinate patch of a surface is given by parametric equations x = (x(u,
Differential Geometry Lia Vas Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form Patching up the Coordinate Patches. Recall that a proper coordinate patch of a surface is given by parametric equations x = (x(u,
Lecture 15. Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov Calculus and Vectors. Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations
 Lecture 15 Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov 10131 - Calculus and Vectors Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations Sergei Fedotov (University of Manchester) MATH10131 2011 1 / 5 Lecture 15 1 Length of a
Lecture 15 Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov 10131 - Calculus and Vectors Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations Sergei Fedotov (University of Manchester) MATH10131 2011 1 / 5 Lecture 15 1 Length of a
Gradient and Directional Derivatives
 Gradient and Directional Derivatives MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Given z = f (x, y) we understand that f : gives the rate of change of z in
Gradient and Directional Derivatives MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Given z = f (x, y) we understand that f : gives the rate of change of z in
MAC2313 Final A. a. The vector r u r v lies in the tangent plane of S at a given point. b. S f(x, y, z) ds = R f(r(u, v)) r u r v du dv.
 MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. Let f(x, y, z) be a function continuous in R 3 and let S be a surface parameterized by r(u, v) with the domain of the parameterization given by R; how many of the following are
MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. Let f(x, y, z) be a function continuous in R 3 and let S be a surface parameterized by r(u, v) with the domain of the parameterization given by R; how many of the following are
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253
 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253. Prove that the following differential equations are satisfied by the given functions: (a) 2 u 2 + 2 u y 2 + 2 u z 2 =0,whereu =(x2 + y 2 + z 2 ) /2. (b) x w + y w y +
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253. Prove that the following differential equations are satisfied by the given functions: (a) 2 u 2 + 2 u y 2 + 2 u z 2 =0,whereu =(x2 + y 2 + z 2 ) /2. (b) x w + y w y +
Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals. Textbook: Section 16.2
 Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals Textbook: Section 16.2 Warm-Up: Derivatives of Vector Functions Suppose r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) ˆk parameterizes a curve C. The vector: is: r (t)
Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals Textbook: Section 16.2 Warm-Up: Derivatives of Vector Functions Suppose r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) ˆk parameterizes a curve C. The vector: is: r (t)
Name: Class: Date: 1. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint.
 . Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
5. y 2 + z 2 + 4z = 0 correct. 6. z 2 + x 2 + 2x = a b = 4 π
 M408D (54690/95/00), Midterm #2 Solutions Multiple choice questions (20 points) See last two pages. Question #1 (25 points) Dene the vector-valued function r(t) = he t ; 2; 3e t i: a) At what point P (x
M408D (54690/95/00), Midterm #2 Solutions Multiple choice questions (20 points) See last two pages. Question #1 (25 points) Dene the vector-valued function r(t) = he t ; 2; 3e t i: a) At what point P (x
Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations
 February 21, 2007 Tangent Planes Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Let P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) be a point on S. Tangent
February 21, 2007 Tangent Planes Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Let P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) be a point on S. Tangent
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral
 Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
MATH 2400: CALCULUS 3 MAY 9, 2007 FINAL EXAM
 MATH 4: CALCULUS 3 MAY 9, 7 FINAL EXAM I have neither given nor received aid on this exam. Name: 1 E. Kim................ (9am) E. Angel.............(1am) 3 I. Mishev............ (11am) 4 M. Daniel...........
MATH 4: CALCULUS 3 MAY 9, 7 FINAL EXAM I have neither given nor received aid on this exam. Name: 1 E. Kim................ (9am) E. Angel.............(1am) 3 I. Mishev............ (11am) 4 M. Daniel...........
Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( ) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent
 Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
13.1. Functions of Several Variables. Introduction to Functions of Several Variables. Functions of Several Variables. Objectives. Example 1 Solution
 13 Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Understand
13 Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Understand
Math 241 Spring 2015 Final Exam Solutions
 Math 4 Spring 5 Final Exam Solutions. Find the equation of the plane containing the line x y z+ and the point (,,). Write [ pts] your final answer in the form ax+by +cz d. Solution: A vector parallel to
Math 4 Spring 5 Final Exam Solutions. Find the equation of the plane containing the line x y z+ and the point (,,). Write [ pts] your final answer in the form ax+by +cz d. Solution: A vector parallel to
16.6. Parametric Surfaces. Parametric Surfaces. Parametric Surfaces. Vector Calculus. Parametric Surfaces and Their Areas
 16 Vector Calculus 16.6 and Their Areas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and Their Areas Here we use vector functions to describe more general
16 Vector Calculus 16.6 and Their Areas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and Their Areas Here we use vector functions to describe more general
Chapter 11. Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Kevin James. MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule
 MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule Theorem (Chain Rule - Case 1) Suppose that z = f (x, y) is a differentiable function and that x(t) and y(t) are both differentiable functions as well. Then, dz dt
MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule Theorem (Chain Rule - Case 1) Suppose that z = f (x, y) is a differentiable function and that x(t) and y(t) are both differentiable functions as well. Then, dz dt
Math (Spring 2009): Lecture 5 Planes. Parametric equations of curves and lines
 Math 18.02 (Spring 2009): Lecture 5 Planes. Parametric equations of curves and lines February 12 Reading Material: From Simmons: 17.1 and 17.2. Last time: Square Systems. Word problem. How many solutions?
Math 18.02 (Spring 2009): Lecture 5 Planes. Parametric equations of curves and lines February 12 Reading Material: From Simmons: 17.1 and 17.2. Last time: Square Systems. Word problem. How many solutions?
d f(g(t), h(t)) = x dt + f ( y dt = 0. Notice that we can rewrite the relationship on the left hand side of the equality using the dot product: ( f
 Gradients and the Directional Derivative In 14.3, we discussed the partial derivatives f f and, which tell us the rate of change of the x y height of the surface defined by f in the x direction and the
Gradients and the Directional Derivative In 14.3, we discussed the partial derivatives f f and, which tell us the rate of change of the x y height of the surface defined by f in the x direction and the
Multiple Integrals. max x i 0
 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Math 126 Final Examination Autumn CHECK that your exam contains 9 problems on 10 pages.
 Math 126 Final Examination Autumn 2016 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name CHECK that your exam contains 9 problems on 10 pages. This exam is closed book. You
Math 126 Final Examination Autumn 2016 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name CHECK that your exam contains 9 problems on 10 pages. This exam is closed book. You
Math 2130 Practice Problems Sec Name. Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate.
 Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
MA 174: Multivariable Calculus Final EXAM (practice) NO CALCULATORS, BOOKS, OR PAPERS ARE ALLOWED. Use the back of the test pages for scrap paper.
 MA 174: Multivariable alculus Final EXAM (practice) NAME lass Meeting Time: NO ALULATOR, BOOK, OR PAPER ARE ALLOWED. Use the back of the test pages for scrap paper. Points awarded 1. (5 pts). (5 pts).
MA 174: Multivariable alculus Final EXAM (practice) NAME lass Meeting Time: NO ALULATOR, BOOK, OR PAPER ARE ALLOWED. Use the back of the test pages for scrap paper. Points awarded 1. (5 pts). (5 pts).
Polar (BC Only) They are necessary to find the derivative of a polar curve in x- and y-coordinates. The derivative
 Polar (BC Only) Polar coordinates are another way of expressing points in a plane. Instead of being centered at an origin and moving horizontally or vertically, polar coordinates are centered at the pole
Polar (BC Only) Polar coordinates are another way of expressing points in a plane. Instead of being centered at an origin and moving horizontally or vertically, polar coordinates are centered at the pole
Preliminary Mathematics of Geometric Modeling (3)
 Preliminary Mathematics of Geometric Modeling (3) Hongxin Zhang and Jieqing Feng 2006-11-27 State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University Differential Geometry of Surfaces Tangent plane and surface normal
Preliminary Mathematics of Geometric Modeling (3) Hongxin Zhang and Jieqing Feng 2006-11-27 State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University Differential Geometry of Surfaces Tangent plane and surface normal
Dr. Allen Back. Nov. 21, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back of Nov. 21, 2014 The most important thing you should know (e.g. for exams and homework) is how to setup (and perhaps compute if not too hard) surface integrals, triple integrals, etc. But
Dr. Allen Back of Nov. 21, 2014 The most important thing you should know (e.g. for exams and homework) is how to setup (and perhaps compute if not too hard) surface integrals, triple integrals, etc. But
WW Prob Lib1 Math course-section, semester year
 WW Prob Lib Math course-section, semester year WeBWorK assignment due /25/06 at :00 PM..( pt) Consider the parametric equation x = 7(cosθ + θsinθ) y = 7(sinθ θcosθ) What is the length of the curve for
WW Prob Lib Math course-section, semester year WeBWorK assignment due /25/06 at :00 PM..( pt) Consider the parametric equation x = 7(cosθ + θsinθ) y = 7(sinθ θcosθ) What is the length of the curve for
Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation
 Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, y = f (x), the rate of change of the dependent variable can dy be found unambiguously by differentiation: f x. In this chapter we explore
Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, y = f (x), the rate of change of the dependent variable can dy be found unambiguously by differentiation: f x. In this chapter we explore
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
1. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) = 0 implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two:
 Final Solutions. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two: z f(x, y), y g(x, z), x h(y, z). If F is differentiable
Final Solutions. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two: z f(x, y), y g(x, z), x h(y, z). If F is differentiable
Calculus III Meets the Final
 Calculus III Meets the Final Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky December 7, 2018 Homework Review for Final Exam on Thursday, December 13, 6:00-8:00 PM Be sure you know which room to go to for the final!
Calculus III Meets the Final Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky December 7, 2018 Homework Review for Final Exam on Thursday, December 13, 6:00-8:00 PM Be sure you know which room to go to for the final!
ds dt ds 1 dt 1 dt v v v dt ds and the normal vector is given by N
 Normal Vectors and Curvature In the last section, we stated that reparameterization by arc length would help us analyze the twisting and turning of a curve. In this section, we ll see precisely how to
Normal Vectors and Curvature In the last section, we stated that reparameterization by arc length would help us analyze the twisting and turning of a curve. In this section, we ll see precisely how to
3. The three points (2, 4, 1), (1, 2, 2) and (5, 2, 2) determine a plane. Which of the following points is in that plane?
 Math 4 Practice Problems for Midterm. A unit vector that is perpendicular to both V =, 3, and W = 4,, is (a) V W (b) V W (c) 5 6 V W (d) 3 6 V W (e) 7 6 V W. In three dimensions, the graph of the equation
Math 4 Practice Problems for Midterm. A unit vector that is perpendicular to both V =, 3, and W = 4,, is (a) V W (b) V W (c) 5 6 V W (d) 3 6 V W (e) 7 6 V W. In three dimensions, the graph of the equation
Math 126C: Week 3 Review
 Math 126C: Week 3 Review Note: These are in no way meant to be comprehensive reviews; they re meant to highlight the main topics and formulas for the week. Doing homework and extra problems is always the
Math 126C: Week 3 Review Note: These are in no way meant to be comprehensive reviews; they re meant to highlight the main topics and formulas for the week. Doing homework and extra problems is always the
Let and be a differentiable function. Let Then be the level surface given by
 Module 12 : Total differential, Tangent planes and normals Lecture 35 : Tangent plane and normal [Section 35.1] > Objectives In this section you will learn the following : The notion tangent plane to a
Module 12 : Total differential, Tangent planes and normals Lecture 35 : Tangent plane and normal [Section 35.1] > Objectives In this section you will learn the following : The notion tangent plane to a
Curves: We always parameterize a curve with a single variable, for example r(t) =
 Final Exam Topics hapters 16 and 17 In a very broad sense, the two major topics of this exam will be line and surface integrals. Both of these have versions for scalar functions and vector fields, and
Final Exam Topics hapters 16 and 17 In a very broad sense, the two major topics of this exam will be line and surface integrals. Both of these have versions for scalar functions and vector fields, and
Surfaces. Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University
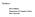 Surfaces Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Representations 1. Parametric Plane, Sphere, Tensor Product x = f (s,t) y = g(s,t) z = h(s,t) 2. Algebraic Plane, Sphere, Torus F(x,
Surfaces Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Representations 1. Parametric Plane, Sphere, Tensor Product x = f (s,t) y = g(s,t) z = h(s,t) 2. Algebraic Plane, Sphere, Torus F(x,
Updated: August 24, 2016 Calculus III Section Math 232. Calculus III. Brian Veitch Fall 2015 Northern Illinois University
 Updated: August 24, 216 Calculus III Section 1.2 Math 232 Calculus III Brian Veitch Fall 215 Northern Illinois University 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves Definition 1: First Derivative of a Parametric
Updated: August 24, 216 Calculus III Section 1.2 Math 232 Calculus III Brian Veitch Fall 215 Northern Illinois University 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves Definition 1: First Derivative of a Parametric
14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations
 14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations Marius Ionescu October 15, 2012 Marius Ionescu () 14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations October 15, 2012 1 / 13 Tangent Planes Marius Ionescu ()
14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations Marius Ionescu October 15, 2012 Marius Ionescu () 14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations October 15, 2012 1 / 13 Tangent Planes Marius Ionescu ()
Tangents of Parametric Curves
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 32 Notes These notes correspond to Section 92 in the text Tangents of Parametric Curves When a curve is described by an equation of the form y = f(x),
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 32 Notes These notes correspond to Section 92 in the text Tangents of Parametric Curves When a curve is described by an equation of the form y = f(x),
3.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 288 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector 3.6.1 Functions of two Variables Directional Derivatives Let us first quickly review, one more time, te
288 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector 3.6.1 Functions of two Variables Directional Derivatives Let us first quickly review, one more time, te
MATH 234. Excercises on Integration in Several Variables. I. Double Integrals
 MATH 234 Excercises on Integration in everal Variables I. Double Integrals Problem 1. D = {(x, y) : y x 1, 0 y 1}. Compute D ex3 da. Problem 2. Find the volume of the solid bounded above by the plane 3x
MATH 234 Excercises on Integration in everal Variables I. Double Integrals Problem 1. D = {(x, y) : y x 1, 0 y 1}. Compute D ex3 da. Problem 2. Find the volume of the solid bounded above by the plane 3x
Dr. Allen Back. Nov. 19, 2014
 Why of Dr. Allen Back Nov. 19, 2014 Graph Picture of T u, T v for a Lat/Long Param. of the Sphere. Why of Graph Basic Picture Why of Graph Why Φ(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)) Tangents T u = (x u,
Why of Dr. Allen Back Nov. 19, 2014 Graph Picture of T u, T v for a Lat/Long Param. of the Sphere. Why of Graph Basic Picture Why of Graph Why Φ(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)) Tangents T u = (x u,
Math Parametric Surfaces
 Math 13 - Parametric Surfaces Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 15, 019 Homework Homework D is due Wednesday Work on Stewart problems for 16.6: 1-5 odd, 33, 39-49 odd Read section 16.7 for Wednesday,
Math 13 - Parametric Surfaces Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 15, 019 Homework Homework D is due Wednesday Work on Stewart problems for 16.6: 1-5 odd, 33, 39-49 odd Read section 16.7 for Wednesday,
GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 1 CHAPTER 5. GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS 1 INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS Contents 1 Geometry in R 3 2 1.1 Lines...............................................
1 CHAPTER 5. GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS 1 INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS Contents 1 Geometry in R 3 2 1.1 Lines...............................................
Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions
 Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions 1 2 1. Determine whether the two lines L 1 and L 2 described below intersect. If yes, find the point of intersection. If not, say whether they
Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions 1 2 1. Determine whether the two lines L 1 and L 2 described below intersect. If yes, find the point of intersection. If not, say whether they
Daily WeBWorK, #1. This means the two planes normal vectors must be multiples of each other.
 Daily WeBWorK, #1 Consider the ellipsoid x 2 + 3y 2 + z 2 = 11. Find all the points where the tangent plane to this ellipsoid is parallel to the plane 2x + 3y + 2z = 0. In order for the plane tangent to
Daily WeBWorK, #1 Consider the ellipsoid x 2 + 3y 2 + z 2 = 11. Find all the points where the tangent plane to this ellipsoid is parallel to the plane 2x + 3y + 2z = 0. In order for the plane tangent to
Name: Final Exam Review. (b) Reparameterize r(t) with respect to arc length measured for the point (1, 0, 1) in the direction of increasing t.
 MATH 127 ALULU III Name: 1. Let r(t) = e t i + e t sin t j + e t cos t k (a) Find r (t) Final Exam Review (b) Reparameterize r(t) with respect to arc length measured for the point (1,, 1) in the direction
MATH 127 ALULU III Name: 1. Let r(t) = e t i + e t sin t j + e t cos t k (a) Find r (t) Final Exam Review (b) Reparameterize r(t) with respect to arc length measured for the point (1,, 1) in the direction
Graded Assignment 2 Maple plots
 Graded Assignment 2 Maple plots The Maple part of the assignment is to plot the graphs corresponding to the following problems. I ll note some syntax here to get you started see tutorials for more. Problem
Graded Assignment 2 Maple plots The Maple part of the assignment is to plot the graphs corresponding to the following problems. I ll note some syntax here to get you started see tutorials for more. Problem
8.1 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing
 Fall 2017 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 8.1 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Outline Ray-Surface Intersections Special cases: sphere, polygon Barycentric coordinates 2 Outline
Fall 2017 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 8.1 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Outline Ray-Surface Intersections Special cases: sphere, polygon Barycentric coordinates 2 Outline
Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area
 Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area What to know: 1. Be able to parametrize standard surfaces, like the ones in the handout.. Be able to understand what a parametrized surface looks like (for this class,
Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area What to know: 1. Be able to parametrize standard surfaces, like the ones in the handout.. Be able to understand what a parametrized surface looks like (for this class,
MA FINAL EXAM Green April 30, 2018 EXAM POLICIES
 MA 6100 FINAL EXAM Green April 0, 018 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN! Write the following in the TEST/QUIZ NUMBER boxes (and blacken
MA 6100 FINAL EXAM Green April 0, 018 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN! Write the following in the TEST/QUIZ NUMBER boxes (and blacken
Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 16 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Ray-Surface Intersection Barycentric Coordinates [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Ray-Surface Intersections
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 16 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Ray-Surface Intersection Barycentric Coordinates [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Ray-Surface Intersections
An introduction to interpolation and splines
 An introduction to interpolation and splines Kenneth H. Carpenter, EECE KSU November 22, 1999 revised November 20, 2001, April 24, 2002, April 14, 2004 1 Introduction Suppose one wishes to draw a curve
An introduction to interpolation and splines Kenneth H. Carpenter, EECE KSU November 22, 1999 revised November 20, 2001, April 24, 2002, April 14, 2004 1 Introduction Suppose one wishes to draw a curve
MATH 230 FALL 2004 FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, :20-2:10 PM
 Problem Score 1 2 Name: SID: Section: Instructor: 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Total MATH 230 FALL 2004 FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2004 12:20-2:10 PM INSTRUCTIONS There are 12 problems on this exam for a total
Problem Score 1 2 Name: SID: Section: Instructor: 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Total MATH 230 FALL 2004 FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2004 12:20-2:10 PM INSTRUCTIONS There are 12 problems on this exam for a total
CS770/870 Spring 2017 Ray Tracing Implementation
 Useful ector Information S770/870 Spring 07 Ray Tracing Implementation Related material:angel 6e: h.3 Ray-Object intersections Spheres Plane/Polygon Box/Slab/Polyhedron Quadric surfaces Other implicit/explicit
Useful ector Information S770/870 Spring 07 Ray Tracing Implementation Related material:angel 6e: h.3 Ray-Object intersections Spheres Plane/Polygon Box/Slab/Polyhedron Quadric surfaces Other implicit/explicit
the straight line in the xy plane from the point (0, 4) to the point (2,0)
 Math 238 Review Problems for Final Exam For problems #1 to #6, we define the following paths vector fields: b(t) = the straight line in the xy plane from the point (0, 4) to the point (2,0) c(t) = the
Math 238 Review Problems for Final Exam For problems #1 to #6, we define the following paths vector fields: b(t) = the straight line in the xy plane from the point (0, 4) to the point (2,0) c(t) = the
14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector 1. Directional Derivatives. Recall z = f (x, y) and the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as f (x 0 + h, y 0 ) f (x 0, y 0 ) f x (x 0, y 0
14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector 1. Directional Derivatives. Recall z = f (x, y) and the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as f (x 0 + h, y 0 ) f (x 0, y 0 ) f x (x 0, y 0
Lecture 6: Chain rule, Mean Value Theorem, Tangent Plane
 Lecture 6: Chain rule, Mean Value Theorem, Tangent Plane Rafikul Alam Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Chain rule Theorem-A: Let x : R R n be differentiable at t 0 and f : R n R be differentiable
Lecture 6: Chain rule, Mean Value Theorem, Tangent Plane Rafikul Alam Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Chain rule Theorem-A: Let x : R R n be differentiable at t 0 and f : R n R be differentiable
Math 348 Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces
 Math 348 Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces Lecture 3 Curves in Calculus Xinwei Yu Sept. 12, 2017 CAB 527, xinwei2@ualberta.ca Department of Mathematical & Statistical Sciences University of
Math 348 Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces Lecture 3 Curves in Calculus Xinwei Yu Sept. 12, 2017 CAB 527, xinwei2@ualberta.ca Department of Mathematical & Statistical Sciences University of
