Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06)
|
|
|
- Mariah Angel McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06) Introduction You need to carry out the stress analysis of an outdoor water tank. Since it has quarter symmetry you start by building only one-fourth of the geometry. Assume that the side wall has a small lip that extends below the tank bottom. That will give you more options on how you may need to restrain the part. Begin by selecting English units, but also plan to activate dual units in millimeters so you have the option to display English or both units in the dimensions: 1. Pick Tools Options Document Properties Units and select the IPS Unit System, select the number of decimal places to display and pick millimeters as the optional dual system (if you wish), as illustrated in Figure If you decide to use dual units then turn them on in the same panel by checking dual dimension display under Document Properties Detailing, as given in Figure 2. Figure 1 Selecting drawing units Figure 2 Option for dual units dimension display Page 1 of 15
2 SolidWorks Part construction Begin the part construction by inserting a sketch in the top plane with a true shape view (Figure 3). Specify the dimensions shown for a quarter of the base plate area in Figure 4. Figure 3 Sketching true shape in the top view Figure 4 Base plate sizes Figure 5 Beginning the extrusion Next you need to select the thickness of the base plate. That is needed both for the extrusion to form the (thin) solid, but also to later set the structural stiffness. The stretching stiffness of a surface is proportional to its thickness, but its bending stiffness is proportional to the cube of the thickness. Choose a thickness of 0.20 inches for that component. After the stress analysis is completed it may be necessary to change this parametric dimension during a design revision. To extrude the bottom thickness: 1. Begin with Extruded Boss/Base in the utility menu (Figure 5). 2. That brings up the Extrude panel of Figure 6 where you type in the chosen base thickness and pick OK (the green arrow button) to execute the extrude process. This is a thin walled tank, so the extrusion of the bottom is hard to see ( Figure 7). Page 2 of 15
3 The outer wall of the tank will also be another thin layer of material. Its thickness (and thus its stiffness) does not have to be the same as the base, so start with a thickness of 0.15 inches. Use that value as the only new parametric dimension on the outer edge of the bottom: 1. Right click Top Insert Sketch, in Figure 7, to prepare to sketch a thin edge to extrude in both directions away from the base (for the wall and supporting lip). 2. Sketch the 4 lines and 2 arcs adjacent to the curved edge so they are easy to see. 3. Then set the actual dimension of the wall thickness as 0.15 to uniquely define the wall area to be extruded (Figure 8). Figure 6 Single direction extrude of the base area Figure 7 Preparing to sketch the thin wall region Page 3 of 15
4 Figure 8 Sketch and then dimension the thin wall The tank wall will be 72 inches (6 feet) above the bottom, while the support lip will be about 3 inches below. Thus, to construct these segments: 1. Select the Extrude Boss/Base option. 2. In the Extrude panel set Direction 1 for the upper (water confining) wall and Direction 2 for the support (lower) wall, as in Figure 9. Figure 10 shows the final part, as viewed from below. Figure 9 Two direction extrusion of the wall Page 4 of 15
5 CosmosWorks static studies Figure 10 The final quarter symmetry part CosmosWorks Manager At this point you are ready to move into the Cosmos finite element study interface by selecting the CosmosWorks Manager (CWManager) icon: 1. Right click on the top name to access Study which opens the Study panel. 2. Assign a Study name, choose Static for the Analysis type. 3. Define the Mesh type to be mid-surface shells, as in Figure 11. Figure 11 Entering CosmosWorks static shell analysis Define the material At this point Mid-surface Shell will appear in the CWManger menu: Page 5 of 15
6 1. Right click on it to apply material data to the shell. The tank is to be made of galvanized steel. 2. Pick Apply Material to All Material panel From library files button Steel and select galvanized steel as illustrated in Figure 12. Figure 12 Selecting a shell material 3. Still in the Material panel, set the Units to English. 4. Accept the linear elastic isotropic default Type, OK. Note that the yield strength (SIGYLD on the bottom line of Figure 13), taken from a uniaxial tension test, is about 29.6e3 psi. Since you selected a ductile material, that material yield property will later be compared to the Von Mises, or Effective, Stress. Our Safety of Factor (for this material) will be this yield stress property divided by the Von Mises Stress. Figure 13 Some properties of galvanized steel Initial Restraints Remember that the actual displacement supports (restraints) can be unclear and you usually need to check for a few possibilities. What looks like minor changes in the restraints of a part Page 6 of 15
7 can cause large changes in the displacements and/or stresses. Also, remember that in a static analysis you must always provide enough restraints to prevent all of the six rigid body motions (RBM) possible in a three-dimensional part. In this example you will use an initial set of restraints, carry out the analysis, evaluate the study, and add new restraints for an additional analysis. Here, begin by supporting the bottom tank edge against vertical motion (only). That prevents 3 rigid body motions: motion in the vertical direction and rotation about the two horizontal axes. Eliminate the 3 RBM that remain: 1. Right click Load/Restraints Restraints (Figure 14) to get the Restraint panel. 2. Zoom in on the bottom wall and pick the flat bottom face and enforce no displacement perpendicular to it. 3. As seen in Figure 15, you first pull down to On flat face to set the Type of entity being restrained, then in the zoomed graphics window you pick the flat bottom edge surface so it enters the Selected entities list. 4. Finally, in the bottom Displacement list you pick the normal-to icon,, and accept the default value of zero. 5. Selecting OK or Preview (eyeglass) icon will give you a graphical verification of the restraints. If the imposed displacements were not zero you would have to choose the correct Units before typing in the non-zero prescribed displacement normal to the face. This is a physical restraint. The next two restraints come from utilizing symmetry as a modeling tool. Since material has been removed at each of the symmetry cutting planes, you must impose displacement restraints that act like the removed material. Figure 14 Activating the Restraints panel Page 7 of 15
8 Figure 15 Bottom edge vertical displacement restraints The symmetry planes are the front (x-z) and left (y-z) planes. To impose symmetry restraints: 1. Activate the Restraint panel (as in Figure 14) and the On flat face Type. Zoom in on and pick the flat front plane surface. Set the symmetry condition of no displacement perpendicular to it. That prevents RBM to the back and RBM rotation about a vertical axis (so 1 RBM remains). Since a shell model will be invoked it, is also necessary to restrain the rotation vector tangent to that plane (i.e. its 2 components in that plane are identically zero). These steps are seen in the next Restraint panel of Figure 16. Note that we also get a visual check of the previous vertical support of the bottom-most face, and a graphical preview of the new displacement and rotation restraints. 2. The final (third) symmetry restraint will go on the left flat face. A zero normal displacement there eliminates the last RBM which was in the left-right direction. 3. Again, for a shell the two in-plane rotation components are zero on a symmetry plane. In the Restraint panel of pick On flat face Type and zero the normal displacement and enplane rotations and preview the restraints given in Figure 17. At this point a total of three sets of generalized displacement restraints exist and all rigid body motions have been eliminated. Remaining tasks include specifying the hydrostatic pressure loads, which will require defining a local coordinate system, and creating the shell mesh. Page 8 of 15
9 Figure 16 Envoking front plane shell symmetry Shell mesh generation You should expect the highest bending stresses will be near the tank bottom-side wall junction region. Thus, we will eventually probably have to control the mesh to make the smallest elements occur there. However, for the first analysis you can accept the default mesh generation: 1. Right click on Mesh Create (and skip Apply Control for now). 2. In the Mesh panel select a coarse Mesh Parameter OK for an initial crude mesh. The first mesh appears. The straight side wall and the curved lip wall need to be flipped (so the shell top will always be against the fluid). 3. Control select those two segments and then right click Mesh and Flip shell elements, as shown in Figure 18. Now, all the (gray) shell tops should match in the fluid contact surfaces (Figure 19). Page 9 of 15
10 Figure 17 Envoking the left face shell symmetry restraints Figure 18 Building an crude initial shell mesh Page 10 of 15
11 Figure 19 Re-orientated initial mesh. Variable pressure loading In the CWManager portion of Figure 19 you can see there are three active restraint sets, but no loads. In order to apply a variable pressure you first need to create a local coordinate system. The worst case water load is when the tank is completely full. Thus, prescribe a hydrostatic pressure load increasing from the top edge by defining a new local coordinate system: 1. Go to Insert Reference Geometry Coordinate System to make the Coordinate System panel appear. 2. First, locate the origin at the top, and then put the local Y-axis downward along a vertical line (so pressure increases directly with the local Y value). 3. It is the only axis you will use so accept the default orientations for the other two local axes. Those steps are shown in Figure 20. There are several uses for local coordinate systems so remember this process. [WARNING: When a variable pressure load changes signs CosmosWorks expects a split line or split surface to be inserted into the model along the zero value contour.] Page 11 of 15
12 Figure 20 Picking a local coordinate origin and Y axis Continue with the application of the pressure loading: 1. Turn on the View Coordinate System. 2. Select Load/Restraints Pressure to impose the hydrostatic pressure load in the local Y-direction. 3. In the Pressure panel use normal to selected face as the Pressure Type. 4. Then pick the surfaces of the tank walls and bottom (but not the small outside bottom support edges). 5. As shown in Figure 21, select the Pressure Value Units as psi (English). 6. Set the pressure dimensional scale Value to psi (since the water density, γ, is lb/in 3 ). That value is multiplied times the non-dimensional quadratic polynomial, in the local x-y coordinate directions, activated by checking a Nonuniform Distribution. 7. Set all the non-dimensional polynomial coefficients to zero except for the unity Y term (so as to create a linear pressure increase with vertical depth). 8. Picking Preview (the eyeglasses) gives you a visual check of the pressure distribution along the edges of the loaded faces. Run the solution Now you can right click on the model name and select Run to start the first crude mesh analysis. Passing windows will keep you posted on the number of equations being solved and the status of the displacement solution process and post-processing. You should get a notice that the analysis was completed (not a failed message). Then you have access to the various CosmosWorks report and plot options needed to review the first analysis. Post-processing Displacement review Start by double clicking the Displacement Plot1 icon (Figure 22). The default plot is a smoothly filled (Gouraud) contour display of the resultant displacement magnitude and the Page 12 of 15
13 Figure 21 Hydrostatic pressures via a local coordinate system Figure 22 Beginning the post-processing Page 13 of 15
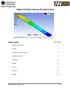
14 Figure 23 Resultant displacement vector plots deformed shape part. However, since displacements are vector quantities consider a vector plot first, as in Figure 23: 1. Access them from a right click, Edit Definitions Displacement Plot. 2. Edit Definitions Vector Plot Options and double click again on the plot icon to create such a view. Still, the contours values are useful at times. If you do not have a color printer and/or if you want a somewhat finer description you may want to change the default plot styles: 1. Click in the graphics window and select Edit Definition Displacement Plot panel Display. 2. Change from the default Gouraud filled image to a Line contour option. 3. Double click again on the Plot icon to get both the magnified deflected shape and the color contours of the displacement values shown in Figure 24. That alternate view may be easier to understand or to plot in grayscale. Stress review Next check the stress levels by double clicking on Stress Plot icon. There are many types of stress evaluations available. The default one is the scalar Von Mises (or Effective) stress. It is actually not a stress but a failure criterion for ductile materials. Since you picked a ductile material it should be examined and compared to the material yield stress (of about 4,000 psi). Figure 25 shows that most of the tank is above the yield point, so you need to change the thickness, the material, and/or the restraint methods. As expected, in that plot, the maximum effective stress occurs near the junction of the tank wall and bottom. That suggests our next mesh should be controlled to give smaller elements in that region. Page 14 of 15
15 Figure 24 Displacement magnitude contours Figure 25 Effective stress distributions Page 15 of 15
16 Next, examine another type of view: 1. Pick Edit Definition Stress plot Display. 2. Chose Vector and Component P1. 3. Then use Color Map with 8 Thin colors. 4. Set the color scale only down 7% from the top of the graphics area. Usually you should check the maximum principal stress vectors to see if the directions of the stresses look reasonable. Often you need to increase their visibility: 1. Pick Vector Plot Options. 2. Dynamically change the Size and Density of the vectors as you watch the plot. As expected, the maximum tension (on the top face of the shell) in Figure 26 occurs in the two segments by the wall-bottom junction. Zooming in on that region you get the principal stress vectors there. (The bottom faces would experience the maximum compression.) Figure 26 Principal stress vectors near the wall-bottom junction Part Revisions This model could also be revised to look at other restrain conditions. For example, if the tank base sits on two 2 x 4 wooden boards (at the bottom edge) you should expect higher stresses. That study would require additional split lines on the current bottom edge lip surface to pick a smaller support surface. Likewise, if you assumed that the tank sinks into the ground (or you eliminate the bottom edge) so the full tank bottom is supported in the vertical direction then you could use the existing geometry. You would just set a vertical (normal only) restraint there. The stresses and deflections would be much smaller in that case. To test that concept, you would only need to add one additional restraint set that provides vertical support to the tank bottom plate. Page 16 of 15
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering. Introduction
 Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering
 Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Here SolidWorks stress simulation tutorials will be re-visited to show how they
Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Here SolidWorks stress simulation tutorials will be re-visited to show how they
16 SW Simulation design resources
 16 SW Simulation design resources 16.1 Introduction This is simply a restatement of the SW Simulation online design scenarios tutorial with a little more visual detail supplied on the various menu picks
16 SW Simulation design resources 16.1 Introduction This is simply a restatement of the SW Simulation online design scenarios tutorial with a little more visual detail supplied on the various menu picks
SDC. Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks. Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003
 Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
The part to be analyzed is the bracket from the tutorial of Chapter 3.
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2007 COSMOSWorks Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the COSMOSWorks finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response of a component
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2007 COSMOSWorks Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the COSMOSWorks finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response of a component
TUTORIAL 2. OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs.
 TUTORIAL 2 OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs. GETTING STARTED: 1. Open the SolidWorks program. 2. Open a new part file.
TUTORIAL 2 OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs. GETTING STARTED: 1. Open the SolidWorks program. 2. Open a new part file.
2: Static analysis of a plate
 2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel.
 Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
SolidWorks. An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs
 An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
PTC Newsletter January 14th, 2002
 PTC Email Newsletter January 14th, 2002 PTC Product Focus: Pro/MECHANICA (Structure) Tip of the Week: Creating and using Rigid Connections Upcoming Events and Training Class Schedules PTC Product Focus:
PTC Email Newsletter January 14th, 2002 PTC Product Focus: Pro/MECHANICA (Structure) Tip of the Week: Creating and using Rigid Connections Upcoming Events and Training Class Schedules PTC Product Focus:
Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University The SolidWorks simulation tutorial on the analysis of an assembly suggested noting another type of boundary condition that is not illustrated
Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University The SolidWorks simulation tutorial on the analysis of an assembly suggested noting another type of boundary condition that is not illustrated
The Essence of Result Post- Processing
 APPENDIX E The Essence of Result Post- Processing Objectives: Manually create the geometry for the tension coupon using the given dimensions then apply finite elements. Manually define material and element
APPENDIX E The Essence of Result Post- Processing Objectives: Manually create the geometry for the tension coupon using the given dimensions then apply finite elements. Manually define material and element
Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2012
 Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2012 Paul M. Kurowski SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2012 Paul M. Kurowski SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
Engineering Analysis with
 Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2013 Paul M. Kurowski SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2013 Paul M. Kurowski SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book:
 Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Introduction to Computer Aided Engineering: Solidworks and Cosmosworks using CosmosXpress
 Introduction to Computer Aided Engineering: Solidworks and Cosmosworks using CosmosXpress Open SolidWorks Tutorial written by Jerry Dutreuil Professor Frank Fisher Stevens Institute of Technology Last
Introduction to Computer Aided Engineering: Solidworks and Cosmosworks using CosmosXpress Open SolidWorks Tutorial written by Jerry Dutreuil Professor Frank Fisher Stevens Institute of Technology Last
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description
 Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Contact Analysis. Learn how to: define surface contact solve a contact analysis display contact results. I-DEAS Tutorials: Simulation Projects
 Contact Analysis I-DEAS Tutorials: Simulation Projects This tutorial shows how to analyze surface contact. The electrical flash contacts in a 35mm camera will be modeled to calculate the contact forces.
Contact Analysis I-DEAS Tutorials: Simulation Projects This tutorial shows how to analyze surface contact. The electrical flash contacts in a 35mm camera will be modeled to calculate the contact forces.
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
CHAPTER 4. Numerical Models. descriptions of the boundary conditions, element types, validation, and the force
 CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: 12 mm mm
 Problem description A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: Prescribed displacement C L 12 mm 48.65 mm A two-dimensional axisymmetric analysis is appropriate here. Data points
Problem description A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: Prescribed displacement C L 12 mm 48.65 mm A two-dimensional axisymmetric analysis is appropriate here. Data points
Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization
 Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner with
Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner with
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 4 Plate With a Hole
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 4 Plate With a Hole Consider the classic example of a circular hole in a rectangular plate of constant thickness. The plate
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 4 Plate With a Hole Consider the classic example of a circular hole in a rectangular plate of constant thickness. The plate
FEA BENDING, TORSION, TENSION, and SHEAR TUTORIAL in CATIA
 1 FEA BENDING, TORSION, TENSION, and SHEAR TUTORIAL in CATIA This tutorial shows the basics of a solid bending, torsional, tension, and shear FEA (Finite Elemental Analysis) model in CATIA. Torsion - page
1 FEA BENDING, TORSION, TENSION, and SHEAR TUTORIAL in CATIA This tutorial shows the basics of a solid bending, torsional, tension, and shear FEA (Finite Elemental Analysis) model in CATIA. Torsion - page
Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer
 Appendix A Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer A.1 INTRODUCTION Pro/ENGINEER is a three-dimensional product design tool that promotes practices in design while ensuring compliance with industry
Appendix A Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer A.1 INTRODUCTION Pro/ENGINEER is a three-dimensional product design tool that promotes practices in design while ensuring compliance with industry
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
Multiframe May 2010 Release Note
 Multiframe 12.02 18 May 2010 Release Note This release note describes the version 12.02 release of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/7. Contents
Multiframe 12.02 18 May 2010 Release Note This release note describes the version 12.02 release of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/7. Contents
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran
 Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior Initial Project Space Setup Static Structural ANSYS ZX Plane
 TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior In this tutorial you will learn how to recognize and deal with a common modeling issues involving stress concentrations
TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior In this tutorial you will learn how to recognize and deal with a common modeling issues involving stress concentrations
Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post
 Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4. ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I. Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC
 Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
Modeling Skills Stress Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mech 417
 Introduction Modeling Skills Stress Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mech 417 Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus,
Introduction Modeling Skills Stress Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mech 417 Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus,
An Overview of Computer Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis
 An Overview of Computer Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Overview... 4 2.0 General Concepts... 4 2.1 What is Computer Aided Design... 4 2.1.1 2D verses
An Overview of Computer Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Overview... 4 2.0 General Concepts... 4 2.1 What is Computer Aided Design... 4 2.1.1 2D verses
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem
 ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem Problem Description In this problem, a segment of an electrical contact switch (steel) is modeled by displacing the upper
ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem Problem Description In this problem, a segment of an electrical contact switch (steel) is modeled by displacing the upper
Sliding Split Tube Telescope
 LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
Installation Guide. Beginners guide to structural analysis
 Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Analysis of Machine Elements Using SolidWorks Simulation 2013
 Analysis of Machine Elements Using SolidWorks Simulation 2013 John R. Steffen, Ph.D., P.E. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com
Analysis of Machine Elements Using SolidWorks Simulation 2013 John R. Steffen, Ph.D., P.E. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com
Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis
 Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis 1. The software is available at the Open Access Labs (OAL) and the Virtual OAL at http://voal.tamu.edu in Programs under the Windows Start menu. The software can also
Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis 1. The software is available at the Open Access Labs (OAL) and the Virtual OAL at http://voal.tamu.edu in Programs under the Windows Start menu. The software can also
Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D
 Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D Buoy Chain Sea Bed Suction Pile Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering 00 Overview
Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D Buoy Chain Sea Bed Suction Pile Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering 00 Overview
SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
TRINITAS. a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis. Introductional Manual
 TRINITAS a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis Introductional Manual Bo Torstenfelt Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Starting the Program
TRINITAS a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis Introductional Manual Bo Torstenfelt Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Starting the Program
Revised Iain A MacLeod
 LUSAS User Guidelines Revised 01.07.15 Iain A MacLeod Contents 1 Geometrical features and meshes... 1 2 Toolbars... 2 3 Inserting points... 2 4 Inserting a line between two points... 2 5 Creating a dataset...
LUSAS User Guidelines Revised 01.07.15 Iain A MacLeod Contents 1 Geometrical features and meshes... 1 2 Toolbars... 2 3 Inserting points... 2 4 Inserting a line between two points... 2 5 Creating a dataset...
SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors. UCF Engineering
 SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors UCF Engineering Solidworks Review Last lesson we discussed several more features that can be added to models in order to increase their complexity. We are now
SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors UCF Engineering Solidworks Review Last lesson we discussed several more features that can be added to models in order to increase their complexity. We are now
Simulation of AJWSP10033_FOLDED _ST_FR
 Phone: 01922 453038 www.hyperon-simulation-and-cad-services.co.uk Simulation of AJWSP10033_FOLDED _ST_FR Date: 06 May 2017 Designer: Study name: AJWSP10033_FOLDED_STATIC Analysis type: Static Description
Phone: 01922 453038 www.hyperon-simulation-and-cad-services.co.uk Simulation of AJWSP10033_FOLDED _ST_FR Date: 06 May 2017 Designer: Study name: AJWSP10033_FOLDED_STATIC Analysis type: Static Description
3D Finite Element Software for Cracks. Version 3.2. Benchmarks and Validation
 3D Finite Element Software for Cracks Version 3.2 Benchmarks and Validation October 217 1965 57 th Court North, Suite 1 Boulder, CO 831 Main: (33) 415-1475 www.questintegrity.com http://www.questintegrity.com/software-products/feacrack
3D Finite Element Software for Cracks Version 3.2 Benchmarks and Validation October 217 1965 57 th Court North, Suite 1 Boulder, CO 831 Main: (33) 415-1475 www.questintegrity.com http://www.questintegrity.com/software-products/feacrack
An Introductory SIGMA/W Example
 1 Introduction An Introductory SIGMA/W Example This is a fairly simple introductory example. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to new SIGMA/W users how to get started, to introduce the usual type of
1 Introduction An Introductory SIGMA/W Example This is a fairly simple introductory example. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to new SIGMA/W users how to get started, to introduce the usual type of
ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IIA FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IIA LOCATION: DPO EXPERIMENT 3D7 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Those who have performed the 3C7 experiment should bring the write-up along to this laboratory Objectives Show that the accuracy
ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IIA LOCATION: DPO EXPERIMENT 3D7 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Those who have performed the 3C7 experiment should bring the write-up along to this laboratory Objectives Show that the accuracy
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5
 ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5 The GREAT Combined Load Problem Moving on to Principal Stresses and von Mises Failure Criteria Open up your ANSYS model
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5 The GREAT Combined Load Problem Moving on to Principal Stresses and von Mises Failure Criteria Open up your ANSYS model
Engineering Optimization
 Engineering Optimization Most engineering design involves using optimization software which minimizes or maximizes a merit or objective function while satisfying functional constraints (such as stress
Engineering Optimization Most engineering design involves using optimization software which minimizes or maximizes a merit or objective function while satisfying functional constraints (such as stress
3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) Figure 3.1 Geometry of a circular footing on a sand layer
 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the Shape before Size Approach Use the
2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the Shape before Size Approach Use the
Static Stress Analysis
 Static Stress Analysis Determine stresses and displacements in a connecting rod assembly. Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000-pound
Static Stress Analysis Determine stresses and displacements in a connecting rod assembly. Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000-pound
Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Introduction Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus, you need
Introduction Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus, you need
MSC/PATRAN LAMINATE MODELER COURSE PAT 325 Workbook
 MSC/PATRAN LAMINATE MODELER COURSE PAT 325 Workbook P3*V8.0*Z*Z*Z*SM-PAT325-WBK - 1 - - 2 - Table of Contents Page 1 Composite Model of Loaded Flat Plate 2 Failure Criteria for Flat Plate 3 Making Plies
MSC/PATRAN LAMINATE MODELER COURSE PAT 325 Workbook P3*V8.0*Z*Z*Z*SM-PAT325-WBK - 1 - - 2 - Table of Contents Page 1 Composite Model of Loaded Flat Plate 2 Failure Criteria for Flat Plate 3 Making Plies
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Workshop 15. Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate
 Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
ME Week 12 Piston Mechanical Event Simulation
 Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis
 Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016
 FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis
 Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition
 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition Objectives: Use MPCs to replicate a Solid with a Surface. Compare stress results of the Solid and Surface 9-1 9-2 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a
LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition Objectives: Use MPCs to replicate a Solid with a Surface. Compare stress results of the Solid and Surface 9-1 9-2 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a
3DEXPERIENCE 2017x FINITE ELEMENT ESSENTIALS IN SDC USING SIMULIA/CATIA APPLICATIONS. Nader G. Zamani
 Nader G. Zamani FINITE ELEMENT ESSENTIALS IN 3DEXPERIENCE 2017x USING SIMULIA/CATIA APPLICATIONS SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Nader G. Zamani FINITE ELEMENT ESSENTIALS IN 3DEXPERIENCE 2017x USING SIMULIA/CATIA APPLICATIONS SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate
 Workshop 9 Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate Objectives Create a geometric representation of a plate. Apply a compression load to two apposite sides of the plate. Run a linear buckling analysis. 9-1
Workshop 9 Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate Objectives Create a geometric representation of a plate. Apply a compression load to two apposite sides of the plate. Run a linear buckling analysis. 9-1
Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
DMU Engineering Analysis Review
 Page 1 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Inserting a CATAnalysis Document Using DMU Space Analysis From CATAnalysis
Page 1 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Inserting a CATAnalysis Document Using DMU Space Analysis From CATAnalysis
Analysis of Composite Aerospace Structures Finite Elements Professor Kelly
 Analysis of Composite Aerospace Structures Finite Elements Professor Kelly John Middendorf #3049731 Assignment #3 I hereby certify that this is my own and original work. Signed, John Middendorf Analysis
Analysis of Composite Aerospace Structures Finite Elements Professor Kelly John Middendorf #3049731 Assignment #3 I hereby certify that this is my own and original work. Signed, John Middendorf Analysis
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench
 Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 LESSON 4 Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam LEGEND 75000. 50000. 25000. 0. -25000. -50000. -75000. 0. 3.50 7.00 10.5 14.0 17.5 21.0 Objectives: Demonstrate multi-step analysis set up in MSC/Advanced_FEA.
LESSON 4 Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam LEGEND 75000. 50000. 25000. 0. -25000. -50000. -75000. 0. 3.50 7.00 10.5 14.0 17.5 21.0 Objectives: Demonstrate multi-step analysis set up in MSC/Advanced_FEA.
Machine Elements Simulation 2017
 Analysis of Machine Elements Using SOLIDWORKS Simulation 2017 Shahin S. Nudehi, Ph.D. John R. Steffen, Ph.D., P.E. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered
Analysis of Machine Elements Using SOLIDWORKS Simulation 2017 Shahin S. Nudehi, Ph.D. John R. Steffen, Ph.D., P.E. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered
Analysis of Machine Elements using SolidWorks Simulation 2010
 Analysis of Machine Elements using SolidWorks Simulation 2010 John R. Steffen, Ph.D., P.E. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation CHAPTER #2 CURVED BEAM ANALYSIS This
Analysis of Machine Elements using SolidWorks Simulation 2010 John R. Steffen, Ph.D., P.E. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation CHAPTER #2 CURVED BEAM ANALYSIS This
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks
 Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Problem description. It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view. 50 radius. Material properties:
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view 30 50 radius 30 Material properties: 5 2 E = 2.07 10 N/mm = 0.29 All dimensions in mm Crack
Problem description It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view 30 50 radius 30 Material properties: 5 2 E = 2.07 10 N/mm = 0.29 All dimensions in mm Crack
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
Getting Started. These tasks should take about 20 minutes to complete. Getting Started
 Getting Started Getting Started This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through your first ELFINI and Generative Part Structural Analysis session, allowing you to get acquainted with the product. You
Getting Started Getting Started This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through your first ELFINI and Generative Part Structural Analysis session, allowing you to get acquainted with the product. You
ANSYS Tutorials. Table of Contents. Grady Lemoine
 ANSYS Tutorials Grady Lemoine Table of Contents Example 1: 2-D Static Stress Analysis in ANSYS...2 Example 2: 3-D Static Stress Analysis...5 Example 3: 2-D Frame With Multiple Materials and Element Types...10
ANSYS Tutorials Grady Lemoine Table of Contents Example 1: 2-D Static Stress Analysis in ANSYS...2 Example 2: 3-D Static Stress Analysis...5 Example 3: 2-D Frame With Multiple Materials and Element Types...10
Stiffened Plate With Pressure Loading
 Supplementary Exercise - 3 Stiffened Plate With Pressure Loading Objective: geometry and 1/4 symmetry finite element model. beam elements using shell element edges. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook Supp3-1
Supplementary Exercise - 3 Stiffened Plate With Pressure Loading Objective: geometry and 1/4 symmetry finite element model. beam elements using shell element edges. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook Supp3-1
Structural Analysis of an Aluminum Spiral Staircase. EMCH 407 Final Project Presented by: Marcos Lopez and Dillan Nguyen
 Structural Analysis of an Aluminum Spiral Staircase EMCH 407 Final Project Presented by: Marcos Lopez and Dillan Nguyen Abstract An old aluminum spiral staircase at Marcos home has been feeling really
Structural Analysis of an Aluminum Spiral Staircase EMCH 407 Final Project Presented by: Marcos Lopez and Dillan Nguyen Abstract An old aluminum spiral staircase at Marcos home has been feeling really
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of. Ansys Workbench 14.0
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench
 Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench Contents Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 2 1. Starting Windows on the MAC... 2 2. Login into Windows... 2 3. Start ANSYS Workbench... 2 4. Configuring
Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench Contents Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 2 1. Starting Windows on the MAC... 2 2. Login into Windows... 2 3. Start ANSYS Workbench... 2 4. Configuring
Introduction to Solid Modeling
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Parametric Modeling 1 Why draw 3D Models? 3D models are easier to interpret. 3D models can be used to perform engineering analysis, finite element analysis (stress, deflection,
Introduction to Solid Modeling Parametric Modeling 1 Why draw 3D Models? 3D models are easier to interpret. 3D models can be used to perform engineering analysis, finite element analysis (stress, deflection,
Memo Block. This lesson includes the commands Sketch, Extruded Boss/Base, Extruded Cut, Shell, Polygon and Fillet.
 Commands Used New Part This lesson includes the commands Sketch, Extruded Boss/Base, Extruded Cut, Shell, Polygon and Fillet. Click File, New on the standard toolbar. Select Part from the New SolidWorks
Commands Used New Part This lesson includes the commands Sketch, Extruded Boss/Base, Extruded Cut, Shell, Polygon and Fillet. Click File, New on the standard toolbar. Select Part from the New SolidWorks
ES 128: Computer Assignment #4. Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010
 ES 128: Computer Assignment #4 Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010 Task 1. Study an elastic-plastic indentation problem. This problem combines plasticity with contact mechanics and has many rich aspects.
ES 128: Computer Assignment #4 Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010 Task 1. Study an elastic-plastic indentation problem. This problem combines plasticity with contact mechanics and has many rich aspects.
CSiBridge 2014 (Version ) Release Notes
 CSiBridge 2014 (Version 16.0.1) Release Notes Copyright Computers and Structures, Inc., 2013 Notice Date: 2013-09-27 This file lists all changes made to CSiBridge since the previous version. Most changes
CSiBridge 2014 (Version 16.0.1) Release Notes Copyright Computers and Structures, Inc., 2013 Notice Date: 2013-09-27 This file lists all changes made to CSiBridge since the previous version. Most changes
Multiframe Oct 2008
 Multiframe 11.01 3 Oct 2008 Windows Release Note This release note describes the Windows version 11.01 of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008.
Multiframe 11.01 3 Oct 2008 Windows Release Note This release note describes the Windows version 11.01 of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008.
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Cosmos- Solidworks Presentation. Presentation Agenda. Introduction to FEA. Introduction to Cosmos. Example #1 (Basic Cosmos Operation)
 Cosmos- Solidworks Presentation Presentation Agenda Created by: Paul Terstappen Jon Vokey Andrew Northcott Mark Howell -Introduction to FEA and Cosmos - -shows the basic uses of the cosmos application
Cosmos- Solidworks Presentation Presentation Agenda Created by: Paul Terstappen Jon Vokey Andrew Northcott Mark Howell -Introduction to FEA and Cosmos - -shows the basic uses of the cosmos application
Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly
 Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000 pound tensile load acting on a connecting rod assembly (consisting of the rod and two pins).
Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000 pound tensile load acting on a connecting rod assembly (consisting of the rod and two pins).
