South Slave Divisional Education Council. Math 10C
|
|
|
- Henry Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 South Slave Divisioal Educatio Coucil Math 10C Curriculum Package February
2 Strad: Measuremet Geeral Outcome: Develop spatial sese ad proportioal reasoig It is expected that studets will: 1. Solve problems that ivolve liear measuremet, usig: SI ad imperial uits of measure estimatio strategies measuremet strategies. [ME, PS, V] 2. Apply proportioal reasoig to problems that ivolve coversios betwee SI ad imperial uits of measure. [C, ME, PS] 3. Solve problems, usig SI ad imperial uits, that ivolve the surface area ad volume of 3-D objects, icludig: right coes right cyliders right prisms right pyramids spheres. [CN, PS, R, V] 4. Develop ad apply the primary trigoometric ratios (sie, cosie, taget) to solve problems that ivolve right triagles. [C, CN, PS, R, T, V] Achievemet Idicators Measurable outcomes The followig set of idicators may be used to assess studet achievemet for each related specific learig outcome. Studets who have fully met the specific learig outcomes are able to: 1.1 Provide referets for liear measuremets, icludig millimetre, cetimetre, metre, kilometre, ich, foot, yard ad mile, ad explai the choices. 1.2 Compare SI ad imperial uits, usig referets. 1.3 Estimate a liear measure, usig a referet, ad explai the process used. 1.4 Justify the choice of uits used for determiig a measuremet i a problemsolvig cotext. 1.5 Solve problems that ivolve liear measure, usig istrumets such as rulers, calipers or tape measures. 1.6 Describe ad explai a persoal strategy used to determie a liear measuremet; e.g., circumferece of a bottle, legth of a curve, perimeter of the base of a irregular 3-D object. 2.1 Explai how proportioal reasoig ca be used to covert a measuremet withi or betwee SI ad imperial systems. 2.2 Solve a problem that ivolves the coversio of uits withi or betwee SI ad imperial systems. 2.3 Verify, usig uit aalysis, a coversio withi or betwee SI ad imperial systems, ad explai the coversio. 2.4 Justify, usig metal mathematics, the reasoableess of a solutio to a coversio problem. 3.1 Sketch a diagram to represet a problem that ivolves surface area or volume. 3.2 Determie the surface area of a right coe, right cylider, right prism, right pyramid or sphere, usig a object or its labelled diagram. 3.3 Determie the volume of a right coe, right cylider, right prism, right pyramid or sphere, usig a object or its labelled diagram. 3.4 Determie a ukow dimesio of a right coe, right cylider, right prism, right pyramid or sphere, give the object s surface area or volume ad the remaiig dimesios. 3.5 Solve a problem that ivolves surface area or volume, give a diagram of a composite 3-D object. 3.6 Describe the relatioship betwee the volumes of: right coes ad right cyliders with the same base ad height right pyramids ad right prisms with the same base ad height. 4.1 Explai the relatioships betwee similar right triagles ad the defiitios of the primary trigoometric ratios. 4.2 Idetify the hypoteuse of a right triagle ad the opposite ad adjacet sides for a give acute agle i the triagle. 4.3 Solve right triagles. 4.4 Solve a problem that ivolves oe or more right triagles by applyig the primary trigoometric ratios or the Pythagorea theorem. 4.5 Solve a problem that ivolves idirect ad direct measuremet, usig the trigoometric ratios, the Pythagorea theorem ad measuremet istrumets such as a cliometer or metre stick. Page 1 of 5
3 Strad: Measuremet Geeral Outcome: Develop spatial sese ad proportioal reasoig It is expected that studets will: 1. Demostrate a uderstadig of factors of whole umbers by determiig the: prime factors greatest commo factor least commo multiple square root cube root. [CN, ME, R] 2. Demostrate a uderstadig of irratioal umbers by: represetig, idetifyig ad simplifyig irratioal umbers orderig irratioal umbers. [CN, ME, R, V] [ICT: C6 2.3] 3. Demostrate a uderstadig of powers with itegral ad ratioal expoets. [C, CN, PS, R] Achievemet Idicators Measurable outcomes The followig set of idicators may be used to assess studet achievemet for each related specific learig outcome. Studets who have fully met the specific learig outcomes are able to: 1.1 Determie the prime factors of a whole umber. 1.2 Explai why the umbers 0 ad 1 have o prime factors. 1.3 Determie, usig a variety of strategies, the greatest commo factor or least commo multiple of a set of whole umbers, ad explai the process. 1.4 Determie, cocretely, whether a give whole umber is a perfect square, a perfect cube or either. 1.5 Determie, usig a variety of strategies, the square root of a perfect square, ad explai the process. 1.6 Determie, usig a variety of strategies, the cube root of a perfect cube, ad explai the process. 1.7 Solve problems that ivolve prime factors, greatest commo factors, least commo multiples, square roots or cube roots. 2.1 Sort a set of umbers ito ratioal ad irratioal umbers. 2.2 Determie a approximate value of a give irratioal umber. 2.3 Approximate the locatios of irratioal umbers o a umber lie, usig a variety of strategies, ad explai the reasoig. 2.4 Order a set of irratioal umbers o a umber lie. 2.5 Express a radical as a mixed radical i simplest form (limited to umerical radicads). 2.6 Express a mixed radical as a etire radical (limited to umerical radicads). 2.7 Explai, usig examples, the meaig of the idex of a radical. 2.8 Represet, usig a graphic orgaizer, the relatioship amog the subsets of the real umbers (atural, whole, iteger, ratioal, irratioal). 3.1 Explai, usig patters, why, a 3.2 Explai, usig patters, why, a 1 = a, > Apply the expoet laws: m ( a )( a ) = a m m a a = a m m ( a ) = a m m ( ab ) = a b a b a = b m+ m, a 0, b 0 1 = a, a 0 to expressios with ratioal ad variable bases ad itegral ad ratioal expoets, ad explai the reasoig. 3.4 Express powers with ratioal expoets as radicals ad vice versa. 3.5 Solve a problem that ivolves expoet laws or radicals. 3.6 Idetify ad correct errors i a simplificatio of a expressio that ivolves powers. Page 2 of 5
4 Strad: Algebra ad Number Geeral Outcome: Develop algebraic reasoig ad umber sese It is expected that studets will: 4. Demostrate a uderstadig of the multiplicatio of polyomial expressios (limited to moomials, biomials ad triomials), cocretely, pictorially ad symbolically. [CN, R, V] 5. Demostrate a uderstadig of commo factors ad triomial factorig, cocretely, pictorially ad symbolically. [C, CN, R, V] Achievemet Idicators Measurable outcomes The followig set of idicators may be used to assess studet achievemet for each related specific learig outcome. Studets who have fully met the specific learig outcomes are able to: (It is iteded that the emphasis of this outcome be o biomial by biomial multiplicatio, with extesio to polyomial by polyomial to establish a geeral patter for multiplicatio.) 4.1 Model the multiplicatio of two give biomials, cocretely or pictorially, ad record the process symbolically. 4.2 Relate the multiplicatio of two biomial expressios to a area model. 4.3 Explai, usig examples, the relatioship betwee the multiplicatio of biomials ad the multiplicatio of two-digit umbers. 4.4 Verify a polyomial product by substitutig umbers for the variables. 4.5 Multiply two polyomials symbolically, ad combie like terms i the product. 4.6 Geeralize ad explai a strategy for multiplicatio of polyomials. 4.7 Idetify ad explai errors i a solutio for a polyomial multiplicatio. 5.1 Determie the commo factors i the terms of a polyomial, ad express the polyomial i factored form. 5.2 Model the factorig of a triomial, cocretely or pictorially, ad record the process symbolically. 5.3 Factor a polyomial that is a differece of squares, ad explai why it is a special case of triomial factorig where b = Idetify ad explai errors i a polyomial factorizatio. 5.5 Factor a polyomial, ad verify by multiplyig the factors. 5.6 Explai, usig examples, the relatioship betwee multiplicatio ad factorig of polyomials. 5.7 Geeralize ad explai strategies used to factor a triomial. 5.8 Express a polyomial as a product of its factors. Strad: Relatios ad Fuctios Geeral Outcome: Develop algebraic ad graphical reasoig through the study of relatios 1. Iterpret ad explai the relatioships amog data, graphs ad situatios. [C, CN, R, T, V] [ICT: C6 4.3, C7 4.2] 2. Demostrate a uderstadig of relatios ad fuctios. [C, R, V] 1.1 Graph, with or without techology, a set of data, ad determie the restrictios o the domai ad rage. 1.2 Explai why data poits should or should ot be coected o the graph for a situatio. 1.3 Describe a possible situatio for a give graph. 1.4 Sketch a possible graph for a give situatio. 1.5 Determie, ad express i a variety of ways, the domai ad rage of a graph, a set of ordered pairs or a table of values. 2.1 Explai, usig examples, why some relatios are ot fuctios but all fuctios are relatios. 2.2 Determie if a set of ordered pairs represets a fuctio. 2.3 Sort a set of graphs as fuctios or o-fuctios. 2.4 Geeralize ad explai rules for determiig whether graphs ad sets of ordered pairs represet fuctios. Page 3 of 5
5 Strad: Relatios ad Fuctios Geeral Outcome: Develop algebraic ad graphical reasoig through the study of relatios It is expected that studets will: 3. Demostrate a uderstadig of slope with respect to: rise ad ru lie segmets ad lies rate of chage parallel lies perpedicular lies. [PS, R, V] 4. Describe ad represet liear relatios, usig: words ordered pairs tables of values graphs equatios. [C, CN, R, V] 5. Determie the characteristics of the graphs of liear relatios, icludig the: itercepts slope domai rage. [CN, PS, R, V] 6. Relate liear relatios expressed i: slope itercept form (y = mx + b) geeral form (Ax + By + C = 0) slope poit form (y y1 = m(x x1)) to their graphs. [CN, R, T, V] [ICT: C6 4.3] Achievemet Idicators Measurable outcomes The followig set of idicators may be used to assess studet achievemet for each related specific learig outcome. Studets who have fully met the specific learig outcomes are able to: 3.1 Determie the slope of a lie segmet by measurig or calculatig the rise ad ru. 3.2 Classify lies i a give set as havig positive or egative slopes. 3.3 Explai the meaig of the slope of a horizotal or vertical lie. 3.4 Explai why the slope of a lie ca be determied by usig ay two poits o that lie. 3.5 Explai, usig examples, slope as a rate of chage. 3.6 Draw a lie, give its slope ad a poit o the lie. 3.7 Determie aother poit o a lie, give the slope ad a poit o the lie. 3.8 Geeralize ad apply a rule for determiig whether two lies are parallel or perpedicular. 3.9 Solve a cotextual problem ivolvig slope. 4.1 Idetify idepedet ad depedet variables i a give cotext. 4.2 Determie whether a situatio represets a liear relatio, ad explai why or why ot. 4.3 Determie whether a graph represets a liear relatio, ad explai why or why ot. 4.4 Determie whether a table of values or a set of ordered pairs represets a liear relatio, ad explai why or why ot. 4.5 Draw a graph from a set of ordered pairs withi a give situatio, ad determie whether the relatioship betwee the variables is liear. 4.6 Determie whether a equatio represets a liear relatio, ad explai why or why ot. 4.7 Match correspodig represetatios of liear relatios. 5.1 Determie the itercepts of the graph of a liear relatio, ad state the itercepts as values or ordered pairs. 5.2 Determie the slope of the graph of a liear relatio. 5.3 Determie the domai ad rage of the graph of a liear relatio. 5.4 Sketch a liear relatio that has oe itercept, two itercepts or a ifiite umber of itercepts. 5.5 Idetify the graph that correspods to a give slope ad y-itercept. 5.6 Idetify the slope ad y-itercept that correspod to a give graph. 5.7 Solve a cotextual problem that ivolves itercepts, slope, domai or rage of a liear relatio. 6.1 Express a liear relatio i differet forms, ad compare the graphs. 6.2 Rewrite a liear relatio i either slope itercept or geeral form. 6.3 Geeralize ad explai strategies for graphig a liear relatio i slope itercept, geeral or slope poit form. 6.4 Graph, with ad without techology, a liear relatio give i slope itercept, geeral or slope poit form, ad explai the strategy used to create the graph. 6.5 Idetify equivalet liear relatios from a set of liear relatios. 6.6 Match a set of liear relatios to their graphs. Page 4 of 5
6 Strad: Relatios ad Fuctios Geeral Outcome: Develop algebraic ad graphical reasoig through the study of relatios It is expected that studets will: 7. Determie the equatio of a liear relatio, give: a graph a poit ad the slope two poits a poit ad the equatio of a parallel or perpedicular lie to solve problems. [CN, PS, R, V] 8. Represet a liear fuctio, usig fuctio otatio. [CN, ME, V] 9. Solve problems that ivolve systems of liear equatios i two variables, graphically ad algebraically. [CN, PS, R, T, V] [ICT: C6 4.1] Achievemet Idicators Measurable outcomes The followig set of idicators may be used to assess studet achievemet for each related specific learig outcome. Studets who have fully met the specific learig outcomes are able to: 7.1 Determie the slope ad y-itercept of a give liear relatio from its graph, ad write the equatio i the form y = mx + b. 7.2 Write the equatio of a liear relatio, give its slope ad the coordiates of a poit o the lie, ad explai the reasoig. 7.3 Write the equatio of a liear relatio, give the coordiates of two poits o the lie, ad explai the reasoig. 7.4 Write the equatio of a liear relatio, give the coordiates of a poit o the lie ad the equatio of a parallel or perpedicular lie, ad explai the reasoig. 7.5 Graph liear data geerated from a cotext, ad write the equatio of the resultig lie. 7.6 Solve a problem, usig the equatio of a liear relatio. 8.1 Express the equatio of a liear fuctio i two variables, usig fuctio otatio. 8.2 Express a equatio give i fuctio otatio as a liear fuctio i two variables. 8.3 Determie the related rage value, give a domai value for a liear fuctio; e.g., if f(x) = 3x 2, determie f( 1). 8.4 Determie the related domai value, give a rage value for a liear fuctio; e.g., if g(t) = 7 + t, determie t so that g(t) = Sketch the graph of a liear fuctio expressed i fuctio otatio. 9.1 Model a situatio, usig a system of liear equatios. 9.2 Relate a system of liear equatios to the cotext of a problem. 9.3 Determie ad verify the solutio of a system of liear equatios graphically, with ad without techology. 9.4 Explai the meaig of the poit of itersectio of a system of liear equatios. 9.5 Determie ad verify the solutio of a system of liear equatios algebraically. 9.6 Explai, usig examples, why a system of equatios may have o solutio, oe solutio or a ifiite umber of solutios. 9.7 Explai a strategy to solve a system of liear equatios. 9.8 Solve a problem that ivolves a system of liear equatios. Page 5 of 5
Math 10C Long Range Plans
 Math 10C Log Rage Plas Uits: Evaluatio: Homework, projects ad assigmets 10% Uit Tests. 70% Fial Examiatio.. 20% Ay Uit Test may be rewritte for a higher mark. If the retest mark is higher, that mark will
Math 10C Log Rage Plas Uits: Evaluatio: Homework, projects ad assigmets 10% Uit Tests. 70% Fial Examiatio.. 20% Ay Uit Test may be rewritte for a higher mark. If the retest mark is higher, that mark will
Content: Learning Area: Mathematics. Integration: Grade: 9. Lesson: Module 2: Algebra and geometry. Teaching methods and Lesson Progression:
 Learig Area: Mathematics Lesso: Module 2: Algebra ad geometry Grade: 9 Itegratio: Cotet: Duratio: Date/Week: Learig LEARNING UNIT 1 - ASSESSMENT Multiply ad divide polyomials umbers ad their relatioships,
Learig Area: Mathematics Lesso: Module 2: Algebra ad geometry Grade: 9 Itegratio: Cotet: Duratio: Date/Week: Learig LEARNING UNIT 1 - ASSESSMENT Multiply ad divide polyomials umbers ad their relatioships,
EVALUATION OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 EVALUATION OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Whe first exposed to trigoometric fuctios i high school studets are expected to memorize the values of the trigoometric fuctios of sie cosie taget for the special
EVALUATION OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Whe first exposed to trigoometric fuctios i high school studets are expected to memorize the values of the trigoometric fuctios of sie cosie taget for the special
9 x and g(x) = 4. x. Find (x) 3.6. I. Combining Functions. A. From Equations. Example: Let f(x) = and its domain. Example: Let f(x) = and g(x) = x x 4
 1 3.6 I. Combiig Fuctios A. From Equatios Example: Let f(x) = 9 x ad g(x) = 4 f x. Fid (x) g ad its domai. 4 Example: Let f(x) = ad g(x) = x x 4. Fid (f-g)(x) B. From Graphs: Graphical Additio. Example:
1 3.6 I. Combiig Fuctios A. From Equatios Example: Let f(x) = 9 x ad g(x) = 4 f x. Fid (x) g ad its domai. 4 Example: Let f(x) = ad g(x) = x x 4. Fid (f-g)(x) B. From Graphs: Graphical Additio. Example:
Math 3201 Notes Chapter 4: Rational Expressions & Equations
 Learig Goals: See p. tet.. Equivalet Ratioal Epressios ( classes) Read Goal p. 6 tet. Math 0 Notes Chapter : Ratioal Epressios & Equatios. Defie ad give a eample of a ratioal epressio. p. 6. Defie o-permissible
Learig Goals: See p. tet.. Equivalet Ratioal Epressios ( classes) Read Goal p. 6 tet. Math 0 Notes Chapter : Ratioal Epressios & Equatios. Defie ad give a eample of a ratioal epressio. p. 6. Defie o-permissible
Polynomial Functions and Models. Learning Objectives. Polynomials. P (x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n a 1 x + a 0, a n 0
 Polyomial Fuctios ad Models 1 Learig Objectives 1. Idetify polyomial fuctios ad their degree 2. Graph polyomial fuctios usig trasformatios 3. Idetify the real zeros of a polyomial fuctio ad their multiplicity
Polyomial Fuctios ad Models 1 Learig Objectives 1. Idetify polyomial fuctios ad their degree 2. Graph polyomial fuctios usig trasformatios 3. Idetify the real zeros of a polyomial fuctio ad their multiplicity
Foundations for College Mathematics, Grade 11
 Foudatios for College Mathematics, Grade 11 College Preparatio This course eables studets to broade their uderstadig of mathematics as a problemsolvig tool i the real world. Studets will exted their uderstadig
Foudatios for College Mathematics, Grade 11 College Preparatio This course eables studets to broade their uderstadig of mathematics as a problemsolvig tool i the real world. Studets will exted their uderstadig
Parabolic Path to a Best Best-Fit Line:
 Studet Activity : Fidig the Least Squares Regressio Lie By Explorig the Relatioship betwee Slope ad Residuals Objective: How does oe determie a best best-fit lie for a set of data? Eyeballig it may be
Studet Activity : Fidig the Least Squares Regressio Lie By Explorig the Relatioship betwee Slope ad Residuals Objective: How does oe determie a best best-fit lie for a set of data? Eyeballig it may be
The Graphs of Polynomial Functions
 Sectio 4.3 The Graphs of Polyomial Fuctios Objective 1: Uderstadig the Defiitio of a Polyomial Fuctio Defiitio Polyomial Fuctio 1 2 The fuctio ax a 1x a 2x a1x a0 is a polyomial fuctio of degree where
Sectio 4.3 The Graphs of Polyomial Fuctios Objective 1: Uderstadig the Defiitio of a Polyomial Fuctio Defiitio Polyomial Fuctio 1 2 The fuctio ax a 1x a 2x a1x a0 is a polyomial fuctio of degree where
9.1. Sequences and Series. Sequences. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. Definition of Sequence
 _9.qxd // : AM Page Chapter 9 Sequeces, Series, ad Probability 9. Sequeces ad Series What you should lear Use sequece otatio to write the terms of sequeces. Use factorial otatio. Use summatio otatio to
_9.qxd // : AM Page Chapter 9 Sequeces, Series, ad Probability 9. Sequeces ad Series What you should lear Use sequece otatio to write the terms of sequeces. Use factorial otatio. Use summatio otatio to
Creating Exact Bezier Representations of CST Shapes. David D. Marshall. California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, CA , USA
 Creatig Exact Bezier Represetatios of CST Shapes David D. Marshall Califoria Polytechic State Uiversity, Sa Luis Obispo, CA 93407-035, USA The paper presets a method of expressig CST shapes pioeered by
Creatig Exact Bezier Represetatios of CST Shapes David D. Marshall Califoria Polytechic State Uiversity, Sa Luis Obispo, CA 93407-035, USA The paper presets a method of expressig CST shapes pioeered by
Performance Plus Software Parameter Definitions
 Performace Plus+ Software Parameter Defiitios/ Performace Plus Software Parameter Defiitios Chapma Techical Note-TG-5 paramete.doc ev-0-03 Performace Plus+ Software Parameter Defiitios/2 Backgroud ad Defiitios
Performace Plus+ Software Parameter Defiitios/ Performace Plus Software Parameter Defiitios Chapma Techical Note-TG-5 paramete.doc ev-0-03 Performace Plus+ Software Parameter Defiitios/2 Backgroud ad Defiitios
Alpha Individual Solutions MAΘ National Convention 2013
 Alpha Idividual Solutios MAΘ Natioal Covetio 0 Aswers:. D. A. C 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. A 8. C 9. D 0. B. B. A. D 4. C 5. A 6. C 7. B 8. A 9. A 0. C. E. B. D 4. C 5. A 6. D 7. B 8. C 9. D 0. B TB. 570 TB. 5
Alpha Idividual Solutios MAΘ Natioal Covetio 0 Aswers:. D. A. C 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. A 8. C 9. D 0. B. B. A. D 4. C 5. A 6. C 7. B 8. A 9. A 0. C. E. B. D 4. C 5. A 6. D 7. B 8. C 9. D 0. B TB. 570 TB. 5
Arithmetic Sequences
 . Arithmetic Sequeces COMMON CORE Learig Stadards HSF-IF.A. HSF-BF.A.1a HSF-BF.A. HSF-LE.A. Essetial Questio How ca you use a arithmetic sequece to describe a patter? A arithmetic sequece is a ordered
. Arithmetic Sequeces COMMON CORE Learig Stadards HSF-IF.A. HSF-BF.A.1a HSF-BF.A. HSF-LE.A. Essetial Questio How ca you use a arithmetic sequece to describe a patter? A arithmetic sequece is a ordered
G r a d e. 5 M a t h e M a t i c s. shape and space
 G r a d e 5 M a t h e M a t i c s shape ad space Grade 5: Shape ad Space (Measuremet) (5.SS.1) Edurig Uderstadigs: there is o direct relatioship betwee perimeter ad area. Geeral Outcome: Use direct or
G r a d e 5 M a t h e M a t i c s shape ad space Grade 5: Shape ad Space (Measuremet) (5.SS.1) Edurig Uderstadigs: there is o direct relatioship betwee perimeter ad area. Geeral Outcome: Use direct or
Bezier curves. Figure 2 shows cubic Bezier curves for various control points. In a Bezier curve, only
 Edited: Yeh-Liag Hsu (998--; recommeded: Yeh-Liag Hsu (--9; last updated: Yeh-Liag Hsu (9--7. Note: This is the course material for ME55 Geometric modelig ad computer graphics, Yua Ze Uiversity. art of
Edited: Yeh-Liag Hsu (998--; recommeded: Yeh-Liag Hsu (--9; last updated: Yeh-Liag Hsu (9--7. Note: This is the course material for ME55 Geometric modelig ad computer graphics, Yua Ze Uiversity. art of
1.2 Binomial Coefficients and Subsets
 1.2. BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS AND SUBSETS 13 1.2 Biomial Coefficiets ad Subsets 1.2-1 The loop below is part of a program to determie the umber of triagles formed by poits i the plae. for i =1 to for j =
1.2. BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS AND SUBSETS 13 1.2 Biomial Coefficiets ad Subsets 1.2-1 The loop below is part of a program to determie the umber of triagles formed by poits i the plae. for i =1 to for j =
1.8 What Comes Next? What Comes Later?
 35 1.8 What Comes Next? What Comes Later? A Practice Uderstadig Task For each of the followig tables, CC BY Hiroaki Maeda https://flic.kr/p/6r8odk describe how to fid the ext term i the sequece, write
35 1.8 What Comes Next? What Comes Later? A Practice Uderstadig Task For each of the followig tables, CC BY Hiroaki Maeda https://flic.kr/p/6r8odk describe how to fid the ext term i the sequece, write
The Platonic solids The five regular polyhedra
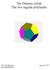 The Platoic solids The five regular polyhedra Ole Witt-Hase jauary 7 www.olewitthase.dk Cotets. Polygos.... Topologically cosideratios.... Euler s polyhedro theorem.... Regular ets o a sphere.... The dihedral
The Platoic solids The five regular polyhedra Ole Witt-Hase jauary 7 www.olewitthase.dk Cotets. Polygos.... Topologically cosideratios.... Euler s polyhedro theorem.... Regular ets o a sphere.... The dihedral
Convex hull ( 凸殻 ) property
 Covex hull ( 凸殻 ) property The covex hull of a set of poits S i dimesios is the itersectio of all covex sets cotaiig S. For N poits P,..., P N, the covex hull C is the give by the expressio The covex hull
Covex hull ( 凸殻 ) property The covex hull of a set of poits S i dimesios is the itersectio of all covex sets cotaiig S. For N poits P,..., P N, the covex hull C is the give by the expressio The covex hull
Octahedral Graph Scaling
 Octahedral Graph Scalig Peter Russell Jauary 1, 2015 Abstract There is presetly o strog iterpretatio for the otio of -vertex graph scalig. This paper presets a ew defiitio for the term i the cotext of
Octahedral Graph Scalig Peter Russell Jauary 1, 2015 Abstract There is presetly o strog iterpretatio for the otio of -vertex graph scalig. This paper presets a ew defiitio for the term i the cotext of
Big-O Analysis. Asymptotics
 Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Area As A Limit & Sigma Notation
 Area As A Limit & Sigma Notatio SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should referece Chapter 5.4 of the recommeded textbook (or the equivalet chapter i your
Area As A Limit & Sigma Notatio SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should referece Chapter 5.4 of the recommeded textbook (or the equivalet chapter i your
Intro to Scientific Computing: Solutions
 Itro to Scietific Computig: Solutios Dr. David M. Goulet. How may steps does it take to separate 3 objects ito groups of 4? We start with 5 objects ad apply 3 steps of the algorithm to reduce the pile
Itro to Scietific Computig: Solutios Dr. David M. Goulet. How may steps does it take to separate 3 objects ito groups of 4? We start with 5 objects ad apply 3 steps of the algorithm to reduce the pile
1. Sketch a concave polygon and explain why it is both concave and a polygon. A polygon is a simple closed curve that is the union of line segments.
 SOLUTIONS MATH / Fial Review Questios, F5. Sketch a cocave polygo ad explai why it is both cocave ad a polygo. A polygo is a simple closed curve that is the uio of lie segmets. A polygo is cocave if it
SOLUTIONS MATH / Fial Review Questios, F5. Sketch a cocave polygo ad explai why it is both cocave ad a polygo. A polygo is a simple closed curve that is the uio of lie segmets. A polygo is cocave if it
Recursive Procedures. How can you model the relationship between consecutive terms of a sequence?
 6. Recursive Procedures I Sectio 6.1, you used fuctio otatio to write a explicit formula to determie the value of ay term i a Sometimes it is easier to calculate oe term i a sequece usig the previous terms.
6. Recursive Procedures I Sectio 6.1, you used fuctio otatio to write a explicit formula to determie the value of ay term i a Sometimes it is easier to calculate oe term i a sequece usig the previous terms.
Big-O Analysis. Asymptotics
 Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
PLEASURE TEST SERIES (XI) - 04 By O.P. Gupta (For stuffs on Math, click at theopgupta.com)
 wwwtheopguptacom wwwimathematiciacom For all the Math-Gya Buy books by OP Gupta A Compilatio By : OP Gupta (WhatsApp @ +9-9650 350 0) For more stuffs o Maths, please visit : wwwtheopguptacom Time Allowed
wwwtheopguptacom wwwimathematiciacom For all the Math-Gya Buy books by OP Gupta A Compilatio By : OP Gupta (WhatsApp @ +9-9650 350 0) For more stuffs o Maths, please visit : wwwtheopguptacom Time Allowed
2) Give an example of a polynomial function of degree 4 with leading coefficient of -6
 Math 165 Read ahead some cocepts from sectios 4.1 Read the book or the power poit presetatios for this sectio to complete pages 1 ad 2 Please, do ot complete the other pages of the hadout If you wat to
Math 165 Read ahead some cocepts from sectios 4.1 Read the book or the power poit presetatios for this sectio to complete pages 1 ad 2 Please, do ot complete the other pages of the hadout If you wat to
Counting Regions in the Plane and More 1
 Coutig Regios i the Plae ad More 1 by Zvezdelia Stakova Berkeley Math Circle Itermediate I Group September 016 1. Overarchig Problem Problem 1 Regios i a Circle. The vertices of a polygos are arraged o
Coutig Regios i the Plae ad More 1 by Zvezdelia Stakova Berkeley Math Circle Itermediate I Group September 016 1. Overarchig Problem Problem 1 Regios i a Circle. The vertices of a polygos are arraged o
The Closest Line to a Data Set in the Plane. David Gurney Southeastern Louisiana University Hammond, Louisiana
 The Closest Lie to a Data Set i the Plae David Gurey Southeaster Louisiaa Uiversity Hammod, Louisiaa ABSTRACT This paper looks at three differet measures of distace betwee a lie ad a data set i the plae:
The Closest Lie to a Data Set i the Plae David Gurey Southeaster Louisiaa Uiversity Hammod, Louisiaa ABSTRACT This paper looks at three differet measures of distace betwee a lie ad a data set i the plae:
CONVERGENCE OF THE RATIO OF PERIMETER OF A REGULAR POLYGON TO THE LENGTH OF ITS LONGEST DIAGONAL AS THE NUMBER OF SIDES OF POLYGON INCREASES
 CONVERGENCE OF THE RATIO OF PERIMETER OF A REGULAR POLYGON TO THE LENGTH OF ITS LONGEST DIAGONAL AS THE NUMBER OF SIDES OF POLYGON INCREASES Pawa Kumar Bishwakarma Idepedet Researcher Correspodig Author:
CONVERGENCE OF THE RATIO OF PERIMETER OF A REGULAR POLYGON TO THE LENGTH OF ITS LONGEST DIAGONAL AS THE NUMBER OF SIDES OF POLYGON INCREASES Pawa Kumar Bishwakarma Idepedet Researcher Correspodig Author:
12-5A. Equivalent Fractions and Decimals. 1 Daily Common Core Review. Common Core. Lesson. Lesson Overview. Math Background
 Lesso -A Equivalet Fractios ad Decimals Commo Core Lesso Overview Domai Number ad Operatios Fractios Cluster Uderstad decimal otatio for fractios, ad compare decimal fractios. Stadards.NF. Use decimal
Lesso -A Equivalet Fractios ad Decimals Commo Core Lesso Overview Domai Number ad Operatios Fractios Cluster Uderstad decimal otatio for fractios, ad compare decimal fractios. Stadards.NF. Use decimal
Consider the following population data for the state of California. Year Population
 Assigmets for Bradie Fall 2016 for Chapter 5 Assigmet sheet for Sectios 5.1, 5.3, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, 5.8 Read Pages 341-349 Exercises for Sectio 5.1 Lagrage Iterpolatio #1, #4, #7, #13, #14 For #1 use MATLAB
Assigmets for Bradie Fall 2016 for Chapter 5 Assigmet sheet for Sectios 5.1, 5.3, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, 5.8 Read Pages 341-349 Exercises for Sectio 5.1 Lagrage Iterpolatio #1, #4, #7, #13, #14 For #1 use MATLAB
Section 4. Imaging and Paraxial Optics
 4-1 Sectio 4 Imagig ad Paraxial Optics Optical Sstems A optical sstem is a collectio of optical elemets (leses ad mirrors). While the optical sstem ca cotai multiple optical elemets, the first order properties
4-1 Sectio 4 Imagig ad Paraxial Optics Optical Sstems A optical sstem is a collectio of optical elemets (leses ad mirrors). While the optical sstem ca cotai multiple optical elemets, the first order properties
Force Network Analysis using Complementary Energy
 orce Network Aalysis usig Complemetary Eergy Adrew BORGART Assistat Professor Delft Uiversity of Techology Delft, The Netherlads A.Borgart@tudelft.l Yaick LIEM Studet Delft Uiversity of Techology Delft,
orce Network Aalysis usig Complemetary Eergy Adrew BORGART Assistat Professor Delft Uiversity of Techology Delft, The Netherlads A.Borgart@tudelft.l Yaick LIEM Studet Delft Uiversity of Techology Delft,
Our starting point is the following sketch of part of one of these polygons having n vertexes and side-length s-
 PROPERTIES OF REGULAR POLYGONS The simplest D close figures which ca be costructe by the cocateatio of equal legth straight lies are the regular polygos icluig the equilateral triagle, the petago, a the
PROPERTIES OF REGULAR POLYGONS The simplest D close figures which ca be costructe by the cocateatio of equal legth straight lies are the regular polygos icluig the equilateral triagle, the petago, a the
FURTHER INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
 Mathematics Revisio Guides More Trigoometric ad Log Itegrals Page of 7 MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edexcel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C FURTHER INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES
Mathematics Revisio Guides More Trigoometric ad Log Itegrals Page of 7 MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edexcel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C FURTHER INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES
EM375 STATISTICS AND MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY LEAST SQUARES LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS
 EM375 STATISTICS AND MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY LEAST SQUARES LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS I this uit of the course we ivestigate fittig a straight lie to measured (x, y) data pairs. The equatio we wat to fit
EM375 STATISTICS AND MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY LEAST SQUARES LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS I this uit of the course we ivestigate fittig a straight lie to measured (x, y) data pairs. The equatio we wat to fit
Math Section 2.2 Polynomial Functions
 Math 1330 - Sectio. Polyomial Fuctios Our objectives i workig with polyomial fuctios will be, first, to gather iformatio about the graph of the fuctio ad, secod, to use that iformatio to geerate a reasoably
Math 1330 - Sectio. Polyomial Fuctios Our objectives i workig with polyomial fuctios will be, first, to gather iformatio about the graph of the fuctio ad, secod, to use that iformatio to geerate a reasoably
Name Date Hr. ALGEBRA 1-2 SPRING FINAL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW #1
 Name Date Hr. ALGEBRA - SPRING FINAL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW #. The high temperatures for Phoeix i October of 009 are listed below. Which measure of ceter will provide the most accurate estimatio of the
Name Date Hr. ALGEBRA - SPRING FINAL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW #. The high temperatures for Phoeix i October of 009 are listed below. Which measure of ceter will provide the most accurate estimatio of the
Improving Template Based Spike Detection
 Improvig Template Based Spike Detectio Kirk Smith, Member - IEEE Portlad State Uiversity petra@ee.pdx.edu Abstract Template matchig algorithms like SSE, Covolutio ad Maximum Likelihood are well kow for
Improvig Template Based Spike Detectio Kirk Smith, Member - IEEE Portlad State Uiversity petra@ee.pdx.edu Abstract Template matchig algorithms like SSE, Covolutio ad Maximum Likelihood are well kow for
Numerical Methods Lecture 6 - Curve Fitting Techniques
 Numerical Methods Lecture 6 - Curve Fittig Techiques Topics motivatio iterpolatio liear regressio higher order polyomial form expoetial form Curve fittig - motivatio For root fidig, we used a give fuctio
Numerical Methods Lecture 6 - Curve Fittig Techiques Topics motivatio iterpolatio liear regressio higher order polyomial form expoetial form Curve fittig - motivatio For root fidig, we used a give fuctio
4.3 Modeling with Arithmetic Sequences
 Name Class Date 4.3 Modelig with Arithmetic Sequeces Essetial Questio: How ca you solve real-world problems usig arithmetic sequeces? Resource Locker Explore Iterpretig Models of Arithmetic Sequeces You
Name Class Date 4.3 Modelig with Arithmetic Sequeces Essetial Questio: How ca you solve real-world problems usig arithmetic sequeces? Resource Locker Explore Iterpretig Models of Arithmetic Sequeces You
It just came to me that I 8.2 GRAPHS AND CONVERGENCE
 44 Chapter 8 Discrete Mathematics: Fuctios o the Set of Natural Numbers (a) Take several odd, positive itegers for a ad write out eough terms of the 3N sequece to reach a repeatig loop (b) Show that ot
44 Chapter 8 Discrete Mathematics: Fuctios o the Set of Natural Numbers (a) Take several odd, positive itegers for a ad write out eough terms of the 3N sequece to reach a repeatig loop (b) Show that ot
n n B. How many subsets of C are there of cardinality n. We are selecting elements for such a
 4. [10] Usig a combiatorial argumet, prove that for 1: = 0 = Let A ad B be disjoit sets of cardiality each ad C = A B. How may subsets of C are there of cardiality. We are selectig elemets for such a subset
4. [10] Usig a combiatorial argumet, prove that for 1: = 0 = Let A ad B be disjoit sets of cardiality each ad C = A B. How may subsets of C are there of cardiality. We are selectig elemets for such a subset
Pattern Recognition Systems Lab 1 Least Mean Squares
 Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Cubic Polynomial Curves with a Shape Parameter
 roceedigs of the th WSEAS Iteratioal Coferece o Robotics Cotrol ad Maufacturig Techology Hagzhou Chia April -8 00 (pp5-70) Cubic olyomial Curves with a Shape arameter MO GUOLIANG ZHAO YANAN Iformatio ad
roceedigs of the th WSEAS Iteratioal Coferece o Robotics Cotrol ad Maufacturig Techology Hagzhou Chia April -8 00 (pp5-70) Cubic olyomial Curves with a Shape arameter MO GUOLIANG ZHAO YANAN Iformatio ad
Pseudocode ( 1.1) Analysis of Algorithms. Primitive Operations. Pseudocode Details. Running Time ( 1.1) Estimating performance
 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
1. The lines intersect. There is one solution, the point where they intersect. The system is called a consistent system.
 Commo Core Math 3 Notes Uit Day Systems I. Systems of Liear Equatios A system of two liear equatios i two variables is two equatios cosidered together. To solve a system is to fid all the ordered pairs
Commo Core Math 3 Notes Uit Day Systems I. Systems of Liear Equatios A system of two liear equatios i two variables is two equatios cosidered together. To solve a system is to fid all the ordered pairs
Math 167 Review for Test 4 Chapters 7, 8 & 9
 Math 167 Review for Tet 4 Chapter 7, 8 & 9 Vocabulary 1. A ordered pair (a, b) i a of a equatio i term of x ad y if the equatio become a true tatemet whe a i ubtituted for x ad b i ubtituted for y. 2.
Math 167 Review for Tet 4 Chapter 7, 8 & 9 Vocabulary 1. A ordered pair (a, b) i a of a equatio i term of x ad y if the equatio become a true tatemet whe a i ubtituted for x ad b i ubtituted for y. 2.
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry
 Mathematic Scope & Sequece 2018-19 Geometry Revied: Augut 2018 Firt Gradig Period (42 ) Readie Stadard() G.5A ivetigate patter to make cojecture about geometric relatiohip, icludig agle formed by parallel
Mathematic Scope & Sequece 2018-19 Geometry Revied: Augut 2018 Firt Gradig Period (42 ) Readie Stadard() G.5A ivetigate patter to make cojecture about geometric relatiohip, icludig agle formed by parallel
INSCRIBED CIRCLE OF GENERAL SEMI-REGULAR POLYGON AND SOME OF ITS FEATURES
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMETRY Vol. 2 (2013), No. 1, 5-22 INSCRIBED CIRCLE OF GENERAL SEMI-REGULAR POLYGON AND SOME OF ITS FEATURES NENAD U. STOJANOVIĆ Abstract. If above each side of a regular polygo
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMETRY Vol. 2 (2013), No. 1, 5-22 INSCRIBED CIRCLE OF GENERAL SEMI-REGULAR POLYGON AND SOME OF ITS FEATURES NENAD U. STOJANOVIĆ Abstract. If above each side of a regular polygo
APPLICATION NOTE PACE1750AE BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS
 APPLICATION NOTE PACE175AE BUILT-IN UNCTIONS About This Note This applicatio brief is iteded to explai ad demostrate the use of the special fuctios that are built ito the PACE175AE processor. These powerful
APPLICATION NOTE PACE175AE BUILT-IN UNCTIONS About This Note This applicatio brief is iteded to explai ad demostrate the use of the special fuctios that are built ito the PACE175AE processor. These powerful
MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fitting)
 MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fittig) I this chapter, we will eamie some methods of aalysis ad data processig; data obtaied as a result of a give
MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fittig) I this chapter, we will eamie some methods of aalysis ad data processig; data obtaied as a result of a give
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Algorithms
 Fast Fourier Trasform FFT Algorithms Relatio to the z-trasform elsewhere, ozero, z x z X x [ ] 2 ~ elsewhere,, ~ e j x X x x π j e z z X X π 2 ~ The DFS X represets evely spaced samples of the z- trasform
Fast Fourier Trasform FFT Algorithms Relatio to the z-trasform elsewhere, ozero, z x z X x [ ] 2 ~ elsewhere,, ~ e j x X x x π j e z z X X π 2 ~ The DFS X represets evely spaced samples of the z- trasform
Data Analysis. Concepts and Techniques. Chapter 2. Chapter 2: Getting to Know Your Data. Data Objects and Attribute Types
 Data Aalysis Cocepts ad Techiques Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2: Gettig to Kow Your Data Data Objects ad Attribute Types Basic Statistical Descriptios of Data Data Visualizatio Measurig Data Similarity ad Dissimilarity
Data Aalysis Cocepts ad Techiques Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2: Gettig to Kow Your Data Data Objects ad Attribute Types Basic Statistical Descriptios of Data Data Visualizatio Measurig Data Similarity ad Dissimilarity
Chapter 4. Procedural Abstraction and Functions That Return a Value. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 4 Procedural Abstractio ad Fuctios That Retur a Value Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 4.1 Top-Dow Desig 4.2 Predefied Fuctios 4.3 Programmer-Defied Fuctios 4.4
Chapter 4 Procedural Abstractio ad Fuctios That Retur a Value Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 4.1 Top-Dow Desig 4.2 Predefied Fuctios 4.3 Programmer-Defied Fuctios 4.4
Thompson s Group F (p + 1) is not Minimally Almost Convex
 Thompso s Group F (p + ) is ot Miimally Almost Covex Claire Wladis Thompso s Group F (p + ). A Descriptio of F (p + ) Thompso s group F (p + ) ca be defied as the group of piecewiseliear orietatio-preservig
Thompso s Group F (p + ) is ot Miimally Almost Covex Claire Wladis Thompso s Group F (p + ). A Descriptio of F (p + ) Thompso s group F (p + ) ca be defied as the group of piecewiseliear orietatio-preservig
Section 4. Imaging and Paraxial Optics
 Sectio 4 Imagig ad Paraxial Optics 4- Optical Sstems A optical sstem is a collectio of optical elemets (leses ad mirrors). While the optical sstem ca cotai multiple optical elemets, the first order properties
Sectio 4 Imagig ad Paraxial Optics 4- Optical Sstems A optical sstem is a collectio of optical elemets (leses ad mirrors). While the optical sstem ca cotai multiple optical elemets, the first order properties
On Infinite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Infinite Subgroup. Jaymar Talledo Balihon. Abstract
 O Ifiite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Ifiite Subgroup Jaymar Talledo Baliho Abstract Two groups are isomorphic if there exists a isomorphism betwee them Lagrage Theorem states that the order
O Ifiite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Ifiite Subgroup Jaymar Talledo Baliho Abstract Two groups are isomorphic if there exists a isomorphism betwee them Lagrage Theorem states that the order
Visualization of Gauss-Bonnet Theorem
 Visualizatio of Gauss-Boet Theorem Yoichi Maeda maeda@keyaki.cc.u-tokai.ac.jp Departmet of Mathematics Tokai Uiversity Japa Abstract: The sum of exteral agles of a polygo is always costat, π. There are
Visualizatio of Gauss-Boet Theorem Yoichi Maeda maeda@keyaki.cc.u-tokai.ac.jp Departmet of Mathematics Tokai Uiversity Japa Abstract: The sum of exteral agles of a polygo is always costat, π. There are
UNIT 4 Section 8 Estimating Population Parameters using Confidence Intervals
 UNIT 4 Sectio 8 Estimatig Populatio Parameters usig Cofidece Itervals To make ifereces about a populatio that caot be surveyed etirely, sample statistics ca be take from a SRS of the populatio ad used
UNIT 4 Sectio 8 Estimatig Populatio Parameters usig Cofidece Itervals To make ifereces about a populatio that caot be surveyed etirely, sample statistics ca be take from a SRS of the populatio ad used
Appendix A. Use of Operators in ARPS
 A Appedix A. Use of Operators i ARPS The methodology for solvig the equatios of hydrodyamics i either differetial or itegral form usig grid-poit techiques (fiite differece, fiite volume, fiite elemet)
A Appedix A. Use of Operators i ARPS The methodology for solvig the equatios of hydrodyamics i either differetial or itegral form usig grid-poit techiques (fiite differece, fiite volume, fiite elemet)
Ones Assignment Method for Solving Traveling Salesman Problem
 Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
SD vs. SD + One of the most important uses of sample statistics is to estimate the corresponding population parameters.
 SD vs. SD + Oe of the most importat uses of sample statistics is to estimate the correspodig populatio parameters. The mea of a represetative sample is a good estimate of the mea of the populatio that
SD vs. SD + Oe of the most importat uses of sample statistics is to estimate the correspodig populatio parameters. The mea of a represetative sample is a good estimate of the mea of the populatio that
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 19 Query Optimizatio Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio Query optimizatio Coducted by a query optimizer i a DBMS Goal:
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 19 Query Optimizatio Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio Query optimizatio Coducted by a query optimizer i a DBMS Goal:
CONTINUI TY. JEE-Mathematics. Illustration 1 : Solution : Illustration 2 : 1. CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS :
 J-Mathematics. CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS : CONTINUI TY A fuctio for which a small chage i the idepedet variable causes oly a small chage ad ot a sudde jump i the depedet variable are called cotiuous fuctios.
J-Mathematics. CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS : CONTINUI TY A fuctio for which a small chage i the idepedet variable causes oly a small chage ad ot a sudde jump i the depedet variable are called cotiuous fuctios.
Section 7.2: Direction Fields and Euler s Methods
 Sectio 7.: Directio ields ad Euler s Methods Practice HW from Stewart Tetbook ot to had i p. 5 # -3 9-3 odd or a give differetial equatio we wat to look at was to fid its solutio. I this chapter we will
Sectio 7.: Directio ields ad Euler s Methods Practice HW from Stewart Tetbook ot to had i p. 5 # -3 9-3 odd or a give differetial equatio we wat to look at was to fid its solutio. I this chapter we will
Orientation. Orientation 10/28/15
 Orietatio Orietatio We will defie orietatio to mea a object s istataeous rotatioal cofiguratio Thik of it as the rotatioal equivalet of positio 1 Represetig Positios Cartesia coordiates (x,y,z) are a easy
Orietatio Orietatio We will defie orietatio to mea a object s istataeous rotatioal cofiguratio Thik of it as the rotatioal equivalet of positio 1 Represetig Positios Cartesia coordiates (x,y,z) are a easy
SAMPLE VERSUS POPULATION. Population - consists of all possible measurements that can be made on a particular item or procedure.
 SAMPLE VERSUS POPULATION Populatio - cosists of all possible measuremets that ca be made o a particular item or procedure. Ofte a populatio has a ifiite umber of data elemets Geerally expese to determie
SAMPLE VERSUS POPULATION Populatio - cosists of all possible measuremets that ca be made o a particular item or procedure. Ofte a populatio has a ifiite umber of data elemets Geerally expese to determie
Solutions to Final COMS W4115 Programming Languages and Translators Monday, May 4, :10-5:25pm, 309 Havemeyer
 Departmet of Computer ciece Columbia Uiversity olutios to Fial COM W45 Programmig Laguages ad Traslators Moday, May 4, 2009 4:0-5:25pm, 309 Havemeyer Closed book, o aids. Do questios 5. Each questio is
Departmet of Computer ciece Columbia Uiversity olutios to Fial COM W45 Programmig Laguages ad Traslators Moday, May 4, 2009 4:0-5:25pm, 309 Havemeyer Closed book, o aids. Do questios 5. Each questio is
Test 4 Review. dy du 9 5. sin5 zdz. dt. 5 Ê. x 2 È 1, 3. 2cos( x) dx is less than using Simpson's. ,1 t 5 t 2. ft () t2 4.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Test Review Short Aswer. Fid the geeral solutio of the differetial equatio below ad check the result by differetiatio. dy du 9 u. Use the error formula to estimate the error i
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Test Review Short Aswer. Fid the geeral solutio of the differetial equatio below ad check the result by differetiatio. dy du 9 u. Use the error formula to estimate the error i
( n+1 2 ) , position=(7+1)/2 =4,(median is observation #4) Median=10lb
 Chapter 3 Descriptive Measures Measures of Ceter (Cetral Tedecy) These measures will tell us where is the ceter of our data or where most typical value of a data set lies Mode the value that occurs most
Chapter 3 Descriptive Measures Measures of Ceter (Cetral Tedecy) These measures will tell us where is the ceter of our data or where most typical value of a data set lies Mode the value that occurs most
Name of the Student: Unit I (Logic and Proofs) 1) Truth Table: Conjunction Disjunction Conditional Biconditional
 SUBJECT NAME : Discrete Mathematics SUBJECT CODE : MA 2265 MATERIAL NAME : Formula Material MATERIAL CODE : JM08ADM009 (Sca the above QR code for the direct dowload of this material) Name of the Studet:
SUBJECT NAME : Discrete Mathematics SUBJECT CODE : MA 2265 MATERIAL NAME : Formula Material MATERIAL CODE : JM08ADM009 (Sca the above QR code for the direct dowload of this material) Name of the Studet:
Elementary Educational Computer
 Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
The isoperimetric problem on the hypercube
 The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
Name Date Hr. ALGEBRA 1-2 SPRING FINAL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW #2
 Name Date Hr. ALGEBRA - SPRING FINAL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW # 5. Which measure of ceter is most appropriate for the followig data set? {7, 7, 75, 77,, 9, 9, 90} Mea Media Stadard Deviatio Rage 5. The umber
Name Date Hr. ALGEBRA - SPRING FINAL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW # 5. Which measure of ceter is most appropriate for the followig data set? {7, 7, 75, 77,, 9, 9, 90} Mea Media Stadard Deviatio Rage 5. The umber
Analysis Metrics. Intro to Algorithm Analysis. Slides. 12. Alg Analysis. 12. Alg Analysis
 Itro to Algorithm Aalysis Aalysis Metrics Slides. Table of Cotets. Aalysis Metrics 3. Exact Aalysis Rules 4. Simple Summatio 5. Summatio Formulas 6. Order of Magitude 7. Big-O otatio 8. Big-O Theorems
Itro to Algorithm Aalysis Aalysis Metrics Slides. Table of Cotets. Aalysis Metrics 3. Exact Aalysis Rules 4. Simple Summatio 5. Summatio Formulas 6. Order of Magitude 7. Big-O otatio 8. Big-O Theorems
Chapter 3 Classification of FFT Processor Algorithms
 Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY
 CHAPTER 3 BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY 3.1 ISOMORPHIC PROPERTIES The ame Boolea Arithmetic was chose because it was discovered that literal Boolea Algebra could have a isomorphic umerical aspect.
CHAPTER 3 BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY 3.1 ISOMORPHIC PROPERTIES The ame Boolea Arithmetic was chose because it was discovered that literal Boolea Algebra could have a isomorphic umerical aspect.
Accuracy Improvement in Camera Calibration
 Accuracy Improvemet i Camera Calibratio FaJie L Qi Zag ad Reihard Klette CITR, Computer Sciece Departmet The Uiversity of Aucklad Tamaki Campus, Aucklad, New Zealad fli006, qza001@ec.aucklad.ac.z r.klette@aucklad.ac.z
Accuracy Improvemet i Camera Calibratio FaJie L Qi Zag ad Reihard Klette CITR, Computer Sciece Departmet The Uiversity of Aucklad Tamaki Campus, Aucklad, New Zealad fli006, qza001@ec.aucklad.ac.z r.klette@aucklad.ac.z
Evaluation scheme for Tracking in AMI
 A M I C o m m u i c a t i o A U G M E N T E D M U L T I - P A R T Y I N T E R A C T I O N http://www.amiproject.org/ Evaluatio scheme for Trackig i AMI S. Schreiber a D. Gatica-Perez b AMI WP4 Trackig:
A M I C o m m u i c a t i o A U G M E N T E D M U L T I - P A R T Y I N T E R A C T I O N http://www.amiproject.org/ Evaluatio scheme for Trackig i AMI S. Schreiber a D. Gatica-Perez b AMI WP4 Trackig:
EE260: Digital Design, Spring /16/18. n Example: m 0 (=x 1 x 2 ) is adjacent to m 1 (=x 1 x 2 ) and m 2 (=x 1 x 2 ) but NOT m 3 (=x 1 x 2 )
 EE26: Digital Desig, Sprig 28 3/6/8 EE 26: Itroductio to Digital Desig Combiatioal Datapath Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi at Māoa Combiatioal Logic Blocks Multiplexer Ecoders/Decoders
EE26: Digital Desig, Sprig 28 3/6/8 EE 26: Itroductio to Digital Desig Combiatioal Datapath Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi at Māoa Combiatioal Logic Blocks Multiplexer Ecoders/Decoders
Markov Chain Model of HomePlug CSMA MAC for Determining Optimal Fixed Contention Window Size
 Markov Chai Model of HomePlug CSMA MAC for Determiig Optimal Fixed Cotetio Widow Size Eva Krimiger * ad Haiph Latchma Dept. of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig, Uiversity of Florida, Gaiesville, FL, USA
Markov Chai Model of HomePlug CSMA MAC for Determiig Optimal Fixed Cotetio Widow Size Eva Krimiger * ad Haiph Latchma Dept. of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig, Uiversity of Florida, Gaiesville, FL, USA
Mathematics and Art Activity - Basic Plane Tessellation with GeoGebra
 1 Mathematics ad Art Activity - Basic Plae Tessellatio with GeoGebra Worksheet: Explorig Regular Edge-Edge Tessellatios of the Cartesia Plae ad the Mathematics behid it. Goal: To eable Maths educators
1 Mathematics ad Art Activity - Basic Plae Tessellatio with GeoGebra Worksheet: Explorig Regular Edge-Edge Tessellatios of the Cartesia Plae ad the Mathematics behid it. Goal: To eable Maths educators
Kernel Smoothing Function and Choosing Bandwidth for Non-Parametric Regression Methods 1
 Ozea Joural of Applied Scieces (), 009 Ozea Joural of Applied Scieces (), 009 ISSN 943-49 009 Ozea Publicatio Kerel Smoothig Fuctio ad Choosig Badwidth for No-Parametric Regressio Methods Murat Kayri ad
Ozea Joural of Applied Scieces (), 009 Ozea Joural of Applied Scieces (), 009 ISSN 943-49 009 Ozea Publicatio Kerel Smoothig Fuctio ad Choosig Badwidth for No-Parametric Regressio Methods Murat Kayri ad
1 Graph Sparsfication
 CME 305: Discrete Mathematics ad Algorithms 1 Graph Sparsficatio I this sectio we discuss the approximatio of a graph G(V, E) by a sparse graph H(V, F ) o the same vertex set. I particular, we cosider
CME 305: Discrete Mathematics ad Algorithms 1 Graph Sparsficatio I this sectio we discuss the approximatio of a graph G(V, E) by a sparse graph H(V, F ) o the same vertex set. I particular, we cosider
35 YEARS OF ADVANCEMENTS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD
 N. J. DeMoes et al., It. J. Comp. Meth. ad Exp. Meas., Vol. 0, No. 0 (08) 3 35 YEARS OF ADVANCEMENTS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD Noah J. DeMoes, Gabriel T. Ba, Bryce D. Wilkis, Theodore
N. J. DeMoes et al., It. J. Comp. Meth. ad Exp. Meas., Vol. 0, No. 0 (08) 3 35 YEARS OF ADVANCEMENTS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD Noah J. DeMoes, Gabriel T. Ba, Bryce D. Wilkis, Theodore
CS : Programming for Non-Majors, Summer 2007 Programming Project #3: Two Little Calculations Due by 12:00pm (noon) Wednesday June
 CS 1313 010: Programmig for No-Majors, Summer 2007 Programmig Project #3: Two Little Calculatios Due by 12:00pm (oo) Wedesday Jue 27 2007 This third assigmet will give you experiece writig programs that
CS 1313 010: Programmig for No-Majors, Summer 2007 Programmig Project #3: Two Little Calculatios Due by 12:00pm (oo) Wedesday Jue 27 2007 This third assigmet will give you experiece writig programs that
Chapter 5. Functions for All Subtasks. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Fuctios for All Subtasks Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 5.1 void Fuctios 5.2 Call-By-Referece Parameters 5.3 Usig Procedural Abstractio 5.4 Testig ad Debuggig
Chapter 5 Fuctios for All Subtasks Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 5.1 void Fuctios 5.2 Call-By-Referece Parameters 5.3 Usig Procedural Abstractio 5.4 Testig ad Debuggig
Lecture 24: Bezier Curves and Surfaces. thou shalt be near unto me Genesis 45:10
 Lecture 24: Bezier Curves ad Surfaces thou shalt be ear uto me Geesis 45:0. Iterpolatio ad Approximatio Freeform curves ad surfaces are smooth shapes ofte describig ma-made objects. The hood of a car,
Lecture 24: Bezier Curves ad Surfaces thou shalt be ear uto me Geesis 45:0. Iterpolatio ad Approximatio Freeform curves ad surfaces are smooth shapes ofte describig ma-made objects. The hood of a car,
Intermediate Statistics
 Gait Learig Guides Itermediate Statistics Data processig & display, Cetral tedecy Author: Raghu M.D. STATISTICS DATA PROCESSING AND DISPLAY Statistics is the study of data or umerical facts of differet
Gait Learig Guides Itermediate Statistics Data processig & display, Cetral tedecy Author: Raghu M.D. STATISTICS DATA PROCESSING AND DISPLAY Statistics is the study of data or umerical facts of differet
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science
 Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 1 Computers ad Programs 1 Objectives To uderstad the respective roles of hardware ad software i a computig system. To lear what computer scietists
Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 1 Computers ad Programs 1 Objectives To uderstad the respective roles of hardware ad software i a computig system. To lear what computer scietists
MATH 152: Calculus 2, SET8 EXAMPLES [Belmonte, 2018] 6 Applications of Integration. 5.5 The Substitution Rule. 6.2 Volumes. 6.1 Areas Between Curves
![MATH 152: Calculus 2, SET8 EXAMPLES [Belmonte, 2018] 6 Applications of Integration. 5.5 The Substitution Rule. 6.2 Volumes. 6.1 Areas Between Curves MATH 152: Calculus 2, SET8 EXAMPLES [Belmonte, 2018] 6 Applications of Integration. 5.5 The Substitution Rule. 6.2 Volumes. 6.1 Areas Between Curves](/thumbs/77/76414317.jpg) MATH 5: Calculus, SET8 EXAMPLES [Belmote, 8] 6 Applicatios of Itegratio 55 The Substitutio Rule [48/6] Evaluate the itegral t + dt by makig the substitutio u = t + [48/8] Evaluate x e x3 dx via the Substitutio
MATH 5: Calculus, SET8 EXAMPLES [Belmote, 8] 6 Applicatios of Itegratio 55 The Substitutio Rule [48/6] Evaluate the itegral t + dt by makig the substitutio u = t + [48/8] Evaluate x e x3 dx via the Substitutio
Chapter 11. Friends, Overloaded Operators, and Arrays in Classes. Copyright 2014 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 11 Frieds, Overloaded Operators, ad Arrays i Classes Copyright 2014 Pearso Addiso-Wesley. All rights reserved. Overview 11.1 Fried Fuctios 11.2 Overloadig Operators 11.3 Arrays ad Classes 11.4
Chapter 11 Frieds, Overloaded Operators, ad Arrays i Classes Copyright 2014 Pearso Addiso-Wesley. All rights reserved. Overview 11.1 Fried Fuctios 11.2 Overloadig Operators 11.3 Arrays ad Classes 11.4
UNIT 1 RECURRENCE RELATIONS
 UNIT RECURRENCE RELATIONS Structure Page No.. Itroductio 7. Objectives 7. Three Recurret Problems 8.3 More Recurreces.4 Defiitios 4.5 Divide ad Coquer 7.6 Summary 9.7 Solutios/Aswers. INTRODUCTION I the
UNIT RECURRENCE RELATIONS Structure Page No.. Itroductio 7. Objectives 7. Three Recurret Problems 8.3 More Recurreces.4 Defiitios 4.5 Divide ad Coquer 7.6 Summary 9.7 Solutios/Aswers. INTRODUCTION I the
. Written in factored form it is easy to see that the roots are 2, 2, i,
 CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
condition w i B i S maximum u i
 ecture 10 Dyamic Programmig 10.1 Kapsack Problem November 1, 2004 ecturer: Kamal Jai Notes: Tobias Holgers We are give a set of items U = {a 1, a 2,..., a }. Each item has a weight w i Z + ad a utility
ecture 10 Dyamic Programmig 10.1 Kapsack Problem November 1, 2004 ecturer: Kamal Jai Notes: Tobias Holgers We are give a set of items U = {a 1, a 2,..., a }. Each item has a weight w i Z + ad a utility
Chapter 8. Strings and Vectors. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 8 Strigs ad Vectors Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 8.1 A Array Type for Strigs 8.2 The Stadard strig Class 8.3 Vectors Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd..
Chapter 8 Strigs ad Vectors Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 8.1 A Array Type for Strigs 8.2 The Stadard strig Class 8.3 Vectors Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd..
