IJREAT International Journal of Research in Engineering & Advanced Technology, Volume 1, Issue 2, April-May, 2013 ISSN:
|
|
|
- Homer Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Optimization of Mesh Reconstruction using Delaunay and Ball Pivoting Algorithm Bharti Sood 1, Kamaldeep Kaur 2 1, 2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, BBSBEC, Fatehgarh Sahib, India Abstract It is very important to approximate a shape from the coordinates of a given set of points for surface reconstruction. The specific shape deals with curves in two dimensions and surfaces in three dimensions. In this paper we have presented a hybrid model of the ball pivoting and Delaunay algorithm for mesh reconstruction from 3D point cloud. The ball of a diameter d pivots around an edge keeping in contact with the edge s endpoints until it touches another point, forming another triangle and the diameter of the ball is increased according to the requirement, when the pivoting ball is not able to reach to some of the sample points, then the pivoting ball is rotated in 3D. This improvement will lead to more effective representation of 3D image. The hybrid model of Ball Pivoting and Delaunay Algorithm is efficient in terms of execution time and storage requirements, number of triangles created, and time spend for computing triangles. Keywords: Ball Pivoting Algorithm, Delaunay Triangulation Algorithm, Surface Reconstruction, 3D point cloud. 1. Introduction Surface reconstruction from range data involves four major steps. First step is data acquisition of surface samples with a laser range scanner. Second is data registration where alignment of several scans is done into a single co-ordinate system. Third step is data integration, the separate registered range maps are integrated into a single surface representation (often a polygon mesh). Fourth step is optimization, the single surface representation can be fitted better to the data, it may be further simplify, or the representation can be converted to some other format (e.g., smooth surfaces). The Ball Pivoting Algorithm makes two mild assumptions about the samples that the samples are distributed over the entire surface. The method is conceptually simple. Starting with a seed triangle, the ball of a radius p pivots around an edge keeping in contact with the edge s endpoints until it touches another point, forming another triangle, which is added to the mesh, and the algorithm considers a new boundary edge for pivoting [9]. The output mesh is a manifold subset of an alpha-shape of the point set [12]. Some of the nice properties of alphashapes can also be proved for our reconstruction. The \ hybrid model of Ball Pivoting and Delaunay Algorithm is efficient in terms of execution time and storage requirements, number of triangles created, and computation of CPU time for creating triangles. It exhibited linear time performance on datasets consisting of millions of input samples. It has been implemented in a form that does not require all of the input data to be loaded into memory simultaneously. The resulting triangular mesh is incrementally saved to external storage during its computation, and does not use any additional memory. This paper focuses on the hybrid model of the ball pivoting and Delaunay algorithm for mesh reconstruction from 3D point cloud. In this paper we have presented a new method for finding a triangle mesh from unorganized set of points and improved the results in terms of execution time and storage requirements, number of triangles created, and time spend for computing triangles. The paper is structured as follows: In section 2 we discuss the triangulation algorithms for surface reconstruction. Section 2 also describes the problem and related work. Section 3 describes the hybrid approach of Ball pivot algorithm and Delaunay algorithm in detail. Section 4 describes the flow of our hybrid approach of algorithms. We present results and discussions in section 5, and conclusion is in section Triangulation Algorithms for Surface Reconstruction The algorithms for surfaces reconstruction from large data have been proposed in the past. Delaunay triangulations are important geometric data structures that are built on the notion of nearness. Many differential properties of curves and surfaces are defined on local neighborhoods. Delaunay triangulations provide a tool to approximate these neighborhoods in the discrete domain. They are defined for a point set in any Euclidean space. These are defined in two dimensions and mention the extensions to three dimensions since the curve and surface reconstruction algorithms are concerned with these two Euclidean spaces. The Delaunay triangulation is formed by joining all the circum circles. 1
2 The hardware projection is used to compute a triangulation from each range scan and then stitch them together. This gives a very fast reconstruction for each range scan. It faces difficulty if the projection of a scan self-overlaps. The consistent stitching of adjacent scans possesses problems. The current methods for stitching are based on stimulating interest as a means of furthering investigation and often create artifacts in the surface. The ball pivoting algorithm of was used to handle millions of sample points. This algorithm builds the surface incrementally by rolling a ball over the sample points. But It requires that the sample points be equally dense everywhere and each sample point have a surface normal. The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm computes a triangle mesh interpolating a given point cloud. Typically the points are surface samples acquired with multiple range scans of an object. The principle of the BPA is very simple: Three points form a triangle if a ball of a user-specified radius p touches them without containing any other point. Starting with a seed triangle, the ball pivots around an edge that means it revolves around the edge while keeping in contact with the edge s endpoints until it touches another point, forming another triangle. The process continues until all reachable edges have been tried, and then starts from another seed triangle, until all points have been considered [9]. The problem is formulated that when the sampling density is too low, means point is located at a larger distance than radius r then some of the edges will not be created, leaving holes and when the curvature of the manifold is larger than 1/p, some of the sample points will not be reached by the pivoting ball, and features will be missed. Standord vrip (Volumetric Range Image Processing) program was used to connect the points within each individual range data scan to provide estimates of surface normals. The plane carvers, large planes of triangles were also removed by using hole-filling algorithms. Our approach fills the holes by increasing the diameter of the ball according to the requirement and the ball pivots around an edge keeping in contact with the edge s endpoints until it touches another point, forming another triangle. In our method Delaunay algorithm is also considered to resolve the problems occurred due to low or high density points. When some of the sample points will not be reached by the pivoting ball, then the pivoting ball is rotated in 3D. The hybrid model of the ball pivot and Delaunay algorithm will lead to improve more effective representation of 3D image.the hybrid model of Ball Pivoting and Delaunay Algorithm is computing the number of triangles very efficiently. Our method is also computing the I/O time, Memory usage and CPU time. I/O time is the time to read and write the file. Memory usage is the total space occupied to store the file. CPU time is time taken for creating one triangle. In our paper these parameters are compared with the past results. Table 1 depicts the results carried out in the past research. We refer a review of research in the field [9]. 3. The Ball Pivot & Delaunay Algorithm The hybrid model of the Ball pivoting algorithm and Delaunay algorithm is implemented for mesh reconstruction from 3D point cloud. The Delaunay triangulation is formed by joining all the circum circles. It is assumed that the distance between the vertices and the points a, b, c in the plane is measured using the standard distance. For a matrix: X 1 Y 1 Z 1 X 2 Y 2 Z X n Y n Z n The distance between the vertices of the matrix and the points a, b, c can be computed by the equation: (1) Delaunay triangulations are data structures that are built on the notion of nearness. Many differential properties of curves and surfaces are defined on local neighbourhoods. The algorithm to approximate the neighbourhoods in discrete domain is: { No =0 for No<3 Neg=Neg No=0 No= r=r+.1 end } In this an approach is made to fill holes that the diameter of the ball is increased according to the requirement and 2
3 the ball pivots around an edge keeping in contact with the edge s endpoints until it touches another point, forming another triangle. In the second approach the Delaunay algorithm is followed, Delaunay triangulations are data structures that are built on the notion of nearness, so when some of the sample points will not be reached by the pivoting ball, then the pivoting ball is rotated in 3D as shown in Fig Implementation 5. Results & Discussions Our experiments for this paper were conducted on a 2.20 GHZ Core i3-2330m processor of Sony Vaio E series running windows 7. In our experiments we used several datasets like bunny, dragon, Buddha. The datasets are taken from the Stanford scanning database. In order to confirm the effectiveness of the research, we modified the ball pivot algorithm. The hybrid model of the Ball pivoting algorithm and Delaunay algorithm was implemented in MATLAB. The whole code is less than 150 lines. In dataset Bunny the number of points i.e. vertices are 34835, in dataset Dragon the total vertices are and in dataset Buddha the number of vertices are d lists the diameter of the pivoting balls, in mm. The initial diameter of the pivoting ball for each dataset Bunny, Dragon, Buddha is fixed. The results are taken by considering a fixed initial value of diameter. With increase in diameter number of triangles will also increase. During simulation of the model the diameter of the ball will automatically increase according to the requirement. The total triangles are the number of triangles created by the hybrid approach of Ball Pivot and Delaunay algorithm. Memory usage is the maximum amount of memory used at any time during mesh generation, in MB. I/O Time is the time taken to read the input binary files and it also includes the time to write the output mesh, in seconds. CPU Time is the average time spent computing the triangulation, in seconds. Fig. 3, Fig.4, Fig. 5 represents the mesh reconstruction of the datasets Bunny, Dragon, Buddha respectively by our method. Table 2 gives the results of calculation of number of triangles, memory usage, I/O time, CPU time in case for Bunny, Dragon and Buddha by hybrid approach of both the algorithms. The hybrid model of Ball Pivoting and Delaunay Algorithm is computing the number of triangles very efficiently. I/O time is the time to read and write the file. Memory usage is the total space occupied to store the file. CPU time is time taken for creating one triangle. In our paper these parameters are compared with the past results. Fig.2. Flow chart of hybrid model of Ball Pivoting Algorithm and Delaunay algorithm 6. Conclusion The hybrid model of Ball Pivoting and Delaunay Algorithm is efficient in terms of execution time and storage requirements, number of triangles created, and time spend for computing triangles. It works on datasets 3
4 consisting of millions of input samples. It has been implemented in a form that does not require all of the input data to be loaded into memory simultaneously. The resulting triangle mesh is incrementally saved to external storage during its computation, and does not use any additional memory. References [1] B. Curless and M. Levoy, A volumetric method for building complex models from range images, Proceedings of the 23rd annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, New Orleans, Louisiana USA, pp [2] Chuan-Chu Kuo and Hong-Tong Yau, A Delaunay-Based Region-Growing Approach to Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Points, Journal of Computer-Aided Design, Vol. 37, No. 8, pp [3] Dominique Attali, r- regular shape reconstruction from unorganized points, Proceedings of the thirteenth annual conference on Computational geometry, Nice, France pp [4] Ernst Peter Mucke, Shapes and Implementations in Three-Dimensional Geometry, PhD dissertation, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. [5] Eric Bittar, Nicolas Tsingos, Marie-paule Gascuel, Automatic reconstruction from unstructured data: Combining a medial axis and implicit surfaces, Proceedings of Eurographics in Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 14, No. 3, pp [6] Esdras Medeiros, Luiz Velho and Helio Lopes, Restricted BPA: Applying Ball-Pivoting on the Plane Proceedings of 17th Brazilian conference Computer Graphics and Image Processing, Curitiba, PR, Brazil, pp [7] F. Bernardini, C. Bajaj, J. Chen, and D. Schilore, Triangulation-based object reconstruction methods, Proceedings of the thirteenth conference on Computational Geometry, Nice, France, pp [8] Fausto Bernardini, and Chandrajit L. Bajaj, Sampling and reconstructing manifolds using alpha-shapes, Proceedings of 9th Canadian Conference Computational Geometry, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, pp [9] Fausto Bernardini, Joshua Mittleman, Holly Rushmeier, Claudio Silva and Gabriel Taubin, The ball-pivoting algorithm for surface reconstruction, IEEE Journal of Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 5, No. 2, pp [10] Gabriel Taubin, A signal processing approach to fair surface design, Proceedings of the 22nd annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, New York, USA, pp [11] H. Hoppe, T.DePose, T.Duchamp, J.McDonald and W.Stuetzle, Surface reconstruction from unorganized points, Proceedings of the 19th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, New York, USA, pp [12] H. Edelsbrunner and E. P. Mücke, Three-dimensional alpha shapes, Journal of ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 13, No.1, pp [13] J. D. Boissonnat, Geometric structures for three-dimensional shape representation, Journal of ACM Transactions on Graphics, vol. 3, pp [14] J. D. Boissonnat and F. Cazals, Smooth surface reconstruction via natural neighbor interpolation of distance functions, Proceedings of the sixteenth annual conference on Computational geometry, Hong Kong, pp [15] Ji Ma, Hsi-Yung Feng, and Lihui Wang, Delaunay-Based Triangular Surface Reconstruction from Points via Umbrella Facet Matching, Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, Toronto, Canada, pp [16] L. Kobbelt and M. Botsch, An interactive approach to point cloud triangulation, Journal of Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 19, No. 3, pp [17] N. Amenta, M. Bern and M. Kamvysselis, A new Voronoi-based Surface Reconstruction Algorithm, Proceedings of 25th annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Florida, USA, pp [18] N. Amenta, S. Choi and R. Kolluri, The power crust, Proceedings of the sixth ACM conference on Solid modeling and applications, Michigan, USA, pp [19] Peer Stelldinger, Topologically Correct Surface Reconstruction Using Alpha Shapes and Relations to Ball-Pivoting, Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Tampa, Florida, USA, pp.1-4. [20] Tamal K. Dey, Joachim Giesen and James Hudson, Delaunay Based Shape Reconstruction from Large Data, Proceedings of the IEEE conference on parallel and large-data visualization and graphics, SanDiego,CA, USA, pp
5 (a) (b) (c) Fig. 1. The Ball Pivoting Algorithm in 3D (a) A circle of diameter d pivots from sample point to sample point, connecting them with edges. (b) When the sampling density is too low, the edges are created by increasing the diameter of the ball. (c) When the pivoting ball is not able to reach to the sample points, then ball starts rotating in other direction. Fig. 3 Bunny 5
6 Fig. 4 Dragon Fig. 5 Buddha Table 1: Summary of Results of Ball Pivoting Algorithm 6
7 7
A Constrained Delaunay Triangle Mesh Method for Three-Dimensional Unstructured Boundary Point Cloud
 International Journal of Computer Systems (ISSN: 2394-1065), Volume 03 Issue 02, February, 2016 Available at http://www.ijcsonline.com/ A Constrained Delaunay Triangle Mesh Method for Three-Dimensional
International Journal of Computer Systems (ISSN: 2394-1065), Volume 03 Issue 02, February, 2016 Available at http://www.ijcsonline.com/ A Constrained Delaunay Triangle Mesh Method for Three-Dimensional
Surface Reconstruction. Gianpaolo Palma
 Surface Reconstruction Gianpaolo Palma Surface reconstruction Input Point cloud With or without normals Examples: multi-view stereo, union of range scan vertices Range scans Each scan is a triangular mesh
Surface Reconstruction Gianpaolo Palma Surface reconstruction Input Point cloud With or without normals Examples: multi-view stereo, union of range scan vertices Range scans Each scan is a triangular mesh
ON THE WAY TO WATER-TIGHT MESH
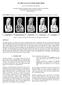 ON THE WAY TO WATER-TIGHT MESH Rui Liu, Darius Burschka, Gerd Hirzinger Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics, German Aerospace Center (DLR) Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany. Rui.Liu@dlr.de KEY
ON THE WAY TO WATER-TIGHT MESH Rui Liu, Darius Burschka, Gerd Hirzinger Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics, German Aerospace Center (DLR) Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany. Rui.Liu@dlr.de KEY
Correctness. The Powercrust Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction. Correctness. Correctness. Delaunay Triangulation. Tools - Voronoi Diagram
 Correctness The Powercrust Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction Nina Amenta Sunghee Choi Ravi Kolluri University of Texas at Austin Boundary of a solid Close to original surface Homeomorphic to original
Correctness The Powercrust Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction Nina Amenta Sunghee Choi Ravi Kolluri University of Texas at Austin Boundary of a solid Close to original surface Homeomorphic to original
Shape and Appearance from Images and Range Data
 SIGGRAPH 2000 Course on 3D Photography Shape and Appearance from Images and Range Data Brian Curless University of Washington Overview Range images vs. point clouds Registration Reconstruction from point
SIGGRAPH 2000 Course on 3D Photography Shape and Appearance from Images and Range Data Brian Curless University of Washington Overview Range images vs. point clouds Registration Reconstruction from point
The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction
 The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction 1. Briefly summarize the paper s contributions. Does it address a new problem? Does it present a new approach? Does it show new types of results?
The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction 1. Briefly summarize the paper s contributions. Does it address a new problem? Does it present a new approach? Does it show new types of results?
Surface reconstruction based on a dynamical system
 EUROGRAPHICS 2002 / G. Drettakis and H.-P. Seidel (Guest Editors) Volume 21 (2002), Number 3 Surface reconstruction based on a dynamical system N.N. Abstract We present an efficient algorithm that computes
EUROGRAPHICS 2002 / G. Drettakis and H.-P. Seidel (Guest Editors) Volume 21 (2002), Number 3 Surface reconstruction based on a dynamical system N.N. Abstract We present an efficient algorithm that computes
Comparative Study of Combinatorial 3D Reconstruction Algorithms
 Comparative Study of Combinatorial 3D Reconstruction Algorithms Abdelaaziz MAHDAOUI #1, Aziz BOUAZI *2, Abdallah. MARHRAOUI HSAINI *2, El Hassan SBAI *2 # Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University
Comparative Study of Combinatorial 3D Reconstruction Algorithms Abdelaaziz MAHDAOUI #1, Aziz BOUAZI *2, Abdallah. MARHRAOUI HSAINI *2, El Hassan SBAI *2 # Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University
LATEST TRENDS on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, SIMULATION, MODELLING
 3D surface reconstruction of objects by using stereoscopic viewing Baki Koyuncu, Kurtuluş Küllü bkoyuncu@ankara.edu.tr kkullu@eng.ankara.edu.tr Computer Engineering Department, Ankara University, Ankara,
3D surface reconstruction of objects by using stereoscopic viewing Baki Koyuncu, Kurtuluş Küllü bkoyuncu@ankara.edu.tr kkullu@eng.ankara.edu.tr Computer Engineering Department, Ankara University, Ankara,
Provably Good Moving Least Squares
 Provably Good Moving Least Squares Ravikrishna Kolluri Computer Science Division University of California at Berkeley 1 Problem Definition Given a set of samples on a closed surface build a representation
Provably Good Moving Least Squares Ravikrishna Kolluri Computer Science Division University of California at Berkeley 1 Problem Definition Given a set of samples on a closed surface build a representation
Geometric Modeling in Graphics
 Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Moving Least Squares Multiresolution Surface Approximation
 Moving Least Squares Multiresolution Surface Approximation BORIS MEDEROS LUIZ VELHO LUIZ HENRIQUE DE FIGUEIREDO IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada Estrada Dona Castorina 110, 22461-320 Rio de
Moving Least Squares Multiresolution Surface Approximation BORIS MEDEROS LUIZ VELHO LUIZ HENRIQUE DE FIGUEIREDO IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada Estrada Dona Castorina 110, 22461-320 Rio de
Geometric Modeling. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo
 Geometric Modeling Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo What are 3D Objects? 3D Object Representations What are 3D objects? The Graphics Process 3D Object Representations Raw
Geometric Modeling Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo What are 3D Objects? 3D Object Representations What are 3D objects? The Graphics Process 3D Object Representations Raw
TERRAIN RECONSTRUCTION FROM GROUND BASED LASER DATA
 TERRAIN RECONSTRUCTION FROM GROUND BASED LASER DATA Bruce King1, Elzbieta Matuk1, Krzysztof Matuk1, Christopher M. Gold 1 Address: The Department of Land Surveying & Geo Informatics The Hong Kong Polytechnic
TERRAIN RECONSTRUCTION FROM GROUND BASED LASER DATA Bruce King1, Elzbieta Matuk1, Krzysztof Matuk1, Christopher M. Gold 1 Address: The Department of Land Surveying & Geo Informatics The Hong Kong Polytechnic
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface Reconstruction
 A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction M. GOPI, SHANKA KISHNAN Univ. of California, Irvine gopi@ics.uci.edu AT&T Labs - esearch krishnas@research.att.com Abstract. We
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction M. GOPI, SHANKA KISHNAN Univ. of California, Irvine gopi@ics.uci.edu AT&T Labs - esearch krishnas@research.att.com Abstract. We
Automatic 3D wig Generation Method using FFD and Robotic Arm
 International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 12, Number 9 (2017) pp. 2104-2108 Automatic 3D wig Generation Method using FFD and Robotic Arm Md Saifur Rahman 1, Chulhyung
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 12, Number 9 (2017) pp. 2104-2108 Automatic 3D wig Generation Method using FFD and Robotic Arm Md Saifur Rahman 1, Chulhyung
SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION FROM MULTI-VALUED GRID DATA
 4 th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, December 26-28, 2001, Dhaka, Bangladesh/pp. VII 29-33 SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION FROM MULTI-VALUED GRID DATA S. Adithya and Dibakar Sen* Department
4 th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, December 26-28, 2001, Dhaka, Bangladesh/pp. VII 29-33 SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION FROM MULTI-VALUED GRID DATA S. Adithya and Dibakar Sen* Department
A THINNING ALGORITHM FOR TOPOLOGICALLY CORRECT 3D SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION
 A THINNING ALGORITHM FOR TOPOLOGICALLY CORRECT 3D SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION Leonid Tcherniavski Department of Informatics University of Hamburg tcherniavski@informatik.uni-hamburg.de ABSTRACT The existing
A THINNING ALGORITHM FOR TOPOLOGICALLY CORRECT 3D SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION Leonid Tcherniavski Department of Informatics University of Hamburg tcherniavski@informatik.uni-hamburg.de ABSTRACT The existing
3D Models from Range Sensors. Gianpaolo Palma
 3D Models from Range Sensors Gianpaolo Palma Who Gianpaolo Palma Researcher at Visual Computing Laboratory (ISTI-CNR) Expertise: 3D scanning, Mesh Processing, Computer Graphics E-mail: gianpaolo.palma@isti.cnr.it
3D Models from Range Sensors Gianpaolo Palma Who Gianpaolo Palma Researcher at Visual Computing Laboratory (ISTI-CNR) Expertise: 3D scanning, Mesh Processing, Computer Graphics E-mail: gianpaolo.palma@isti.cnr.it
A Volumetric Method for Building Complex Models from Range Images
 A Volumetric Method for Building Complex Models from Range Images Brian Curless Marc Levoy Computer Graphics Laboratory Stanford University Introduction Goal Given a set of aligned, dense range images,
A Volumetric Method for Building Complex Models from Range Images Brian Curless Marc Levoy Computer Graphics Laboratory Stanford University Introduction Goal Given a set of aligned, dense range images,
Complex Models from Range Images. A Volumetric Method for Building. Brian Curless. Marc Levoy. Computer Graphics Laboratory. Stanford University
 A Volumetric Method for Building Complex Models from Range Images Computer Graphics Laboratory Stanford University Brian Curless Marc Levoy Introduction Goal Given a set of aligned, dense range images,
A Volumetric Method for Building Complex Models from Range Images Computer Graphics Laboratory Stanford University Brian Curless Marc Levoy Introduction Goal Given a set of aligned, dense range images,
A fast algorithm for manifold reconstruction of surfaces
 Proceedings of the IMProVe 2011 International conference on Innovative Methods in Product Design June 15 th 17 th, 2011, Venice, Italy L. Di Angelo (a), L. Giaccari (a) (a) Department of Industrial Engineering,
Proceedings of the IMProVe 2011 International conference on Innovative Methods in Product Design June 15 th 17 th, 2011, Venice, Italy L. Di Angelo (a), L. Giaccari (a) (a) Department of Industrial Engineering,
A New Voronoi-Based Surface Reconstruction Algorithm
 A New Voronoi-Based Surface Reconstruction Algorithm Nina Amenta UT - Austin Marshall Bern Xerox PARC Manolis Kamvysselis M.I.T. Abstract We describe our experience with a new algorithm for the reconstruction
A New Voronoi-Based Surface Reconstruction Algorithm Nina Amenta UT - Austin Marshall Bern Xerox PARC Manolis Kamvysselis M.I.T. Abstract We describe our experience with a new algorithm for the reconstruction
Performance analysis of different surface reconstruction algorithms for 3D reconstruction of outdoor objects from their digital images
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-2425-9 RESEARCH Open Access Performance analysis of different surface reconstruction algorithms for 3D reconstruction of outdoor objects from their digital images Abhik Maiti * and
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-2425-9 RESEARCH Open Access Performance analysis of different surface reconstruction algorithms for 3D reconstruction of outdoor objects from their digital images Abhik Maiti * and
Outline. Reconstruction of 3D Meshes from Point Clouds. Motivation. Problem Statement. Applications. Challenges
 Reconstruction of 3D Meshes from Point Clouds Ming Zhang Patrick Min cs598b, Geometric Modeling for Computer Graphics Feb. 17, 2000 Outline - problem statement - motivation - applications - challenges
Reconstruction of 3D Meshes from Point Clouds Ming Zhang Patrick Min cs598b, Geometric Modeling for Computer Graphics Feb. 17, 2000 Outline - problem statement - motivation - applications - challenges
Survey of Surface Reconstruction Algorithms
 Journal of Signal and Information Processing, 2014, 5, 63-79 Published Online August 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsip http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jsip.2014.53009 Survey of Surface Reconstruction
Journal of Signal and Information Processing, 2014, 5, 63-79 Published Online August 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsip http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jsip.2014.53009 Survey of Surface Reconstruction
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface Reconstruction
 A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction M. GOPI 1, SHANKA KISHNAN 2 1 Univ. of California, Irvine gopi@ics.uci.edu 2 AT&T Labs - esearch krishnas@research.att.com Abstract.
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction M. GOPI 1, SHANKA KISHNAN 2 1 Univ. of California, Irvine gopi@ics.uci.edu 2 AT&T Labs - esearch krishnas@research.att.com Abstract.
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface Reconstruction
 A ast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction Category: esearch Paper (Number: papers 1364) Abstract We present a fast, memory efficient, linear time algorithm that generates
A ast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction Category: esearch Paper (Number: papers 1364) Abstract We present a fast, memory efficient, linear time algorithm that generates
A Volumetric Method for Building Complex Models from Range Images
 A Volumetric Method for Building Complex Models from Range Images 1. Briefly summarize the paper s contributions. Does it address a new problem? Does it present a new approach? Does it show new types of
A Volumetric Method for Building Complex Models from Range Images 1. Briefly summarize the paper s contributions. Does it address a new problem? Does it present a new approach? Does it show new types of
Point-based Simplification Algorithm
 Point-based Simplification Algorithm Pai-Feng Lee 1, Bin-Shyan Jong 2 Department of Information Management, Hsing Wu College 1 Dept. of Information and Computer Engineering Engineering, Chung Yuan Christian
Point-based Simplification Algorithm Pai-Feng Lee 1, Bin-Shyan Jong 2 Department of Information Management, Hsing Wu College 1 Dept. of Information and Computer Engineering Engineering, Chung Yuan Christian
Outline of the presentation
 Surface Reconstruction Petra Surynková Charles University in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics petra.surynkova@mff.cuni.cz Outline of the presentation My work up to now Surfaces of Building Practice
Surface Reconstruction Petra Surynková Charles University in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics petra.surynkova@mff.cuni.cz Outline of the presentation My work up to now Surfaces of Building Practice
Estimating Geometry and Topology from Voronoi Diagrams
 Estimating Geometry and Topology from Voronoi Diagrams Tamal K. Dey The Ohio State University Tamal Dey OSU Chicago 07 p.1/44 Voronoi diagrams Tamal Dey OSU Chicago 07 p.2/44 Voronoi diagrams Tamal Dey
Estimating Geometry and Topology from Voronoi Diagrams Tamal K. Dey The Ohio State University Tamal Dey OSU Chicago 07 p.1/44 Voronoi diagrams Tamal Dey OSU Chicago 07 p.2/44 Voronoi diagrams Tamal Dey
Fast 3D surface reconstruction from point clouds using graph-based fronts propagation
 Fast 3D surface reconstruction from point clouds using graph-based fronts propagation Abdallah El Chakik, Xavier Desquesnes, Abderrahim Elmoataz UCBN, GREYC - UMR CNRS 6972, 6.Bvd Marechal Juin, 14050
Fast 3D surface reconstruction from point clouds using graph-based fronts propagation Abdallah El Chakik, Xavier Desquesnes, Abderrahim Elmoataz UCBN, GREYC - UMR CNRS 6972, 6.Bvd Marechal Juin, 14050
Filling holes in complex surfaces using volumetric diffusion
 Submitted to SIGGRAPH 2001 Filling holes in complex surfaces using volumetric diffusion Steve Marschner James Davis Matt Garr Marc Levoy Stanford University Abstract We address the problem of building
Submitted to SIGGRAPH 2001 Filling holes in complex surfaces using volumetric diffusion Steve Marschner James Davis Matt Garr Marc Levoy Stanford University Abstract We address the problem of building
Surface Reconstruction
 Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2006) Surface Reconstruction 2009.12.29 Some methods for surface reconstruction Classification 1. Based on Delaunay triangulation(or Voronoi diagram) Alpha
Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2006) Surface Reconstruction 2009.12.29 Some methods for surface reconstruction Classification 1. Based on Delaunay triangulation(or Voronoi diagram) Alpha
A qualitative approach for medial computation
 A qualitative approach for medial computation Jacklin Michael 1 Dr. M. Ramanathan 2 Prof. S. Vinothkumar 3 Dept. of Computer Science Dept. of Engineering Design Dept. of Computer Science SNS College of
A qualitative approach for medial computation Jacklin Michael 1 Dr. M. Ramanathan 2 Prof. S. Vinothkumar 3 Dept. of Computer Science Dept. of Engineering Design Dept. of Computer Science SNS College of
Ray Tracing Point Set Surfaces
 Ray Tracing Point Set Surfaces Anders Adamson Marc Alexa TU Darmstadt, GRIS Fraunhoferstr. 5, 64283 Darmstadt {aadamson,alexa}@gris.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Abstract Point set surfaces are a smooth manifold
Ray Tracing Point Set Surfaces Anders Adamson Marc Alexa TU Darmstadt, GRIS Fraunhoferstr. 5, 64283 Darmstadt {aadamson,alexa}@gris.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Abstract Point set surfaces are a smooth manifold
Generating 3D Meshes from Range Data
 Princeton University COS598B Lectures on 3D Modeling Generating 3D Meshes from Range Data Robert Kalnins Robert Osada Overview Range Images Optical Scanners Error sources and solutions Range Surfaces Mesh
Princeton University COS598B Lectures on 3D Modeling Generating 3D Meshes from Range Data Robert Kalnins Robert Osada Overview Range Images Optical Scanners Error sources and solutions Range Surfaces Mesh
Multi-View Matching & Mesh Generation. Qixing Huang Feb. 13 th 2017
 Multi-View Matching & Mesh Generation Qixing Huang Feb. 13 th 2017 Geometry Reconstruction Pipeline RANSAC --- facts Sampling Feature point detection [Gelfand et al. 05, Huang et al. 06] Correspondences
Multi-View Matching & Mesh Generation Qixing Huang Feb. 13 th 2017 Geometry Reconstruction Pipeline RANSAC --- facts Sampling Feature point detection [Gelfand et al. 05, Huang et al. 06] Correspondences
Processing 3D Surface Data
 Processing 3D Surface Data Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 12 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics 3D Surfaces 1 3D surface data... where from? Iso-surfacing
Processing 3D Surface Data Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 12 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics 3D Surfaces 1 3D surface data... where from? Iso-surfacing
Plotting technologies for the study of functions of two real variables
 Plotting technologies for the study of functions of two real variables David Zeitoun 1 and Thierry Dana-Picard 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Orot College of Education, Rehovot, Israel, ed.technologie@gmail.com
Plotting technologies for the study of functions of two real variables David Zeitoun 1 and Thierry Dana-Picard 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Orot College of Education, Rehovot, Israel, ed.technologie@gmail.com
03 - Reconstruction. Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung. CSCI-GA Geometric Modeling - Spring 17 - Daniele Panozzo
 3 - Reconstruction Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Geometry Acquisition Pipeline Scanning: results in range images Registration: bring all range images to one coordinate system Stitching/ reconstruction:
3 - Reconstruction Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Geometry Acquisition Pipeline Scanning: results in range images Registration: bring all range images to one coordinate system Stitching/ reconstruction:
VoroCrust: Simultaneous Surface Reconstruction and Volume Meshing with Voronoi cells
 VoroCrust: Simultaneous Surface Reconstruction and Volume Meshing with Voronoi cells Scott A. Mitchell (speaker), joint work with Ahmed H. Mahmoud, Ahmad A. Rushdi, Scott A. Mitchell, Ahmad Abdelkader
VoroCrust: Simultaneous Surface Reconstruction and Volume Meshing with Voronoi cells Scott A. Mitchell (speaker), joint work with Ahmed H. Mahmoud, Ahmad A. Rushdi, Scott A. Mitchell, Ahmad Abdelkader
Smooth Surface Reconstruction from Noisy Clouds
 Smooth Surface Reconstruction from Noisy Clouds Boris Mederos, Luiz Velho and Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada, Estrada Dona Castorina 110, 22461-320 Rio de Janeiro,
Smooth Surface Reconstruction from Noisy Clouds Boris Mederos, Luiz Velho and Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada, Estrada Dona Castorina 110, 22461-320 Rio de Janeiro,
Surface segmentation for improved isotropic remeshing
 J. Edwards (Univ. of Texas) IMR 2012 1 / 20 Surface segmentation for improved isotropic remeshing John Edwards, Wenping Wang, Chandrajit Bajaj Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at
J. Edwards (Univ. of Texas) IMR 2012 1 / 20 Surface segmentation for improved isotropic remeshing John Edwards, Wenping Wang, Chandrajit Bajaj Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at
A Robust Procedure to Eliminate Degenerate Faces from Triangle Meshes
 A Robust Procedure to Eliminate Degenerate Faces from Triangle Meshes Mario Botsch, Leif P. Kobbelt Computer Graphics Group, RWTH Aachen, kobbelt,botsch @cs.rwth-aachen.de Abstract When using triangle
A Robust Procedure to Eliminate Degenerate Faces from Triangle Meshes Mario Botsch, Leif P. Kobbelt Computer Graphics Group, RWTH Aachen, kobbelt,botsch @cs.rwth-aachen.de Abstract When using triangle
Technical Report A Digital Topology-based Method for the Topological Filtering of a Reconstructed Surface
 Technical Report 2008-004 A Digital Topology-based Method for the Topological Filtering of a Reconstructed Surface D. Li a, M. Allili b a Université de Sherbrooke Department of Computer Science Sherbrooke,
Technical Report 2008-004 A Digital Topology-based Method for the Topological Filtering of a Reconstructed Surface D. Li a, M. Allili b a Université de Sherbrooke Department of Computer Science Sherbrooke,
Skeleton Based Solid Representation with Topology Preservation
 Skeleton Based Solid Representation with Topology Preservation Ariel Shamir The Interdisciplinary Center Shaham Amir Tel-Aviv University Corresponding author: Dr. Ariel Shamir Efi Arazi School of Computer
Skeleton Based Solid Representation with Topology Preservation Ariel Shamir The Interdisciplinary Center Shaham Amir Tel-Aviv University Corresponding author: Dr. Ariel Shamir Efi Arazi School of Computer
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface Reconstruction
 High Performance Computer Graphics, Multimedia and Visualisation Volume 1,(2000), Number 1 pp. 1-12 A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface Reconstruction M. Gopi Department of Computer
High Performance Computer Graphics, Multimedia and Visualisation Volume 1,(2000), Number 1 pp. 1-12 A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface Reconstruction M. Gopi Department of Computer
Feature Extraction for Illustrating 3D Stone Tools from Unorganized Point Clouds
 Feature Extraction for Illustrating 3D Stone Tools from Unorganized Point Clouds Enkhbayar Altantsetseg 1) Yuta Muraki 2) Katsutsugu Matsuyama 2) Fumito Chiba 3) Kouichi Konno 2) 1) Graduate School of
Feature Extraction for Illustrating 3D Stone Tools from Unorganized Point Clouds Enkhbayar Altantsetseg 1) Yuta Muraki 2) Katsutsugu Matsuyama 2) Fumito Chiba 3) Kouichi Konno 2) 1) Graduate School of
Geometric Modeling Based on Polygonal Meshes
 ³ ³ Æ I N F O R M A T I K «Geometric Modeling Based on Polygonal Meshes Leif P. Kobbelt Stephan Bischoff Mario Botsch Kolja Kähler Christian Rössl Robert Schneider Jens Vorsatz MPI I 2000 4-002 July 2000
³ ³ Æ I N F O R M A T I K «Geometric Modeling Based on Polygonal Meshes Leif P. Kobbelt Stephan Bischoff Mario Botsch Kolja Kähler Christian Rössl Robert Schneider Jens Vorsatz MPI I 2000 4-002 July 2000
Computing and Rendering Point Set Surfaces
 Computing and Rendering Point Set Surfaces Marc Alexa TU Darmstadt Johannes Behr ZGDV Darmstadt Daniel Cohen-Or Tel Aviv University Shachar Fleishman Tel Aviv University David Levin Tel Aviv University
Computing and Rendering Point Set Surfaces Marc Alexa TU Darmstadt Johannes Behr ZGDV Darmstadt Daniel Cohen-Or Tel Aviv University Shachar Fleishman Tel Aviv University David Levin Tel Aviv University
G 2 Interpolation for Polar Surfaces
 1 G 2 Interpolation for Polar Surfaces Jianzhong Wang 1, Fuhua Cheng 2,3 1 University of Kentucky, jwangf@uky.edu 2 University of Kentucky, cheng@cs.uky.edu 3 National Tsinhua University ABSTRACT In this
1 G 2 Interpolation for Polar Surfaces Jianzhong Wang 1, Fuhua Cheng 2,3 1 University of Kentucky, jwangf@uky.edu 2 University of Kentucky, cheng@cs.uky.edu 3 National Tsinhua University ABSTRACT In this
Geometric Modeling and Processing
 Geometric Modeling and Processing Tutorial of 3DIM&PVT 2011 (Hangzhou, China) May 16, 2011 4. Geometric Registration 4.1 Rigid Registration Range Scanning: Reconstruction Set of raw scans Reconstructed
Geometric Modeling and Processing Tutorial of 3DIM&PVT 2011 (Hangzhou, China) May 16, 2011 4. Geometric Registration 4.1 Rigid Registration Range Scanning: Reconstruction Set of raw scans Reconstructed
A Global Laplacian Smoothing Approach with Feature Preservation
 A Global Laplacian Smoothing Approach with Feature Preservation hongping Ji Ligang Liu Guojin Wang Department of Mathematics State Key Lab of CAD&CG hejiang University Hangzhou, 310027 P.R. China jzpboy@yahoo.com.cn,
A Global Laplacian Smoothing Approach with Feature Preservation hongping Ji Ligang Liu Guojin Wang Department of Mathematics State Key Lab of CAD&CG hejiang University Hangzhou, 310027 P.R. China jzpboy@yahoo.com.cn,
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing. David Eppstein
 Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Medial Scaffolds for 3D data modelling: status and challenges. Frederic Fol Leymarie
 Medial Scaffolds for 3D data modelling: status and challenges Frederic Fol Leymarie Outline Background Method and some algorithmic details Applications Shape representation: From the Medial Axis to the
Medial Scaffolds for 3D data modelling: status and challenges Frederic Fol Leymarie Outline Background Method and some algorithmic details Applications Shape representation: From the Medial Axis to the
Minimizing Edge Length to Connect Sparsely Sampled Unstructured Point Sets
 Minimizing Edge Length to Connect Sparsely Sampled Unstructured Point Sets Stefan Ohrhallinger a,b, Sudhir Mudur a, Michael Wimmer b a Concordia University, Montréal b Vienna University of Technology Abstract
Minimizing Edge Length to Connect Sparsely Sampled Unstructured Point Sets Stefan Ohrhallinger a,b, Sudhir Mudur a, Michael Wimmer b a Concordia University, Montréal b Vienna University of Technology Abstract
Minimum Surface Area Based Complex Hole Filling Algorithm of 3D Mesh
 Minimum Surface Area Based Complex Hole Filling Algorithm of 3D Mesh Enkhbayar Altantsetseg 1) Katsutsugu Matsuyama ) Kouichi Konno ) 1) National University of Mongolia ) Iwate University {enkhbayar.a}
Minimum Surface Area Based Complex Hole Filling Algorithm of 3D Mesh Enkhbayar Altantsetseg 1) Katsutsugu Matsuyama ) Kouichi Konno ) 1) National University of Mongolia ) Iwate University {enkhbayar.a}
LASER ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING PROCESS PLANNING AND AUTOMATION
 LASER ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING PROCESS PLANNING AND AUTOMATION Jun Zhang, Jianzhong Ruan, Frank Liou Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics Intelligent Systems Center
LASER ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING PROCESS PLANNING AND AUTOMATION Jun Zhang, Jianzhong Ruan, Frank Liou Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics Intelligent Systems Center
Reconstructing Surfaces Using Envelopes: Bridging the Gap between Theory and Practice
 Reconstructing Surfaces Using Envelopes: Bridging the Gap between Theory and Practice Justin Bisceglio Blue Sky Studios, and University of Connecuticut, Department of Computer Science T.J. Peters University
Reconstructing Surfaces Using Envelopes: Bridging the Gap between Theory and Practice Justin Bisceglio Blue Sky Studios, and University of Connecuticut, Department of Computer Science T.J. Peters University
Fan-Meshes: A Geometric Primitive for Point-based Description of 3D Models and Scenes
 Fan-Meshes: A Geometric Primitive for Point-based Description of 3D Models and Scenes Xiaotian Yan, Fang Meng, Hongbin Zha National Laboratory on Machine Perception Peking University, Beijing, P. R. China
Fan-Meshes: A Geometric Primitive for Point-based Description of 3D Models and Scenes Xiaotian Yan, Fang Meng, Hongbin Zha National Laboratory on Machine Perception Peking University, Beijing, P. R. China
Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Point Cloud Data via Progressive Local Mesh Matching
 Western Uniersity Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 2011 Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Point Cloud Data ia Progressie Local Mesh Matching Ji Ma The Uniersity
Western Uniersity Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 2011 Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Point Cloud Data ia Progressie Local Mesh Matching Ji Ma The Uniersity
Saab. Kyle McDonald. Polygon Meshes
 Saab Kyle McDonald Polygon Meshes Siddhartha Chaudhuri http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~cs749 What is a polygon mesh? Like a point cloud, it is a discrete sampling of a surface... but, it adds linear (flat)
Saab Kyle McDonald Polygon Meshes Siddhartha Chaudhuri http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~cs749 What is a polygon mesh? Like a point cloud, it is a discrete sampling of a surface... but, it adds linear (flat)
The Medial Axis of the Union of Inner Voronoi Balls in the Plane
 The Medial Axis of the Union of Inner Voronoi Balls in the Plane Joachim Giesen a, Balint Miklos b,, Mark Pauly b a Max-Planck Institut für Informatik, Saarbrücken, Germany b Applied Geometry Group, ETH
The Medial Axis of the Union of Inner Voronoi Balls in the Plane Joachim Giesen a, Balint Miklos b,, Mark Pauly b a Max-Planck Institut für Informatik, Saarbrücken, Germany b Applied Geometry Group, ETH
coding of various parts showing different features, the possibility of rotation or of hiding covering parts of the object's surface to gain an insight
 Three-Dimensional Object Reconstruction from Layered Spatial Data Michael Dangl and Robert Sablatnig Vienna University of Technology, Institute of Computer Aided Automation, Pattern Recognition and Image
Three-Dimensional Object Reconstruction from Layered Spatial Data Michael Dangl and Robert Sablatnig Vienna University of Technology, Institute of Computer Aided Automation, Pattern Recognition and Image
3D Object Representation. Michael Kazhdan ( /657)
 3D Object Representation Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) 3D Objects How can this object be represented in a computer? 3D Objects This one? H&B Figure 10.46 3D Objects This one? H&B Figure 9.9 3D Objects
3D Object Representation Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) 3D Objects How can this object be represented in a computer? 3D Objects This one? H&B Figure 10.46 3D Objects This one? H&B Figure 9.9 3D Objects
CS 468, Spring 2013 Differential Geometry for Computer Science Justin Solomon and Adrian Butscher
 http://alice.loria.fr/index.php/publications.html?redirect=0&paper=vsdm@2011&author=levy CS 468, Spring 2013 Differential Geometry for Computer Science Justin Solomon and Adrian Butscher µ R 3 µ R 2 http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/bc/double_torus_illustration.png
http://alice.loria.fr/index.php/publications.html?redirect=0&paper=vsdm@2011&author=levy CS 468, Spring 2013 Differential Geometry for Computer Science Justin Solomon and Adrian Butscher µ R 3 µ R 2 http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/bc/double_torus_illustration.png
Sculpture Scanning. 3D Photography. Applications. Graphics Research. Why Scan Sculptures? Why Scan Sculptures? The Pietà Project
 3D Photography Obtaining 3D shape (and sometimes color) of real-world objects Applications Determine whether manufactured parts are within tolerances Plan surgery on computer model, visualize in real time
3D Photography Obtaining 3D shape (and sometimes color) of real-world objects Applications Determine whether manufactured parts are within tolerances Plan surgery on computer model, visualize in real time
3D SPATIAL DATA ACQUISITION AND MODELING OF ANGHEL SALIGNY MONUMENT USING TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING SCIENCES VOL. 2(15), issue 2_2012 ISSN 2247-3769 ISSN-L 2247-3769 (Print) / e-issn:2284-7197 3D SPATIAL DATA ACQUISITION AND MODELING OF ANGHEL SALIGNY MONUMENT USING TERRESTRIAL
JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING SCIENCES VOL. 2(15), issue 2_2012 ISSN 2247-3769 ISSN-L 2247-3769 (Print) / e-issn:2284-7197 3D SPATIAL DATA ACQUISITION AND MODELING OF ANGHEL SALIGNY MONUMENT USING TERRESTRIAL
COMPUTING CONSTRAINED DELAUNAY
 COMPUTING CONSTRAINED DELAUNAY TRIANGULATIONS IN THE PLANE By Samuel Peterson, University of Minnesota Undergraduate The Goal The Problem The Algorithms The Implementation Applications Acknowledgments
COMPUTING CONSTRAINED DELAUNAY TRIANGULATIONS IN THE PLANE By Samuel Peterson, University of Minnesota Undergraduate The Goal The Problem The Algorithms The Implementation Applications Acknowledgments
Point Cloud Library - Toyota Code Sprint Final Report
 Point Cloud Library - Toyota Code Sprint Final Report Alexandru E. Ichim April 1, 2012 1 Work Done This section will present the work I have done in addition to the results presented in the midterm report.
Point Cloud Library - Toyota Code Sprint Final Report Alexandru E. Ichim April 1, 2012 1 Work Done This section will present the work I have done in addition to the results presented in the midterm report.
Reverse Engineering: Mechanical. Dr. Tarek A. Tutunji
 Reverse Engineering: Mechanical Dr. Tarek A. Tutunji Mechanical RE References: 1. RE (reverse engineering) as necessary phase by rapid product development by Sokovic and Kopac 2. A Practical Appreciation
Reverse Engineering: Mechanical Dr. Tarek A. Tutunji Mechanical RE References: 1. RE (reverse engineering) as necessary phase by rapid product development by Sokovic and Kopac 2. A Practical Appreciation
AUTOMATED 3D MODELING OF URBAN ENVIRONMENTS
 AUTOMATED 3D MODELING OF URBAN ENVIRONMENTS Ioannis Stamos Department of Computer Science Hunter College, City University of New York 695 Park Avenue, New York NY 10065 istamos@hunter.cuny.edu http://www.cs.hunter.cuny.edu/
AUTOMATED 3D MODELING OF URBAN ENVIRONMENTS Ioannis Stamos Department of Computer Science Hunter College, City University of New York 695 Park Avenue, New York NY 10065 istamos@hunter.cuny.edu http://www.cs.hunter.cuny.edu/
Computational Topology in Reconstruction, Mesh Generation, and Data Analysis
 Computational Topology in Reconstruction, Mesh Generation, and Data Analysis Tamal K. Dey Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Ohio State University Dey (2014) Computational Topology CCCG
Computational Topology in Reconstruction, Mesh Generation, and Data Analysis Tamal K. Dey Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Ohio State University Dey (2014) Computational Topology CCCG
Using Semi-Regular 4 8 Meshes for Subdivision Surfaces
 Using Semi-Regular 8 Meshes for Subdivision Surfaces Luiz Velho IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada Abstract. Semi-regular 8 meshes are refinable triangulated quadrangulations. They provide a
Using Semi-Regular 8 Meshes for Subdivision Surfaces Luiz Velho IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada Abstract. Semi-regular 8 meshes are refinable triangulated quadrangulations. They provide a
3D Modeling Using Planar Segments And Mesh Elements. Gene Yu and George Wolberg. City College / CUNY New York, NY 10031
 3D Modeling Using Planar Segments And Mesh Elements Ioannis Stamos Dept. of Computer Science Hunter College / CUNY New York, NY 10021 istamos@hunter.cuny.edu Gene Yu and George Wolberg Dept. of Computer
3D Modeling Using Planar Segments And Mesh Elements Ioannis Stamos Dept. of Computer Science Hunter College / CUNY New York, NY 10021 istamos@hunter.cuny.edu Gene Yu and George Wolberg Dept. of Computer
Polygonal representation of 3D urban terrain point-cloud data
 Polygonal representation of 3D urban terrain point-cloud data part I Borislav Karaivanov The research is supported by ARO MURI 23 February 2011 USC 1 Description of problem Assumptions: unstructured 3D
Polygonal representation of 3D urban terrain point-cloud data part I Borislav Karaivanov The research is supported by ARO MURI 23 February 2011 USC 1 Description of problem Assumptions: unstructured 3D
Surface Reconstruction from Point Clouds by Transforming the Medial Scaffold
 Surface Reconstruction from Point Clouds by Transforming the Medial Scaffold Ming-Ching Chang LEMS, Engineering Brown University, USA mcchang@lems.brown.edu Frederic F. Leymarie Goldsmiths College University
Surface Reconstruction from Point Clouds by Transforming the Medial Scaffold Ming-Ching Chang LEMS, Engineering Brown University, USA mcchang@lems.brown.edu Frederic F. Leymarie Goldsmiths College University
Structured light 3D reconstruction
 Structured light 3D reconstruction Reconstruction pipeline and industrial applications rodola@dsi.unive.it 11/05/2010 3D Reconstruction 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance
Structured light 3D reconstruction Reconstruction pipeline and industrial applications rodola@dsi.unive.it 11/05/2010 3D Reconstruction 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance
Shape Reconstruction from Unorganized Cross-sections
 Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2007) Alexander Belyaev, Michael Garland (Editors) Shape Reconstruction from Unorganized Cross-sections Jean-Daniel BOISSONNAT Pooran MEMARI INRIA Sophia-Antipolis,
Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2007) Alexander Belyaev, Michael Garland (Editors) Shape Reconstruction from Unorganized Cross-sections Jean-Daniel BOISSONNAT Pooran MEMARI INRIA Sophia-Antipolis,
Filling Holes in Meshes
 Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing(2003) L. Kobbelt, P. Schröder, H. Hoppe (Editors) Filling Holes in Meshes Peter Liepa Alias Wavefront Abstract We describe a method for filling holes in unstructured
Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing(2003) L. Kobbelt, P. Schröder, H. Hoppe (Editors) Filling Holes in Meshes Peter Liepa Alias Wavefront Abstract We describe a method for filling holes in unstructured
Approximating Polygonal Objects by Deformable Smooth Surfaces
 Approximating Polygonal Objects by Deformable Smooth Surfaces Ho-lun Cheng and Tony Tan School of Computing, National University of Singapore hcheng,tantony@comp.nus.edu.sg Abstract. We propose a method
Approximating Polygonal Objects by Deformable Smooth Surfaces Ho-lun Cheng and Tony Tan School of Computing, National University of Singapore hcheng,tantony@comp.nus.edu.sg Abstract. We propose a method
Approximation of 3D-Parametric Functions by Bicubic B-spline Functions
 International Journal of Mathematical Modelling & Computations Vol. 02, No. 03, 2012, 211-220 Approximation of 3D-Parametric Functions by Bicubic B-spline Functions M. Amirfakhrian a, a Department of Mathematics,
International Journal of Mathematical Modelling & Computations Vol. 02, No. 03, 2012, 211-220 Approximation of 3D-Parametric Functions by Bicubic B-spline Functions M. Amirfakhrian a, a Department of Mathematics,
3D Modeling of Objects Using Laser Scanning
 1 3D Modeling of Objects Using Laser Scanning D. Jaya Deepu, LPU University, Punjab, India Email: Jaideepudadi@gmail.com Abstract: In the last few decades, constructing accurate three-dimensional models
1 3D Modeling of Objects Using Laser Scanning D. Jaya Deepu, LPU University, Punjab, India Email: Jaideepudadi@gmail.com Abstract: In the last few decades, constructing accurate three-dimensional models
Implicit Surfaces. Misha Kazhdan CS598b
 Implicit Surfaces Misha Kazhdan CS598b Definition: Given a function F the implicit surface S generated by this function is the set of zero points of F: S ( ) { p F = } = p The interior I is the set of
Implicit Surfaces Misha Kazhdan CS598b Definition: Given a function F the implicit surface S generated by this function is the set of zero points of F: S ( ) { p F = } = p The interior I is the set of
Surface Reconstruction by Structured Light Projection
 J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.), 2010, 15(5): 587-595 DOI: 10.1007/s12204-010-1052-9 Surface Reconstruction by Structured Light Projection YANG Rong-qian 1,2 ( ), CHEN Ya-zhu 2 ( ) (1. Department of
J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.), 2010, 15(5): 587-595 DOI: 10.1007/s12204-010-1052-9 Surface Reconstruction by Structured Light Projection YANG Rong-qian 1,2 ( ), CHEN Ya-zhu 2 ( ) (1. Department of
Point Set Surfaces. Abstract. 1 Introduction. Shachar Fleishman. Marc Alexa. Daniel Cohen-Or. Johannes Behr. David Levin. Claudio T.
 Point Set Surfaces Marc Alexa TU Darmstadt Johannes Behr ZGDV Darmstadt Daniel Cohen-Or Tel Aviv University Shachar Fleishman Tel Aviv University David Levin Tel Aviv University Claudio T. Silva AT&T Labs
Point Set Surfaces Marc Alexa TU Darmstadt Johannes Behr ZGDV Darmstadt Daniel Cohen-Or Tel Aviv University Shachar Fleishman Tel Aviv University David Levin Tel Aviv University Claudio T. Silva AT&T Labs
Surface Curvature Estimation for Edge Spinning Algorithm *
 Surface Curvature Estimation for Edge Spinning Algorithm * Martin Cermak and Vaclav Skala University of West Bohemia in Pilsen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Republic {cermakm skala}@kiv.zcu.cz
Surface Curvature Estimation for Edge Spinning Algorithm * Martin Cermak and Vaclav Skala University of West Bohemia in Pilsen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Republic {cermakm skala}@kiv.zcu.cz
To appear in IEEE Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2 our framework. Results from synthetic range images and from real space carved data sets
 To appear in IEEE Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1 Reconstructing Surfaces By Volumetric Regularization Using Radial Basis Functions Huong Quynh Dinh 1, Greg Turk 1, and Greg Slabaugh 2 1 Graphics,
To appear in IEEE Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1 Reconstructing Surfaces By Volumetric Regularization Using Radial Basis Functions Huong Quynh Dinh 1, Greg Turk 1, and Greg Slabaugh 2 1 Graphics,
A Simple Algorithm for Homeomorphic Surface Reconstruction
 A Simple Algorithm for Homeomorphic Surface Reconstruction N. Amenta* S. Choit T.K. Dey ~ N. Leekha Abstract 1 Introduction The problem of computing a piecewise linear approximation to a surface from a
A Simple Algorithm for Homeomorphic Surface Reconstruction N. Amenta* S. Choit T.K. Dey ~ N. Leekha Abstract 1 Introduction The problem of computing a piecewise linear approximation to a surface from a
Topology Preserving Tetrahedral Decomposition of Trilinear Cell
 Topology Preserving Tetrahedral Decomposition of Trilinear Cell Bong-Soo Sohn Department of Computer Engineering, Kyungpook National University Daegu 702-701, South Korea bongbong@knu.ac.kr http://bh.knu.ac.kr/
Topology Preserving Tetrahedral Decomposition of Trilinear Cell Bong-Soo Sohn Department of Computer Engineering, Kyungpook National University Daegu 702-701, South Korea bongbong@knu.ac.kr http://bh.knu.ac.kr/
A Hole-Filling Algorithm for Triangular Meshes. Abstract
 A Hole-Filling Algorithm for Triangular Meshes Lavanya Sita Tekumalla, Elaine Cohen UUCS-04-019 School of Computing University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 84112 USA December 20, 2004 Abstract Data obtained
A Hole-Filling Algorithm for Triangular Meshes Lavanya Sita Tekumalla, Elaine Cohen UUCS-04-019 School of Computing University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 84112 USA December 20, 2004 Abstract Data obtained
Proximity Graphs for Defining Surfaces over Point Clouds
 Proximity Graphs for Defining Surfaces over Point Clouds Germany Gabriel Zachmann University of Bonn Germany Zurich June, 2004 Surface Definition based on MLS Surface can be approximated by implicit function,
Proximity Graphs for Defining Surfaces over Point Clouds Germany Gabriel Zachmann University of Bonn Germany Zurich June, 2004 Surface Definition based on MLS Surface can be approximated by implicit function,
Computer Rubbings with Three-Dimensional Measurement Data
 Computer Rubbings with Three-Dimensional Measurement Data OOI Ken ichirou*, TSUKAMOTO Toshio**, SATO Kosuke* * Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Japan ** Gangoji Institute for Cultural
Computer Rubbings with Three-Dimensional Measurement Data OOI Ken ichirou*, TSUKAMOTO Toshio**, SATO Kosuke* * Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Japan ** Gangoji Institute for Cultural
Three-Dimensional α Shapes
 Herbert Edelsbrunner and Ernst P. Mücke ACM Tran. Graph. 13(1), 1994 20 September 2005 1 2 α-complexes Edelsbrunner s Algorithm 3 Properties Surface Reconstruction Shape Question Given a set of points,
Herbert Edelsbrunner and Ernst P. Mücke ACM Tran. Graph. 13(1), 1994 20 September 2005 1 2 α-complexes Edelsbrunner s Algorithm 3 Properties Surface Reconstruction Shape Question Given a set of points,
Triangulating Point Set Surfaces with Bounded Error
 Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2005) M. Desbrun, H. Pottmann (Editors) Triangulating Point Set Surfaces with Bounded Error Carlos E. Scheidegger Shachar Fleishman Cláudio T. Silva University
Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2005) M. Desbrun, H. Pottmann (Editors) Triangulating Point Set Surfaces with Bounded Error Carlos E. Scheidegger Shachar Fleishman Cláudio T. Silva University
2) For any triangle edge not on the boundary, there is exactly one neighboring
 Triangulating Trimmed NURBS Surfaces Chang Shu and Pierre Boulanger Abstract. This paper describes techniques for the piecewise linear approximation of trimmed NURBS surfaces. The problem, called surface
Triangulating Trimmed NURBS Surfaces Chang Shu and Pierre Boulanger Abstract. This paper describes techniques for the piecewise linear approximation of trimmed NURBS surfaces. The problem, called surface
IBM Pietà 3D Scanning Project :
 The IBM Pieta Project: A Historical Perspective Gabriel Taubin Brown University IBM Pietà 3D Scanning Project : 1998-2000 Shape Appearance http://www.research.ibm.com/pieta IBM Visual and Geometric Computing
The IBM Pieta Project: A Historical Perspective Gabriel Taubin Brown University IBM Pietà 3D Scanning Project : 1998-2000 Shape Appearance http://www.research.ibm.com/pieta IBM Visual and Geometric Computing
Other Voronoi/Delaunay Structures
 Other Voronoi/Delaunay Structures Overview Alpha hulls (a subset of Delaunay graph) Extension of Voronoi Diagrams Convex Hull What is it good for? The bounding region of a point set Not so good for describing
Other Voronoi/Delaunay Structures Overview Alpha hulls (a subset of Delaunay graph) Extension of Voronoi Diagrams Convex Hull What is it good for? The bounding region of a point set Not so good for describing
