Comparative Study of Combinatorial 3D Reconstruction Algorithms
|
|
|
- Rodney Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comparative Study of Combinatorial 3D Reconstruction Algorithms Abdelaaziz MAHDAOUI #1, Aziz BOUAZI *2, Abdallah. MARHRAOUI HSAINI *2, El Hassan SBAI *2 # Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University Moulay Ismail, Meknes, Morocco *Ecole Supérieure de Technologie, University Moulay Ismail, Meknes, Morocco Equipe Commande des systèmes et Traitement de l Information (C.S.T.I) Abstract---We present in this paper a comparative study between different combinatorial methods of reconstruction 3D from point cloud. Indeed, point cloud obtained experimentally from a laser scanner, we applied different reconstruction methods: Poisson, Marching-cube, Ball-pivoting and Alpha-shape. Our comparison criterion is based on the computation time as well as the quality of the mesh.quality is obtained by the measurement of the compactness of the triangles which constitute this mesh. We then lay out the results obtained in the form of a summary table highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each method. Keywords mesh, points cloud, compactness, Poisson, Marching-cube, Alpha-shape, Ball-pivoting. I. INTRODUCTION Given a set of points P R 3 sampled on a surface S, the objective of the surface reconstruction is to compute a continuous model of S from P. This model is called reconstruction of S from P. Surface reconstruction takes place in a large number of applications. Ithas been the subject of research for thirty years in the communities of graphical computing, geometric modelling and algorithmic geometry [1, 2]. This area has developed considerably in recent years, with the development of 3D technology acquisition. Surface reconstruction techniques can be classified into two main approaches: the combinatorial approach and the adjustment approach of a predefined model. A large number of combinatorial methods have the principle of establishing adjacency relations between the points of a sample [3, 4, 6]. The second approach is based on the idea of approximating the surface sampled using predefined models [5], based on global or local assumptions about the shape to be reconstructed. This work outlinesa brief introduction to mesh combinatorial reconstruction methods. Its main objective is to analyse and compare some methods and main approaches on the basis of two criteria: a criterion for compactness of surface and a criterion of run times. This paper is organized as follows. In section 2, we would recall reconstruction methods. In section 3, we lay out the evaluation of mesh quality. Afterwards,section 4 would outlines the comparison results. Finally, we make conclusion some conclusions will be drawn from the study. II. RECONSTRUCTION METHODS CATEGORIES A. Combinatorial approach The aim of combinatorial methods is to establish connectivity relations between neighboring points on the sampled surface. To achieve this objective in the absence of knowledge on the organization of the data, the topological information can be deduced from the proximity relations between the 3D points under certain assumptions concerning the density of the sample. The principal combinatorial methods of which we distinguish three main categories according to the nature of the algorithm, are: volumetric methods, surface expansion methods and methods based on Delaunay triangulation using the poles. Volumetric methods: This surface reconstruction approach is the first method to be based on the Delaunay triangulation. It was introduced by Boissonnat [11] with the Sculpture algorithm. Surface expansion reconstruction methods: Surface expansion methods reconstruct an incrementally triangulated surface from the edges of an initial surface. The latter can be constructed by directly considering an overall topological criterionor at the end of a postprocessing phase of a set of facets. Several other algorithms adopting this principle of incremental construction by advance of front have been developed such as the algorithm Ball-pivoting [14]. Methods using the pole: the previously described algorithms rely primarily on local criteria to establish or select valid connectivity relationships. A family of algorithms exploits the fact that a solid object can be seen as an infinite union of maximal balls centred on its median axis. B. Adjustment of models Methods of surface reconstruction by adjustment of models,for example the method adopted in paper [5], seek to constrain a mathematical model of global or local surface determined a priori to minimize the gap between the model and the data. The reconstruction ISSN: Page 247
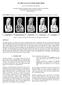
2 process is then mainly a problem of optimization. The surface can be constrained to pass through the data points, we are talking about of interpolation or in the proximity, and we are talking about then of approximation. The objective model can be defined as a function depending on a number of parameters. The objective is then to find the values of the parameters so that the model wouldinterpolate or approximates the input data according to a global or local approach. More generally, a model can be represented by a function in a parametric or implicit manner. There are two main categories: Reconstruction by adjusting an implicit surface model: The problem is equivalent to interpolating or approximating the data using a continuous function f R 3 R where the set of zeros represents a surface close to the sampled surface [12, 13]. Deformable Models: Methods in this category deform an initial surface until a good approximation of the sample of points is obtained. The surface is considered as an elastic membrane to which a deformation process is applied to minimize energy functional such as Zhao et al. [15]. In this work, we outline a comparative study of four combinatorial methods [9]representative of the combinatorial approaches mentioned above. These methods are most commonly used in the literature and a source of inspiration for many works. IV. RESULTS In this section, we will make an empirical comparison between the four methods of combinatorial reconstruction: the Poisson surface reconstruction method [10], the Alpha-Shape method [16], the Marching Cube method [17] and the Ball-Pivoting algorithm [14]. The comparison between these methods is conducted from the point of view of computation time and mesh quality (TABLE I) and the number of triangles per mesh (TABLE II). The four methods are executed on a computer with the following features: Core i3 CPU, 3.40 GHz, 2GB RAM. To validate the effectiveness of these methods, we have opted for Stanford bunny (Fig. 1). TABLE I shows the numerical results obtained by the implementation of the four methods, in between these results are the compactness and the computing time. Fig. 2 presents mesh and compactness histogram for each method. TABLE 2 contains Results relative to number of triangles per mesh. III. EVALUATION OF MESH QUALITY A usual way of quantifying the quality of a mesh is made by the quality of the elements that makes it up. A quality criterion commonly used to quantify the quality of a triangle is the criterion of form. A triangle is regular if it maximizes its measure for a given measure of its boundary. Among the criteria of form are the ratio of the rays, the ratio of the means, the coefficient of the interpolation error and the ratio of the edges. In this work, we will adopt the criterion of the form ratio of means. To measure the quality of the obtained meshes, we compute the quality of the triangles using the compactness formula proposed by Guéziec [7]: (a) c = 4 3a l l l (1) 3 where l i are the lengths of the edges of a triangle and a is the area of the triangle. We notice that this measureequals1 for an equilateral triangle and 0 for a triangle whose vertices are collinear. According to [8], a triangle is of acceptable quality if c 0.6. Fig. 1 Point cloud of Stanford bunny ISSN: Page 248
3 (d) (b) Fig. 2 Reconstruction of 3D bunny, (a) Poisson, (b) Alpha-shape, (c) Marching cube, (d) Ball-Pivoting. (c) In particular, the Marching cube [17] method does not achieve a high level of reconstruction. In addition, it generally records the worst result in terms of compactness (TABLE I, Fig.5) and calculation time (TABLE I, Fig.3). On the other hand, it is interesting to conclude that this method produces the best results at the level of the number of triangles (TABLE II, Fig.4). Thebest results in terms of compactness (TABLE I, Fig.5) and calculation time (TABLE I, Fig.3) are given by Ball-pivoting algorithm [14]. It is interesting to notice that the method of Ballpivoting[14] and Poisson surface reconstruction [10]have produced thebest results in terms of speed. Bycontrast, the method of Marching-cube is the slowest. TABLE. I CALCULATION TIME AND THE PERCENTAGE OF TRIANGLES WITH A COMPACTNESS 0.6 OBTAINED BY APPLYING THE FOUR RECONSTRUCTION METHODS TO THE SAME OBJECT Methods object Triangles with a compactness 0.6 (%) Time (ms) Poisson Alpha shape Alpha=1.6 Marching cubes Ball pivoting r=3.1 bunny ISSN: Page 249
4 TABLE. II NUMBER OF TRIANGLES OBTAINED BY APPLYING THE FOUR RECONSTRUCTION METHODS ON THE SAME OBJECT Methods object Number of vertex Number of faces (triangles) Poisson Alpha shape Alpha=1.6 Marching cubes bunny Ball pivoting r= Fig. 5 Percentage of triangles with a compactness greater than 0.6 (%) V. CONCLUSION This work has presented a brief overview of surface reconstruction methods. We have presented different characteristics of four basic reconstruction methods.four implementations have been performed on a set of data. In addition, the results of an empirical comparison have been presented. We have compared the computational time and quality of meshes. From the point of view of quality, the results have showed that methods ball-pivoting algorithm and alpha-shape algorithm have given the best results in terms of compactness. In term of calculation time Ball-pivoting algorithm have given the best time. Fig. 3 The figure shows the performance of point of view calculation time Fig. 4 The figure shows the performance of four approaches of point of view of number of triangles. Acknowledgment We thank Stanford University Computer Graphics Laboratory for bunny database. References [1] R. Mencl and H. Müller. Interpolation and approximation of surfaces from three-dimensional scattered data points. Eurographics State of the Art Report, pages 51 67, [2] O. Schall and M. Samozino. Surface from scattered points: A brief survey of recent developments. In First International Workshop on Semantic Virtual Environments, pages , [3] F. Cazals and J. Giesen. Delaunay Triangulation based Surface Reconstruction: Ideas and Algorithms. Technical Report 5393, INRIA, November [4] T. K. Dey. Curve and surface reconstruction. Chapter in Handbook of Discrete and Computational Geometry, Goodman and O Rourke eds., CRC press, 2nd edition, [5] A.M. Hsaini, A. Bouazi, A. Mahdaoui, E.H. Sbai. Reconstruction and adjustment of surfaces from a 3-D point cloud. International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology (IJCTT) V37(2): , July [6] R. Allègre, R. Chaine, and S. Akkouche. A Dynamic Surface Reconstruction Framework for Large Point Sets. In Proc. IEEE/Eurographics Symposium on Point-Based Graphics, pages 17 26, [7] A. Guéziec. Locally Toleranced Surface Simplification. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, pp , [8] E. Bank Randolph. PLTMG: A Software Package for Solving Elliptic Partial Differential Equations. User's Guide 6.0, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, PA, ISSN: Page 250
5 [9] F. Bernardini, J. Mittleman, H. Rushmeier, C. Silva, G. Taubin. The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics, pp , [10] M. Kazhdan, M. Bolitho, H. Hoppe.Poisson surface reconstruction.proceeding SGP '06 Proceedings of the fourth Eurographics symposium on Geometry processing Pages Cagliari, Sardinia, Italy June 26-28, 2006 [11] J.-D. Boissonnat. Geometric structures for three-dimensional shape representation. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 3(4) : , [12] H. Hoppe, T. DeRose, T. Duchamp, J. McDonald, and W. Stuetzle. Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Points. Computer Graphics (Proc. SIGGRAPH), 26(2) :71 78, [13] D. Levin. The approximation power of moving least-squares. Math. Comp., 67(224) : , [14] F. Bernardini, J. Mittleman, H. Rushmeier, C. Silva, and G. Taubin. The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 5(4) : , [15] H.-K. Zhao, S. Osher, and R. Fedkiw. Fast Surface Reconstruction using the Level Set Method. InProc. IEEE Workshop on Variational and Level Set Methods in Computer Vision (VLSM), pages , [16] Herbert Edelsbrunner, Ernst P Mücke. Three-dimensional alpha shapes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG). 13(1) : 43-72, [17] Öztireli, A. C., Guennebaud, G. and Gross, M. (2009), Feature Preserving Point Set Surfaces based on Non-Linear Kernel Regression. Computer Graphics Forum, 28: ISSN: Page 251
Surface Reconstruction. Gianpaolo Palma
 Surface Reconstruction Gianpaolo Palma Surface reconstruction Input Point cloud With or without normals Examples: multi-view stereo, union of range scan vertices Range scans Each scan is a triangular mesh
Surface Reconstruction Gianpaolo Palma Surface reconstruction Input Point cloud With or without normals Examples: multi-view stereo, union of range scan vertices Range scans Each scan is a triangular mesh
ON THE WAY TO WATER-TIGHT MESH
 ON THE WAY TO WATER-TIGHT MESH Rui Liu, Darius Burschka, Gerd Hirzinger Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics, German Aerospace Center (DLR) Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany. Rui.Liu@dlr.de KEY
ON THE WAY TO WATER-TIGHT MESH Rui Liu, Darius Burschka, Gerd Hirzinger Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics, German Aerospace Center (DLR) Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany. Rui.Liu@dlr.de KEY
A Constrained Delaunay Triangle Mesh Method for Three-Dimensional Unstructured Boundary Point Cloud
 International Journal of Computer Systems (ISSN: 2394-1065), Volume 03 Issue 02, February, 2016 Available at http://www.ijcsonline.com/ A Constrained Delaunay Triangle Mesh Method for Three-Dimensional
International Journal of Computer Systems (ISSN: 2394-1065), Volume 03 Issue 02, February, 2016 Available at http://www.ijcsonline.com/ A Constrained Delaunay Triangle Mesh Method for Three-Dimensional
Comparison of K-Means and Fuzzy C-Means Algorithms on Simplification of 3D Point Cloud Based on Entropy Estimation
 Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal Vol. 2, No. 5, 38-44 (2017) www.astesj.com Proceedings of International Conference on Applied Mathematics (ICAM 2017), Taza, Morocco ASTES
Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal Vol. 2, No. 5, 38-44 (2017) www.astesj.com Proceedings of International Conference on Applied Mathematics (ICAM 2017), Taza, Morocco ASTES
IJREAT International Journal of Research in Engineering & Advanced Technology, Volume 1, Issue 2, April-May, 2013 ISSN:
 Optimization of Mesh Reconstruction using Delaunay and Ball Pivoting Algorithm Bharti Sood 1, Kamaldeep Kaur 2 1, 2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, BBSBEC, Fatehgarh Sahib, India
Optimization of Mesh Reconstruction using Delaunay and Ball Pivoting Algorithm Bharti Sood 1, Kamaldeep Kaur 2 1, 2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, BBSBEC, Fatehgarh Sahib, India
Point-based Simplification Algorithm
 Point-based Simplification Algorithm Pai-Feng Lee 1, Bin-Shyan Jong 2 Department of Information Management, Hsing Wu College 1 Dept. of Information and Computer Engineering Engineering, Chung Yuan Christian
Point-based Simplification Algorithm Pai-Feng Lee 1, Bin-Shyan Jong 2 Department of Information Management, Hsing Wu College 1 Dept. of Information and Computer Engineering Engineering, Chung Yuan Christian
Outline of the presentation
 Surface Reconstruction Petra Surynková Charles University in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics petra.surynkova@mff.cuni.cz Outline of the presentation My work up to now Surfaces of Building Practice
Surface Reconstruction Petra Surynková Charles University in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics petra.surynkova@mff.cuni.cz Outline of the presentation My work up to now Surfaces of Building Practice
LATEST TRENDS on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, SIMULATION, MODELLING
 3D surface reconstruction of objects by using stereoscopic viewing Baki Koyuncu, Kurtuluş Küllü bkoyuncu@ankara.edu.tr kkullu@eng.ankara.edu.tr Computer Engineering Department, Ankara University, Ankara,
3D surface reconstruction of objects by using stereoscopic viewing Baki Koyuncu, Kurtuluş Küllü bkoyuncu@ankara.edu.tr kkullu@eng.ankara.edu.tr Computer Engineering Department, Ankara University, Ankara,
Geometric Modeling. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo
 Geometric Modeling Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo What are 3D Objects? 3D Object Representations What are 3D objects? The Graphics Process 3D Object Representations Raw
Geometric Modeling Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo What are 3D Objects? 3D Object Representations What are 3D objects? The Graphics Process 3D Object Representations Raw
Surface reconstruction based on a dynamical system
 EUROGRAPHICS 2002 / G. Drettakis and H.-P. Seidel (Guest Editors) Volume 21 (2002), Number 3 Surface reconstruction based on a dynamical system N.N. Abstract We present an efficient algorithm that computes
EUROGRAPHICS 2002 / G. Drettakis and H.-P. Seidel (Guest Editors) Volume 21 (2002), Number 3 Surface reconstruction based on a dynamical system N.N. Abstract We present an efficient algorithm that computes
Moving Least Squares Multiresolution Surface Approximation
 Moving Least Squares Multiresolution Surface Approximation BORIS MEDEROS LUIZ VELHO LUIZ HENRIQUE DE FIGUEIREDO IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada Estrada Dona Castorina 110, 22461-320 Rio de
Moving Least Squares Multiresolution Surface Approximation BORIS MEDEROS LUIZ VELHO LUIZ HENRIQUE DE FIGUEIREDO IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada Estrada Dona Castorina 110, 22461-320 Rio de
Shape and Appearance from Images and Range Data
 SIGGRAPH 2000 Course on 3D Photography Shape and Appearance from Images and Range Data Brian Curless University of Washington Overview Range images vs. point clouds Registration Reconstruction from point
SIGGRAPH 2000 Course on 3D Photography Shape and Appearance from Images and Range Data Brian Curless University of Washington Overview Range images vs. point clouds Registration Reconstruction from point
Outline. Reconstruction of 3D Meshes from Point Clouds. Motivation. Problem Statement. Applications. Challenges
 Reconstruction of 3D Meshes from Point Clouds Ming Zhang Patrick Min cs598b, Geometric Modeling for Computer Graphics Feb. 17, 2000 Outline - problem statement - motivation - applications - challenges
Reconstruction of 3D Meshes from Point Clouds Ming Zhang Patrick Min cs598b, Geometric Modeling for Computer Graphics Feb. 17, 2000 Outline - problem statement - motivation - applications - challenges
3-Dimensional Object Modeling with Mesh Simplification Based Resolution Adjustment
 3-Dimensional Object Modeling with Mesh Simplification Based Resolution Adjustment Özgür ULUCAY Sarp ERTÜRK University of Kocaeli Electronics & Communication Engineering Department 41040 Izmit, Kocaeli
3-Dimensional Object Modeling with Mesh Simplification Based Resolution Adjustment Özgür ULUCAY Sarp ERTÜRK University of Kocaeli Electronics & Communication Engineering Department 41040 Izmit, Kocaeli
A Sketch Interpreter System with Shading and Cross Section Lines
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 9 (2005), No. 2, 177 189. A Sketch Interpreter System with Shading and Cross Section Lines Kunio Kondo 1, Haruki Shizuka 1, Weizhong Liu 1, Koichi Matsuda 2 1 Dept.
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 9 (2005), No. 2, 177 189. A Sketch Interpreter System with Shading and Cross Section Lines Kunio Kondo 1, Haruki Shizuka 1, Weizhong Liu 1, Koichi Matsuda 2 1 Dept.
Surface Reconstruction
 Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2006) Surface Reconstruction 2009.12.29 Some methods for surface reconstruction Classification 1. Based on Delaunay triangulation(or Voronoi diagram) Alpha
Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2006) Surface Reconstruction 2009.12.29 Some methods for surface reconstruction Classification 1. Based on Delaunay triangulation(or Voronoi diagram) Alpha
A fast algorithm for manifold reconstruction of surfaces
 Proceedings of the IMProVe 2011 International conference on Innovative Methods in Product Design June 15 th 17 th, 2011, Venice, Italy L. Di Angelo (a), L. Giaccari (a) (a) Department of Industrial Engineering,
Proceedings of the IMProVe 2011 International conference on Innovative Methods in Product Design June 15 th 17 th, 2011, Venice, Italy L. Di Angelo (a), L. Giaccari (a) (a) Department of Industrial Engineering,
Feature Extraction for Illustrating 3D Stone Tools from Unorganized Point Clouds
 Feature Extraction for Illustrating 3D Stone Tools from Unorganized Point Clouds Enkhbayar Altantsetseg 1) Yuta Muraki 2) Katsutsugu Matsuyama 2) Fumito Chiba 3) Kouichi Konno 2) 1) Graduate School of
Feature Extraction for Illustrating 3D Stone Tools from Unorganized Point Clouds Enkhbayar Altantsetseg 1) Yuta Muraki 2) Katsutsugu Matsuyama 2) Fumito Chiba 3) Kouichi Konno 2) 1) Graduate School of
A Global Laplacian Smoothing Approach with Feature Preservation
 A Global Laplacian Smoothing Approach with Feature Preservation hongping Ji Ligang Liu Guojin Wang Department of Mathematics State Key Lab of CAD&CG hejiang University Hangzhou, 310027 P.R. China jzpboy@yahoo.com.cn,
A Global Laplacian Smoothing Approach with Feature Preservation hongping Ji Ligang Liu Guojin Wang Department of Mathematics State Key Lab of CAD&CG hejiang University Hangzhou, 310027 P.R. China jzpboy@yahoo.com.cn,
SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION FROM MULTI-VALUED GRID DATA
 4 th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, December 26-28, 2001, Dhaka, Bangladesh/pp. VII 29-33 SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION FROM MULTI-VALUED GRID DATA S. Adithya and Dibakar Sen* Department
4 th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, December 26-28, 2001, Dhaka, Bangladesh/pp. VII 29-33 SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION FROM MULTI-VALUED GRID DATA S. Adithya and Dibakar Sen* Department
Data Handling in Large-Scale Surface Reconstruction
 Data Handling in Large-Scale Surface Reconstruction Thomas Wiemann 1, Marcel Mrozinski 1, Dominik Feldschnieders 1, Kai Lingemann 2, and Joachim Hertzberg 1,2 1 Knowledge Bases Systems Group, Osnabrück
Data Handling in Large-Scale Surface Reconstruction Thomas Wiemann 1, Marcel Mrozinski 1, Dominik Feldschnieders 1, Kai Lingemann 2, and Joachim Hertzberg 1,2 1 Knowledge Bases Systems Group, Osnabrück
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface Reconstruction
 A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction M. GOPI, SHANKA KISHNAN Univ. of California, Irvine gopi@ics.uci.edu AT&T Labs - esearch krishnas@research.att.com Abstract. We
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction M. GOPI, SHANKA KISHNAN Univ. of California, Irvine gopi@ics.uci.edu AT&T Labs - esearch krishnas@research.att.com Abstract. We
Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Points
 Survey of Methods in Computer Graphics: Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Points H. Hoppe, T. DeRose, T. Duchamp, J. McDonald, W. Stuetzle SIGGRAPH 1992. Article and Additional Material at: http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/hoppe/proj/recon/
Survey of Methods in Computer Graphics: Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Points H. Hoppe, T. DeRose, T. Duchamp, J. McDonald, W. Stuetzle SIGGRAPH 1992. Article and Additional Material at: http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/hoppe/proj/recon/
03 - Reconstruction. Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung. CSCI-GA Geometric Modeling - Spring 17 - Daniele Panozzo
 3 - Reconstruction Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Geometry Acquisition Pipeline Scanning: results in range images Registration: bring all range images to one coordinate system Stitching/ reconstruction:
3 - Reconstruction Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Geometry Acquisition Pipeline Scanning: results in range images Registration: bring all range images to one coordinate system Stitching/ reconstruction:
Correctness. The Powercrust Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction. Correctness. Correctness. Delaunay Triangulation. Tools - Voronoi Diagram
 Correctness The Powercrust Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction Nina Amenta Sunghee Choi Ravi Kolluri University of Texas at Austin Boundary of a solid Close to original surface Homeomorphic to original
Correctness The Powercrust Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction Nina Amenta Sunghee Choi Ravi Kolluri University of Texas at Austin Boundary of a solid Close to original surface Homeomorphic to original
Progressive Compression for Lossless Transmission of Triangle Meshes in Network Applications
 Progressive Compression for Lossless Transmission of Triangle Meshes in Network Applications Timotej Globačnik * Institute of Computer Graphics Laboratory for Geometric Modelling and Multimedia Algorithms
Progressive Compression for Lossless Transmission of Triangle Meshes in Network Applications Timotej Globačnik * Institute of Computer Graphics Laboratory for Geometric Modelling and Multimedia Algorithms
Fast 3D surface reconstruction from point clouds using graph-based fronts propagation
 Fast 3D surface reconstruction from point clouds using graph-based fronts propagation Abdallah El Chakik, Xavier Desquesnes, Abderrahim Elmoataz UCBN, GREYC - UMR CNRS 6972, 6.Bvd Marechal Juin, 14050
Fast 3D surface reconstruction from point clouds using graph-based fronts propagation Abdallah El Chakik, Xavier Desquesnes, Abderrahim Elmoataz UCBN, GREYC - UMR CNRS 6972, 6.Bvd Marechal Juin, 14050
Survey of Surface Reconstruction Algorithms
 Journal of Signal and Information Processing, 2014, 5, 63-79 Published Online August 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsip http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jsip.2014.53009 Survey of Surface Reconstruction
Journal of Signal and Information Processing, 2014, 5, 63-79 Published Online August 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsip http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jsip.2014.53009 Survey of Surface Reconstruction
Dimension-Independent Data Structures for Arbitrary Simplicial Complexes
 Dimension-Independent Data Structures for Arbitrary Simplicial Complexes David Canino (canino.david@gmail.com) The Incidence Simplicial (IS) data structure The Generalized Indexed data structure with Adjacencies
Dimension-Independent Data Structures for Arbitrary Simplicial Complexes David Canino (canino.david@gmail.com) The Incidence Simplicial (IS) data structure The Generalized Indexed data structure with Adjacencies
Geometric and Solid Modeling. Problems
 Geometric and Solid Modeling Problems Define a Solid Define Representation Schemes Devise Data Structures Construct Solids Page 1 Mathematical Models Points Curves Surfaces Solids A shape is a set of Points
Geometric and Solid Modeling Problems Define a Solid Define Representation Schemes Devise Data Structures Construct Solids Page 1 Mathematical Models Points Curves Surfaces Solids A shape is a set of Points
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama Solid modeling 2 Solid models Thin shapes represented by single polygons Unorientable Clear definition of inside & outside
Introduction to Computer Graphics Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama Solid modeling 2 Solid models Thin shapes represented by single polygons Unorientable Clear definition of inside & outside
Lecture notes: Object modeling
 Lecture notes: Object modeling One of the classic problems in computer vision is to construct a model of an object from an image of the object. An object model has the following general principles: Compact
Lecture notes: Object modeling One of the classic problems in computer vision is to construct a model of an object from an image of the object. An object model has the following general principles: Compact
Performance analysis of different surface reconstruction algorithms for 3D reconstruction of outdoor objects from their digital images
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-2425-9 RESEARCH Open Access Performance analysis of different surface reconstruction algorithms for 3D reconstruction of outdoor objects from their digital images Abhik Maiti * and
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-2425-9 RESEARCH Open Access Performance analysis of different surface reconstruction algorithms for 3D reconstruction of outdoor objects from their digital images Abhik Maiti * and
THE FORCE DENSITY METHOD: A BRIEF INTRODUCTION
 Technical Report TR-NCCA-2011-02 THE FORCE DENSITY METHOD: A BRIEF INTRODUCTION Richard Southern The National Centre for Computer Animation Bournemouth Media School Bournemouth University Talbot Campus,
Technical Report TR-NCCA-2011-02 THE FORCE DENSITY METHOD: A BRIEF INTRODUCTION Richard Southern The National Centre for Computer Animation Bournemouth Media School Bournemouth University Talbot Campus,
Provably Good Moving Least Squares
 Provably Good Moving Least Squares Ravikrishna Kolluri Computer Science Division University of California at Berkeley 1 Problem Definition Given a set of samples on a closed surface build a representation
Provably Good Moving Least Squares Ravikrishna Kolluri Computer Science Division University of California at Berkeley 1 Problem Definition Given a set of samples on a closed surface build a representation
Shape fitting and non convex data analysis
 Shape fitting and non convex data analysis Petra Surynková, Zbyněk Šír Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague Sokolovská 83, 186 7 Praha 8, Czech Republic email: petra.surynkova@mff.cuni.cz,
Shape fitting and non convex data analysis Petra Surynková, Zbyněk Šír Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague Sokolovská 83, 186 7 Praha 8, Czech Republic email: petra.surynkova@mff.cuni.cz,
Robust Poisson Surface Reconstruction
 Robust Poisson Surface Reconstruction V. Estellers, M. Scott, K. Tew, and S. Soatto Univeristy of California, Los Angeles Brigham Young University June 2, 2015 1/19 Goals: Surface reconstruction from noisy
Robust Poisson Surface Reconstruction V. Estellers, M. Scott, K. Tew, and S. Soatto Univeristy of California, Los Angeles Brigham Young University June 2, 2015 1/19 Goals: Surface reconstruction from noisy
A Robust Procedure to Eliminate Degenerate Faces from Triangle Meshes
 A Robust Procedure to Eliminate Degenerate Faces from Triangle Meshes Mario Botsch, Leif P. Kobbelt Computer Graphics Group, RWTH Aachen, kobbelt,botsch @cs.rwth-aachen.de Abstract When using triangle
A Robust Procedure to Eliminate Degenerate Faces from Triangle Meshes Mario Botsch, Leif P. Kobbelt Computer Graphics Group, RWTH Aachen, kobbelt,botsch @cs.rwth-aachen.de Abstract When using triangle
A Developer s Survey of Polygonal Simplification algorithms. CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Fan Wu Mar. 31, 2005
 A Developer s Survey of Polygonal Simplification algorithms CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Fan Wu Mar. 31, 2005 Some questions to ask Why simplification? What are my models like? What matters
A Developer s Survey of Polygonal Simplification algorithms CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Fan Wu Mar. 31, 2005 Some questions to ask Why simplification? What are my models like? What matters
Discrete representations of geometric objects: Features, data structures and adequacy for dynamic simulation. Part I : Solid geometry
 Discrete representations of geometric objects: Features, data structures and adequacy for dynamic simulation. Surfaces Part I : Solid geometry hachar Fleishman Tel Aviv University David Levin Claudio T.
Discrete representations of geometric objects: Features, data structures and adequacy for dynamic simulation. Surfaces Part I : Solid geometry hachar Fleishman Tel Aviv University David Levin Claudio T.
Parameterization of Triangular Meshes with Virtual Boundaries
 Parameterization of Triangular Meshes with Virtual Boundaries Yunjin Lee 1;Λ Hyoung Seok Kim 2;y Seungyong Lee 1;z 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology
Parameterization of Triangular Meshes with Virtual Boundaries Yunjin Lee 1;Λ Hyoung Seok Kim 2;y Seungyong Lee 1;z 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology
Surface Curvature Estimation for Edge Spinning Algorithm *
 Surface Curvature Estimation for Edge Spinning Algorithm * Martin Cermak and Vaclav Skala University of West Bohemia in Pilsen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Republic {cermakm skala}@kiv.zcu.cz
Surface Curvature Estimation for Edge Spinning Algorithm * Martin Cermak and Vaclav Skala University of West Bohemia in Pilsen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Republic {cermakm skala}@kiv.zcu.cz
A New Voronoi-Based Surface Reconstruction Algorithm
 A New Voronoi-Based Surface Reconstruction Algorithm Nina Amenta UT - Austin Marshall Bern Xerox PARC Manolis Kamvysselis M.I.T. Abstract We describe our experience with a new algorithm for the reconstruction
A New Voronoi-Based Surface Reconstruction Algorithm Nina Amenta UT - Austin Marshall Bern Xerox PARC Manolis Kamvysselis M.I.T. Abstract We describe our experience with a new algorithm for the reconstruction
Shape from LIDAR Data. Univ. of Florida
 Shape from LIDAR Data Yusuf Sahillioğlu Alper Üngör Univ. of Florida 1. Introduction LIght Detection And Ranging systems, LIDAR, are capable of acquiring data to produce accurate digital elevation models
Shape from LIDAR Data Yusuf Sahillioğlu Alper Üngör Univ. of Florida 1. Introduction LIght Detection And Ranging systems, LIDAR, are capable of acquiring data to produce accurate digital elevation models
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface Reconstruction
 A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction M. GOPI 1, SHANKA KISHNAN 2 1 Univ. of California, Irvine gopi@ics.uci.edu 2 AT&T Labs - esearch krishnas@research.att.com Abstract.
A Fast and Efficient Projection-Based Approach for Surface econstruction M. GOPI 1, SHANKA KISHNAN 2 1 Univ. of California, Irvine gopi@ics.uci.edu 2 AT&T Labs - esearch krishnas@research.att.com Abstract.
Multi-Scale Free-Form Surface Description
 Multi-Scale Free-Form Surface Description Farzin Mokhtarian, Nasser Khalili and Peter Yuen Centre for Vision Speech and Signal Processing Dept. of Electronic and Electrical Engineering University of Surrey,
Multi-Scale Free-Form Surface Description Farzin Mokhtarian, Nasser Khalili and Peter Yuen Centre for Vision Speech and Signal Processing Dept. of Electronic and Electrical Engineering University of Surrey,
LAPLACIAN MESH SMOOTHING FOR TETRAHEDRA BASED VOLUME VISUALIZATION 1. INTRODUCTION
 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol.4/2002, ISSN 642-6037 Rafał STĘGIERSKI *, Paweł MIKOŁAJCZAK * volume data,triangle mesh generation, mesh smoothing, marching tetrahedra LAPLACIAN MESH
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol.4/2002, ISSN 642-6037 Rafał STĘGIERSKI *, Paweł MIKOŁAJCZAK * volume data,triangle mesh generation, mesh smoothing, marching tetrahedra LAPLACIAN MESH
Space Subdivision for the Adaptive Edge Spinning Polygonization
 Space Subdivision for the Adaptive Edge Spinning Polygonization MARTIN CERMAK 1, VACLAV SKALA Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of West Bohemia in Pilsen Univerzitni 8, 306 14 Plzen
Space Subdivision for the Adaptive Edge Spinning Polygonization MARTIN CERMAK 1, VACLAV SKALA Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of West Bohemia in Pilsen Univerzitni 8, 306 14 Plzen
Overview of 3D Object Representations
 Overview of 3D Object Representations Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 597D, Fall 2003 3D Object Representations What makes a good 3D object representation? Stanford and Hearn & Baker 1 3D Object
Overview of 3D Object Representations Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 597D, Fall 2003 3D Object Representations What makes a good 3D object representation? Stanford and Hearn & Baker 1 3D Object
A Multiresolutional Approach for Facial Motion Retargetting Using Subdivision Wavelets
 A Multiresolutional Approach for Facial Motion Retargetting Using Subdivision Wavelets Kyungha Min and Moon-Ryul Jung Dept. of Media Technology, Graduate School of Media Communications, Sogang Univ., Seoul,
A Multiresolutional Approach for Facial Motion Retargetting Using Subdivision Wavelets Kyungha Min and Moon-Ryul Jung Dept. of Media Technology, Graduate School of Media Communications, Sogang Univ., Seoul,
Interaction of Fluid Simulation Based on PhysX Physics Engine. Huibai Wang, Jianfei Wan, Fengquan Zhang
 4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Interaction of Fluid Simulation Based on PhysX Physics Engine Huibai Wang, Jianfei Wan, Fengquan Zhang College
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Interaction of Fluid Simulation Based on PhysX Physics Engine Huibai Wang, Jianfei Wan, Fengquan Zhang College
Medial Scaffolds for 3D data modelling: status and challenges. Frederic Fol Leymarie
 Medial Scaffolds for 3D data modelling: status and challenges Frederic Fol Leymarie Outline Background Method and some algorithmic details Applications Shape representation: From the Medial Axis to the
Medial Scaffolds for 3D data modelling: status and challenges Frederic Fol Leymarie Outline Background Method and some algorithmic details Applications Shape representation: From the Medial Axis to the
Simulation in Computer Graphics. Deformable Objects. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Deformable Objects Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction forces performance collision handling visualization University
Simulation in Computer Graphics Deformable Objects Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction forces performance collision handling visualization University
A Comparison of Mesh Simplification Algorithms
 A Comparison of Mesh Simplification Algorithms Nicole Ortega Project Summary, Group 16 Browser Based Constructive Solid Geometry for Anatomical Models - Orthotics for cerebral palsy patients - Fusiform
A Comparison of Mesh Simplification Algorithms Nicole Ortega Project Summary, Group 16 Browser Based Constructive Solid Geometry for Anatomical Models - Orthotics for cerebral palsy patients - Fusiform
Level Set Extraction from Gridded 2D and 3D Data
 Level Set Extraction from Gridded 2D and 3D Data David Eberly, Geometric Tools, Redmond WA 98052 https://www.geometrictools.com/ This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
Level Set Extraction from Gridded 2D and 3D Data David Eberly, Geometric Tools, Redmond WA 98052 https://www.geometrictools.com/ This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM
 Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM Remya C R 1, Suji P 2 1 M Tech Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sri Vellappaly Natesan College of Engineering, Pallickal P O, Mavelikara, Kerala,
Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM Remya C R 1, Suji P 2 1 M Tech Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sri Vellappaly Natesan College of Engineering, Pallickal P O, Mavelikara, Kerala,
A Real-time Rendering Method Based on Precomputed Hierarchical Levels of Detail in Huge Dataset
 32 A Real-time Rendering Method Based on Precomputed Hierarchical Levels of Detail in Huge Dataset Zhou Kai, and Tian Feng School of Computer and Information Technology, Northeast Petroleum University,
32 A Real-time Rendering Method Based on Precomputed Hierarchical Levels of Detail in Huge Dataset Zhou Kai, and Tian Feng School of Computer and Information Technology, Northeast Petroleum University,
An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization
 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -2 th, June 205, Sydney Australia An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization Weisheng Zhang, Xu Guo
th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -2 th, June 205, Sydney Australia An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization Weisheng Zhang, Xu Guo
A texture-mapping approach for the compression of colored 3D triangulations
 1 Introduction A texture-mapping approach for the compression of colored 3D triangulations Marc Soucy, Guy Godin, Marc Rioux Visual Information Technology Group, Institute for Information Technology, National
1 Introduction A texture-mapping approach for the compression of colored 3D triangulations Marc Soucy, Guy Godin, Marc Rioux Visual Information Technology Group, Institute for Information Technology, National
An Automatic Hole Filling Method of Point Cloud for 3D Scanning
 An Automatic Hole Filling Method of Point Cloud for 3D Scanning Yuta MURAKI Osaka Institute of Technology Osaka, Japan yuta.muraki@oit.ac.jp Koji NISHIO Osaka Institute of Technology Osaka, Japan koji.a.nishio@oit.ac.jp
An Automatic Hole Filling Method of Point Cloud for 3D Scanning Yuta MURAKI Osaka Institute of Technology Osaka, Japan yuta.muraki@oit.ac.jp Koji NISHIO Osaka Institute of Technology Osaka, Japan koji.a.nishio@oit.ac.jp
Point Cloud Library - Toyota Code Sprint Final Report
 Point Cloud Library - Toyota Code Sprint Final Report Alexandru E. Ichim April 1, 2012 1 Work Done This section will present the work I have done in addition to the results presented in the midterm report.
Point Cloud Library - Toyota Code Sprint Final Report Alexandru E. Ichim April 1, 2012 1 Work Done This section will present the work I have done in addition to the results presented in the midterm report.
CS 468, Spring 2013 Differential Geometry for Computer Science Justin Solomon and Adrian Butscher
 http://alice.loria.fr/index.php/publications.html?redirect=0&paper=vsdm@2011&author=levy CS 468, Spring 2013 Differential Geometry for Computer Science Justin Solomon and Adrian Butscher µ R 3 µ R 2 http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/bc/double_torus_illustration.png
http://alice.loria.fr/index.php/publications.html?redirect=0&paper=vsdm@2011&author=levy CS 468, Spring 2013 Differential Geometry for Computer Science Justin Solomon and Adrian Butscher µ R 3 µ R 2 http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/bc/double_torus_illustration.png
Seismic regionalization based on an artificial neural network
 Seismic regionalization based on an artificial neural network *Jaime García-Pérez 1) and René Riaño 2) 1), 2) Instituto de Ingeniería, UNAM, CU, Coyoacán, México D.F., 014510, Mexico 1) jgap@pumas.ii.unam.mx
Seismic regionalization based on an artificial neural network *Jaime García-Pérez 1) and René Riaño 2) 1), 2) Instituto de Ingeniería, UNAM, CU, Coyoacán, México D.F., 014510, Mexico 1) jgap@pumas.ii.unam.mx
The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction
 The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction 1. Briefly summarize the paper s contributions. Does it address a new problem? Does it present a new approach? Does it show new types of results?
The Ball-Pivoting Algorithm for Surface Reconstruction 1. Briefly summarize the paper s contributions. Does it address a new problem? Does it present a new approach? Does it show new types of results?
implicit surfaces, approximate implicitization, B-splines, A- patches, surface fitting
 24. KONFERENCE O GEOMETRII A POČÍTAČOVÉ GRAFICE ZBYNĚK ŠÍR FITTING OF PIECEWISE POLYNOMIAL IMPLICIT SURFACES Abstrakt In our contribution we discuss the possibility of an efficient fitting of piecewise
24. KONFERENCE O GEOMETRII A POČÍTAČOVÉ GRAFICE ZBYNĚK ŠÍR FITTING OF PIECEWISE POLYNOMIAL IMPLICIT SURFACES Abstrakt In our contribution we discuss the possibility of an efficient fitting of piecewise
Dimensionality Reduction of Laplacian Embedding for 3D Mesh Reconstruction
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Dimensionality Reduction of Laplacian Embedding for 3D Mesh Reconstruction To cite this article: I Mardhiyah et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 725
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Dimensionality Reduction of Laplacian Embedding for 3D Mesh Reconstruction To cite this article: I Mardhiyah et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 725
CS123 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Describing Shapes. Constructing Objects in Computer Graphics 1/15
 Describing Shapes Constructing Objects in Computer Graphics 1/15 2D Object Definition (1/3) Lines and polylines: Polylines: lines drawn between ordered points A closed polyline is a polygon, a simple polygon
Describing Shapes Constructing Objects in Computer Graphics 1/15 2D Object Definition (1/3) Lines and polylines: Polylines: lines drawn between ordered points A closed polyline is a polygon, a simple polygon
SURFACE CONSTRUCTION USING TRICOLOR MARCHING CUBES
 SURFACE CONSTRUCTION USING TRICOLOR MARCHING CUBES Shaojun Liu, Jia Li Oakland University Rochester, MI 4839, USA Email: sliu2@oakland.edu, li4@oakland.edu Xiaojun Jing Beijing University of Posts and
SURFACE CONSTRUCTION USING TRICOLOR MARCHING CUBES Shaojun Liu, Jia Li Oakland University Rochester, MI 4839, USA Email: sliu2@oakland.edu, li4@oakland.edu Xiaojun Jing Beijing University of Posts and
Geometric Modeling and Processing
 Geometric Modeling and Processing Tutorial of 3DIM&PVT 2011 (Hangzhou, China) May 16, 2011 4. Geometric Registration 4.1 Rigid Registration Range Scanning: Reconstruction Set of raw scans Reconstructed
Geometric Modeling and Processing Tutorial of 3DIM&PVT 2011 (Hangzhou, China) May 16, 2011 4. Geometric Registration 4.1 Rigid Registration Range Scanning: Reconstruction Set of raw scans Reconstructed
Ray Tracing Point Set Surfaces
 Ray Tracing Point Set Surfaces Anders Adamson Marc Alexa TU Darmstadt, GRIS Fraunhoferstr. 5, 64283 Darmstadt {aadamson,alexa}@gris.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Abstract Point set surfaces are a smooth manifold
Ray Tracing Point Set Surfaces Anders Adamson Marc Alexa TU Darmstadt, GRIS Fraunhoferstr. 5, 64283 Darmstadt {aadamson,alexa}@gris.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Abstract Point set surfaces are a smooth manifold
A Subdivision-Regularization Framework for Preventing Over Fitting of Data by a Model
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 8, Issue 1 (June 2013), pp. 178-190 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) A Subdivision-Regularization
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 8, Issue 1 (June 2013), pp. 178-190 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) A Subdivision-Regularization
coding of various parts showing different features, the possibility of rotation or of hiding covering parts of the object's surface to gain an insight
 Three-Dimensional Object Reconstruction from Layered Spatial Data Michael Dangl and Robert Sablatnig Vienna University of Technology, Institute of Computer Aided Automation, Pattern Recognition and Image
Three-Dimensional Object Reconstruction from Layered Spatial Data Michael Dangl and Robert Sablatnig Vienna University of Technology, Institute of Computer Aided Automation, Pattern Recognition and Image
3D MORPHISM & IMPLICIT SURFACES
 3D MORPHISM & IMPLICIT SURFACES ROMAIN BALP AND CHARLEY PAULUS Abstract. The purpose of this paper is to present a framework based on implicit surfaces that allows to visualize dynamic shapes, and see
3D MORPHISM & IMPLICIT SURFACES ROMAIN BALP AND CHARLEY PAULUS Abstract. The purpose of this paper is to present a framework based on implicit surfaces that allows to visualize dynamic shapes, and see
Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures To cite this article: S K Ruhit et al 2018 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures To cite this article: S K Ruhit et al 2018 IOP
Efficient surface reconstruction using generalized Coulomb potentials Jalba, A.C.; Roerdink, J.B.T.M.
 Efficient surface reconstruction using generalized Coulomb potentials Jalba, A.C.; Roerdink, J.B.T.M. Published in: IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2007.70553
Efficient surface reconstruction using generalized Coulomb potentials Jalba, A.C.; Roerdink, J.B.T.M. Published in: IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2007.70553
Automatic 3D wig Generation Method using FFD and Robotic Arm
 International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 12, Number 9 (2017) pp. 2104-2108 Automatic 3D wig Generation Method using FFD and Robotic Arm Md Saifur Rahman 1, Chulhyung
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 12, Number 9 (2017) pp. 2104-2108 Automatic 3D wig Generation Method using FFD and Robotic Arm Md Saifur Rahman 1, Chulhyung
Three-Dimensional α Shapes
 Herbert Edelsbrunner and Ernst P. Mücke ACM Tran. Graph. 13(1), 1994 20 September 2005 1 2 α-complexes Edelsbrunner s Algorithm 3 Properties Surface Reconstruction Shape Question Given a set of points,
Herbert Edelsbrunner and Ernst P. Mücke ACM Tran. Graph. 13(1), 1994 20 September 2005 1 2 α-complexes Edelsbrunner s Algorithm 3 Properties Surface Reconstruction Shape Question Given a set of points,
Open Topology: A Toolkit for Brain Isosurface Correction
 Open Topology: A Toolkit for Brain Isosurface Correction Sylvain Jaume 1, Patrice Rondao 2, and Benoît Macq 2 1 National Institute of Research in Computer Science and Control, INRIA, France, sylvain@mit.edu,
Open Topology: A Toolkit for Brain Isosurface Correction Sylvain Jaume 1, Patrice Rondao 2, and Benoît Macq 2 1 National Institute of Research in Computer Science and Control, INRIA, France, sylvain@mit.edu,
Fast K-nearest neighbors searching algorithms for point clouds data of 3D scanning system 1
 Acta Technica 62 No. 3B/2017, 141 148 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Fast K-nearest neighbors searching algorithms for point clouds data of 3D scanning system 1 Zhang Fan 2, 3, Tan Yuegang
Acta Technica 62 No. 3B/2017, 141 148 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Fast K-nearest neighbors searching algorithms for point clouds data of 3D scanning system 1 Zhang Fan 2, 3, Tan Yuegang
MULTIVIEW REPRESENTATION OF 3D OBJECTS OF A SCENE USING VIDEO SEQUENCES
 MULTIVIEW REPRESENTATION OF 3D OBJECTS OF A SCENE USING VIDEO SEQUENCES Mehran Yazdi and André Zaccarin CVSL, Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Laval University Ste-Foy, Québec GK 7P4, Canada
MULTIVIEW REPRESENTATION OF 3D OBJECTS OF A SCENE USING VIDEO SEQUENCES Mehran Yazdi and André Zaccarin CVSL, Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Laval University Ste-Foy, Québec GK 7P4, Canada
The Geometric Primitive MatOrus Francisco A. Madera 1, Jorge Madera-Valdez 2
 The Geometric Primitive MatOrus Francisco A. Madera 1, Jorge Madera-Valdez 2 1 Mathematics Faculty, Universidad Autonoma de Yucatan, Merida, Yucatan, Mexico 2 School of Architecture, Universidad Marista,
The Geometric Primitive MatOrus Francisco A. Madera 1, Jorge Madera-Valdez 2 1 Mathematics Faculty, Universidad Autonoma de Yucatan, Merida, Yucatan, Mexico 2 School of Architecture, Universidad Marista,
Minimum Surface Area Based Complex Hole Filling Algorithm of 3D Mesh
 Minimum Surface Area Based Complex Hole Filling Algorithm of 3D Mesh Enkhbayar Altantsetseg 1) Katsutsugu Matsuyama ) Kouichi Konno ) 1) National University of Mongolia ) Iwate University {enkhbayar.a}
Minimum Surface Area Based Complex Hole Filling Algorithm of 3D Mesh Enkhbayar Altantsetseg 1) Katsutsugu Matsuyama ) Kouichi Konno ) 1) National University of Mongolia ) Iwate University {enkhbayar.a}
Surfaces, meshes, and topology
 Surfaces from Point Samples Surfaces, meshes, and topology A surface is a 2-manifold embedded in 3- dimensional Euclidean space Such surfaces are often approximated by triangle meshes 2 1 Triangle mesh
Surfaces from Point Samples Surfaces, meshes, and topology A surface is a 2-manifold embedded in 3- dimensional Euclidean space Such surfaces are often approximated by triangle meshes 2 1 Triangle mesh
PARAMETRIC STUDY WITH GEOFRAC: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC FRACTURE FLOW MODEL. Alessandra Vecchiarelli, Rita Sousa, Herbert H.
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 3, 23 SGP-TR98 PARAMETRIC STUDY WITH GEOFRAC: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 3, 23 SGP-TR98 PARAMETRIC STUDY WITH GEOFRAC: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC
Model-based segmentation and recognition from range data
 Model-based segmentation and recognition from range data Jan Boehm Institute for Photogrammetry Universität Stuttgart Germany Keywords: range image, segmentation, object recognition, CAD ABSTRACT This
Model-based segmentation and recognition from range data Jan Boehm Institute for Photogrammetry Universität Stuttgart Germany Keywords: range image, segmentation, object recognition, CAD ABSTRACT This
Multi-View Matching & Mesh Generation. Qixing Huang Feb. 13 th 2017
 Multi-View Matching & Mesh Generation Qixing Huang Feb. 13 th 2017 Geometry Reconstruction Pipeline RANSAC --- facts Sampling Feature point detection [Gelfand et al. 05, Huang et al. 06] Correspondences
Multi-View Matching & Mesh Generation Qixing Huang Feb. 13 th 2017 Geometry Reconstruction Pipeline RANSAC --- facts Sampling Feature point detection [Gelfand et al. 05, Huang et al. 06] Correspondences
Using Semi-Regular 4 8 Meshes for Subdivision Surfaces
 Using Semi-Regular 8 Meshes for Subdivision Surfaces Luiz Velho IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada Abstract. Semi-regular 8 meshes are refinable triangulated quadrangulations. They provide a
Using Semi-Regular 8 Meshes for Subdivision Surfaces Luiz Velho IMPA Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada Abstract. Semi-regular 8 meshes are refinable triangulated quadrangulations. They provide a
Outline. Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete. Noise
 Fundamentals Data Outline Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete Noise 2 Data Data : Function dependent on one or more variables. Example Audio (1D) - depends
Fundamentals Data Outline Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete Noise 2 Data Data : Function dependent on one or more variables. Example Audio (1D) - depends
Minimizing Edge Length to Connect Sparsely Sampled Unstructured Point Sets
 Minimizing Edge Length to Connect Sparsely Sampled Unstructured Point Sets Stefan Ohrhallinger a,b, Sudhir Mudur a, Michael Wimmer b a Concordia University, Montréal b Vienna University of Technology Abstract
Minimizing Edge Length to Connect Sparsely Sampled Unstructured Point Sets Stefan Ohrhallinger a,b, Sudhir Mudur a, Michael Wimmer b a Concordia University, Montréal b Vienna University of Technology Abstract
weighted minimal surface model for surface reconstruction from scattered points, curves, and/or pieces of surfaces.
 weighted minimal surface model for surface reconstruction from scattered points, curves, and/or pieces of surfaces. joint work with (S. Osher, R. Fedkiw and M. Kang) Desired properties for surface reconstruction:
weighted minimal surface model for surface reconstruction from scattered points, curves, and/or pieces of surfaces. joint work with (S. Osher, R. Fedkiw and M. Kang) Desired properties for surface reconstruction:
Discretized Marching Cubes
 Discretized Marching Cubes C. Montani, R. Scateni, R. Scopigno I.E.I. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Via S. Maria 46, 56126 Pisa, ITALY Centro di Ricerca, Sviluppo e Studi Superiori Sardegna (CRS4),
Discretized Marching Cubes C. Montani, R. Scateni, R. Scopigno I.E.I. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Via S. Maria 46, 56126 Pisa, ITALY Centro di Ricerca, Sviluppo e Studi Superiori Sardegna (CRS4),
CURVES OF CONSTANT WIDTH AND THEIR SHADOWS. Have you ever wondered why a manhole cover is in the shape of a circle? This
 CURVES OF CONSTANT WIDTH AND THEIR SHADOWS LUCIE PACIOTTI Abstract. In this paper we will investigate curves of constant width and the shadows that they cast. We will compute shadow functions for the circle,
CURVES OF CONSTANT WIDTH AND THEIR SHADOWS LUCIE PACIOTTI Abstract. In this paper we will investigate curves of constant width and the shadows that they cast. We will compute shadow functions for the circle,
Geometric Modeling in Graphics
 Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing. David Eppstein
 Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Advanced geometry tools for CEM
 Advanced geometry tools for CEM Introduction Modern aircraft designs are extremely complex CAD models. For example, a BAE Systems aircraft assembly consists of over 30,000 individual components. Since
Advanced geometry tools for CEM Introduction Modern aircraft designs are extremely complex CAD models. For example, a BAE Systems aircraft assembly consists of over 30,000 individual components. Since
The Quality Of 3D Models
 The Quality Of 3D Models Problems and Solutions for Applications Post-Design Fathi El-Yafi Senior Product Engineer Product Department of EXA Corporation 1 : Overview Status Problems Identified Defect Sources
The Quality Of 3D Models Problems and Solutions for Applications Post-Design Fathi El-Yafi Senior Product Engineer Product Department of EXA Corporation 1 : Overview Status Problems Identified Defect Sources
Reconstructing Surfaces Using Envelopes: Bridging the Gap between Theory and Practice
 Reconstructing Surfaces Using Envelopes: Bridging the Gap between Theory and Practice Justin Bisceglio Blue Sky Studios, and University of Connecuticut, Department of Computer Science T.J. Peters University
Reconstructing Surfaces Using Envelopes: Bridging the Gap between Theory and Practice Justin Bisceglio Blue Sky Studios, and University of Connecuticut, Department of Computer Science T.J. Peters University
3D Reconstruction from Multi-View Stereo: Implementation Verification via Oculus Virtual Reality
 3D Reconstruction from Multi-View Stereo: Implementation Verification via Oculus Virtual Reality Andrew Moran MIT, Class of 2014 andrewmo@mit.edu Ben Eysenbach MIT, Class of 2017 bce@mit.edu Abstract We
3D Reconstruction from Multi-View Stereo: Implementation Verification via Oculus Virtual Reality Andrew Moran MIT, Class of 2014 andrewmo@mit.edu Ben Eysenbach MIT, Class of 2017 bce@mit.edu Abstract We
Topology Preserving Tetrahedral Decomposition of Trilinear Cell
 Topology Preserving Tetrahedral Decomposition of Trilinear Cell Bong-Soo Sohn Department of Computer Engineering, Kyungpook National University Daegu 702-701, South Korea bongbong@knu.ac.kr http://bh.knu.ac.kr/
Topology Preserving Tetrahedral Decomposition of Trilinear Cell Bong-Soo Sohn Department of Computer Engineering, Kyungpook National University Daegu 702-701, South Korea bongbong@knu.ac.kr http://bh.knu.ac.kr/
Geometry Processing & Geometric Queries. Computer Graphics CMU /15-662
 Geometry Processing & Geometric Queries Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662 Last time: Meshes & Manifolds Mathematical description of geometry - simplifying assumption: manifold - for polygon meshes: fans,
Geometry Processing & Geometric Queries Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662 Last time: Meshes & Manifolds Mathematical description of geometry - simplifying assumption: manifold - for polygon meshes: fans,
