NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 April 15.
|
|
|
- Augustus Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging ; : ENTROPY BASED DTI QUALITY CONTROL VIA REGIONAL ORIENTATION DISTRIBUTION M Farzinfar 1, C Dietrich 1, RG Smith 1,2, Y Li 3, A Gupta 1, Z Liu 3, and MA Styner 1,2 1 Dept Psychiatry, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, US 2 Dept Computer Science, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, US 3 Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China Abstract Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) has received increasing attention in the neuroimaging community. However, the complex Diffusion Weighted Images (DWI) acquisition protocol are prone to artifacts induced by motion and low signal-to-noise rations(snrs). A rigorous quality control (QC) and error correction procedure is absolutely necessary for DTI data analysis. Most existing QC procedures are conducted in the DWI domain and/or on a voxel level, but our own experiments show that these methods often do not fully detect and eliminate certain types of artifacts. We propose a new regional, alignment-independent DTI-QC measure that is based in the DTI domain employing the entropy of the regional distribution of the principal directions. This new QC measurement is intended to complement the existing set of QC procedures by detecting and correcting residual artifacts. Experiments show that our automatic method can reliably detect and potentially correct such residual artifacts. The results indicate its usefulness for general quality assessment in DTI studies. 1. INTRODUCTION Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) has received increasing attention in the neuro-imaging community due to its ability to investigate the microstructural features, integrity and changes of white matter in normal, developing, aging and pathological human brains [1, 2]. DTI employs a diffusion coefficient to quantify the rate and directionality of water displacement in various brain tissues. The coefficient is estimated from a series of DWI by using several (at least six) non-collinear diffusion sensitizing gradients [3]. Using such an imaging modality in a clinical environment is difficult and can suffer from many types of artifacts as a result of either a limitation or malfunction in the hardware or software of the scanning device. In addition, severe artifacts may also originate from the source of physiological noise such as bulk head motion and respiratory motion. Three different categories of post-processing approaches have been proposed to improve induced errors in DT-MRI. In the first category, one aims to estimate signal in MRI from a noisy signal. For instance, Tristán-Vega later proposed a DWI filtering method which was intended to take advantage of joint information from all DWIs and the correlation between them [4]. In the second category, regularization of tensor images is employed in addition to estimating the tensor [5]. Fillard. et. al. proposed a maximum-a-posterior framework estimation to couple tensor estimation and regularization to better capture information from noisy images [6]. In the third category, new diffusion tensor estimation techniques are performed from qualified DWIs where outliers are detected and removed from data set [7]. Mangin, J. et al. [7] proposed a robust DTI estimation approach, in which following eddycurrent artifact correction, the weight of each data point is set to a function of the residuals
2 Farzinfar et al. Page 2 of the previous iteration while iteratively doing re-weighted least-squares fitting. Artifactual data are thus given lower weights in the tensor estimation. Despite the efforts invested in improving the DTI estimation, there is plenty of room for improvement in DTI-QC. In this paper, we propose a new approach to assess quality control of DTI and refurbish DWIs using an entropy-based measurement on the orientational distribution of principal directions. Our method is employed in a complementary process to our existing, open-source DWI-QC tool, DTIPrep [8], which detects and corrects DWI issues such as inter-slice brightness artifacts, eddy current artifacts, within-dwi and between-dwi patient motion. The orientational distribution is computed via an icosahedron subdivision based spherical histogram of the principal directions within the following regions: total brain, whole brain gray matter and whole brain white matter. Our experiments show that the proposed DTI-QC approach is especially sensitive in detecting and correcting artifacts of dominating directions of diffusion. 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1. Artifacts of dominating directions 2.2. Overview 2.3. Subjects The proposed approach is based on the assumption that standard QC procedures are illsuited to identify artifacts that are mainly present in the DTI domain such as dominating directions of diffusion (see Fig. 1). Such artifacts can be detected visually by identifying a dominant background color tone in a colorized Fractional Anisotropy (FA) image. Fig. 1 displays an artifact free scan (with no discernible dominant color tone) alongside scans displaying artifacts of dominating directions in the colorized FA as well as the spherical PD histogram. Standard DWI-QC as well as DWI or DTI based filtering approaches cannot detect or correct such artifacts, whereas our approach is able to detect and potentially correct them. As the proposed QC procedure is intended to complement the existing set of DWI-QC procedures, we first apply DWI-QC using DTIPrep followed by DTI estimation via a weightedleast square fit (see Fig 2). Prior tissue segmentation masks of whole brain white matter and gray matter are used to define the regions within the PD distributions are computed. The PD distributions are represented as spherical histograms with bins defined by a quasi-uniform, icosahedron based spherical subdivision. Finally, the entropy is computed from the histogram and compared with prior training data that defines the expected range of the entropy for artifact-free scans. A leaveone- out scheme is employed to potentially correct the DWI set by excluding individual DWI images and test for optimal improvement in the entropy values. We tested our approach on two sets of data: a) 20 pediatric dataset (6-14 months of age, subjects at low or high risk of developing autism [9]) acquired with a multi-b-value ( ) sequence and 25 unique gradient directions, b) 26 adult datasets from a Huntington s Disease study [10] with 3 different acquisition protocols. For both datasets, a set of artifact-free scans were first detected via visual assessment of the colorized FA, as well as manually guided streamline fiber tractography within 3D Slicer (by rater CD). For the pediatric dataset we employed 12 artifact-free scans and 8 tests scans, whereas for the adult dataset we used 14 artifact-free scans and 11 test scans. All datasets were judge by automatic and visual QC procedure to appear perfectly normal based on DWI-only QC.
3 Farzinfar et al. Page Distribution of Principal Directions In order to represent PD distribution, we employ a spherical coordinate system on which we compute the PD histogram. The spherical histogram bins are computed via a subdivision of the unit sphere. Two different subdivisions have mainly been employed in literature[11]. The first option subdivides the unit sphere based on the spherical or geographical coordinates/angles (ϕ,θ), where a rectangular grid is defined as a uniform subdivision of longitudes (ϕ) and latitudes (θ) [12]. However, such an angular coordinate grid is not optimal for the computation of spherical histograms[11], as the actual size of the subdivision face area on the unit sphere varies widely from the equatorial to polar regions. The second, common option for a spherical subdivision is the quasi-uniform icosahedron subdivision, in which the triangular faces of an icosahedron is linearly or recursively subdivided into smaller triangles whose vertices are projected to the unit sphere. While the icosahedron is uniform in spacing and area, the icosahedron subdivision is not, but can be considered a quasiuniform spherical subdivision due to the small variance in spacing and area, especially when compared to the above angular subdivision. Using an angular resolution of 5, which leads to (360 /5 ) (90 /5 ) = 1296 faces, variability in face area of an angular subdivision of the unit sphere is σ = with mean μ = and average relative error = 48% (max error / %). The variability in face area of the icosahedron subdivision approach computed at subdivision level 8 is σ = , with mean μ = and average relative error = 5.34% (max error = 35.52%). While face-wise binning could be chosen for the spherical histogram, we chose nearest-vertex based binning for the PD histogram due to its implementational simplicity. Using subdivision level 8, 812 bins are generated cover sufficient data (79832 voxels) to estimate the distribution of PD reliably Orientational Entropy for DTI QC One of the goals of our orientation based DTI QC metric was to be independent to the patient s position in the scanner or scan. We chose to use Shannon s entropy, a concept well known from information theory [13], to summarize the PD distribution. In our application, entropy of a distribution of PDs represents the scatter and spread of dominating directions within brain regions measured independent of alignment of the spherical parametrization. Higher entropy indicates that the PDs distribution is more uniform. Lower entropy demonstrates clustering of the PDs distribution and a higher degree of such clustering is a consequence of the before mentioned artifact of dominating directions. Given the PD histogram, the proposed orientational entropy is defined as: where K is the number of vertices/bins and p is the normalized frequency in the PD histogram at bin i. Detection In order to detect scans with unexpected value of entropy (lower values of entropy for artifacts of dominating directions), we compare a given DT scan s entropy to values learned from a prior set of artifact-free samples. We employ z-score to categorize the quality of a DT scan into three categories: acceptable (z < 1.64/90%), suspicious (z 1.64/90%) and unacceptable (z 2.58/99%). For our experiments here, we evaluate the DTI quality within white matter, gray matter and whole brain regions. Correction For our correction step, we employed an iterative leave-one-out-strategy over all individual DWI images by recomputing DTI images and corresponding entropies. At (1)
4 Farzinfar et al. Page 4 each iteration, the DWI with maximal improvement is removed and all leave-one-out entropies are recomputed. This process is continued until the z-score is in acceptable range. 3. RESULTS 3.1. Detection Step 3.2. Correction Pediatric Data Seven of the selected test images presented with a red (medial-lateral) dominating direction of varying degree and one with a green (anterior-posterior) dominating direction. Fig. 3 plots the z-scores of the orientational entropies for all 20 images within white matter, gray matter and whole brain regions. All test images showed by at least one of the regional z-scores as classified as suspicious (indexed from 13 to 20), with z- scores correlating well with the qualitative, visual QC assessment (not shown here). These experiments surprisingly showed that the white matter z-score seems most suitable value for the detection of artifacts of dominating directions, even though visual assessment mostly focuses on gray matter areas. The dataset with the largest z-score suffers from single case with green dominating direction. Adult Data In the adult data, we chose to use a more diverse set of testing images to study whether our method can pick up other artifacts as well. While one test image suffered from red dominating direction artifact, others showed focused directional artifacts within the pre-frontal cortex, or general noise-related artifacts and checkerboard artifacts on the FA image. Our experiments show that the method is able to detect all of these artifacts only if they cover a sufficiently large area. Fig. 4 plots the z-scores of the orientational entropies for all 25 images (test images indexed 14 to 25). The presence of a dominant direction artifact in one of the sample is quite obvious. Two cases suffering from focused directional artifacts in the pre-frontal cortex can be successfully detected in the gray matter region only. Three cases with noise-related artifacts are detected at higher entropies in white matter. We performed the proposed correction on all cases categorized as suspicious. Fig. 5 presents an example case (pediatric case 14) that suffered from a red dominating direction. After correction, most of the artifactual red regions were visibly improved in contrast between different tracts with reduced artifact appearance in the colorized FA image. In order to assess the correction results quantitatively, we applied our atlasbased fiber analysis [14] before (left) and after(right) employing our correction step using the same atlas mapping. The FA profiles of genu and splenium fibers indicate that the correction results in higher FA values, which indicates an improvement in the fiber based analysis. Fig. 6 shows the assessment of a different case with a minor red dominating direction via fiducial fiber tractography in 3D Slicer in the splenium tract center. The tractography result of the corrected image is clearly improved. While these examples demonstrate promising correction results for DTI quality control compared with the original image, it has to be noted that many cases detected with the proposed orientational entropy were not salvageable. 4. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION In this work, we proposed a new approach for DTI-QC which is majorly focused on detection of artifacts of dominant directions employing the entropy of regional distributions of principal directions. We tested our approach in two small-scale studies on pediatric and adult subjects. The results show that artifacts of dominant directions are successfully detected using the proposed approach. In the adult data, focused gray matter artifacts and noise-related artifacts were also successfully detected. Furthermore, we proposed a
5 Farzinfar et al. Page 5 Acknowledgments References correction strategy that shows considerable promise in datasets with minor artifacts. Major artifacts have shown to be rarely salvegeable. We are currently applying this method to several large scale studies to further test the method s usefulness in routine DWI/DTI QC procedures. Eric Maltbie and Clement Vachet are acknowledged for advice and the following NIH grants provided support: NA-MIC U54 EB005149, R01 HD055741, P30 HD03110, and P50 MH Hsu JL, Leemans A, Bai CH, Lee CH, Tsai YF, Chiu HC, Chen WH. Gender differences and agerelated white matter changes of the human brain: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroimage. 2008; 39(2): [PubMed: ] 2. Unrath A, Müller HP, Riecker A, Ludolph AC, Sperfeld AD, Kassubek J. Whole brain-based analysis of regional white matter tract alterations in rare motor neuron diseases by diffusion tensor imaging. Human brain mapping Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LEBiHAN D, et al. Estimation of the effective selfdiffusion tensor from the nmr spin echo. Journal of Magnetic Resonance-Series B. 1994; 103(3): [PubMed: ] 4. Tristán-Vega A, Aja-Fernández S. Dwi filtering using joint information for dti and hardi. Medical Image Analysis. 2010; 14(2): [PubMed: ] 5. Wang Z, Vemuri BC, Chen Y, Mareci TH. A constrained variational principle for direct estimation and smoothing of the diffusion tensor field from complex dwi. Medical Imaging, IEEE Transactions on. 2004; 23(8): Fillard P, Pennec X, Arsigny V, Ayache N. Clinical dt-mri estimation, smoothing, and fiber tracking with log-euclidean metrics. Medical Imaging IEEE Transactions on. 2007; 26(11): Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark C, Le Bihan D, Bloch I. Distortion correction and robust tensor estimation for mr diffusion imaging. Medical Image Analysis. 2002; 6(3): [PubMed: ] 8. Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gerig, G.; Gouttard, S.; Tao, R.; Fletcher, T.; Styner, M. Quality control of diffusion weighted images. Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; p Jason J, Wolff, et al. Differences in white matter fiber tract development present from 6 to 24 months in infants with autism. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2011:1 20. in press. [PubMed: ] 10. Dumas, Eve M., et al. Early changes in white matter pathways of the sensorimotor cortex in premanifest Huntington s disease. Human brain mapping. Jan Clarke, KC. Discrete global grids: A web book. University of California; Santa Barbara: Criteria and measures for the comparison of global geocoding systems Cui JL, Wen CY, Hu Y, Mak KC, Mak KHH, Luk KDK. Orientation entropy analysis of diffusion tensor in healthy and myelopathic spinal cord. NeuroImage Shannon CE. A mathematical theory of communication. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review. 2001; 5(1): Casey B, Goodlett P, Fletcher Thomas, Gilmore John H, Gerig Guido. Group analysis of dti fiber tract statistics with application to neurodevelopment. NeuroImage. 2009; 45(1, Supplement 1):S133 S142. [PubMed: ]
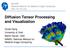
6 Farzinfar et al. Page 6 Fig. 1. (A) Slide number 41 of artifact free scan (top) followed by scans suffering from artifact of dominant green direction (middle) and dominant red direction (bottom) in the colorized FA image. (B) Corresponding spherical histograms of the PD distribution within the entire brain region (viewpoints rotated to indicate locations of highest histogram frequency).
7 Farzinfar et al. Page 7 Fig. 2. Schematic overview of the proposed DTI-QC.
8 Farzinfar et al. Page 8 Fig. 3. Plot of all z-scores in the pediatric data. The dashed lines represent the cutoff the suspicious category.
9 Farzinfar et al. Page 9 Fig. 4. Plot of all z-scores in the adult data. The dashed lines represent the cutoff the suspicious category.
10 Farzinfar et al. Page 10 Fig. 5. A) Improvement in contrast of cingulum and fornix fibers in corrected image(right). B) FAprofiles of genu and splenium fibers before (red) and after correction (blue).
11 Farzinfar et al. Page 11 Fig. 6. The fiber tractography of splenium of sample 20 th in Fig. 3 before (left) and after (right) our correction step.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 July 05.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2013 March 13; 8669: 1667549. doi:10.1117/12.2006925. DTI Quality Control Assessment via Error Estimation
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2013 March 13; 8669: 1667549. doi:10.1117/12.2006925. DTI Quality Control Assessment via Error Estimation
Diffusion Imaging Quality Control with DTIPrep
 NA-MIC National Alliance for Medical Image Computing http://na-mic.org Diffusion Imaging Quality Control with DTIPrep Martin Styner Francois Budin University of North Carolina Neuro Image Research and
NA-MIC National Alliance for Medical Image Computing http://na-mic.org Diffusion Imaging Quality Control with DTIPrep Martin Styner Francois Budin University of North Carolina Neuro Image Research and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc SPIE. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 December 31.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc SPIE. 2013 March 13; 8669:. doi:10.1117/12.2007093. UNC-Utah NA-MIC DTI framework: Atlas Based Fiber Tract Analysis with Application
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc SPIE. 2013 March 13; 8669:. doi:10.1117/12.2007093. UNC-Utah NA-MIC DTI framework: Atlas Based Fiber Tract Analysis with Application
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators
 Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators D. Merhof 1, G. Greiner 2, M. Buchfelder 3, C. Nimsky 4 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany 2 Computer Graphics
Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators D. Merhof 1, G. Greiner 2, M. Buchfelder 3, C. Nimsky 4 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany 2 Computer Graphics
Evaluation of Local Filter Approaches for Diffusion Tensor based Fiber Tracking
 Evaluation of Local Filter Approaches for Diffusion Tensor based Fiber Tracking D. Merhof 1, M. Buchfelder 2, C. Nimsky 3 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz 2 Department of Neurosurgery,
Evaluation of Local Filter Approaches for Diffusion Tensor based Fiber Tracking D. Merhof 1, M. Buchfelder 2, C. Nimsky 3 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz 2 Department of Neurosurgery,
Diffusion Tensor Processing and Visualization
 NA-MIC National Alliance for Medical Image Computing http://na-mic.org Diffusion Tensor Processing and Visualization Guido Gerig University of Utah Martin Styner, UNC NAMIC: National Alliance for Medical
NA-MIC National Alliance for Medical Image Computing http://na-mic.org Diffusion Tensor Processing and Visualization Guido Gerig University of Utah Martin Styner, UNC NAMIC: National Alliance for Medical
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 December 4.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 December 4. Published in final edited form as: Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 December 4. Published in final edited form as: Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv.
Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Investigation of Cerebral Gray and White Matter Diseases
 Quantities Measured by MR - Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Investigation of Cerebral Gray and White Matter Diseases Static parameters (influenced by molecular environment): T, T* (transverse relaxation)
Quantities Measured by MR - Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Investigation of Cerebral Gray and White Matter Diseases Static parameters (influenced by molecular environment): T, T* (transverse relaxation)
Automatic Quantification of DTI Parameters along Fiber Bundles
 Automatic Quantification of DTI Parameters along Fiber Bundles Jan Klein 1, Simon Hermann 1, Olaf Konrad 1, Horst K. Hahn 1, and Heinz-Otto Peitgen 1 1 MeVis Research, 28359 Bremen Email: klein@mevis.de
Automatic Quantification of DTI Parameters along Fiber Bundles Jan Klein 1, Simon Hermann 1, Olaf Konrad 1, Horst K. Hahn 1, and Heinz-Otto Peitgen 1 1 MeVis Research, 28359 Bremen Email: klein@mevis.de
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
Automatic Quantification of DTI Parameters along Fiber Bundles
 Automatic Quantification of DTI Parameters along Fiber Bundles Jan Klein, Simon Hermann, Olaf Konrad, Horst K. Hahn, Heinz-Otto Peitgen MeVis Research, 28359 Bremen Email: klein@mevis.de Abstract. We introduce
Automatic Quantification of DTI Parameters along Fiber Bundles Jan Klein, Simon Hermann, Olaf Konrad, Horst K. Hahn, Heinz-Otto Peitgen MeVis Research, 28359 Bremen Email: klein@mevis.de Abstract. We introduce
Reconstruction of Fiber Trajectories via Population-Based Estimation of Local Orientations
 IDEA Reconstruction of Fiber Trajectories via Population-Based Estimation of Local Orientations Pew-Thian Yap, John H. Gilmore, Weili Lin, Dinggang Shen Email: ptyap@med.unc.edu 2011-09-21 Poster: P2-46-
IDEA Reconstruction of Fiber Trajectories via Population-Based Estimation of Local Orientations Pew-Thian Yap, John H. Gilmore, Weili Lin, Dinggang Shen Email: ptyap@med.unc.edu 2011-09-21 Poster: P2-46-
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc SPIE. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 October 10.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc SPIE. 2011 ; 7962: 79620S. doi:10.1117/12.878291. Efficient, Graph-based White Matter Connectivity from Orientation Distribution
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc SPIE. 2011 ; 7962: 79620S. doi:10.1117/12.878291. Efficient, Graph-based White Matter Connectivity from Orientation Distribution
Generating Fiber Crossing Phantoms Out of Experimental DWIs
 Generating Fiber Crossing Phantoms Out of Experimental DWIs Matthan Caan 1,2, Anne Willem de Vries 2, Ganesh Khedoe 2,ErikAkkerman 1, Lucas van Vliet 2, Kees Grimbergen 1, and Frans Vos 1,2 1 Department
Generating Fiber Crossing Phantoms Out of Experimental DWIs Matthan Caan 1,2, Anne Willem de Vries 2, Ganesh Khedoe 2,ErikAkkerman 1, Lucas van Vliet 2, Kees Grimbergen 1, and Frans Vos 1,2 1 Department
Automatic corpus callosum segmentation using a deformable active Fourier contour model
 Automatic corpus callosum segmentation using a deformable active Fourier contour model Clement Vachet a, Benjamin Yvernault a, Kshamta Bhatt a, Rachel G. Smith a,b, Guido Gerig c, Heather Cody Hazlett
Automatic corpus callosum segmentation using a deformable active Fourier contour model Clement Vachet a, Benjamin Yvernault a, Kshamta Bhatt a, Rachel G. Smith a,b, Guido Gerig c, Heather Cody Hazlett
syngo.mr Neuro 3D: Your All-In-One Post Processing, Visualization and Reporting Engine for BOLD Functional and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging Datasets
 syngo.mr Neuro 3D: Your All-In-One Post Processing, Visualization and Reporting Engine for BOLD Functional and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging Datasets Julien Gervais; Lisa Chuah Siemens Healthcare, Magnetic
syngo.mr Neuro 3D: Your All-In-One Post Processing, Visualization and Reporting Engine for BOLD Functional and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging Datasets Julien Gervais; Lisa Chuah Siemens Healthcare, Magnetic
Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Reading Development
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Reading Development Bob Dougherty Stanford Institute for Reading and Learning Reading and Anatomy Every brain is different... Not all brains optimized for highly proficient
Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Reading Development Bob Dougherty Stanford Institute for Reading and Learning Reading and Anatomy Every brain is different... Not all brains optimized for highly proficient
Group Statistics of DTI Fiber Bundles Using Spatial Functions of Tensor Measures
 Group Statistics of DTI Fiber Bundles Using Spatial Functions of Tensor Measures Casey B. Goodlett 1,2, P. Thomas Fletcher 1,2, John H. Gilmore 3, and Guido Gerig 1,2 1 School of Computing, University
Group Statistics of DTI Fiber Bundles Using Spatial Functions of Tensor Measures Casey B. Goodlett 1,2, P. Thomas Fletcher 1,2, John H. Gilmore 3, and Guido Gerig 1,2 1 School of Computing, University
Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators
 Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators D. Merhofl, G. Greiner 2, M. Buchfelder 3, C. Nimsky4 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany 2 Computer Graphics
Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators D. Merhofl, G. Greiner 2, M. Buchfelder 3, C. Nimsky4 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany 2 Computer Graphics
Correction of Partial Volume Effects in Arterial Spin Labeling MRI
 Correction of Partial Volume Effects in Arterial Spin Labeling MRI By: Tracy Ssali Supervisors: Dr. Keith St. Lawrence and Udunna Anazodo Medical Biophysics 3970Z Six Week Project April 13 th 2012 Introduction
Correction of Partial Volume Effects in Arterial Spin Labeling MRI By: Tracy Ssali Supervisors: Dr. Keith St. Lawrence and Udunna Anazodo Medical Biophysics 3970Z Six Week Project April 13 th 2012 Introduction
A Ray-based Approach for Boundary Estimation of Fiber Bundles Derived from Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 A Ray-based Approach for Boundary Estimation of Fiber Bundles Derived from Diffusion Tensor Imaging M. H. A. Bauer 1,3, S. Barbieri 2, J. Klein 2, J. Egger 1,3, D. Kuhnt 1, B. Freisleben 3, H.-K. Hahn
A Ray-based Approach for Boundary Estimation of Fiber Bundles Derived from Diffusion Tensor Imaging M. H. A. Bauer 1,3, S. Barbieri 2, J. Klein 2, J. Egger 1,3, D. Kuhnt 1, B. Freisleben 3, H.-K. Hahn
Subvoxel Segmentation and Representation of Brain Cortex Using Fuzzy Clustering and Gradient Vector Diffusion
 Subvoxel Segmentation and Representation of Brain Cortex Using Fuzzy Clustering and Gradient Vector Diffusion Ming-Ching Chang Xiaodong Tao GE Global Research Center {changm, taox} @ research.ge.com SPIE
Subvoxel Segmentation and Representation of Brain Cortex Using Fuzzy Clustering and Gradient Vector Diffusion Ming-Ching Chang Xiaodong Tao GE Global Research Center {changm, taox} @ research.ge.com SPIE
Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute, University of Utah, Salt Lake City
 UNC-Utah NA-MIC DTI framework: Atlas Based Fiber Tract Analysis with Application to a Study of Nicotine Smoking Addiction Audrey R Verde1, Jean-Baptiste Berger1, Aditya Gupta1,7, Mahshid Farzinfar1, Adrien
UNC-Utah NA-MIC DTI framework: Atlas Based Fiber Tract Analysis with Application to a Study of Nicotine Smoking Addiction Audrey R Verde1, Jean-Baptiste Berger1, Aditya Gupta1,7, Mahshid Farzinfar1, Adrien
NEURO M203 & BIOMED M263 WINTER 2014
 NEURO M203 & BIOMED M263 WINTER 2014 MRI Lab 2: Neuroimaging Connectivity Lab In today s lab we will work with sample diffusion imaging data and the group averaged fmri data collected during your scanning
NEURO M203 & BIOMED M263 WINTER 2014 MRI Lab 2: Neuroimaging Connectivity Lab In today s lab we will work with sample diffusion imaging data and the group averaged fmri data collected during your scanning
MITK-DI. A new Diffusion Imaging Component for MITK. Klaus Fritzsche, Hans-Peter Meinzer
 MITK-DI A new Diffusion Imaging Component for MITK Klaus Fritzsche, Hans-Peter Meinzer Division of Medical and Biological Informatics, DKFZ Heidelberg k.fritzsche@dkfz-heidelberg.de Abstract. Diffusion-MRI
MITK-DI A new Diffusion Imaging Component for MITK Klaus Fritzsche, Hans-Peter Meinzer Division of Medical and Biological Informatics, DKFZ Heidelberg k.fritzsche@dkfz-heidelberg.de Abstract. Diffusion-MRI
Automatic MS Lesion Segmentation by Outlier Detection and Information Theoretic Region Partitioning Release 0.00
 Automatic MS Lesion Segmentation by Outlier Detection and Information Theoretic Region Partitioning Release 0.00 Marcel Prastawa 1 and Guido Gerig 1 Abstract July 17, 2008 1 Scientific Computing and Imaging
Automatic MS Lesion Segmentation by Outlier Detection and Information Theoretic Region Partitioning Release 0.00 Marcel Prastawa 1 and Guido Gerig 1 Abstract July 17, 2008 1 Scientific Computing and Imaging
Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Diffusion-Weighted Images from Distortion Compensated Orthogonal Anisotropic Acquisitions.
 Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Diffusion-Weighted Images from Distortion Compensated Orthogonal Anisotropic Acquisitions. Benoit Scherrer Ali Gholipour Simon K. Warfield Children s Hospital Boston,
Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Diffusion-Weighted Images from Distortion Compensated Orthogonal Anisotropic Acquisitions. Benoit Scherrer Ali Gholipour Simon K. Warfield Children s Hospital Boston,
Diffusion Imaging Visualization
 Diffusion Imaging Visualization Thomas Schultz URL: http://cg.cs.uni-bonn.de/schultz/ E-Mail: schultz@cs.uni-bonn.de 1 Outline Introduction to Diffusion Imaging Basic techniques Glyph-based Visualization
Diffusion Imaging Visualization Thomas Schultz URL: http://cg.cs.uni-bonn.de/schultz/ E-Mail: schultz@cs.uni-bonn.de 1 Outline Introduction to Diffusion Imaging Basic techniques Glyph-based Visualization
The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity
 1 The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity Journal: Journal of Neurophysiology Author: B. T. Thomas Yeo, et al Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21653723
1 The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity Journal: Journal of Neurophysiology Author: B. T. Thomas Yeo, et al Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21653723
Advanced MRI Techniques (and Applications)
 Advanced MRI Techniques (and Applications) Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Department of Neurology Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Brain Research Institute Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Advanced MRI Techniques (and Applications) Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Department of Neurology Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Brain Research Institute Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Corpus Callosum Subdivision based on a Probabilistic Model of Inter-Hemispheric Connectivity
 Corpus Callosum Subdivision based on a Probabilistic Model of Inter-Hemispheric Connectivity Martin A. Styner 1,2, Ipek Oguz 1, Rachel Gimpel Smith 2, Carissa Cascio 2, and Matthieu Jomier 1 1 Dept. of
Corpus Callosum Subdivision based on a Probabilistic Model of Inter-Hemispheric Connectivity Martin A. Styner 1,2, Ipek Oguz 1, Rachel Gimpel Smith 2, Carissa Cascio 2, and Matthieu Jomier 1 1 Dept. of
Automatic segmentation of the cortical grey and white matter in MRI using a Region Growing approach based on anatomical knowledge
 Automatic segmentation of the cortical grey and white matter in MRI using a Region Growing approach based on anatomical knowledge Christian Wasserthal 1, Karin Engel 1, Karsten Rink 1 und André Brechmann
Automatic segmentation of the cortical grey and white matter in MRI using a Region Growing approach based on anatomical knowledge Christian Wasserthal 1, Karin Engel 1, Karsten Rink 1 und André Brechmann
Quantitative Analysis of White Matter Fiber Properties along Geodesic Paths
 Quantitative Analysis of White Matter Fiber Properties along Geodesic Paths Pierre Fillard 1,4, John Gilmore 2, Joseph Piven 2, Weili Lin 3, and Guido Gerig 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science, 2 Department
Quantitative Analysis of White Matter Fiber Properties along Geodesic Paths Pierre Fillard 1,4, John Gilmore 2, Joseph Piven 2, Weili Lin 3, and Guido Gerig 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science, 2 Department
Network connectivity via inference over curvature-regularizing line graphs
 Network connectivity via inference over curvature-regularizing line graphs Asian Conference on Computer Vision Maxwell D. Collins 1,2, Vikas Singh 2,1, Andrew L. Alexander 3 1 Department of Computer Sciences
Network connectivity via inference over curvature-regularizing line graphs Asian Conference on Computer Vision Maxwell D. Collins 1,2, Vikas Singh 2,1, Andrew L. Alexander 3 1 Department of Computer Sciences
n o r d i c B r a i n E x Tutorial DTI Module
 m a k i n g f u n c t i o n a l M R I e a s y n o r d i c B r a i n E x Tutorial DTI Module Please note that this tutorial is for the latest released nordicbrainex. If you are using an older version please
m a k i n g f u n c t i o n a l M R I e a s y n o r d i c B r a i n E x Tutorial DTI Module Please note that this tutorial is for the latest released nordicbrainex. If you are using an older version please
Dual Tensor Atlas Generation Based on a Cohort of Coregistered non-hardi Datasets
 Dual Tensor Atlas Generation Based on a Cohort of Coregistered non-hardi Datasets Matthan Caan 1,2, Caroline Sage 3, Maaike van der Graaf 1, Cornelis Grimbergen 1, Stefan Sunaert 3, Lucas van Vliet 2,
Dual Tensor Atlas Generation Based on a Cohort of Coregistered non-hardi Datasets Matthan Caan 1,2, Caroline Sage 3, Maaike van der Graaf 1, Cornelis Grimbergen 1, Stefan Sunaert 3, Lucas van Vliet 2,
Head motion in diffusion MRI
 Head motion in diffusion MRI Anastasia Yendiki HMS/MGH/MIT Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging 11/06/13 Head motion in diffusion MRI 0/33 Diffusion contrast Basic principle of diffusion
Head motion in diffusion MRI Anastasia Yendiki HMS/MGH/MIT Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging 11/06/13 Head motion in diffusion MRI 0/33 Diffusion contrast Basic principle of diffusion
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators. Preprocessing. fmri Preprocessing
 SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction
 Tina Memo No. 2007-003 Published in Proc. MIUA 2007 A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction P. A. Bromiley and N.A. Thacker Last updated 13 / 4 / 2007 Imaging Science and
Tina Memo No. 2007-003 Published in Proc. MIUA 2007 A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction P. A. Bromiley and N.A. Thacker Last updated 13 / 4 / 2007 Imaging Science and
Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing
 Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization
Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization
The Effects of Inter-slice Gap Thickness on Parametric Methods for Diffusion Tensor Imaging Abstract
 The Effects of Inter-slice Gap Thickness on Parametric Methods for Diffusion Tensor Imaging Beth Hutchinson; Neuroscience Training program, Statistics 592 Abstract Although high-resolution, whole-brain
The Effects of Inter-slice Gap Thickness on Parametric Methods for Diffusion Tensor Imaging Beth Hutchinson; Neuroscience Training program, Statistics 592 Abstract Although high-resolution, whole-brain
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 7.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2011 March ; 7962: 796225-1 796225-7. doi:10.1117/12.878405. Automatic Skull-stripping of Rat MRI/DTI
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2011 March ; 7962: 796225-1 796225-7. doi:10.1117/12.878405. Automatic Skull-stripping of Rat MRI/DTI
Joint Reconstruction of Multi-contrast MR Images for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation
 Joint Reconstruction of Multi-contrast MR Images for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation Pedro A Gómez 1,2,3, Jonathan I Sperl 3, Tim Sprenger 2,3, Claudia Metzler-Baddeley 4, Derek K Jones 4, Philipp
Joint Reconstruction of Multi-contrast MR Images for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation Pedro A Gómez 1,2,3, Jonathan I Sperl 3, Tim Sprenger 2,3, Claudia Metzler-Baddeley 4, Derek K Jones 4, Philipp
Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit
 Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit John Melonakos 1, Ramsey Al-Hakim 1, James Fallon 2 and Allen Tannenbaum 1 1 Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta GA 30332,
Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit John Melonakos 1, Ramsey Al-Hakim 1, James Fallon 2 and Allen Tannenbaum 1 1 Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta GA 30332,
Subcortical Structure Segmentation using Probabilistic Atlas Priors
 Subcortical Structure Segmentation using Probabilistic Atlas Priors Sylvain Gouttard 1, Martin Styner 1,2, Sarang Joshi 3, Brad Davis 2, Rachel G. Smith 1, Heather Cody Hazlett 1, Guido Gerig 1,2 1 Department
Subcortical Structure Segmentation using Probabilistic Atlas Priors Sylvain Gouttard 1, Martin Styner 1,2, Sarang Joshi 3, Brad Davis 2, Rachel G. Smith 1, Heather Cody Hazlett 1, Guido Gerig 1,2 1 Department
Generation of Hulls Encompassing Neuronal Pathways Based on Tetrahedralization and 3D Alpha Shapes
 Generation of Hulls Encompassing Neuronal Pathways Based on Tetrahedralization and 3D Alpha Shapes Dorit Merhof 1,2, Martin Meister 1, Ezgi Bingöl 1, Peter Hastreiter 1,2, Christopher Nimsky 2,3, Günther
Generation of Hulls Encompassing Neuronal Pathways Based on Tetrahedralization and 3D Alpha Shapes Dorit Merhof 1,2, Martin Meister 1, Ezgi Bingöl 1, Peter Hastreiter 1,2, Christopher Nimsky 2,3, Günther
Direct Registration of White Matter Tractographies with Application to Atlas Construction
 Direct Registration of White Matter Tractographies with Application to Atlas Construction Arnaldo Mayer, Hayit Greenspan Medical image processing lab, Tel-Aviv University, Ramat-Aviv, Israel arnakdom@post.tau.ac.il,
Direct Registration of White Matter Tractographies with Application to Atlas Construction Arnaldo Mayer, Hayit Greenspan Medical image processing lab, Tel-Aviv University, Ramat-Aviv, Israel arnakdom@post.tau.ac.il,
Blood Particle Trajectories in Phase-Contrast-MRI as Minimal Paths Computed with Anisotropic Fast Marching
 Blood Particle Trajectories in Phase-Contrast-MRI as Minimal Paths Computed with Anisotropic Fast Marching Michael Schwenke 1, Anja Hennemuth 1, Bernd Fischer 2, Ola Friman 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute
Blood Particle Trajectories in Phase-Contrast-MRI as Minimal Paths Computed with Anisotropic Fast Marching Michael Schwenke 1, Anja Hennemuth 1, Bernd Fischer 2, Ola Friman 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute
An Introduction To Automatic Tissue Classification Of Brain MRI. Colm Elliott Mar 2014
 An Introduction To Automatic Tissue Classification Of Brain MRI Colm Elliott Mar 2014 Tissue Classification Tissue classification is part of many processing pipelines. We often want to classify each voxel
An Introduction To Automatic Tissue Classification Of Brain MRI Colm Elliott Mar 2014 Tissue Classification Tissue classification is part of many processing pipelines. We often want to classify each voxel
A Novel Contrast for DTI Visualization for Thalamus Delineation
 A Novel Contrast for DTI Visualization for Thalamus Delineation Xian Fan a, Meredith Thompson a,b, John A. Bogovic a, Pierre-Louis Bazin c, Jerry L. Prince a,c a Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD,
A Novel Contrast for DTI Visualization for Thalamus Delineation Xian Fan a, Meredith Thompson a,b, John A. Bogovic a, Pierre-Louis Bazin c, Jerry L. Prince a,c a Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD,
MITK-DI. A new Diffusion Imaging Component for MITK. Klaus Fritzsche, Hans-Peter Meinzer
 MITK-DI A new Diffusion Imaging Component for MITK Klaus Fritzsche, Hans-Peter Meinzer Division of Medical and Biological Informatics, DKFZ Heidelberg k.fritzsche@dkfz-heidelberg.de Abstract. Diffusion-MRI
MITK-DI A new Diffusion Imaging Component for MITK Klaus Fritzsche, Hans-Peter Meinzer Division of Medical and Biological Informatics, DKFZ Heidelberg k.fritzsche@dkfz-heidelberg.de Abstract. Diffusion-MRI
Diffusion-MRI processing for group analysis
 Diffusion-MRI processing for group analysis Felix Renard IRMaGe: Inserm US 17 / CNRS UMS 3552 University Hospital of Grenoble - France 25/09/2015 felixrenard@gmail.com 1 Diffusion-MRI processing for group
Diffusion-MRI processing for group analysis Felix Renard IRMaGe: Inserm US 17 / CNRS UMS 3552 University Hospital of Grenoble - France 25/09/2015 felixrenard@gmail.com 1 Diffusion-MRI processing for group
ISMI: A classification index for High Angular Resolution Diffusion Imaging
 ISMI: A classification index for High Angular Resolution Diffusion Imaging D. Röttger, D. Dudai D. Merhof and S. Müller Institute for Computational Visualistics, University of Koblenz-Landau, Germany Visual
ISMI: A classification index for High Angular Resolution Diffusion Imaging D. Röttger, D. Dudai D. Merhof and S. Müller Institute for Computational Visualistics, University of Koblenz-Landau, Germany Visual
Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images
 16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
EPI Data Are Acquired Serially. EPI Data Are Acquired Serially 10/23/2011. Functional Connectivity Preprocessing. fmri Preprocessing
 Functional Connectivity Preprocessing Geometric distortion Head motion Geometric distortion Head motion EPI Data Are Acquired Serially EPI Data Are Acquired Serially descending 1 EPI Data Are Acquired
Functional Connectivity Preprocessing Geometric distortion Head motion Geometric distortion Head motion EPI Data Are Acquired Serially EPI Data Are Acquired Serially descending 1 EPI Data Are Acquired
Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques
 Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques Sea Chen Department of Biomedical Engineering Advisors: Dr. Charles A. Bouman and Dr. Mark J. Lowe S. Chen Final Exam October
Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques Sea Chen Department of Biomedical Engineering Advisors: Dr. Charles A. Bouman and Dr. Mark J. Lowe S. Chen Final Exam October
Diffusion model fitting and tractography: A primer
 Diffusion model fitting and tractography: A primer Anastasia Yendiki HMS/MGH/MIT Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging 03/18/10 Why n how Diffusion model fitting and tractography 0/18 Why
Diffusion model fitting and tractography: A primer Anastasia Yendiki HMS/MGH/MIT Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging 03/18/10 Why n how Diffusion model fitting and tractography 0/18 Why
MITK Global Tractography
 MITK Global Tractography Peter F. Neher a, Bram Stieltjes b, Marco Reisert c, Ignaz Reicht a, Hans-Peter Meinzer a, Klaus H. Fritzsche a,b a German Cancer Research Center, Medical and Biological Informatics,
MITK Global Tractography Peter F. Neher a, Bram Stieltjes b, Marco Reisert c, Ignaz Reicht a, Hans-Peter Meinzer a, Klaus H. Fritzsche a,b a German Cancer Research Center, Medical and Biological Informatics,
A Method for Registering Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Images
 A Method for Registering Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Images Xiaodong Tao and James V. Miller GE Research, Niskayuna, New York, USA Abstract. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance (DWMR or DW)
A Method for Registering Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Images Xiaodong Tao and James V. Miller GE Research, Niskayuna, New York, USA Abstract. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance (DWMR or DW)
Lecture 13 Theory of Registration. ch. 10 of Insight into Images edited by Terry Yoo, et al. Spring (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt)
 Lecture 13 Theory of Registration ch. 10 of Insight into Images edited by Terry Yoo, et al. Spring 2018 16-725 (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt) Dr. John Galeotti The content of these slides by John Galeotti,
Lecture 13 Theory of Registration ch. 10 of Insight into Images edited by Terry Yoo, et al. Spring 2018 16-725 (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt) Dr. John Galeotti The content of these slides by John Galeotti,
Building an Average Population HARDI Atlas
 Building an Average Population HARDI Atlas Sylvain Bouix 1, Yogesh Rathi 1, and Mert Sabuncu 2 1 Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
Building an Average Population HARDI Atlas Sylvain Bouix 1, Yogesh Rathi 1, and Mert Sabuncu 2 1 Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
FROM IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION TO CONNECTIVITY ANALYSIS: A JOURNEY THROUGH THE BRAIN'S WIRING. Francesca Pizzorni Ferrarese
 FROM IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION TO CONNECTIVITY ANALYSIS: A JOURNEY THROUGH THE BRAIN'S WIRING Francesca Pizzorni Ferrarese Pipeline overview WM and GM Segmentation Registration Data reconstruction Tractography
FROM IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION TO CONNECTIVITY ANALYSIS: A JOURNEY THROUGH THE BRAIN'S WIRING Francesca Pizzorni Ferrarese Pipeline overview WM and GM Segmentation Registration Data reconstruction Tractography
Introduction of a Quantitative Evaluation Method for White Matter Tractography using a HARDI-based Reference
 Introduction of a Quantitative Evaluation Method for White Matter Tractography using a HARDI-based Reference Peter F. Neher 1, Bram Stieltjes 2, Hans-Peter Meinzer 1, and Klaus H. Fritzsche 1,2, 1 German
Introduction of a Quantitative Evaluation Method for White Matter Tractography using a HARDI-based Reference Peter F. Neher 1, Bram Stieltjes 2, Hans-Peter Meinzer 1, and Klaus H. Fritzsche 1,2, 1 German
Generation of Triangle Meshes from Time-of-Flight Data for Surface Registration
 Generation of Triangle Meshes from Time-of-Flight Data for Surface Registration Thomas Kilgus, Thiago R. dos Santos, Alexander Seitel, Kwong Yung, Alfred M. Franz, Anja Groch, Ivo Wolf, Hans-Peter Meinzer,
Generation of Triangle Meshes from Time-of-Flight Data for Surface Registration Thomas Kilgus, Thiago R. dos Santos, Alexander Seitel, Kwong Yung, Alfred M. Franz, Anja Groch, Ivo Wolf, Hans-Peter Meinzer,
ECSE 626 Project Report Multimodality Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information
 ECSE 626 Project Report Multimodality Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information Emmanuel Piuze McGill University Montreal, Qc, Canada. epiuze@cim.mcgill.ca Abstract In 1997, Maes et al.
ECSE 626 Project Report Multimodality Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information Emmanuel Piuze McGill University Montreal, Qc, Canada. epiuze@cim.mcgill.ca Abstract In 1997, Maes et al.
Basic fmri Design and Analysis. Preprocessing
 Basic fmri Design and Analysis Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial filtering
Basic fmri Design and Analysis Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial filtering
A Generic Lie Group Model for Computer Vision
 A Generic Lie Group Model for Computer Vision Within this research track we follow a generic Lie group approach to computer vision based on recent physiological research on how the primary visual cortex
A Generic Lie Group Model for Computer Vision Within this research track we follow a generic Lie group approach to computer vision based on recent physiological research on how the primary visual cortex
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators. Preprocessing
 SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
Susceptibility Distortion Correction for Echo Planar Images with Non-uniform B-Spline Grid Sampling: A Diffusion Tensor Image Study
 Susceptibility Distortion Correction for Echo Planar Images with Non-uniform B-Spline Grid Sampling: A Diffusion Tensor Image Study M.O. Irfanoglu 1,L.Walker 3,S.Sammet 2, C. Pierpaoli 3,andR.Machiraju
Susceptibility Distortion Correction for Echo Planar Images with Non-uniform B-Spline Grid Sampling: A Diffusion Tensor Image Study M.O. Irfanoglu 1,L.Walker 3,S.Sammet 2, C. Pierpaoli 3,andR.Machiraju
Analysis of White Matter Fiber Tracts via Fiber Clustering and Parametrization
 Analysis of White Matter Fiber Tracts via Fiber Clustering and Parametrization Sylvain Gouttard 2,4, Isabelle Corouge 1,2, Weili Lin 3, John Gilmore 2, and Guido Gerig 1,2 1 Departments of Computer Science,
Analysis of White Matter Fiber Tracts via Fiber Clustering and Parametrization Sylvain Gouttard 2,4, Isabelle Corouge 1,2, Weili Lin 3, John Gilmore 2, and Guido Gerig 1,2 1 Departments of Computer Science,
Functional MRI data preprocessing. Cyril Pernet, PhD
 Functional MRI data preprocessing Cyril Pernet, PhD Data have been acquired, what s s next? time No matter the design, multiple volumes (made from multiple slices) have been acquired in time. Before getting
Functional MRI data preprocessing Cyril Pernet, PhD Data have been acquired, what s s next? time No matter the design, multiple volumes (made from multiple slices) have been acquired in time. Before getting
Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit
 Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit John Melonakos 1, Ramsey Al-Hakim 1, James Fallon 2 and Allen Tannenbaum 1 1 Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta GA 30332,
Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit John Melonakos 1, Ramsey Al-Hakim 1, James Fallon 2 and Allen Tannenbaum 1 1 Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta GA 30332,
Non local diffusion weighted image super resolution using collaborative joint information
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 15: 217-225, 2018 Non local diffusion weighted image super resolution using collaborative joint information ZHIPENG YANG 1,2, PEIYU HE 1, JILIU ZHOU 3 and XI WU 3
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 15: 217-225, 2018 Non local diffusion weighted image super resolution using collaborative joint information ZHIPENG YANG 1,2, PEIYU HE 1, JILIU ZHOU 3 and XI WU 3
ECE1778 Final Report MRI Visualizer
 ECE1778 Final Report MRI Visualizer David Qixiang Chen Alex Rodionov Word Count: 2408 Introduction We aim to develop a mobile phone/tablet based neurosurgical MRI visualization application with the goal
ECE1778 Final Report MRI Visualizer David Qixiang Chen Alex Rodionov Word Count: 2408 Introduction We aim to develop a mobile phone/tablet based neurosurgical MRI visualization application with the goal
Feasibility and Advantages of Diffusion Weighted Imaging Atlas Construction in Q-Space
 Feasibility and Advantages of Diffusion Weighted Imaging Atlas Construction in Q-Space Thijs Dhollander 1,2, Jelle Veraart 3,WimVanHecke 1,4,5, Frederik Maes 1,2, Stefan Sunaert 1,4,JanSijbers 3, and Paul
Feasibility and Advantages of Diffusion Weighted Imaging Atlas Construction in Q-Space Thijs Dhollander 1,2, Jelle Veraart 3,WimVanHecke 1,4,5, Frederik Maes 1,2, Stefan Sunaert 1,4,JanSijbers 3, and Paul
Free-Form Fibers: A Whole Brain Fiber-to-DTI Registration Method
 Free-Form Fibers: A Whole Brain Fiber-to-DTI Registration Method Chao Li 1,2, Xiaotian He 2,3, Vincent Mok 4, Winnie Chu 5, Jing Yuan 5, Ying Sun 1, and Xiaogang Wang 2,3 1 Department of Electrical and
Free-Form Fibers: A Whole Brain Fiber-to-DTI Registration Method Chao Li 1,2, Xiaotian He 2,3, Vincent Mok 4, Winnie Chu 5, Jing Yuan 5, Ying Sun 1, and Xiaogang Wang 2,3 1 Department of Electrical and
ANALYSIS OF PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN MRI, USING AN ELASTIC REGISTRATION TECHNIQUE IN A MODEL OF FIBROSIS: Scleroderma
 ANALYSIS OF PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN MRI, USING AN ELASTIC REGISTRATION TECHNIQUE IN A MODEL OF FIBROSIS: Scleroderma ORAL DEFENSE 8 th of September 2017 Charlotte MARTIN Supervisor: Pr. MP REVEL M2 Bio Medical
ANALYSIS OF PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN MRI, USING AN ELASTIC REGISTRATION TECHNIQUE IN A MODEL OF FIBROSIS: Scleroderma ORAL DEFENSE 8 th of September 2017 Charlotte MARTIN Supervisor: Pr. MP REVEL M2 Bio Medical
The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy
 The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy Sokratis K. Makrogiannis, PhD From post-doctoral research at SBIA lab, Department of Radiology,
The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy Sokratis K. Makrogiannis, PhD From post-doctoral research at SBIA lab, Department of Radiology,
Shape-based Diffeomorphic Registration on Hippocampal Surfaces Using Beltrami Holomorphic Flow
 Shape-based Diffeomorphic Registration on Hippocampal Surfaces Using Beltrami Holomorphic Flow Abstract. Finding meaningful 1-1 correspondences between hippocampal (HP) surfaces is an important but difficult
Shape-based Diffeomorphic Registration on Hippocampal Surfaces Using Beltrami Holomorphic Flow Abstract. Finding meaningful 1-1 correspondences between hippocampal (HP) surfaces is an important but difficult
Automatic Generation of Training Data for Brain Tissue Classification from MRI
 MICCAI-2002 1 Automatic Generation of Training Data for Brain Tissue Classification from MRI Chris A. Cocosco, Alex P. Zijdenbos, and Alan C. Evans McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological
MICCAI-2002 1 Automatic Generation of Training Data for Brain Tissue Classification from MRI Chris A. Cocosco, Alex P. Zijdenbos, and Alan C. Evans McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological
Lilla Zöllei A.A. Martinos Center, MGH; Boston, MA
 Lilla Zöllei lzollei@nmr.mgh.harvard.edu A.A. Martinos Center, MGH; Boston, MA Bruce Fischl Gheorghe Postelnicu Jean Augustinack Anastasia Yendiki Allison Stevens Kristen Huber Sita Kakonoori + the FreeSurfer
Lilla Zöllei lzollei@nmr.mgh.harvard.edu A.A. Martinos Center, MGH; Boston, MA Bruce Fischl Gheorghe Postelnicu Jean Augustinack Anastasia Yendiki Allison Stevens Kristen Huber Sita Kakonoori + the FreeSurfer
Diffusion Imaging Models 1: from DTI to HARDI models
 Diffusion Imaging Models 1: from DTI to HARDI models Flavio Dell Acqua, PhD. www.natbrainlab.com flavio.dellacqua@kcl.ac.uk @flaviodellacqua Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) z λ 1 λ 2 The profile of the
Diffusion Imaging Models 1: from DTI to HARDI models Flavio Dell Acqua, PhD. www.natbrainlab.com flavio.dellacqua@kcl.ac.uk @flaviodellacqua Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) z λ 1 λ 2 The profile of the
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 October 07.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2014 March 21; 9034: 903442. doi:10.1117/12.2042915. MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation and Necrosis Detection
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2014 March 21; 9034: 903442. doi:10.1117/12.2042915. MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation and Necrosis Detection
UNC 4D Infant Cortical Surface Atlases, from Neonate to 6 Years of Age
 UNC 4D Infant Cortical Surface Atlases, from Neonate to 6 Years of Age Version 1.0 UNC 4D infant cortical surface atlases from neonate to 6 years of age contain 11 time points, including 1, 3, 6, 9, 12,
UNC 4D Infant Cortical Surface Atlases, from Neonate to 6 Years of Age Version 1.0 UNC 4D infant cortical surface atlases from neonate to 6 years of age contain 11 time points, including 1, 3, 6, 9, 12,
Mapping Tractography Across Subjects
 Mapping Tractography Across Subjects Thien Bao Nguyen, Emanuele Olivetti, and Paolo Avesani arxiv:1601.08165v1 [stat.ml] 29 Jan 2016 NeuroInformatics Laboratory (NILab), Bruno Kessler Foundation, Trento,
Mapping Tractography Across Subjects Thien Bao Nguyen, Emanuele Olivetti, and Paolo Avesani arxiv:1601.08165v1 [stat.ml] 29 Jan 2016 NeuroInformatics Laboratory (NILab), Bruno Kessler Foundation, Trento,
RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges
 27 giugno 2018 Dipartimento di Fisica Università degli Studi di Milano RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges Dr. Francesca Botta Medical Physicist Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milano)
27 giugno 2018 Dipartimento di Fisica Università degli Studi di Milano RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges Dr. Francesca Botta Medical Physicist Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milano)
Diffusion MRI Acquisition. Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford
 Diffusion MRI Acquisition Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford karla@fmrib.ox.ac.uk Diffusion Imaging How is diffusion weighting achieved? How is the image acquired? What are the limitations,
Diffusion MRI Acquisition Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford karla@fmrib.ox.ac.uk Diffusion Imaging How is diffusion weighting achieved? How is the image acquired? What are the limitations,
Estimation of Extracellular Volume from Regularized Multi-shell Diffusion MRI
 Estimation of Extracellular Volume from Regularized Multi-shell Diffusion MRI The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Estimation of Extracellular Volume from Regularized Multi-shell Diffusion MRI The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Annales UMCS Informatica AI 1 (2003) UMCS. Registration of CT and MRI brain images. Karol Kuczyński, Paweł Mikołajczak
 Annales Informatica AI 1 (2003) 149-156 Registration of CT and MRI brain images Karol Kuczyński, Paweł Mikołajczak Annales Informatica Lublin-Polonia Sectio AI http://www.annales.umcs.lublin.pl/ Laboratory
Annales Informatica AI 1 (2003) 149-156 Registration of CT and MRI brain images Karol Kuczyński, Paweł Mikołajczak Annales Informatica Lublin-Polonia Sectio AI http://www.annales.umcs.lublin.pl/ Laboratory
Optimized diffusion gradient orientation schemes for corrupted clinical DTI data sets
 Magn Reson Mater Phy (2006) DOI 10.1007/s10334-006-0036-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE J. Dubois C. Poupon F. Lethimonnier D. Le Bihan Optimized diffusion gradient orientation schemes for corrupted clinical DTI data
Magn Reson Mater Phy (2006) DOI 10.1007/s10334-006-0036-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE J. Dubois C. Poupon F. Lethimonnier D. Le Bihan Optimized diffusion gradient orientation schemes for corrupted clinical DTI data
Appendix E1. Supplementary Methods. MR Image Acquisition. MR Image Analysis
 RSNA, 2015 10.1148/radiol.2015150532 Appendix E1 Supplementary Methods MR Image Acquisition By using a 1.5-T system (Avanto, Siemens Medical, Erlangen, Germany) under a program of regular maintenance (no
RSNA, 2015 10.1148/radiol.2015150532 Appendix E1 Supplementary Methods MR Image Acquisition By using a 1.5-T system (Avanto, Siemens Medical, Erlangen, Germany) under a program of regular maintenance (no
MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION
 MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Prepared by : Monil Shah What is Segmentation? Partitioning a region or regions of interest in images such that each region corresponds to one or more anatomic structures Classification
MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Prepared by : Monil Shah What is Segmentation? Partitioning a region or regions of interest in images such that each region corresponds to one or more anatomic structures Classification
Computational Neuroanatomy
 Computational Neuroanatomy John Ashburner john@fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk Smoothing Motion Correction Between Modality Co-registration Spatial Normalisation Segmentation Morphometry Overview fmri time-series kernel
Computational Neuroanatomy John Ashburner john@fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk Smoothing Motion Correction Between Modality Co-registration Spatial Normalisation Segmentation Morphometry Overview fmri time-series kernel
NeuroQLab A Software Assistant for Neurosurgical Planning and Quantitative Image Analysis
 NeuroQLab A Software Assistant for Neurosurgical Planning and Quantitative Image Analysis Florian Weiler 1, Jan Rexilius 2, Jan Klein 1, Horst K. Hahn 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Universitätsallee 29, 28359
NeuroQLab A Software Assistant for Neurosurgical Planning and Quantitative Image Analysis Florian Weiler 1, Jan Rexilius 2, Jan Klein 1, Horst K. Hahn 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Universitätsallee 29, 28359
UNC-Utah NA-MIC Framework for DTI Fiber Tract Analysis
 UNC-Utah NA-MIC Framework for DTI Fiber Tract Analysis Audrey Rose Verde, Francois Budin, Jean-Baptiste Berger, Aditya Gupta, Mahshid Farzinfar, Adrien Kaiser, Mihye Ahn, Hans J Johnson, Joy Matsui, Heather
UNC-Utah NA-MIC Framework for DTI Fiber Tract Analysis Audrey Rose Verde, Francois Budin, Jean-Baptiste Berger, Aditya Gupta, Mahshid Farzinfar, Adrien Kaiser, Mihye Ahn, Hans J Johnson, Joy Matsui, Heather
Robust Realignment of fmri Time Series Data
 Robust Realignment of fmri Time Series Data Ben Dodson bjdodson@stanford.edu Olafur Gudmundsson olafurg@stanford.edu December 12, 2008 Abstract FMRI data has become an increasingly popular source for exploring
Robust Realignment of fmri Time Series Data Ben Dodson bjdodson@stanford.edu Olafur Gudmundsson olafurg@stanford.edu December 12, 2008 Abstract FMRI data has become an increasingly popular source for exploring
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 December 11.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2004 ; 2: 1521 1524. doi:10.1109/iembs.2004.1403466. An Elliptic PDE Approach for Shape Characterization
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2004 ; 2: 1521 1524. doi:10.1109/iembs.2004.1403466. An Elliptic PDE Approach for Shape Characterization
BDP: BrainSuite Diffusion Pipeline. Chitresh Bhushan
 BDP: BrainSuite Diffusion Pipeline Chitresh Bhushan Why diffusion MRI? T 2 weighted MPRAGE FA map Fiber track Quantify microstructural tissue characteristics Structural connectivity Connectome Clinical
BDP: BrainSuite Diffusion Pipeline Chitresh Bhushan Why diffusion MRI? T 2 weighted MPRAGE FA map Fiber track Quantify microstructural tissue characteristics Structural connectivity Connectome Clinical
