KEEP THIS COPY FOR REPRODUCTION PURPOSES
|
|
|
- Duane Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AD A Ind IMASTER COPY KEEP THIS COPY FOR REPRODUCTION PURPOSES I i Form Approved REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Fom Apov04-o188,nis estimated to average 1 hour er"rej:oe.,nciudng the time for reviewing instrouctlon. earching elmting lata sources. et Ing and reviewing the collection Of information Send comments regarding this burden estimate or any other aspect of this lu(ing this ourd * to Washington meadquater Services. Direcorate for information Operations and Repots Q IS jeffso to the Office of Management and Budget. Paperwork Reduction Project ( ), Washington. DC IN , REPOTDT March 15, 1991 I 3!PR TYEAND DATES COVERED Final Report, 3/87-12/90 S. FUNDING NUMBERS Configuration Synthesis and Efficient Motion Programming of Robot Manipulators P og 6. AUTHOR(S) K.C. Gupta DAAL K PERFORMING ORGANIZATION NAME(S) AND ADDRESS(ES) "o. B. PERFORMING IEPORT IrMBE ORGANIZATION R Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Illinois at Chicago ".- Chicago, IL SPOIJ WORING/MONITORING AGENCY NAME(S) AND ADDRESS(ES) 10. SPONSORING/MONITORING AGENCY REPORT NUMBER U. S. Army Research Office P. G. dox Research Triangle Park, NC AU al " SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES The view, opinions and/or findings contained in this report are those of the author(s) and should not be construed as an official Department of thf! Army position, policy, or decision, unless so designated by other documentation. 12a. DISTRIBUTION / AVAILABILITY STATEMENT 12b. DISTRIBUTION CODE Approved for public release; distribution unlimited. 13. ABSTRACT (Maximum 200 words) One objective (f this research was to study the factors which influence the design of robot arms and wrists (configuration synthesis). Another objective was to develop efficient computational software tools for the manipulation of industrial robots. These software tools were to address the critical problems which arise in smooth trajectory planning, inverse kinematics of general robots, dynamic control of realistic robots, and parameter identification and compensation. 14. SUBJECT TERMS 15, NUMBER OF PAGES?v'Yv.c, Robot Kinematics, Robot Dynamics, Robot Parameters, Numerical Methods, Jacobians :S. PRICE CODE SECURITY CLASSIFICATION 18. SECURITY CLASSIFICATION 19. SECURITY CLASSIFICATION 20. LIMITATION OF ABSTRACT OF REPORT OF THIS PAGE OF ABSTRACT UNCLASSTrTFD UNCLASSIFIED UNCLASSIFIED I. NSN Standard Form 298 (Rev 2-89) Presc ribed by ANSI St S lbs. 102
2 Configuration Synthesis and Efficient Motion Programming of Robot Manipulators Final Report / by K. C. Gupta " Professor of Mechanical Engineering University of Illinois at Chicago i\ \ Chicago, IL 60680J ' "rx March 15, 1991 U. S. Army Research Office EG/DA AL03-87-K-0041 Approved for public release/distribution unlimited
3 Objectives One objective of this research was to study the factors which influence the design of robot arms and wrists (configuration synthesis). Another objective was to develop efficient computational software tools for the manipulation of industrial robots. These softxare tools were to address the critical problems which arise in smooth trajectory planning, inverse kinematics of general robots, dynamic control of realistic robots, and parameter identification and compensation. Summary of Results An extensive patent search was conducted for the geared robot wrist designs. Such wrists use remote motors for joint actuation and are compact when compared with simple serial designs with joint mounted motors. Many variations of geared wrists with orthogonal and oblique joint axes were found. The tabulation method outlined in [Gupta 85-ASME JMTAD 107: ] was explored more fully and applied to such wrist designs in [Ma 88-MS Thesis][Ma and Gupta 89-JRS 6(5): ]. Wrists with oblique, co-intersecting joint axes have a continuous 3-roll property. Another wrist configuration with continuous 3-roll property was analyzed in [Gupta 88-1EEE JR&A 4(4): ]. The first order differential analysis of the manipulator is a basic step in robot dynamics and control. The velocity Jacobian of the manipulator plays a critical role in this analysis. This Jacobian can be defined with respect to various end-effector points and link coordinate systems. A simple method to derive the velocity Jacobian by utilizing a new velocity-nimilarit prin~ciple for the 4x4 velocity matrices was presented in [Ma 88-MS Thesis][Gupta and Ma 90-Robotica 8:81-84]. When a set of discrete stations are specified along a robot task path, it becomes necessary to find a related smooth trajectory either at joint level or at endeffector level. The usual approach for this problem of trajectory planning is to fit piecewise-smooth polynomial functions. A different approach which was deveioped in [Mirman 87-MS Thesis][Mirman and Gupta 87-JRS 4(5): is as follows. Suppose that a trajectory is available which is not sufficiently smooth--in the simplest case, it could be piecewise-linear. A convolution smoothing process was developed which yielded a succession of related smooth trajectories in an a,'.omatic way. These automatically generated trajectories were analyzed for their higher order derivatives as well as for their frequency spectrum. These analyses suggested that continuity beyond the second or third derivatives is not always desirable. Efforts to develop robust and efficient iterative algorithms for inverse kinematics of general robots. which were initiated under a previous USARO contract, were continued. For the position analysis of manipulators, it is common to write their governing matrix equatior, say by lising the 4x4 Denavit-HarigrZ m-ices or the 4x4 displacement matrices, which result in an overdetermined system of nonlinear equations. An algorithm which is robust near singularities can be developed by handling this overdetermined 2
4 system of equations directly, but such an algorithm is too slow. On the other hand, an efficient algorithm can be developed by selecting a particular subset of independent equations, but then the algorithm is not robust because its behavior near robot singularities is very sensitive to the choice of the particular subset. To avoid these difficulties,we have relied upon the formulations which explicitly involve the manipulator Jacobian. It is wellknown that the manipulator Jacobian produces a minimal and complete set of first order relations, whether we are interested in velocities or small changes in position. Then, we have developed two types of robust and efficient algorithms. One of these uses the predictor-corrector method to solve the first order differential equations which are just the velocity Jacobian relations for the manipulator [Singh 87-MS Thesis][Gupta and Singh 89-Robotica 7: and [Cheng 89-PhD Thesis][Cheng and Gupta 91-JRS 8(2):xxx]. Another way is to formulate the Newton-Raphson type of step change by directly utilizing the manipulator Jacobian [Singh and Gupta 89-Proc. ASME DTCIDA 3: ]. Furthermore, both types of algorithms were made robust by incorporating a strict-descent feature. This feature was implemented by monitoring the error of deviation at the end-effector level and insuring that only those steps are taken which move the end-effector closer to its target position. If a step tends to increase this deviation error, it is halved successively until a decrease in the deviation error becomes possible. If even an extremely small step fails to move the end-effector any closer to its target position, then the manipulator is considered to be too close to its singularity position. The algorithm developed by [Singh 87-MS Thesis] paid special attention to robustness and efficiency under a serial-cpu (central processing unit of the computer) environment, while that by [Cheng 89-PhD Thesis] also considered these factors under a vector-cpu environment. Furthermore, Cheng demonstrated the feasibility of a completely portable, personal-computer based iterative inverse kinematics algorithm, with real-time computational capabilities. Robot parameter estimation is an important problem for industrial robots. Due to manufacturing tolerances, or usage related degradation, the nominal values of geometry parameters may differ significantly from their actual values. The geometry parameter correction amounts were determined from numerically simulated positioning data by using a novel statistically oriented, iterative parameter identification algorithm. The formulation was based upon the development of special Jacobian matrices: J0, Js, Ja, Ja, which led to a compact and efficient scheme. An iterative compensation algorithm was developed which utilized these parameter corrections to modify the nominal parameter based closed-form solution. The influence of a fixed number of iterations upon the accuracy of compensation was also investigated [Mirman 90-PhD Thesis]. Th, effect of dynamic model errors on the performance of robot control system was considered in rsamak 89-PhD Thesis][Samak and Gupta 90-Proc. ASME DTC/M 24: This study was conducted for some realistic types of sixaxis manipulators, rather than for very simple two or three iik pianar manipulators. The objective was to quantitatively assess the degradation in control system performance when the geometry and mass-inertia parameters of the dynamic model w"re not known accurately. Thte cnnclut;on wag that a high degree of trajectory precision could be achieved by the controller when the geometry errors were less than 0.1% and mass-inertia errors were less than 5%. However, the trajectory precision was poor with geometry errors of % and mass-inertia errors of 25-50%. Of course, the reports of more 3
5 optimistic expectations in the literature are not based upon manipulator configurations of realistic spatial complexity. In compiling the related technical literature, we found that there were many inconsistencies of historical nature with respect to the formulas of finite rotations and their composition. This motivated us to explore this matter further in [Cheng 89-PhD Thesis][Cheng and Gupta 89-ASME JAM 56: What we found was really surprising. The so-called Rodrigues formula for finite rotations was actually derived by Euler in onc of his papers; so it should correctly be called Euler's formula for finite rotations. On the other hand, the composition formula for two successive finite rotations, which is mostly unattributed, was formally derived in an analytical way by Rodrigues in his famous paper, which was in fact a combined review/original contribution paper without a comprehensive list of earlier works. This composition formula is also identical to the multiplication rule which is later found in Hamilton's quaternion aigebra. Of course, Rodrigues was specifically concerned with the practical problems of spatial rigid body rotations, while Hamilton was interested in developing a whole new system of quaternion algebra which has since been superseded by Gibbs' vectors, Cayley's matrices and Einstein' tensors. The quaternions, nevertheless, offer some practically useful advantages in applications such as spatial linkages, spacecraft dynamics, multi-body systems and molecular dynamics. Theses Completed C. J. Mirman, Robot Trajectory Planning Using the Convolution Operator, MS, University of Illinois at Chicago, V. K. Singh, A Velocity Integration Based Numerical Algorithm for Robot Inverse Kinematics Using Rodrigues-Gibbs Formulas, MS, University of Illinois at Chicago, R. Ma, Kinematics of Robots with Oblique Bevel Geared Wrists, MS, University of Illinois at Chicago, H. Cheng, Computational Aspects of Robot Manipulation, PhD, University of Illinois at Chicago, S. M. Samak, Dynamic Model Error Analysis of Robot Manipulators, PhD, University of Illinois at Chicago, 1989 C. J. Mirman, Iterative Parameter Identification and Compensation for Robots using The"ia! Jacobiun Matrices, PhD, University of Illinois at Chicago,
6 Papers C. R. Mirman and K. C. Gupta, "Robot Trajectory Planning Using the Convolution Operator," Proc. 10th Applied Mechanisms Conf., New Orleans, 1:3CI-3C7, 1987; J. Robotic Systems 4(5): , 1987 (revised). K. C. Gupta and V. K. Singh, "A Numerical Algorithm for Solving Robot Inverse Kinematics," 7th IFToMM World Congress, Spain, 2: , 1987; Robotica 7: , 1989 (revised). K. C. Gupta, "Kinematics of a Robot with Continuous Roll Wrist," IEEE J. Robotics and Automation 4(4): , V. K. Singh and K. C. Gupta, "A Manipulator Jacobian Based Modified Newton- Raphson Algorithm (JMNR) for Robot Inverse Kinematics," Proc. ASME Design Automation Conf., Montreal, 3: , R. Ma and K. C. Gupta, "On the Motion of Oblique Bevel Geared Robot Wrists," Proc. IEEE Robotics and Automation Conf., Arizona, , 1989; J. Robotic Systems 6(5): , 1989 (revised). H. Cheng and K. C. Gupta, "An Historical Note on Finite Rotations," ASME J. Applied Mechanics 56: , H. Cheng and K. C. Gupta, "Parametric Studies of a New MPC Algorithm for Robot Inverse Kinematics," Proc. Ist. Nal. Conf. Applied Mechanisms and Robotics, Cincinnati, I:4A I-4A6, K. C. Gupta and R. Ma, "Formulation of Manipulator Jacobian using the Velocity Similarity Principle," Robotica 8:81-84, H. Cheng and K. C. Gupta, "A Study of Numerical Robot Inverse Kinematics based upon the ODE Solution Method," Proc ASME Mechanisms Conf.- Mechanisms Synthesis and Analysis, DE25: , S. M. Samak and K. C. Gupta, "Effect of Dynamic Model Errors on Robot Precision," Proc ASME Mechanisms Conf.-Flexible Mechanism, Dynamics, and Robot Trajectories, DE24:73-77, H. Cheng and K. C. Gupta, "A Study of Robot Inverse Kinematics based upon the Solution of Differential Equations," J. Robotic Systems 8(2):xxx, 1991 (to appear). 5
Parallel Robots. Mechanics and Control H AMID D. TAG HI RAD. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group. Taylor & Francis Croup, Boca Raton London NewYoric
 Parallel Robots Mechanics and Control H AMID D TAG HI RAD CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYoric CRC Press Is an Imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informs business Contents
Parallel Robots Mechanics and Control H AMID D TAG HI RAD CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYoric CRC Press Is an Imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informs business Contents
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Table of Contents Introduction Historical Review of Robotic Orienting Devices Kinematic Position Analysis Instantaneous Kinematic Analysis
 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Background in Robotics 1 1.2 Robot Mechanics 1 1.2.1 Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics 2 1.3 Robot Architecture 4 1.4 Robotic Wrists 4 1.5 Origins of the Carpal
Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Background in Robotics 1 1.2 Robot Mechanics 1 1.2.1 Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics 2 1.3 Robot Architecture 4 1.4 Robotic Wrists 4 1.5 Origins of the Carpal
Inverse Kinematics. Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector
 Inverse Kinematics Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector q ( q, q, q ) 1 2 n Find the joint variables which can bring the robot the desired configuration z y x 1 The Inverse
Inverse Kinematics Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector q ( q, q, q ) 1 2 n Find the joint variables which can bring the robot the desired configuration z y x 1 The Inverse
An Efficient Method for Solving the Direct Kinematics of Parallel Manipulators Following a Trajectory
 An Efficient Method for Solving the Direct Kinematics of Parallel Manipulators Following a Trajectory Roshdy Foaad Abo-Shanab Kafr Elsheikh University/Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kafr Elsheikh,
An Efficient Method for Solving the Direct Kinematics of Parallel Manipulators Following a Trajectory Roshdy Foaad Abo-Shanab Kafr Elsheikh University/Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kafr Elsheikh,
Table of Contents. Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE
 Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots.... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Geometric modeling... 2 1.2.1. Geometric description... 2 1.2.2. Direct geometric
Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots.... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Geometric modeling... 2 1.2.1. Geometric description... 2 1.2.2. Direct geometric
COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS
 COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS THIRD EDITION AHMED A. SHABANA Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Engineering University of Illinois at Chicago A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS COMPUTATIONAL
COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS THIRD EDITION AHMED A. SHABANA Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Engineering University of Illinois at Chicago A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS COMPUTATIONAL
Cecilia Laschi The BioRobotics Institute Scuola Superiore Sant Anna, Pisa
 University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTRÉAL
 ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTRÉAL MODELIZATION OF A 3-PSP 3-DOF PARALLEL MANIPULATOR USED AS FLIGHT SIMULATOR MOVING SEAT. MASTER IN ENGINEERING PROJET III MEC693 SUBMITTED TO: Luc Baron Ph.D. Mechanical
ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTRÉAL MODELIZATION OF A 3-PSP 3-DOF PARALLEL MANIPULATOR USED AS FLIGHT SIMULATOR MOVING SEAT. MASTER IN ENGINEERING PROJET III MEC693 SUBMITTED TO: Luc Baron Ph.D. Mechanical
Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions.
 Path and Trajectory specification Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions. Specifying the desired motion to achieve a specified goal is often a
Path and Trajectory specification Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions. Specifying the desired motion to achieve a specified goal is often a
Dynamic Analysis of Manipulator Arm for 6-legged Robot
 American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, Vol. 1, No. 7, 365-369 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/1/7/42 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-1-7-42 Dynamic Analysis
American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, Vol. 1, No. 7, 365-369 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/1/7/42 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-1-7-42 Dynamic Analysis
Resolution of spherical parallel Manipulator (SPM) forward kinematic model (FKM) near the singularities
 Resolution of spherical parallel Manipulator (SPM) forward kinematic model (FKM) near the singularities H. Saafi a, M. A. Laribi a, S. Zeghloul a a. Dept. GMSC, Pprime Institute, CNRS - University of Poitiers
Resolution of spherical parallel Manipulator (SPM) forward kinematic model (FKM) near the singularities H. Saafi a, M. A. Laribi a, S. Zeghloul a a. Dept. GMSC, Pprime Institute, CNRS - University of Poitiers
Simulation-Based Design of Robotic Systems
 Simulation-Based Design of Robotic Systems Shadi Mohammad Munshi* & Erik Van Voorthuysen School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052 shadimunshi@hotmail.com,
Simulation-Based Design of Robotic Systems Shadi Mohammad Munshi* & Erik Van Voorthuysen School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052 shadimunshi@hotmail.com,
Some algebraic geometry problems arising in the field of mechanism theory. J-P. Merlet INRIA, BP Sophia Antipolis Cedex France
 Some algebraic geometry problems arising in the field of mechanism theory J-P. Merlet INRIA, BP 93 06902 Sophia Antipolis Cedex France Abstract Mechanism theory has always been a favorite field of study
Some algebraic geometry problems arising in the field of mechanism theory J-P. Merlet INRIA, BP 93 06902 Sophia Antipolis Cedex France Abstract Mechanism theory has always been a favorite field of study
DIMENSIONAL SYNTHESIS OF SPATIAL RR ROBOTS
 DIMENSIONAL SYNTHESIS OF SPATIAL RR ROBOTS ALBA PEREZ Robotics and Automation Laboratory University of California, Irvine Irvine, CA 9697 email: maperez@uci.edu AND J. MICHAEL MCCARTHY Department of Mechanical
DIMENSIONAL SYNTHESIS OF SPATIAL RR ROBOTS ALBA PEREZ Robotics and Automation Laboratory University of California, Irvine Irvine, CA 9697 email: maperez@uci.edu AND J. MICHAEL MCCARTHY Department of Mechanical
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction This dissertation will describe the mathematical modeling and development of an innovative, three degree-of-freedom robotic manipulator. The new device, which has been named the
Chapter 1: Introduction This dissertation will describe the mathematical modeling and development of an innovative, three degree-of-freedom robotic manipulator. The new device, which has been named the
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces 1/4
 Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Models of Robot Manipulation - EE 54 - Department of Electrical Engineering - University of Washington Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Models of Robot Manipulation - EE 54 - Department of Electrical Engineering - University of Washington Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot
Jacobians. 6.1 Linearized Kinematics. Y: = k2( e6)
 Jacobians 6.1 Linearized Kinematics In previous chapters we have seen how kinematics relates the joint angles to the position and orientation of the robot's endeffector. This means that, for a serial robot,
Jacobians 6.1 Linearized Kinematics In previous chapters we have seen how kinematics relates the joint angles to the position and orientation of the robot's endeffector. This means that, for a serial robot,
MTRX4700 Experimental Robotics
 MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
Robot Inverse Kinematics Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Mechanical Engieering
 PR 5 Robot Dynamics & Control /8/7 PR 5: Robot Dynamics & Control Robot Inverse Kinematics Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Mechanical Engieering The Inverse Kinematics The determination of all possible
PR 5 Robot Dynamics & Control /8/7 PR 5: Robot Dynamics & Control Robot Inverse Kinematics Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Mechanical Engieering The Inverse Kinematics The determination of all possible
NEW FINITE ELEMENT / MULTIBODY SYSTEM ALGORITHM FOR MODELING FLEXIBLE TRACKED VEHICLES
 NEW FINITE ELEMENT / MULTIBODY SYSTEM ALGORITHM FOR MODELING FLEXIBLE TRACKED VEHICLES Paramsothy Jayakumar, Mike Letherwood US Army RDECOM TARDEC Ulysses Contreras, Ashraf M. Hamed, Abdel-Nasser A. Mohamed,
NEW FINITE ELEMENT / MULTIBODY SYSTEM ALGORITHM FOR MODELING FLEXIBLE TRACKED VEHICLES Paramsothy Jayakumar, Mike Letherwood US Army RDECOM TARDEC Ulysses Contreras, Ashraf M. Hamed, Abdel-Nasser A. Mohamed,
Automatic Control Industrial robotics
 Automatic Control Industrial robotics Prof. Luca Bascetta (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Prof. Luca Bascetta Industrial robots
Automatic Control Industrial robotics Prof. Luca Bascetta (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Prof. Luca Bascetta Industrial robots
1. Introduction 1 2. Mathematical Representation of Robots
 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Brief History 1 1.3 Types of Robots 7 1.4 Technology of Robots 9 1.5 Basic Principles in Robotics 12 1.6 Notation 15 1.7 Symbolic Computation and Numerical Analysis
1. Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Brief History 1 1.3 Types of Robots 7 1.4 Technology of Robots 9 1.5 Basic Principles in Robotics 12 1.6 Notation 15 1.7 Symbolic Computation and Numerical Analysis
10/25/2018. Robotics and automation. Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi. Chapter two. Introduction To Robot Manipulators
 Robotics and automation Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter two Introduction To Robot Manipulators 1 Robotic Industrial Manipulators A robot manipulator is an electronically controlled mechanism, consisting of
Robotics and automation Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter two Introduction To Robot Manipulators 1 Robotic Industrial Manipulators A robot manipulator is an electronically controlled mechanism, consisting of
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces 1/4
 Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Advanced Robotic - MAE 6D - Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - UCLA Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot is often used to manipulate
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Advanced Robotic - MAE 6D - Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - UCLA Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot is often used to manipulate
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
AUTONOMOUS PLANETARY ROVER CONTROL USING INVERSE SIMULATION
 AUTONOMOUS PLANETARY ROVER CONTROL USING INVERSE SIMULATION Kevin Worrall (1), Douglas Thomson (1), Euan McGookin (1), Thaleia Flessa (1) (1)University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12 8QQ, UK, Email: kevin.worrall@glasgow.ac.uk
AUTONOMOUS PLANETARY ROVER CONTROL USING INVERSE SIMULATION Kevin Worrall (1), Douglas Thomson (1), Euan McGookin (1), Thaleia Flessa (1) (1)University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12 8QQ, UK, Email: kevin.worrall@glasgow.ac.uk
Recent developments in simulation, optimization and control of flexible multibody systems
 Recent developments in simulation, optimization and control of flexible multibody systems Olivier Brüls Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Liège o.bruls@ulg.ac.be Katholieke
Recent developments in simulation, optimization and control of flexible multibody systems Olivier Brüls Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Liège o.bruls@ulg.ac.be Katholieke
A DH-parameter based condition for 3R orthogonal manipulators to have 4 distinct inverse kinematic solutions
 Wenger P., Chablat D. et Baili M., A DH-parameter based condition for R orthogonal manipulators to have 4 distinct inverse kinematic solutions, Journal of Mechanical Design, Volume 17, pp. 150-155, Janvier
Wenger P., Chablat D. et Baili M., A DH-parameter based condition for R orthogonal manipulators to have 4 distinct inverse kinematic solutions, Journal of Mechanical Design, Volume 17, pp. 150-155, Janvier
1 Trajectories. Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733. Figure 1: Robot control system.
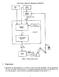 Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Written exams of Robotics 2
 Written exams of Robotics 2 http://www.diag.uniroma1.it/~deluca/rob2_en.html All materials are in English, unless indicated (oldies are in Year Date (mm.dd) Number of exercises Topics 2018 07.11 4 Inertia
Written exams of Robotics 2 http://www.diag.uniroma1.it/~deluca/rob2_en.html All materials are in English, unless indicated (oldies are in Year Date (mm.dd) Number of exercises Topics 2018 07.11 4 Inertia
Trajectory Optimization
 Trajectory Optimization Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We heard about RRT*, a sampling-based planning in high-dimensional cost
Trajectory Optimization Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We heard about RRT*, a sampling-based planning in high-dimensional cost
REDUCED END-EFFECTOR MOTION AND DISCONTINUITY IN SINGULARITY HANDLING TECHNIQUES WITH WORKSPACE DIVISION
 REDUCED END-EFFECTOR MOTION AND DISCONTINUITY IN SINGULARITY HANDLING TECHNIQUES WITH WORKSPACE DIVISION Denny Oetomo Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology Marcelo Ang Jr. Dept. of Mech. Engineering
REDUCED END-EFFECTOR MOTION AND DISCONTINUITY IN SINGULARITY HANDLING TECHNIQUES WITH WORKSPACE DIVISION Denny Oetomo Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology Marcelo Ang Jr. Dept. of Mech. Engineering
Robotics kinematics and Dynamics
 Robotics kinematics and Dynamics C. Sivakumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BSA Crescent Institute of Science and Technology 1 Robot kinematics KINEMATICS the analytical study
Robotics kinematics and Dynamics C. Sivakumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BSA Crescent Institute of Science and Technology 1 Robot kinematics KINEMATICS the analytical study
Inverse Kinematics Analysis for Manipulator Robot With Wrist Offset Based On the Closed-Form Algorithm
 Inverse Kinematics Analysis for Manipulator Robot With Wrist Offset Based On the Closed-Form Algorithm Mohammed Z. Al-Faiz,MIEEE Computer Engineering Dept. Nahrain University Baghdad, Iraq Mohammed S.Saleh
Inverse Kinematics Analysis for Manipulator Robot With Wrist Offset Based On the Closed-Form Algorithm Mohammed Z. Al-Faiz,MIEEE Computer Engineering Dept. Nahrain University Baghdad, Iraq Mohammed S.Saleh
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Modern mechanical and aerospace systems are often very complex and consist of many components interconnected by joints and force elements such as springs, dampers, and actuators.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Modern mechanical and aerospace systems are often very complex and consist of many components interconnected by joints and force elements such as springs, dampers, and actuators.
IN-SITU CALIBRATION OF A REDUNDANT MEASUREMENT SYSTEM FOR MANIPULATOR POSITIONING
 IN-SIU CALIBRAION OF A REDUNDAN MEASUREMEN SYSEM FOR MANIPULAOR POSIIONING Piotr J. Meyer Philips Center for Industrial echnology (CF, Lynnfield, MA, U.S.A. Prof. Dr. Jan van Eijk Philips Center for Industrial
IN-SIU CALIBRAION OF A REDUNDAN MEASUREMEN SYSEM FOR MANIPULAOR POSIIONING Piotr J. Meyer Philips Center for Industrial echnology (CF, Lynnfield, MA, U.S.A. Prof. Dr. Jan van Eijk Philips Center for Industrial
Matlab Simulator of a 6 DOF Stanford Manipulator and its Validation Using Analytical Method and Roboanalyzer
 Matlab Simulator of a 6 DOF Stanford Manipulator and its Validation Using Analytical Method and Roboanalyzer Maitreyi More 1, Rahul Abande 2, Ankita Dadas 3, Santosh Joshi 4 1, 2, 3 Department of Mechanical
Matlab Simulator of a 6 DOF Stanford Manipulator and its Validation Using Analytical Method and Roboanalyzer Maitreyi More 1, Rahul Abande 2, Ankita Dadas 3, Santosh Joshi 4 1, 2, 3 Department of Mechanical
THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF FLEXIBILITY IN MOBILE ROBOTIC MANIPULATOR SYSTEMS
 Proc. VIII World Congress on the Theroy of Machines and Mechanisms, Prague, Czechoslavakia, July 1991- Revised 1/1/9 THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF FLEXIBILITY IN MOBILE ROBOTIC MANIPULATOR SYSTEMS S. Dubowsky
Proc. VIII World Congress on the Theroy of Machines and Mechanisms, Prague, Czechoslavakia, July 1991- Revised 1/1/9 THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF FLEXIBILITY IN MOBILE ROBOTIC MANIPULATOR SYSTEMS S. Dubowsky
Introduction to Robotics
 Université de Strasbourg Introduction to Robotics Bernard BAYLE, 2013 http://eavr.u-strasbg.fr/ bernard Modelling of a SCARA-type robotic manipulator SCARA-type robotic manipulators: introduction SCARA-type
Université de Strasbourg Introduction to Robotics Bernard BAYLE, 2013 http://eavr.u-strasbg.fr/ bernard Modelling of a SCARA-type robotic manipulator SCARA-type robotic manipulators: introduction SCARA-type
A Geometric Newton-Raphson Method for Gough-Stewart Platforms
 A Geometric Newton-Raphson Method for Gough-Stewart Platforms J.M. Selig and Hui Li Abstract A geometric version of the well known Newton-Raphson methods is introduced. This root finding method is adapted
A Geometric Newton-Raphson Method for Gough-Stewart Platforms J.M. Selig and Hui Li Abstract A geometric version of the well known Newton-Raphson methods is introduced. This root finding method is adapted
A Pair of Measures of Rotational Error for Axisymmetric Robot End-Effectors
 A Pair of Measures of Rotational Error for Axisymmetric Robot End-Effectors Sébastien Briot and Ilian A. Bonev Department of Automated Manufacturing Engineering, École de Technologie Supérieure (ÉTS),
A Pair of Measures of Rotational Error for Axisymmetric Robot End-Effectors Sébastien Briot and Ilian A. Bonev Department of Automated Manufacturing Engineering, École de Technologie Supérieure (ÉTS),
Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion
 Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion 1.1 Overview of the Lesson The purpose of this lesson is to provide you with a brief overview of Pro/MECHANICA Motion, also called Motion in this book. Motion
Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion 1.1 Overview of the Lesson The purpose of this lesson is to provide you with a brief overview of Pro/MECHANICA Motion, also called Motion in this book. Motion
Animation Lecture 10 Slide Fall 2003
 Animation Lecture 10 Slide 1 6.837 Fall 2003 Conventional Animation Draw each frame of the animation great control tedious Reduce burden with cel animation layer keyframe inbetween cel panoramas (Disney
Animation Lecture 10 Slide 1 6.837 Fall 2003 Conventional Animation Draw each frame of the animation great control tedious Reduce burden with cel animation layer keyframe inbetween cel panoramas (Disney
DESIGN AND MODELLING OF A 4DOF PAINTING ROBOT
 DESIGN AND MODELLING OF A 4DOF PAINTING ROBOT MSc. Nilton Anchaygua A. Victor David Lavy B. Jose Luis Jara M. Abstract The following project has as goal the study of the kinematics, dynamics and control
DESIGN AND MODELLING OF A 4DOF PAINTING ROBOT MSc. Nilton Anchaygua A. Victor David Lavy B. Jose Luis Jara M. Abstract The following project has as goal the study of the kinematics, dynamics and control
Triangulation: A new algorithm for Inverse Kinematics
 Triangulation: A new algorithm for Inverse Kinematics R. Müller-Cajar 1, R. Mukundan 1, 1 University of Canterbury, Dept. Computer Science & Software Engineering. Email: rdc32@student.canterbury.ac.nz
Triangulation: A new algorithm for Inverse Kinematics R. Müller-Cajar 1, R. Mukundan 1, 1 University of Canterbury, Dept. Computer Science & Software Engineering. Email: rdc32@student.canterbury.ac.nz
DETERMINING suitable types, number and locations of
 108 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 47, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 1998 Instrumentation Architecture and Sensor Fusion for Systems Control Michael E. Stieber, Member IEEE, Emil Petriu,
108 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 47, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 1998 Instrumentation Architecture and Sensor Fusion for Systems Control Michael E. Stieber, Member IEEE, Emil Petriu,
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control. Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics
 MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics Denavit-Hartenberg Convention Reading: SHV Chapter 3 Mechanical Engineering Hanz Richter, PhD MCE503 p.1/12 Aims of
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics Denavit-Hartenberg Convention Reading: SHV Chapter 3 Mechanical Engineering Hanz Richter, PhD MCE503 p.1/12 Aims of
A Detailed Look into Forward and Inverse Kinematics
 A Detailed Look into Forward and Inverse Kinematics Kinematics = Study of movement, motion independent of the underlying forces that cause them September 19-26, 2016 Kinematics Preliminaries Preliminaries:
A Detailed Look into Forward and Inverse Kinematics Kinematics = Study of movement, motion independent of the underlying forces that cause them September 19-26, 2016 Kinematics Preliminaries Preliminaries:
Kinematics and dynamics analysis of micro-robot for surgical applications
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (2009) No. 1, pp. 22-29 Kinematics and dynamics analysis of micro-robot for surgical applications Khaled Tawfik 1, Atef A.
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (2009) No. 1, pp. 22-29 Kinematics and dynamics analysis of micro-robot for surgical applications Khaled Tawfik 1, Atef A.
1498. End-effector vibrations reduction in trajectory tracking for mobile manipulator
 1498. End-effector vibrations reduction in trajectory tracking for mobile manipulator G. Pajak University of Zielona Gora, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Zielona Góra, Poland E-mail: g.pajak@iizp.uz.zgora.pl
1498. End-effector vibrations reduction in trajectory tracking for mobile manipulator G. Pajak University of Zielona Gora, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Zielona Góra, Poland E-mail: g.pajak@iizp.uz.zgora.pl
Introduction to Multi-body Dynamics
 division Graduate Course ME 244) Tentative Draft Syllabus 1. Basic concepts in 3-D rigid-body mechanics 1. Rigid body vs flexible body 2. Spatial kinematics (3-D rotation transformations) and Euler theorem
division Graduate Course ME 244) Tentative Draft Syllabus 1. Basic concepts in 3-D rigid-body mechanics 1. Rigid body vs flexible body 2. Spatial kinematics (3-D rotation transformations) and Euler theorem
Visualization and Analysis of Inverse Kinematics Algorithms Using Performance Metric Maps
 Visualization and Analysis of Inverse Kinematics Algorithms Using Performance Metric Maps Oliver Cardwell, Ramakrishnan Mukundan Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Canterbury
Visualization and Analysis of Inverse Kinematics Algorithms Using Performance Metric Maps Oliver Cardwell, Ramakrishnan Mukundan Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Canterbury
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Multi-body Kinematics
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Multi-body Kinematics 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Multi-body Kinematics 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco
AC : ADAPTIVE ROBOT MANIPULATORS IN GLOBAL TECHNOLOGY
 AC 2009-130: ADAPTIVE ROBOT MANIPULATORS IN GLOBAL TECHNOLOGY Alireza Rahrooh, University of Central Florida Alireza Rahrooh is aprofessor of Electrical Engineering Technology at the University of Central
AC 2009-130: ADAPTIVE ROBOT MANIPULATORS IN GLOBAL TECHNOLOGY Alireza Rahrooh, University of Central Florida Alireza Rahrooh is aprofessor of Electrical Engineering Technology at the University of Central
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Modern mechanical and aerospace systems are often very complex and consist of many components interconnected by joints and force elements such as springs, dampers, and actuators.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Modern mechanical and aerospace systems are often very complex and consist of many components interconnected by joints and force elements such as springs, dampers, and actuators.
A NOVEL METHOD FOR THE DESIGN OF 2-DOF PARALLEL MECHANISMS FOR MACHINING APPLICATIONS
 A NOVEL METHOD FOR THE DESIGN OF 2-DOF PARALLEL MECHANISMS FOR MACHINING APPLICATIONS Félix Majou Institut de Recherches en Communications et Cybernétique de Nantes 1, 1 rue de la Noë, 44321 Nantes, FRANCE
A NOVEL METHOD FOR THE DESIGN OF 2-DOF PARALLEL MECHANISMS FOR MACHINING APPLICATIONS Félix Majou Institut de Recherches en Communications et Cybernétique de Nantes 1, 1 rue de la Noë, 44321 Nantes, FRANCE
Inverse Kinematics Software Design and Trajectory Control Programming of SCARA Manipulator robot
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 11, Number 11 (2018), pp. 1759-1779 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Inverse Kinematics
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 11, Number 11 (2018), pp. 1759-1779 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Inverse Kinematics
An Improved Dynamic Modeling of a 3-RPS Parallel Manipulator using the concept of DeNOC Matrices
 An Improved Dynamic Modeling of a 3-RPS Parallel Manipulator using the concept of DeNOC Matrices A. Rahmani Hanzaki, E. Yoosefi Abstract A recursive dynamic modeling of a three-dof parallel robot, namely,
An Improved Dynamic Modeling of a 3-RPS Parallel Manipulator using the concept of DeNOC Matrices A. Rahmani Hanzaki, E. Yoosefi Abstract A recursive dynamic modeling of a three-dof parallel robot, namely,
Kinematics. Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position.
 Kinematics Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position. 1/31 Statics deals with the forces and moments which are aplied on the mechanism
Kinematics Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position. 1/31 Statics deals with the forces and moments which are aplied on the mechanism
LEVEL-SET METHOD FOR WORKSPACE ANALYSIS OF SERIAL MANIPULATORS
 LEVEL-SET METHOD FOR WORKSPACE ANALYSIS OF SERIAL MANIPULATORS Erika Ottaviano*, Manfred Husty** and Marco Ceccarelli* * LARM: Laboratory of Robotics and Mechatronics DiMSAT University of Cassino Via Di
LEVEL-SET METHOD FOR WORKSPACE ANALYSIS OF SERIAL MANIPULATORS Erika Ottaviano*, Manfred Husty** and Marco Ceccarelli* * LARM: Laboratory of Robotics and Mechatronics DiMSAT University of Cassino Via Di
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW. Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Control Part 4 Other control strategies These slides are devoted to two advanced control approaches, namely Operational space control Interaction
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Control Part 4 Other control strategies These slides are devoted to two advanced control approaches, namely Operational space control Interaction
PPGEE Robot Dynamics I
 PPGEE Electrical Engineering Graduate Program UFMG April 2014 1 Introduction to Robotics 2 3 4 5 What is a Robot? According to RIA Robot Institute of America A Robot is a reprogrammable multifunctional
PPGEE Electrical Engineering Graduate Program UFMG April 2014 1 Introduction to Robotics 2 3 4 5 What is a Robot? According to RIA Robot Institute of America A Robot is a reprogrammable multifunctional
Solution of inverse kinematic problem for serial robot using dual quaterninons and plucker coordinates
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2009 Solution of inverse kinematic problem for
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2009 Solution of inverse kinematic problem for
CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics. Lecture 3 : Kinematics
 CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture 3 : Kinematics Traditional Cell Animation, hand drawn, 2D Lead Animator for keyframes http://animation.about.com/od/flashanimationtutorials/ss/flash31detanim2.htm
CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture 3 : Kinematics Traditional Cell Animation, hand drawn, 2D Lead Animator for keyframes http://animation.about.com/od/flashanimationtutorials/ss/flash31detanim2.htm
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) office hour: LEE
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) office hour: LEE
Robot. A thesis presented to. the faculty of. In partial fulfillment. of the requirements for the degree. Master of Science. Zachary J.
 Uncertainty Analysis throughout the Workspace of a Macro/Micro Cable Suspended Robot A thesis presented to the faculty of the Russ College of Engineering and Technology of Ohio University In partial fulfillment
Uncertainty Analysis throughout the Workspace of a Macro/Micro Cable Suspended Robot A thesis presented to the faculty of the Russ College of Engineering and Technology of Ohio University In partial fulfillment
Trajectory Planning of Redundant Planar Mechanisms for Reducing Task Completion Duration
 Trajectory Planning of Redundant Planar Mechanisms for Reducing Task Completion Duration Emre Uzunoğlu 1, Mehmet İsmet Can Dede 1, Gökhan Kiper 1, Ercan Mastar 2, Tayfun Sığırtmaç 2 1 Department of Mechanical
Trajectory Planning of Redundant Planar Mechanisms for Reducing Task Completion Duration Emre Uzunoğlu 1, Mehmet İsmet Can Dede 1, Gökhan Kiper 1, Ercan Mastar 2, Tayfun Sığırtmaç 2 1 Department of Mechanical
This week. CENG 732 Computer Animation. Warping an Object. Warping an Object. 2D Grid Deformation. Warping an Object.
 CENG 732 Computer Animation Spring 2006-2007 Week 4 Shape Deformation Animating Articulated Structures: Forward Kinematics/Inverse Kinematics This week Shape Deformation FFD: Free Form Deformation Hierarchical
CENG 732 Computer Animation Spring 2006-2007 Week 4 Shape Deformation Animating Articulated Structures: Forward Kinematics/Inverse Kinematics This week Shape Deformation FFD: Free Form Deformation Hierarchical
Constraint and velocity analysis of mechanisms
 Constraint and velocity analysis of mechanisms Matteo Zoppi Dimiter Zlatanov DIMEC University of Genoa Genoa, Italy Su S ZZ-2 Outline Generalities Constraint and mobility analysis Examples of geometric
Constraint and velocity analysis of mechanisms Matteo Zoppi Dimiter Zlatanov DIMEC University of Genoa Genoa, Italy Su S ZZ-2 Outline Generalities Constraint and mobility analysis Examples of geometric
The Collision-free Workspace of the Tripteron Parallel Robot Based on a Geometrical Approach
 The Collision-free Workspace of the Tripteron Parallel Robot Based on a Geometrical Approach Z. Anvari 1, P. Ataei 2 and M. Tale Masouleh 3 1,2 Human-Robot Interaction Laboratory, University of Tehran
The Collision-free Workspace of the Tripteron Parallel Robot Based on a Geometrical Approach Z. Anvari 1, P. Ataei 2 and M. Tale Masouleh 3 1,2 Human-Robot Interaction Laboratory, University of Tehran
ME 115(b): Final Exam, Spring
 ME 115(b): Final Exam, Spring 2011-12 Instructions 1. Limit your total time to 5 hours. That is, it is okay to take a break in the middle of the exam if you need to ask me a question, or go to dinner,
ME 115(b): Final Exam, Spring 2011-12 Instructions 1. Limit your total time to 5 hours. That is, it is okay to take a break in the middle of the exam if you need to ask me a question, or go to dinner,
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control. Lecture 1: Introduction
 MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 1: Introduction Reading: SHV Chapter 1 Robotics and Automation Handbook, Chapter 1 Assigned readings from several articles. Cleveland State University
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 1: Introduction Reading: SHV Chapter 1 Robotics and Automation Handbook, Chapter 1 Assigned readings from several articles. Cleveland State University
A Novel Approach for Direct Kinematics Solution of 3-RRR Parallel Manipulator Following a Trajectory
 16 th. Annual (International) Conference on Mechanical EngineeringISME2008 May 1416, 2008, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Iran A Novel Approach for Direct Kinematics Solution of 3RRR Parallel Manipulator
16 th. Annual (International) Conference on Mechanical EngineeringISME2008 May 1416, 2008, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Iran A Novel Approach for Direct Kinematics Solution of 3RRR Parallel Manipulator
TENTH WORLD CONGRESS ON THE THEORY OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS Oulu, Finland, June 20{24, 1999 THE EFFECT OF DATA-SET CARDINALITY ON THE DESIGN AND STR
 TENTH WORLD CONGRESS ON THE THEORY OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS Oulu, Finland, June 20{24, 1999 THE EFFECT OF DATA-SET CARDINALITY ON THE DESIGN AND STRUCTURAL ERRORS OF FOUR-BAR FUNCTION-GENERATORS M.J.D.
TENTH WORLD CONGRESS ON THE THEORY OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS Oulu, Finland, June 20{24, 1999 THE EFFECT OF DATA-SET CARDINALITY ON THE DESIGN AND STRUCTURAL ERRORS OF FOUR-BAR FUNCTION-GENERATORS M.J.D.
Force control of redundant industrial robots with an approach for singularity avoidance using extended task space formulation (ETSF)
 Force control of redundant industrial robots with an approach for singularity avoidance using extended task space formulation (ETSF) MSc Audun Rønning Sanderud*, MSc Fredrik Reme**, Prof. Trygve Thomessen***
Force control of redundant industrial robots with an approach for singularity avoidance using extended task space formulation (ETSF) MSc Audun Rønning Sanderud*, MSc Fredrik Reme**, Prof. Trygve Thomessen***
Structure and Synthesis of Robot Motion
 Structure and Synthesis of Robot Motion Dynamics: Constraints, Continua, etc. Subramanian Ramamoorthy School of Informatics 5 February, 2009 Recap Last time, we discussed two major approaches to describing
Structure and Synthesis of Robot Motion Dynamics: Constraints, Continua, etc. Subramanian Ramamoorthy School of Informatics 5 February, 2009 Recap Last time, we discussed two major approaches to describing
Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685
 Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685 Previously Representation of rigid body motion Two different interpretations - as transformations between different coord. frames - as operators acting on a rigid body
Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685 Previously Representation of rigid body motion Two different interpretations - as transformations between different coord. frames - as operators acting on a rigid body
Prof. Fanny Ficuciello Robotics for Bioengineering Visual Servoing
 Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level
Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level
METR 4202: Advanced Control & Robotics
 Position & Orientation & State t home with Homogenous Transformations METR 4202: dvanced Control & Robotics Drs Surya Singh, Paul Pounds, and Hanna Kurniawati Lecture # 2 July 30, 2012 metr4202@itee.uq.edu.au
Position & Orientation & State t home with Homogenous Transformations METR 4202: dvanced Control & Robotics Drs Surya Singh, Paul Pounds, and Hanna Kurniawati Lecture # 2 July 30, 2012 metr4202@itee.uq.edu.au
Singularity Handling on Puma in Operational Space Formulation
 Singularity Handling on Puma in Operational Space Formulation Denny Oetomo, Marcelo Ang Jr. National University of Singapore Singapore d oetomo@yahoo.com mpeangh@nus.edu.sg Ser Yong Lim Gintic Institute
Singularity Handling on Puma in Operational Space Formulation Denny Oetomo, Marcelo Ang Jr. National University of Singapore Singapore d oetomo@yahoo.com mpeangh@nus.edu.sg Ser Yong Lim Gintic Institute
θ x Week Date Lecture (M: 2:05p-3:50, 50-N202) 1 23-Jul Introduction + Representing Position & Orientation & State 2 30-Jul
 θ x 2018 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (M: 2:05p-3:50, 50-N202) 1 23-Jul Introduction + Representing Position
θ x 2018 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (M: 2:05p-3:50, 50-N202) 1 23-Jul Introduction + Representing Position
Design of a Three-Axis Rotary Platform
 Design of a Three-Axis Rotary Platform William Mendez, Yuniesky Rodriguez, Lee Brady, Sabri Tosunoglu Mechanics and Materials Engineering, Florida International University 10555 W Flagler Street, Miami,
Design of a Three-Axis Rotary Platform William Mendez, Yuniesky Rodriguez, Lee Brady, Sabri Tosunoglu Mechanics and Materials Engineering, Florida International University 10555 W Flagler Street, Miami,
A simple example. Assume we want to find the change in the rotation angles to get the end effector to G. Effect of changing s
 CENG 732 Computer Animation This week Inverse Kinematics (continued) Rigid Body Simulation Bodies in free fall Bodies in contact Spring 2006-2007 Week 5 Inverse Kinematics Physically Based Rigid Body Simulation
CENG 732 Computer Animation This week Inverse Kinematics (continued) Rigid Body Simulation Bodies in free fall Bodies in contact Spring 2006-2007 Week 5 Inverse Kinematics Physically Based Rigid Body Simulation
Self-Correcting Projectile Launcher. Josh Schuster Yena Park Diana Mirabello Ryan Kindle
 Self-Correcting Projectile Launcher Josh Schuster Yena Park Diana Mirabello Ryan Kindle Motivation & Applications Successfully reject disturbances without use of complex sensors Demonstrate viability of
Self-Correcting Projectile Launcher Josh Schuster Yena Park Diana Mirabello Ryan Kindle Motivation & Applications Successfully reject disturbances without use of complex sensors Demonstrate viability of
NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582 ROBOT ENGINEERING. Dr. Stephen Bruder NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582
 ROBOT ENGINEERING Dr. Stephen Bruder Course Information Robot Engineering Classroom UNM: Woodward Hall room 147 NMT: Cramer 123 Schedule Tue/Thur 8:00 9:15am Office Hours UNM: After class 10am Email bruder@aptec.com
ROBOT ENGINEERING Dr. Stephen Bruder Course Information Robot Engineering Classroom UNM: Woodward Hall room 147 NMT: Cramer 123 Schedule Tue/Thur 8:00 9:15am Office Hours UNM: After class 10am Email bruder@aptec.com
Contents. I Basics 1. Copyright by SIAM. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
Synthesis of Spatial RPRP Loops for a Given Screw System
 Synthesis of Spatial RPRP Loops for a Given Screw System A. Perez-Gracia Institut de Robotica i Informatica Industrial (IRI) UPC/CSIC, Barcelona, Spain and: College of Engineering, Idaho State Univesity,
Synthesis of Spatial RPRP Loops for a Given Screw System A. Perez-Gracia Institut de Robotica i Informatica Industrial (IRI) UPC/CSIC, Barcelona, Spain and: College of Engineering, Idaho State Univesity,
Integration of automatic differentiation tools within object-oriented codes: accuracy and timings
 Integration of automatic differentiation tools within object-oriented codes: accuracy and timings Deliverable 2.2 Marco Morandini Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale, Politecnico di Milano Introduction
Integration of automatic differentiation tools within object-oriented codes: accuracy and timings Deliverable 2.2 Marco Morandini Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale, Politecnico di Milano Introduction
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 Name Code Class Branch Page 1 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : ROBOTICS (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 0 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : A7055 : IV B. Tech I Semester : MECHANICAL
Name Code Class Branch Page 1 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : ROBOTICS (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 0 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : A7055 : IV B. Tech I Semester : MECHANICAL
DETC APPROXIMATE MOTION SYNTHESIS OF SPHERICAL KINEMATIC CHAINS
 Proceedings of the ASME 2007 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 2007 September 4-7, 2007, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA DETC2007-34372
Proceedings of the ASME 2007 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 2007 September 4-7, 2007, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA DETC2007-34372
Dual-loop Control for Backlash Correction in Trajectory-tracking of a Planar 3-RRR Manipulator
 Dual-loop Control for Backlash Correction in Trajectory-tracking of a Planar -RRR Manipulator Abhishek Agarwal, Chaman Nasa, Sandipan Bandyopadhyay Abstract The presence of backlash in the gearheads is
Dual-loop Control for Backlash Correction in Trajectory-tracking of a Planar -RRR Manipulator Abhishek Agarwal, Chaman Nasa, Sandipan Bandyopadhyay Abstract The presence of backlash in the gearheads is
Humanoid Robotics. Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning Maren Bennewitz 1 Motivation Planning for object manipulation Whole-body motion to reach a desired goal configuration Generate a sequence
Humanoid Robotics Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning Maren Bennewitz 1 Motivation Planning for object manipulation Whole-body motion to reach a desired goal configuration Generate a sequence
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO. Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
 Page 1 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF3480 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: May 31 st 2010 Exam hours: 3 hours This examination paper consists of 5 page(s).
Page 1 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF3480 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: May 31 st 2010 Exam hours: 3 hours This examination paper consists of 5 page(s).
SCREW-BASED RELATIVE JACOBIAN FOR MANIPULATORS COOPERATING IN A TASK
 ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics - Vol. 3 - pp.276-285 Copyright c 2008 by ABCM SCREW-BASED RELATIVE JACOBIAN FOR MANIPULATORS COOPERATING IN A TASK Luiz Ribeiro, ribeiro@ime.eb.br Raul Guenther,
ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics - Vol. 3 - pp.276-285 Copyright c 2008 by ABCM SCREW-BASED RELATIVE JACOBIAN FOR MANIPULATORS COOPERATING IN A TASK Luiz Ribeiro, ribeiro@ime.eb.br Raul Guenther,
Redundancy Resolution by Minimization of Joint Disturbance Torque for Independent Joint Controlled Kinematically Redundant Manipulators
 56 ICASE :The Institute ofcontrol,automation and Systems Engineering,KOREA Vol.,No.1,March,000 Redundancy Resolution by Minimization of Joint Disturbance Torque for Independent Joint Controlled Kinematically
56 ICASE :The Institute ofcontrol,automation and Systems Engineering,KOREA Vol.,No.1,March,000 Redundancy Resolution by Minimization of Joint Disturbance Torque for Independent Joint Controlled Kinematically
Planar Robot Kinematics
 V. Kumar lanar Robot Kinematics The mathematical modeling of spatial linkages is quite involved. t is useful to start with planar robots because the kinematics of planar mechanisms is generally much simpler
V. Kumar lanar Robot Kinematics The mathematical modeling of spatial linkages is quite involved. t is useful to start with planar robots because the kinematics of planar mechanisms is generally much simpler
Kinematics of Closed Chains
 Chapter 7 Kinematics of Closed Chains Any kinematic chain that contains one or more loops is called a closed chain. Several examples of closed chains were encountered in Chapter 2, from the planar four-bar
Chapter 7 Kinematics of Closed Chains Any kinematic chain that contains one or more loops is called a closed chain. Several examples of closed chains were encountered in Chapter 2, from the planar four-bar
Singularity Analysis of an Extensible Kinematic Architecture: Assur Class N, Order N 1
 David H. Myszka e-mail: dmyszka@udayton.edu Andrew P. Murray e-mail: murray@notes.udayton.edu University of Dayton, Dayton, OH 45469 James P. Schmiedeler The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210 e-mail:
David H. Myszka e-mail: dmyszka@udayton.edu Andrew P. Murray e-mail: murray@notes.udayton.edu University of Dayton, Dayton, OH 45469 James P. Schmiedeler The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210 e-mail:
