... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c 1
|
|
|
- Vernon Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c 1 1 #include <GL/glut.h> 2 #include <math.h> 3 #include <GL/freeglut.h> 4 #include <GL/freeglut_ext.h> 5 #include <GL/freeglut_std.h> 6 #include <stdio.h> 7 8 int spot=0; 9 int location=0; 10 int time=0; 11 double h=0.4; int state=0; 14 int e1=0; 15 int e2=0; 16 int shoot=0; 17 double planeb1=16; 18 double planeb2=19; 19 double us=7.5; 20 double target=7.5;//7.5 or 5 21 double treestump=14; 22 double treeleaves=13; 23 double treestump2=25; 24 double treeleaves2=24; 25 double cl=21; 26 double cl2=30; 27 double rx=6; 28 double ry=8; #include <GL/gl.h> 31 #include <GL/glu.h> 32 #include <stdlib.h> #define DEFAULT_WIDTH #define DEFAULT_HEIGHT int width = DEFAULT_WIDTH; 38 int height = DEFAULT_HEIGHT; typedef GLubyte Pixel[3]; /*represents red green blue*/ int Width, Height; /*of image*/ /*array of pixels*/ 45 Pixel *Image; /*name of image file*/ 48 char *Filename = "./planeg.ppm"; 49 char *Filename1 = "./planeb.ppm"; 50 char *Filename2 = "./bark.ppm"; 51 char *Filename3 = "./leaves.ppm"; 52 char *Filename4 = "./explosion.ppm";
2 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c 2 53 char *Filename5 = "./rocket.ppm"; 54 char *Filename6 = "./go.ppm"; 55 char *Filename7 = "./cloud.ppm"; int allowedsize(int x)/*returns max power of 2 <= x*/ 58 { 59 int r;r = 1; 60 while(r < x) r=(r<<1); if(r==x) return r; 63 else return r>>1; /*reads image file assumes ppm format*/ 66 void readimage(int p){ 67 int w,h,max;int i,j; 68 unsigned int r,g,b,al; 69 int k;char ch;file *fp; if(p==0){fp = fopen(filename,"r"); 72 if(p==1){fp = fopen(filename1,"r"); 73 if(p==2){fp = fopen(filename2,"r"); 74 if(p==3){fp = fopen(filename3,"r"); 75 if(p==4){fp = fopen(filename4,"r"); 76 if(p==5){fp = fopen(filename5,"r"); 77 if(p==6){fp = fopen(filename6,"r"); 78 if(p==7){fp = fopen(filename7,"r"); /*read the header*/ 82 fscanf(fp, "P%c\n", &ch); 83 if (ch!= '3') { 84 fprintf(stderr, "Only ascii mode 3 channel PPM files"); 85 exit( 1); /*strip comment lines*/ 89 ch = getc(fp); 90 while (ch == '#') { 91 do { 92 ch = getc(fp); while (ch!= '\n'); 95 ch = getc(fp); ungetc(ch, fp); /*read the width*/ 100 fscanf(fp,"%d",&w); 101 /*read the height*/ 102 fscanf(fp,"%d",&h); 103 /*max intensity not used here*/ 104 fscanf(fp,"%d",&max);
3 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c /*width and height must be powers of 2 here of finding the max power of 2 <= w and h*/ Width = allowedsize(w); Height = allowedsize(h); //printf("width = %d, Height = %d\n",width,height); Image = (Pixel *)malloc(width*height*sizeof(pixel)); for(i=0;i<height;++i){ for(j=0;j<width;++j) { fscanf(fp,"%d %d %d",&r,&g,&b); k = i*width+j; (*(Image+k))[0] = (GLubyte)r; (*(Image+k))[1] = (GLubyte)g; (*(Image+k))[2] = (GLubyte)b; (*(Image+k))[3] = (GLubyte)al; /*better scan to the end of the row*/ for(j=width; j<w; ++j) fscanf(fp,"%c %c %c",&r,&g,&b); fclose(fp); void initialisetextures(int p){ GLint level = 0;/*only one level no level of detail*/ GLint components = 3; /*R,G,B components only*/ GLint border = 0; /*no border around the image*/ /*read the given image file*/ readimage(p); /*each pixelrow on a byte alignment boundary*/ glpixelstorei(gl_unpack_alignment,1); /*define information about the image*/ glteximage2d(gl_texture_2d,level,components, (GLsizei)Width, (GLsizei)Height, border, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE,Image); /*ensures that image is not wrapped*/ gltexparameteri (GL_TEXTURE_2D,GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S,GL_CLAMP); gltexparameteri (GL_TEXTURE_2D,GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T,GL_CLAMP); /*chooses mapping type from texels to pixels*/ gltexparameterf (GL_TEXTURE_2D,GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER,GL_LINEAR); gltexparameterf (GL_TEXTURE_2D,GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER,GL_LINEAR); /*GL_LINEAR which performs a linear interpolation on the 4 surrounding texels*/ /*GL_DECAL overwrite pixel with texture colour*/ gltexenvf(gl_texture_env,gl_texture_env_mode,gl_decal); /*alternative is GL_MODULATE. modulates the lighting
4 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c by the texel value by multiplication*/ void init(){ 157 glclearcolor(1.0,1.0,1.0,0.0); 158 glmatrixmode(gl_projection); 159 glloadidentity(); 160 gluortho2d(0.0,20.0,0.0,13.0); 161 srand((unsigned) 500); void planeg(){//our plane 165 initialisetextures(0); 166 glenable(gl_texture_2d); 167 glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(0.3,us); 170 gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(0.3,us+2); 171 gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(4.0,us+2); 172 gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(4.0,us); 173 glend(); gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void planebad1(){//enemy plane if(e1==0){initialisetextures(1); 180 else{initialisetextures(4); 181 glenable(gl_texture_2d); 182 glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(planeb1,7.5); 185 gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(planeb1,9.5); 186 gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(planeb1+3,9.5); 187 gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(planeb1+3,7.5); 188 glend(); gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void planebad2(){//enemy plane if(e2==0){initialisetextures(1); 195 else{initialisetextures(4); 196 glenable(gl_texture_2d); 197 glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(planeb2,5.0); 200 gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(planeb2,7.0); 201 gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(planeb2+3,7.0); 202 gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(planeb2+3,5.0); 203 glend(); 204
5 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void rocket(){ initialisetextures(5); glenable(gl_texture_2d); if(shoot==1){ gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(rx 2,ry); gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(rx 2,ry+1); gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(rx,ry+1); gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(rx,ry); glend(); else{ rx= 1; gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(rx 1, 1); gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(rx 1, 1); gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(rx, 1); gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(rx, 1); glend(); gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void ground(){ glcolor3f(0.0,0.3,0.0); glvertex2f(0,0.0); glvertex2f(0,1.0); glvertex2f(20.0,1.0); glvertex2f(20.0,0.0); glend(); void tree(){ initialisetextures(2); glenable(gl_texture_2d); gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(treestump,1.0); gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(treestump,1.5); gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(treestump+1.0,1.5); gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(treestump+1,1.0); glend(); initialisetextures(3); gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(treeleaves,1.5); gltexcoord2f(0.5,1);glvertex2f(treeleaves+1.5,4.0); gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(treeleaves+3,1.5);
6 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c glend(); 258 gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void tree2(){ 262 initialisetextures(2); 263 glenable(gl_texture_2d); gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(treestump2,1.0); 267 gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(treestump2,1.5); 268 gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(treestump2+1.0,1.5); 269 gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(treestump2+1,1.0); 270 glend(); initialisetextures(3); gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(treeleaves2,1.5); 275 gltexcoord2f(0.5,1);glvertex2f(treeleaves2+1.5,4.0); 276 gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(treeleaves2+3,1.5); 277 glend(); 278 gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void cloud(){ 282 initialisetextures(7); 283 glenable(gl_texture_2d); 284 glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(cl,11.0); 287 gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(cl,12.0); 288 gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(cl+3,12.0); 289 gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(cl+3,11.0); 290 glend(); 291 gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void cloud2(){ 295 initialisetextures(7); 296 glenable(gl_texture_2d); 297 glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(cl2,11.0); 300 gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(cl2,12.0); 301 gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(cl2+3,12.0); 302 gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(cl2+3,11.0); 303 glend(); 304 gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void sun(){ 308 glcolor3f(1.0,1.0,0.0);
7 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c glvertex2f( 2,10.0); 311 glvertex2f( 2,14.0); 312 glvertex2f(3,14.0); 313 glvertex2f(1,11.0); 314 glend(); void gameover(){ 318 initialisetextures(6); 319 glenable(gl_texture_2d); 320 glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); gltexcoord2f(0,0);glvertex2f(1,1.0); 323 gltexcoord2f(0,1);glvertex2f(1,14.0); 324 gltexcoord2f(1,1);glvertex2f(19,14.0); 325 gltexcoord2f(1,0);glvertex2f(19,1.0); 326 glend(); 327 gldisable(gl_texture_2d); void display(){ 331 glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); planeg(); 334 planebad1(); 335 planebad2(); 336 rocket(); 337 cloud(); 338 cloud2(); 339 sun(); 340 tree(); 341 tree2(); 342 ground(); 343 if(state==1){gameover(); 344 glflush(); void mouseclick(int button,int state,int x,int y){ 348 if(button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN){ 349 if(target==7.5){ 350 shoot=1; 351 rx=6; 352 ry=8; if(target==5){ 356 shoot=1; 357 rx=6; 358 ry=5.5;
8 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c glutpostredisplay(); void Keyboard(unsigned char k, int x, int y){ 365 if(k == 'w'){//near side tables 366 target=7.5; else if(k =='s'){ 369 target=5; glutpostredisplay(); void idle(){//handle animations 377 //time++; if(state==0){ 380 //move plane to where it should be 381 if(us>target){us =.3; 382 if(us<target){us+=.3; //move necessary objects 385 if(e1==0){planeb1=planeb1.1; 386 else{e1++; 387 if(e2==0){planeb2=planeb2.1; 388 else{e2++; 389 treestump =.2; 390 treeleaves =.2; 391 treestump2 =.2; 392 treeleaves2 =.2; 393 rx=rx+.3; 394 cl=cl.1; 395 cl2=cl2.1; if(rx>planeb1 && ry>6){shoot=0;e1=1; 398 if(rx>planeb2 && ry<6){shoot=0;e2=2; 399 if(planeb1 < 4.0){state=1; 400 if(planeb2 < 4.0){state=1; 401 if(cl< 4){cl=21.0; 402 if(cl2< 4){cl2=21.0; 403 if(treeleaves< 2){ 404 treeleaves=21; 405 treestump=22; if(treeleaves2< 2){ 408 treeleaves2=21; 409 treestump2=22; if(e1>10){e1=0; planeb1=20; 412 if(e2>10){e2=0; planeb2=20;
9 ... Print PROGRAMS\Final Project final\planes\planeshoot.c //end state glutpostredisplay(); int main(int argc, char** argv){ 420 glutinit(&argc, argv); 421 glutinitdisplaymode(glut_rgb GLUT_SINGLE); 422 glutinitwindowsize(400,400); 423 glutcreatewindow("planeshooter"); 424 glutdisplayfunc(display); 425 glutmousefunc(mouseclick); 426 glutidlefunc(idle); 427 glutkeyboardfunc(keyboard); 428 init(); 429 glutmainloop();
Lecture 3. Understanding of OPenGL programming
 Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Autumn 2009 CS4815
 Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4. C++ - OpenGL
 FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM 3213 - INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4 C++ - OpenGL Part 1- C++ - Texture Mapping 1. Download texture file and put it into your current folder
FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM 3213 - INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4 C++ - OpenGL Part 1- C++ - Texture Mapping 1. Download texture file and put it into your current folder
Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1
 Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1 1. The endpoints of a given line are (0, 0) and (18, 6). Compute the first 4 values of y manually using Bresenham's Line Algorithm as x steps
Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1 1. The endpoints of a given line are (0, 0) and (18, 6). Compute the first 4 values of y manually using Bresenham's Line Algorithm as x steps
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Spring CS4815
 Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Lecture 22 Sections 8.8, 8.9, Wed, Oct 28, 2009
 s The s Lecture 22 Sections 8.8, 8.9, 8.10 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 28, 2009 Outline s The 1 2 3 4 5 The 6 7 8 Outline s The 1 2 3 4 5 The 6 7 8 Creating Images s The To create a texture image internally,
s The s Lecture 22 Sections 8.8, 8.9, 8.10 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 28, 2009 Outline s The 1 2 3 4 5 The 6 7 8 Outline s The 1 2 3 4 5 The 6 7 8 Creating Images s The To create a texture image internally,
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
 OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
Erik Anchondo cse 520 lab 4
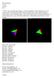 Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
C OMPUTER G RAPHICS Thursday
 C OMPUTER G RAPHICS 2017.04.27 Thursday Professor s original PPT http://calab.hanyang.ac.kr/ Courses Computer Graphics practice3.pdf TA s current PPT not uploaded yet GRAPHICS PIPELINE What is Graphics
C OMPUTER G RAPHICS 2017.04.27 Thursday Professor s original PPT http://calab.hanyang.ac.kr/ Courses Computer Graphics practice3.pdf TA s current PPT not uploaded yet GRAPHICS PIPELINE What is Graphics
To Do. Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) Course Outline. Course Outline. Methodology for Lecture. Demo: Surreal (HW 3)
 Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2
 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson
 C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
Assignment 1. Simple Graphics program using OpenGL
 Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT
 Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_PROJECTION, GL_MODELVIEW
 OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
2a. The triangles scale increases (expands) when the 'e' key is pressed and decreases (contracts) when the 'c' key is pressed.
 Erik Anchondo 1-29-19 cse 520 lab 3 1. Wrote a shader program to display three colored triangles, with one of each triangle being red, green, and blue. The colors change which triangle they are applied
Erik Anchondo 1-29-19 cse 520 lab 3 1. Wrote a shader program to display three colored triangles, with one of each triangle being red, green, and blue. The colors change which triangle they are applied
Computer Graphics. OpenGL
 Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
Graphics Hardware and OpenGL
 Graphics Hardware and OpenGL Ubi Soft, Prince of Persia: The Sands of Time What does graphics hardware have to do fast? Camera Views Different views of an object in the world 1 Camera Views Lines from
Graphics Hardware and OpenGL Ubi Soft, Prince of Persia: The Sands of Time What does graphics hardware have to do fast? Camera Views Different views of an object in the world 1 Camera Views Lines from
Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader
 Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader Summary: The purpose of lab 4 is to produce a pyramid tetrahedron that we are able to rotate it when clicked. Part 1: Color Tetrahedron Part 2: Rotation to show
Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader Summary: The purpose of lab 4 is to produce a pyramid tetrahedron that we are able to rotate it when clicked. Part 1: Color Tetrahedron Part 2: Rotation to show
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING. 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M
 UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
Using OpenGL with CUDA
 Using OpenGL with CUDA Installing OpenGL and GLUT; compiling with nvcc Basics of OpenGL and GLUT in C Interoperability between OpenGL and CUDA OpenGL = Open Graphic Library creation of 3D graphic primitives
Using OpenGL with CUDA Installing OpenGL and GLUT; compiling with nvcc Basics of OpenGL and GLUT in C Interoperability between OpenGL and CUDA OpenGL = Open Graphic Library creation of 3D graphic primitives
Drawing Primitives. OpenGL basics
 CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
Graphics Programming. August 31, Programming of the Sierpinski gasket. Programming with OpenGL and C/C++
 Computer Graphics Graphics Programming August 31, 2005 Contents Our Goal in This Chapter Programming of the Sierpinski gasket How To? Programming with OpenGL and C/C++ OpenGL API (Application Programmer
Computer Graphics Graphics Programming August 31, 2005 Contents Our Goal in This Chapter Programming of the Sierpinski gasket How To? Programming with OpenGL and C/C++ OpenGL API (Application Programmer
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions
 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Objectives Develop a more sophisticated
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Objectives Develop a more sophisticated
Computer Graphics. Making Pictures. Computer Graphics CSC470 1
 Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
CSE4030 Introduction to Computer Graphics
 CSE4030 Introduction to Computer Graphics Dongguk University Jeong-Mo Hong Week 2 The first step on a journey to the virtual world An introduction to computer graphics and interactive techniques How to
CSE4030 Introduction to Computer Graphics Dongguk University Jeong-Mo Hong Week 2 The first step on a journey to the virtual world An introduction to computer graphics and interactive techniques How to
Lectures OpenGL Introduction
 Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009
![QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009 QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009](/thumbs/91/107455423.jpg) 2 COS340-A QUESTION 1 [10] a) OpenGL uses z-buffering for hidden surface removal. Explain how the z-buffer algorithm works and give one advantage of using this method. (5) Answer: OpenGL uses a hidden-surface
2 COS340-A QUESTION 1 [10] a) OpenGL uses z-buffering for hidden surface removal. Explain how the z-buffer algorithm works and give one advantage of using this method. (5) Answer: OpenGL uses a hidden-surface
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger Reception hours: by - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using
 Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 1. INTRODUCTION TO OpenGL
 Visual Computing and Multimedia Abel J. P. Gomes 1. Getting Started 2. Installing Graphics Libraries: OpenGL and GLUT 3. Setting up an IDE to run graphics programs in OpenGL/GLUT 4. A First OpenGL/GLUT
Visual Computing and Multimedia Abel J. P. Gomes 1. Getting Started 2. Installing Graphics Libraries: OpenGL and GLUT 3. Setting up an IDE to run graphics programs in OpenGL/GLUT 4. A First OpenGL/GLUT
Bob s Concise Introduction to Doxygen
 Bob s Concise Introduction to Doxygen by Robert S Laramee Visual and Interactive Computing Group Department of Computer Science Swansea University Swansea, Wales, UK 1 Comment Standard February 14, 2011
Bob s Concise Introduction to Doxygen by Robert S Laramee Visual and Interactive Computing Group Department of Computer Science Swansea University Swansea, Wales, UK 1 Comment Standard February 14, 2011
CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure. Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL:
 CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Understand the basic OpenGL program structure and how OpenGL supports
CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Understand the basic OpenGL program structure and how OpenGL supports
1 /* 4 C:\opencv\build\include. 6 C:\opencv\build\x86\vc10\lib
 1 1. Program 1 OpenCV (OpenCV Sample001) 1 /* 2 - > - > - >VC++ 3 ( ) 4 C:\opencv\build\include 5 ( ) 6 C:\opencv\build\x86\vc10\lib 7 - > - > - > - > 8 (240 O p e n C V ) 9 opencv_core240d.lib 10 opencv_imgproc240d.lib
1 1. Program 1 OpenCV (OpenCV Sample001) 1 /* 2 - > - > - >VC++ 3 ( ) 4 C:\opencv\build\include 5 ( ) 6 C:\opencv\build\x86\vc10\lib 7 - > - > - > - > 8 (240 O p e n C V ) 9 opencv_core240d.lib 10 opencv_imgproc240d.lib
Lecture 07: Buffers and Textures
 Lecture 07: Buffers and Textures CSE 40166 Computer Graphics Peter Bui University of Notre Dame, IN, USA October 26, 2010 OpenGL Pipeline Today s Focus Pixel Buffers: read and write image data to and from
Lecture 07: Buffers and Textures CSE 40166 Computer Graphics Peter Bui University of Notre Dame, IN, USA October 26, 2010 OpenGL Pipeline Today s Focus Pixel Buffers: read and write image data to and from
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
(21) OpenGL GUI. OpenGL GUI 1 UNIX MAGAZINE UNIX. SGI (Silicon Graphics Inc.) Windows PC GUI. UNIX Windows GUI. Java. 1 prefposition() X X
 (21) OpenGL GUI UNIX Windows Macintosh UNIX Windows PC SGI (Silicon Graphics Inc.) Windows PC GUI UNIX Windows GUI Java OpenGL OpenGL SGI 3 / GL GUI OpenGL GL OpenGL SGI 3 GL SGI 3 / 3 1 GL /* GL sample
(21) OpenGL GUI UNIX Windows Macintosh UNIX Windows PC SGI (Silicon Graphics Inc.) Windows PC GUI UNIX Windows GUI Java OpenGL OpenGL SGI 3 / GL GUI OpenGL GL OpenGL SGI 3 GL SGI 3 / 3 1 GL /* GL sample
Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole. Real Pinhole. Real + lens. Depth of field
 Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole Real Pinhole Real + lens Depth of field 1 Z-buffer How do we draw objects? Polygon Based Fast Raytracing Ray/Object intersections Slow Copyright Pixar 2 Raytracing for each
Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole Real Pinhole Real + lens Depth of field 1 Z-buffer How do we draw objects? Polygon Based Fast Raytracing Ray/Object intersections Slow Copyright Pixar 2 Raytracing for each
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL)
 Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam kielmann@cs.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction), ((57))
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam kielmann@cs.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction), ((57))
by modifying the glutinitwindowsize() function you can change the screen size to whatever you please.
 Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Computer Graphics 1 Computer Graphics 1
 Projects: an example Developed by Nate Robbins Shapes Tutorial What is OpenGL? Graphics rendering API high-quality color images composed of geometric and image primitives window system independent operating
Projects: an example Developed by Nate Robbins Shapes Tutorial What is OpenGL? Graphics rendering API high-quality color images composed of geometric and image primitives window system independent operating
RECITATION - 1. Ceng477 Fall
 RECITATION - 1 Ceng477 Fall 2007-2008 2/ 53 Agenda General rules for the course General info on the libraries GLUT OpenGL GLUI Details about GLUT Functions Probably we will not cover this part 3/ 53 General
RECITATION - 1 Ceng477 Fall 2007-2008 2/ 53 Agenda General rules for the course General info on the libraries GLUT OpenGL GLUI Details about GLUT Functions Probably we will not cover this part 3/ 53 General
Computer Graphics Course 2005
 Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Display Lists in OpenGL
 Display Lists in OpenGL Display lists are a mechanism for improving performance of interactive OpenGL applications. A display list is a group of OpenGL commands that have been stored for later execution.
Display Lists in OpenGL Display lists are a mechanism for improving performance of interactive OpenGL applications. A display list is a group of OpenGL commands that have been stored for later execution.
Assignment #6 2D Vector Field Visualization Arrow Plot and LIC
 Assignment #6 2D Vector Field Visualization Arrow Plot and LIC Due Oct.15th before midnight Goal: In this assignment, you will be asked to implement two visualization techniques for 2D steady (time independent)
Assignment #6 2D Vector Field Visualization Arrow Plot and LIC Due Oct.15th before midnight Goal: In this assignment, you will be asked to implement two visualization techniques for 2D steady (time independent)
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
OpenGL JOGL. OpenGL & JOGL. Shaoting Zhang, or Tony. September 12, 2007
 September 12, 2007 1 Program 2 HW: Graphing in I m Program Cross-language (C, C++, C#, Java, Python, Delphi) Cross-platform (Linux, Windows, Unix, PS3) Low-level (provides only rendering func.) State machine
September 12, 2007 1 Program 2 HW: Graphing in I m Program Cross-language (C, C++, C#, Java, Python, Delphi) Cross-platform (Linux, Windows, Unix, PS3) Low-level (provides only rendering func.) State machine
Graphics Programming
 Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
2. OpenGL -I. 2.1 What is OpenGL? Things OpenGL can do: -23-
 2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
Basic Graphics Programming
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL
 Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL What we are going to do OpenGL Glut Small Example using OpenGl and Glut Alexandra Junghans 2 What is OpenGL? OpenGL Two Parts most widely used and supported graphics API
Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL What we are going to do OpenGL Glut Small Example using OpenGl and Glut Alexandra Junghans 2 What is OpenGL? OpenGL Two Parts most widely used and supported graphics API
Interaction Computer Graphics I Lecture 3
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 3 Interaction Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations January 21, 2003 [Angel Ch. 3] Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 3 Interaction Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations January 21, 2003 [Angel Ch. 3] Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013
 CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
Graphics. Texture Mapping 고려대학교컴퓨터그래픽스연구실.
 Graphics Texture Mapping 고려대학교컴퓨터그래픽스연구실 3D Rendering Pipeline 3D Primitives 3D Modeling Coordinates Model Transformation 3D World Coordinates Lighting 3D World Coordinates Viewing Transformation 3D Viewing
Graphics Texture Mapping 고려대학교컴퓨터그래픽스연구실 3D Rendering Pipeline 3D Primitives 3D Modeling Coordinates Model Transformation 3D World Coordinates Lighting 3D World Coordinates Viewing Transformation 3D Viewing
20 GLuint objects; 36 Scale += 0.1; 37 break; 38 case GLUT_KEY_DOWN:
 1 1. 1 #include 2 #include 3 Program 1 (OpenGL Sample016) 4 // 5 static int MouseX = 0; // X 6 static int MouseY = 0; // Y 7 static float SpinX = 0; // X 8 static float SpinY = 0;
1 1. 1 #include 2 #include 3 Program 1 (OpenGL Sample016) 4 // 5 static int MouseX = 0; // X 6 static int MouseY = 0; // Y 7 static float SpinX = 0; // X 8 static float SpinY = 0;
6. Make use of glviewport() to display two sine curves on the same screen, one on the
 Duc Nguyen CSE-420: Computer Graphics 10/17/18 1. Modify lines.cpp to display lines in the following patterns: a. a long dash and a dot, (.. ) b. two close dots followed by a distant dot (...... ) 2. Modify
Duc Nguyen CSE-420: Computer Graphics 10/17/18 1. Modify lines.cpp to display lines in the following patterns: a. a long dash and a dot, (.. ) b. two close dots followed by a distant dot (...... ) 2. Modify
VR-programming tools (procedural) More VRML later in this course! (declarative)
 Realtime 3D Computer Graphics & Virtual Reality OpenGL Introduction VR-programming Input and display devices are the main hardware interface to users Immersion embeds users through the generation of live-like
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics & Virtual Reality OpenGL Introduction VR-programming Input and display devices are the main hardware interface to users Immersion embeds users through the generation of live-like
Chapter 9 Texture Mapping An Overview and an Example Steps in Texture Mapping A Sample Program Specifying the Texture Texture Proxy Replacing All or
 Chapter 9 Texture Mapping An Overview and an Example Steps in Texture Mapping A Sample Program Specifying the Texture Texture Proxy Replacing All or Part of a Texture Image One Dimensional Textures Using
Chapter 9 Texture Mapping An Overview and an Example Steps in Texture Mapping A Sample Program Specifying the Texture Texture Proxy Replacing All or Part of a Texture Image One Dimensional Textures Using
1)Write a shader program that renders a regular pentagon with textured image like the one shown below.
 Andrew Yenalavitch CSE520 Winter 2015 Quiz 2 Report 1)Write a shader program that renders a regular pentagon with textured image like the one shown below. Use the following provided image for the texture:
Andrew Yenalavitch CSE520 Winter 2015 Quiz 2 Report 1)Write a shader program that renders a regular pentagon with textured image like the one shown below. Use the following provided image for the texture:
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs Computer Graphics I, Fall
 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
Chapter 7 Display Lists
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 7 Display Lists Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Understand how display lists can
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 7 Display Lists Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Understand how display lists can
Source code: #include <iostream>
 Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 4 CSE 520 - Winter 2015 1. ( 10 points ) Write a program that finds the knot vector ( u 0,..., u n-1 ) of a B-spline. It asks for 'number of control points' and 'degree of spline'
Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 4 CSE 520 - Winter 2015 1. ( 10 points ) Write a program that finds the knot vector ( u 0,..., u n-1 ) of a B-spline. It asks for 'number of control points' and 'degree of spline'
Overview of Graphics Systems Hearn & Baker Chapter 2. Some slides are taken from Robert Thomsons notes.
 Overview of Graphics Systems Hearn & Baker Chapter 2 Some slides are taken from Robert Thomsons notes. OVERVIEW Video Display Devices Raster Scan Systems Graphics Workstations and Viewing Systems Input
Overview of Graphics Systems Hearn & Baker Chapter 2 Some slides are taken from Robert Thomsons notes. OVERVIEW Video Display Devices Raster Scan Systems Graphics Workstations and Viewing Systems Input
OpenGL/GLUT Intro. Week 1, Fri Jan 12
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
1) Here is the various stages of the tetrahedron:
 Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 3 CSE 520 - Winter 2015 1) ( 20 points ) Write a shader program that renders a colored tetrahedron, which gradually shrinks to a point and expands back to its original shape.
Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 3 CSE 520 - Winter 2015 1) ( 20 points ) Write a shader program that renders a colored tetrahedron, which gradually shrinks to a point and expands back to its original shape.
Input and Interaction. 1. Interaction. Chapter 3. Introduction: - We now turn to the development of interactive graphics programs.
 Input and Interaction Chapter 3 Introduction: - We now turn to the development of interactive graphics programs. - Our discussion has three main parts First, we consider the variety of devices available
Input and Interaction Chapter 3 Introduction: - We now turn to the development of interactive graphics programs. - Our discussion has three main parts First, we consider the variety of devices available
to OpenGL Introduction Pipeline Graphics pipeline OpenGL pipeline OpenGL syntax Modeling Arrays Conclusion 1 Introduction Introduction to OpenGL
 to to ning Lecture : introduction to Lab : first steps in and - 25/02/2009 Lecture/Lab : transformations and hierarchical - 04/03/2009 to Lecture : lights and materials in - 11/03/2009 Lab : lights and
to to ning Lecture : introduction to Lab : first steps in and - 25/02/2009 Lecture/Lab : transformations and hierarchical - 04/03/2009 to Lecture : lights and materials in - 11/03/2009 Lab : lights and
Introduction to OpenGL
 Introduction to OpenGL Tutorial 1: Create a window and draw a 2D square Introduction: The aim of the first tutorial is to introduce you to the magic world of graphics based on the OpenGL and GLUT APIs.
Introduction to OpenGL Tutorial 1: Create a window and draw a 2D square Introduction: The aim of the first tutorial is to introduce you to the magic world of graphics based on the OpenGL and GLUT APIs.
COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# March 25 th 2007 p1/15
 COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# 3257 495 9 March 25 th 2007 p1/15 Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student#: 3257 495 9 COS340A Date submitted: March 25, 2007 Question 1... p2 3 Question 2... p4 Question
COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# 3257 495 9 March 25 th 2007 p1/15 Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student#: 3257 495 9 COS340A Date submitted: March 25, 2007 Question 1... p2 3 Question 2... p4 Question
CS621 Lab 1 Name: Ihab Zbib
 CS621 Lab 1 Name: Ihab Zbib 1) The program draw.cpp draws two rectangles and two triangles. The program compiles and executes successfully. What follows are the snap shots of the output. Illustration 1:
CS621 Lab 1 Name: Ihab Zbib 1) The program draw.cpp draws two rectangles and two triangles. The program compiles and executes successfully. What follows are the snap shots of the output. Illustration 1:
Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Create applications that
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Create applications that
Computer Graphics Introduction to OpenGL
 Computer Graphics 2015 3. Introduction to OpenGL Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-09-28 2. 2D Graphics Algorithms (cont.) Rasterization Computer Graphics @ ZJU Hongxin Zhang,
Computer Graphics 2015 3. Introduction to OpenGL Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-09-28 2. 2D Graphics Algorithms (cont.) Rasterization Computer Graphics @ ZJU Hongxin Zhang,
1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back.
 Karl Zachary Maier CSE 520 Homework 1 1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back. /* morph.cpp */ #include #include #include
Karl Zachary Maier CSE 520 Homework 1 1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back. /* morph.cpp */ #include #include #include
CS Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
// double buffering and RGB glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGBA); // your own initializations
 #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
#include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
Rendering Pipeline/ OpenGL
 Chapter 2 Basics of Computer Graphics: Your tasks for the weekend Piazza Discussion Group: Register Post review questions by Mon noon Use private option, rev1 tag Start Assignment 1 Test programming environment
Chapter 2 Basics of Computer Graphics: Your tasks for the weekend Piazza Discussion Group: Register Post review questions by Mon noon Use private option, rev1 tag Start Assignment 1 Test programming environment
Transformation, Input and Interaction. Hanyang University
 Transformation, Input and Interaction Hanyang University Transformation, projection, viewing Pipeline of transformations Standard sequence of transforms Cornell CS4620 Fall 2008 Lecture 8 3 2008 Steve
Transformation, Input and Interaction Hanyang University Transformation, projection, viewing Pipeline of transformations Standard sequence of transforms Cornell CS4620 Fall 2008 Lecture 8 3 2008 Steve
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
Introduction to OpenGL
 Introduction to OpenGL Banafsheh Azari http://www.uni-weimar.de/cms/medien/cg.html What You ll See Today What is OpenGL? Related Libraries OpenGL Command Syntax B. Azari http://www.uni-weimar.de/cms/medien/cg.html
Introduction to OpenGL Banafsheh Azari http://www.uni-weimar.de/cms/medien/cg.html What You ll See Today What is OpenGL? Related Libraries OpenGL Command Syntax B. Azari http://www.uni-weimar.de/cms/medien/cg.html
Interaction. CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
Introduction to MS Visual C/C++
 3/4/2002 Burkhard Wünsche Introduction to C/C++ Page 1 of 9 0. Introduction: Introduction to MS Visual C/C++ This tutorial gives a simple introduction to MS Visual C/C++ with an emphasis on OpenGL graphics
3/4/2002 Burkhard Wünsche Introduction to C/C++ Page 1 of 9 0. Introduction: Introduction to MS Visual C/C++ This tutorial gives a simple introduction to MS Visual C/C++ with an emphasis on OpenGL graphics
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics
 CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Part 3 Anatomy of OpenGL Programs Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Reading Angel Chapter 2 Red Book Chapter 4 Matt Burlick - Drexel University
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Part 3 Anatomy of OpenGL Programs Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Reading Angel Chapter 2 Red Book Chapter 4 Matt Burlick - Drexel University
Fourier Series. Given a periodic function, x(t), (-T <t <T): + b n sin n t T. a n cos n t T. 2 a 0 + Z T. a n = 1 T. x(t) cos n t T. b n = 1 T.
 x(t) = 1 1X 2 a 0 + Fourier Series Given a periodic function, x(t), (-T
x(t) = 1 1X 2 a 0 + Fourier Series Given a periodic function, x(t), (-T
Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow
 Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow lgca.cpp // Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow 1 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 using namespace std;
Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow lgca.cpp // Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow 1 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 using namespace std;
Computer Graphics, Chapt 08
 Computer Graphics, Chapt 08 Creating an Image Components, parts of a scene to be displayed Trees, terrain Furniture, walls Store fronts and street scenes Atoms and molecules Stars and galaxies Describe
Computer Graphics, Chapt 08 Creating an Image Components, parts of a scene to be displayed Trees, terrain Furniture, walls Store fronts and street scenes Atoms and molecules Stars and galaxies Describe
PART-I: Lab for MCS-051 (Advanced Internet Technologies)
 PART-I: Lab for MCS-051 (Advanced Internet Technologies) Q.1. Write a Program using Servlet and JDBC for developing online application for students attendance management for MCA V semester students of
PART-I: Lab for MCS-051 (Advanced Internet Technologies) Q.1. Write a Program using Servlet and JDBC for developing online application for students attendance management for MCA V semester students of
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011
 Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
OpenGL refresher. Advanced Computer Graphics 2012
 Advanced Computer Graphics 2012 What you will see today Outline General OpenGL introduction Setting up: GLUT and GLEW Elementary rendering Transformations in OpenGL Texture mapping Programmable shading
Advanced Computer Graphics 2012 What you will see today Outline General OpenGL introduction Setting up: GLUT and GLEW Elementary rendering Transformations in OpenGL Texture mapping Programmable shading
BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 07 BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM /* * GL07BouncingBall.cpp: A ball bouncing inside the window */ #include // for MS Windows #include
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 07 BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM /* * GL07BouncingBall.cpp: A ball bouncing inside the window */ #include // for MS Windows #include
Drawing and Coordinate Systems
 Drawing and Coordinate Systems Coordinate Systems Screen Coordinate system World Coordinate system World window Viewport Window to viewport mapping Screen Coordinate System Glut OpenGL (0,0) Screen Coordinate
Drawing and Coordinate Systems Coordinate Systems Screen Coordinate system World Coordinate system World window Viewport Window to viewport mapping Screen Coordinate System Glut OpenGL (0,0) Screen Coordinate
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction
 Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring Department of Computer and Information Science
 Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1. I am located in room 4115 in EDIT-huset 2. Email: 3. Phone: 031-772 1775 (office) 4. Course assistant: Tomas Akenine-Mőller
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1. I am located in room 4115 in EDIT-huset 2. Email: 3. Phone: 031-772 1775 (office) 4. Course assistant: Tomas Akenine-Mőller
Lecture 2 Sections 3.6, 3.7. Fri, Aug 28, 2009
 User User Lecture 2 Sections 3.6, 3.7 Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Aug 28, 2009 Outline User 1 2 3 4 5 User Definition ( ) A callback function is a programmer-specified function that the library will call
User User Lecture 2 Sections 3.6, 3.7 Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Aug 28, 2009 Outline User 1 2 3 4 5 User Definition ( ) A callback function is a programmer-specified function that the library will call
1.2 Basic Graphics Programming
 Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 1.2 Basic Graphics Programming Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Last time Last Time Story Computer Graphics Image Last Time 3D Printing 3D Capture Animation Modeling
Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 1.2 Basic Graphics Programming Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Last time Last Time Story Computer Graphics Image Last Time 3D Printing 3D Capture Animation Modeling
