Εισαγωγή στην Επιστήμη και Τεχνολογία των Υπηρεσιών
|
|
|
- Darcy Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στην Επιστήμη και Τεχνολογία των Υπηρεσιών Ενότητα 6: XML, XSLT and XPATH - 2 Χρήστος Νικολάου Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών
2 Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται στην άδεια χρήσης Creative Commons και ειδικότερα Αναφορά Μη εμπορική Χρήση Όχι Παράγωγο Έργο v. 3.0 (Attribution Non Commercial Non-derivatives ) Εξαιρείται από την ως άνω άδεια υλικό που περιλαμβάνεται στις διαφάνειες του μαθήματος, και υπόκειται σε άλλου τύπου άδεια χρήσης. Η άδεια χρήσης στην οποία υπόκειται το υλικό αυτό αναφέρεται ρητώς.
3 Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί στα πλαίσια του εκπαιδευτικού έργου του διδάσκοντα. Το έργο «Ανοικτά Ακαδημαϊκά Μαθήματα στο Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης» έχει χρηματοδοτήσει μόνο τη αναδιαμόρφωση του εκπαιδευτικού υλικού. Το έργο υλοποιείται στο πλαίσιο του Επιχειρησιακού Προγράμματος «Εκπαίδευση και Δια Βίου Μάθηση» και συγχρηματοδοτείται από την Ευρωπαϊκή Ένωση (Ευρωπαϊκό Κοινωνικό Ταμείο) και από εθνικούς πόρους.
4 XML XSLT and XPATH (Part / II) David Silberberg Lecture 13 1
5 XPath Path of document elements and attributes is an important aspect of XSLT XPath provides a mechanism for pointing at parts of the source XML document XPath expressions specify location path in a document Step-by-step instructions about how to get to a place in the source document You need to know where you are to get to where you are going Thus, there is implicit context node in XPath. Primarily important for XSLT Also important for other XML tools such as XQuery, XPointer, etc. 2
6 XML Documents as Trees Augmented supplier.xml document <?xml version= 1.0?> <order> <!-- A single order --> <date> </date> <company cid= >Animal World</company> <item> </item> <for> </for> </order> <code version= 2.3 >CC-10456</code> <description>cat Chow</description> <qty>2</qty> <name>frank Thomas</name> <street>10 Maple Street</street> <city country= US >Columbia, MD 22222</city> 3
7 Document Representation Parts of a document are called nodes Elements Attributes Comments Processing Instructions Nodes are just parts of a document tree node-sets are sets of nodes If XPath specifies a location path for elements, several nodes may be returned The set of these nodes is called, not surprisingly, a node-set 4
8 Tree Representation of supplier.xml Document root?xml version 1.0 <order> <!-- A single order --> <date> <company >... Animal World cid
9 Document Root Matching the document root / <xsl:template match= / > </xsl:template> Document root serves as a reference for To move to the order node Absolute path /order <xsl:template match= /order > Relative path all other nodes Assuming that the root node (/) is the current context node order (without the absolute path from the root node) <xsl:template match= order > 6
10 Recursive Descent Descend the entire document looking for matches For example, look for all names in customer.xml //name The node name can be at any level Attributes are accessible with symbol To find the xml version /?xml/@version To find all versions in the document //@version Picks up /?xml/@version Picks up /order/item/code/@version 7
11 Recursive Descent (cont.) Recursive descent is very powerful. It is inefficient because entire document must be Use it sparingly! It can significantly slow your XSLT processor. read. 8
12 Specific Location Paths To access specific nodes: Match can be based on having sub-elements Match can be based on having sub-attributes Search for nodes with specific data values Use the [] notation Filters the nodes selected /order[date] Matches all tags <order> that are direct children of the document root (/) and that also have a date element (<date>) child order[date] Matches all tags <order> that are direct children of current context and that also have a date element (<date>) child 9
13 Specific Location Paths (cont.) Matches all tags <company> that are direct children of the current context and that also have a cid attribute company[@cid = ] Matches all tags <company> that are direct children of the current context and that also have a cid attribute with value Notice that single quotes are used. This is because the XPath expression will be inside of double quotes. <xsl:template match= company[@cid= ] > This could be reversed - just need to keep it straight <xsl:template match='company[@cid=" "]'> 10
14 Specific Location Paths (cont.) Matches all attributes cid that are attributes of elements <company> with respect to the current context order[company = Animal World ] Matches all tags <order> that are direct children of the current context and that also have a company element with a value Animal World company[. = Animal World ] Matches all tags <company> that are direct children of the current context and that also have a value Animal World 11
15 Specific Location Paths (cont.) Location paths can be arbitrarily complex = 2.3 ] Matches all tags <code> that are direct or indirect descendents of the <order> tag, which is a direct child of the document root, and that has an attribute version with a value of 2.3. //order[company/@cid = ] Matches all tags <order> that are direct or indirect descendents of the document root and that have a child element <company> that has an attribute cid with a value of
16 Reading Location Paths /order[date = ]/item/code[@version First, break it down into the path /order/item/code Then, select the most specific elements /order/item/code[@version = 2.3 ] Finally, select only those paths with certain dates /order[date = ]/item/code[@version = 2.3 ] With a little practice, it should become easy to read. = 2.3 ] 13
17 XPath Functions Sometimes, pure path expressions are not powerful enough to retrieve what is desired Beyond parent/child and element/attribute Can work with strings and numbers Can format values for output Syntax: function(parameters) function() relationships 14
18 Node Functions - name() Node functions work with nodes name() Returns the name of the node Can be called with a parameter: name(.) Name of context node Same as name() To return a sorted list of names of nodes that are children of <order>: <xsl:template match= /order > <xsl:for-each select= * > <p><xsl:sort select= name() /></p> </xsl:for-each> </xsl:template> 15
19 Node Functions - node() node() returns the node Same as. Not really necessary itself 16
20 Node Functions - processing-instruction() Returns processing instructions This: <xsl:template match= processing-instruction() > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:template> Returns all processing instructions This: <xsl:template match= processing-instruction( xml ) > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:template> Returns?xml processing instructions: <?xml version= 1.0?> Not all parser return the <?xml?> element 17
21 Node Functions - comment() Matches comments in the XML document This: <xsl:template match= //comment() > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:template> Returns all the comments in the <!-- A single order --> XML document: Parsers are not required to return comments so your may never get a comment to process. XSLT 18
22 Node Functions - text() Text lets you select the PCDATA content of a node When you match a node, you generally get back and all of its descendents. Example XML fragment: <outerlayer> This is text for the outer layer <middlelayer> This is text for the middle layer <innerlayer> This is text for the inner layer </innerlayer> </middlelayer> </outerlayer> the node 19
23 Node Functions - text() - (cont.) Applying this: <xsl:output method="text /> <xsl:template match= outerlayer > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:template > Yields all outerlayer, middlelayer, and innerlayer text This is text for the outer layer This is text for the middle layer This is text for the inner layer 20
24 Node Functions - text() - (cont.) To get just the outerlayer text, apply this: <xsl:output method="text /> <xsl:template match= outerlayer > <xsl:value-of select= text() /> </xsl:template > This yields only: This is text for the outer layer 21
25 Positional Functions - position() When you want the position of a node within a node-set Using customer.xml, get the position of William Tell Yields: <xsl:template match= //name[. = Tell, William ] > <xsl:value-of select= position() /> </xsl:template > <xsl:template match="//name"/> 2 Because: Node set is: text - <name> - text - <name> - text "Tell, William" is the first element of <bad> customers 22
26 Positional Functions - position() - (cont.) When you want to search for a node at a specific position To look for the second name, apply the <xsl:template match= //name[position() = 2] > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:template > <xsl:template match="//name"/> Which yields: Li, Sue Carr, Sam Shorthand notation <xsl:template match= //name[2] > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:template > template: 23
27 Positional Functions - last() Use last() to find the last position in a node set. <xsl:template match= //name[position() = last()] > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:template > <xsl:template match= //name"/> Which yields: Carnot, John Carr, Sam 24
28 Positional Functions - last()-1 Use last() to find the next to last position in a node set. <xsl:template match= //name[position() = last()-1] > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:template > <xsl:template match= //name"/> Which yields: Li, Sue Tell, William 25
29 Positional Functions - count() Use count() to find the number of elements in a node set. <xsl:template match= / > <xsl:value-of select= count(//name) /> </xsl:template > Which yields: 5 26
30 Numeric Functions - number() The number function converts PCDATA from a character string to a number To get a numeric count of the number of items ordered: <xsl:template match= / > <xsl:value-of select= number(/order/item/qty) /> </xsl:template > This yields the number: 2 27
31 Numeric Functions - sum() Produces the sum of a node-set Given an XML document: <employee id= > <hours day= 1 >7</hours> <hours day= 2 >10</hours> <hours day= 3 >7</hours> <hours day= 4 >8</hours> <hours day= 5 >8</hours> </employee> Apply to get the total hours worked for the week (40): <xsl:template match= / > <xsl:value-of select= sum(employee/hours) /> </xsl:template> 28
32 Boolean Functions - boolean() Used for boolean math boolean() Evaluates to either true or false If value is number, it is false if value is 0 and true otherwise If value is string, it is true if the length > 0 and false otherwise If value is node-set, it is false if empty and true otherwise Applied to customers.xml <xsl:template match= / > <xsl:if test= boolean(//name) > <p>we have some customers :-)</p> </xsl:if> </xsl:template> 29
33 Boolean Functions - not() Test the opposite condition of boolean Applied to customers.xml statement <xsl:template match= / > <xsl:if test= not(boolean(//name)) > <p>we do not have any customers :-(</p> </xsl:if> </xsl:template> 30
34 Boolean Functions - true() and false() true() and false() always respectively. Useful for debugging evaluate to true and false, <xsl:template match= / > <xsl:if test= true() > <p>always print this line.</p> </xsl:if> </xsl:template> 31
35 String Functions - string() Converts any value to a string Useful for converting from string to numbers, calculations, and converting back to string. performing <xsl:template match= / > <p> The number of hours worked this week is: <xsl:value-of select= string(sum(employee/hours)) /> </p> </xsl:template> 32
36 String Functions - string-length() Finds the length of the string To length of each customer name <xsl:template match= //name > <xsl:value-of select= string-length() /> </xsl:template > 33
37 String Functions - contains() Determines if a substring is contained in a string Prints all customers with the string William names <xsl:template match= //name > <xsl:if test= contains(., William ) > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:if> </xsl:template > This yields: Tell, William in their contains() is case-sensitive, like all string functions. 34
38 String Functions - starts-with() Determines if a string starts with a certain string. Prints all customers with last names that <xsl:template match= //name > <xsl:if test= starts-with(text(), L ) > <xsl:value-of select=. /> </xsl:if> </xsl:template > start with L Yields: Li, Sue 35
39 String Functions - substring() Finds a substring of a string Applying to customer.xml: Yields: <xsl:template match= //name[1] > <xsl:value-of select= substring(., 8) /> </xsl:template > <xsl:template match="//name"/> Fred illiam This works as well: <xsl:template match= //name[1] > <xsl:value-of select= substring(., </xsl:template > <xsl:template match="//name"/> 8, 4) /> 36
40 String Functions - substring-after() Finds substring after a string Applying to customer.xml: <xsl:template match= //name[1] > <xsl:value-of select= substring-after(.,, ) /> </xsl:template > <xsl:template match="//name"/> Yields: Fred William 37
41 String Functions - substring-before() Finds substring before a string Applying to customer.xml: Yields: <xsl:template match= //name[1] > <xsl:value-of select= substring-before(.,, ) /> </xsl:template > <xsl:template match="//name"> Jones Tell 38
42 String Functions - concat() Puts multiple strings together Applying to customer.xml: <xsl:template match= //name[1] > <xsl:value-of select= concat(substring-after(.,, ),, substring-before(.,, )) /> </xsl:template > <xsl:template Yields: Fred Jones William Tell match="//name"> 39
43 String Functions - translate() Translates one character set to another translate(string-to-translate, match-string, translate-string) Applying to customer.xml: Yields <xsl:template match= //name > <xsl:value-of select= translate(., abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz, bcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyza ) /> </xsl:template > Jpoft, Fsfe Lf, Svf Cbsopu, Jpio Temm, Wjmmjbn Cbss, Sbn 40
44 String Functions - translate() - (cont.) Remember that translate is case-sensitive If the second string is longer than the third string, the extra character is stripped out of the result translate( abcd, bcd, BC ) Yields: abc 41
45 Axis Names Axis names are a way to specify any node of a document with respect to any other node (or itself) Up until now, we dealt with parents and children. Now, we can use axis names to deal with other node relationships. 42
46 Remember supplier.xml? Document root?xml version 1.0 <order> <!-- A single order --> <date> <company >... Animal World cid
47 self child Some Axis Commands The self axis refers to the node at the current context. is equal to self::node() <xsl:for-each select=. > = <xsl:for-each select= self::node() > If current context is the <order> tag, then both produce <order> Child is used most often so it is the default date is equal to child::date <xsl:for-each select= date > = <xsl:for-each select= child::date > If our current context is the <order> tag, then both produce <date> 44
48 More on Children child child::* produces all children elements of the current context <xsl:for-each select= * > = <xsl:for-each select= child::* > If current node is <order>, this produces <date>, <company>, etc. child::@* produces all children attributes of the current <xsl:for-each > = <xsl:for-each select= child::@* > = <xsl:for-each select= attribute::* > If current node is <company>, this produces cid context 45
49 Descendants descendent descendent::date produces all elements <date> which are children, childrens children, etc. elements of the current context <xsl:for-each select= descendent::date > If current node is <order> or the document root (/), this produces <date> descendent-or-self descendent-or-self::date produces all elements <date> which are the same, children, childrens children, etc. elements of the current context <xsl:for-each select= descendent-or-self::date > = <xsl:for-each select=.//date > If current node is <date>, <order>, or the document root (/), this produces <date> 46
50 Ancestors parent parent::order produces the element <order> which is a parent of the current context <xsl:for-each select= parent::order > = <xsl:for-each select=../order > If current node is <date>, this produces <order> <xsl:for-each select= date/parent::order > = <xsl:for-each select= date/../order > 47
51 Ancestors (cont.) ancestor ancestor::order produces the element <order> which is an ancestor of the current node <xsl:for-each select= ancestor::order > If current node is <date>, <company>, cid, etc., this produces <order> ancestor-or-self ancestor-or-self::order produces the element <order> which is an ancestor of the current node or the current node itself <xsl:for-each select= ancestor-or-self::order > If current node is <date>, <company>, cid, etc., this produces <order> 48
52 Siblings following-sibling following-sibling::company produces the next element <company> which is the sibling following the current node <xsl:for-each select= /order/date/following-sibling::company > This produces <company>, etc. Does not work for attributes preceding-sibling preceding-sibling::date produces the previous element <date> which is the sibling preceding the current node <xsl:for-each select= /order/date/company/preceding-sibling::date > This produces the previous element: <date> Does not work for attributes 49
53 Siblings (cont.) following following::* produces the next elements (including descendents) which follow the current node <xsl:for-each select= /following::* > produces all the next elements of the root node: <order>, <date>, <company>, etc. preceding preceding::* produces the preceding elements of the current node <xsl:for-each select= /order/date/company/preceding::* > This produces all the previous elements: <date>, <order>, and root 50
54 Τέλος Ενότητας
Εισαγωγή στον Προγραμματισμό Introduction to Programming
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στον Προγραμματισμό Introduction to Programming Διάλεξη 9: Ροή Εισόδου/Εξόδου Γ. Παπαγιαννάκης Άδειες Χρήσης - Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται στην
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στον Προγραμματισμό Introduction to Programming Διάλεξη 9: Ροή Εισόδου/Εξόδου Γ. Παπαγιαννάκης Άδειες Χρήσης - Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται στην
Εισαγωγή στα Δίκτυα Υπηρεσιών
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στα Δίκτυα Υπηρεσιών Assisting Lecture 6 - Java Restful Web Services Examples (JAX-RS) Μύρων Παπαδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών CS-592: Introduction
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στα Δίκτυα Υπηρεσιών Assisting Lecture 6 - Java Restful Web Services Examples (JAX-RS) Μύρων Παπαδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών CS-592: Introduction
Συστήματα Διαχείρισης Βάσεων Δεδομένων
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Συστήματα Διαχείρισης Βάσεων Δεδομένων Διάλεξη 3η: Access methods: Hash Indexes Δημήτρης Πλεξουσάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών ACCESS METHODS: HASH INDEXES 1 Hash
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Συστήματα Διαχείρισης Βάσεων Δεδομένων Διάλεξη 3η: Access methods: Hash Indexes Δημήτρης Πλεξουσάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών ACCESS METHODS: HASH INDEXES 1 Hash
Εισαγωγή στα Δίκτυα Υπηρεσιών
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στα Δίκτυα Υπηρεσιών Assisting Lecture 10 WS-BPEL Mύρων Παπαδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Introduction to Service Networks CS-592 Spring 2014 Assisting
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στα Δίκτυα Υπηρεσιών Assisting Lecture 10 WS-BPEL Mύρων Παπαδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Introduction to Service Networks CS-592 Spring 2014 Assisting
Εισαγωγή στον Προγραμματισμό Introduction to Programming
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στον Προγραμματισμό Introduction to Programming Διάλεξη 14.β: Συναρτήσεις και Γραφικά Γ. Παπαγιαννάκης Άδειες Χρήσης - Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Εισαγωγή στον Προγραμματισμό Introduction to Programming Διάλεξη 14.β: Συναρτήσεις και Γραφικά Γ. Παπαγιαννάκης Άδειες Χρήσης - Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται
Υλοποίηση γλωσσών συναρτησιακού προγραμματισμού
 Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Τομέας Τεχνολογίας Πληροφορικής και Υπολογιστών Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Γλώσσες Προγραμματισμού ΙΙ Διδάσκοντες: Νικόλαος Παπασπύρου, Κωστής Σαγώνας
Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Τομέας Τεχνολογίας Πληροφορικής και Υπολογιστών Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Γλώσσες Προγραμματισμού ΙΙ Διδάσκοντες: Νικόλαος Παπασπύρου, Κωστής Σαγώνας
Εξόρυξη γνώσης από Βάσεις Δεδομένων και τον Παγκόσμιο Ιστό
 Εξόρυξη γνώσης από Βάσεις Δεδομένων και τον Παγκόσμιο Ιστό Ενότητα # 1: Εισαγωγή Διδάσκων: Μιχάλης Βαζιργιάννης Τμήμα: Προπτυχιακό Πρόγραμμα Σπουδών Πληροφορικής Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό
Εξόρυξη γνώσης από Βάσεις Δεδομένων και τον Παγκόσμιο Ιστό Ενότητα # 1: Εισαγωγή Διδάσκων: Μιχάλης Βαζιργιάννης Τμήμα: Προπτυχιακό Πρόγραμμα Σπουδών Πληροφορικής Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό
Διδάσκοντες: Π. Αγγελάτος, Δ. Ζήνδρος Επιμέλεια διαφανειών: Δ. Ζήνδρος Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών
 Διδάσκοντες: Π. Αγγελάτος, Δ. Ζήνδρος Επιμέλεια διαφανειών: Δ. Ζήνδρος Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης Creative
Διδάσκοντες: Π. Αγγελάτος, Δ. Ζήνδρος Επιμέλεια διαφανειών: Δ. Ζήνδρος Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης Creative
Ψηφιακή Επεξεργασία Εικόνας
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΪΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ψηφιακή Επεξεργασία Εικόνας Τμηματοποίηση εικόνας Διδάσκων : Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Νίκου Χριστόφορος Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΪΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ψηφιακή Επεξεργασία Εικόνας Τμηματοποίηση εικόνας Διδάσκων : Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Νίκου Χριστόφορος Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται
Computer Science E-259
 Computer Science E-259 XML with Java Lecture 4: XPath 1.0 (and 2.0) and XSLT 1.0 (and 2.0) 21 February 2007 David J. Malan malan@post.harvard.edu 1 Computer Science E-259 Last Time DOM Level 3 JAXP 1.3
Computer Science E-259 XML with Java Lecture 4: XPath 1.0 (and 2.0) and XSLT 1.0 (and 2.0) 21 February 2007 David J. Malan malan@post.harvard.edu 1 Computer Science E-259 Last Time DOM Level 3 JAXP 1.3
XML & Databases. Tutorial. 3. XPath Queries. Universität Konstanz. Database & Information Systems Group Prof. Marc H. Scholl
 XML & Databases Tutorial Christian Grün, Database & Information Systems Group University of, Winter 2007/08 XPath Introduction navigational access to XML documents sub-language in XQuery, XSLT, or XPointer
XML & Databases Tutorial Christian Grün, Database & Information Systems Group University of, Winter 2007/08 XPath Introduction navigational access to XML documents sub-language in XQuery, XSLT, or XPointer
Course: The XPath Language
 1 / 27 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble, 2012 2013 2 / 27 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any kind of
1 / 27 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble, 2012 2013 2 / 27 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any kind of
XML databases. Jan Chomicki. University at Buffalo. Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9
 XML databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9 Outline 1 XML data model 2 XPath 3 XQuery Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 2
XML databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9 Outline 1 XML data model 2 XPath 3 XQuery Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 2
XSLT: How Do We Use It?
 XSLT: How Do We Use It? Nancy Hallberg Nikki Massaro Kauffman 1 XSLT: Agenda Introduction & Terminology XSLT Walkthrough Client-Side XSLT/XHTML Server-Side XSLT/XHTML More Creative Server-Side XSLT 2 XSLT:
XSLT: How Do We Use It? Nancy Hallberg Nikki Massaro Kauffman 1 XSLT: Agenda Introduction & Terminology XSLT Walkthrough Client-Side XSLT/XHTML Server-Side XSLT/XHTML More Creative Server-Side XSLT 2 XSLT:
Course: The XPath Language
 1 / 30 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble Alpes, 2017 2018 2 / 30 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any
1 / 30 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble Alpes, 2017 2018 2 / 30 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any
Web Services Week 3. Fall Emrullah SONUÇ. Department of Computer Engineering Karabuk University
 Web Services Week 3 Emrullah SONUÇ Department of Computer Engineering Karabuk University Fall 2017 1 Recap XML, Writing XML Rules for Writing XML Elements, Attributes, and Values XSL, XSLT 2 Contents Homework
Web Services Week 3 Emrullah SONUÇ Department of Computer Engineering Karabuk University Fall 2017 1 Recap XML, Writing XML Rules for Writing XML Elements, Attributes, and Values XSL, XSLT 2 Contents Homework
XPath Lecture 34. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Apr 11, 2012
 XPath Lecture 34 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPathLecture 34 Wed, Apr 11, 2012 1 / 20 1 XPath Functions 2 Predicates 3 Axes Robb T.
XPath Lecture 34 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPathLecture 34 Wed, Apr 11, 2012 1 / 20 1 XPath Functions 2 Predicates 3 Axes Robb T.
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 9. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 9 Dr Nick Hayward DEV Week assessment Course total = 25% project outline and introduction developed using a chosen markup language consider and
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 9 Dr Nick Hayward DEV Week assessment Course total = 25% project outline and introduction developed using a chosen markup language consider and
H2 Spring B. We can abstract out the interactions and policy points from DoDAF operational views
 1. (4 points) Of the following statements, identify all that hold about architecture. A. DoDAF specifies a number of views to capture different aspects of a system being modeled Solution: A is true: B.
1. (4 points) Of the following statements, identify all that hold about architecture. A. DoDAF specifies a number of views to capture different aspects of a system being modeled Solution: A is true: B.
TDDD43. Theme 1.2: XML query languages. Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p:// TDDD43
 Theme 1.2: XML query languages Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p://www.ida.liu.se/~ Query languages for XML Xpath o Path expressions with conditions o Building block of other standards (XQuery, XSLT, XLink, XPointer,
Theme 1.2: XML query languages Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p://www.ida.liu.se/~ Query languages for XML Xpath o Path expressions with conditions o Building block of other standards (XQuery, XSLT, XLink, XPointer,
ARM Compiler and assembly on QEMU
 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering N.T.U.A. Embedded System Design Dimitrios Soudris ARM Compiler and assembly on QEMU Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης Creative
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering N.T.U.A. Embedded System Design Dimitrios Soudris ARM Compiler and assembly on QEMU Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης Creative
Generating Web Pages Using XSLT
 Generating Web Pages Using XSLT 238 XSLT for Data Interchange 239 6.1.xml: An Employee List Document
Generating Web Pages Using XSLT 238 XSLT for Data Interchange 239 6.1.xml: An Employee List Document
Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda
 NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 6 XSLT 9. 4. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline XSLT Principles Templates Instructions
NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 6 XSLT 9. 4. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline XSLT Principles Templates Instructions
XML Data Management. 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath
 XML Data Management 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath Werner Nutt based on slides by Sara Cohen, Jerusalem 1 Extracting Data from XML Data stored in an XML document must be extracted to use it with various
XML Data Management 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath Werner Nutt based on slides by Sara Cohen, Jerusalem 1 Extracting Data from XML Data stored in an XML document must be extracted to use it with various
Introduction to XSLT. Version 1.0 July nikos dimitrakas
 Introduction to XSLT Version 1.0 July 2011 nikos dimitrakas Table of contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 XSLT... 3 1.2 PREREQUISITES... 3 1.3 STRUCTURE... 3 2 SAMPLE DATA... 4 3 XSLT... 6 4 EXAMPLES... 7
Introduction to XSLT Version 1.0 July 2011 nikos dimitrakas Table of contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 XSLT... 3 1.2 PREREQUISITES... 3 1.3 STRUCTURE... 3 2 SAMPLE DATA... 4 3 XSLT... 6 4 EXAMPLES... 7
Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef
 Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef Author(s) Thomas Eitzenberger Version 0.2 Status Ready for review Page 1 of 11 Content Selecting Nodes...3 Predicates...3 Selecting Unknown Nodes...4 Selecting Several Paths...5
Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef Author(s) Thomas Eitzenberger Version 0.2 Status Ready for review Page 1 of 11 Content Selecting Nodes...3 Predicates...3 Selecting Unknown Nodes...4 Selecting Several Paths...5
XPath and XSLT. Overview. Context. Context The Basics of XPath. XPath and XSLT. Nodes Axes Expressions. Stylesheet templates Transformations
 XPath and XSLT Michael B. Spring Department of Information Science and Telecommunications University of Pittsburgh spring@imap.pitt.edu http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~spring Context The Basics of XPath Nodes
XPath and XSLT Michael B. Spring Department of Information Science and Telecommunications University of Pittsburgh spring@imap.pitt.edu http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~spring Context The Basics of XPath Nodes
6/3/2016 8:44 PM 1 of 35
 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 1 of 35 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 2 of 35 2) Background Well-formed XML HTML XSLT Processing Model 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 3 of 35 3) XPath XPath locates items within an XML file It relies on the XML
6/3/2016 8:44 PM 1 of 35 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 2 of 35 2) Background Well-formed XML HTML XSLT Processing Model 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 3 of 35 3) XPath XPath locates items within an XML file It relies on the XML
Semi-structured Data. 8 - XPath
 Semi-structured Data 8 - XPath Andreas Pieris and Wolfgang Fischl, Summer Term 2016 Outline XPath Terminology XPath at First Glance Location Paths (Axis, Node Test, Predicate) Abbreviated Syntax What is
Semi-structured Data 8 - XPath Andreas Pieris and Wolfgang Fischl, Summer Term 2016 Outline XPath Terminology XPath at First Glance Location Paths (Axis, Node Test, Predicate) Abbreviated Syntax What is
Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 Learning Programming Using VISUAL BASIC.NET
 Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 APPENDIX D XSLT XSLT is a programming language defined by the World Wide Web Consortium, W3C (http://www.w3.org/tr/xslt), that provides the mechanism to transform a
Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 APPENDIX D XSLT XSLT is a programming language defined by the World Wide Web Consortium, W3C (http://www.w3.org/tr/xslt), that provides the mechanism to transform a
One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while
 1 One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while leaving the engine to choose the best way of fulfilling
1 One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while leaving the engine to choose the best way of fulfilling
XPath. Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
 XPath Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Overview What is XPath? Queries The XPath Data Model Location Paths Expressions
XPath Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Overview What is XPath? Queries The XPath Data Model Location Paths Expressions
Computer Science E-259
 Computer Science E-259 XML with Java Lecture 5: XPath 1.0 (and 2.0) and XSLT 1.0 (and 2.0), Continued 22 October 2007 David J. Malan malan@post.harvard.edu 1 Computer Science E-259 Last Time CSS Level
Computer Science E-259 XML with Java Lecture 5: XPath 1.0 (and 2.0) and XSLT 1.0 (and 2.0), Continued 22 October 2007 David J. Malan malan@post.harvard.edu 1 Computer Science E-259 Last Time CSS Level
XML Data Management. 6. XPath 1.0 Principles. Werner Nutt
 XML Data Management 6. XPath 1.0 Principles Werner Nutt 1 XPath Expressions and the XPath Document Model XPath expressions are evaluated over documents XPath operates on an abstract document structure
XML Data Management 6. XPath 1.0 Principles Werner Nutt 1 XPath Expressions and the XPath Document Model XPath expressions are evaluated over documents XPath operates on an abstract document structure
XML. Objectives. Duration. Audience. Pre-Requisites
 XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT. CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University
 Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XPath Language for addressing parts of an XML document XSLT Xpointer XQuery Tree model based on DOM W3C Recommendation
Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XPath Language for addressing parts of an XML document XSLT Xpointer XQuery Tree model based on DOM W3C Recommendation
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2008S-19 B-Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 19-0: Indexing Operations: Add an element Remove an element Find an element,
Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2008S-19 B-Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 19-0: Indexing Operations: Add an element Remove an element Find an element,
Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4
 Chapter 4 CHAPTER 4 Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4 Path expressions are used to navigate input documents to select elements and attributes of interest. This chapter explains how to use path expressions
Chapter 4 CHAPTER 4 Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4 Path expressions are used to navigate input documents to select elements and attributes of interest. This chapter explains how to use path expressions
XML Technologies. Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. Web pages:
 XML Technologies Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. holubova@ksi.mff.cuni.cz Web pages: http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~holubova/nprg036/ Outline Introduction to XML format, overview of XML technologies DTD
XML Technologies Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. holubova@ksi.mff.cuni.cz Web pages: http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~holubova/nprg036/ Outline Introduction to XML format, overview of XML technologies DTD
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis
 T O Y H Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 26 February 2013 Semester 2 Week 6 E H U N I V E R S I
T O Y H Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 26 February 2013 Semester 2 Week 6 E H U N I V E R S I
XSLT. Lecture 38. Robb T. Koether. Mon, Apr 21, Hampden-Sydney College. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XSLT Mon, Apr 21, / 26
 XSLT Lecture 38 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Apr 21, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XSLT Mon, Apr 21, 2014 1 / 26 1 XSLT 2 Running XSLT 3 XSLT Files 4 Output Modes 5 XSLT
XSLT Lecture 38 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Apr 21, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XSLT Mon, Apr 21, 2014 1 / 26 1 XSLT 2 Running XSLT 3 XSLT Files 4 Output Modes 5 XSLT
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contents. Part I: Introduction 1. Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3. Chapter 2: Well-Formed XML 23. Acknowledgments
 Acknowledgments Introduction ix xxvii Part I: Introduction 1 Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3 Of Data, Files, and Text 3 Binary Files 4 Text Files 5 A Brief History of Markup 6 So What Is XML? 7 What Does XML
Acknowledgments Introduction ix xxvii Part I: Introduction 1 Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3 Of Data, Files, and Text 3 Binary Files 4 Text Files 5 A Brief History of Markup 6 So What Is XML? 7 What Does XML
XPath an XML query language
 XPath an XML query language Some XML query languages: XML-QL XPath XQuery Many others 1 XML-QL http://www.w3.org/tr/note-xml-ql (8/98) Features: regular path expressions patterns, templates Skolem Functions
XPath an XML query language Some XML query languages: XML-QL XPath XQuery Many others 1 XML-QL http://www.w3.org/tr/note-xml-ql (8/98) Features: regular path expressions patterns, templates Skolem Functions
EXAM XML 1.1 and Related Technologies TYPE: DEMO
 IBM EXAM - 000-142 XML 1.1 and Related Technologies TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/000-142.html 1 Question: 1 XML data is stored and retrieved within a relational database for a data-centric application
IBM EXAM - 000-142 XML 1.1 and Related Technologies TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/000-142.html 1 Question: 1 XML data is stored and retrieved within a relational database for a data-centric application
Presentation. Separating Content and Presentation Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) XML and XSLT
 Presentation Separating Content and Presentation Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) XML and XSLT WordPress Projects Theme Generators WYSIWYG editor Look at tools to support generation of themes Design a new
Presentation Separating Content and Presentation Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) XML and XSLT WordPress Projects Theme Generators WYSIWYG editor Look at tools to support generation of themes Design a new
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis
 Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 23 February 2016 Semester 2 Week 6 http://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da16
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 23 February 2016 Semester 2 Week 6 http://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da16
Outline of this part (I) Part IV. Querying XML Documents. Querying XML Documents. Outline of this part (II)
 Outline of this part (I) Part IV Querying XML Documents Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2007/08 164 8 XPath Navigational access to XML documents Overview Context Location steps Navigation
Outline of this part (I) Part IV Querying XML Documents Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2007/08 164 8 XPath Navigational access to XML documents Overview Context Location steps Navigation
Introduction to Concurrent Programming
 Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Τομέας Τεχνολογίας Πληροφορικής και Υπολογιστών Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Γλώσσες Προγραμματισμού ΙΙ Διδάσκοντες: Νικόλαος Παπασπύρου, Κωστής Σαγώνας
Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Τομέας Τεχνολογίας Πληροφορικής και Υπολογιστών Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Γλώσσες Προγραμματισμού ΙΙ Διδάσκοντες: Νικόλαος Παπασπύρου, Κωστής Σαγώνας
Databases and Information Systems 1. Prof. Dr. Stefan Böttcher
 9. XPath queries on XML data streams Prof. Dr. Stefan Böttcher goals of XML stream processing substitution of reverse-axes an automata-based approach to XPath query processing Processing XPath queries
9. XPath queries on XML data streams Prof. Dr. Stefan Böttcher goals of XML stream processing substitution of reverse-axes an automata-based approach to XPath query processing Processing XPath queries
XML and Databases. Lecture 9 Properties of XPath. Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW
 XML and Databases Lecture 9 Properties of XPath Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW CSE@UNSW -- Semester 1, 2009 Outline 1. XPath Equivalence 2. No Looking Back: How to Remove Backward Axes 3. Containment
XML and Databases Lecture 9 Properties of XPath Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW CSE@UNSW -- Semester 1, 2009 Outline 1. XPath Equivalence 2. No Looking Back: How to Remove Backward Axes 3. Containment
Generating Variants Using XSLT Tutorial
 Table of Contents 1. Overview... 1 2. About this tutorial... 1 3. Setting up the pure::variants project... 1 4. Setting up the feature model... 3 5. Setting up the family model... 4 6. Setting up the XSLT
Table of Contents 1. Overview... 1 2. About this tutorial... 1 3. Setting up the pure::variants project... 1 4. Setting up the feature model... 3 5. Setting up the family model... 4 6. Setting up the XSLT
XSLT. Announcements (October 24) XSLT. CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems. Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due November 9
 XSLT CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements (October 24) 2 Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due November 9 XSLT 3 XML-to-XML rule-based transformation language Used most
XSLT CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements (October 24) 2 Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due November 9 XSLT 3 XML-to-XML rule-based transformation language Used most
Term selector datatype
 Term selector datatype Installation Guide Xuntos B.V. www.xuntos.nl Oktober 2012 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 XML Data save example... 3 Revision History... 3 Before installing this package... 4
Term selector datatype Installation Guide Xuntos B.V. www.xuntos.nl Oktober 2012 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 XML Data save example... 3 Revision History... 3 Before installing this package... 4
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis
 Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 28 February 2017 Semester 2 Week 6 https://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da17
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 28 February 2017 Semester 2 Week 6 https://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da17
XML Query Reformulation for XPath, XSLT and XQuery
 XML Query Reformulation for XPath, XSLT and XQuery (Sven.Groppe@deri.org, http://members.deri.at/~sveng/) Tutorial at DBA 2006/Innsbruck 2/17/2006 1:29:13 Copyright 2006 Digital Enterprise Research Institute.
XML Query Reformulation for XPath, XSLT and XQuery (Sven.Groppe@deri.org, http://members.deri.at/~sveng/) Tutorial at DBA 2006/Innsbruck 2/17/2006 1:29:13 Copyright 2006 Digital Enterprise Research Institute.
XPath Expression Syntax
 XPath Expression Syntax SAXON home page Contents Introduction Constants Variable References Parentheses and operator precedence String Expressions Boolean Expressions Numeric Expressions NodeSet expressions
XPath Expression Syntax SAXON home page Contents Introduction Constants Variable References Parentheses and operator precedence String Expressions Boolean Expressions Numeric Expressions NodeSet expressions
XPath. Lecture 36. Robb T. Koether. Wed, Apr 16, Hampden-Sydney College. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, / 28
 XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
~ Ian Hunneybell: DIA Revision Notes ~
 XML is based on open standards, and is text-based, thereby making it accessible to all. It is extensible, thus allowing anyone to customise it for their own needs, to publish for others to use, and to
XML is based on open standards, and is text-based, thereby making it accessible to all. It is extensible, thus allowing anyone to customise it for their own needs, to publish for others to use, and to
XML. Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior
 XML Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior XML INTRODUCTION 2 THE XML LANGUAGE XML: Extensible Markup Language Standard for the presentation and transmission of information.
XML Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior XML INTRODUCTION 2 THE XML LANGUAGE XML: Extensible Markup Language Standard for the presentation and transmission of information.
Navigating an XML Document
 University of Dublin Trinity College Navigating an XML Document Owen.Conlan@scss.tcd.ie Athanasios.Staikopoulos@scss.tcd.ie What is XPath? Language for addressing parts of an XML document Used in XSLT,
University of Dublin Trinity College Navigating an XML Document Owen.Conlan@scss.tcd.ie Athanasios.Staikopoulos@scss.tcd.ie What is XPath? Language for addressing parts of an XML document Used in XSLT,
Example using multiple predicates
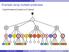 XPath Example using multiple predicates //performance[conductor][date] L C C C C p c s p p s o t d p p c p p Peter Wood (BBK) XML Data Management 162 / 366 XPath Further examples with predicates //performance[composer='frederic
XPath Example using multiple predicates //performance[conductor][date] L C C C C p c s p p s o t d p p c p p Peter Wood (BBK) XML Data Management 162 / 366 XPath Further examples with predicates //performance[composer='frederic
An introduction to searching in oxygen using XPath
 1/47 An introduction to searching in oxygen using XPath James Cummings @jamescummings 11 November 2014 2/47 XPath XPath is the basis of most other XML querying and transformation languages (such as XSLT
1/47 An introduction to searching in oxygen using XPath James Cummings @jamescummings 11 November 2014 2/47 XPath XPath is the basis of most other XML querying and transformation languages (such as XSLT
XML and Databases. Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS. Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW
 XML and Databases Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW CSE@UNSW -- Semester 1, 2009 Outline 1. Recall pre / post encoding 2. XPath with //, ancestor, @, and text() 3.
XML and Databases Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW CSE@UNSW -- Semester 1, 2009 Outline 1. Recall pre / post encoding 2. XPath with //, ancestor, @, and text() 3.
Introduction to XPath
 Introduction to XPath TEI@Oxford July 2009 XPath XPath is the basis of most other XML querying and transformation languages. It is just a way of locating nodes in an XML document. Accessing your TEI document
Introduction to XPath TEI@Oxford July 2009 XPath XPath is the basis of most other XML querying and transformation languages. It is just a way of locating nodes in an XML document. Accessing your TEI document
EXAM IN SEMI-STRUCTURED DATA Study Code Student Id Family Name First Name
 EXAM IN SEMI-STRUCTURED DATA 184.705 28. 10. 2016 Study Code Student Id Family Name First Name Working time: 100 minutes. Exercises have to be solved on this exam sheet; Additional slips of paper will
EXAM IN SEMI-STRUCTURED DATA 184.705 28. 10. 2016 Study Code Student Id Family Name First Name Working time: 100 minutes. Exercises have to be solved on this exam sheet; Additional slips of paper will
XPath and XSLT without the pain!
 XPath and XSLT without the pain! Bertrand Delacrétaz ApacheCon EU 2007, Amsterdam bdelacretaz@apache.org www.codeconsult.ch slides revision: 2007-05-04 Goal Learning to learn XPath and XSLT because it
XPath and XSLT without the pain! Bertrand Delacrétaz ApacheCon EU 2007, Amsterdam bdelacretaz@apache.org www.codeconsult.ch slides revision: 2007-05-04 Goal Learning to learn XPath and XSLT because it
XSL Concepts: Conditions and Loops. Robert Kiffe, Senior Web Developer OmniUpdate, Inc.
 XSL Concepts: Conditions and Loops Robert Kiffe, Senior Web Developer OmniUpdate, Inc. Quick XSL Recap Conditional Statements If Choose XPath Conditional Loops For-Each For-Each-Group Apply-Templates Activities!
XSL Concepts: Conditions and Loops Robert Kiffe, Senior Web Developer OmniUpdate, Inc. Quick XSL Recap Conditional Statements If Choose XPath Conditional Loops For-Each For-Each-Group Apply-Templates Activities!
Part XII. Mapping XML to Databases. Torsten Grust (WSI) Database-Supported XML Processors Winter 2008/09 321
 Part XII Mapping XML to Databases Torsten Grust (WSI) Database-Supported XML Processors Winter 2008/09 321 Outline of this part 1 Mapping XML to Databases Introduction 2 Relational Tree Encoding Dead Ends
Part XII Mapping XML to Databases Torsten Grust (WSI) Database-Supported XML Processors Winter 2008/09 321 Outline of this part 1 Mapping XML to Databases Introduction 2 Relational Tree Encoding Dead Ends
XML Wrap-up. CS 431 March 1, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University
 XML Wrap-up CS 431 March 1, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XSLT Processing Model Input XSL doc parse Input XML doc parse Parsed tree serialize Input XML doc Parsed tree Xformed tree Output doc (xml,
XML Wrap-up CS 431 March 1, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XSLT Processing Model Input XSL doc parse Input XML doc parse Parsed tree serialize Input XML doc Parsed tree Xformed tree Output doc (xml,
Hypermedia and the Web XSLT and XPath
 Hypermedia and the Web XSLT and XPath XSLT Extensible Stylesheet Language for Transformations Compare/contrast with CSS: CSS is used to change display characteristics of primarily HTML documents. But,
Hypermedia and the Web XSLT and XPath XSLT Extensible Stylesheet Language for Transformations Compare/contrast with CSS: CSS is used to change display characteristics of primarily HTML documents. But,
Semantic Web. XSLT: XML Transformation. Morteza Amini. Sharif University of Technology Fall 95-96
 ه عا ی Semantic Web XSLT: XML Transformation Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 95-96 Outline Fundamentals of XSLT XPath extensible Stylesheet Language Cocoon 2 XSLT XSLT stands for extensible
ه عا ی Semantic Web XSLT: XML Transformation Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 95-96 Outline Fundamentals of XSLT XPath extensible Stylesheet Language Cocoon 2 XSLT XSLT stands for extensible
An Algorithm for Streaming XPath Processing with Forward and Backward Axes
 An Algorithm for Streaming XPath Processing with Forward and Backward Axes Charles Barton, Philippe Charles, Deepak Goyal, Mukund Raghavchari IBM T.J. Watson Research Center Marcus Fontoura, Vanja Josifovski
An Algorithm for Streaming XPath Processing with Forward and Backward Axes Charles Barton, Philippe Charles, Deepak Goyal, Mukund Raghavchari IBM T.J. Watson Research Center Marcus Fontoura, Vanja Josifovski
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections
 Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
Presentation 19: XML technologies part 2: XSL, XSLT, XSL-FO, XPath & XML Programming
 Presentation 19: XML technologies part 2: XSL, XSLT, XSL-FO, XPath & XML Programming Outline XML recap Formatting CSS or XSL? XPath XSL/XSLT XSL-FO XML Programming Slide 2 XML markup recap XML based on
Presentation 19: XML technologies part 2: XSL, XSLT, XSL-FO, XPath & XML Programming Outline XML recap Formatting CSS or XSL? XPath XSL/XSLT XSL-FO XML Programming Slide 2 XML markup recap XML based on
Databases and Information Systems 1 - XPath queries on XML data streams -
 Databases and Information Systems 1 - XPath queries on XML data streams - Dr. Rita Hartel Fakultät EIM, Institut für Informatik Universität Paderborn WS 211 / 212 XPath - looking forward (1) - why? News
Databases and Information Systems 1 - XPath queries on XML data streams - Dr. Rita Hartel Fakultät EIM, Institut für Informatik Universität Paderborn WS 211 / 212 XPath - looking forward (1) - why? News
Semi-structured Data 11 - XSLT
 Semi-structured Data 11 - XSLT Andreas Pieris and Wolfgang Fischl, Summer Term 2016 Outline What is XSLT? XSLT at First Glance XSLT Templates Creating Output Further Features What is XSLT? XSL = extensible
Semi-structured Data 11 - XSLT Andreas Pieris and Wolfgang Fischl, Summer Term 2016 Outline What is XSLT? XSLT at First Glance XSLT Templates Creating Output Further Features What is XSLT? XSL = extensible
XSLT program. XSLT elements. XSLT example. An XSLT program is an XML document containing
 XSLT CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems Announcements (March 24) 2 Homework #3 will be assigned next Tuesday Reading assignment due next Wednesday XML processing in Lore (VLDB 1999) and Niagara (VLDB 2003)
XSLT CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems Announcements (March 24) 2 Homework #3 will be assigned next Tuesday Reading assignment due next Wednesday XML processing in Lore (VLDB 1999) and Niagara (VLDB 2003)
XML, XPath, and XSLT. Jim Fawcett Software Modeling Copyright
 XML, XPath, and XSLT Jim Fawcett Software Modeling Copyright 1999-2017 Topics XML is an acronym for extensible Markup Language. Its purpose is to describe structured data. XPath is a language for navigating
XML, XPath, and XSLT Jim Fawcett Software Modeling Copyright 1999-2017 Topics XML is an acronym for extensible Markup Language. Its purpose is to describe structured data. XPath is a language for navigating
2006 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. XPath
 Data-centric XML XPath XPath Overview Non-XML language for identifying particular parts of XML documents First person element of a document Seventh child element of third person element ID attribute of
Data-centric XML XPath XPath Overview Non-XML language for identifying particular parts of XML documents First person element of a document Seventh child element of third person element ID attribute of
XML. <subtitle>xslt (cont)</subtitle> <author>prof. Dr. Christian Pape</author>
 XML xslt (cont) prof. Dr. Christian Pape Content Expressions and Functions Copying nodes Using variables and parameters Conditional Processing XSLT 5-2 Expressions
XML xslt (cont) prof. Dr. Christian Pape Content Expressions and Functions Copying nodes Using variables and parameters Conditional Processing XSLT 5-2 Expressions
4D2b Navigating an XML Document
 University of Dublin Trinity College 4D2b Navigating an XML Document Owen.Conlan@scss.tcd.ie What is XPath? Addresses parts of an XML document W3C Recommendation (16 November 1999) Expression language
University of Dublin Trinity College 4D2b Navigating an XML Document Owen.Conlan@scss.tcd.ie What is XPath? Addresses parts of an XML document W3C Recommendation (16 November 1999) Expression language
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
Evaluating XPath Queries
 Chapter 8 Evaluating XPath Queries Peter Wood (BBK) XML Data Management 201 / 353 Introduction When XML documents are small and can fit in memory, evaluating XPath expressions can be done efficiently But
Chapter 8 Evaluating XPath Queries Peter Wood (BBK) XML Data Management 201 / 353 Introduction When XML documents are small and can fit in memory, evaluating XPath expressions can be done efficiently But
EXAM IN SEMI-STRUCTURED DATA Study Code Student Id Family Name First Name
 EXAM IN SEMI-STRUCTURED DATA 184.705 10. 01. 2017 Study Code Student Id Family Name First Name Working time: 100 minutes. Exercises have to be solved on this exam sheet; Additional slips of paper will
EXAM IN SEMI-STRUCTURED DATA 184.705 10. 01. 2017 Study Code Student Id Family Name First Name Working time: 100 minutes. Exercises have to be solved on this exam sheet; Additional slips of paper will
Introductory SQL SQL Joins: Viewing Relationships Pg 1
 Introductory SQL SQL Joins: Viewing Relationships Pg 1 SQL Joins: Viewing Relationships Ray Lockwood Points: The relational model uses foreign keys to establish relationships between tables. SQL uses Joins
Introductory SQL SQL Joins: Viewing Relationships Pg 1 SQL Joins: Viewing Relationships Ray Lockwood Points: The relational model uses foreign keys to establish relationships between tables. SQL uses Joins
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Representing Web Data: XML
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
XPath and XQuery. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018
 XPath and XQuery Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 23) Homework #3 due in two weeks Project milestone #1 feedback : we are a bit behind, but will definitely release
XPath and XQuery Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 23) Homework #3 due in two weeks Project milestone #1 feedback : we are a bit behind, but will definitely release
Introduction to XSLT. Version 1.3 March nikos dimitrakas
 Introduction to XSLT Version 1.3 March 2018 nikos dimitrakas Table of contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 XSLT... 3 1.2 PREREQUISITES... 3 1.3 STRUCTURE... 3 2 SAMPLE DATA... 4 3 XSLT... 6 4 EXAMPLES... 7
Introduction to XSLT Version 1.3 March 2018 nikos dimitrakas Table of contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 XSLT... 3 1.2 PREREQUISITES... 3 1.3 STRUCTURE... 3 2 SAMPLE DATA... 4 3 XSLT... 6 4 EXAMPLES... 7
Introduction. " Documents have tags giving extra information about sections of the document
 Chapter 10: XML Introduction! XML: Extensible Markup Language! Defined by the WWW Consortium (W3C)! Originally intended as a document markup language not a database language " Documents have tags giving
Chapter 10: XML Introduction! XML: Extensible Markup Language! Defined by the WWW Consortium (W3C)! Originally intended as a document markup language not a database language " Documents have tags giving
XML Query Processing. Announcements (March 31) Overview. CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems. Course project milestone 2 due today
 XML Query Processing CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems Announcements (March 31) 2 Course project milestone 2 due today Hardcopy in class or otherwise email please I will be out of town next week No class
XML Query Processing CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems Announcements (March 31) 2 Course project milestone 2 due today Hardcopy in class or otherwise email please I will be out of town next week No class
Introduction. " Documents have tags giving extra information about sections of the document
 Chapter 10: XML Introduction! XML: Extensible Markup Language! Defined by the WWW Consortium (W3C)! Originally intended as a document markup language not a database language " Documents have tags giving
Chapter 10: XML Introduction! XML: Extensible Markup Language! Defined by the WWW Consortium (W3C)! Originally intended as a document markup language not a database language " Documents have tags giving
6/6/2016 3:23 PM 1 of 15
 6/6/2016 3:23 PM 1 of 15 6/6/2016 3:23 PM 2 of 15 2) XSLT Selection XSLT allows for selection with two statements xsl:if chooses to do or not to do (very basic) xsl:choose chooses from several alternatives
6/6/2016 3:23 PM 1 of 15 6/6/2016 3:23 PM 2 of 15 2) XSLT Selection XSLT allows for selection with two statements xsl:if chooses to do or not to do (very basic) xsl:choose chooses from several alternatives
Transcript of Abel Braaksma's Talk on XSLT Streaming at XML Prague 2014
 Transcript of Abel Braaksma's Talk on XSLT Streaming at XML Prague 2014 The video of Abel's talk is here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kaupzeew4xg&t=318m25s Abel's slides are here: http://exselt.net/portals/1/streaming%20for%20the%20masses.zip
Transcript of Abel Braaksma's Talk on XSLT Streaming at XML Prague 2014 The video of Abel's talk is here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kaupzeew4xg&t=318m25s Abel's slides are here: http://exselt.net/portals/1/streaming%20for%20the%20masses.zip
XML and Databases. Outline. Outline - Lectures. Outline - Assignments. from Lecture 3 : XPath. Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW
 Outline XML and Databases Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS 1. Recall / encoding 2. XPath with //,, @, and text() 3. XPath with / and -sibling: use / size / level encoding Sebastian Maneth NICTA
Outline XML and Databases Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS 1. Recall / encoding 2. XPath with //,, @, and text() 3. XPath with / and -sibling: use / size / level encoding Sebastian Maneth NICTA
COP 4814 Florida International University Kip Irvine XSLT. Updated: 2/9/2016 Based on Goldberg, Chapter 2. Irvine COP 4814
 COP 4814 Florida International University Kip Irvine XSLT Updated: 2/9/2016 Based on Goldberg, Chapter 2 XSL Overview XSL Extensible Stylesheet Language A family of languages used to transform and render
COP 4814 Florida International University Kip Irvine XSLT Updated: 2/9/2016 Based on Goldberg, Chapter 2 XSL Overview XSL Extensible Stylesheet Language A family of languages used to transform and render
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Section 5.5. Left subtree The left subtree of a vertex V on a binary tree is the graph formed by the left child L of V, the descendents
 Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Introduction to XSLT
 Introduction to XSLT Justin Tilton, Chief Executive Officer instructional media + magic, inc. at the JA-SIG Conference Vancouver, BC Sunday, June 9, 2002 The Abstract Looking for a methodology to quickly
Introduction to XSLT Justin Tilton, Chief Executive Officer instructional media + magic, inc. at the JA-SIG Conference Vancouver, BC Sunday, June 9, 2002 The Abstract Looking for a methodology to quickly
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars and Parsing 1 Recall: Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Parser Static Analyzer Intermediate Representation Front End Back
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars and Parsing 1 Recall: Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Parser Static Analyzer Intermediate Representation Front End Back
