Lecture 13. Instructor: Craig Duckett. Boolean Expressions, Logical Operators, and Return Values
|
|
|
- Augustus Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 13 Instructor: Craig Duckett Boolean Expressions, Logical Operators, and Return Values
2 Assignment 3: The Maze DUE TONIGHT! Uploaded to StudentTracker by midnight If you are submitting as part of a team make sure that all team member names are on both the.java program and.doc summary files. Also only one member of the team has to submit, but I will return the graded assignment to all members of the team. I've already graded several 'early bird' submissions Assignment 3 Revision DUE Lecture 16
3 Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday, January 31 st Assignment 1 Revision (LECTURE 10) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday, February 7 th Assignment 2 Revision (LECTURE 12) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday, February 14 th Assignment 3 (LECTURE 13) TONIGHT Section 1: Wednesday, February 21 st The Fickle Finger of Fate Assignment 3 Revision (LECTURE 16) Section 1: Monday, March 5 th Assignment 4 (LECTURE 18) NO REVISION AVAILABLE! Section 1: Monday, March 12 th 3
4 Assignment 3: Maze Reminder This is what you turn in This is what I add to grade it I will also be testing with only 25 or 33 things in the backpack to start to make sure the Robot successfully completes the Maze even if the backpack is runs out of Things to put down.
5 Today s Topics Boolean Expressions and Logical Operators &&,,! Our First Look at Non-Robotic Code (Straight Java, No Chaser) Return Values: What Good Are They and How Do They Work?
6 TODAY NO Warm-Up Question because of Mish-Mash and longer ICE
7 REMEMBER: The World Wide Web is your GREATEST programming ALLY! Google It!
8 Boolean Expressions and Logical Operators A Boolean Expression is an expression that results in a Boolean value, that is, in a value that is either true or false. More complex Boolean expressions can be built out of simpler expressions, using the Boolean Logical Operators.
9 Boolean Expressions and Comparison Operators Operator Operation < Less than <= Less than or equal > Greater than >= Greater than or equal == Equal!= Not equal Using Comparison Operators, the test in if and while statements are Boolean expressions that return a true or false answer to a question. So far, our questions have been simple. As our programming skills grow, however, we will want to ask more complex questions, which will need more complex Boolean expressions to answer. Just like the mathematic operators (+ - / *) can be combined to form more complex expressions like s = (( x + y) * (w z)) / 2 so too can Boolean expressions be combined to create more complex and utility expressions using and ( represented by && ) and or ( represented by )
10 Logical Operators: && ( And ) and II ( Or ) In many programming languages like Java, JavaScript, C++, and C# the logical operators and and or are represented in the code by a double ampersand && and double pipe And && Double Ampersand Or Double Pipe There is also the not operator represented by a single exclamation point! which I ll talk about in a moment. Not! Single Exclamation Point NOTE: Java also has a single & and single characters, called bitwise operators, but for the purposes of this course we won t be discussing them. These will come a bit later (pun intended) along your journey in learning programming languages.
11 Before We Continue: What Pipe Character? Where is the pipe character located on the keyboard? AN INTERESTING NOTE: The pipe character goes by several different names, depending on the particular group using it: besides being called the pipe, it can also be called the pipeline, vertical bar, Sheffer stroke, polon, verti-bar, vbar, stick, vertical line, vertical slash, bar, or glidus.
12 Logical Operators Logical Operators AND && A && B are true only if both A and B are true OR A B are true if A is true or B is true or they're both true NOT!A is the opposite of A. If A is true, then!a is false. If A is false,!a is true. The double ampersand && and double pipe are called short circuit logical operators! AND Operator OR Operator TRUE && TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE && FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE && TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
13 Logical Operator: Some Examples AND int a = 7; int b = 10; if( a > 4 && b < 20 ) // This will be true since both operands of the && operator evaluate to true OR NOT int c = 10; int d = 40; if( c == 7 d > c ) // This will be true. Even though the first operand evaluates to false, // the second will evaluate to true. int e = 7; int f = 10; if(!(e == f) ) // This will evaluate to true since e == f will be false, // and the NOT operator will reverse it Example: LogicalOperatorsExample.java
14 Logical Operators: Checking Ranges
15 Logical Operators: Checking Ranges ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Example: Checks to see whether user input is INSIDE or OUTSIDE of a given range // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// import java.util.*; public class CheckingRanges extends Object public static void main(string[] args) Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Test to see if a number is a number between 1 and 10, inclusive.\n"); System.out.println("Please enter a number: \n"); if(keyboard.hasnextint()) int userinput = keyboard.nextint(); // Testing with AND (&&) if(userinput > 0 && userinput < 11) System.out.println("\nYour number " + userinput + " is between 1 & 10, inclusive.\n"); // Testing with OR ( ) if(userinput < 1 userinput > 10) System.out.println("\nYour number " + userinput + " is NOT between 1 & 10, inclusive.\n"); Example: CheckingRanges.java
16 Logical Operator: Gotchas int x = 5; if( 0 < x < 11) // Testing to see if x is in range of 1 to 10 System.out.println("X is in range"); int x = 5; if( x > 0 && < 11) // Testing to see if x is in range of 1 to 10 System.out.println("X is in range");
17 Logical Operator: Gotchas int x = 5; if( x > 0 && x < 11) // Testing to see if x is in range of 1 to 10 System.out.println("X is in range"); So, remember: you need whatever you are comparing whether variables or methods listed on both sides of the logical operators. if( getstreet() > 0 && getstreet() < 11)
18 Logical Operator: Robotic Examples if(this.countthingsinbackpack() > 0 && this.frontisclear()) this.putthing(); this.move(); // Notice the use of the wrapping parenthesis if((this.isfacingeast() this.isfacingwest()) && this.frontisclear()) this.move(); if(!(this.frontisclear()) ) this.turnleft(); Example: LogicalOperatorRobot.java
19 Non-Robotic Java Programming Writing Java programs without using the Becker Robot class or any robots in the code is now deemed non-robotic.
20 Start Looking for Non-Robotic Java * * Of course any new topics we learn under the heading Non-Robotic Java can still be used when working with Robots, like Return Values and Static Methods, as we will see Straight Java, No Chaser Starting today, we will begin introducing more Non-Robotic Java into the mix, which will find its way into the PowerPoint slides, some of the example code, several of the ICEs, and even one of the Assignments, Assignment 4 (Advanced). Example: LogicalOperatorsExample.java
21 The Return Statement and Return Values
22 Return Values An Illustrated Introduction to Return Values First, a look at non-return Up to now we ve seen how to use void methods public void movemultiple(int numberofintersections) int counter = 0; while( counter < numberofintersections) this.move(); counter = counter + 1; rob.movemultiple(5); You can pass an argument to a void method and it will do whatever it is meant to do, but nothing is returned as a separate value that the program might use later on.
23 Void: Means Nothing is Returned The meaning of void Up to now we ve seen how to use void methods. 5 public void movemultiple(int numberofintersections) int counter = 0; while( counter < numberofintersections) this.move(); counter = counter + 1; and down in main: rob.movemultiple(5); movemultiple void means that nothing is returned back to the program; the method does something, it just doesn t return something back into the program once it s finished doing whatever it is it s been doing. In other words, it is a closed method.
24 Two Types of void 5 Method 1 Method 2 Nothing goes in, nothing comes out move(); Something goes in, nothing comes out movemultiple(5);
25 Return: By Way of A Cooking Eggs Analogy The overeasy() method does exactly what it is supposed to do it cooks the egg over easy, but that s as far as it goes customer.overeasy() Alas, nothing is returned. Hungry customer not happy. kitchen class diningroom class
26 A Sad Scenario WTF? * * Where s the food?
27 Cooking Eggs Analogy egg.sunnysideup() egg.overeasy() egg.overmedium() egg.overhard() egg.scrambled() egg.poached() egg.hardboiled() egg.softboiled() plate = customer.overeasy() Hooray, overeasy() returns the cooked egg and puts it in the plate! Plate is now used to transport egg to happy customer!
28 A Happy Scenario Breakfast is served!
29 Return: The Return Type must be specified public int countmoves( ) int will be returned chugga-chugga int will be returned return counter; public int addsum(int num) chugga-chugga true or false will be returned int return sum; public boolean isnorth(int num) chugga-chugga int The Return Value is a way to send the information back into the program so the program can use it in another way. return true; true
30 Two Types of Return 3 Method 1 Method 2 Nothing goes in, something comes out FileName.java Something goes in, something comes out FileName2.java We ll visit these two code examples after the next slide
31 Example: Nothing Goes In, Something Comes Out // Example of a method returning a value //////////////////////////////////////// class returnit extends Object public int returnyear() int year = 2018; return year; public class methodreturn extends Object public static void main(string[] args) returnit bernie = new returnit(); int num; num = bernie.returnyear(); System.out.println(num); methodreturn.java
32 Example: Nothing Goes In, Something Comes Out // Example of a method returning a value //////////////////////////////////////// class returnit extends Object public int returnyear() int year = 2018; return year; public class methodreturn extends Object public static void main(string[] args) returnit bernie = new returnit(); int num; num = bernie.returnyear(); System.out.println(num); Anatomy of a Method Return 1) The returnyear() method is called by the bernie object 2) The returnyear() method returns the value of year 3) Value of year shoots of out the returnyear() method and deposited in the num variable container 4) The value of num is printed out.
33 Example: Something Goes In, Something Comes Out // EXAMPLE: A number goes in, a revised number comes out class SumNum extends Object public int Tally(int num) int sum = 0; sum = num + 5; return sum; public class NumberTest extends Object public static void main(string[] args) SumNum sn = new SumNum(); int number = 0; number = sn.tally(3); System.out.println(number); NumberTest.java
34 Walkthrough: FileName.java class PrintHelper extends Object public int printnum() System.out.println("Going to print, some number of times!"); int howmanyprints = 0; while(howmanyprints < 2) System.out.println("Printing!"); howmanyprints++; // This is a basic counter return howmanyprints; public class FileName extends Object public static void main(string[] args) PrintHelper Gutenberg = new PrintHelper(); int num; num = Gutenberg.printNum(); // This method is called by an object System.out.println( "The method printed " + num + " times!");
35 class PrintHelper extends Object public int printnum() System.out.println("Going to print, some number of times!"); int howmanyprints = 0; while(howmanyprints < 2) System.out.println("Printing!"); howmanyprints++; // This is a basic counter return howmanyprints; Class Idea / Attributes public class FileName extends Object public static void main(string[] args) PrintHelper Gutenberg = new PrintHelper(); int num; num = Gutenberg.printNum(); System.out.println( "The method printed " + num + " times!"); Class Object (Instance of Class)
36 class PrintHelper extends Object public int printnum() System.out.println("Going to print, some number of times!"); int howmanyprints = 0; while(howmanyprints < 2) System.out.println("Printing!"); howmanyprints++; // This is a basic counter return howmanyprints; howmanyprints public class FileName extends Object public static void main(string[] args) PrintHelper Gutenberg = new PrintHelper(); int num = 0; num num = Gutenberg.printNum(); System.out.println( "The method printed " + num + " times!");
37 class PrintHelper extends Object public int printnum() System.out.println("Going to print, some number of times!"); int howmanyprints = 0; while(howmanyprints < 2) System.out.println("Printing!"); howmanyprints++; // This is a basic counter 2 return howmanyprints; howmanyprints public class FileName extends Object public static void main(string[] args) PrintHelper Gutenberg = new PrintHelper(); int num; num = Gutenberg.printNum(); 2 num 2 howmanyprints System.out.println( "The method printed " + num + " times!"); 2
38 Example Code: Return Let s look at some more examples using return NumberTest.java SumOfTwoNumbers.java AverageOfTwoNumbers.java RetrunValues_Demo.java
39 ICE 14: Logical Operators and Boolean Returns Before starting today s ICE, you may want to look at the Boolean return examples: BooleanReturns1.java BooleanReturns2.java BooleanReturns3.java
Lecture 10. Instructor: Craig Duckett
 Lecture 10 Instructor: Craig Duckett Announcements Assignment 1 Revision DUE TONIGHT in StudentTracker by midnight If you have not yet submitted an Assignment 1, this is your last chance to do so to earn
Lecture 10 Instructor: Craig Duckett Announcements Assignment 1 Revision DUE TONIGHT in StudentTracker by midnight If you have not yet submitted an Assignment 1, this is your last chance to do so to earn
Lecture 6. Instructor: Craig Duckett
 Lecture 6 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment 1, 2, and A1 Revision Assignment 1 I have finished correcting and have already returned the Assignment 1 submissions. If you did not submit an Assignment
Lecture 6 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment 1, 2, and A1 Revision Assignment 1 I have finished correcting and have already returned the Assignment 1 submissions. If you did not submit an Assignment
Lecture 8 " INPUT " Instructor: Craig Duckett
 Lecture 8 " INPUT " Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignments Assignment 2 Due TONIGHT Lecture 8 Assignment 1 Revision due Lecture 10 Assignment 2 Revision Due Lecture 12 We'll Have a closer look at Assignment
Lecture 8 " INPUT " Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignments Assignment 2 Due TONIGHT Lecture 8 Assignment 1 Revision due Lecture 10 Assignment 2 Revision Due Lecture 12 We'll Have a closer look at Assignment
Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15. Instructor: Craig Duckett
 Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday,
Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday,
Lecture 11. Instructor: Craig Duckett. Instance Variables
 Lecture 11 Instructor: Craig Duckett Instance Variables Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday,
Lecture 11 Instructor: Craig Duckett Instance Variables Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday,
Lecture 17. Instructor: Craig Duckett. Passing & Returning Arrays
 Lecture 17 Instructor: Craig Duckett Passing & Returning Arrays Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section
Lecture 17 Instructor: Craig Duckett Passing & Returning Arrays Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section
Instructor: Craig Duckett
 Instructor: Craig Duckett cduckett@cascadia.edu Announcements Assignment 1 Due Lecture 5 by MIDNIGHT I will double dog dare try to have Assignment 1 graded and back to you by Wednesday, January 24 th hopefully
Instructor: Craig Duckett cduckett@cascadia.edu Announcements Assignment 1 Due Lecture 5 by MIDNIGHT I will double dog dare try to have Assignment 1 graded and back to you by Wednesday, January 24 th hopefully
BIT 115: Introduction To Programming LECTURE 3. Instructor: Craig Duckett
 BIT 115: Introduction To Programming LECTURE 3 Instructor: Craig Duckett cduckett@cascadia.edu Lecture 3 Announcements By now everyone should be up and running with Java, jgrasp, and the Becker Robots
BIT 115: Introduction To Programming LECTURE 3 Instructor: Craig Duckett cduckett@cascadia.edu Lecture 3 Announcements By now everyone should be up and running with Java, jgrasp, and the Becker Robots
Lecture 12. Instructor: Craig Duckett
 Lecture 12 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment 2 Revision DUE TONIGHT! Uploaded to StudentTracker by midnight YOUR LAST CHANCE TO EARN POINTS! Assignment 3 Maze DUE Lecture 13 Uploaded to StudentTracker
Lecture 12 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment 2 Revision DUE TONIGHT! Uploaded to StudentTracker by midnight YOUR LAST CHANCE TO EARN POINTS! Assignment 3 Maze DUE Lecture 13 Uploaded to StudentTracker
Lecture 8. A series on variable types This episode starring Parameter Variables
 Lecture 8 A series on variable types This episode starring Parameter Variables Declaring an Integer Variable Variable Types Variable Type How it is defined Scope (how long it lasts) Uses Local Variable
Lecture 8 A series on variable types This episode starring Parameter Variables Declaring an Integer Variable Variable Types Variable Type How it is defined Scope (how long it lasts) Uses Local Variable
Lecture 7. Instructor: Craig Duckett OUTPUT
 Lecture 7 Instructor: Craig Duckett OUTPUT Lecture 7 Announcements ASSIGNMENT 2 is due LECTURE 8 NEXT LECTURE uploaded to StudentTracker by midnight Assignment 2!!! Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment
Lecture 7 Instructor: Craig Duckett OUTPUT Lecture 7 Announcements ASSIGNMENT 2 is due LECTURE 8 NEXT LECTURE uploaded to StudentTracker by midnight Assignment 2!!! Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment
Control Structures: if and while A C S L E C T U R E 4
 Control Structures: if and while A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 4 Control structures 3 constructs are essential building blocks for programs Sequences compound statement Decisions if, switch, conditional operator
Control Structures: if and while A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 4 Control structures 3 constructs are essential building blocks for programs Sequences compound statement Decisions if, switch, conditional operator
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics. COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction
 CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
Over and Over Again GEEN163
 Over and Over Again GEEN163 There is no harm in repeating a good thing. Plato Homework A programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard You have to convert three flowcharts into programs Upload the
Over and Over Again GEEN163 There is no harm in repeating a good thing. Plato Homework A programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard You have to convert three flowcharts into programs Upload the
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 4: Flow Control Loops Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 4: Flow Control Loops Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Check the calendar on the course webpage regularly for updates on tutorials and office hours.
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 4: Flow Control Loops Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Check the calendar on the course webpage regularly for updates on tutorials and office hours.
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists 1 A programming problem Consider the following task: Double values representing grades are read until the user enters a negative
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists 1 A programming problem Consider the following task: Double values representing grades are read until the user enters a negative
Linked Lists. private int num; // payload for the node private Node next; // pointer to the next node in the list }
 Linked Lists Since a variable referencing an object just holds the address of the object in memory, we can link multiple objects together to form dynamic lists or other structures. In our case we will
Linked Lists Since a variable referencing an object just holds the address of the object in memory, we can link multiple objects together to form dynamic lists or other structures. In our case we will
Claremont McKenna College Computer Science
 Claremont McKenna College Computer Science CS 51 Handout 4: Problem Set 4 February 10, 2011 This problem set is due 11:50pm on Wednesday, February 16. As usual, you may hand in yours until I make my solutions
Claremont McKenna College Computer Science CS 51 Handout 4: Problem Set 4 February 10, 2011 This problem set is due 11:50pm on Wednesday, February 16. As usual, you may hand in yours until I make my solutions
CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1. Name SOLUTION
 CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1 Name SOLUTION Page Points Score 2 15 3 8 4 18 5 10 6 7 7 7 8 14 9 11 10 10 Total 100 1 P age 1. Program Traces (41 points, 50 minutes)
CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1 Name SOLUTION Page Points Score 2 15 3 8 4 18 5 10 6 7 7 7 8 14 9 11 10 10 Total 100 1 P age 1. Program Traces (41 points, 50 minutes)
CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops
 CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 17, 2009 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements are executed
CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 17, 2009 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements are executed
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
Loops. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
Java Programming. What is a program? Programs Recipes. Programs as Recipes 8/16/12. Pancakes In one bowl. mix: 1½ cup flour
 What is a program? Java Programming CS 160, Fall Semester 2012 TOPICS Computer Programs Using Eclipse Program Program Components Definition: a sequence of instructions telling a computer what to do Analogy:
What is a program? Java Programming CS 160, Fall Semester 2012 TOPICS Computer Programs Using Eclipse Program Program Components Definition: a sequence of instructions telling a computer what to do Analogy:
Menu Driven Systems. While loops, menus and the switch statement. Mairead Meagher Dr. Siobhán Drohan. Produced by:
 Menu Driven Systems While loops, menus and the switch statement Produced by: Mairead Meagher Dr. Siobhán Drohan Department of Computing and Mathematics http://www.wit.ie/ Topics list while loops recap
Menu Driven Systems While loops, menus and the switch statement Produced by: Mairead Meagher Dr. Siobhán Drohan Department of Computing and Mathematics http://www.wit.ie/ Topics list while loops recap
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 8: for Loops, Nested Loops and Arrays Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 8: for Loops, Nested Loops and Arrays Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Review What is the difference between a while loop and an if statement? What is an off-by-one
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 8: for Loops, Nested Loops and Arrays Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Review What is the difference between a while loop and an if statement? What is an off-by-one
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen Administrative Details Lab 1 handout is online Prelab (should be completed before lab): Lab 1 design doc
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen Administrative Details Lab 1 handout is online Prelab (should be completed before lab): Lab 1 design doc
(Refer Slide Time: 00:26)
 Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute Technology, Madras Module 07 Lecture 07 Contents Repetitive statements
Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute Technology, Madras Module 07 Lecture 07 Contents Repetitive statements
Robots. Byron Weber Becker. chapter 6
 Using Variables Robots Learning to Program with Java Byron Weber Becker chapter 6 Announcements (Oct 3) Reminder: Reading for today y( (Oct 3 rd ) Ch 6.1-6.4 Reading for Wednesday (Oct 3 rd ) The rest
Using Variables Robots Learning to Program with Java Byron Weber Becker chapter 6 Announcements (Oct 3) Reminder: Reading for today y( (Oct 3 rd ) Ch 6.1-6.4 Reading for Wednesday (Oct 3 rd ) The rest
Loops. GEEN163 Introduction to Computer Programming
 Loops GEEN163 Introduction to Computer Programming Simplicity is prerequisite for reliability. Edsger W. Dijkstra Programming Assignment A new programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard for this
Loops GEEN163 Introduction to Computer Programming Simplicity is prerequisite for reliability. Edsger W. Dijkstra Programming Assignment A new programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard for this
First Java Program - Output to the Screen
 First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
Darrell Bethea May 10, MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011
 Darrell Bethea May 10, 2011 MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011 1 Office hours: MW 1-2 PM If you still cannot make it to either office hour, email me to set up an appointment if you need help with an assignment.
Darrell Bethea May 10, 2011 MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011 1 Office hours: MW 1-2 PM If you still cannot make it to either office hour, email me to set up an appointment if you need help with an assignment.
CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables and constants Top Down Programming For loops Nested Loops
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
St. Edmund Preparatory High School Brooklyn, NY
 AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
Example Program. public class ComputeArea {
 COMMENTS While most people think of computer programs as a tool for telling computers what to do, programs are actually much more than that. Computer programs are written in human readable language for
COMMENTS While most people think of computer programs as a tool for telling computers what to do, programs are actually much more than that. Computer programs are written in human readable language for
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Darrell Bethea May 20, 2011
 Darrell Bethea May 20, 2011 Program 2 due Monday Midterm in one week Moved to SN014 (next door) Will cover up to yesterday (Ch. 1-4) Future office hours moved to FB331 2 3 Briefly go over Strings and Loops
Darrell Bethea May 20, 2011 Program 2 due Monday Midterm in one week Moved to SN014 (next door) Will cover up to yesterday (Ch. 1-4) Future office hours moved to FB331 2 3 Briefly go over Strings and Loops
Object Oriented Programming. Java-Lecture 1
 Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
Lec 3. Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables
 Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
The for Loop, Accumulator Variables, Seninel Values, and The Random Class. CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming
 The for Loop, Accumulator Variables, Seninel Values, and The Random Class CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming Review General Form of a switch statement: switch (SwitchExpression) { case CaseExpression1:
The for Loop, Accumulator Variables, Seninel Values, and The Random Class CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming Review General Form of a switch statement: switch (SwitchExpression) { case CaseExpression1:
Repetition, Looping. While Loop
 Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Handout 5 cs180 - Programming Fundamentals Spring 15 Page 1 of 8. Handout 5. Loops.
 Handout 5 cs180 - Programming Fundamentals Spring 15 Page 1 of 8 Handout 5 Loops. Loops implement repetitive computation, a k a iteration. Java loop statements: while do-while for 1. Start with the while-loop.
Handout 5 cs180 - Programming Fundamentals Spring 15 Page 1 of 8 Handout 5 Loops. Loops implement repetitive computation, a k a iteration. Java loop statements: while do-while for 1. Start with the while-loop.
Administration. Conditional Statements. Agenda. Syntax. Flow of control. Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP
 Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1
Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Java Basics
 WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
Lecture 9. Assignment. Logical Operations. Logical Operations - Motivation 2/8/18
 Assignment Lecture 9 Logical Operations Formatted Print Printf Increment and decrement Read through 3.9, 3.10 Read 4.1. 4.2, 4.3 Go through checkpoint exercise 4.1 Logical Operations - Motivation Logical
Assignment Lecture 9 Logical Operations Formatted Print Printf Increment and decrement Read through 3.9, 3.10 Read 4.1. 4.2, 4.3 Go through checkpoint exercise 4.1 Logical Operations - Motivation Logical
Bjarne Stroustrup. creator of C++
 We Continue GEEN163 I have always wished for my computer to be as easy to use as my telephone; my wish has come true because I can no longer figure out how to use my telephone. Bjarne Stroustrup creator
We Continue GEEN163 I have always wished for my computer to be as easy to use as my telephone; my wish has come true because I can no longer figure out how to use my telephone. Bjarne Stroustrup creator
Topic 4 Expressions and variables
 Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 3 Branching
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 3 Branching 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements in a program are executed is called the flow of control So far we have only seen
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 3 Branching 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements in a program are executed is called the flow of control So far we have only seen
COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2011) - All Sections Example Questions for In-Class Quiz
 COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2011) - All Sections Example Questions for In-Class Quiz The in-class quiz is intended to give you a taste of the midterm, give you some early feedback about
COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2011) - All Sections Example Questions for In-Class Quiz The in-class quiz is intended to give you a taste of the midterm, give you some early feedback about
In this chapter, you will:
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 4 Control Structures I: Selection In this chapter, you will: Make decisions with the if and if else structures Use compound statements in an
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 4 Control Structures I: Selection In this chapter, you will: Make decisions with the if and if else structures Use compound statements in an
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science. Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style
 CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style c 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 4 : Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style c 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 4 : Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering. Lecture No. #06 Loops: Operators
 Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering Lecture No. #06 Loops: Operators We have seen comparison operators, like less then, equal to, less than or equal. to and
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering Lecture No. #06 Loops: Operators We have seen comparison operators, like less then, equal to, less than or equal. to and
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch
 Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise
 COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
Iteration statements - Loops
 Iteration statements - Loops : ) הוראות חזרה / לולאות ( statements Java has three kinds of iteration WHILE FOR DO... WHILE loop loop loop Iteration (repetition) statements causes Java to execute one or
Iteration statements - Loops : ) הוראות חזרה / לולאות ( statements Java has three kinds of iteration WHILE FOR DO... WHILE loop loop loop Iteration (repetition) statements causes Java to execute one or
Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - Solutions
 Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - s Note: These aren't from actual AP tests. I've created these questions based on looking at actual AP tests. Also, in cases where it's not necessary to have
Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - s Note: These aren't from actual AP tests. I've created these questions based on looking at actual AP tests. Also, in cases where it's not necessary to have
Intro to Programming in Java Practice Midterm
 600.107 Intro to Programming in Java Practice Midterm This test is closed book/notes. SHORT ANSWER SECTION [18 points total] 1) TRUE/FALSE - Please circle your choice: Tr for true, Fa for false. [1 point
600.107 Intro to Programming in Java Practice Midterm This test is closed book/notes. SHORT ANSWER SECTION [18 points total] 1) TRUE/FALSE - Please circle your choice: Tr for true, Fa for false. [1 point
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each)
 1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
Java I/O and Control Structures
 Java I/O and Control Structures CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying
Java I/O and Control Structures CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying
Warm up Exercise. What are the types and values of the following expressions: * (3 + 1) 3 / / 2.0 (int)1.0 / 2
 Warm up Exercise What are the types and values of the following expressions: 3.0+4 * (3 + 1) 3 / 2 + 1.0 1.0 / 2.0 (int)1.0 / 2 COMP-202 - Programming Basics 1 Warm up Exercise What are the types and values
Warm up Exercise What are the types and values of the following expressions: 3.0+4 * (3 + 1) 3 / 2 + 1.0 1.0 / 2.0 (int)1.0 / 2 COMP-202 - Programming Basics 1 Warm up Exercise What are the types and values
Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1
 Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1 Motivation In the programs we have written thus far, statements are executed one after the other, in the order in which they appear. Programs often
Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1 Motivation In the programs we have written thus far, statements are executed one after the other, in the order in which they appear. Programs often
Building Java Programs. Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Lesson 7 Part 2 Flags
 Lesson 7 Part 2 Flags A Flag is a boolean variable that signals when some condition exists in a program. When a flag is set to true, it means some condition exists When a flag is set to false, it means
Lesson 7 Part 2 Flags A Flag is a boolean variable that signals when some condition exists in a program. When a flag is set to true, it means some condition exists When a flag is set to false, it means
Evaluating the Style of your programs
 Evaluating the Style of your programs Objectives At the end of this exercise, students will: Roles Be able to evaluate a program for conformance to style guide for the class. Be able to evaluate arithmetic
Evaluating the Style of your programs Objectives At the end of this exercise, students will: Roles Be able to evaluate a program for conformance to style guide for the class. Be able to evaluate arithmetic
Introduction to OOP with Java. Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017
 Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Prof. Navrati Saxena TA: Rochak Sachan
 JAVA Prof. Navrati Saxena TA: Rochak Sachan Operators Operator Arithmetic Relational Logical Bitwise 1. Arithmetic Operators are used in mathematical expressions. S.N. 0 Operator Result 1. + Addition 6.
JAVA Prof. Navrati Saxena TA: Rochak Sachan Operators Operator Arithmetic Relational Logical Bitwise 1. Arithmetic Operators are used in mathematical expressions. S.N. 0 Operator Result 1. + Addition 6.
CS 161: Object Oriented Problem Solving
 About this course CS 161: Object Oriented Problem Solving About this course Course webpage: http://www.cs.colostate.edu/~cs161/ The course webpage is our major communication tool. Check it on a daily basis!
About this course CS 161: Object Oriented Problem Solving About this course Course webpage: http://www.cs.colostate.edu/~cs161/ The course webpage is our major communication tool. Check it on a daily basis!
Java Programming Fundamentals - Day Instructor: Jason Yoon Website:
 Java Programming Fundamentals - Day 1 07.09.2016 Instructor: Jason Yoon Website: http://mryoon.weebly.com Quick Advice Before We Get Started Java is not the same as javascript! Don t get them confused
Java Programming Fundamentals - Day 1 07.09.2016 Instructor: Jason Yoon Website: http://mryoon.weebly.com Quick Advice Before We Get Started Java is not the same as javascript! Don t get them confused
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Event-based Programming Misc. Java Operator Precedence Java Formatting
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Event-based Programming Misc. Java Operator Precedence Java Formatting
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE
 CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 topics: introduction to java, part 1
 topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
COSC 243. Data Representation 3. Lecture 3 - Data Representation 3 1. COSC 243 (Computer Architecture)
 COSC 243 Data Representation 3 Lecture 3 - Data Representation 3 1 Data Representation Test Material Lectures 1, 2, and 3 Tutorials 1b, 2a, and 2b During Tutorial a Next Week 12 th and 13 th March If you
COSC 243 Data Representation 3 Lecture 3 - Data Representation 3 1 Data Representation Test Material Lectures 1, 2, and 3 Tutorials 1b, 2a, and 2b During Tutorial a Next Week 12 th and 13 th March If you
Arrays. Friday, November 9, Department of Computer Science Wellesley College
 Arrays Friday, November 9, CS Computer Programming Department of Computer Science Wellesley College Arrays: Motivation o o o Lists are great for representing a collection of values, but can only access
Arrays Friday, November 9, CS Computer Programming Department of Computer Science Wellesley College Arrays: Motivation o o o Lists are great for representing a collection of values, but can only access
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015 Assignment Due Date Assignment 1 is now due on Tuesday, Jan 20 th, 11:59pm. Quiz 1 is
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015 Assignment Due Date Assignment 1 is now due on Tuesday, Jan 20 th, 11:59pm. Quiz 1 is
AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A
 AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A CONTROL FLOW Aug 28 2017 Week 2 http://apcs.cold.rocks 1 More operators! not!= not equals to % remainder! Goes ahead of boolean!= is used just like == % is used just like / http://apcs.cold.rocks
AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A CONTROL FLOW Aug 28 2017 Week 2 http://apcs.cold.rocks 1 More operators! not!= not equals to % remainder! Goes ahead of boolean!= is used just like == % is used just like / http://apcs.cold.rocks
Oct Decision Structures cont d
 Oct. 29 - Decision Structures cont d Programming Style and the if Statement Even though an if statement usually spans more than one line, it is really one statement. For instance, the following if statements
Oct. 29 - Decision Structures cont d Programming Style and the if Statement Even though an if statement usually spans more than one line, it is really one statement. For instance, the following if statements
CPS109 Lab 7. Source: Big Java, Chapter 7 Preparation: read Chapter 7 and the lecture notes for this week.
 1 CPS109 Lab 7 Source: Big Java, Chapter 7 Preparation: read Chapter 7 and the lecture notes for this week. Objectives: 1. To practice using one- and two-dimensional arrays 2. To practice using partially
1 CPS109 Lab 7 Source: Big Java, Chapter 7 Preparation: read Chapter 7 and the lecture notes for this week. Objectives: 1. To practice using one- and two-dimensional arrays 2. To practice using partially
Last Class. While loops Infinite loops Loop counters Iterations
 Last Class While loops Infinite loops Loop counters Iterations public class January31{ public static void main(string[] args) { while (true) { forloops(); if (checkclassunderstands() ) { break; } teacharrays();
Last Class While loops Infinite loops Loop counters Iterations public class January31{ public static void main(string[] args) { while (true) { forloops(); if (checkclassunderstands() ) { break; } teacharrays();
Week 2: Data and Output
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 2: Data and Output Learning to speak Java Types, Values and Variables Output Objects and Methods What s the Plan? Topic I: A little review IPO, hardware, software and Java
CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 2: Data and Output Learning to speak Java Types, Values and Variables Output Objects and Methods What s the Plan? Topic I: A little review IPO, hardware, software and Java
Intro to Programming. Unit 7. What is Programming? What is Programming? Intro to Programming
 Intro to Programming Unit 7 Intro to Programming 1 What is Programming? 1. Programming Languages 2. Markup vs. Programming 1. Introduction 2. Print Statement 3. Strings 4. Types and Values 5. Math Externals
Intro to Programming Unit 7 Intro to Programming 1 What is Programming? 1. Programming Languages 2. Markup vs. Programming 1. Introduction 2. Print Statement 3. Strings 4. Types and Values 5. Math Externals
News and information! Review: Java Programs! Feedback after Lecture 2! Dead-lines for the first two lab assignment have been posted.!
 True object-oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Reference Variables D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design Lecture 3 Static Object-Oriented Programming UML" knows-about Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111,
True object-oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Reference Variables D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design Lecture 3 Static Object-Oriented Programming UML" knows-about Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111,
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site I have decided to keep this site for the whole semester I still hope to have blackboard up and running, but you
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site I have decided to keep this site for the whole semester I still hope to have blackboard up and running, but you
Lecture 14. 'for' loops and Arrays
 Lecture 14 'for' loops and Arrays For Loops for (initiating statement; conditional statement; next statement) // usually incremental body statement(s); The for statement provides a compact way to iterate
Lecture 14 'for' loops and Arrays For Loops for (initiating statement; conditional statement; next statement) // usually incremental body statement(s); The for statement provides a compact way to iterate
Controls Structure for Repetition
 Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
CS103 Handout 29 Winter 2018 February 9, 2018 Inductive Proofwriting Checklist
 CS103 Handout 29 Winter 2018 February 9, 2018 Inductive Proofwriting Checklist In Handout 28, the Guide to Inductive Proofs, we outlined a number of specifc issues and concepts to be mindful about when
CS103 Handout 29 Winter 2018 February 9, 2018 Inductive Proofwriting Checklist In Handout 28, the Guide to Inductive Proofs, we outlined a number of specifc issues and concepts to be mindful about when
Robots. Byron Weber Becker. chapter 6
 Using Variables Robots Learning to Program with Java Byron Weber Becker chapter 6 Announcements (Oct 5) Chapter 6 You don t have to spend much time on graphics in Ch6 Just grasp the concept Reminder: Reading
Using Variables Robots Learning to Program with Java Byron Weber Becker chapter 6 Announcements (Oct 5) Chapter 6 You don t have to spend much time on graphics in Ch6 Just grasp the concept Reminder: Reading
CS 161: Object Oriented Problem Solving
 CS 161: Object Oriented Problem Solving About this course Like 160 your first CS course - cs161 is a combination of programming and discrete math. Why is math important to us? What math have you learned
CS 161: Object Oriented Problem Solving About this course Like 160 your first CS course - cs161 is a combination of programming and discrete math. Why is math important to us? What math have you learned
Conditionals, Loops, and Style
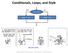 Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
BM214E Object Oriented Programming Lecture 4
 BM214E Object Oriented Programming Lecture 4 Computer Numbers Integers (byte, short, int, long) whole numbers exact relatively limited in magnitude (~10 19 ) Floating Point (float, double) fractional often
BM214E Object Oriented Programming Lecture 4 Computer Numbers Integers (byte, short, int, long) whole numbers exact relatively limited in magnitude (~10 19 ) Floating Point (float, double) fractional often
Conditionals, Loops, and Style. Control flow thus far. if statement. Control flow. Common branching statement Evaluate a boolean expression
 Conditionals, Loops, and Style Control flow thus far yes no x > y? max = x; max = y; public class ArgsExample time 0 String product = args[0]; time 1 int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); time 2 double
Conditionals, Loops, and Style Control flow thus far yes no x > y? max = x; max = y; public class ArgsExample time 0 String product = args[0]; time 1 int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); time 2 double
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Jan-Apr 2006 Tamara Munzner
 University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Jan-Apr 2006 Tamara Munzner Conditionals II Lecture 11, Thu Feb 9 2006 based on slides by Kurt Eiselt http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~tmm/courses/cpsc111-06-spr
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Jan-Apr 2006 Tamara Munzner Conditionals II Lecture 11, Thu Feb 9 2006 based on slides by Kurt Eiselt http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~tmm/courses/cpsc111-06-spr
Final Examination Semester 3 / Year 2012
 Final Examination Semester 3 / Year 2012 COURSE : INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING COURSE CODE : PROG1013 TIME : 2 1/2 HOURS DEPARTMENT : COMPUTER SCIENCE LECTURER : LIM PEI GEOK Student s ID : Batch No. :
Final Examination Semester 3 / Year 2012 COURSE : INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING COURSE CODE : PROG1013 TIME : 2 1/2 HOURS DEPARTMENT : COMPUTER SCIENCE LECTURER : LIM PEI GEOK Student s ID : Batch No. :
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-4: do/while loops, assertions reading: 5.1, 5.5 1 The do/while loop do/while loop: Performs its test at the end of each repetition. Guarantees that the loop's
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-4: do/while loops, assertions reading: 5.1, 5.5 1 The do/while loop do/while loop: Performs its test at the end of each repetition. Guarantees that the loop's
1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop.
 Practice Exam 2 Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop. 2. The < (less than)
Practice Exam 2 Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop. 2. The < (less than)
Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support
 Java Essentials CSCI 136: Spring 2018 Handout 2 February 2 Language Basics Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support Data abstraction Code reuse Modular development
Java Essentials CSCI 136: Spring 2018 Handout 2 February 2 Language Basics Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support Data abstraction Code reuse Modular development
