ADVANCE OSPF DEPLOYMENT
|
|
|
- Kellie Haynes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ADVANCE OSPF DEPLOYMENT SESSION 1 Agenda OSPF Deployment Tips OSPF Dialup Design Tips Fast Convergence Non-Stop Forwarding Stub Router Advertisement Flood Reduction 2 Printed in USA.
2 Market Segments Market segments a) Service providers b) Enterprise Manufacturing Retail 3 SP Deployment Characteristics SPs should have only one instance of IGP running throughout network (exceptions are there) BGP carries external reachability IGP carries only nexthop (loopbacks are better for e.g., nexthop-self) Area 6/L1 BGP 1 POP POP Area 1/L1 BGP 1 IP Backbone Area 5/L1 BGP 1 POP Area0/L2 BGP 1 POP POP Area 2/L1 BGP 1 Area 4/L1 BGP 1 Area 3/L1 BGP 1 POP 4 Printed in USA.
3 SP Architecture Major routing information is 110K via BGP POP Area 1/L1 BGP 1 POP Area 2/L1 BGP 1 Largest known IGP routing table is ~6 7K Total of 117K 6K/117K~5% of IGP routes in an ISP network A very small factor but has a huge impact on network convergence! Area 6/L1 BGP 1 POP IP Backbone Area 5/L1 BGP 1 POP Area0/L2 BGP 1 Area 4/L1 BGP 1 POP Area 3/L1 BGP 1 POP 5 SP Architecture You can reduce the IGP size from 6K to approx the number of routers in your network Regional Core NMS This will bring really fast convergence RR WAN Optimized where you must and summarize where you can Access IGP Stops unnecessary flapping PE PE PE CE CE CE 6 Printed in USA.
4 SP Architecture The link between PE-CE needs to be known for management purpose BGP next-hop-self should be done on all access routers unless PE-CE are on shared media (rare case) This will cut down the size of the IGP For PE-CE link do redistributed connected in BGP These connected subnets should ONLY be sent through RR to NMS for management purpose; this can be done through BGP communities BGP Access PE RR PE Regional Core WAN PE CE CE CE NMS 7 SP Architecture Where do we define area boundaries? WAN routers can be L1L2 in ISIS or ABR in case of OSPF Hide the pop infrastructure from your core Traffic engineering if needed can be done in core from WAN routers Access WAN Regional Core ABR or L1L2 L1/Area NMS PE PE PE CE CE CE 8 Printed in USA.
5 SP Architecture Physical address between ABR and PE should be in a contiguous blocks These physical links should be filtered via Type 3 filtering from area 0 into other areas Why? To reduce the size of the routing table within each pop Every area will carry only loopback addresses for all routers Only NMS station will keep track of those physical links PE device will not carry other Pop s PE s physical address in the routing table Access PE WAN Regional Core PE ABR/L1L2 PE CE CE CE NMS L2/Area 0 L1/Area 1 9 SP Architecture Area 0 will contain all the routes This is the most intelligent form of routing and also there will not be too many routes in IGP If there are 500 pops and every pop contains 4 routers; then instead of having 6K routes you will only have 2K This is scalable and hack proof network! Area 3/L1 BGP 1 POP POP Area1/L1 BGP 1 IP Backbone Area 4/L1 BGP 1 POP L2/Area 0 BGP 1 POP POP Area 2/L1 BGP 1 Area 5/L1 BGP 1 Area 6/L1 BGP 1 POP 10 Printed in USA.
6 Accidental Redistribution Prevention (OSPF) Areas should be defined as stub to prevent accidental redistribution of ebgp into OSPF Type 3 LSA filtering should be used at ABR s and only routers loopbacks should be allowed to leak into other areas Loopback should be in private address space to make LSA type 3 filtering easier; for e.g., /8 ibgp routes can not be redistributed into IGP by default NMS resides in area 0 here OSPF Stub Area POP POP OSPF Stub Area OSPF Stub Area POP ibgp Core/Area 0 ebgp ebgp ABR ebgp OSPF Stub Area ebgp POP 11 Market Segments Market segments a) Service providers b) Enterprise Manufacturing Retail 12 Printed in USA.
7 Enterprise Retail OSPF is not very good choice for hub and spokes EIGRP, ODR, RIPv2 and BGP are better choice here Enterprise BGP is not complicated You do not need to play with lot of attributes 13 Enterprise Retail The link between 2 hub routes should be equal to the number of areas Summarization of areas will require specific routing information between the ABR s This is to avoid suboptimal routing As you grow the number of areas, you will grow the number of VLAN/PVC s This is protocol limitation Trunk with One VLAN in Each Flooding Domain 14 Printed in USA.
8 Enterprise Retail Spoke router in one area will contains route for the other spoke router since they are in the same area Acquisitions and merger will create another sets of problem Rearrangement of topology required if the area or the router limitation has been reached Very difficult to preserve the protocol s hierarchical design Acquisition 15 Enterprise Manufacturing Can have multiple islands of IGPs Islands tied together by a BGP core Brazil Canada IGP 6 IGP 5 May be a requirement for redistribution IGP 1 BGP Core IGP 4 USA Japan IGP 2 IGP 3 France Germany 16 Printed in USA.
9 Agenda OSPF Deployment Tips OSPF Dialup Design Tips Fast Convergence Non-Stop Forwarding Stub Router Advertisement Flood Reduction 17 Dial Backup and OSPF Dial-on-demand techniques: Use virtual profiles Virtual interface gets assigned to the area associated with the calling router Area configuration and IP address for virtual interface are dynamic 18 Printed in USA.
10 Dial Backup and OPSF Virtual Profiles AAA Server Virtual Interface Area 3 NAS Area 4 Area 0 Dial Backup Primary Link 19 Dialup Design Practices Two kinds of Pools can be defined on NAS: Static Pools and Distributed Pools Static Pool: address range remain within a single NAS easier to manage from routing perspective Dynamic Pool: address range may be distributed into multiple NAS s hard to from a routing perspective Core Agg. Router Routes Injected by Each NAS 20 Printed in USA.
11 Dialup Design with Static Pool Addresses Three ways to propagate dialup routes from NAS: Either Static route to pool address to null 0 with redistribute static on NAS or Assign the pool add on a loopback on NAS with OSPF p2p network-type including loopback in an OSPF area or Static route on ABR for the pool address pointing towards NAS (ASBRs) this is a preferred method because summarization can be done at ABR Static pool do not require redistribute connected subnets on NAS Area 0 ABR Routes Injected by Each NAS 21 Dialup Design with Dynamic Pool Addresses Distributed pool REQUIRES REDISTRIBUTE CONNECT SUBNETS If pool is distributed, you can t summarize the pools at ABR because of REDISTRIBUTE CONNECTED SUBNETS on NASs unless it s an NSSA, why? NSSA can summarize routes at ABR or ASBR NSSA Area 0 ABR Routes Injected by Each NAS 22 Printed in USA.
12 Dialup Design Practices Scalability Issues If an area has too many routes injected by NAS then break it up in more than one area Area should be configured as NSSA for controlling type 5 at ABR level NSSA ABR can filter type 5 originated by NAS servers Configure totally NSSA so one area type 5 will not go into other areas NAS ABR Area 0 Area 1 Area 2 NAS NAS NAS Routes Injected by Each NAS 23 Agenda OSPF Deployment Tips OSPF Dialup Design Tips Fast Convergence Non-Stop Forwarding Stub Router Advertisement Flood Reduction 24 Printed in USA.
13 Network Convergence Network convergence is the time needed for traffic to be rerouted to the alternative or more optimal path after the network event Network convergence requires all affected routers to process the event and update the appropriate data structures used for forwarding 25 Network Convergence Network convergence is the time required to: Detect the event Propagate the event Process the event Update the routing table/fib 26 Printed in USA.
14 Network Convergence: Event Detection When physical interface changes state, driver must notify the routing process This should happen in a ms range Carrier-delay default is 2s Some events are detected by IGP LAN is a typical example Neighbor is lost, but interface is UP/UP Hello mechanism has to detect the neighbor lost Min Hello interval is 1 second currently 27 Interface Event Dampening When interface state changes both RT and RPs are notified Unstable interface cause excessive RT processing and RP updates Purpose is to dampen the interface from the RT and RPs perspective (only works for IP) CSCdt88027 CLI: interface x/y dampening [half-life] [reuse suppress max-time] [restart [penalty]] 28 Printed in USA.
15 Interface Event Dampening Up Interface State Down Actual Penalty Maximum Penalty Suppress Threshold Reuse Threshold Interface State Perceived by IP RP 29 Network Convergence: Subsecond Hellos Problem: At what frequency should hellos be sent? Neighbor can be declare down due to the Hello(s) being dropped/lost over a very short congestion period Router may not be able to send Hellos fast enough if most of its resources are used for other tasks 30 Printed in USA.
16 Network Convergence: Event Detection OSPF Hello packet contains values of Hello and Dead interval Must match between neighbors Values are in seconds HelloInterval Options Rtr Pri RouterDeadInterval 31 Network Convergence: OSPF Subsecond Hellos CSCdu67116: DeadInterval minimum 1 second Hello multiplier is used to specify how many Hellos to send within 1 second Hello interval will be advertised as 0 second CLI: interface x/y ip ospf dead-interval minimal hello-multiplier <3-20> 32 Printed in USA.
17 Network Convergence: OSPF Subsecond Hellos Topvar(config)#int eth 1/3 Topvar(config-if)#ip ospf dead-interval minimal hello-multiplier 3 Topvar#sh ip ospf int eth 1/3 Ethernet1/3 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address /24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID , Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 10 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State BDR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) , Interface address Backup Designated router (ID) , Interface address Timer intervals configured, Hello 333 msec, Dead 1, Wait 1, Retransmit 5 Hello due in 149 msec Topvar#sh ip ospf neigh det Neighbor , interface address In the area 0 via interface Ethernet1/3 Neighbor priority is 1, State is FULL, 6 state changes DR is BDR is Options is 0x52 LLS Options is 0x1 (LR) Dead timer due in 896 msec 33 Fast Hello s: Scaling Issues Scaling Is a Major Issue 300 Interfaces x 10 Neighbors/Interface = 3000 Neighbors 3 Hello Packets per Second on Each Interface Router Has to Generate 900 Hellos per Second 3000 Neighbors Each Send 3 Hellos per Second to This Router Router Has to Accept and Process 9000 Hellos per Second Router Has to Deal with 9900 Hellos per Second One Hello Every 10,000 th of a Second 34 Printed in USA.
18 Network Convergence Network convergence is the time required to: Detect the event Propagate the event Process the event Update the routing table/fib 35 Network Convergence: OSPF Event Propagation After an event has been detected, LSA is generated to reflect the change LSA is not generated immediately OSPF_LSA_DELAY_INTERVAL 500ms delay Only used when generating router and network LSA The reason for this delay is to collect any changes that happens during the delay interval and include them all in the new LSA 36 Printed in USA.
19 Network Convergence: OSPF Event Propagation Origination of the new instance of the LSA is limited at the originator MinLSInterval The minimum time between distinct originations of any particular LSA; the value of MinLSInterval is set to 5 seconds Old CLI: timers lsa-interval <sec> 5s by default (as in spec) 37 Network Convergence: OSPF Event Propagation Receiving of the LSAs is limited by the receiver MinLSArrival For any particular LSA, the minimum time that must elapse between reception of new LSA instances during flooding. LSA instances received at higher frequencies are discarded. The value of MinLSArrival is set to 1 second. Old CLI: timers lsa-arrival <sec> 1 second by default (as in spec) 38 Printed in USA.
20 OSPF LSA Generation Exp. Backoff LSAs are generated quickly after initial triggers Prolonged instability slows down the LSA generation process CSCdt21415 CLI timers throttle lsa all <lsa-start> <lsa-hold> <lsa-max> timers lsa arrival <timer> all values are in ms 39 OSPF LSA Generation Exp. Backoff Events Causing LSA Generation 1000 timers throttle lsa all previous LSA generation at t0 (t1 t0) > 5000 ms t1 t2 LSA Generation Time [ms] LSA Generation Backoff Alg. Time [ms] t1+10 t2+10 Time [ms] 40 Printed in USA.
21 OSPF LSA Generation Backoff Current RFC: MinLSArrival is set to 1 second LSA instances received at higher frequencies are discarded Need to set the MinLSArrival to lsa-hold timers lsa arrival < lsa-hold > 41 Network Convergence: Event Propagation LSA has to be processed on each node Detect if the LSA is newer/older If the LSA is newer, detect if it carries any change Number of links in the LSA (link comparison) Size of the database (search) If change detected schedule SPF (full/partial) Install in the database Above processing time is rather small For Router-LSA with 10 links: 0.5ms For Router-LSA with 100 links: 1ms 42 Printed in USA.
22 Network Convergence: Event Propagation If LSA is declared newer, it s flooded over a certain set of interfaces Excluding the neighbor from which the LSA has been received LSA is not flooded immediately Link state update packets are paced Pacing timer is 33ms by default (jittered by 10%) 43 Network Convergence: OSPF Event Propagation With default values and no retransmission each node can add 33ms delay to the event propagation CSCds86112 make packet pacing configurable Default values are 33 msec/66 msec timers pacing flood <timer> timers pacing retransmission <timer> 44 Printed in USA.
23 Network Convergence Network convergence is the time required to: Detect the event Propagate the event Process the event Update the routing table/fib 45 Network Convergence: OSPF Event Processing If there was a change detected in the LSA during the flooding, an SPF (full/partial) is scheduled Full SPF computation is delayed to protect router CPU resources spf-delay interval 5 seconds by default spf-holdtime 10 seconds by default Old CLI (before CSCdt21362) timers spf <spf-delay> <spf-holdtime> Both timers in seconds Partial SPF is not delayed 46 Printed in USA.
24 Network Convergence: OSPF SPF Backoff spf-delay and spf-holdtime protect the router resources, but significantly slows down the convergence Solution: Exponential SPF backoff (CSCdt21362) spf-delay/spf-holdtime changed to dynamic timers Values configured in ms timers throttle spf <spf-start> <spf-hold> <spf-max> <spf-start> Delay between receiving a change to SPF calculation <spf-hold> Delay between first and second SPF calculation <spf-max> Maximum wait time in milliseconds for SPF calculations 47 Network Convergence: SPF Two types of SPF Full SPF Triggered by the change in router or network LSA SPT tree is recomputed All LSA types (Type-1/2/3/4/5/7) are processed Partial SPF Triggered by the change in Type-3/4/5/7 LSA If triggered by Type-3/ all Type-3 LSAs that contribute to the certain destination are processed If triggered by Type-5/7 all Type-5/7 LSAs that contribute to the certain destination are processed If triggered by Type-4 all Type-4 LSAs that announce a certain ASBR and all Type-5/7 LSAs are processed 48 Printed in USA.
25 Network Convergence: SPF Time SPF calculation time Full spf: Depends on: Number of nodes/links in the area Number of Type-3/4/5/7 LSAs Some experimental numbers (GSR/7500) 50 nodes fully connected topology~10ms 100 node fully connected topology~25ms 500 nodes~50 ms 1000 nodes~100 ms Partial SPF: Fast less then 0.5 ms 49 Network Convergence: SPF Any change in the router/network LSA triggers full SPF Some changes does not represent the topology change: Stub network UP/DOWN IP address change on link During the full SPF the whole SPT is rebuilt Change in the topology may not require the whole SPT rebuild Major part of the tree may stay the same in many cases 50 Printed in USA.
26 Network Convergence: Incremental SPF Incremental SPF Modified Dijkstra algorithm We keep the unchanged part of the tree We rebuild only the affected parts of the tree Re-attach the affected parts of the tree to the unchanged part of the tree 51 Network Convergence: Incremental SPF Gain of incremental SPF depends on how far (topologically) the change happens from the calculating node If the change affects only a small part of the topology, gain is significant We were able to run SPF and update the RT for the 1000 node network in less then 10 ms If the change is close to the calculating node and affect almost the whole topology, there will be no gain in i-spf 52 Printed in USA.
27 Network Convergence: Incremental SPF There are always nodes close (closer) to the topological change and nodes that are remote (more remote) to it Flooding takes some time nodes that are most remote from the change are usually notified last If full SPF runs on all nodes regardless of the change, then routers notified as last about it will converge last (giving that it takes same amount of time to run SPF on each node) With i-spf, more remote the node is from the change, less work it needs to do during i-spf, resulting in faster network wide convergence 53 Network Convergence: Incremental SPF Stub link down event (IP prefix lost): Full SPF: Sep 25 14:07:37.795: OSPF: Begin SPF at ms, process time ms Sep 25 14:07:37.795: spf_time 2d04h, wait_interval 10s Sep 25 14:07:37.839: OSPF: End SPF at ms, Total elapsed time 44ms Sep 25 14:07:37.839: Intra: 44ms, Inter: 0ms, External: 0ms Sep 25 14:07:37.839: R: 506, N: 786, Stubs: 620 Sep 25 14:07:37.839: SN: 0, SA: 0, X5: 0, X7: 0 Sep 25 14:07:37.839: SPF suspends: 0 intra, 0 total Incremental SPF: Sep 25 14:06:27.715: OSPF: Begin SPF at ms, process time ms Sep 25 14:06:27.715: spf_time 2d04h, wait_interval 10s Sep 25 14:06:27.719: OSPF: End SPF at ms, Total elapsed time 4ms Sep 25 14:06:27.719: Incremental-SPF: 0ms Sep 25 14:06:27.719: Intra: 0ms, Inter: 0ms, External: 0ms Sep 25 14:06:27.719: R: 0, N: 0, Stubs: 1 Sep 25 14:06:27.719: SN: 0, SA: 0, X5: 0, X7: 0 Sep 25 14:06:27.723: SPF suspends: 0 intra, 0 total 54 Printed in USA.
28 Network Convergence: Incremental SPF Link up Event part of the network becomes reachable: Full SPF: Sep 25 14:27:13.463: OSPF: Begin SPF at ms, process time ms Sep 25 14:27:13.463: spf_time 2d04h, wait_interval 5s Sep 25 14:27:13.515: OSPF: End SPF at ms, Total elapsed time 52ms Sep 25 14:27:13.515: Intra: 48ms, Inter: 0ms, External: 0ms Sep 25 14:27:13.515: R: 488, N: 758, Stubs: 598 Sep 25 14:27:13.515: SN: 0, SA: 0, X5: 0, X7: 0 Sep 25 14:27:13.515: SPF suspends: 0 intra, 0 total Incremental SPF: Sep 25 14:23:13.467: OSPF: Begin SPF at ms, process time ms Sep 25 14:23:13.467: spf_time 2d04h, wait_interval 5s Sep 25 14:23:13.479: OSPF: End SPF at ms, Total elapsed time 12ms Sep 25 14:23:13.479: Incremental-SPF: 0ms Sep 25 14:23:13.479: Intra: 8ms, Inter: 0ms, External: 0ms Sep 25 14:23:13.479: R: 18, N: 29, Stubs: 22 Sep 25 14:23:13.479: SN: 0, SA: 0, X5: 0, X7: 0 Sep 25 14:23:13.479: SPF suspends: 0 intra, 0 total 55 Network Convergence: Incremental SPF Time it takes to run the SPF with the transit link flap Time in msec Link Flap Number of Nodes x 100 SPF ispf 56 Printed in USA.
29 Network Convergence: Incremental SPF Time it takes to run the SPF with the transit link flap Link Flap Time in msec Number of Nodes x 2000 SPF ispf 57 Network Convergence: OSPF Incremental SPF CLI Router ospf <process number> ispf debug ip ospf Includes i-spf related output sh ip ospf Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID and Domain ID Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes Supports opaque LSA It is an area border and autonomous system boundary router Redistributing External Routes from, SPF schedule delay 5 secs, Hold time between two SPFs 10 secs Incremental-SPF enabled Minimum LSA interval 5 secs; minimum LSA arrival 1 secs 58 Printed in USA.
30 Network Convergence Network convergence is the time required to: Detect the event Propagate the event Process the event Update the routing table/fib 59 Network Convergence: Update the Routing Table/FIB Based on some experiments, this represents a significant time in the convergence Projects are under way to make the RIB faster, more scalable and to improve the FIB info download to the linecards 60 Printed in USA.
31 Network Convergence: Summary With the mentioned features deployed sub-second network convergence is possible with OSPF Fast convergence must not affect the stability and scalability of the network 61 Agenda OSPF Deployment Tips OSPF Dialup Design Tips Fast Convergence Non-Stop Forwarding Stub Router Advertisement Flood Reduction 62 Printed in USA.
32 NSF 2 Issues (with the existing OSPF deployments) When a RP/LC gets reset, we tear down the whole adjacency If LSDB has to be resynched, we have to put the neighbor FSM state into ExStart State, which causes the adjacencies to be removed from the router-lsas 63 NSF Issues addressed (via): [Hellos] From a restarting-router point-of-view OSPF Hello Packets will carry additional information which includes The LR Bit The RS Bit In the EO-TLV which is a part of LLS data block By doing this, the restarting router is saying to its neighbors not to reset/tear down their adjacency to this router 64 Printed in USA.
33 NSF Issues addressed (via): [Hellos] From the neighboring-router(s) point-of-view Should skip the two-way connectivity check with the announcing neighbor Not generate a 1-WayReceived event for the neighbor if it does not find its own router ID in the list of neighbors 65 NSF Issues addressed (via): [LSDB Sync] LSDBD packet includes a new R Bit Indicating the OOB Resynchronization OPSF Nei. Data structure includes a new field OOBResync indicating the router is currently performing OOB LSDB resynchronization 66 Printed in USA.
34 NSF The Options Field * O DC L N/P MC E * E MC N/P DC O L Describes the Way AS External-LSAs Are flooded Describes Whether IP MultiCast Datagrams Are Flooded Handling of Type-7 LSAs Describes the Router s Handling of Demand Circuits Describes the Router s Willingness to Receive and Forward Opaque-LSAs Link Local Signaling (LLS) 67 NSF LLS Data Block IP Header Length OSPF Header Length OSPF Data Authentication Data LLS Data IP HL=HL+X+Y+Z OSPF HL=X Y Z 68 Printed in USA.
35 NSF Two new TLVs have been defined as part of LLS data block Extended Options TLV Cryptographic Authentication TLV # of Octets Checksum 2 LLS Data Length 2 LLS TLVs Variable 69 NSF Extended Options TLV Type 1 4-Bytes long Should appear once in the LLS data block # of Octets EO-TLV #: 1 2 Length 2 Extended Options 4 70 Printed in USA.
36 NSF EO-TLV has the following information carried in the Data Portion of the TLV (in the Extended Options) LR Bit (LSDB Resynchronization) RS Bit (Restart Signal) * * * * RS LR 71 NSF LR Bit (LSDB Resynchronization) To announce OOB Resynchronization capability to the neighbors as part of both Hello and DBD packets Uses 0x in the EO-TLV [part of LLS] * * * * RS LR 72 Printed in USA.
37 NSF RS Bit (Restart Signal) Restarting Router should set this Bit in the EO-TLV attached in the Hello Packet to tell the neighbors to preserve their adjacencies Receiving Router with RS Bit should not generate a 1- WayReceived event for the neighbor Receiving Router should send a Unicast Hello back to Restarting Router in reply to a Hello Packet with the RS Bit The RS Bit may not be set in Hello Packets longer than RouterDeadInterval seconds Uses 0x in the EO-TLV [part of LLS] * * * * RS LR 73 OSPF: NSF Hello Exchange RestartState Restarting Router Hello NSF-Aware Neighbor NID RS = 1, LR = 1 Hello ResyncTimeout RS = 0, LR = 1 74 Printed in USA.
38 NSF The Database Description packet will include a new flag indicating OOB LSDB Resynchronization R I M MS R LSDB Resync Active Bit 75 OSPF: OOB Resync oob_resync oob_resync NID Restarting Router DBD NSF-Aware Neighbor NID R=1,I=1,M=1,MS=1 DBD R=1,I=1,M=1,MS=1 76 Printed in USA.
39 OSPF NSF CLI The following commands are configured under router ospf <proc> nsf [enforce global] The enforce global option causes NSF processing to terminate for entire OSPF process, whereas the default behavior is that NSF will abort per-interface where non- NSF-aware neighbors are discovered timers nsf wait <interval> Hidden command For setting the interface wait interval during NSF restart, as well as the first NSF Restart Timer period timers nsf flush <interval> Hidden command For setting how much time to wait after RIB convergence, before flushing stale LSAs 77 OSPF Configuration Example(s) Restarting-Router Show IP OSPF [Abbreviated Output] HA-Router#show ip ospf Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes Supports opaque LSA Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Non-Stop Forwarding enabled, last NSF restart 00:25:00 ago (took 32 secs) 78 Printed in USA.
40 OSPF Configuration Example(s) NSF-Aware Neighbor Show IP OSPF [Abbreviated Output] NSF-Aware-Router#show ip ospf Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa External flood list length 0 Non-Stop Forwarding enabled Router is not operating in SSO mode 79 OSPF Configuration Example(s) Restarting-Router Show IP OSPF Neighbor Detail [Abbreviated Output] HA-Router#show ip ospf neighbor detail Neighbor , interface address In the area 1 via interface POS3/0 Neighbor priority is 0, State is FULL, 7 state changes DR is BDR is Options is 0x58 LLS Options is 0x1 (LR), last OOB-Resync 00:26:13 ago Dead timer due in 00:00:31 Neighbor is up for 00:26:34 80 Printed in USA.
41 OSPF Configuration Example(s) NSF-Aware Neighbor Show IP OSPF Neighbor Detail [Abbreviated Output] NSF-Aware-Router#show ip ospf neighbor detail Neighbor , interface address In the area 1 via interface POS4/0 Neighbor priority is 0, State is FULL, 42 state changes DR is BDR is Options is 0x58 LLS Options is 0x1 (LR), last OOB-Resync 00:46:35 ago Dead timer due in 00:00:34 81 OSPF Configuration Example(s) Show IP OSPF Database HA-Router#show ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 1) Router Link States (Area 1) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count x x7EA s x C 0xE7B Printed in USA.
42 NSF: Non-Stop Forwarding More Details draft-nguyen-ospf-oob-resync-xx.txt Describes OSPF out-of-band resynchronization (oob-resync) draft-nguyen-ospf-restart-xx.txt Describes protocol restart signaling draft-nguyen-ospf-lls-xx.txt Describes extending the OSPF options field 83 Agenda OSPF Deployment Tips OSPF Dialup Design Tips Fast Convergence Non-Stop Forwarding Stub Router Advertisement Flood Reduction 84 Printed in USA.
43 Stub Router Advertisement There are situations, when we may want to avoid using the router that is connected in a network Some time before/after upgrade, scheduled downtime When the router is converging a large RT typically BGP with full Net routes; OSPF has converged, but we do not want to send the transit traffic through the box until BGP has converged While the router is reconfigured 85 Stub Router Advertisement Router-LSA advertises: (1) p2p links to other router (2) Transit network (3) Stub network (4) VL 1, 2, 4 are transit links Transit links are used for traffic that passes through the router (destination is not directly connected to the router) 86 Printed in USA.
44 Stub Router Advertisement If we want to avoid transit traffic through the box we set the metric of all transit links advertised by the router in its router LSA to 0xFFFF (max metric) All other routers will avoid the router and use alternative paths if such paths exist If no other paths are available: Routers that implements RFC1247 links with max-metric will be simply ignored Routers that implements RFC2328 links with max-metric will be used if no alternative paths exists 87 OSPF Stub Router Advertisement New Flow of Traffic OSPF Router Can Now Be Upgraded with Minimal Network Interruption Primary Flow of Traffic router ospf 123 max-metric router-lsa 88 Printed in USA.
45 Stub Router Advertisement max-metric router-lsa [ on-startup {wait-for-bgp <announce-time>} ] Syntax description router-lsa Always originate router-lsas with maximum metric on-startup Set max-metric temporarily after reboot announce-time Time, in seconds, router-lsas are originated with max-metric (default is 600s) wait-for-bgp Let BGP decide when to originate router-lsa with normal metric (i.e., stop sending router-lsa with max-metric) 89 Stub Router Advertisement Output of "show ip ospf" command: Routing Process "ospf 1998" with ID Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes Supports opaque LSA It is an area border and autonomous system boundary router Redistributing External Routes from, static, includes subnets in redistribution Originating router-lsas with maximum metric, Time remaining: 00:01:18 Condition: on startup while BGP is converging, State: active SPF schedule delay 5 secs, Hold time between two SPFs 10 secs Minimum LSA interval 5 secs. Minimum LSA arrival 1 secs Number of external LSA 7. Checksum Sum 0x47261 Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x Printed in USA.
46 Stub Router Advertisement Link connected to: a Transit Network Output of "show ip ospf database router" command: (Link ID) Designated Router address: (Link Data) Router Interface address: Exception Flag: Announcing maximum link costs Number of TOS metrics: 0 LS age: 68 TOS 0 Metrics: (metric used for local calculation: 10) Options: (No TOS-capability, DC) LS Type: Router Links Link connected to: a Transit Network Link State ID: (Link ID) Designated Router address: Advertising Router: (Link Data) Router Interface address: LS Seq Number: Number of TOS metrics: 0 Checksum: 0x175D TOS 0 Metrics: (metric used for local Length: 60 calculation: 10) Area Border Router AS Boundary Router Link connected to: a Stub Network Number of Links: 3 (Link ID) Network/subnet number: (Link Data) Network Mask: Number of TOS metrics: 0 TOS 0 Metrics: 1 91 Agenda OSPF Deployment Tips OSPF Dialup Design Tips Fast Convergence Non-Stop Forwarding Stub Router Advertisement Flood Reduction 92 Printed in USA.
47 Flood Reduction Each LSA has its age When LSA is originated its age is set to 0 LSA is flushed from the area/domain when its age reaches MAXAGE (3600s) Each router must periodically refresh all self-generated LSAs Refresh period is +/- 1800s 93 Flood Reduction Why do we need to refresh periodically? At the time the spec was written it looked to be a good to refresh to keep the databases in sync Flooding is reliable and all changes are propagated reliably to all routers in area 94 Printed in USA.
48 Flood Reduction OSPF has the concept of preventing the refresh for DC (Demand Circuit), like dialup links, ISDN, Do Not Age LSAs DN bit DC has some drawbacks Hellos are not sent over DC, which can prevent the neighbor loss detection 95 Flood Reduction We can generalize the Do Not Age concept FR (Flood Reduction) link same as DC, but Hellos are sent over it as over any p2p link All LSAs sent over FR link will have the DN bit set Those LSA will never timeout in the databases of routers behind the FR link 96 Printed in USA.
49 Flood Reduction LSAs does not need to be refreshed over the FR links at all Changed LSA are flooded over FR link ip ospf flood-reduction on the interface CSCdp80470 draft-pillay-esnault-ospf-flooding-xx.txt Possible extension is to refresh at configured interval 97 Summary What We Learned? Effective OSPF Deployment Tips. How to use those techniques in your OSPF network Understanding of how OSPF Fast Convergence works Understanding of how Non Stop Forwarding works We learned about the Stub Router advertisement and where to use this feature We learned about Flood reduction feature and where to use it 98 Printed in USA.
50 Recommended Reading RFC 2328(OSPF) 1587(NSSA) New RFC (Demand Circuit) RFC 2370 (for opaque support) Large-scale IP network solutions: CCIE Professional Development by Khalid Raza and Mark Turner ISBN: Troubleshooting IP Routing Protocols by Faraz Shamim, Zaheer Aziz, Johnson Liu and Abe Martey ISBN: Available on-site at the Cisco Company Store 99 Complete Your Online Session Evaluation! WHAT: WHY: Complete an online session evaluation and your name will be entered into a daily drawing Win fabulous prizes! Give us your feedback! WHERE: Go to the Internet stations located throughout the Convention Center HOW: Winners will be posted on the onsite Networkers Website; four winners per day 100 Printed in USA.
51 101 Printed in USA.
Deployment and Analysis of Link State Protocols
 Deployment and Analysis of Link State Protocols Session 2 Copyright Printed in USA. Agenda Pre-Requisite Link State Protocol Refresher Fundamental Deployment and Analysis OSPF Configuration Examples ISIS
Deployment and Analysis of Link State Protocols Session 2 Copyright Printed in USA. Agenda Pre-Requisite Link State Protocol Refresher Fundamental Deployment and Analysis OSPF Configuration Examples ISIS
BRKRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 Deploying OSPF in a Large-Scale Networks 2 Agenda Market Segments Service Provider Deployments Enterprise Deployments Design Best Practices Fast Convergence 3 Market Segments Market Segments Service Providers
Deploying OSPF in a Large-Scale Networks 2 Agenda Market Segments Service Provider Deployments Enterprise Deployments Design Best Practices Fast Convergence 3 Market Segments Market Segments Service Providers
OSPF Convergence Details
 OSPF Convergence Details (C) Herbert Haas 2009/05/02 Introduction In this section we analyze all the more or less "hidden" delays that are required by the OSPF RFCs Our results will be, That standard OSPF
OSPF Convergence Details (C) Herbert Haas 2009/05/02 Introduction In this section we analyze all the more or less "hidden" delays that are required by the OSPF RFCs Our results will be, That standard OSPF
Scaling IGPs in ISP Networks. Philip Smith SANOG 8, Karachi 3rd August 2006
 Scaling IGPs in ISP Networks Philip Smith SANOG 8, Karachi 3rd August 2006 Agenda Definition of Scaling IGP Design Tuning OSPF What Does Scaling a Network Mean? Scaling is very important for an SP network
Scaling IGPs in ISP Networks Philip Smith SANOG 8, Karachi 3rd August 2006 Agenda Definition of Scaling IGP Design Tuning OSPF What Does Scaling a Network Mean? Scaling is very important for an SP network
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability
 OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability Contents Introduction Prerequisites Background Information Scenario 1 Network Diagram: Abstract from RFC 2328 Section 16.2 Scenario 2 Network Diagram: Abstract from
OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability Contents Introduction Prerequisites Background Information Scenario 1 Network Diagram: Abstract from RFC 2328 Section 16.2 Scenario 2 Network Diagram: Abstract from
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration RIP Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
OSPF Stub Router Advertisement
 The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
Link State Routing. Link State Packets. Link State Protocol. Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and pitfalls
 Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/09 11:25:31) Tuesday, March 7, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and
Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/09 11:25:31) Tuesday, March 7, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Configuring OSPF network management 39 Enabling message logging 39 Enabling the advertisement and reception of opaque LSAs 40 Configuring OSPF to
 Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 OSPF areas 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported OSPF features 17 Protocols and
Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 OSPF areas 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported OSPF features 17 Protocols and
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
MPLS Core Networks Николай Милованов/Nikolay Milovanov
 Tuning Core Routing Protocols Николай Милованов/Nikolay Milovanov Contents ISIS overview ISIS tuning http://niau.org 2 ISIS overview 3 IP routing design requirements Requirements towards the IGP protocols:
Tuning Core Routing Protocols Николай Милованов/Nikolay Milovanov Contents ISIS overview ISIS tuning http://niau.org 2 ISIS overview 3 IP routing design requirements Requirements towards the IGP protocols:
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
Cabrillo College. Rick Graziani, Instructor
 Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
OSPF Stub neighbor Draft
 OSPF Stub neighbor Draft draft-raza-ospf-stub-neighbor-00 Faraz Shamim Cisco Padma Pillay-Esnault Cisco Khalid Raza Viptela Andrew Kulawiak Bank of America John Cavanaugh 405 Labs Abstract Enhancement
OSPF Stub neighbor Draft draft-raza-ospf-stub-neighbor-00 Faraz Shamim Cisco Padma Pillay-Esnault Cisco Khalid Raza Viptela Andrew Kulawiak Bank of America John Cavanaugh 405 Labs Abstract Enhancement
Operation Manual IPv4 Routing H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Configuring Networking Protocols
 11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
Link State Routing. Link State Packets. Link State Protocol. Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and pitfalls
 Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 17.4, 2017/11/30 12:33:57) Tuesday, November 28, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems
Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 17.4, 2017/11/30 12:33:57) Tuesday, November 28, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information. Contents
 Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Logging neighbor state changes 38 Configuring OSPF network management 39 Enabling message logging 39 Enabling the advertisement and reception of
 Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 Area based OSPF network partition 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported features
Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 Area based OSPF network partition 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported features
Optimizations for Routing Protocol Stability and Convergence
 Optimizations for Routing Protocol Stability and Convergence Brian Daugherty, CSE, CCIE #5879 Higher Education and Research Network Initiatives bdaugher@cisco.com 1 Convergence? con ver gence (k?n-vûr
Optimizations for Routing Protocol Stability and Convergence Brian Daugherty, CSE, CCIE #5879 Higher Education and Research Network Initiatives bdaugher@cisco.com 1 Convergence? con ver gence (k?n-vûr
OSPF Virtual Link. Contents. Prerequisites. Document ID: Requirements. Components Used
 OSPF Virtual Link Document ID: 47866 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations How the Virtual Link Operates Calculate the Shortest
OSPF Virtual Link Document ID: 47866 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations How the Virtual Link Operates Calculate the Shortest
The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s
 Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF
 Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Fast IP Convergence. Section 4. Period from when a topology change occurs, to the moment when all the routers have a consistent view of the network.
 Fast IP Convergence Section 4 2899_05_2001_c1 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 IP Convergence Convergence Time Period from when a topology change occurs, to the moment when all the routers
Fast IP Convergence Section 4 2899_05_2001_c1 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 IP Convergence Convergence Time Period from when a topology change occurs, to the moment when all the routers
FiberstoreOS. IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
Explanation: In order to verify proper route redistribution, use the "show ip route" command on all routers
 QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
Networkers 2001, Australia
 Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting OSPF Jono Ladmore 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. Presentation_ID 2 Agenda LSA Details Troubleshooting Commands Common Issues Troubleshooting
Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting OSPF Jono Ladmore 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. Presentation_ID 2 Agenda LSA Details Troubleshooting Commands Common Issues Troubleshooting
Configuring OSPF. Cisco s OSPF Implementation
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
OSPF. Unless otherwise noted, OSPF refers to OSPFv2 throughout this document.
 Open Shortest Path First () is a link state based interior gateway protocol developed by the working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). At present, version 2 (RFC2328) is used. Introduction
Open Shortest Path First () is a link state based interior gateway protocol developed by the working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). At present, version 2 (RFC2328) is used. Introduction
DD2490 p Link-state routing and OSPF. Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC
 DD2490 p4 200 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex) and
DD2490 p4 200 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex) and
Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability. Buy Full Product.
 Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/4a0-101.html Examskey Alcatel-lucent 4A0-101 exam demo product is
Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/4a0-101.html Examskey Alcatel-lucent 4A0-101 exam demo product is
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally
IS-IS for ISPs. ISP Workshops. Last updated 25 th August 2015
 IS-IS for ISPs ISP Workshops Last updated 25 th August 2015 1 Configuring IS-IS in Cisco IOS p Starting IS-IS in Cisco IOS router isis [name] n Where the optional name can specify the name of the ISIS
IS-IS for ISPs ISP Workshops Last updated 25 th August 2015 1 Configuring IS-IS in Cisco IOS p Starting IS-IS in Cisco IOS router isis [name] n Where the optional name can specify the name of the ISIS
OSPFv2 deep dive. Михайловский Василий Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015
 OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
Config. Router# show ip ospf
 Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
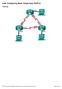 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
 OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Open : specification publicly available RFC 1247, RFC 2328 Working group formed in 1988 Goals: Large, heterogeneous internetworks Uses the Link State algorithm Topology
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Open : specification publicly available RFC 1247, RFC 2328 Working group formed in 1988 Goals: Large, heterogeneous internetworks Uses the Link State algorithm Topology
OSPF Commands. adjacency stagger, page 7. authentication-key (OSPF), page 14
 OSPF Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and
OSPF Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and
OSPF Protocol Overview on page 187. OSPF Standards on page 188. OSPF Area Terminology on page 188. OSPF Routing Algorithm on page 190
 Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands
 Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Command Manual IPv4 Routing H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1.1 delete static-routes all... 1-1 1.1.2 ip route-static...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1.1 delete static-routes all... 1-1 1.1.2 ip route-static...
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
OSPF. About OSPF. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.4 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
Operation Manual Routing Protocol. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IP Routing Protocol Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to IP Route and Routing Table... 1-1 1.1.1 IP Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Routing Table... 1-1 1.2 Routing Management
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IP Routing Protocol Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to IP Route and Routing Table... 1-1 1.1.1 IP Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Routing Table... 1-1 1.2 Routing Management
OSPF Commands on Cisco IOS XR Software
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent. Exam Code: 4A Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability.
 Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent Exam Code: 4A0-101 Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Version: Demo QUESTION 1 When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match
Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent Exam Code: 4A0-101 Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Version: Demo QUESTION 1 When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match
OSPFv3 Commands. address-family (OSPFv3), page 4. authentication (OSPFv3), page 7
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3
 Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
OSPF Demand Circuit Feature
 OSPF Demand Circuit Feature Document ID: 5132 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How Is OSPF over Demand Circuit Different from a Normal Circuit? Suppressed Periodic
OSPF Demand Circuit Feature Document ID: 5132 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How Is OSPF over Demand Circuit Different from a Normal Circuit? Suppressed Periodic
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
 OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Open : specification publicly available RFC 1247, RFC 2328 Working group formed in 1988 Goals: Large, heterogeneous internetworks Uses the Link State algorithm Topology
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Open : specification publicly available RFC 1247, RFC 2328 Working group formed in 1988 Goals: Large, heterogeneous internetworks Uses the Link State algorithm Topology
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands
 Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
9.1. Routing Protocols
 9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions. Net412- Network troubleshooting
 Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-5-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-5-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
Introduction to OSPF OSPF. Link State Routing. Link State. Fast Convergence. Low Bandwidth Utilisation
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IP Workshops OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 47) Designed for TCP/IP Internet environment Fast convergence
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IP Workshops OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 47) Designed for TCP/IP Internet environment Fast convergence
OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF
OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF
Planning for Information Network
 Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing
 Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPF Commands: A through Z
 OSPF Commands: A through Z area nssa, page 3 area nssa translate, page 5 area virtual-link, page 9 capability vrf-lite, page 13 capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), page 15 clear ip ospf, page 17 compatible rfc1587,
OSPF Commands: A through Z area nssa, page 3 area nssa translate, page 5 area virtual-link, page 9 capability vrf-lite, page 13 capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), page 15 clear ip ospf, page 17 compatible rfc1587,
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
EECS 122, Lecture 16. Link Costs and Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Static Cost Metrics.
 EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
Passit4Sure.4A Questions 4A Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
 Passit4Sure.4A0-101.300Questions Number: 4A0-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
Passit4Sure.4A0-101.300Questions Number: 4A0-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networks Spring 2016
 CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networks Spring 2016 Lecture 13 Router Algorithms and Design Chapter 5 1 Topics Router Algorithms Routing in General Hierarchical routing Interior Gateway Protocols OSPF mention of
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networks Spring 2016 Lecture 13 Router Algorithms and Design Chapter 5 1 Topics Router Algorithms Routing in General Hierarchical routing Interior Gateway Protocols OSPF mention of
Introduction to Routing
 1 Introduction to Routing Session 2 Presentation_ID.scr 1 Agenda Addressing Concepts Routing Protocols Statics and Defaults 3 ISO OSI Reference Model Routing Information Protocol (RIP and RIPv2) L7 L6
1 Introduction to Routing Session 2 Presentation_ID.scr 1 Agenda Addressing Concepts Routing Protocols Statics and Defaults 3 ISO OSI Reference Model Routing Information Protocol (RIP and RIPv2) L7 L6
debug ip ospf database external default-metric subnet area 0 stub distribute-list in Serial0/1
 Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Network Working Group. Category: Standards Track Stanford University March 1994
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1587 Category: Standards Track R. Coltun RainbowBridge Communications V. Fuller Stanford University March 1994 The OSPF NSSA Option Status of this Memo This
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1587 Category: Standards Track R. Coltun RainbowBridge Communications V. Fuller Stanford University March 1994 The OSPF NSSA Option Status of this Memo This
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information. Last Updated: June 24, 2011
 Configuring OSPF Finding Feature Information Configuring OSPF Last Updated: June 24, 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP)
Configuring OSPF Finding Feature Information Configuring OSPF Last Updated: June 24, 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP)
Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP
 Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training
 REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1
 IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: andrea.detti@uniroma2.it Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2 Slide
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: andrea.detti@uniroma2.it Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2 Slide
HP Load Balancing Module
 HP Load Balancing Module Appendix Protocol Reference Part number: 5998-4222 Software version: Feature 3221 Document version: 6PW100-20130326 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
HP Load Balancing Module Appendix Protocol Reference Part number: 5998-4222 Software version: Feature 3221 Document version: 6PW100-20130326 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
Link State. 1 Flooding of link-state information. 5 Routing Table. 3 SPF Algorithm. 2 Building a Topological Database. 4 SPF Tree
 Link State 1 Flooding of link-state information 5 Routing Table 2 Building a Topological Database 3 SPF Algorithm 4 SPF Tree OSPF Hello Protocol OSPF routers send Hellos on OSPF enabled interfaces: Default
Link State 1 Flooding of link-state information 5 Routing Table 2 Building a Topological Database 3 SPF Algorithm 4 SPF Tree OSPF Hello Protocol OSPF routers send Hellos on OSPF enabled interfaces: Default
Advanced Network Design
 Advanced Network Design Eugene Odnoralets Routing Protocols Team 23.11.15 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Introduction 2 23.11.15 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Advanced Network Design Eugene Odnoralets Routing Protocols Team 23.11.15 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Introduction 2 23.11.15 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Routing Protocol - IS-IS
 Routing Protocol - IS-IS What is IS-IS? Intermediate System to Intermediate System intra-domain routing protocol :: IS, ES Is a Link State Protocol Is a dynamic routing protocol based on SPF routing algorithm
Routing Protocol - IS-IS What is IS-IS? Intermediate System to Intermediate System intra-domain routing protocol :: IS, ES Is a Link State Protocol Is a dynamic routing protocol based on SPF routing algorithm
Routed Fast Convergence and High Availability
 Routed Fast Convergence and High Availability Denise Fishburne Abstract This session discusses various mechanisms network engineers can use to improve their network's convergence time and availability,
Routed Fast Convergence and High Availability Denise Fishburne Abstract This session discusses various mechanisms network engineers can use to improve their network's convergence time and availability,
IPv6 Routing: OSPFv3
 Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0
 Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Configuring Cisco NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy
 CHAPTER 9 Configuring Cisco NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy This chapter describes how to configure supervisor engine redundancy using Cisco nonstop forwarding (NSF) with stateful switchover
CHAPTER 9 Configuring Cisco NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy This chapter describes how to configure supervisor engine redundancy using Cisco nonstop forwarding (NSF) with stateful switchover
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
OSPF Deployment in Modern Networks
 OSPF Deployment in Modern Networks Faraz Shamim Technical Leader BRKRST-2337 OSPF Deployment in Modern Networks WAN Aggregation Core Data Center Mobile Worker Internet VPN Firewall Mail Servers Internet
OSPF Deployment in Modern Networks Faraz Shamim Technical Leader BRKRST-2337 OSPF Deployment in Modern Networks WAN Aggregation Core Data Center Mobile Worker Internet VPN Firewall Mail Servers Internet
IPv6 Commands: sn to v
 IPv6 Commands: sn to v sntp address, page 3 spd extended-headroom, page 5 spd headroom, page 7 spf-interval (IPv6), page 9 split-horizon (IPv6 RIP), page 11 standby ipv6, page 13 summary-prefix (IPv6 IS-IS),
IPv6 Commands: sn to v sntp address, page 3 spd extended-headroom, page 5 spd headroom, page 7 spf-interval (IPv6), page 9 split-horizon (IPv6 RIP), page 11 standby ipv6, page 13 summary-prefix (IPv6 IS-IS),
Operation Manual OSPF. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 OSPF Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to OSPF... 1-1 1.1.2 Process of OSPF Route Calculation... 1-2 1.1.3 OSPF Packets... 1-2 1.1.4 LSA Type... 1-3 1.1.5
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 OSPF Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to OSPF... 1-1 1.1.2 Process of OSPF Route Calculation... 1-2 1.1.3 OSPF Packets... 1-2 1.1.4 LSA Type... 1-3 1.1.5
