Configuring EtherChannel
|
|
|
- Allan O’Connor’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 L4 Configuring EtherChannel Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-1
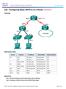
2 Objectives In this lab you will first verify that one of the parallel connections to the core switch is blocked by STP. You will then configure these parallel links as an EtherChannel group and verify that both are being used. Finally you will verify that if one of the links in the EtherChannel group goes down, the other continues to function, with no interruption to the data flow. The objectives for this lab are: Examine STP operation. Configure EtherChannel. Examine and verify EtherChannel behavior. Reconfigure pod devices for subsequent labs. Important Substitute your pod number for x and the router number for y in all instructions and commands. The passwords configured on the devices at this point are: Console and vty access: username: ccna, password: cisco enable secret: sanfran L4-2 Global Knowledge Training LLC
3 Lab Topology The following diagram illustrates the logical topology used in this lab, along with the IP addresses configured. Command List The following table lists the commands used in this lab, in alphabetical order. Cisco IOS Commands Used In This Lab Command #<CTRL><SHIFT><6> (config-if)#channel-group number mode active #clear arp-cache #configure terminal #copy running-config startupconfig >enable (config)#end #exit (config)#interface type number Description Break sequence; use to stop pings. Configures the interface as part of the portchannel with the specified number. The portchannel uses LACP active mode. Clears the ARP cache on a switch. Enters global configuration mode. Saves the running configuration (in RAM) into the startup configuration (in NVRAM). Enters the EXEC privileged mode. Terminates configuration mode. Exit the current mode and go up one level. Enters interface configuration mode. Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-3
4 (config)#interface type number.subinterface (config)#interface range type number/number - number (config-if)#[no] ip address address mask (config)#ip default-gateway address (config-router)#[no] network address wildcard-mask area area Enters configuration mode for the subinterface. Enters interface range configuration mode, to put the same configuration on multiple interfaces simultaneously. Assigns interface IP address and subnet mask. With the no keyword removes the address from the interface. Configures the specified IP address as the default gateway for the switch. Specifies which interfaces run OSPF and in which area. With the no parameter, removes the interface from running OSPF in the area. #ping [address] Sends an echo request to the specified address. With no parameters specified, enters extended ping. (config)#router ospf process-id Configures an OSPF routing process. #show etherchannel port-channel Displays EtherChannel port-channel information on the switch. #show interfaces port-channel number Displays status of the specified port-channel interface on the switch. #show spanning tree [vlan vlan] Displays spanning tree information, for all or a specified VLAN. (config-if)#[no] shutdown Disables the specified interface. With the no parameter, enables the interface. Windows Commands Used In This Lab Command ping address Description Causes an ICMP echo message to be sent to the destination, which should cause an ICMP echo reply message to be returned. L4-4 Global Knowledge Training LLC
5 Procedure In this lab you will first verify that one of the parallel connections to the core switch is blocked by STP. You will then configure these parallel links as an EtherChannel group and verify that both are being used. Finally you will verify that if one of the links in the EtherChannel group goes down, the other continues to function, with no interruption to the data flow. Note This lab requires that the previous lab was completed correctly. If you have any doubts, reset to this lab, as described in Lab 0: Introduction, and Connecting to and Using the Remote Lab Environment. Examine STP operation 1. Connect to your PxSW switch. Your switch is connected to the core switch by two parallel links, creating a bridging loop. To prevent adverse looping effects, STP automatically blocks one of the interfaces for user data. Examine the spanning tree status for VLAN 1 on your switch. PxSW#show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority Address fcfb.fbb Cost 19 Port 11 (FastEthernet0/11) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority (priority sys-id-ext 1) Address 2401.c70f.4d80 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 sec Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type Fa0/1 Desg FWD P2p Edge Fa0/11 Root FWD P2p Fa0/12 Altn BLK P2p PxSW# For VLAN 1 you can see that the Root ID and Bridge ID s address fields are different, indicating that your switch is not the root for VLAN 1 (because the core switch is the root). FastEthernet 0/1 and 11 are forwarding (FWD), and FastEthernet 0/12 is blocked (BLK). FastEthernet 0/1 is the designated port for the segment connecting the switch to PxR1, and FastEthernet 0/11 is the switch s root port. The FastEthernet 0/12 link runs parallel to the link from FastEthernet 0/11, and was blocked to prevent looping. Recall that FastEthernet Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-5
6 0/11 won the battle because the path costs are equal (both are 19), but the port identifiers (port numbers) are not and the lowest (11 in this case) wins. (FastEthernet 0/2, 0/9, and 0/10 don t show up in the VLAN 1 section, because they are on other VLANs.) So there are two links connecting the two switches, but only one link (FastEthernet 0/11) is being used for traffic. FastEthernet 0/12 is not being used for traffic. Configure EtherChannel To allow both links between the switches to be used, you will now configure them as an EtherChannel group. 2. Configure FastEthernet 0/11 and FastEthernet 0/12 as EtherChannel members; use 1 as the port channel identifier and use LACP active mode. Note The core switch is already configured for EtherChannel. PxSW(config)#interface range fa0/11-12 PxSW(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode active Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 PxSW(config-if-range)#end 3. Examine the spanning tree status for VLAN 1 on your switch again. PxSW#show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority Address fcfb.fbb Cost 12 Port 64 (Port-channel1) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority (priority sys-id-ext 1) Address 2401.c70f.4d80 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 sec Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type Fa0/1 Desg FWD P2p Edge Po1 Root FWD P2p PxSW# Instead of FastEthernet 0/11 and 0/12 there is interface Po1, the port-channel that is the bundle of the two interfaces. It is in FWD state, which means that it (and therefore FastEthernet 0/11 and 0/12) are forwarding. L4-6 Global Knowledge Training LLC
7 4. Examine the state of the port-channel 1 interface on your switch. Lab 4: Configuring EtherChannel PxSW#show interfaces port-channel 1 Port-channel1 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is EtherChannel, address is 2401.c70f.4d8c (bia 2401.c70f.4d8c) <output omitted> Port-channel 1 is up and up. 5. Examine the EtherChannel port-channel information on your switch. PxSW#show etherchannel port-channel Channel-group listing: Group: Port-channels in the group: Port-channel: Po1 (Primary Aggregator) Age of the Port-channel = 0d:00h:06m:04s Logical slot/port = 2/1 Number of ports = 2 HotStandBy port = null Port state = Port-channel Ag-Inuse Protocol = LACP Port security = Disabled Ports in the Port-channel: Index Load Port EC state No of bits Fa0/11 Active Fa0/12 Active 0 Time since last port bundled: 0d:00h:06m:01s Fa0/11 PxSW# Port-channel 1 is in use and uses the LACP protocol. Interfaces FastEthernet 0/11 and FastEthernet 0/12 are in the port-channel. Verify EtherChannel redundancy 6. Connect to PxR1. To verify EtherChannel redundancy, start a string of pings from PxR1 to the TFTP server, using the extended ping feature of IOS. PxR1#ping Protocol [ip]:<enter> Target IP address: Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: <Enter> Timeout in seconds [2]: <Enter> Extended commands [n]: <Enter> Sweep range of sizes [n]: <Enter> Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-7
8 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending , 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: (this goes on and on ) 7. Leave the pings running, and shut down the switch s FastEthernet 0/11 interface, one of the members of the port-channel 1. PxSW#configure terminal PxSW(config)#interface fastethernet 0/11 PxSW(config-if)#shutdown PxSW(config-if)#end 8. After the switch s FastEthernet 0/11 goes down, look at PxR1 s console output. Do you see any missed pings? You should not see any interruption of the stream of pings. 9. Examine the EtherChannel port-channel information on your switch again. PxSW#show etherchannel port-channel Channel-group listing: Group: Port-channels in the group: Port-channel: Po1 (Primary Aggregator) Age of the Port-channel = 0d:00h:09m:48s Logical slot/port = 2/1 Number of ports = 1 HotStandBy port = null Port state = Port-channel Ag-Inuse Protocol = LACP Port security = Disabled Ports in the Port-channel: Index Load Port EC state No of bits Fa0/12 Active 0 Time since last port bundled: 0d:00h:09m:44s Fa0/11 Time since last port Un-bundled: 0d:00h:00m:48s Fa0/11 PxSW# Port-channel 1 is in use and uses the LACP protocol. Only interface FastEthernet 0/12 is in the port-channel now. You can see the time since the port-channel was last unbundled, which was when interface FastEthernet 0/11 was shutdown. L4-8 Global Knowledge Training LLC
9 10. With the pings from PxR1 still running, bring the switch s FastEthernet 0/11 interface back up, leave config mode, and again examine the output on PxR1. PxSW#configure terminal PxSW(config)#interface fastethernet 0/11 PxSW(config-if)#no shutdown PxSW(config-if)#end 11. Do you see any missed pings? You should not see any interruption of the stream of pings. 12. Examine the EtherChannel port-channel information on your switch again. PxSW#show etherchannel port-channel Channel-group listing: Group: Port-channels in the group: Port-channel: Po1 (Primary Aggregator) Age of the Port-channel = 0d:00h:13m:20s Logical slot/port = 2/1 Number of ports = 2 HotStandBy port = null Port state = Port-channel Ag-Inuse Protocol = LACP Port security = Disabled Ports in the Port-channel: Index Load Port EC state No of bits Fa0/11 Active Fa0/12 Active 0 Time since last port bundled: 0d:00h:02m:10s Fa0/11 Time since last port Un-bundled: 0d:00h:04m:20s Fa0/11 PxSW# Port-channel 1 is in use and uses the LACP protocol. Interfaces FastEthernet 0/11 and FastEthernet 0/12 are again in the port-channel. You can see the time since the portchannel was last bundled, which was when interface FastEthernet 0/11 was enabled. 13. Stop the pings on PxR1 using the <CTRL><SHIFT><6> break sequence: PxR1#<CTRL><SHIFT><6> Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-9
10 Reconfigure the pod devices Important The following steps are necessary to prepare the pod devices for subsequent labs. As an alternative to doing these steps, you can rest to the next lab you are going to do. 14. Shutdown PxSW s interfaces FastEthernet 0/11 and FastEthernet 0/12, connected to the core switch. PxSW(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/11-12 PxSW(config-if-range)#shutdown PxSW(config-if-range)#exit 15. Change PxSW s address in VLAN 1 to x.3/24 and change its default gateway to x.1. In all addresses, x is your pod number. Exit config mode. PxSW(config)#interface vlan 1 PxSW(config-if)#ip address x PxSW(config-if)#exit PxSW(config)#ip default-gateway x.1 PxSW(config)#end 16. On the switch, clear the ARP cache. PxSW#clear arp-cache 17. Enter configuration mode on PxR1. Change the address on PxR1 s GigabitEthernet 0/0.1 subinterface to x.1/24, where x is your pod number. PxR1#configure terminal PxR1(config)#interface gi0/0.1 PxR1(config-subif)#ip address x PxR1(config-subif)#exit 18. Change the OSPF process 1 configuration on PxR1 to route over the x.0/24 subnet for area 0, and not route over the /24 subnet for area 0. PxR1(config)#router ospf 1 PxR1(config-router)#no network area 0 PxR1(config-router)#network x area 0 PxR1(config-router)#exit 19. Enable PxR1 s GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface to the core. PxR1(config)#interface gi0/1 PxR1(config-if)#no shutdown PxR1(config-if)#exit 20. Wait a minute or so until you see that PxR1 has formed a FULL OSPF neighbor relationship with the core router. PXR1# *Mar 5 15:35:57.294: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr on GigabitEthernet0 /1 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done L4-10 Global Knowledge Training LLC
11 21. From your switch ping the TFTP server ( , reached via the core router) and both PCs, to verify connectivity. All pings should be successful. PxSW#ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/8 ms PxSW# PxSW#ping 10.1.x.10 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.x.10, timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/4/9 ms PxSW# PxSW#ping 10.2.x.20 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.2.x.20, timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/4/9 ms PxSW# 22. Connect to PC1 and PC2. From PC1 and PC2, ping the TFTP server ( ), to verify connectivity. All pings should be successful. Here is PC1 pinging the TFTP server (from the example Pod 6): Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-11
12 Here is PC2 pinging the TFTP server (from the example Pod 6): Save the configurations 23. Save all of your pod device configurations to startup-config. PxSW#copy running-config startup-config PxR1#copy running-config startup-config PxR2#copy running-config startup-config Lab Complete L4-12 Global Knowledge Training LLC
13 Completed Configuration Your configuration should be similar to the example below. PC1 has address 10.1.x.10, with subnet mask Its default gateway is set to 10.1.x.1. PC2 has address 10.2.x.20, with subnet mask Its default gateway is set to 10.2.x.1. Note These example configurations include no shutdown commands on some interfaces and the crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024 command. You will not see these commands in the output of the show running-config command. In the PxSW configuration you will also see more detail in the crypto pki certificate section in the output of the show running-config command. PxSW: version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname PxSW boot-start-marker boot-end-marker enable secret 5 $1$MwWB$mlGhntn.NW88DZkZ6Bu5E0 username ccna secret 5 $1$4ply$OXbD45OeKajioPlV5EHdQ0 no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 vtp mode transparent no ip domain-lookup ip domain-name cisco.com crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024 crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed enrollment selfsigned subject-name cn=ios-self-signed-certificate revocation-check none rsakeypair TP-self-signed crypto pki certificate chain TP-self-signed certificate self-signed 01 nvram:ios-self-sig#5.cer Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-13
14 spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id spanning-tree vlan 1 priority spanning-tree vlan 1x,2x,3x priority vlan internal allocation policy ascending vlan 1x name VLAN1x vlan 2x name VLAN2x vlan 3x name VLAN3x ip ssh version 2 interface Port-channel1 switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,1x,2x,3x switchport mode trunk interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,1x,2x,3x switchport mode trunk spanning-tree portfast trunk interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 3x spanning-tree portfast interface FastEthernet0/3 interface FastEthernet0/4 interface FastEthernet0/5 interface FastEthernet0/6 interface FastEthernet0/7 interface FastEthernet0/8 interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport access vlan 1x spanning-tree portfast interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport access vlan 2x spanning-tree portfast L4-14 Global Knowledge Training LLC
15 interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,1x,2x,3x switchport mode trunk shutdown channel-group 1 mode active interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,1x,2x,3x switchport mode trunk shutdown channel-group 1 mode active interface FastEthernet0/13 interface FastEthernet0/14 interface FastEthernet0/15 interface FastEthernet0/16 interface FastEthernet0/17 interface FastEthernet0/18 interface FastEthernet0/19 interface FastEthernet0/20 interface FastEthernet0/21 interface FastEthernet0/22 interface FastEthernet0/23 interface FastEthernet0/24 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 interface GigabitEthernet0/2 interface Vlan1 ip address x no shutdown ip default-gateway x.1 ip http server ip http secure-server logging esm config line con 0 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local transport input ssh Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-15
16 line vty 5 15 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local transport input ssh end PxR1: version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname PxR1 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker enable secret 4 NUtXpRU892oGmKT2hPuxM6rMJlDMKfYF3czf8T.rrWA no aaa new-model ip cef no ip domain lookup ip domain name cisco.com ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated license udi pid CISCO2901/K9 sn FTX170480E4 crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024 username ccna secret 4 tnhtc92dxbhelxjyk8lwjrpv36s2i4ntxrpb4rfmfqy ip ssh version 2 csdb tcp synwait-time 30 csdb tcp idle-time 3600 csdb tcp finwait-time 5 csdb tcp reassembly max-memory 1024 csdb tcp reassembly max-queue-length 16 csdb udp idle-time 30 csdb icmp idle-time 10 csdb session max-session L4-16 Global Knowledge Training LLC
17 interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address speed auto duplex auto no shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0.1 encapsulation dot1q 1 native ip address x ipv6 address 2001:DB8:10:x::1/64 no shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0.1x encapsulation dot1q 1x ip address 10.1.x ip access-group 100 in ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1:x::1/64 no shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2x encapsulation dot1q 2x ip address 10.2.x ip access-group 100 in ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2:x::1/64 no shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3x encapsulation dot1q 3x ip address 10.3.x ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3:x::1/64 no shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address xx speed auto duplex auto ipv6 address autoconfig no shutdown interface Serial0/0/0 no ip address shutdown interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown router ospf 1 router-id 1.1.x.1 network 10.1.x area 0 network 10.2.x area 0 Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-17
18 network 10.3.x area 0 network x area 0 network xx area 0 ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server access-list 100 deny tcp host 10.1.x.10 host xx.3 eq telnet access-list 100 deny tcp host 10.2.x.20 host xx.3 eq telnet access-list 100 permit ip any any ipv6 route ::/0 GigabitEthernet0/1 2001:DB8:168:xx::3 control-plane line con 0 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local transport input ssh line vty 5 15 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local transport input ssh scheduler allocate end PxR2: version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname PxR2 boot-start-marker L4-18 Global Knowledge Training LLC
19 boot-end-marker enable secret 4 NUtXpRU892oGmKT2hPuxM6rMJlDMKfYF3czf8T.rrWA no aaa new-model ip cef no ip domain lookup ip domain name cisco.com ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated license udi pid CISCO2901/K9 sn FTX170480EA crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024 username ccna secret 4 tnhtc92dxbhelxjyk8lwjrpv36s2i4ntxrpb4rfmfqy ip ssh version 2 csdb tcp synwait-time 30 csdb tcp idle-time 3600 csdb tcp finwait-time 5 csdb tcp reassembly max-memory 1024 csdb tcp reassembly max-queue-length 16 csdb udp idle-time 30 csdb icmp idle-time 10 csdb session max-session interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 10.3.x speed auto duplex auto ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3:x::2/64 no shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown speed auto Lab 4: Configuring EtherChannel Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-19
20 duplex auto interface Serial0/0/0 no ip address shutdown clock rate interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server ip route x.1 ipv6 route ::/0 GigabitEthernet0/0 2001:DB8:3:x::1 control-plane line con 0 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local transport input ssh line vty 5 15 exec-timeout 60 0 logging synchronous login local transport input ssh scheduler allocate end L4-20 Global Knowledge Training LLC
Troubleshooting VLANs and Trunks
 L2 Troubleshooting VLANs and Trunks Global Knowledge Training LLC L2-1 Objectives In this lab you will download configuration files into PxSW s running configuration to introduce VLAN and trunking issues
L2 Troubleshooting VLANs and Trunks Global Knowledge Training LLC L2-1 Objectives In this lab you will download configuration files into PxSW s running configuration to introduce VLAN and trunking issues
Implementing EIGRP. Global Knowledge Training LLC L7-1
 L7 Implementing EIGRP Global Knowledge Training LLC L7-1 Objectives In this lab you will configure EIGRP on your pod routers. The core router is already configured for EIGRP. You will first remove the
L7 Implementing EIGRP Global Knowledge Training LLC L7-1 Objectives In this lab you will configure EIGRP on your pod routers. The core router is already configured for EIGRP. You will first remove the
Configuring HSRP. Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1
 L5 Configuring HSRP Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1 Objectives In this lab you will examine the hot standby router protocol (HSRP). First you will configure PxR2 similar to PxR1, so they are both possible
L5 Configuring HSRP Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1 Objectives In this lab you will examine the hot standby router protocol (HSRP). First you will configure PxR2 similar to PxR1, so they are both possible
ICND2 SuperLab (Step-by-Step)
 D ICND2 SuperLab (Step-by-Step) Global Knowledge Training LLC D-1 Objectives In this lab you will load new configuration files into your pod devices; these files contain a basic configuration. You will
D ICND2 SuperLab (Step-by-Step) Global Knowledge Training LLC D-1 Objectives In this lab you will load new configuration files into your pod devices; these files contain a basic configuration. You will
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
CONFIGURATION DU SWITCH
 Current configuration : 2037 bytes version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero
Current configuration : 2037 bytes version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure trunking, VTP, and inter-vlan routing using router-on-a stick Configure GLBP Configure
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure trunking, VTP, and inter-vlan routing using router-on-a stick Configure GLBP Configure
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Lab Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 Static Routes (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme. Topology. Objectives. Background / Scenario
 CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
Lab 5.5.2: Challenge Spanning Tree Protocol
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QnQ) and L2PT on L2 Ports
 Revised: November 11, 2011, OL-20468-01 First Published: November 11, 2011 Last Updated: November 11, 2011 This feature provides Layer 2 Tunneling support for QnQ and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT)
Revised: November 11, 2011, OL-20468-01 First Published: November 11, 2011 Last Updated: November 11, 2011 This feature provides Layer 2 Tunneling support for QnQ and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT)
NATIONAL_WATER_CONSERVATION#sh run Building configuration...
 NATIONAL_WATER_CONSERVATION#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 6390 bytes Last configuration change at 13:01:34 UTC Tue Jul 4 2017 by kembo version 15.4 service timestamps debug datetime
NATIONAL_WATER_CONSERVATION#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 6390 bytes Last configuration change at 13:01:34 UTC Tue Jul 4 2017 by kembo version 15.4 service timestamps debug datetime
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configuring EtherChannel. Topology. Objective. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv6 Switch. Configure EtherChannel.
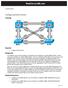 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
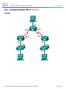 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Solution)
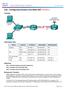 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Configuring Port Address Translation (PAT) (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement Multiple Spanning Tree Leverage VTP version 3 with MST Background Cisco s Per VLAN Spanning Tree
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement Multiple Spanning Tree Leverage VTP version 3 with MST Background Cisco s Per VLAN Spanning Tree
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
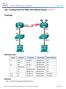 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security
 ABOUT CONTACT FAQ JOIN HOME CCNA CCNP COMPTIA DESIGN You are here: Home / 101 CCNP Labs Solutions / CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security Lab Objective:
ABOUT CONTACT FAQ JOIN HOME CCNA CCNP COMPTIA DESIGN You are here: Home / 101 CCNP Labs Solutions / CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security Lab Objective:
QUESTION/SOLUTION SET LAB 4
 QUESTION/SOLUTION SET LAB 4 CCIE lab Routing & Switching (v4.0) lab:4 Updated Testing Guidelines 1. The equipment on the rack assigned to you is physically Cabled and should not be tempered with. 2. Router
QUESTION/SOLUTION SET LAB 4 CCIE lab Routing & Switching (v4.0) lab:4 Updated Testing Guidelines 1. The equipment on the rack assigned to you is physically Cabled and should not be tempered with. 2. Router
Lab Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype
 Lab 7.3.3 Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype Device Designation Device Name IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0.1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1 BR4 Fa0/0.10 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
Lab 7.3.3 Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype Device Designation Device Name IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0.1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1 BR4 Fa0/0.10 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
Advanced IPv6 Training Course. Lab Manual. v1.3 Page 1
 Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Table of Contents. isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ
 king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
Lab Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
If this is your first time configuring the switch, you will notice that the Switch IOS is almost identical to Router IOS.
 Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Lab Configuring Switch Security Features (Solution) Topology
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 172.16.99.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 99 172.16.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.16.99.1 PC-A NIC
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 172.16.99.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 99 172.16.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.16.99.1 PC-A NIC
Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP and load balancing Configure HSRP authentication
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP and load balancing Configure HSRP authentication
Describing the STP. Enhancements to STP. Configuring PortFast. Describing PortFast. Configuring. Verifying
 Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol.
 CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure DHCP for IPv4 Configure Stateless DHCP for IPv6 Configure Stateful DHCP for IPv6 Background To practice the various
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure DHCP for IPv4 Configure Stateless DHCP for IPv6 Configure Stateful DHCP for IPv6 Background To practice the various
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 on a Router (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.2.253
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.2.253
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE
 CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE Table of Contents (After Clicking Link Hit HOME to Return to TOC) 1) Add Hostname... 2 2) Add Username and Password... 2 3) Create Secret Password... 2 4) Encrypt Password...
CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE Table of Contents (After Clicking Link Hit HOME to Return to TOC) 1) Add Hostname... 2 2) Add Username and Password... 2 3) Create Secret Password... 2 4) Encrypt Password...
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway. Ports Assignment Network
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Lab - Configuring a Switch Management Address
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Part 1: Configure a Basic Network
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Part 1: Configure a Basic Network
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Chapter 8 Lab 8-1, IP Service Level Agreements and Remote SPAN in a Campus Environment INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 8 Lab 8-1, IP Service Level Agreements and Remote SPAN in a Campus Environment INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Configure trunking, VTP, and SVIs. Implement IP
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 8 Lab 8-1, IP Service Level Agreements and Remote SPAN in a Campus Environment INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Configure trunking, VTP, and SVIs. Implement IP
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup
 Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks
 Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks Packet Tracer Practice with Dans Sample http://www.danscourses.com/ In this lab, you will learn how to configure the following tasks: IPv4 Addressing
Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks Packet Tracer Practice with Dans Sample http://www.danscourses.com/ In this lab, you will learn how to configure the following tasks: IPv4 Addressing
Lab Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
Lab 1: OSPF With Three Routers
 Lab 1: OSPF With Three Routers The physical topology is as shown in FIG 18.1 - Advanced OSPF Lab. FIG 18.1 - Advanced OSPF Lab Lab Exercise Your task is to configure the network in FIG 18.1 - Advanced
Lab 1: OSPF With Three Routers The physical topology is as shown in FIG 18.1 - Advanced OSPF Lab. FIG 18.1 - Advanced OSPF Lab Lab Exercise Your task is to configure the network in FIG 18.1 - Advanced
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
 Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Default Gateway Fa0/ N/A. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Felix Rohrer Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.0.9 255.255.255.252
Felix Rohrer Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.0.9 255.255.255.252
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Assembling Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tools
 Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Assembling Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tools Physical Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Assembling Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tools Physical Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Synchronizing Campus Network Devices using Network Time Protocol (NTP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Synchronizing Campus Network Devices using Network Time Protocol (NTP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objective Background Configure network to synchronize time using the
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Synchronizing Campus Network Devices using Network Time Protocol (NTP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objective Background Configure network to synchronize time using the
Lab Configuring EtherChannel
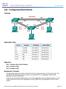 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Lab Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test
 Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Troubleshooting Scenarios
 C Troubleshooting Scenarios Global Knowledge Training LLC C-1 Procedure These are the troubleshooting scenarios at the time this lab guide was written. Troubleshooting VLANs and Trunks VLAN-a.txt VLAN-b.txt
C Troubleshooting Scenarios Global Knowledge Training LLC C-1 Procedure These are the troubleshooting scenarios at the time this lab guide was written. Troubleshooting VLANs and Trunks VLAN-a.txt VLAN-b.txt
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
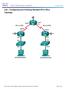 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
ECMP Load Balancing. MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series) 1
 Equal-cost multi-path routing (ECMP) is a routing strategy where next-hop packet forwarding to a single destination can occur over multiple "best paths" which tie for top place in routing metric calculations.
Equal-cost multi-path routing (ECMP) is a routing strategy where next-hop packet forwarding to a single destination can occur over multiple "best paths" which tie for top place in routing metric calculations.
 switch# switch#configure terminal switch(config)#spanning-tree mode pvst switch(config)#spanning-tree extend system-id switch(config)#vtp mode transparent switch(config)#vlan 4093 Switch(config-vlan)#exit
switch# switch#configure terminal switch(config)#spanning-tree mode pvst switch(config)#spanning-tree extend system-id switch(config)#vtp mode transparent switch(config)#vlan 4093 Switch(config-vlan)#exit
Basic Router Configuration using SDM
 Basic Router Configuration using SDM Document ID: 71305 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Interface Configuration NAT Configuration Routing Configuration
Basic Router Configuration using SDM Document ID: 71305 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Interface Configuration NAT Configuration Routing Configuration
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol
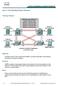 Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Multicast Music-on-Hold Support on Cisco UBE
 First Published: July 22, 2011 Last Updated: July 22, 2011 The Multicast Music-on-Hold (MMOH) feature enables you to subscribe to a music streaming service when you are using a Cisco Unified Border Element.
First Published: July 22, 2011 Last Updated: July 22, 2011 The Multicast Music-on-Hold (MMOH) feature enables you to subscribe to a music streaming service when you are using a Cisco Unified Border Element.
Design and Implementation Plan for Network Based on the ALOHA Point of Sale System. Proposed by Jedadiah Casey. Introduction
 Design and Implementation Plan for Network Based on the ALOHA Point of Sale System Proposed by Jedadiah Casey Introduction The goal of this design document is to provide a framework of suggested implementation
Design and Implementation Plan for Network Based on the ALOHA Point of Sale System Proposed by Jedadiah Casey Introduction The goal of this design document is to provide a framework of suggested implementation
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
BẮT 10 GIAO THỨC (SNMP, HTTP, HTTPS, NETMEETING, NTP, TELNET, SSH, H323, SIP, DOMAIN )
 SƠ ĐỒ MẠNG VISIO SƠ ĐỒ GNS3 BẮT 10 GIAO THỨC (SNMP, HTTP, HTTPS, NETMEETING, NTP, TELNET, SSH, H323, SIP, DOMAIN ) PING TẠO RA LƯU LƯỢNG SAU KHI CẤM PING FILE CẤU HÌNH CÁC ROUTER ROUTER SAIGON Last configuration
SƠ ĐỒ MẠNG VISIO SƠ ĐỒ GNS3 BẮT 10 GIAO THỨC (SNMP, HTTP, HTTPS, NETMEETING, NTP, TELNET, SSH, H323, SIP, DOMAIN ) PING TẠO RA LƯU LƯỢNG SAU KHI CẤM PING FILE CẤU HÌNH CÁC ROUTER ROUTER SAIGON Last configuration
Quick Note. Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016
 Quick Note Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Outline... 3 1.2 Assumptions...
Quick Note Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Outline... 3 1.2 Assumptions...
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Chapter 1 Lab - Preparing the Switch INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 1 Lab - Preparing the Switch INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Clear the configuration of all the switches in your pod Configure the database template used by all the switches
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 1 Lab - Preparing the Switch INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Clear the configuration of all the switches in your pod Configure the database template used by all the switches
Implementing IS-IS Routing and DHCP Services in an IPv4 Network
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Fall 2015 Implementing IS-IS Routing and DHCP Services in an IPv4 Network Laura
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Fall 2015 Implementing IS-IS Routing and DHCP Services in an IPv4 Network Laura
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy
 Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab Troubleshooting VTP Configuration
 Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway. Ports Assignment Network
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com. Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram
 Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram Default Cisco Terminal Options: 9600 bits/second No hardware flow control 8-bit ASCII No parity 1 stop bit Setting
Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram Default Cisco Terminal Options: 9600 bits/second No hardware flow control 8-bit ASCII No parity 1 stop bit Setting
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
CCNA Basic Questions. Question 1. What is the first 24 bits in a MAC address called? A. NIC B. BIA C. OUI D. VAI. Answer: C.
 CCNA Basic Questions http://www.9tut.com/new-ccna-basic-questions Question 1 What is the first 24 bits in a MAC address called? A. NIC B. BIA C. OUI D. VAI Answer: C Question 2 Which of the following statements
CCNA Basic Questions http://www.9tut.com/new-ccna-basic-questions Question 1 What is the first 24 bits in a MAC address called? A. NIC B. BIA C. OUI D. VAI Answer: C Question 2 Which of the following statements
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior
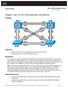 Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to
RR> RR> RR>en RR# RR# RR# RR# *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 RR#
 RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
Converged Access CT 5760 AVC Deployment Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3
 Converged Access CT 5760 AVC Deployment Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3 Last Updated: November, 2013 Introduction This guide is designed to help you deploy and monitor new features introduced in the IOS
Converged Access CT 5760 AVC Deployment Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3 Last Updated: November, 2013 Introduction This guide is designed to help you deploy and monitor new features introduced in the IOS
Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0. Cisco Certified Network Associate
 200-120 Number: 000-000 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco Certified Network Associate Экзамен A QUESTION 1 What is the first 24 bits in a MAC address
200-120 Number: 000-000 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco Certified Network Associate Экзамен A QUESTION 1 What is the first 24 bits in a MAC address
Lab Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
