Design and Implementation Plan for Network Based on the ALOHA Point of Sale System. Proposed by Jedadiah Casey. Introduction
|
|
|
- Brice Dalton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design and Implementation Plan for Network Based on the ALOHA Point of Sale System Proposed by Jedadiah Casey Introduction The goal of this design document is to provide a framework of suggested implementation for a computer network based on the Aloha Point of Sale software. Aloha uses a central server for all processing and management tasks, which all terminals connect to over the Local Area Network (LAN). By implementing a solid network infrastructure, operational downtime is reduced which increases the return on investment and lowers overall cost. This document explains the current network environment, and the recommended best practices moving forward with the installation of new locations. Many of the topics can be retroactively applied to the current restaurant installations, though certain aspects (such as the physical cabling layout) may not be cost feasible. Design Requirements The requirements of the network design are to provide Layer 2 switched connectivity between the Aloha terminals and the Aloha Back of House (BOH) server. The BOH server must also have access to the Internet for credit card processing. Reliable wireless Internet access must also be provided for the customers on a network that is logically separated from the internal LAN. Aloha terminals must also be able to communicate with serial-based printers over Ethernet cabling. This requires a minimum of two RJ-45 Ethernet ports available per terminal station. Existing Network Infrastructure The physical cabling of the LAN uses Cat5e/6-based Ethernet technology. Communication between the terminals and server occur over Ethernet through a traditional network switch. Communication between the terminals and the printers also travels over the installed Ethernet cable runs; however the communication is electrically an OSI Layer 1 serial connection and does not use OSI Layer 2 frames and does not pass through any switches. All of the terminals are connected to a switch via an Ethernet patch panel in the manager s office. In three of the four COMPANY locations (Location 004 being the exception), all of the serial printer connections that travel over the installed Ethernet cable runs are direct from the terminals to the printers and do not pass through the patch panel. For example, the current Terminal 6 of the 003 location connects to a kitchen printer in the center aisle via an Ethernet cable that runs into the ceiling and passes over the walkway, then terminates on the other side. By having the infrastructure cabled in this manner instead of all cable runs terminating at the manager s office patch panel, only Terminal neckercube.com Page 1 of 15
2 can control that particular printer (in this example). If all of the Ethernet cable runs terminated at a patch panel, as they do in the 004 location, printers can quickly and easily be assigned to different terminals by adjusting the patch cable on the patch panel. However, it might not be cost-feasible to upgrade the pre-existing cabling in these locations. Currently, three of the four COMPANY locations (Location 001 being the exception) are configured to rely on the installed router for all communications, even those between the terminals and the server (which do not require Internet access through the router). This configuration has the side effect of temporarily disconnecting the terminals from the server if the router needs to be reset. The recommended practice has been implemented at Location 001 where the Aloha server is dual homed (it has two Ethernet cards installed). This creates two separate networks. The server communicates with the other terminals via Ethernet switch in one network. The server uses the other Ethernet card to connect to the router for Internet access for credit card processing. With this logical separation, resetting the router does not affect the terminals. Currently, the LAN is logically arranged in the following manner: Internet Manager s PC Aloha BOH Server Wireless Router Brighthouse Patch Panel Switch Terminal Kitchen Printer The current infrastructure uses Cisco WRVS4400n Small Business wireless routers at all four locations. While these routers do currently provide adequate functionality, they occasionally require a power cycle to reset them. All installed switches are ordinary non-managed Layer 2 switches. The hardware of all BOH servers has been either been upgraded from the original Radiant hardware, or has been assembled as part of a new server. At least one COMPANY location is currently using an SSD drive for primary storage. We have found this greatly increases network performance and stability due to the fact that rebooting the server can typically be done rapidly enough to prevent the terminals from rebooting. Currently, the routers, servers and terminals all use slightly different IP addressing schemes between each location. For example, the server IP at Location 004 is , while the server at Location 002 is This inconsistency does not affect daily operations, however by having addressing inconsistency between locations it can increase the troubleshooting time when problems arise neckercube.com Page 2 of 15
3 Each location, with the exception of 001, are using static IP addresses provided by Brighthouse. These are assigned by Brighthouse in blocks of six addresses. This is an unnecessary expense, as a single dynamic IP address (as configured at Location 001) is all that is required. Design To eliminate or otherwise reduce the problems mentioned previously, the LAN should be designed with physical redundancy and logical separation. To accomplish this, each terminal should have four Ethernet cable runs: two for operation (terminal and printer), and two for redundancy in case the ports go bad (which we have seen happen over time at each of the locations). All physical cable runs should be labeled and terminate to a patch panel in the manager s office. Currently, the 004 location is cabled in this manner, though without the redundancy of four ports at each terminal. By including two extra cable runs per terminal, the initial build cost is higher, but it increases the longevity of the network and reduces the time and cost of repairs in the future, since cables connected to non-working ports can be moved to working ports. This type of connectivity is most likely not cost-feasible to retrofit the existing locations, however it is very strongly recommended for all newly-built locations. The new infrastructure logical plan looks like the following: Manager s PC Aloha BOH Server Patch Panel Cisco Catalyst 2950 Layer 2 Managed Switch Cisco 3725 Router Brighthouse Internet Terminal Kitchen Printer Cisco WRVS4400n Wireless In the above logical diagram, any terminal that connects to a kitchen printer has two connections to the central patch panel. The terminal is then physically routed to the kitchen printer with a short patch cable at the patch panel. If the terminal needs to be replaced, the kitchen printer can be physically rewired to a different terminal temporarily and quickly by adjusting the short patch cable. Currently, this type of adjustment can only be done at the 004 location. The heart of the network resides in a Cisco 3725 model access router, and a Cisco Catalyst 2950 Layer 2 managed switch. The 3725 router connects directly to the Brighthouse cable modem and to the 2950 switch. All other network devices connect to the 2950 through the patch panel. The existing WRVS4400n routers will be repurposed as wireless access points to provide guest wireless access services only neckercube.com Page 3 of 15
4 Each 2950 switch port is configurable, and groups of ports can be configured for separate, isolated subnetworks. For example, though all network devices connect to the same switch, the terminals and server will be separated into their own logical private sub-network (VLAN). The repurposed wireless routers connect to another separate private VLAN and cannot reach the terminals or the rest of the network; only the Internet. This dramatically increases security over the current implementation and helps with regards to PCI DSS compliance. Additionally, the Catalyst 2950 is a managed switch, which means it can be logged into (both in-band and out-of-band) for both configuration and monitoring/troubleshooting. For example, if one of the ports is having an issue, the switch is configurable to send an alert. This increases the overall dependability and reliability of the network because one malfunctioning port does not take down the entire system, as it does now. The 3725 router offers similar functionality. If the cable modem or wireless router needs to be reset, it does not affect the rest of the network, as it does now. The Cisco 3725 and 2950 are designed to never need to be reset unless a manual software upgrade occurs, with potential uptime measured in months and even years. The Brighthouse cable modem connects directly the Cisco 3725 router. The 3725 provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and stealth firewall services so the other network segments have configurable protected Internet access via Access Control Lists (ACLs). For example, even though all devices are connected to the same 2950 switch, the VLAN containing the terminals can be prevented from reaching the Internet or the wireless users to maintain data security. The terminals and one of the Ethernet interfaces on the BOH server reside in VLAN 100 on the switch. The BOH servers will be configured with the IP address /24, with each terminal being statically configured as /24 for T1,.102 for T2, and so on. No gateway or DNS configuration is required for this network, as it will not participate on the Internet or any other part of the LAN. The BOH server s Ethernet interface must be assigned to LAN CARD #0 with LANACFG. Please view the Appendix for more information on configuration. The terminals connect to corresponding port numbers on the 2950 switch. For example, port 1 for T1, port 2 for T2, etc. This aids in troubleshooting. The server connects to the last port in the series. For example, if there are nine terminals, the BOH server connects to port 10. The other Ethernet interface on the BOH server, the manager PC, the office printer, and any other network devices besides the Cisco WRVS4400n wireless router connect to VLAN 20 and use the IP address scheme /24. The 3725 router is configured with the in-band management IP address /24. The printer is configured as /24. The Cisco WRVS4400n is reconfigured to act as a guest wireless access point. The LAN port 1 of the WRVS4400n is connected to the 2950 port 23. The 2950 switch port 23 resides in VLAN 30 and uses the /24 network. As a required part of the overall design, extra 3725 routers and 2950 switches must be acquired to use as immediate replacement in case of failure. The ideal replacement plan would be to keep one extra 3725 and 2950 per location, however a more cost-reasonable plan would be to keep 1-2 extras of each 2012 neckercube.com Page 4 of 15
5 to use across all locations for immediate replacement until new replacements can be ordered. As the number of locations increases, the number of extras should also increase. Proof of Concept Two of the major components of this design have already been proven in the existing operations. With the 004 location, most kitchen printers are not directly connected to the terminals. They pass through the patch panel in the manager s office. This allows a kitchen printer to be connected to different terminals, should the need arise. This is the only location, currently, that has this capability. With the 001 location, the server is multi-homed with the terminals and the server residing on their own private network. This has the two-fold effect of the terminals being unaffected by external network events, such as the Internet going down or the router being reset, as well as isolating the terminals from the rest of the network which helps to prevent malicious damage to the terminals from issues such as viruses. Additionally, we have seen that a BOH server equipped with an SSD instead of a traditional hard drive is able to reboot quickly enough to return to full operation before the terminals are able to time out and reboot themselves. This in itself saves an enormous amount of time when issues arise with the BOH server. To further prove the effectiveness of the new logical network layout, a pilot test using a single location is necessary. Since the 001 location is currently logically arranged closest to this proposed network design, we should install a 3725 router and 2950 switch at this location for a pilot test of perhaps a few weeks. If the test is successful and network reliability is increased, we should implement the changes to the other locations. Physical Cabling For New Restaurant Locations: Implementation Plan Run four Cat5e/6 Ethernet cables to a 4-port wall box at each terminal location (two ports will be unused initially and serve for redundancy purposes). Each port should be punched down to a patch panel containing 48 or more ports in the manager s office. Both ends of the cable must be labeled with the same number. For example, if one of the cables punches down at port 23 on the patch panel, the port at the other end at the wall box must be labeled 23. This aids in troubleshooting issues and eases physical cabling in the manager s office. For each kitchen printer, run two cables: one for active use, and one for redundancy. Use a patch cable to connect the Ethernet port of the terminal to a port in the wall jack. If the patch cable connects to port 23 in the wall jack, locate port 23 at the patch panel in the manager s office neckercube.com Page 5 of 15
6 Connect a patch cable from port 23 on the patch panel to the appropriate port on the 2950 switch. For example, if it is Terminal 3 you just connected, the patch cable connects from port 23 on the patch panel to port 3 on the Catalyst 2950 switch. Use a patch cable with a serial adapter to connect from one of the terminal s COM ports to an RJ-45 port in the wall jack. Use an Ethernet patch cable at the patch panel to connect to the printer. For example, if the patch cable from the terminal s COM3 port connects to the wall jack labeled port 24, and the kitchen printer connects to the wall jack labeled port 37, use a short Ethernet patch cable to connect port 24 to port 37 on the patch panel. This creates a Layer 1 physical serial connection between the terminal and the kitchen printer. Cisco WVRS4400n Configuration: Backup router configuration for rollback purposes Set username and password to XXXXXX / XXXXXX Change device IP to /24 Connect LAN Port 1 to Port 23 on the Catalyst 2950 switch. Verify Internet connectivity with a wireless device. Verify the internal VLANs cannot be accessed by pinging , (it should fail) Cisco Catalyst 2950 Configuration: Port 1 10: VLAN 100 (Aloha VLAN) Port 11 22: VLAN 20 (Management VLAN) Port 23: VLAN 30 (Wireless VLAN) Port 24: 802.1q Trunk port which connects to 3725 router s F0/1 interface Switch SSHv2 Management IP in VLAN20: Login: XXXXXX / XXXXXX For configuration script, see Appendix. Cisco 3725 Router Configuration: Interface FastEthernet 0/0 either DHCP or Static (depending on location) Interface FastEthernet 0/1.100: /24 VLAN 100 Interface FastEthernet 0/1.20: /24 VLAN 20 Interface FastEthernet 0/1.30: /24 VLAN 30 VLAN 30 Wireless users have 15-minute renewable DHCP lease SSHv2 Management from VLAN20 only: Login: XXXXXX / XXXXXX Stateful firewall configured via Cisco IOS Firewall and Access Control Lists (ACLs) For configuration script, see Appendix neckercube.com Page 6 of 15
7 Server Configuration: Install 2 nd Ethernet card, if necessary Connect ALOHA LAN link to Port 10 on the Catalyst 2950 switch Connect ALOHA Internet link to port 11 on the Catalyst 2950 switch Use LANACFG to set the ALOHA LAN Ethernet card to #0 (if necessary, see Appendix) Set the IP of Card #0 to with no gateway or DNS server. Open a command prompt and verify connectivity with one of the terminals: ping Set the IP of the Internet-facing interface to DHCP. Verify Internet connectivity. Terminal Configuration: Set the IP address to xx, where xx represents the terminal number (ie 04 for Terminal 4) Open a command prompt and verify connectivity with the server: ping Miscellaneous Configuration: Reset PRINTER IP address to Connect PRINTER and XXXXXX Server to available ports in the MGMT VLAN (ports 11-22) ==================== Aloha BOH Server LANACFG Instructions: Appendix The Aloha BOH server must use LAN CARD #0 to connect to the terminals. This can be reset with the LANACFG utility (which can be downloaded at as of this writing). To reset the configuration, open a command prompt (in Administrator mode, if the BOH server is running Windows 7), and type: lanacfg showlanapaths If you see a different interface than intended using #0, you must reassign it to an unused number: lanacfg setlananumber 0 9 Verify the change: lanacfg showlanpaths Using the previous command, note the intended network interface that should be set to 0. Using interface 5 as an example, reset it to 0 by typing: lanacfg setlananumber 5 0 Verify the change: lanacfg showlanpaths 2012 neckercube.com Page 7 of 15
8 Type: exit Reboot the server. ==================== Cisco Catalyst 2950 Switch Configuration: version 12.1 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime service password-encryption hostname Cat2950 aaa new-model aaa authentication login default local aaa authorization exec default local enable secret <OMITTED> username <OMITTED> privilege 15 secret <OMITTED> ip subnet-zero ip domain-name domain.local ip ssh time-out 120 ip ssh authentication-retries 3 ip ssh version 2 spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst no spanning-tree optimize bpdu transmission spanning-tree extend system-id interface FastEthernet0/1 interface FastEthernet0/ neckercube.com Page 8 of 15
9 interface FastEthernet0/3 interface FastEthernet0/4 interface FastEthernet0/5 interface FastEthernet0/6 interface FastEthernet0/7 interface FastEthernet0/8 interface FastEthernet0/9 interface FastEthernet0/10 interface FastEthernet0/11 interface FastEthernet0/ neckercube.com Page 9 of 15
10 interface FastEthernet0/13 interface FastEthernet0/14 interface FastEthernet0/15 interface FastEthernet0/16 interface FastEthernet0/17 interface FastEthernet0/18 interface FastEthernet0/19 interface FastEthernet0/20 interface FastEthernet0/21 interface FastEthernet0/ neckercube.com Page 10 of 15
11 interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 30 interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/25 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/26 shutdown interface Vlan1 no ip address no ip route-cache shutdown interface Vlan20 ip address no ip route-cache ip default-gateway no ip http server access-list 1 remark BLOCK_NON_MGMT access-list 1 permit line con 0 password <OMITTED> logging synchronous line vty 0 4 access-class 1 in password <OMITTED> transport input ssh line vty 5 15 access-class 1 in password <OMITTED> transport input ssh ntp clock-period ntp peer neckercube.com Page 11 of 15
12 end ==================== Cisco 3725 Router Configuration: version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption hostname Cisco3725 boot-start-marker boot system flash: <OMITTED> boot-end-marker enable secret <OMITTED> aaa new-model aaa authentication login default local aaa authorization exec default local aaa session-id common memory-size iomem 50 ip cef ip inspect name FIREWALL tcp ip inspect name FIREWALL udp no ip dhcp use vrf connected ip dhcp excluded-address ip dhcp excluded-address ip dhcp pool WIRELESS dns-server network default-router lease ip dhcp pool MGMT 2012 neckercube.com Page 12 of 15
13 dns-server network default-router ip domain name domain.local ip name-server ip name-server multilink bundle-name authenticated username <OMITTED> privilege 15 secret <OMITTED> archive log config hidekeys ip ssh version 2 interface FastEthernet0/0 description BRIGHTHOUSE ip address dhcp ip access-group FIREWALL in ip inspect FIREWALL out ip nat outside ip virtual-reassembly duplex auto speed auto interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address duplex auto speed auto interface FastEthernet0/1.20 description MGMT encapsulation dot1q 20 ip address ip nat inside ip virtual-reassembly 2012 neckercube.com Page 13 of 15
14 interface FastEthernet0/1.30 description WIRELESS encapsulation dot1q 30 ip address ip access-group BLK_WLAN in ip nat inside ip virtual-reassembly interface FastEthernet0/1.100 description ALOHA encapsulation dot1q 100 ip address no ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server ip nat inside source list 1 interface FastEthernet0/0 overload ip access-list standard MGMT_SSH permit ip access-list extended BLK_WLAN remark Deny Wireless From Other VLANs deny ip any deny ip any permit ip any any ip access-list extended FIREWALL permit udp any eq bootps any eq bootpc permit gre any any permit icmp any any echo-reply permit icmp any any traceroute access-list 1 permit access-list 1 permit access-list 101 deny ip any any control-plane line con 0 password <OMITTED> logging synchronous 2012 neckercube.com Page 14 of 15
15 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 access-class MGMT_SSH in password <OMITTED> transport input ssh line vty 5 15 access-class MGMT_SSH in password <OMITTED> transport input ssh ntp peer end 2012 neckercube.com Page 15 of 15
CONFIGURATION DU SWITCH
 Current configuration : 2037 bytes version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero
Current configuration : 2037 bytes version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Advanced IPv6 Training Course. Lab Manual. v1.3 Page 1
 Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Solution)
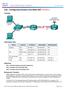 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode
 How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode MB5000 has a configurable serial port. With this serial port, MB5000 can be used as DCE device to be connected with Cisco router s console port so that MB5000
How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode MB5000 has a configurable serial port. With this serial port, MB5000 can be used as DCE device to be connected with Cisco router s console port so that MB5000
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Support for policy-based routing applies to the Barracuda Web Security Gateway running version 6.x only.
 Support for policy-based routing applies to the Barracuda Web Security Gateway running version 6.x only. Transparently Routing Web Traffic to the Barracuda Web Security Gateway This article demonstrates
Support for policy-based routing applies to the Barracuda Web Security Gateway running version 6.x only. Transparently Routing Web Traffic to the Barracuda Web Security Gateway This article demonstrates
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab Configuring Port Address Translation (PAT) (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
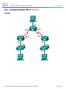 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
Lab Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 Static Routes (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
when interoperating with a Cisco Layer 3 Switch Situation: VLAN 1 shutdown, no IP on default VLAN on Cisco switch
 CONFIGURING VLANS ON MNS-6K AND MNS-6K-SECURE when interoperating with a Cisco Layer 3 Switch Situation: VLAN 1 shutdown, no IP on default VLAN on Cisco switch A Technical Brief from GarrettCom, Inc.,
CONFIGURING VLANS ON MNS-6K AND MNS-6K-SECURE when interoperating with a Cisco Layer 3 Switch Situation: VLAN 1 shutdown, no IP on default VLAN on Cisco switch A Technical Brief from GarrettCom, Inc.,
IOS Router : Easy VPN (EzVPN) in Network Extension Mode (NEM) with Split tunnelling Configuration Example
 IOS Router : Easy VPN (EzVPN) in Network Extension Mode (NEM) with Split tunnelling Configuration Example Document ID: 63098 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions
IOS Router : Easy VPN (EzVPN) in Network Extension Mode (NEM) with Split tunnelling Configuration Example Document ID: 63098 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Assembling Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tools
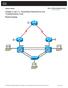 Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Assembling Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tools Physical Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Assembling Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tools Physical Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 on a Router (Solution)
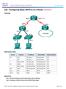 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.2.253
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.2.253
Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme. Topology. Objectives. Background / Scenario
 CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
QUESTION/SOLUTION SET LAB 4
 QUESTION/SOLUTION SET LAB 4 CCIE lab Routing & Switching (v4.0) lab:4 Updated Testing Guidelines 1. The equipment on the rack assigned to you is physically Cabled and should not be tempered with. 2. Router
QUESTION/SOLUTION SET LAB 4 CCIE lab Routing & Switching (v4.0) lab:4 Updated Testing Guidelines 1. The equipment on the rack assigned to you is physically Cabled and should not be tempered with. 2. Router
Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings
 APPENDIX A Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings The following is a sample configuration of a Business Ready Branch. There are many permutations of feature combinations when setting up the
APPENDIX A Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings The following is a sample configuration of a Business Ready Branch. There are many permutations of feature combinations when setting up the
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy
 Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
VPN Connection through Zone based Firewall Router Configuration Example
 VPN Connection through Zone based Firewall Router Configuration Example Document ID: 112051 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
VPN Connection through Zone based Firewall Router Configuration Example Document ID: 112051 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services?
 CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway. Ports Assignment Network
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
CWA URL Redirect support on C891FW
 Introduction, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 2 Configuring, page 3 HTTP Proxy Configuration, page 8 Configuration Examples for, page 8 Important Notes, page 14 Additional References for, page 14 Feature
Introduction, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 2 Configuring, page 3 HTTP Proxy Configuration, page 8 Configuration Examples for, page 8 Important Notes, page 14 Additional References for, page 14 Feature
Lab - Configuring a Switch Management Address
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Part 1: Configure a Basic Network
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Part 1: Configure a Basic Network
Quick Note. Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016
 Quick Note Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Outline... 3 1.2 Assumptions...
Quick Note Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Outline... 3 1.2 Assumptions...
Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels
 Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configuration Problem Configuration Solution and
Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configuration Problem Configuration Solution and
Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure DHCP for IPv4 Configure Stateless DHCP for IPv6 Configure Stateful DHCP for IPv6 Background To practice the various
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure DHCP for IPv4 Configure Stateless DHCP for IPv6 Configure Stateful DHCP for IPv6 Background To practice the various
exam. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND)
 100-105.exam Number: 100-105 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO 100-105 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Exam A QUESTION 1 Which route source code represents the routing
100-105.exam Number: 100-105 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO 100-105 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Exam A QUESTION 1 Which route source code represents the routing
L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients
 L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients The L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients feature allows mulitple Windows client to connect to an IPsec-enabled Cisco IOS Layer 2 Tunneling
L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients The L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients feature allows mulitple Windows client to connect to an IPsec-enabled Cisco IOS Layer 2 Tunneling
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 ( )
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (100-101) Exam Description: The 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) is a 1.5- hour exam with 50 60 questions. The 100-101 Interconnecting
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (100-101) Exam Description: The 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) is a 1.5- hour exam with 50 60 questions. The 100-101 Interconnecting
Deployment of Cisco IP Mobility Solution on Enterprise Class Teleworker Network
 Deployment Guide Deployment of Cisco IP Mobility Solution on Enterprise Class Teleworker Network The Cisco Service Oriented Network Architecture (SONA) framework helps enterprise customers evolve their
Deployment Guide Deployment of Cisco IP Mobility Solution on Enterprise Class Teleworker Network The Cisco Service Oriented Network Architecture (SONA) framework helps enterprise customers evolve their
Cisco Virtual Office: Easy VPN Deployment Guide
 Cisco Virtual Office: Easy VPN Deployment Guide This guide provides detailed design and implementation information for deployment of Easy VPN in client mode with the Cisco Virtual Office. Please refer
Cisco Virtual Office: Easy VPN Deployment Guide This guide provides detailed design and implementation information for deployment of Easy VPN in client mode with the Cisco Virtual Office. Please refer
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) Course Overview
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) Course Overview This course will teach students about building a simple network, establishing internet connectivity, managing network device security,
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) Course Overview This course will teach students about building a simple network, establishing internet connectivity, managing network device security,
CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE
 CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE Table of Contents (After Clicking Link Hit HOME to Return to TOC) 1) Add Hostname... 2 2) Add Username and Password... 2 3) Create Secret Password... 2 4) Encrypt Password...
CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE Table of Contents (After Clicking Link Hit HOME to Return to TOC) 1) Add Hostname... 2 2) Add Username and Password... 2 3) Create Secret Password... 2 4) Encrypt Password...
CCNA Security 1.0 Student Packet Tracer Manual
 1.0 Student Packet Tracer Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
1.0 Student Packet Tracer Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Lab Troubleshooting VTP Configuration
 Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0)
 CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0) 1. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function
CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0) 1. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
CCNA Security PT Practice SBA
 A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any Exam windows during the exam. 2. Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done.
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any Exam windows during the exam. 2. Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done.
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
No Service Password-Recovery
 No Service Password-Recovery Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The No Service Password-Recovery feature is a security enhancement that prevents anyone with console access from accessing the router configuration
No Service Password-Recovery Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The No Service Password-Recovery feature is a security enhancement that prevents anyone with console access from accessing the router configuration
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QnQ) and L2PT on L2 Ports
 Revised: November 11, 2011, OL-20468-01 First Published: November 11, 2011 Last Updated: November 11, 2011 This feature provides Layer 2 Tunneling support for QnQ and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT)
Revised: November 11, 2011, OL-20468-01 First Published: November 11, 2011 Last Updated: November 11, 2011 This feature provides Layer 2 Tunneling support for QnQ and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT)
Lab - Troubleshooting ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Loading Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) (CDR-882/780/790/990 Cellular Router)
 Loading Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) (CDR-882/780/790/990 Cellular Router) Call Direct Document version 1.4 Last updated 17 December, 2010 support@call-direct.com.au Loading IPSec To support IPSec
Loading Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) (CDR-882/780/790/990 Cellular Router) Call Direct Document version 1.4 Last updated 17 December, 2010 support@call-direct.com.au Loading IPSec To support IPSec
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Troubleshooting VLANs and Trunks
 L2 Troubleshooting VLANs and Trunks Global Knowledge Training LLC L2-1 Objectives In this lab you will download configuration files into PxSW s running configuration to introduce VLAN and trunking issues
L2 Troubleshooting VLANs and Trunks Global Knowledge Training LLC L2-1 Objectives In this lab you will download configuration files into PxSW s running configuration to introduce VLAN and trunking issues
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall
 Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall Document ID: 43068 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall Document ID: 43068 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
SSG Configuration Example
 APPENDIX A Example A-1 is a sample SSG configuration for the Cisco 10000 series router based on the topology in Figure A-1. The configuration includes AAA, PPP, SSG, and RADIUS. The SSG configuration enables
APPENDIX A Example A-1 is a sample SSG configuration for the Cisco 10000 series router based on the topology in Figure A-1. The configuration includes AAA, PPP, SSG, and RADIUS. The SSG configuration enables
Implementing IS-IS Routing and DHCP Services in an IPv4 Network
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Fall 2015 Implementing IS-IS Routing and DHCP Services in an IPv4 Network Laura
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Fall 2015 Implementing IS-IS Routing and DHCP Services in an IPv4 Network Laura
Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram
 Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram Default Cisco Terminal Options: 9600 bits/second No hardware flow control 8-bit ASCII No parity 1 stop bit Setting
Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram Default Cisco Terminal Options: 9600 bits/second No hardware flow control 8-bit ASCII No parity 1 stop bit Setting
IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling
 IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker duplicating encrypted packets by assigning a unique sequence
IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker duplicating encrypted packets by assigning a unique sequence
Configuring FXS Ports for Basic Calls
 Configuring FXS Ports for Basic Calls First Published: October 2, 2008 Last updated: March 19, 2010 This module describes how to configure analog Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) ports on a Cisco Integrated
Configuring FXS Ports for Basic Calls First Published: October 2, 2008 Last updated: March 19, 2010 This module describes how to configure analog Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) ports on a Cisco Integrated
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 1: OSPF With Three Routers
 Lab 1: OSPF With Three Routers The physical topology is as shown in FIG 18.1 - Advanced OSPF Lab. FIG 18.1 - Advanced OSPF Lab Lab Exercise Your task is to configure the network in FIG 18.1 - Advanced
Lab 1: OSPF With Three Routers The physical topology is as shown in FIG 18.1 - Advanced OSPF Lab. FIG 18.1 - Advanced OSPF Lab Lab Exercise Your task is to configure the network in FIG 18.1 - Advanced
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Lab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Seattle Cisco Users Group
 Seattle Cisco Users Group CCNA Lab Project #3 Joe Rinehart MBA, CCIE #14256 CCNP/DP/VP June 10, 2011 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1. The CCNA Certification... 3 1.2. Purpose of the Lab Project...
Seattle Cisco Users Group CCNA Lab Project #3 Joe Rinehart MBA, CCIE #14256 CCNP/DP/VP June 10, 2011 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1. The CCNA Certification... 3 1.2. Purpose of the Lab Project...
 Seite von 7 05.0.200 Close Window Assessment System Exam Viewer - CCNA Practice Certification Exam # - (Version 4.0) Below you will find the assessment items as presented on the exam as well as the scoring
Seite von 7 05.0.200 Close Window Assessment System Exam Viewer - CCNA Practice Certification Exam # - (Version 4.0) Below you will find the assessment items as presented on the exam as well as the scoring
Basic Router Configuration using SDM
 Basic Router Configuration using SDM Document ID: 71305 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Interface Configuration NAT Configuration Routing Configuration
Basic Router Configuration using SDM Document ID: 71305 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Interface Configuration NAT Configuration Routing Configuration
Configuring a Terminal/Comm Server
 Configuring a Terminal/Comm Server Document ID: 5466 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Cabling Design Strategy Configure Network Diagram Configurations Command Summary
Configuring a Terminal/Comm Server Document ID: 5466 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Cabling Design Strategy Configure Network Diagram Configurations Command Summary
Three interface Router without NAT Cisco IOS Firewall Configuration
 Three interface Router without NAT Cisco IOS Firewall Configuration Document ID: 13893 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Three interface Router without NAT Cisco IOS Firewall Configuration Document ID: 13893 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Skills Assessment Student Training
 Skills Assessment Student Training Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (6 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (33 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure Switch
Skills Assessment Student Training Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (6 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (33 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure Switch
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express 7921 Push-to-talk
 Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express 7921 Push-to-talk Application Note May 13, 2008 Cisco Revision History Revision Date Author Comments 1 03/29/2007 Tony Huynh Version 1.0 Table of Contents 1
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express 7921 Push-to-talk Application Note May 13, 2008 Cisco Revision History Revision Date Author Comments 1 03/29/2007 Tony Huynh Version 1.0 Table of Contents 1
NATIONAL_WATER_CONSERVATION#sh run Building configuration...
 NATIONAL_WATER_CONSERVATION#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 6390 bytes Last configuration change at 13:01:34 UTC Tue Jul 4 2017 by kembo version 15.4 service timestamps debug datetime
NATIONAL_WATER_CONSERVATION#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 6390 bytes Last configuration change at 13:01:34 UTC Tue Jul 4 2017 by kembo version 15.4 service timestamps debug datetime
CCNP TSHOOT. Quick Reference Sheet Exam
 CCNP TSHOOT Quick Reference Sheet Exam 300-135 Chapter 1. Network Principles Troubleshooting Steps Problem Identification Collection of Information Examination and Action Plan Verification Basic Troubleshooting
CCNP TSHOOT Quick Reference Sheet Exam 300-135 Chapter 1. Network Principles Troubleshooting Steps Problem Identification Collection of Information Examination and Action Plan Verification Basic Troubleshooting
Secure ACS Database Replication Configuration Example
 Secure ACS Database Replication Configuration Example Document ID: 71320 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Scenario I Scenario
Secure ACS Database Replication Configuration Example Document ID: 71320 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Scenario I Scenario
Configuring EtherChannel
 L4 Configuring EtherChannel Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-1 Objectives In this lab you will first verify that one of the parallel connections to the core switch is blocked by STP. You will then configure
L4 Configuring EtherChannel Global Knowledge Training LLC L4-1 Objectives In this lab you will first verify that one of the parallel connections to the core switch is blocked by STP. You will then configure
TestOut Routing and Switching Pro - English 6.0.x COURSE OUTLINE. Modified
 TestOut Routing and Switching Pro - English 6.0.x COURSE OUTLINE Modified 2017-07-10 TestOut Routing and Switching Pro Outline- English 6.0.x Videos: 133 (15:42:34) Demonstrations: 78 (7:22:19) Simulations:
TestOut Routing and Switching Pro - English 6.0.x COURSE OUTLINE Modified 2017-07-10 TestOut Routing and Switching Pro Outline- English 6.0.x Videos: 133 (15:42:34) Demonstrations: 78 (7:22:19) Simulations:
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 100-105 Title : Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1 v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 100-105 Title : Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1 v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version
Lab Student Lab Orientation
 Lab 1.1.1 Student Lab Orientation Objective In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Review the lab bundle equipment Understand the security pod topology Understand the pod naming and
Lab 1.1.1 Student Lab Orientation Objective In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Review the lab bundle equipment Understand the security pod topology Understand the pod naming and
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure trunking, VTP, and inter-vlan routing using router-on-a stick Configure GLBP Configure
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure trunking, VTP, and inter-vlan routing using router-on-a stick Configure GLBP Configure
Policy Based Routing with the Multiple Tracking Options Feature Configuration Example
 Policy Based Routing with the Multiple Tracking Options Feature Configuration Example Document ID: 48003 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
Policy Based Routing with the Multiple Tracking Options Feature Configuration Example Document ID: 48003 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
 CHAPTER 3 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Ethernet-to-Ethernet routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT). Multiple PCs can be connected to
CHAPTER 3 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Ethernet-to-Ethernet routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT). Multiple PCs can be connected to
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup
 Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Teacher s Reference Manual
 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Teacher s Reference Manual Subject: Security in Computing Practical with effect from the academic year 2018 2019 Practical 1: Packet Tracer - Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP,
UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Teacher s Reference Manual Subject: Security in Computing Practical with effect from the academic year 2018 2019 Practical 1: Packet Tracer - Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP,
Cisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide Cisco DSL Router Acting as a PPPoE Client with a Dynamic IP Address
 Cisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide Cisco DSL Router Acting as a PPPoE Client with a Dynamic IP Address Document ID: 71118 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Cisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide Cisco DSL Router Acting as a PPPoE Client with a Dynamic IP Address Document ID: 71118 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Lab Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling
 IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling First Published: February 28, 2005 Last Updated: March 24, 2011 Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker
IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling First Published: February 28, 2005 Last Updated: March 24, 2011 Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker
CISCO EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 100-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 35.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: CCNA Interconnecting
CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 100-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 35.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: CCNA Interconnecting
Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP and load balancing Configure HSRP authentication
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP and load balancing Configure HSRP authentication
Configuration Professional: Site to Site IPsec VPN Between Two IOS Routers Configuration Example
 Configuration Professional: Site to Site IPsec VPN Between Two IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113337 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuration
Configuration Professional: Site to Site IPsec VPN Between Two IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113337 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuration
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software
 Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
DHCP Server RADIUS Proxy
 The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server RADIUS Proxy is a RADIUS-based address assignment mechanism in which a DHCP server authorizes remote clients and allocates addresses based on replies
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server RADIUS Proxy is a RADIUS-based address assignment mechanism in which a DHCP server authorizes remote clients and allocates addresses based on replies
Lab Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
