Depth-First Search A B D E C
|
|
|
- Herbert Dalton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 epth-first Search
2 Outline and Reading efinitions (6.1) Subgraph onnectivity Spanning trees and forests epth-first search (6.3.1) lgorithm xample Properties nalysis pplications of FS (6.5) Path finding ycle finding epth-first Search 2
3 Subgraphs subgraph S of a graph G is a graph such that the vertices of S are a subset of the vertices of G the edges of S are a subset of the edges of G Subgraph spanning subgraph of G is a subgraph that contains all the vertices of G Spanning subgraph epth-first Search 3
4 onnectivity graph is connected if there is a path between every pair of vertices connected component of a graph G is a maximal connected subgraph of G onnected graph Non connected graph with two connected components epth-first Search 4
5 Trees and Forests (free) tree is an undirected graph T such that T is connected T has no cycles This definition of tree is different from the one of a rooted tree Tree forest is an undirected graph without cycles The connected components of a forest are trees Forest epth-first Search 5
6 Spanning Trees and Forests spanning tree of a connected graph is a spanning subgraph that is a tree spanning tree is not unique unless the graph is a tree Spanning trees have applications to the design of communication networks Graph spanning forest of a graph is a spanning subgraph that is a forest Spanning tree epth-first Search 6
7 epth-first Search epth-first search (FS) is a general technique for traversing a graph. FS traversal of a graph G visits all the vertices and edges of G determines whether G is connected computes the connected components of G computes a spanning forest of G FS on a graph with n vertices and m edges takes O(n + m) time FS can be further extended to solve other graph problems find and report a path between two given vertices find a cycle in the graph epth-first search is to graphs what uler tour is to binary trees epth-first Search 7
8 FS lgorithm The algorithm uses a mechanism for setting and getting labels of vertices and edges. lgorithm FS(G) Input graph G Output labeling of the edges of G as discovery edges and back edges for all u G.vertices() setlabel(u, UNXPLOR) for all e G.edges() setlabel(e, UNXPLOR) for all v G.vertices() if getlabel(v) = UNXPLOR FS(G, v) lgorithm FS(G, v) Input graph G and a start vertex v of G Output labeling of the edges of G in the connected component of v as discovery edges and back edges setlabel(v, VISIT) for all e G.incidentdges(v) if getlabel(e) = UNXPLOR w G.opposite(v,e) if getlabel(w) = UNXPLOR setlabel(e, ISOVRY) FS(G, w) else setlabel(e, K) epth-first Search 8
9 xample unexplored vertex visited vertex unexplored edge discovery edge back edge epth-first Search 9
10 xample (cont.) epth-first Search 10
11 FS and Maze Traversal The FS algorithm is similar to a classic strategy for exploring a maze We mark each intersection, corner and dead end (vertex) visited We mark each corridor (edge ) traversed We keep track of the path back to the entrance (start vertex) by means of a rope (recursion stack) epth-first Search 11
12 Properties of FS Property 1 FS(G, v) visits all the vertices and edges in the connected component of v Property 2 The discovery edges labeled by FS(G, v) form a spanning tree of the connected component of v epth-first Search 12
13 nalysis of FS Setting/getting a vertex/edge label takes O(1) time ach vertex is labeled twice once as UNXPLOR once as VISIT ach edge is labeled twice once as UNXPLOR once as ISOVRY or K Method incidentdges is called once for each vertex FS runs in O(n + m) time provided the graph is represented by the adjacency list structure Recall that Σ v deg(v) = 2m epth-first Search 13
14 Path Finding We can specialize the FS algorithm to find a path between two given vertices u and z using the template method pattern We call FS(G, u) with u as the start vertex We use a stack S to keep track of the path between the start vertex and the current vertex s soon as destination vertex z is encountered, we return the path as the contents of the stack lgorithm pathfs(g, v, z) setlabel(v, VISIT) S.push(v) if v = z return S.elements() for all e G.incidentdges(v) if getlabel(e) = UNXPLOR w opposite(v, e) if getlabel(w) = UNXPLOR setlabel(e, ISOVRY) S.push(e) pathfs(g, w, z) S.pop() { e gets popped } else setlabel(e, K) S.pop() { v gets popped } epth-first Search 14
15 ycle Finding We can specialize the FS algorithm to find a simple cycle using the template method pattern We use a stack S to keep track of the path between the start vertex and the current vertex s soon as a back edge (v, w) is encountered, we return the cycle as the portion of the stack from the top to vertex w lgorithm cyclefs(g, v) setlabel(v, VISIT) S.push(v) for all e G.incidentdges(v) if getlabel(e) = UNXPLOR w opposite(v,e) S.push(e) if getlabel(w) = UNXPLOR setlabel(e, ISOVRY) cyclefs(g, w) S.pop() else new empty stack repeat o S.pop().push(o) until o = w return.elements() S.pop() epth-first Search 15
Data Structures Lecture 14
 Fall 2018 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. ept. Management Information Systems, National hengchi University ata Structures Lecture 14 Graphs efinition, Implementation and Traversal Graphs Formally speaking,
Fall 2018 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. ept. Management Information Systems, National hengchi University ata Structures Lecture 14 Graphs efinition, Implementation and Traversal Graphs Formally speaking,
Breadth-First Search L 1 L Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Breadth-First Search 1
 readth-irst Search 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser readth-irst Search 1 readth-irst Search readth-first search (S) is a general technique for traversing a graph S traversal of a graph G Visits all
readth-irst Search 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser readth-irst Search 1 readth-irst Search readth-first search (S) is a general technique for traversing a graph S traversal of a graph G Visits all
Lecture 14: Graph Representation, DFS and Applications
 Lecture 14: Graph Representation, FS and pplications SFO OR LX FW ourtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Graph Representation dge List djacency List djacency Matrix
Lecture 14: Graph Representation, FS and pplications SFO OR LX FW ourtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Graph Representation dge List djacency List djacency Matrix
Graph ADT. Lecture18: Graph II. Adjacency Matrix. Representation of Graphs. Data Vertices and edges. Methods
 Graph T S33: ata Structures (0) Lecture8: Graph II ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr ata Vertices and edges endvertices(e): an array of the two endvertices of e opposite(v,e): the vertex opposite
Graph T S33: ata Structures (0) Lecture8: Graph II ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr ata Vertices and edges endvertices(e): an array of the two endvertices of e opposite(v,e): the vertex opposite
DFS on Directed Graphs BOS. Outline and Reading ( 6.4) Digraphs. Reachability ( 6.4.1) Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG s) ( 6.4.4)
 S on irected Graphs OS OR JK SO LX W MI irected Graphs S 1.3 1 Outline and Reading ( 6.4) Reachability ( 6.4.1) irected S Strong connectivity irected cyclic Graphs (G s) ( 6.4.4) Topological Sorting irected
S on irected Graphs OS OR JK SO LX W MI irected Graphs S 1.3 1 Outline and Reading ( 6.4) Reachability ( 6.4.1) irected S Strong connectivity irected cyclic Graphs (G s) ( 6.4.4) Topological Sorting irected
Depth-First Search and Template Patterns
 Depth-First Search and Template Patterns A B D E C 1 Outline Template Patterns and Search Depth-first search Algorithm Example Properties Analysis Applications of DFS Path finding Cycle finding CS 4407,
Depth-First Search and Template Patterns A B D E C 1 Outline Template Patterns and Search Depth-first search Algorithm Example Properties Analysis Applications of DFS Path finding Cycle finding CS 4407,
Digraphs ( 12.4) Directed Graphs. Digraph Application. Digraph Properties. A digraph is a graph whose edges are all directed.
 igraphs ( 12.4) irected Graphs OR OS digraph is a graph whose edges are all directed Short for directed graph pplications one- way streets flights task scheduling irected Graphs 1 irected Graphs 2 igraph
igraphs ( 12.4) irected Graphs OR OS digraph is a graph whose edges are all directed Short for directed graph pplications one- way streets flights task scheduling irected Graphs 1 irected Graphs 2 igraph
Applications of BFS and DFS
 pplications of S and S S all // : PM Some pplications of S and S S o find the shortest path from a vertex s to a vertex v in an unweighted graph o find the length of such a path o construct a S tree/forest
pplications of S and S S all // : PM Some pplications of S and S S o find the shortest path from a vertex s to a vertex v in an unweighted graph o find the length of such a path o construct a S tree/forest
CHAPTER 13 GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CHPTER 13 GRPH LGORITHMS SFO LX ORD DFW 1 CKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES RE DPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DT STRUCTURES ND LGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TMSSI ND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) ND SLIDES FROM JORY DENNY
CHPTER 13 GRPH LGORITHMS SFO LX ORD DFW 1 CKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES RE DPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DT STRUCTURES ND LGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TMSSI ND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) ND SLIDES FROM JORY DENNY
Graphs ORD SFO LAX DFW. Data structures and Algorithms
 SFO 143 ORD 337 1743 02 Graphs LAX 1233 DFW Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich, Tamassia and
SFO 143 ORD 337 1743 02 Graphs LAX 1233 DFW Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich, Tamassia and
Graphs ORD SFO LAX DFW. Graphs 1
 Graphs ORD 1843 SFO 802 1743 337 1233 LAX DFW Graphs 1 Outline and Reading Graphs ( 12.1) Definition Applications Terminology Properties ADT Data structures for graphs ( 12.2) Edge list structure Adjacency
Graphs ORD 1843 SFO 802 1743 337 1233 LAX DFW Graphs 1 Outline and Reading Graphs ( 12.1) Definition Applications Terminology Properties ADT Data structures for graphs ( 12.2) Edge list structure Adjacency
Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
Graph Terminology and Representations
 Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Graph Terminology and Representations 1 Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Graph Terminology and Representations 1 Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where
CS 225. April 16 Graph Traversal. Data Structures. Wade Fagen-Ulmschneider
 CS 225 Data Structures April 16 Graph Traversal Wade Fagen-Ulmschneider Graph ADT Data: - Vertices - Edges - Some data structure maintaining the structure between vertices and edges. d V W f b e X Y g
CS 225 Data Structures April 16 Graph Traversal Wade Fagen-Ulmschneider Graph ADT Data: - Vertices - Edges - Some data structure maintaining the structure between vertices and edges. d V W f b e X Y g
Directed Graphs BOS Goodrich, Tamassia Directed Graphs 1 ORD JFK SFO DFW LAX MIA
 Directed Graphs BOS ORD JFK SFO LAX DFW MIA 2010 Goodrich, Tamassia Directed Graphs 1 Digraphs A digraph is a graph whose edges are all directed Short for directed graph Applications one-way streets flights
Directed Graphs BOS ORD JFK SFO LAX DFW MIA 2010 Goodrich, Tamassia Directed Graphs 1 Digraphs A digraph is a graph whose edges are all directed Short for directed graph Applications one-way streets flights
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees 0 OS SO LX PV OR 0 JK 0 WI 00 W MI 00 Goodrich, Tamassia Minimum Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning
Minimum Spanning Trees 0 OS SO LX PV OR 0 JK 0 WI 00 W MI 00 Goodrich, Tamassia Minimum Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning
Outline and Reading. Minimum Spanning Tree. Minimum Spanning Tree. Cycle Property. Minimum Spanning Trees ( 12.7)
 Outline and Reading Minimum Spanning Tree PV 1 1 1 1 JK 1 15 SO 11 1 LX 15 Minimum Spanning Trees ( 1.) efinitions crucial fact Prim-Jarnik s lgorithm ( 1..) Kruskal s lgorithm ( 1..1) 111 // :1 PM Minimum
Outline and Reading Minimum Spanning Tree PV 1 1 1 1 JK 1 15 SO 11 1 LX 15 Minimum Spanning Trees ( 1.) efinitions crucial fact Prim-Jarnik s lgorithm ( 1..) Kruskal s lgorithm ( 1..1) 111 // :1 PM Minimum
Lecture 16: Directed Graphs
 Lecture 16: Directed Graphs ORD JFK BOS SFO LAX DFW MIA Courtesy of Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Directed Graphs Properties Algorithms for Directed Graphs DFS and
Lecture 16: Directed Graphs ORD JFK BOS SFO LAX DFW MIA Courtesy of Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Directed Graphs Properties Algorithms for Directed Graphs DFS and
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Graphs ORD SFO LAX DFW
 Graphs SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of odes, called vertices E is a collectio of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices ad edges are positios ad
Graphs SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of odes, called vertices E is a collectio of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices ad edges are positios ad
Graphs ORD SFO LAX DFW Goodrich, Tamassia Graphs 1
 Graphs SFO 33 143 ORD 02 LAX 1233 DFW 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia Graphs 1 What is a Graph? (in computer science, it s not a data plot) General structure for representing positions with an arbitrary connectivity
Graphs SFO 33 143 ORD 02 LAX 1233 DFW 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia Graphs 1 What is a Graph? (in computer science, it s not a data plot) General structure for representing positions with an arbitrary connectivity
DEPTH-FIRST SEARCH A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P. Graph Traversals. Depth-First Search
 PTH-IRST SRH raph Traversals epth-irst Search H I J K L M N O P epth-irst Search 1 xploring a Labyrinth Without etting Lost depth-first search (S) in an undirected graph is like wandering in a labyrinth
PTH-IRST SRH raph Traversals epth-irst Search H I J K L M N O P epth-irst Search 1 xploring a Labyrinth Without etting Lost depth-first search (S) in an undirected graph is like wandering in a labyrinth
L10 Graphs. Alice E. Fischer. April Alice E. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 April / 37
 L10 Graphs lice. Fischer pril 2016 lice. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 pril 2016 1 / 37 Outline 1 Graphs efinition Graph pplications Graph Representations 2 Graph Implementation 3 Graph lgorithms Sorting
L10 Graphs lice. Fischer pril 2016 lice. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 pril 2016 1 / 37 Outline 1 Graphs efinition Graph pplications Graph Representations 2 Graph Implementation 3 Graph lgorithms Sorting
Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Karen Daniels
 UMass Lowell omputer Science 91.404 nalysis of lgorithms Prof. Karen aniels Spring, 2013 hapter 22: raph lgorithms & rief Introduction to Shortest Paths [Source: ormen et al. textbook except where noted]
UMass Lowell omputer Science 91.404 nalysis of lgorithms Prof. Karen aniels Spring, 2013 hapter 22: raph lgorithms & rief Introduction to Shortest Paths [Source: ormen et al. textbook except where noted]
GRAPH THEORY. What are graphs? Why graphs? Graphs are usually used to represent different elements that are somehow related to each other.
 GRPH THEORY Hadrian ng, Kyle See, March 2017 What are graphs? graph G is a pair G = (V, E) where V is a nonempty set of vertices and E is a set of edges e such that e = {a, b where a and b are vertices.
GRPH THEORY Hadrian ng, Kyle See, March 2017 What are graphs? graph G is a pair G = (V, E) where V is a nonempty set of vertices and E is a set of edges e such that e = {a, b where a and b are vertices.
DataStruct 13. Graph Algorithms
 2013-2 DataStruct 13. Graph Algorithms Michael T. Goodrich, et. al, Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, 2 nd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011. December 10, 2013 Advanced Networking Technology Lab.
2013-2 DataStruct 13. Graph Algorithms Michael T. Goodrich, et. al, Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, 2 nd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011. December 10, 2013 Advanced Networking Technology Lab.
Chapter 9: Elementary Graph Algorithms Basic Graph Concepts
 hapter 9: Elementary Graph lgorithms asic Graph oncepts msc 250 Intro to lgorithms graph is a mathematical object that is used to model different situations objects and processes: Linked list Tree (partial
hapter 9: Elementary Graph lgorithms asic Graph oncepts msc 250 Intro to lgorithms graph is a mathematical object that is used to model different situations objects and processes: Linked list Tree (partial
CHAPTER 14 GRAPH ALGORITHMS ORD SFO LAX DFW
 SO OR HPTR 1 GRPH LGORITHMS LX W KNOWLGMNT: THS SLIS R PT ROM SLIS PROVI WITH T STRUTURS N LGORITHMS IN JV, GOORIH, TMSSI N GOLWSSR (WILY 16) 6 OS MINIMUM SPNNING TRS SO 16 PV OR 1 1 16 61 JK 1 1 11 WI
SO OR HPTR 1 GRPH LGORITHMS LX W KNOWLGMNT: THS SLIS R PT ROM SLIS PROVI WITH T STRUTURS N LGORITHMS IN JV, GOORIH, TMSSI N GOLWSSR (WILY 16) 6 OS MINIMUM SPNNING TRS SO 16 PV OR 1 1 16 61 JK 1 1 11 WI
Spanning Tree. Lecture19: Graph III. Minimum Spanning Tree (MSP)
 Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
CISC 320 Introduction to Algorithms Fall Lecture 15 Depth First Search
 IS 320 Introduction to lgorithms all 2014 Lecture 15 epth irst Search 1 Traversing raphs Systematic search of every edge and vertex of graph (directed or undirected) fficiency: each edge is visited no
IS 320 Introduction to lgorithms all 2014 Lecture 15 epth irst Search 1 Traversing raphs Systematic search of every edge and vertex of graph (directed or undirected) fficiency: each edge is visited no
12/5/17. trees. CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks. rooted trees. rooted trees
 trees CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks rooted trees Rooted trees. Given a tree T, choose
trees CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks rooted trees Rooted trees. Given a tree T, choose
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search
 Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Graphs II. Lecture 27. Prof.
 242 ata Structures and lgorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/242/ Graphs II Lecture 27 Prof. ric Polizzi Summary Previous Lecture omposed of vertices (nodes) and edges vertex or node edges
242 ata Structures and lgorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/242/ Graphs II Lecture 27 Prof. ric Polizzi Summary Previous Lecture omposed of vertices (nodes) and edges vertex or node edges
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Weighted Graphs ( 12.5) Shortest Paths. Shortest Paths ( 12.6) Shortest Path Properties PVD ORD SFO LGA HNL LAX DFW MIA PVD PVD ORD ORD SFO SFO LGA
 Shortest Paths A Weighted Graphs (.) In a weighted graph, each edge has an associated numerical value, called the weight of the edge dge weights may represent, distances, costs, etc. xample: In a flight
Shortest Paths A Weighted Graphs (.) In a weighted graph, each edge has an associated numerical value, called the weight of the edge dge weights may represent, distances, costs, etc. xample: In a flight
Agenda. Graph Representation DFS BFS Dijkstra A* Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp
 Graph Charles Lin genda Graph Representation FS BFS ijkstra * Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp Graph Representation djacency Matrix bool way[100][100];
Graph Charles Lin genda Graph Representation FS BFS ijkstra * Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp Graph Representation djacency Matrix bool way[100][100];
Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph.
 Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph. Motivating example: In a video game, you are searching for a path from a point in a maze to the exit. The maze can be modeled
Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph. Motivating example: In a video game, you are searching for a path from a point in a maze to the exit. The maze can be modeled
Lesson 22: Basic Graph Concepts
 Lesson 22: asic Graph oncepts msc 175 iscrete Mathematics 1. Introduction graph is a mathematical object that is used to model different relations between objects and processes: Linked list Flowchart of
Lesson 22: asic Graph oncepts msc 175 iscrete Mathematics 1. Introduction graph is a mathematical object that is used to model different relations between objects and processes: Linked list Flowchart of
Computational Geometry
 Orthogonal Range Searching omputational Geometry hapter 5 Range Searching Problem: Given a set of n points in R d, preprocess them such that reporting or counting the k points inside a d-dimensional axis-parallel
Orthogonal Range Searching omputational Geometry hapter 5 Range Searching Problem: Given a set of n points in R d, preprocess them such that reporting or counting the k points inside a d-dimensional axis-parallel
Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017
 1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017 1 We demo A8 Your space ship is on earth, and you hear a distress signal from a distance Planet X. Your job: 1. Rescue stage: Fly your ship
1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017 1 We demo A8 Your space ship is on earth, and you hear a distress signal from a distance Planet X. Your job: 1. Rescue stage: Fly your ship
Campus Tour. 1/18/2005 4:08 AM Campus Tour 1
 ampus Tour //00 :0 M ampus Tour Outline and Reading Overview of the assignment Review djacency matrix structure (..) Kruskal s MST algorithm (..) Partition T and implementation (..) The decorator pattern
ampus Tour //00 :0 M ampus Tour Outline and Reading Overview of the assignment Review djacency matrix structure (..) Kruskal s MST algorithm (..) Partition T and implementation (..) The decorator pattern
Undirected Graphs. V = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 } E = { 1-2, 1-3, 2-3, 2-4, 2-5, 3-5, 3-7, 3-8, 4-5, 5-6 } n = 8 m = 11
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees 04 6 33 135 49 PVD 1 40 146 61 JFK 14 15 0 111 34 Minimum Spanning Trees 1 Outline and Reading Minimum Spanning Trees Definitions A crucial fact The Prim-Jarnik Algorithm Kruskal's
Minimum Spanning Trees 04 6 33 135 49 PVD 1 40 146 61 JFK 14 15 0 111 34 Minimum Spanning Trees 1 Outline and Reading Minimum Spanning Trees Definitions A crucial fact The Prim-Jarnik Algorithm Kruskal's
Spanning Trees 4/19/17. Prelim 2, assignments. Undirected trees
 /9/7 Prelim, assignments Prelim is Tuesday. See the course webpage for details. Scope: up to but not including today s lecture. See the review guide for details. Deadline for submitting conflicts has passed.
/9/7 Prelim, assignments Prelim is Tuesday. See the course webpage for details. Scope: up to but not including today s lecture. See the review guide for details. Deadline for submitting conflicts has passed.
Spanning Trees. Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2017
 1 Spanning Trees Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2017 1 Prelim 2, assignments Prelim 2 is Tuesday. See the course webpage for details. Scope: up to but not including today s lecture. See the review guide for
1 Spanning Trees Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2017 1 Prelim 2, assignments Prelim 2 is Tuesday. See the course webpage for details. Scope: up to but not including today s lecture. See the review guide for
Introduction to Graphs. common/notes/ppt/
 Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Single Source, Shortest Path Problem
 Lecture : From ijkstra to Prim Today s Topics: ijkstra s Shortest Path lgorithm epth First Search Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s lgorithm overed in hapter 9 in the textbook Some slides based
Lecture : From ijkstra to Prim Today s Topics: ijkstra s Shortest Path lgorithm epth First Search Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s lgorithm overed in hapter 9 in the textbook Some slides based
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES. Chapter 11
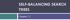 SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
Graphs V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
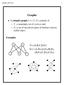 Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Today s Outline CSE 221: Algorithms and Data Structures Graphs (with no Axes to Grind)
 Today s Outline S : lgorithms and ata Structures raphs (with no xes to rind) Steve Wolfman 0W Topological Sort: etting to Know raphs with a Sort raph T and raph Representations raph Terminology (a lot
Today s Outline S : lgorithms and ata Structures raphs (with no xes to rind) Steve Wolfman 0W Topological Sort: etting to Know raphs with a Sort raph T and raph Representations raph Terminology (a lot
Lecture 25 Spanning Trees
 Lecture 25 Spanning Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning, Iliano Cervesato The following is a simple example of a connected, undirected graph with 5 vertices (A,
Lecture 25 Spanning Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning, Iliano Cervesato The following is a simple example of a connected, undirected graph with 5 vertices (A,
Graphs and Genetics. Outline. Computational Biology IST. Ana Teresa Freitas 2015/2016. Slides source: AED (MEEC/IST); Jones and Pevzner (book)
 raphs and enetics Computational Biology IST Ana Teresa Freitas / Slides source: AED (MEEC/IST); Jones and Pevzner (book) Outline l Motivacion l Introduction to raph Theory l Eulerian & Hamiltonian Cycle
raphs and enetics Computational Biology IST Ana Teresa Freitas / Slides source: AED (MEEC/IST); Jones and Pevzner (book) Outline l Motivacion l Introduction to raph Theory l Eulerian & Hamiltonian Cycle
Information Science 2
 Information Science 2 - Applica(ons of Basic ata Structures- Week 03 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Agenda l Week 02 review l Introduction to Graph Theory - Basic
Information Science 2 - Applica(ons of Basic ata Structures- Week 03 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Agenda l Week 02 review l Introduction to Graph Theory - Basic
Multicast routing principles in Internet
 Multicast routing principles in Internet Motivation Recap on graphs Principles and algorithms Multicast1-1 Multicast capability has been and is under intensive development since the 1990 s Mone used to
Multicast routing principles in Internet Motivation Recap on graphs Principles and algorithms Multicast1-1 Multicast capability has been and is under intensive development since the 1990 s Mone used to
10/31/18. About A6, Prelim 2. Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Facts about trees. Undirected trees
 //8 About A, Prelim Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture CS Fall 8 Prelim : Thursday, November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it (: or 7:) and what
//8 About A, Prelim Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture CS Fall 8 Prelim : Thursday, November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it (: or 7:) and what
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees 04 6 33 49 PVD 1 40 146 61 14 15 0 Minimum Spanning Trees 1 Minimum Spanning Trees ( 1.) Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning tree 1
Minimum Spanning Trees 04 6 33 49 PVD 1 40 146 61 14 15 0 Minimum Spanning Trees 1 Minimum Spanning Trees ( 1.) Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning tree 1
Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018
 1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018 1 About A6, Prelim 2 Prelim 2: Thursday, 15 November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it
1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018 1 About A6, Prelim 2 Prelim 2: Thursday, 15 November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it
Paths. Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph.
 Paths Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph. Formal Definition of a Path (Undirected) Let n be a nonnegative integer
Paths Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph. Formal Definition of a Path (Undirected) Let n be a nonnegative integer
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
Shortest Paths D E. Shortest Paths 1
 Shortest Paths A 2 7 2 B C D 2 E F Shortest Paths Outline and Reading Weighted graphs ( 7.) Shortest path problem Shortest path properties Dijkstra s algorithm ( 7..) Algorithm Edge relaxation The Bellman-Ford
Shortest Paths A 2 7 2 B C D 2 E F Shortest Paths Outline and Reading Weighted graphs ( 7.) Shortest path problem Shortest path properties Dijkstra s algorithm ( 7..) Algorithm Edge relaxation The Bellman-Ford
CS 125 Section #6 Graph Traversal and Linear Programs 10/13/14
 CS 125 Section #6 Graph Traversal and Linear Programs 10/13/14 1 Depth first search 1.1 The Algorithm Besides breadth first search, which we saw in class in relation to Dijkstra s algorithm, there is one
CS 125 Section #6 Graph Traversal and Linear Programs 10/13/14 1 Depth first search 1.1 The Algorithm Besides breadth first search, which we saw in class in relation to Dijkstra s algorithm, there is one
Graphs ADTs and Implementations
 Graphs ADTs and Implementations SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW - 1 - Applications of Graphs Ø Electronic circuits cslab1a cslab1b q Printed circuit board math.brown.edu q Integrated circuit Ø Transportation
Graphs ADTs and Implementations SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW - 1 - Applications of Graphs Ø Electronic circuits cslab1a cslab1b q Printed circuit board math.brown.edu q Integrated circuit Ø Transportation
CS 270 Algorithms. Oliver Kullmann. Analysing BFS. Depth-first search. Analysing DFS. Dags and topological sorting.
 General remarks Week 5 2 We finish, by analysing it. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider one application of, of graphs. Reading from CLRS for week 5 Chapter
General remarks Week 5 2 We finish, by analysing it. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider one application of, of graphs. Reading from CLRS for week 5 Chapter
These definitions cover some basic terms and concepts of graph theory and how they have been implemented as C++ classes.
 hapter 5. raph Theory *raph Theory, *Mathematics raph theory is an area of mathematics which has been incorporated into IS to solve some specific problems in oolean operations and sweeping. It may be also
hapter 5. raph Theory *raph Theory, *Mathematics raph theory is an area of mathematics which has been incorporated into IS to solve some specific problems in oolean operations and sweeping. It may be also
Graphs Weighted Graphs. Reading: 12.5, 12.6, 12.7
 Graphs Weighted Graphs Reading: 1.5, 1.6, 1. Weighted Graphs, a.k.a. Networks In a weighted graph, each edge has an associated numerical value, called the weight or cost of the edge Edge weights may represent,
Graphs Weighted Graphs Reading: 1.5, 1.6, 1. Weighted Graphs, a.k.a. Networks In a weighted graph, each edge has an associated numerical value, called the weight or cost of the edge Edge weights may represent,
lecture27: Graph Traversals
 lecture27: Largely based on slides by Cinda Heeren CS 225 UIUC 25th July, 2013 Announcements mp7.1 extra credit due tomorrow night (7/26) Code challenge tomorrow night (7/26) at 6pm in 0224 lab hash due
lecture27: Largely based on slides by Cinda Heeren CS 225 UIUC 25th July, 2013 Announcements mp7.1 extra credit due tomorrow night (7/26) Code challenge tomorrow night (7/26) at 6pm in 0224 lab hash due
A region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that is divided up by the network.
 Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M.
 Lecture 9 Graphs Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M. Wootters (2017) 1 Graphs A graph is a set of vertices
Lecture 9 Graphs Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M. Wootters (2017) 1 Graphs A graph is a set of vertices
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Multicast routing principles in Internet
 Multicast routing principles in Internet Motivation Recap on graphs Principles and algortihms Multicast1-1 Multicast capability has been and is under intensive development since the 1990 s Mone used to
Multicast routing principles in Internet Motivation Recap on graphs Principles and algortihms Multicast1-1 Multicast capability has been and is under intensive development since the 1990 s Mone used to
Graphs Definitions. Gunnar Gotshalks. GraphDefinitions 1
 Graphs Definitions GraphDefinitions 1 Examples of Graphs Street maps» Vertices are the intersections» Edges are the streets Power line network» Vertices are the houses & power stations» Edges are the power
Graphs Definitions GraphDefinitions 1 Examples of Graphs Street maps» Vertices are the intersections» Edges are the streets Power line network» Vertices are the houses & power stations» Edges are the power
Solutions to Midterm 2 - Monday, July 11th, 2009
 Solutions to Midterm - Monday, July 11th, 009 CPSC30, Summer009. Instructor: Dr. Lior Malka. (liorma@cs.ubc.ca) 1. Dynamic programming. Let A be a set of n integers A 1,..., A n such that 1 A i n for each
Solutions to Midterm - Monday, July 11th, 009 CPSC30, Summer009. Instructor: Dr. Lior Malka. (liorma@cs.ubc.ca) 1. Dynamic programming. Let A be a set of n integers A 1,..., A n such that 1 A i n for each
Note. Out of town Thursday afternoon. Willing to meet before 1pm, me if you want to meet then so I know to be in my office
 raphs and Trees Note Out of town Thursday afternoon Willing to meet before pm, email me if you want to meet then so I know to be in my office few extra remarks about recursion If you can write it recursively
raphs and Trees Note Out of town Thursday afternoon Willing to meet before pm, email me if you want to meet then so I know to be in my office few extra remarks about recursion If you can write it recursively
Spanning Trees. CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 17: Minimum Spanning Trees. Motivation. Observations. Spanning tree via DFS
 Spanning Trees S: ata Structures & lgorithms Lecture : Minimum Spanning Trees simple problem: iven a connected undirected graph =(V,), find a minimal subset of edges such that is still connected graph
Spanning Trees S: ata Structures & lgorithms Lecture : Minimum Spanning Trees simple problem: iven a connected undirected graph =(V,), find a minimal subset of edges such that is still connected graph
Graph Theory. ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl
 Graph Theory ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl What can graphs model? Cost of wiring electronic components together. Shortest route between two cities. Finding the shortest distance
Graph Theory ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl What can graphs model? Cost of wiring electronic components together. Shortest route between two cities. Finding the shortest distance
Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u, v V, then u is adjacent to v if {u, v} E. We also use the notation u v to denote that u is adjacent to v.
 Graph Adjacent Endpoint of an edge Incident Neighbors of a vertex Degree of a vertex Theorem Graph relation Order of a graph Size of a graph Maximum and minimum degree Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u,
Graph Adjacent Endpoint of an edge Incident Neighbors of a vertex Degree of a vertex Theorem Graph relation Order of a graph Size of a graph Maximum and minimum degree Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u,
Data Struct. & Prob. Solving, M.C.Q. BANK, FOR UNIT 3, SECOND YEAR COMP. ENGG. SEM 1, 2012 PATTERN, U.O.P.
 UNIT distribution for +1+1 + 1 + + = 11 (Only 1 will be asked for marks, s will be asked for 1 & s asked for marks ) Syllabus for Graphs Programmers perspective of graphs, Graph operations, storage structure,
UNIT distribution for +1+1 + 1 + + = 11 (Only 1 will be asked for marks, s will be asked for 1 & s asked for marks ) Syllabus for Graphs Programmers perspective of graphs, Graph operations, storage structure,
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE, Winter 8 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture : Graphs, DFS (Undirected, Directed), DAGs Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse-w8/ Graphs Internet topology Graphs Gene-gene interactions
CSE, Winter 8 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture : Graphs, DFS (Undirected, Directed), DAGs Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse-w8/ Graphs Internet topology Graphs Gene-gene interactions
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
K 4 C 5. Figure 4.5: Some well known family of graphs
 08 CHAPTER. TOPICS IN CLASSICAL GRAPH THEORY K, K K K, K K, K K, K C C C C 6 6 P P P P P. Graph Operations Figure.: Some well known family of graphs A graph Y = (V,E ) is said to be a subgraph of a graph
08 CHAPTER. TOPICS IN CLASSICAL GRAPH THEORY K, K K K, K K, K K, K C C C C 6 6 P P P P P. Graph Operations Figure.: Some well known family of graphs A graph Y = (V,E ) is said to be a subgraph of a graph
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms. Brute-Force Approach
 CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
COP 4531 Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms
 COP Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Overview of Graphs Breadth irst Search, and Depth irst Search hanks to several people who contributed to these slides including Piyush Kumar and
COP Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Overview of Graphs Breadth irst Search, and Depth irst Search hanks to several people who contributed to these slides including Piyush Kumar and
Lecture 14: March 9, 2015
 324: tate-space, F, F, Uninformed earch. pring 2015 Lecture 14: March 9, 2015 Lecturer: K.R. howdhary : Professor of (VF) isclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny reserved for
324: tate-space, F, F, Uninformed earch. pring 2015 Lecture 14: March 9, 2015 Lecturer: K.R. howdhary : Professor of (VF) isclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny reserved for
Algorithms. Definition: An algorithm is a set of rules followed to solve a problem. In general, an algorithm has the steps:
 Matchings 7.2 99 lgorithms efinition: n algorithm is a set of rules followed to solve a problem. In general, an algorithm has the steps: 1 Organize the input. 2 Repeatedly apply some steps until a termination
Matchings 7.2 99 lgorithms efinition: n algorithm is a set of rules followed to solve a problem. In general, an algorithm has the steps: 1 Organize the input. 2 Repeatedly apply some steps until a termination
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value
 The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees 04 6 33 135 49 1 40 146 61 14 15 0 111 34 Minimum Spanning Trees 1 Minimum Spanning Trees ( 1.) Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning
Minimum Spanning Trees 04 6 33 135 49 1 40 146 61 14 15 0 111 34 Minimum Spanning Trees 1 Minimum Spanning Trees ( 1.) Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning
LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS
 Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
Week 5. 1 Analysing BFS. 2 Depth-first search. 3 Analysing DFS. 4 Dags and topological sorting. 5 Detecting cycles. CS 270 Algorithms.
 1 2 Week 5 3 4 5 General remarks We finish, by analysing it. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider one application of, of graphs. Reading from CLRS for week
1 2 Week 5 3 4 5 General remarks We finish, by analysing it. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider one application of, of graphs. Reading from CLRS for week
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms. Graph Traversals. Autumn Shrirang (Shri) Mare
 SE 373: ata Structures and lgorithms Graph Traversals utumn 2018 Shrirang (Shri) Mare shri@cs.washington.edu Thanks to Kasey hampion, en Jones, dam lank, Michael Lee, Evan Mcarty, Robbie Weber, Whitaker
SE 373: ata Structures and lgorithms Graph Traversals utumn 2018 Shrirang (Shri) Mare shri@cs.washington.edu Thanks to Kasey hampion, en Jones, dam lank, Michael Lee, Evan Mcarty, Robbie Weber, Whitaker
Prim & Kruskal Algorithm
 Prim & Kruskal Algorithm Minimum Spanning Tree Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning tree 1 10 PIT Spanning subgraph that is itself a (free) tree Minimum spanning
Prim & Kruskal Algorithm Minimum Spanning Tree Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning tree 1 10 PIT Spanning subgraph that is itself a (free) tree Minimum spanning
Graph Algorithms shortest paths, minimum spanning trees, etc.
 Graph Algorithms shortest paths, minimum spanning trees, etc. SFO ORD LAX DFW Graphs 1 Outline and Reading Graphs ( 1.1) Definition Applications Terminology Properties ADT Data structures for graphs (
Graph Algorithms shortest paths, minimum spanning trees, etc. SFO ORD LAX DFW Graphs 1 Outline and Reading Graphs ( 1.1) Definition Applications Terminology Properties ADT Data structures for graphs (
TCOM 501: Networking Theory & Fundamentals. Lecture 11 April 16, 2003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis
 TOM 50: Networking Theory & undamentals Lecture pril 6, 2003 Prof. Yannis. Korilis 2 Topics Routing in ata Network Graph Representation of a Network Undirected Graphs Spanning Trees and Minimum Weight
TOM 50: Networking Theory & undamentals Lecture pril 6, 2003 Prof. Yannis. Korilis 2 Topics Routing in ata Network Graph Representation of a Network Undirected Graphs Spanning Trees and Minimum Weight
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
Graph Algorithms. Imran Rashid. Jan 16, University of Washington
 Graph Algorithms Imran Rashid University of Washington Jan 16, 2008 1 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs & Topological Ordering 3 DFS 2 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs
Graph Algorithms Imran Rashid University of Washington Jan 16, 2008 1 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs & Topological Ordering 3 DFS 2 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs
This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science.
 Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Breadth First Search. cse2011 section 13.3 of textbook
 Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Suggested Study Strategy
 Final Exam Thursday, 7 August 2014,19:00 22:00 Closed Book Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (hash tables, binary search trees, sorting, graphs) Suggested Study Strategy
Final Exam Thursday, 7 August 2014,19:00 22:00 Closed Book Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (hash tables, binary search trees, sorting, graphs) Suggested Study Strategy
