Maps and Dictionaries
|
|
|
- Clement Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Map and ictionary Ts Maps and ictionaries The dictionary T models a searchable collection of key-element items The main operations of a dictionary are searching, inserting, and deleting items MP: Multiple items with the same key are NOT allowed ITIONRY: Multiple items with the same key RE allowed pplications: address book student-record database credit card authorization ictionary T methods: Map T methods: find(k): if the dictionary has an entry with key k, returns the entry; otherwise, returns null insert(k, o): inserts an entry (k, o) into the dictionary remove(e): removes entry e from the dictionary and returns the entry; otherwise, returns null if e not found size(), isempty() entries(): returns the key-value entries stored findll(k): returns an iterator of all entries with key k get(k): if the map has an entry with key k, returns the entry; otherwise, returns null put(k, o): adds an entry (k, o) into the map if it doesn t exist; otherwise, the old value is replaced remove(k): removes entry with key k from the map and returns its value; otherwise, returns null if k not found size(), isempty() keys(): returns an iterator of keys stored in the map values(): returns an iterator of values associated with keys stored in the map 4
2 ictionary Ts Implementing a ictionary with an Unordered Sequence Ordered dictionary: total order relation defined by some comparator for the keys Unordered dictionary: no order relation defined for keys searching and removing takes O(n) time inserting takes O() time applications to log files (frequent insertions, rare searches and removals) 5 Implementing a ictionary with an Ordered Sequence inary Search narrow down the search range in stages high-low game Example: find(7) searching takes O(log n) time (binary search) inserting and removing takes O(n) time application to look-up tables (frequent searches, rare insertions and removals) 7 l l m h m h l m h l=m =h 8
3 Pseudocode for inary Search lgorithm inarysearch(s, k, low, high) if low > high then return NO_SUH_KEY else mid (low+high) / if k = key(mid) then return key(mid) else if k < key(mid) then return inarysearch(s, k, low, mid-) else return inarysearch(s, k, mid+, high) Running Time of inary Search The range of candidate items to be searched is divided into half after each comparison low mid high low mid high low mid In the array-based implementation, access by rank takes O() time, thus binary search runs in O(log n) time inary Search Trees inary Search Trees Searching ost of Searching Insertion eletion < > 4 = 8 binary search tree is a binary tree T such that each internal node stores an entry (k, e) of a dictionary. keys stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to k. keys stored at nodes in the right subtree of v are greater than or equal to k. external nodes do not hold elements but serve as place holders.
4 regor 7 Fabio Nicole ob Frank Question: How can we traverse the tree so that we visit the elements in increasing key order? 4 Operations Search Searching: find(k) Inserting: insert(k, o) Removing: remove(k) 5 To search for a key k, we trace a downward path starting at the root The next node visited depends on the outcome of the comparison of k with the key of the current node If we reach a leaf, the key is not found and we return NO_SUH_KEY Example: find(4) call TreeSearch(4,root) lgorithm TreeSearch(k, v) if T.isExternal (v) return NO_SUH_KEY if k < key(v) return TreeSearch(k, T.left(v)) else if k = key(v) return element(v) else { k > key(v) } return TreeSearch(k, T.right(v)) < > 4 = 8
5 Search Example I Search Example II Successful find(7) 7>44 7>5 7<88 7<8 Unsuccessful find(5) 5<44 5>7 5< 5<8 leaf node successful search traverses a path starting at the root and ending at an internal node 7 n unsuccessful search traverses a path starting at the root and ending at an external node 8 ost of Search: Worst ase ost of Search: Worst ase a account verage # of comparisons in the worst case: Successful search frica apple 4 arc Path to node i has length i, to get there we do O(i) comparisons vg cost= (/n) O(i) = n a account verage # of comparisons in the worst case: Unsuccessful search frica apple 4 arc n unsuccessful search always takes O(n) comparisons for n internal nodes
6 ost of Search: est ase ost of Search: est ase Leaves are on the same level or on an adjacent level. Leaves are on the same level or on an adjacent level. Length of path from root to node i = log i Length of path from root to node i = log i For a successful search, we do comparisons at each node along the path plus one at the end. For a failed search, we do comparisons at each node along the path plus two at the end. omparisons to node i: O(log i) Only paths to external nodes count. verage # of comparisons in the best case n n Σ O(log i) = O((n log n)/ n) = O(log n) i= So, always O(log n) Insertion I inserttexternal(v): To perform insert(k,e), call TreeInsert(k, e, T.root()) Let w be the node returned by TreeSearch(k, T.root()) If w is external, we know that k is not stored in T. We call inserttexternal(w) on T and store (k, e) in w Transform v from an external node into an internal node by creating two new children E E new new inserttexternal(v): new and new are the new nodes if isexternal(v) v.left new v.right new size size + 4
7 Insertion II If w is internal, we know another item with key k is stored at w. We call the algorithm recursively starting at T.right(w) or T.left(w) The idea is to store the new item in an external node which either precedes or follows the items with the same key in an inorder traversal. onstruct a Tree What would be the result of constructing a tree from repeated insertions of the following sequences? a. 5,8,,7,,,,4, b.,,,4,5,,7,8, c. 5,4,,,7,,8,, 5 eletion I removeexternal(v): To perform operation remove(k), we search for key k ssume key k is in the tree, and let v be the node storing k If node v has a leaf child w, we remove v and w from the tree with operation removeexternal(w) Example: remove 4 < > 4 v 8 w F E 7 8
8 v F E removeexternal(v): if isexternal(v) { p parent(v) s sibling(v) if isroot(v) s.parent null and root s else { g parent(p) if (p is lefthild(g) g.left s else g.right s s.parent g } size size - } eletion II Practice, practice, practice We consider the case where the key k to be removed is stored at a node v whose children are both internal we find the internal node w that follows v in an inorder traversal we copy key(w) into node v we remove node w and its left child z (which must be a leaf) by means of operation removeexternal(z) Example: remove v w 5 z v a. elete the from the tree you got in the (a). b. Now delete node 5.
9 ost of Inserting and eleting = ost of Search Summary: onsider a dictionary with n items implemented by means of a binary search tree of height h the space used is O(n) methods find, insert and remove take O(h) time onclusion To achieve good running time, we need to keep the tree balanced, i.e., with O(log n) height. Various balancing schemes will be explored next. The height h is O(n) in the worst case and O(log n) in the best case 4
Dictionaries. 2/17/2006 Dictionaries 1
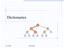 Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
Binary Search Trees > = 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser. Binary Search Trees 1
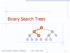 Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Binary Search Trees (10.1) Dictionary ADT (9.5.1)
 Binary Search Trees (10.1) CSE 011 Winter 011 4 March 011 1 Dictionary ADT (..1) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
Binary Search Trees (10.1) CSE 011 Winter 011 4 March 011 1 Dictionary ADT (..1) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
SEARCHING. the dictionary ADT. binary search. binary search trees. Searching
 the dictionary ADT binary search binary search trees SEARCHING 44 17 78 32 50 88 48 62 1 The Dictionary ADT a dictionary is an abstract model of a database like a priority queue, a dictionary stores key-element
the dictionary ADT binary search binary search trees SEARCHING 44 17 78 32 50 88 48 62 1 The Dictionary ADT a dictionary is an abstract model of a database like a priority queue, a dictionary stores key-element
CSE Data Structures and Introduction to Algorithms... In Java! Instructor: Fei Wang. Binary Search Trees. CSE2100 DS & Algorithms 1
 CSE 2100 Data Structures and Introduction to Algorithms...! In Java!! Instructor: Fei Wang! Binary Search Trees 1 R-10.6, 10.7!!! Draw the 11-entry hash table that results from using the hash function
CSE 2100 Data Structures and Introduction to Algorithms...! In Java!! Instructor: Fei Wang! Binary Search Trees 1 R-10.6, 10.7!!! Draw the 11-entry hash table that results from using the hash function
Search Trees (Ch. 9) > = Binary Search Trees 1
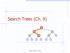 Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presentation for use ith the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Ch.03 Binary Search Trees Binary Search Binary search can perform nearest neighbor queries
Presentation for use ith the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Ch.03 Binary Search Trees Binary Search Binary search can perform nearest neighbor queries
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures
 Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures Basic Data Structures Stacks Queues Vectors, Linked Lists Trees (Including Balanced Trees) Priority Queues and Heaps Dictionaries and Hash Tables Spring 2014 CS 315 2 Two
Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures Basic Data Structures Stacks Queues Vectors, Linked Lists Trees (Including Balanced Trees) Priority Queues and Heaps Dictionaries and Hash Tables Spring 2014 CS 315 2 Two
Chapter 10: Search Trees
 < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 Chapter 10: Search Trees Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++,
< 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 Chapter 10: Search Trees Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++,
Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
CSE 326: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
Final Exam. EECS 2011 Prof. J. Elder - 1 -
 Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
Priority Queues and Heaps. More Data Structures. Priority Queue ADT ( 2.4.1) Total Order Relation. Sorting with a Priority Queue ( 2.4.
 More Data Structures Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues, Comparators, Locators, Dictionaries More Data Structures v. More Data Structures v. Priority Queue ADT (.4.) Total Order Relation A priority
More Data Structures Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues, Comparators, Locators, Dictionaries More Data Structures v. More Data Structures v. Priority Queue ADT (.4.) Total Order Relation A priority
Search Trees - 2. Venkatanatha Sarma Y. Lecture delivered by: Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore. M.S Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies - Bangalore
 Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 1 Venkatanatha Sarma Y
 Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Multi-Way Search Tree
 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Dr. CAS SD01 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page Outline Ordered
Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Dr. CAS SD01 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page Outline Ordered
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia. (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree ( 9.4.1) A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d 1 key-element items
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree ( 9.4.1) A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d 1 key-element items
Final Exam. CSE 2011 Prof. J. Elder Last Updated: :41 PM
 Final Exam Ø Tue, 17 Apr 2012 19:00 22:00 LAS B Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps, hashing, binary search trees, sorting,
Final Exam Ø Tue, 17 Apr 2012 19:00 22:00 LAS B Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps, hashing, binary search trees, sorting,
Operations on Heap Tree The major operations required to be performed on a heap tree are Insertion, Deletion, and Merging.
 Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Priority queues. Priority queues. Priority queue operations
 Priority queues March 30, 018 1 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined
Priority queues March 30, 018 1 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined
Tree traversals and binary trees
 Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
CS350: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 Binary Search Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree that
Binary Search Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree that
Splay Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Dickerson. Splay Trees 1
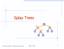 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Binomial Queue deletemin ADTs Seen So Far
 Today s Outline Trees (inary Search Trees) hapter in Weiss S ata Structures Ruth nderson nnouncements Written HW # due next riday, 1/ Project due next Monday, /1 Today s Topics: Priority Queues inomial
Today s Outline Trees (inary Search Trees) hapter in Weiss S ata Structures Ruth nderson nnouncements Written HW # due next riday, 1/ Project due next Monday, /1 Today s Topics: Priority Queues inomial
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
CS127: B-Trees. B-Trees
 CS127: B-Trees B-Trees 1 Data Layout on Disk Track: one ring Sector: one pie-shaped piece. Block: intersection of a track and a sector. Disk Based Dictionary Structures Use a disk-based method when the
CS127: B-Trees B-Trees 1 Data Layout on Disk Track: one ring Sector: one pie-shaped piece. Block: intersection of a track and a sector. Disk Based Dictionary Structures Use a disk-based method when the
Searching: Introduction
 Searching: Introduction Searching is a major topic in data structures and algorithms Applications: Search for students transcripts from ARR Search for faculty contact email address, office Search for books,
Searching: Introduction Searching is a major topic in data structures and algorithms Applications: Search for students transcripts from ARR Search for faculty contact email address, office Search for books,
CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary
CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary
COSC 2011 Section N. Trees: Terminology and Basic Properties
 COSC 2011 Tuesday, March 27 2001 Overview Trees and Binary Trees Quick review of definitions and examples Tree Algorithms Depth, Height Tree and Binary Tree Traversals Preorder, postorder, inorder Binary
COSC 2011 Tuesday, March 27 2001 Overview Trees and Binary Trees Quick review of definitions and examples Tree Algorithms Depth, Height Tree and Binary Tree Traversals Preorder, postorder, inorder Binary
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees. Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler
 Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
A Binary Search Tree Implementation
 A Binary Search Tree Implementation Chapter 25 Getting Started Contents An Interface for the Binary Search Tree Duplicate Entries Beginning the Class Definition Searching and Retrieving Traversing Adding
A Binary Search Tree Implementation Chapter 25 Getting Started Contents An Interface for the Binary Search Tree Duplicate Entries Beginning the Class Definition Searching and Retrieving Traversing Adding
Heaps Goodrich, Tamassia. Heaps 1
 Heaps Heaps 1 Recall Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry with key k
Heaps Heaps 1 Recall Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry with key k
Stores a collection of elements each with an associated key value
 CH9. PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 201) PRIORITY QUEUES Stores a collection
CH9. PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 201) PRIORITY QUEUES Stores a collection
8. Binary Search Tree
 8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
CS S-06 Binary Search Trees 1
 CS245-2008S-06 inary Search Trees 1 06-0: Ordered List T Operations: Insert an element in the list Check if an element is in the list Remove an element from the list Print out the contents of the list,
CS245-2008S-06 inary Search Trees 1 06-0: Ordered List T Operations: Insert an element in the list Check if an element is in the list Remove an element from the list Print out the contents of the list,
Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates
 Binary Search Trees Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates Implementing Set On Monday and Wednesday, we saw how to implement the Map and Lexicon, respectively. Let's now turn our attention to the Set.
Binary Search Trees Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates Implementing Set On Monday and Wednesday, we saw how to implement the Map and Lexicon, respectively. Let's now turn our attention to the Set.
Maps, Hash Tables and Dictionaries. Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.5
 Maps, Hash Tables and Dictionaries Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.5 Outline Maps Hashing Dictionaries Ordered Maps & Dictionaries Outline Maps Hashing Dictionaries Ordered Maps & Dictionaries Maps A map
Maps, Hash Tables and Dictionaries Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.5 Outline Maps Hashing Dictionaries Ordered Maps & Dictionaries Outline Maps Hashing Dictionaries Ordered Maps & Dictionaries Maps A map
CSCI-401 Examlet #5. Name: Class: Date: True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false.
 Name: Class: Date: CSCI-401 Examlet #5 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The root node of the standard binary tree can be drawn anywhere in the tree diagram. 2.
Name: Class: Date: CSCI-401 Examlet #5 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The root node of the standard binary tree can be drawn anywhere in the tree diagram. 2.
Heaps. 2/13/2006 Heaps 1
 Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
CPSC 223 Algorithms & Data Abstract Structures
 PS 223 lgorithms & ata bstract Structures Lecture 17: Self-alancing inary Search Trees * Material adapted from. arrano, K. Yerion, and K. ant Today Quiz alanced inary Search Trees (STs) Quick review of
PS 223 lgorithms & ata bstract Structures Lecture 17: Self-alancing inary Search Trees * Material adapted from. arrano, K. Yerion, and K. ant Today Quiz alanced inary Search Trees (STs) Quick review of
Heaps 2. Recall Priority Queue ADT. Heaps 3/19/14
 Heaps 3// Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 Heaps Heaps Recall Priority Queue ADT
Heaps 3// Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 Heaps Heaps Recall Priority Queue ADT
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II. Binary Search Trees
 CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees Symbol table applications BST definitions and terminologies Search and insert Traversal Ordered operations Delete Symbol
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees Symbol table applications BST definitions and terminologies Search and insert Traversal Ordered operations Delete Symbol
csci 210: Data Structures Trees
 csci 210: Data Structures Trees 1 Summary Topics general trees, definitions and properties interface and implementation tree traversal algorithms depth and height pre-order traversal post-order traversal
csci 210: Data Structures Trees 1 Summary Topics general trees, definitions and properties interface and implementation tree traversal algorithms depth and height pre-order traversal post-order traversal
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Suggested Study Strategy
 Final Exam Thursday, 7 August 2014,19:00 22:00 Closed Book Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (hash tables, binary search trees, sorting, graphs) Suggested Study Strategy
Final Exam Thursday, 7 August 2014,19:00 22:00 Closed Book Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (hash tables, binary search trees, sorting, graphs) Suggested Study Strategy
Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees
 Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees CS 62 Fall 2017 Kim Bruce & Alexandra Papoutsaki 1 BST A binary tree is a binary search tree iff it is empty or if the value of every node is both greater than or equal
Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees CS 62 Fall 2017 Kim Bruce & Alexandra Papoutsaki 1 BST A binary tree is a binary search tree iff it is empty or if the value of every node is both greater than or equal
CH 9 : MAPS AND DICTIONARIES
 CH 9 : MAPS AND DICTIONARIES 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM JORY
CH 9 : MAPS AND DICTIONARIES 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM JORY
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Chapter 9: Maps, Dictionaries, Hashing
 Chapter 9: 0 1 025-612-0001 2 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 Maps, Dictionaries, Hashing Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided
Chapter 9: 0 1 025-612-0001 2 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 Maps, Dictionaries, Hashing Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures
 T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture 4a inary Trees Review of Linked Lists Linked-Lists dynamic length arbitrary memory locations access by following links an only traverse link in forward direction
T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture 4a inary Trees Review of Linked Lists Linked-Lists dynamic length arbitrary memory locations access by following links an only traverse link in forward direction
Uses for Trees About Trees Binary Trees. Trees. Seth Long. January 31, 2010
 Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Tree Traversal. Lecture12: Tree II. Preorder Traversal
 Tree Traersal (0F) Lecture: Tree II Process of isiting nodes in a tree systematically Some algorithms need to isit all nodes in a tree. Example: printing, counting nodes, etc. Implementation Can be done
Tree Traersal (0F) Lecture: Tree II Process of isiting nodes in a tree systematically Some algorithms need to isit all nodes in a tree. Example: printing, counting nodes, etc. Implementation Can be done
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Trees. CSE 373 Data Structures
 Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Data Structures. Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees
 Data Structures Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parentchild relation Applications:
Data Structures Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parentchild relation Applications:
Augmenting Data Structures
 Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Search Trees. Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Binary Search Trees
 Unit 9, Part 2 Search Trees Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Binary Search Trees Search-tree property: for each node k: all nodes in k s left subtree are < k all nodes
Unit 9, Part 2 Search Trees Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Binary Search Trees Search-tree property: for each node k: all nodes in k s left subtree are < k all nodes
Orthogonal range searching. Range Trees. Orthogonal range searching. 1D range searching. CS Spring 2009
 CS 5633 -- Spring 2009 Orthogonal range searching Range Trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms 1 Input: n points in d dimensions
CS 5633 -- Spring 2009 Orthogonal range searching Range Trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms 1 Input: n points in d dimensions
Balanced Search Trees
 Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
21# 33# 90# 91# 34# # 39# # # 31# 98# 0# 1# 2# 3# 4# 5# 6# 7# 8# 9# 10# #
 1. Prove that n log n n is Ω(n). York University EECS 11Z Winter 1 Problem Set 3 Instructor: James Elder Solutions log n n. Thus n log n n n n n log n n Ω(n).. Show that n is Ω (n log n). We seek a c >,
1. Prove that n log n n is Ω(n). York University EECS 11Z Winter 1 Problem Set 3 Instructor: James Elder Solutions log n n. Thus n log n n n n n log n n Ω(n).. Show that n is Ω (n log n). We seek a c >,
Tree. A path is a connected sequence of edges. A tree topology is acyclic there is no loop.
 Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2
 CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
2-3 and Trees. COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli
 2-3 and 2-3-4 Trees COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli Multi-Way Trees A binary search tree: One value in each node At most 2 children An M-way search tree: Between 1 to (M-1) values
2-3 and 2-3-4 Trees COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli Multi-Way Trees A binary search tree: One value in each node At most 2 children An M-way search tree: Between 1 to (M-1) values
Binary Search Trees. Nearest Neighbor Binary Search Trees Insertion Predecessor and Successor Deletion Algorithms on Trees.
 Binary Search Trees Nearest Neighbor Binary Search Trees Insertion Predecessor and Successor Deletion Algorithms on Trees Philip Bille Binary Search Trees Nearest Neighbor Binary Search Trees Insertion
Binary Search Trees Nearest Neighbor Binary Search Trees Insertion Predecessor and Successor Deletion Algorithms on Trees Philip Bille Binary Search Trees Nearest Neighbor Binary Search Trees Insertion
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques () Lecture 6 January 24, 2018 Binary Search Trees (Lecture notes Chapter 7) Announcements Homework 2: Computing Human Evolution due Tuesday, September 19 th Reading:
Programming Languages and Techniques () Lecture 6 January 24, 2018 Binary Search Trees (Lecture notes Chapter 7) Announcements Homework 2: Computing Human Evolution due Tuesday, September 19 th Reading:
Priority queues. Priority queues. Priority queue operations
 Priority queues March 8, 08 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined by
Priority queues March 8, 08 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined by
Binary Search Trees. Binary Search Trees. Nearest Neighbor. Nearest Neighbor
 Philip Bille Nearest Neighbor Nearest neighbor. Maintain dynamic set S supporting the following operations. Each element has key x.key and satellite data x.data. PREDECESSOR(k): return element with largest
Philip Bille Nearest Neighbor Nearest neighbor. Maintain dynamic set S supporting the following operations. Each element has key x.key and satellite data x.data. PREDECESSOR(k): return element with largest
Overview of Presentation. Heapsort. Heap Properties. What is Heap? Building a Heap. Two Basic Procedure on Heap
 Heapsort Submitted by : Hardik Parikh(hjp0608) Soujanya Soni (sxs3298) Overview of Presentation Heap Definition. Adding a Node. Removing a Node. Array Implementation. Analysis What is Heap? A Heap is a
Heapsort Submitted by : Hardik Parikh(hjp0608) Soujanya Soni (sxs3298) Overview of Presentation Heap Definition. Adding a Node. Removing a Node. Array Implementation. Analysis What is Heap? A Heap is a
Trees 3/19/14. Mammal. Dog Pig Cat
 Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Red-Black Trees (2) Antonio Carzaniga. Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano. April 26, Antonio Carzaniga 1
 Red-lack Trees (2) ntonio arzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano pril 26, 2012 2006 ntonio arzaniga 1 Recap on Red-lack Trees 12 5 18 2 9 15 19 4 13 17 Red-black-tree property 2. 4. 5. 1.
Red-lack Trees (2) ntonio arzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano pril 26, 2012 2006 ntonio arzaniga 1 Recap on Red-lack Trees 12 5 18 2 9 15 19 4 13 17 Red-black-tree property 2. 4. 5. 1.
COMP26120: Algorithms and Imperative Programming. Lecture 1 Trees
 COMP26120: Algorithms and Imperative Programming Lecture 1 Trees Lecture outline n Motivation n Definitions n Ordered trees n Generic methods for tree operations n Tree traversal (preorder, postorder,
COMP26120: Algorithms and Imperative Programming Lecture 1 Trees Lecture outline n Motivation n Definitions n Ordered trees n Generic methods for tree operations n Tree traversal (preorder, postorder,
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Priority Queues & Heaps. Chapter 9
 Priority Queues & Heaps Chapter 9 The Java Collections Framework (Ordered Data Types) Interface Abstract Class Class Iterable Collection Queue Abstract Collection List Abstract Queue Abstract List Priority
Priority Queues & Heaps Chapter 9 The Java Collections Framework (Ordered Data Types) Interface Abstract Class Class Iterable Collection Queue Abstract Collection List Abstract Queue Abstract List Priority
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Topics on the Midterm
 Midterm Review Topics on the Midterm Data Structures & Object-Oriented Design Run-Time Analysis Linear Data Structures The Java Collections Framework Recursion Trees Priority Queues & Heaps Maps, Hash
Midterm Review Topics on the Midterm Data Structures & Object-Oriented Design Run-Time Analysis Linear Data Structures The Java Collections Framework Recursion Trees Priority Queues & Heaps Maps, Hash
A set of nodes (or vertices) with a single starting point
 Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Multiway Search Trees. Multiway-Search Trees (cont d)
 Multiway Search Trees Each internal node v of a multi-way search tree T has at least two children contains d-1 items, where d is the number of children of v an item is of the form (k i,x i ) for 1 i d-1,
Multiway Search Trees Each internal node v of a multi-way search tree T has at least two children contains d-1 items, where d is the number of children of v an item is of the form (k i,x i ) for 1 i d-1,
In a postorder traversal, a node is visited after its descendants Application: compute space used by files in a directory and its subdirectories 9 1
 What is a Tree Trees Stock Fraud Make Money Fast! Winning Lotto / Bank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes ith a parent-child relation
What is a Tree Trees Stock Fraud Make Money Fast! Winning Lotto / Bank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes ith a parent-child relation
Binary Search Trees. EECS 214, Fall 2018
 Binary Search Trees EECS 214, Fall 2018 2 A data structure for dictionaries There are several data structures that we can use to represent dictionaries: A list of keys-value pairs A hash table An array
Binary Search Trees EECS 214, Fall 2018 2 A data structure for dictionaries There are several data structures that we can use to represent dictionaries: A list of keys-value pairs A hash table An array
BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015
 BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due tonight at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must
BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due tonight at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10)
 IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
Binary Search Trees. See Section 11.1 of the text.
 Binary Search Trees See Section 11.1 of the text. Consider the following Binary Search Tree 17 This tree has a nice property: for every node, all of the nodes in its left subtree have values less than
Binary Search Trees See Section 11.1 of the text. Consider the following Binary Search Tree 17 This tree has a nice property: for every node, all of the nodes in its left subtree have values less than
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
CS350: Data Structures AVL Trees
 S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
Splay Trees. Splay Trees 1
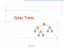 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Best-Case upper limit on the time for insert/delete/find of an element for a BST withnelements?
 S673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees 1 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)>(value stored in left subtree) For each node n, (value stored at node n)
S673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees 1 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)>(value stored in left subtree) For each node n, (value stored at node n)
Motivation Computer Information Systems Storage Retrieval Updates. Binary Search Trees. OrderedStructures. Binary Search Tree
 Binary Search Trees CMPUT 115 - Lecture Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Revised 21-Mar-05 In this lecture we study an important data structure: Binary Search Tree (BST) Motivation
Binary Search Trees CMPUT 115 - Lecture Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Revised 21-Mar-05 In this lecture we study an important data structure: Binary Search Tree (BST) Motivation
If you took your exam home last time, I will still regrade it if you want.
 Some Comments about HW2: 1. You should have used a generic node in your structure one that expected an Object, and not some other type. 2. Main is still too long for some people 3. braces in wrong place,
Some Comments about HW2: 1. You should have used a generic node in your structure one that expected an Object, and not some other type. 2. Main is still too long for some people 3. braces in wrong place,
Why Trees? Alternatives. Want: Ordered arrays. Linked lists. A data structure that has quick insertion/deletion, as well as fast search
 Why Trees? Alternatives Ordered arrays Fast searching (binary search) Slow insertion (must shift) Linked lists Want: Fast insertion Slow searching (must start from head of list) A data structure that has
Why Trees? Alternatives Ordered arrays Fast searching (binary search) Slow insertion (must shift) Linked lists Want: Fast insertion Slow searching (must start from head of list) A data structure that has
CSCI Trees. Mark Redekopp David Kempe
 CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS
 0 1 2 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH,
0 1 2 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH,
