3. Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Device Family
|
|
|
- Ralph Burns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 December 2011 CIII Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family CIII The Cyclone III deice family (Cyclone III and Cyclone III LS deices) features embedded memory structures to address the on-chip memory needs of Altera Cyclone III deice family designs. The embedded memory structure consists of columns of M9K memory blocks that you can configure to proide arious memory functions, such as RAM, shift registers, ROM, and FIFO buffers. This chapter contains the following sections: Memory Modes on page 3 7 Clocking Modes on page 3 14 Design Considerations on page 3 15 Oeriew M9K blocks support the following features: 8,192 memory bits per block (9,216 bits per block including parity) Independent read-enable (rden) and write-enable (wren) signals for each port Packed mode in which the M9K memory block is split into two 4.5 K single-port RAMs Variable port configurations Single-port and simple dual-port modes support for all port widths True dual-port (one read and one write, two reads, or two writes) operation Byte enables for data input masking during writes Two clock-enable control signals for each port (port A and port B) Initialization file to pre-load memory content in RAM and ROM modes 2011 Altera Corporation. All rights resered. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos are trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as trademarks or serice marks are the property of their respectie holders as described at Altera warrants performance of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reseres the right to make changes to any products and serices at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or serice described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are adised to obtain the latest ersion of deice specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or serices. ISO 9001:2008 Registered Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Subscribe
2 3 2 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Oeriew Table 3 1 lists the features supported by the M9K memory Table 3 1. Summary of M9K Memory Features Feature Configurations (depth width) Parity bits Byte enable Packed mode Address clock enable Single-port mode Simple dual-port mode True dual-port mode Embedded shift register mode (1) ROM mode FIFO buffer (1) Simple dual-port mixed width support True dual-port mixed width support (2) Memory initialization file (.mif) Mixed-clock mode Power-up condition Register asynchronous clears Latch asynchronous clears Write or read operation triggering Same-port read-during-write Mixed-port read-during-write M9K Blocks Outputs cleared Read address registers and output registers only Output latches only Write and read: Rising clock edges Outputs set to Old Data or New Data Outputs set to Old Data or Don t Care Notes to Table 3 1: (1) FIFO buffers and embedded shift registers that require external logic elements (LEs) for implementing control logic. (2) Width modes of 32 and 36 are not aailable. f For information about the number of M9K memory blocks for the Cyclone III deice family, refer to the Cyclone III Deice Family Oeriew chapter. Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
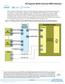
3 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family 3 3 Oeriew Control Signals Figure 3 1. M9K Control Signal Selection The clock-enable control signal controls the clock entering the input and output registers and the entire M9K memory block. This signal disables the clock so that the M9K memory block does not see any clock edges and does not perform any operations. The rden and wren control signals control the read and write operations for each port of M9K memory blocks. You can disable the rden or wren signals independently to sae power wheneer the operation is not required. Figure 3 1 shows how the register clock, clear, and control signals are implemented in the Cyclone III deice family M9K memory block. Dedicated Row LAB Clocks 6 Local Interconnect clock_b clocken_b rden_b wren_b aclr_b addressstall_b byteena_b clock_a clocken_a rden_a wren_a aclr_a addressstall_a byteena_a Parity Bit Support Parity checking for error detection is possible with the parity bit along with internal logic resources. The Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks support a parity bit for each storage byte. You can use this bit as either a parity bit or as an additional data bit. No parity function is actually performed on this bit. December 2011 Altera Corporation Cyclone III Deice Handbook
4 3 4 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Oeriew Byte Enable Support The Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks support byte enables that mask the input data so that only specific bytes of data are written. The unwritten bytes retain the preious written alue. The wren signals, along with the byte-enable (byteena) signals, control the write operations of the RAM block. The default alue of the byteena signals is high (enabled), in which case writing is controlled only by the wren signals. There is no clear port to the byteena registers. M9K blocks support byte enables when the write port has a data width of 16, 18, 32, or 36 bits. Byte enables operate in one-hot manner, with the LSB of the byteena signal corresponding to the least significant byte of the data bus. For example, if byteena = 01 and you are using a RAM block in 18 mode, data[8..0] is enabled and data[17..9] is disabled. Similarly, if byteena = 11, both data[8..0] and data[17..9] are enabled. Byte enables are actie high. Table 3 2 lists the byte selection. Table 3 2. byteena for Cyclone III Deice Family M9K Blocks (1) byteena[3..0] Affected Bytes datain 16 datain 18 datain 32 datain 36 [0] = 1 [7..0] [8..0] [7..0] [8..0] [1] = 1 [15..8] [17..9] [15..8] [17..9] [2] = 1 [23..16] [26..18] [3] = 1 [31..24] [35..27] Note to Table 3 2: (1) Any combination of byte enables is possible. Figure 3 2 shows how the wren and byteena signals control the RAM operations. Figure 3 2. Cyclone III Deice Family byteena Functional Waeform (1) inclock wren rden address an a0 a1 a2 a0 a1 a2 data XXXX ABCD XXXX byteena XX XX contents at a0 FFFF ABFF contents at a1 FFFF FFCD contents at a2 FFFF ABCD q (asynch) doutn ABFF FFCD ABCD ABFF FFCD ABCD Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
5 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family 3 5 Oeriew Figure 3 2. Cyclone III Deice Family byteena Functional Waeform (1) Note to Figure 3 2: (1) For this functional waeform, New Data mode is selected. When a byteena bit is deasserted during a write cycle, the old data in the memory appears in the corresponding data-byte output. When a byteena bit is asserted during a write cycle, the corresponding data-byte output depends on the setting chosen in the Quartus II software. The setting can either be the newly written data or the old data at that location. Packed Mode Support Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks support packed mode. You can implement two single-port memory blocks in a single block under the following conditions: Each of the two independent block sizes is less than or equal to half of the M9K block size. The maximum data width for each independent block is 18 bits wide. Each of the single-port memory blocks is configured in single-clock mode. For more information about packed mode support, refer to Single-Port Mode on page 3 8 and Single-Clock Mode on page Address Clock Enable Support Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks support an actie-low address clock enable, which holds the preious address alue for as long as the addressstall signal is high (addressstall = '1'). When you configure M9K memory blocks in dual-port mode, each port has its own independent address clock enable. Figure 3 3 shows an address clock enable block diagram. The address register output feeds back to its input using a multiplexer. The multiplexer output is selected by the address clock enable (addressstall) signal. Figure 3 3. Cyclone III Deice Family Address Clock Enable Block Diagram address[0] address[0] register address[0] address[n] address[n] register address[n] addressstall clock December 2011 Altera Corporation Cyclone III Deice Handbook
6 3 6 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Oeriew The address clock enable is typically used to improe the effectieness of cache memory applications during a cache-miss. The default alue for the address clock enable signals is low. Figure 3 4 and Figure 3 5 show the address clock enable waeform during read and write cycles, respectiely. Figure 3 4. Cyclone III Deice Family Address Clock Enable During Read Cycle Waeform inclock rdaddress a0 a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 a6 rden addressstall latched address (inside memory) an a0 a1 a4 a5 q (synch) doutn-1 doutn dout0 dout1 dout1 dout1 dout4 q (asynch) doutn dout0 dout1 dout1 dout1 dout4 dout5 Figure 3 5. Cyclone III Deice Family Address Clock Enable During Write Cycle Waeform inclock wraddress a0 a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 a6 wren addressstall data latched address (inside memory) contents at a0 an a0 a1 a4 a5 XX 00 contents at a1 contents at a2 contents at a3 XX XX XX 03 contents at a4 contents at a5 XX 04 XX 05 Mixed-Width Support M9K memory blocks support mixed data widths. When using simple dual-port, true dual-port, or FIFO modes, mixed width support allows you to read and write different data widths to an M9K memory block. For more information about the different widths supported per memory mode, refer to Memory Modes on page 3 7. Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
7 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family 3 7 Memory Modes Asynchronous Clear The Cyclone III deice family supports asynchronous clears for read address registers, output registers, and output latches only. Input registers other than read address registers are not supported. When applied to output registers, the asynchronous clear signal clears the output registers and the effects are immediately seen. If your RAM does not use output registers, you can still clear the RAM outputs using the output latch asynchronous clear feature. 1 Asserting asynchronous clear to the read address register during a read operation might corrupt the memory content. Figure 3 6 shows the functional waeform for the asynchronous clear feature. Figure 3 6. Output Latch Asynchronous Clear Waeform clk aclr aclr at latch q a1 a0 a1 a2 1 You can selectiely enable asynchronous clears per logical memory using the Quartus II RAM MegaWizard Plug-In Manager. f For more information, refer to the Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) User Guide. There are three ways to reset registers in the M9K blocks: Power up the deice Use the aclr signal for output register only Assert the deice-wide reset signal using the DEV_CLRn option Memory Modes Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks allow you to implement fully-synchronous SRAM memory in multiple modes of operation. Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks do not support asynchronous (unregistered) memory inputs. M9K memory blocks support the following modes: Single-port Simple dual-port True dual-port Shift-register ROM FIFO December 2011 Altera Corporation Cyclone III Deice Handbook
8 3 8 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Memory Modes 1 Violating the setup or hold time on the M9K memory block input registers may corrupt memory contents. This applies to both read and write operations. Single-Port Mode Single-port mode supports non-simultaneous read and write operations from a single address. Figure 3 7 shows the single-port memory configuration for Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks. Figure 3 7. Single-Port Memory (1), (2) data[ ] address[ ] wren byteena[] addressstall inclock inclocken rden aclr q[] outclock outclocken Notes to Figure 3 7: (1) You can implement two single-port memory blocks in a single M9K block. (2) For more information, refer to Packed Mode Support on page 3 5. During a write operation, the behaior of the RAM outputs is configurable. If you actiate rden during a write operation, the RAM outputs show either the new data being written or the old data at that address. If you perform a write operation with rden deactiated, the RAM outputs retain the alues they held during the most recent actie rden signal. To choose the desired behaior, set the Read-During-Write option to either New Data or Old Data in the RAM MegaWizard Plug-In Manager in the Quartus II software. For more information about read-during-write mode, refer to Read-During-Write Operations on page The port width configurations for M9K blocks in single-port mode are as follow: Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
9 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family 3 9 Memory Modes Figure 3 8 shows timing waeforms for read and write operations in single-port mode with unregistered outputs. Registering the outputs of the RAM simply delays the q output by one clock cycle. Figure 3 8. Cyclone III Deice Family Single-Port Mode Timing Waeforms clk_a wren_a rden_a address_a a0 a1 data_a A B C D E F q_a (old data) a0(old data) A B a1(old data) D E q_a (new data) A B C D E F Simple Dual-Port Mode Simple dual-port mode supports simultaneous read and write operations to different locations. Figure 3 9 shows the simple dual-port memory configuration. Figure 3 9. Cyclone III Deice Family Simple Dual-Port Memory (1) data[ ] wraddress[ ] wren byteena[] wr_addressstall wrclock wrclocken aclr rdaddress[ ] rden q[ ] rd_addressstall rdclock rdclocken Note to Figure 3 9: (1) Simple dual-port RAM supports input or output clock mode in addition to the read or write clock mode shown. Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks support mixed-width configurations, allowing different read and write port widths. Table 3 3 lists mixed-width configurations. Table 3 3. Cyclone III Deice Family M9K Block Mixed-Width Configurations (Simple Dual-Port Mode) (Part 1 of 2) Write Port Read Port December 2011 Altera Corporation Cyclone III Deice Handbook
10 3 10 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Memory Modes Table 3 3. Cyclone III Deice Family M9K Block Mixed-Width Configurations (Simple Dual-Port Mode) (Part 2 of 2) Read Port Write Port In simple dual-port mode, M9K memory blocks support separate wren and rden signals. You can sae power by keeping the rden signal low (inactie) when not reading. Read-during-write operations to the same address can either output Don t Care data at that location or output Old Data. To choose the desired behaior, set the Read-During-Write option to either Don t Care or Old Data in the RAM MegaWizard Plug-In Manager in the Quartus II software. For more information about this behaior, refer to Read-During-Write Operations on page Figure 3 10 shows the timing waeforms for read and write operations in simple dual-port mode with unregistered outputs. Registering the outputs of the RAM simply delays the q output by one clock cycle. Figure Cyclone III Deice Family Simple Dual-Port Timing Waeforms wrclock wren wraddress data an-1 an a0 a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 a6 din-1 din din4 din5 din6 rdclock rden rdaddress bn b0 b1 b2 b3 q (asynch) doutn-1 doutn dout0 Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
11 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family 3 11 Memory Modes True Dual-Port Mode True dual-port mode supports any combination of two-port operations: two reads, two writes, or one read and one write, at two different clock frequencies. Figure 3 11 shows the Cyclone III deice family true dual-port memory configuration. Figure Cyclone III Deice Family True Dual-Port Memory (1) data_a[ ] address_a[ ] wren_a byteena_a[] addressstall_a clock_a clocken_a rden_a aclr_a q_a[] data_b[ ] address_b[] wren_b byteena_b[] addressstall_b clock_b clocken_b rden_b aclr_b q_b[] Note to Figure 3 11: (1) True dual-port memory supports input or output clock mode in addition to the independent clock mode shown. 1 The widest bit configuration of the M9K blocks in true dual-port mode is bit (18-bit with parity). Table 3 4 lists the possible M9K block mixed-port width configurations. Table 3 4. Cyclone III Deice Family M9K Block Mixed-Width Configurations (True Dual-Port Mode) Read Port Write Port In true dual-port mode, M9K memory blocks support separate wren and rden signals. You can sae power by keeping the rden signal low (inactie) when not reading. Read-during-write operations to the same address can either output New Data at that location or Old Data. To choose the desired behaior, set the Read-During- Write option to either New Data or Old Data in the RAM MegaWizard Plug-In Manager in the Quartus II software. For more information about this behaior, refer to Read-During-Write Operations on page December 2011 Altera Corporation Cyclone III Deice Handbook
12 3 12 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Memory Modes In true dual-port mode, you can access any memory location at any time from either port A or port B. Howeer, when accessing the same memory location from both ports, you must aoid possible write conflicts. When you attempt to write to the same address location from both ports at the same time, a write conflict happens. This results in unknown data being stored to that address location. There is no conflict resolution circuitry built into the Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks. You must handle address conflicts external to the RAM block. Figure 3 12 shows true dual-port timing waeforms for the write operation at port A and read operation at port B. Registering the outputs of the RAM simply delays the q outputs by one clock cycle. Figure Cyclone III Deice Family True Dual-Port Timing Waeforms clk_a wren_a address_a data_a an-1 an a0 a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 a6 din-1 din din4 din5 din6 rden_a q_a (asynch) din-1 din dout0 dout1 dout2 dout3 din4 din5 clk_b wren_b address_b bn b0 b1 b2 b3 rden_b q_b (asynch) doutn-1 doutn dout0 dout1 dout2 Shift Register Mode Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks can implement shift registers for digital signal processing (DSP) applications, such as finite impulse response (FIR) filters, pseudo-random number generators, multi-channel filtering, and auto-correlation and cross-correlation functions. These and other DSP applications require local data storage, traditionally implemented with standard flipflops that quickly exhaust many logic cells for large shift registers. A more efficient alternatie is to use embedded memory as a shift register block, which saes logic cell and routing resources. The size of a (w m n) shift register is determined by the input data width (w), the length of the taps (m), and the number of taps (n), and must be less than or equal to the maximum number of memory bits, which is 9,216 bits. In addition, the size of (w n) must be less than or equal to the maximum width of the block, which is 36 bits. If you need a larger shift register, you can cascade the M9K memory blocks. Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
13 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family 3 13 Memory Modes Figure 3 13 shows the Cyclone III deice family M9K memory block in the shift register mode. Figure Cyclone III Deice Family Shift Register Mode Configuration w m n Shift Register m-bit Shift Register W W m-bit Shift Register W W n Number of Taps m-bit Shift Register W W m-bit Shift Register W W ROM Mode Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks support ROM mode. A.mif initializes the ROM contents of these blocks. The address lines of the ROM are registered. The outputs can be registered or unregistered. The ROM read operation is identical to the read operation in the single-port RAM configuration. FIFO Buffer Mode Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks support single-clock or dual-clock FIFO buffers. Dual clock FIFO buffers are useful when transferring data from one clock domain to another clock domain. Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks do not support simultaneous read and write from an empty FIFO buffer. f For more information about FIFO buffers, refer to the SCFIFO and DCFIFO Megafunctions user guide. December 2011 Altera Corporation Cyclone III Deice Handbook
14 3 14 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Clocking Modes Clocking Modes Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks support the following clocking modes: Independent Input or output Read or write Single-clock When using read or write clock mode, if you perform a simultaneous read or write to the same address location, the output read data is unknown. If you require the output data to be a known alue, use either single-clock mode or I/O clock mode and choose the appropriate read-during-write behaior in the MegaWizard Plug-In Manager. 1 Violating the setup or hold time on the memory block input registers might corrupt the memory contents. This applies to both read and write operations. 1 Asynchronous clears are aailable on read address registers, output registers, and output latches only. Table 3 5 lists the clocking mode ersus memory mode support matrix. Independent Clock Mode I/O Clock Mode Table 3 5. Cyclone III Deice Family Memory Clock Modes Clocking Mode True Dual-Port Mode Simple Dual-Port Mode Single-Port Mode ROM Mode FIFO Mode Independent Input or output Read or write Single-clock Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks can implement independent clock mode for true dual-port memories. In this mode, a separate clock is aailable for each port (port A and port B). clock A controls all registers on the port A side, while clock B controls all registers on the port B side. Each port also supports independent clock enables for port A and B registers. Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks can implement input or output clock mode for FIFO, single-port, true, and simple dual-port memories. In this mode, an input clock controls all input registers to the memory block, including data, address, byteena, wren, and rden registers. An output clock controls the data-output registers. Each memory block port also supports independent clock enables for input and output registers. Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
15 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family 3 15 Design Considerations Read or Write Clock Mode Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks can implement read or write clock mode for FIFO and simple dual-port memories. In this mode, a write clock controls the data inputs, write address, and wren registers. Similarly, a read clock controls the data outputs, read address, and rden registers. M9K memory blocks support independent clock enables for both the read and write clocks. When using read or write mode, if you perform a simultaneous read or write to the same address location, the output read data is unknown. If you require the output data to be a known alue, use either single-clock mode, input clock mode, or output clock mode and choose the appropriate read-during-write behaior in the MegaWizard Plug-In Manager. Single-Clock Mode Design Considerations Cyclone III deice family M9K memory blocks can implement single-clock mode for FIFO, ROM, true dual-port, simple dual-port, and single-port memories. In this mode, you can control all registers of the M9K memory block with a single clock together with clock enable. This section describes designing with M9K memory blocks. Read-During-Write Operations Same-Port Read-During-Write Mode on page 3 16 and Mixed-Port Read-During- Write Mode on page 3 16 describe the functionality of the arious RAM configurations when reading from an address during a write operation at that same address. There are two read-during-write data flows: same-port and mixed-port. Figure 3 14 shows the difference between these flows. Figure Cyclone III Deice Family Read-During-Write Data Flow write_a Port A data in Port B data in write_b Mixed-port data flow Same-port data flow read_a Port A data out Port B data out read_b December 2011 Altera Corporation Cyclone III Deice Handbook
16 3 16 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Design Considerations Same-Port Read-During-Write Mode This mode applies to a single-port RAM or the same port of a true dual-port RAM. In the same port read-during-write mode, there are two output choices: New Data mode (or flow-through) and Old Data mode. In New Data mode, new data is aailable on the rising edge of the same clock cycle on which it was written. In Old Data mode, the RAM outputs reflect the old data at that address before the write operation proceeds. When using New Data mode together with byteena, you can control the output of the RAM. When byteena is high, the data written into the memory passes to the output (flow-through). When byteena is low, the masked-off data is not written into the memory and the old data in the memory appears on the outputs. Therefore, the output can be a combination of new and old data determined by byteena. Figure 3 15 and Figure 3 16 show sample functional waeforms of same port read-during-write behaior with both New Data and Old Data modes, respectiely. Figure Same Port Read-During Write: New Data Mode clk_a wren_a rden_a address_a a0 a1 data_a A B C D E F q_a (asynch) A B C D E F Figure Same Port Read-During-Write: Old Data Mode clk_a wren_a rden_a address_a a0 a1 data_a A B C D E F q_a (asynch) a0(old data) A B a1(old data) D E Mixed-Port Read-During-Write Mode This mode applies to a RAM in simple or true dual-port mode, which has one port reading and the other port writing to the same address location with the same clock. Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
17 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family 3 17 Design Considerations In this mode, you also hae two output choices: Old Data mode or Don't Care mode. In Old Data mode, a read-during-write operation to different ports causes the RAM outputs to reflect the old data at that address location. In Don't Care mode, the same operation results in a Don't Care or unknown alue on the RAM outputs. f For more information about how to implement the desired behaior, refer to the Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) User Guide. Figure 3 17 shows a sample functional waeform of mixed port read-during-write behaior for the Old Data mode. In Don't Care mode, the old data is replaced with Don't Care. Figure Mixed Port Read-During-Write: Old Data Mode clk_a&b wren_a address_a a b data_a A B C D E F rden_b address_b a b q_b (asynch) a (old data) A B b (old data) D E 1 For mixed-port read-during-write operation with dual clocks, the relationship between the clocks determines the output behaior of the memory. If you use the same clock for the two clocks, the output is the old data from the address location. Howeer, if you use different clocks, the output is unknown during the mixed-port read-during-write operation. This unknown alue may be the old or new data at the address location, depending on whether the read happens before or after the write. Conflict Resolution When you are using M9K memory blocks in true dual-port mode, it is possible to attempt two write operations to the same memory location (address). Because there is no conflict resolution circuitry built into M9K memory blocks, this results in unknown data being written to that location. Therefore, you must implement conflict-resolution logic external to the M9K memory block. December 2011 Altera Corporation Cyclone III Deice Handbook
18 3 18 Chapter 3: Memory Blocks in the Cyclone III Deice Family Document Reision History Power-Up Conditions and Memory Initialization The M9K memory block outputs of the Cyclone III deice family power up to zero (cleared) regardless of whether the output registers are used or bypassed. All M9K memory blocks support initialization using a.mif. You can create.mifs in the Quartus II software and specify their use using the RAM MegaWizard Plug-In Manager when instantiating memory in your design. Een if memory is pre-initialized (for example, using a.mif), it still powers up with its outputs cleared. Only the subsequent read after power up outputs the pre-initialized alues. f For more information about.mifs, refer to the Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) User Guide and the Quartus II Handbook. Power Management The M9K memory block clock enables of the Cyclone III deice family allow you to control clocking of each M9K memory block to reduce AC power consumption. Use the rden signal to ensure that read operations only occur when necessary. If your design does not require read-during-write, reduce power consumption by deasserting the rden signal during write operations, or any period when there are no memory operations. The Quartus II software automatically powers down any unused M9K memory blocks to sae static power. Document Reision History Table 3 6. Document Reision History Table 3 6 lists the reision history for this document. Date Version Changes December Minor text edits. December Minor changes to the text. July Made minor correction to the part number. June Updated to include Cyclone III LS information Updated chapter part number. Updated Introduction on page 3 1. Updated Oeriew on page 3 1. Updated Table 3 1 on page 3 2. Updated Control Signals on page 3 3. Updated Memory Modes on page 3 8. Updated Simple Dual-Port Mode on page Updated Read or Write Clock Mode on page October Updated chapter to new template. May Reised the maximum performance of the M9K blocks to 315 MHz in Introduction and Oeriew sections, and in Table 3-1. Updated Address Clock Enable Support section. July Added chapter TOC and Referenced Documents section. March Initial release. Cyclone III Deice Handbook December 2011 Altera Corporation
3. Memory Blocks in Cyclone III Devices
 3. Memory Blocks in Cyclone III Deices CIII51003-2.0 Introduction Oeriew Cyclone III family deices (Cyclone III and Cyclone III LS deices) feature embedded memory structures to address the on-chip memory
3. Memory Blocks in Cyclone III Deices CIII51003-2.0 Introduction Oeriew Cyclone III family deices (Cyclone III and Cyclone III LS deices) feature embedded memory structures to address the on-chip memory
MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide
 MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide Subscribe UG- M10MEMORY 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 Embedded Memory Overview... 1-1 MAX 10 Embedded Memory Architecture
MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide Subscribe UG- M10MEMORY 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 Embedded Memory Overview... 1-1 MAX 10 Embedded Memory Architecture
MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide
 MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide UG-M10MEMORY 2017.02.21 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 MAX 10 Embedded Memory Overview... 4 2 MAX 10 Embedded Memory Architecture and Features... 5 2.1 MAX
MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide UG-M10MEMORY 2017.02.21 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 MAX 10 Embedded Memory Overview... 4 2 MAX 10 Embedded Memory Architecture and Features... 5 2.1 MAX
Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide
 Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory Overview...4 2. Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory Architecture
Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory Overview...4 2. Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory Architecture
2. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices
 2. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices SII52002-4.5 Introduction Stratix II and Stratix II GX devices feature the TriMatrix memory structure, consisting of three sizes
2. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices SII52002-4.5 Introduction Stratix II and Stratix II GX devices feature the TriMatrix memory structure, consisting of three sizes
Embedded Memory Blocks in Arria V Devices
 Embedded Memory Blocks in Arria V Devices 2 AV-52002 Subscribe The embedded memory blocks in the devices are flexible and designed to provide an optimal amount of small- and large-sized memory arrays to
Embedded Memory Blocks in Arria V Devices 2 AV-52002 Subscribe The embedded memory blocks in the devices are flexible and designed to provide an optimal amount of small- and large-sized memory arrays to
Intel Cyclone 10 LP Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook
 Intel Cyclone 10 LP Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Logic Elements and Logic Array Blocks in Intel Cyclone 10 LP Devices...
Intel Cyclone 10 LP Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Logic Elements and Logic Array Blocks in Intel Cyclone 10 LP Devices...
On-Chip Memory Implementations
 On-Chip Memory Implementations Using Cyclone Memory Blocks March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 252 Introduction Cyclone devices feature embedded memory blocks that can be easily configured to support
On-Chip Memory Implementations Using Cyclone Memory Blocks March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 252 Introduction Cyclone devices feature embedded memory blocks that can be easily configured to support
Using TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks
 Using TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in Stratix & Stratix GX evices November 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 203 Introduction TriMatrix Memory Stratix and Stratix GX devices feature the TriMatrix memory
Using TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in Stratix & Stratix GX evices November 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 203 Introduction TriMatrix Memory Stratix and Stratix GX devices feature the TriMatrix memory
Embedded Memory (RAM: 1-PORT, RAM: 2-PORT, ROM: 1-PORT, and ROM: 2-PORT) User Guide
 Embedded Memory (RAM: 1-PORT, RAM: 2-PORT, ROM: 1-PORT, and ROM: 2-PORT) User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents
Embedded Memory (RAM: 1-PORT, RAM: 2-PORT, ROM: 1-PORT, and ROM: 2-PORT) User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents
4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices
 January 2011 HIV51004-2.2 4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices HIV51004-2.2 This chapter describes TriMatrix memory blocks, modes, features, and design considerations in HardCopy
January 2011 HIV51004-2.2 4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices HIV51004-2.2 This chapter describes TriMatrix memory blocks, modes, features, and design considerations in HardCopy
Intel Stratix 10 Embedded Memory User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 Embedded Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 Embedded Memory Overview...
Intel Stratix 10 Embedded Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 Embedded Memory Overview...
Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook
 Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook Subscribe A10-HANDBOOK 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules in Arria 10 Devices
Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook Subscribe A10-HANDBOOK 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules in Arria 10 Devices
Intel Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook
 Intel Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules in Intel Arria
Intel Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules in Intel Arria
Stratix V Device Handbook
 Stratix V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration Subscribe SV5V1 2013.06.21 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Stratix V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device
Stratix V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration Subscribe SV5V1 2013.06.21 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Stratix V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device
Cyclone V Device Handbook
 Cyclone V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration Subscribe CV-5V2 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Cyclone V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces
Cyclone V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration Subscribe CV-5V2 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Cyclone V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces
Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet
 Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet This section provides designers with the data sheet specifications for Cyclone devices. The chapters contain feature definitions of the internal architecture,
Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet This section provides designers with the data sheet specifications for Cyclone devices. The chapters contain feature definitions of the internal architecture,
Arria V Device Handbook
 Arria V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration Subscribe AV-5V2 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Arria V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and
Arria V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration Subscribe AV-5V2 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Arria V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and
Designing with ESBs in APEX II Devices
 Designing with ESBs in APEX II Devices March 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 179 Introduction In APEX TM II devices, enhanced embedded system blocks (ESBs) support memory structures, such as single-port
Designing with ESBs in APEX II Devices March 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 179 Introduction In APEX TM II devices, enhanced embedded system blocks (ESBs) support memory structures, such as single-port
Stratix V Device Handbook
 Stratix V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration Subscribe SV-5V1 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Stratix V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces
Stratix V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration Subscribe SV-5V1 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Stratix V Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces
Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet
 Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet This section provides designers with the data sheet specifications for Cyclone devices. The chapters contain feature definitions of the internal architecture,
Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet This section provides designers with the data sheet specifications for Cyclone devices. The chapters contain feature definitions of the internal architecture,
2. Stratix II Architecture
 2. Stratix II Architecture SII51002-4.3 Functional Description Stratix II devices contain a two-dimensional row- and column-based architecture to implement custom logic. A series of column and row interconnects
2. Stratix II Architecture SII51002-4.3 Functional Description Stratix II devices contain a two-dimensional row- and column-based architecture to implement custom logic. A series of column and row interconnects
Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet
 Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet This section provides designers with the data sheet specifications for Cyclone devices. The chapters contain feature definitions of the internal architecture,
Section I. Cyclone FPGA Family Data Sheet This section provides designers with the data sheet specifications for Cyclone devices. The chapters contain feature definitions of the internal architecture,
1. Device Interfaces and Integration Basics for Cyclone V Devices
 November 2011 CV-55001-1.1 1. Device Interfaces and Integration Basics for Cyclone V Devices CV-55001-1.1 This chapter contains basic information of specific feature in the Cyclone V device interfaces
November 2011 CV-55001-1.1 1. Device Interfaces and Integration Basics for Cyclone V Devices CV-55001-1.1 This chapter contains basic information of specific feature in the Cyclone V device interfaces
Using DCFIFO for Data Transfer between Asynchronous Clock Domains
 Using DCFIFO for Data Transfer between Asynchronous Clock Domains, version 1.0 Application Note 473 Introduction In the design world, there are very few designs with a single clock domain. With increasingly
Using DCFIFO for Data Transfer between Asynchronous Clock Domains, version 1.0 Application Note 473 Introduction In the design world, there are very few designs with a single clock domain. With increasingly
Intel Stratix 10 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Stratix 10 LAB and Overview... 3 2 HyperFlex
Intel Stratix 10 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Stratix 10 LAB and Overview... 3 2 HyperFlex
Stratix. Introduction. Features... Programmable Logic Device Family. Preliminary Information
 Stratix Programmable Logic Device Family February 2002, ver. 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction Preliminary Information The Stratix family of programmable logic devices (PLDs) is based on a 1.5-V, 0.13-µm, all-layer
Stratix Programmable Logic Device Family February 2002, ver. 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction Preliminary Information The Stratix family of programmable logic devices (PLDs) is based on a 1.5-V, 0.13-µm, all-layer
Stratix. Introduction. Features... 10,570 to 114,140 LEs; see Table 1. FPGA Family. Preliminary Information
 Stratix FPGA Family December 2002, ver. 3.0 Data Sheet Introduction Preliminary Information The Stratix TM family of FPGAs is based on a 1.5-V, 0.13-µm, all-layer copper SRAM process, with densities up
Stratix FPGA Family December 2002, ver. 3.0 Data Sheet Introduction Preliminary Information The Stratix TM family of FPGAs is based on a 1.5-V, 0.13-µm, all-layer copper SRAM process, with densities up
ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction User Guide
 ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01089-2.2 Feedback Subscribe 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE,
ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01089-2.2 Feedback Subscribe 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE,
10. Introduction to UniPHY IP
 10. Introduction to Uni IP November 2012 EMI_RM_008-2.1 EMI_RM_008-2.1 The Altera,, and LP SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, RLDRAM II controller with Uni, and RLDRAM
10. Introduction to Uni IP November 2012 EMI_RM_008-2.1 EMI_RM_008-2.1 The Altera,, and LP SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, RLDRAM II controller with Uni, and RLDRAM
8. Introduction to UniPHY IP
 8. Introduction to Uni IP November 2011 EMI_RM_008-1.1 EMI_RM_008-1.1 The Altera and SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, and RLDRAM II controller with Uni provide
8. Introduction to Uni IP November 2011 EMI_RM_008-1.1 EMI_RM_008-1.1 The Altera and SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, and RLDRAM II controller with Uni provide
Chapter 2. Cyclone II Architecture
 Chapter 2. Cyclone II Architecture CII51002-1.0 Functional Description Cyclone II devices contain a two-dimensional row- and column-based architecture to implement custom logic. Column and row interconnects
Chapter 2. Cyclone II Architecture CII51002-1.0 Functional Description Cyclone II devices contain a two-dimensional row- and column-based architecture to implement custom logic. Column and row interconnects
7. External Memory Interfaces in Cyclone IV Devices
 March 2016 CYIV-51007-2.6 7. External Memory Interaces in Cyclone IV Devices CYIV-51007-2.6 This chapter describes the memory interace pin support and the external memory interace eatures o Cyclone IV
March 2016 CYIV-51007-2.6 7. External Memory Interaces in Cyclone IV Devices CYIV-51007-2.6 This chapter describes the memory interace pin support and the external memory interace eatures o Cyclone IV
16. Design Debugging Using In-System Sources and Probes
 June 2012 QII53021-12.0.0 16. Design Debugging Using In-System Sources and Probes QII53021-12.0.0 This chapter provides detailed instructions about how to use the In-System Sources and Probes Editor and
June 2012 QII53021-12.0.0 16. Design Debugging Using In-System Sources and Probes QII53021-12.0.0 This chapter provides detailed instructions about how to use the In-System Sources and Probes Editor and
11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices
 11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices February 2011 SIV51011-3.2 SIV51011-3.2 This chapter describes how to use the error detection cyclical redundancy check (CRC) feature when a Stratix IV device is
11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices February 2011 SIV51011-3.2 SIV51011-3.2 This chapter describes how to use the error detection cyclical redundancy check (CRC) feature when a Stratix IV device is
Nios II Performance Benchmarks
 Subscribe Performance Benchmarks Overview This datasheet lists the performance and logic element (LE) usage for the Nios II Classic and Nios II Gen2 soft processor, and peripherals. Nios II is configurable
Subscribe Performance Benchmarks Overview This datasheet lists the performance and logic element (LE) usage for the Nios II Classic and Nios II Gen2 soft processor, and peripherals. Nios II is configurable
Section I. Cyclone II Device Family Data Sheet
 Section I. Cyclone II Device Family Data Sheet This section provides provides information for board layout designers to successfully layout their boards for Cyclone II devices. It contains the required
Section I. Cyclone II Device Family Data Sheet This section provides provides information for board layout designers to successfully layout their boards for Cyclone II devices. It contains the required
Phase-Locked Loop Reconfiguration (ALTPLL_RECONFIG) Megafunction
 Phase-Locked Loop Reconfiguration (ALTPLL_RECONFIG) Megafunction UG-032405-6.0 User Guide This user guide describes the features and behavior of the ALTPLL_RECONFIG megafunction that you can configure
Phase-Locked Loop Reconfiguration (ALTPLL_RECONFIG) Megafunction UG-032405-6.0 User Guide This user guide describes the features and behavior of the ALTPLL_RECONFIG megafunction that you can configure
9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices
 9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices May 2013 CYIV-51009-1.3 CYIV-51009-1.3 This chapter describes the cyclical redundancy check (CRC) error detection feature in user mode and how to recover from soft
9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices May 2013 CYIV-51009-1.3 CYIV-51009-1.3 This chapter describes the cyclical redundancy check (CRC) error detection feature in user mode and how to recover from soft
System Debugging Tools Overview
 9 QII53027 Subscribe About Altera System Debugging Tools The Altera system debugging tools help you verify your FPGA designs. As your product requirements continue to increase in complexity, the time you
9 QII53027 Subscribe About Altera System Debugging Tools The Altera system debugging tools help you verify your FPGA designs. As your product requirements continue to increase in complexity, the time you
Implementing 9.8G CPRI in Arria V GT and ST FPGAs
 03..06 AN 686 Subscribe This application note describes the implementation of 9.8304 Gbps Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) using the Arria V GT and Arria V ST FPGA transceivers. The hard physical coding
03..06 AN 686 Subscribe This application note describes the implementation of 9.8304 Gbps Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) using the Arria V GT and Arria V ST FPGA transceivers. The hard physical coding
Cyclone II FPGA Family
 ES-030405-1.3 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Cyclone II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the issues.
ES-030405-1.3 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Cyclone II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the issues.
Intel Arria 10 Native Floating- Point DSP Intel FPGA IP User Guide
 Intel Arria 10 Native Floating- Point DSP Intel FPGA IP User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Parameterizing the Intel Arria 10 Native Floating-Point
Intel Arria 10 Native Floating- Point DSP Intel FPGA IP User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Parameterizing the Intel Arria 10 Native Floating-Point
3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices
 July 2014 SIV53004-2014.07.09 3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices SIV53004-2014.07.09 This document describes how to define and instantiate the ALTGX_RECONFIG IP core using the
July 2014 SIV53004-2014.07.09 3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices SIV53004-2014.07.09 This document describes how to define and instantiate the ALTGX_RECONFIG IP core using the
MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
 MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-M10UFM 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 User Flash Memory
MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-M10UFM 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 User Flash Memory
Simulating the ASMI Block in Your Design
 2015.08.03 AN-720 Subscribe Supported Devices Overview You can simulate the ASMI block in your design for the following devices: Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10 Cyclone V Stratix V In the Quartus II software,
2015.08.03 AN-720 Subscribe Supported Devices Overview You can simulate the ASMI block in your design for the following devices: Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10 Cyclone V Stratix V In the Quartus II software,
PCI Express Multi-Channel DMA Interface
 2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
9. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in Stratix IV Devices
 February 2011 SIV51009-3.2 9. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in Stratix IV Devices SIV51009-3.2 This chapter describes hot-socketing specifications, power-on reset (POR) requirements, and their implementation
February 2011 SIV51009-3.2 9. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in Stratix IV Devices SIV51009-3.2 This chapter describes hot-socketing specifications, power-on reset (POR) requirements, and their implementation
Implementing Double Data Rate I/O Signaling in Stratix & Stratix GX Devices. Introduction. DDR I/O Elements. Input Configuration
 Implementing Double Data Rate I/O Signaling in Stratix & Stratix GX Devices November 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 212 Introduction Typical I/O architectures transmit a single data word on each positive
Implementing Double Data Rate I/O Signaling in Stratix & Stratix GX Devices November 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 212 Introduction Typical I/O architectures transmit a single data word on each positive
AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices
 AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices AN-558-3.8 Application Note This application note describes how to use the dynamic reconfiguration feature and why you may want use this
AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices AN-558-3.8 Application Note This application note describes how to use the dynamic reconfiguration feature and why you may want use this
9. Functional Description Example Designs
 November 2012 EMI_RM_007-1.3 9. Functional Description Example Designs EMI_RM_007-1.3 This chapter describes the example designs and the traffic generator. Two independent example designs are created during
November 2012 EMI_RM_007-1.3 9. Functional Description Example Designs EMI_RM_007-1.3 This chapter describes the example designs and the traffic generator. Two independent example designs are created during
SERDES Transmitter/Receiver (ALTLVDS) Megafunction User Guide
 SERDES Transmitter/Receiver (ALTLVDS) Megafunction User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version: 8.1 Document Version: 4.0 Document Date: November 2008 UG-MF9504-4.0
SERDES Transmitter/Receiver (ALTLVDS) Megafunction User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version: 8.1 Document Version: 4.0 Document Date: November 2008 UG-MF9504-4.0
Phase-Locked Loops (ALTPLL) Megafunction User Guide
 Phase-Locked Loops (ALTPLL) Megafunction User Guide 101 Innoation Drie San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Document Version: 7.0 Document Date: December 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera Corporation. All rights
Phase-Locked Loops (ALTPLL) Megafunction User Guide 101 Innoation Drie San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Document Version: 7.0 Document Date: December 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera Corporation. All rights
AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices
 AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices AN-558-3.1 Application Note This application note describes how to use the dynamic reconfiguration feature and why you may want use this
AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices AN-558-3.1 Application Note This application note describes how to use the dynamic reconfiguration feature and why you may want use this
Recommended Protocol Configurations for Stratix IV GX FPGAs
 Recommended Protocol s for Stratix IV GX FPGAs AN-577-3.0 Application Note The architecture of the Altera Stratix IV GX FPGA is designed to accommodate the widest range of protocol standards spread over
Recommended Protocol s for Stratix IV GX FPGAs AN-577-3.0 Application Note The architecture of the Altera Stratix IV GX FPGA is designed to accommodate the widest range of protocol standards spread over
4. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in MAX V Devices
 December 2010 MV51004-1.0 4. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in MAX V Devices MV51004-1.0 This chapter provides information about hot-socketing specifications, power-on reset (POR) requirements, and their
December 2010 MV51004-1.0 4. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in MAX V Devices MV51004-1.0 This chapter provides information about hot-socketing specifications, power-on reset (POR) requirements, and their
8. Migrating Stratix II Device Resources to HardCopy II Devices
 8. Migrating Stratix II Device Resources to HardCopy II Devices H51024-1.3 Introduction Altera HardCopy II devices and Stratix II devices are both manufactured on a 1.2-V, 90-nm process technology and
8. Migrating Stratix II Device Resources to HardCopy II Devices H51024-1.3 Introduction Altera HardCopy II devices and Stratix II devices are both manufactured on a 1.2-V, 90-nm process technology and
Low Power Design Techniques
 Low Power Design Techniques August 2005, ver 1.0 Application Note 401 Introduction This application note provides low-power logic design techniques for Stratix II and Cyclone II devices. These devices
Low Power Design Techniques August 2005, ver 1.0 Application Note 401 Introduction This application note provides low-power logic design techniques for Stratix II and Cyclone II devices. These devices
OTU2 I.9 FEC IP Core (IP-OTU2EFECI9) Data Sheet
 OTU2 I.9 FEC IP Core (IP-OTU2EFECI9) Data Sheet Revision 0.02 Release Date 2015-02-11 Document number . All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and ARRIA words
OTU2 I.9 FEC IP Core (IP-OTU2EFECI9) Data Sheet Revision 0.02 Release Date 2015-02-11 Document number . All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and ARRIA words
Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide
 Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide... 3
Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide... 3
Digital Systems Design
 Digital Systems Design Memory Implementation on Altera CYCLONE V Devices Electrical & Computer Engineering Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 6-1 Embedded Memory 10 Kb M10K blocks blocks of dedicated memory resources
Digital Systems Design Memory Implementation on Altera CYCLONE V Devices Electrical & Computer Engineering Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 6-1 Embedded Memory 10 Kb M10K blocks blocks of dedicated memory resources
5. Using MAX V Devices in Multi-Voltage Systems
 June 2017 MV51005-2017.06.16 5. Using MAX V Devices in Multi-Voltage Systems MV51005-2017.06.16 This chapter describes how to implement Altera devices in multi-voltage systems without damaging the device
June 2017 MV51005-2017.06.16 5. Using MAX V Devices in Multi-Voltage Systems MV51005-2017.06.16 This chapter describes how to implement Altera devices in multi-voltage systems without damaging the device
AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current
 AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current January 2009 AN-547-10 Introduction To save power, the MAX II CPLD can be completely powered down into hibernation mode
AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current January 2009 AN-547-10 Introduction To save power, the MAX II CPLD can be completely powered down into hibernation mode
7. External Memory Interfaces in Stratix IV Devices
 February 2011 SIV51007-3.2 7. External Memory Interfaces in Stratix IV evices SIV51007-3.2 This chapter describes external memory interfaces available with the Stratix IV device family and that family
February 2011 SIV51007-3.2 7. External Memory Interfaces in Stratix IV evices SIV51007-3.2 This chapter describes external memory interfaces available with the Stratix IV device family and that family
EFEC20 IP Core. Features
 EFEC20 IP Core DS-1034-1.2 Data Sheet The Altera 20% Enhanced Forward Error Correction (EFEC20) IP core includes a highperformance encoder and decoder for Optical Transport Network (OTN) FEC applications.
EFEC20 IP Core DS-1034-1.2 Data Sheet The Altera 20% Enhanced Forward Error Correction (EFEC20) IP core includes a highperformance encoder and decoder for Optical Transport Network (OTN) FEC applications.
Using Flexible-LVDS I/O Pins in
 Using Flexible-LVDS I/O Pins in APEX II Devices August 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 167 Introduction Recent expansion in the telecommunications market and growth in Internet use have created a demand
Using Flexible-LVDS I/O Pins in APEX II Devices August 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 167 Introduction Recent expansion in the telecommunications market and growth in Internet use have created a demand
Double Data Rate I/O (ALTDDIO_IN, ALTDDIO_OUT, and ALTDDIO_BIDIR) IP Cores User Guide
 2015.01.23 Double Data Rate I/O (ALTDDIO_IN, ALTDDIO_OUT, and ALTDDIO_BIDIR) IP Cores User Guide UG-DDRMGAFCTN Subscribe The Altera DDR I/O megafunction IP cores configure the DDR I/O registers in APEX
2015.01.23 Double Data Rate I/O (ALTDDIO_IN, ALTDDIO_OUT, and ALTDDIO_BIDIR) IP Cores User Guide UG-DDRMGAFCTN Subscribe The Altera DDR I/O megafunction IP cores configure the DDR I/O registers in APEX
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler May 2006, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler May 2006, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1.
Feature EPF10K30E EPF10K50E EPF10K50S
 FLEX 10KE Embedded Programmable Logic Family August 1999, ver. 2.02 Data Sheet Features... Embedded programmable logic devices (PLDs), providing System-on-a-Programmable-Chip TM integration in a single
FLEX 10KE Embedded Programmable Logic Family August 1999, ver. 2.02 Data Sheet Features... Embedded programmable logic devices (PLDs), providing System-on-a-Programmable-Chip TM integration in a single
Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design
 Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design August 22, ver. 2.3 Application Note 173 Introduction The Excalibur devices are excellent system development platforms, offering flexibility, performance, and
Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design August 22, ver. 2.3 Application Note 173 Introduction The Excalibur devices are excellent system development platforms, offering flexibility, performance, and
Stratix II FPGA Family
 October 2008, ver. 2.1 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Stratix II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the
October 2008, ver. 2.1 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Stratix II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the
Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
 Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory
Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory
White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices
 Introduction White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices One of the challenges faced by engineers designing communications equipment is that memory devices
Introduction White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices One of the challenges faced by engineers designing communications equipment is that memory devices
PowerPlay Early Power Estimator User Guide
 PowerPlay Early Power Estimator 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01070-7.1 Feedback Subscribe 2012 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX,
PowerPlay Early Power Estimator 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01070-7.1 Feedback Subscribe 2012 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX,
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler August 2007, Compiler Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler August 2007, Compiler Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version
Using Flexible-LVDS Circuitry in Mercury Devices
 Using Flexible-LVDS Circuitry in Mercury Devices November 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 186 Introduction With the ever increasing demand for high bandwidth and low power consumption in the telecommunications
Using Flexible-LVDS Circuitry in Mercury Devices November 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 186 Introduction With the ever increasing demand for high bandwidth and low power consumption in the telecommunications
SameFrame Pin-Out Design for FineLine BGA Packages
 SameFrame Pin-Out Design for Packages June 1999, er. 1 Application Note 90 Introduction A key adantage of designing with programmable logic is the flexibility which allows designers to quickly modify or
SameFrame Pin-Out Design for Packages June 1999, er. 1 Application Note 90 Introduction A key adantage of designing with programmable logic is the flexibility which allows designers to quickly modify or
Error Correction Code (ALTECC_ENCODER and ALTECC_DECODER) Megafunctions User Guide
 Error Correction Code (ALTECC_ENCODER and ALTECC_DECODER) Megafunctions User Guide 11 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version 8. Document Version: 2. Document Date: June 28
Error Correction Code (ALTECC_ENCODER and ALTECC_DECODER) Megafunctions User Guide 11 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version 8. Document Version: 2. Document Date: June 28
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. Section I. Stratix II Device Family Data Sheet This section provides the
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. Section I. Stratix II Device Family Data Sheet This section provides the
LVDS SERDES Transmitter / Receiver (ALTLVDS_TX and ALTLVDS_RX) Megafunction User Guide
 LVDS SERDES Transmitter / Receiver (ALTLVDS_TX and ALTLVDS_RX) Megafunction 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-MF9504-9.1 Document last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite version:
LVDS SERDES Transmitter / Receiver (ALTLVDS_TX and ALTLVDS_RX) Megafunction 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-MF9504-9.1 Document last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite version:
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler march 2007, Compiler Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 7.0.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler march 2007, Compiler Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 7.0.
Section III. Transport and Communication
 Section III. Transport and Communication This section describes communication and transport peripherals provided for SOPC Builder systems. This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 16, SPI
Section III. Transport and Communication This section describes communication and transport peripherals provided for SOPC Builder systems. This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 16, SPI
Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide
 Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Generic
Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Generic
Errata Sheet for Cyclone IV Devices
 Errata Sheet for Cyclone IV Devices ES-01027-2.3 Errata Sheet This errata sheet provides updated information on known device issues affecting Cyclone IV devices. Table 1 lists specific Cyclone IV issues,
Errata Sheet for Cyclone IV Devices ES-01027-2.3 Errata Sheet This errata sheet provides updated information on known device issues affecting Cyclone IV devices. Table 1 lists specific Cyclone IV issues,
Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide
 2015.05.04 Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide UG-01155 Subscribe The Altera IOPLL megafunction IP core allows you to configure the settings of Arria 10 I/O PLL. Altera IOPLL
2015.05.04 Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide UG-01155 Subscribe The Altera IOPLL megafunction IP core allows you to configure the settings of Arria 10 I/O PLL. Altera IOPLL
ALTDQ_DQS2 IP Core User Guide
 2017.05.08 UG-01089 Subscribe The Altera ALTDQ_DQS2 megafunction IP core controls the double data rate (DDR) I/O elements (IOEs) for the data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS) signals in Arria V, Cyclone V, and
2017.05.08 UG-01089 Subscribe The Altera ALTDQ_DQS2 megafunction IP core controls the double data rate (DDR) I/O elements (IOEs) for the data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS) signals in Arria V, Cyclone V, and
OTU2 I.4 FEC IP Core (IP-OTU2EFECI4Z) Data Sheet
 OTU2 I.4 FEC IP Core (IP-OTU2EFECI4Z) Data Sheet Revision 0.08 Release Date 2014-03-29 Document number TD0307 . All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX
OTU2 I.4 FEC IP Core (IP-OTU2EFECI4Z) Data Sheet Revision 0.08 Release Date 2014-03-29 Document number TD0307 . All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX
Intel Xeon with FPGA IP Asynchronous Core Cache Interface (CCI-P) Shim
 Intel Xeon with FPGA IP Asynchronous Core Cache Interface (CCI-P) Shim AN-828 2017.10.02 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Conventions...3 1.2 Glossary...3 1.3 Introduction...3 1.4 Design...
Intel Xeon with FPGA IP Asynchronous Core Cache Interface (CCI-P) Shim AN-828 2017.10.02 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Conventions...3 1.2 Glossary...3 1.3 Introduction...3 1.4 Design...
White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface
 White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface Introduction Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) is a bidirectional two-wire interface protocol, requiring only two bus lines; a serial data/address
White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface Introduction Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) is a bidirectional two-wire interface protocol, requiring only two bus lines; a serial data/address
Technical Note TN1201
 for MachXO2 Devices July 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1201 This technical note discusses the memory usage for the Lattice MachXO2 PLD family. It is intended to be used by design engineers as a guide
for MachXO2 Devices July 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1201 This technical note discusses the memory usage for the Lattice MachXO2 PLD family. It is intended to be used by design engineers as a guide
Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet
 2016.05.30 CF52012 Subscribe This datasheet describes quad-serial configuration (EPCQ) devices. EPCQ is an in-system programmable NOR flash memory. Supported Devices Table 1: Supported Altera EPCQ Devices
2016.05.30 CF52012 Subscribe This datasheet describes quad-serial configuration (EPCQ) devices. EPCQ is an in-system programmable NOR flash memory. Supported Devices Table 1: Supported Altera EPCQ Devices
RAM-Based Shift Register (ALTSHIFT_TAPS) IP Core User Guide
 RAM-Based Shift Register (ALTSHIFT_TAPS) IP Core User Guide RAM-Based Shift Register (ALTSHIFT_TAPS) IP Core User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01009-3.0 Document last
RAM-Based Shift Register (ALTSHIFT_TAPS) IP Core User Guide RAM-Based Shift Register (ALTSHIFT_TAPS) IP Core User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01009-3.0 Document last
Introduction. Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Memory. Converting Memory from Asynchronous to Synchronous for Stratix & Stratix GX Designs
 Converting from synchronous to Synchronous for Stratix & Stratix GX esigns November 2002, ver. 2.0 pplication Note 210 Introduction The Stratix TM and Stratix GX device families provide a unique memory
Converting from synchronous to Synchronous for Stratix & Stratix GX esigns November 2002, ver. 2.0 pplication Note 210 Introduction The Stratix TM and Stratix GX device families provide a unique memory
MAX 10. Memory Modules
 MAX 10 Memory Modules Three types of on-chip memory FF based memory embedded in the LEs Most efficient for very small memories Compiler driven Embedded SRAM block 8K bits + 1024 parity bits (9216b) MAX
MAX 10 Memory Modules Three types of on-chip memory FF based memory embedded in the LEs Most efficient for very small memories Compiler driven Embedded SRAM block 8K bits + 1024 parity bits (9216b) MAX
Quartus II Software Version 10.0 SP1 Device Support
 Quartus II Software Version 10.0 SP1 Device Support RN-01057 Release Notes This document provides late-breaking information about device support in the 10.0 SP1 version of the Altera Quartus II software.
Quartus II Software Version 10.0 SP1 Device Support RN-01057 Release Notes This document provides late-breaking information about device support in the 10.0 SP1 version of the Altera Quartus II software.
lpm_rom Megafunction User Guide
 lpm_rom Megafunction User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 www.altera.com Software Version: 4.2 Document Version: 1.0 Document Date: March 2005 Copyright 2005 Altera Corporation.
lpm_rom Megafunction User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 www.altera.com Software Version: 4.2 Document Version: 1.0 Document Date: March 2005 Copyright 2005 Altera Corporation.
ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide
 ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.... 3 1.1. Ports...4 1.2.
ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.... 3 1.1. Ports...4 1.2.
Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide
 Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide UG-20068 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Ports...4 1.2 Parameters... 5
Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide UG-20068 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Ports...4 1.2 Parameters... 5
Laboratory Exercise 8
 Laboratory Exercise 8 Memory Blocks In computer systems it is necessary to provide a substantial amount of memory. If a system is implemented using FPGA technology it is possible to provide some amount
Laboratory Exercise 8 Memory Blocks In computer systems it is necessary to provide a substantial amount of memory. If a system is implemented using FPGA technology it is possible to provide some amount
Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor IP Core User Guide
 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor IP Core User Guide UG-01074 2017.09.14 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents... 3 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor Features...3 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor Functional Description...
Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor IP Core User Guide UG-01074 2017.09.14 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents... 3 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor Features...3 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor Functional Description...
