2014, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 1042
|
|
|
- Bethany Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volume 4, Issue 2, February 2014 ISSN: X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Applications Transforming Technology of future Bluetooth Mrs.RANBIR KAUR Head of Department in Computers Doraha Institute of Management & Technology India Abstract: Bluetooth is a new short-range wireless technology designed to enable wireless communication between diverse devices. It is gaining increasing popularity and acceptance in the world today. There is a growing body of research on the subject, but very few, if any of the analyses, provide a balanced view of the technology, which describe its pros and cons and implications for businesses. This paper attempts to critically analyze the Bluetooth technology from a various perspectives. It begins with a description of the technology in terms of its hardware, software, and network infrastructure. Then it addresses the related issues of interference, security, and reliability. This microanalysis is followed by a larger macroanalytical view, which includes the advantages of this technology, its role in the global third generation (3G) wireless scheme, health/safety issues, and business implications. It concludes with the applications of Bluetooth and its future potential. Bluetooth technology unplugs our digital peripherals and makes a cable clutter a thing of the past. In short, it is a wireless replacement for many of the cables we currently use to transmit voice and data signals. It is the result of the joint achievements of nine leading companies: 3COM, Lucent Technologies, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, Motorola, Nokia, Toshiba, Ericsson, altogether known as the Blue Tooth Special Interest Group (SIG). The idea is to create a single wireless protocol to address the end-user problems arising from proliferation of various mobile devices. It aims at low power consumption and provides security for both stationary and mobile devices. A Bluetooth chip (9mm x 9mm) takes the information normally carried by the cable, and transmits it at a special frequency to a receiver. Bluetooth radio modules use Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying (GFSK) for modulation. Keywords: Communications Devices,Usage, Economical Solution, Network Topology, Frequency-Hopping, Long Term Applications Transforming technology of future Bluetooth I. Introduction: A look around at the moment! Keyboard connected to the computer, as well as a printer, mouse, monitor and so on. What (literally) joins all of these together? They are connected by cables. Cables have become the bane of many offices, homes etc. That is what the Bluetooth technology aims at a cable replacement technology! Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology designed to enable such communication without the need for Companies that manufacture computers, entertainment systems, and other electronic devices have realized that the incredible array of cables and connectors involved in their products make it difficult for even expert technicians to correctly set up a complete system on the first try. II. Bluetooth - In detail: One of the most significant recent developments in wireless technologies is the emergence of Wireless personal area networking (WPAN). Developed in 1998, WPAN is based on a new technology called Bluetooth, which uses short-range radio frequencies to transmit both voice and data. This technology wirelessly and transparently synchronizes data across devices and creates access to networks and the Internet within a range of ten meters. The short-range networks Bluetooth enables are called Personal Area Networks (PANs) or piconets. Bluetooth is more able to move from frequency to frequency, making it better able to handle interference than competing protocols. Bluetooth technology is the result of the joint achievements of nine leading companies: 3com, lucent technologies, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, Motorola, Nokia, Toshiba, Ericsson altogether known as the Blue Tooth Special Interest Group (SIG), which has widespread participation by many companies. Originally initiated by L M Ericsson, it was designed as a short-range communications medium for wireless headsets to communicate with cellular phones. Bluetooth technology Features: a) It separates the frequency band into hops. This spread spectrum is used to hop from one channel to another, which adds a strong layer of security. b) Signals can be transmitted through walls and briefcases, thus eliminating the need for line-of-sight. Devices do not need to be pointed at each other, as signals are omni-directional. c) Both synchronous and asynchronous applications are supported, making it easy to implement on a variety of devices and for a variety of services, such as voice and Internet. 2014, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 1042
2 d) Governments worldwide regulate it, so it is possible to utilize the same standard wherever one travels. The Aim of "Bluetooth" has been set quite high. It is to arrive at a specification for a technology that optimizes the usage model of all mobile computing and communications devices, and providing: I. Global usage,voice and data handling. II. The ability to establish ad-hoc connections. III. The ability to withstand interference from other sources in open band IV. Very small size, in order to accommodate integration into variety of devices with negligible power consumption in comparison to other devices for similar use. An open interface standard and competitively low cost of all units, as compared to their non-bluetooth correspondents. BLUETOOTH is used in Phones and pagers and Headsets, Modems and LAN access devices, Notebook computers, Desktop and handheld computers, Printers and Fax machines, Keyboards and Joysticks. Bluetooth Specification: Bluetooth is a global specification for a small form-factor, low-cost radio solution providing links between mobile computers, mobile phones, and other portable handheld devices, as well as connectivity to the Internet. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has given the IEEE standard. A Time-Division Duplex (TDD) scheme is used for full-duplex transmission. Its main strength is its ability to simultaneously handle both data and voice transmissions. A mobile computer equipped with Bluetooth technology, for example, could link to a similarly equipped mobile phone to connect to the Internet. Multiple Bluetooth units form a Wireless Personal Area Network, called and up to seven client devices. A Bluetooth WPAN is capable of supporting an asynchronous data link with each client and synchronous voice links with up to three client devices. It provides a range of up to 10m at a transmit power of 1 mwatt. The range can be extended to 100m if the transmit power is increased to 100 mwatt. Bluetooth has a data rate of 1 Mbps. Bluetooth is a standard for a small (9mm x 9mm), cheap radio chip to be plugged into computers, printers, mobile phones, etc. A Bluetooth chip takes the information normally carried by the cable, and transmits it at a special frequency to a receiver. Bluetooth chip, which will then give the information received to the computer, phone whatever. Bluetooth offers the most economical solution for low-to-medium-speed device connectivity. It aims at low power consumption and provides security for both stationary and mobile devices. The basic function is to provide a standard wireless technology to replace the multitude of propriety cables currently linking computing devices. Technical standards and performance levels 1. Bluetooth is based upon small, high performance integrated radio transceivers, each of which is allocated a unique 48-bit address derived from the IEEE 802 standards. 2. It operates in the unrestricted 2.45 GHz ISM "free band", which is available globally, although slight variation of location and width of band apply. 3. The range is set at 10 meters to optimize for target market of mobile and business user. The range can, however, be increased. 4. Gross data rate is 1Mbit/s, with second generation plans to increase to 2 Mbit/s. One-to-one connections allow maximum data transfer rate of 721 kbits/s (corresponding to 3 voice channels). 5. Bluetooth uses a packet switching protocol, based on a frequency hop scheme with 1600 hops/sek. to enable high performance in noisy radio environments. The entire available frequency spectrum is used with 79 hops of 1 Mhz bandwidth, analogous to the IEEE standard. 6. It has low power consumption, drawing only 0.3 ma in standby mode. This enables maximum performance longevity for battery powered devices. During data transfer the maximum current drain is 30 ma. However, during pauses or at lower data rates the drain would be lower. The Bluetooth Network Topology: There are 3 types of connections in Bluetooth, as shown below: Either: Single-slave or Multi-slave (up to 7 slaves on one master) or Scatternet. Multiple Bluetooth units form a Wireless Personal Area Network, called a piconet. A piconet consists of one hub device and up to seven client devices. It is possible to support more devices in a piconet by placing one or more of the clients into what is referred to as park mode. In order to exchange information with the parked client, the hub must take it out of parked mode and return it to active mode. Only seven clients can be in active mode at any given time. When two piconets are in close proximity, they have overlapping coverage areas - a scenario referred to as a scatternet Clients in one piconet can participate in another piconet as either a hub or client. This is accomplished through time division on multiplexing. In a scatternet, the two (or more) piconets are not synchronized in either time or frequency. Each of the piconets operates in its own frequencyhopping channel, while any devices in multiple piconets participate at the appropriate time via time division multiplexing. A piconet can be created in one of 4 ways: A page (used by Master to connect to Slave) or A page scan (a unit listens for its device access code) or A Master Slave switch is made or An Unpark of a unit is made (provided there are no active slaves). Personal Networking Hardware And the Protocol Stack Layers:Bluetooth radio modules use Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying (GFSK) for modulation. The data is transmitted at a data rate of 1 Mb/second. The Bluetooth Baseband Layer: The baseband layer performs functions like Bluetooth packet assembly, forward error correction (FEC), automatic repeat request (ARQ), data whitening, Bluetooth clock synchronization, and frequency hopping control. 2014, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 1043
3 The Bluetooth Link Manager Layer: The Link Manager forms the piconet by inquiring what other Bluetooth radios are in the area, establishing connection and maintaining the piconet. The Link Manager also handles security issues like authentication and encryption. Radio: The Radio layer defines the requirements for a Bluetooth transceiver operating in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Base band: This layer describes the specification of the Bluetooth Link Controller (LC) which carriesout the baseband protocols and other low-level link routines.the Link Manager Protocol (LMP) is used by the Link Managers (on either side) for link set-up and control.the Host Controller Interface (HCI) provides a command interface to the Baseband Link Controller and Link Manager, and access to hardware status and control registers..logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) supports higher level protocol multiplexing, packet segmentation and reassembly, and the conveying of quality of service information. L2CAP, which adapts upper layer protocols over the Baseband, provides data services to the high layer protocols with group abstractions. The RFCOMM protocol provides emulation of serial ports over the L2CAP protocol. The protocol is based on the ETSI standard TS The Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) provides a means for applications to discover which services are provided by or available through a Bluetooth device. Device information, services and the characteristics of the services can be queried using the SDP. The Power Modes: Bluetooth provides for three low power modes to conserve battery life: sniff mode, hold mode, and park mode. While in the sniff mode, a device listens to the piconet at a reduced rate. The sniff interval is programmable, providing flexibility for different applications. In hold mode, only an internal timer is running, and data transfer restarts when units transition out of the hold mode. Park mode is used to handle more than seven clients - since only seven clients can be active at any time, one client can be parked and another one activated. The advantage of frequency-hopping Bluetooth has been designed to operate in noisy radio frequency environments, and uses a fast acknowledgement and frequency-hopping scheme to make the link robust, communication-wise. Bluetooth radio modules avoid interference from other signals by hopping to a new frequency after transmitting or receiving a packet. Compared with other systems operating in the same frequency band, the Bluetooth radio typically hops faster and uses shorter packets. This is because short packages and fast hopping limit the impact of microwave ovens and other sources of disturbances. Use of Forward Error Correction (FEC) limits the impact of random noise on long-distance links. Bluetooth can support an asynchronous data channel, or up to 3 simultaneous synchronous voice channels, or a channel which simultaneously supports asynchronous data and synchronous voice. Safer transmission of data: Security : Bluetooth has built in sufficient encryption and authentication and is thus very secure in any environment. In addition to this, a frequency-hopping scheme with 1600 hops/sec. is employed. This is far quicker than any other competing system. This, together with an automatic output power adaption to reduce the range exactly to requirement, makes the system extremely difficult to eavesdrop. The transmitting power is far too weak to be noticeable for humans. Moreover, the radiation is not concentrated in a beam, but dispersed more or less in all directions. Hence not dangerous!! Bluetooth units often have to contend with electro-magnetically noisy environments. Thus, the need for some kind of error-detection and -correction. When errors are detected, there are 3 error-correction schemes defined for Bluetooth: 1/3 rate FEC (Forward Error Correction), 2/3 rate FEC, ARQ unnumbered scheme (Automatic Repeat Request). In Bluetooth, it has these components: Random Number Generation, Encryption, Encryption Key Management and Authentication. Application Examples: 1. A Bluetooth-mouse or a Bluetooth-keyboard could be used at a further distance from a monitor, and while moving about in the room. 2. Use while your portable PC is still in the briefcase! When your portable PC receives an , you'll get an alert on your mobile phone. 3. A travelling businessman could ask his laptop computer to locate a suitable printer as soon as he enters a hotel lobby, and send a printout to that printer when it has been found, and replied in a positive manner. 4. Cable-less connection to printers and faxes, to digital cameras and video projectors. Cordless connection from cell phone to handsfree headset. 5. Bluetooth interface to office PBX and Dial-up networking and automatic and use cell phone as office cordless phone. Use of PC or PDA as handsfree phone. 6. Automatic exchange of files, electronic business cards, calendars etc. III. Challenges In Bluetooth Design The Bluetooth specifications have left several design issues open to implementation, when it comes to its use as a networking technology. The objective is to allow designers flexibility so as to cater to the individual network requirements. However for adapting the technology towards large scale deployment in adhoc networks it is imperative that there be a systematic procedure sharing the communication channel associated with each master. 2014, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 1044
4 Similarly, the number of bridge nodes that should exist between different piconets is also unclear. Many bridges can facilitate load distribution and improve connectivity, but this comes at the cost of increasing the complexity of synchronizing communication schedules an added overhead when switching from piconet a bi-partite graph. This is because neither masters nor slaves can communicate directly, and therefore the set of nodes associated with masters only has edges to the set of nodes corresponding to slaves. Similarly, the constraint that a piconet cannot contain more than 7 slaves implies that all nodes associated with masters must have a degree less than or equal to 7. This also implies that if at any time the total number of masters is less than one eighth of the total number of nodes, then certain nodes will not belong to any piconet and thus the topology remains disconnected. These are constraints that any topology formation algorithm must take into account. In addition, it is not only the choice of role, i.e., master, slave, or bridge, that is important in determining connectivity, but the order in which nodes are assigned their role is also a key factor. In particular, because connectivity between piconets is ensured through bridge nodes and not all (slave) nodes are capable of playing such a role (the node must be able to hear the master of each piconet), connectivity between two piconets may be precluded if the corresponding node attempts to join one of the piconets after the piconet has become full, i.e., already has 7 slaves. This can possibly be fixed by having some slaves relinquish their membership in the piconet, but identifying when this is needed, e.g., connectivity might still exist between the piconets through a multi-hop path, and which node should leave the piconet, is a complex problem. Achieving connectivity is, therefore, a complex and possibly unachievable task, but it provides a benchmark against which heuristics can be evaluated. Our second design objective, namely a distributed operation and low overhead, is a must for any practical solution. As pointed out earlier, node state changes should be triggered in response to changes in the physical topology. Our third design objective of maximizing throughput, while obviously desirable, unfortunately adds complexity of its own to an already complex problem to piconet (recall that a node can be active in only one piconet at the time). Assuming that some initial answers can be given to the problems we have just outlined, it is unlikely that static solutions will be sufficient in the context of adhoc networks. As a result, yet another level of complexity gets added when trying to determine when and how node states should change over time. Some of the factors that need to be taken account include the activity status of nodes themselves, e.g., a node may suspend its activities for some time and enter a sleep state in order to save power. Another aspect that needs to be considered is the dynamic nature of adhoc networks, where the number and position of nodes involved is likely to continuously vary. Obviously, node configuration and network topology need to evolve in response to such changes. For example, if a master moves out of the transmission range of its slaves, then the piconet must identify a new master, presumably from the existing members of the piconet, and this calls for a change of state from slave to master in one of the nodes. The difficulty in making such decisions, even in the simple example just outlined, is in their distributed nature. Deciding when and which node state to change requires a significant amount of information exchange and processing, which besides its intrinsic cost can also translate into substantial latency. As a result, any feasible solution calls for some tradeoff between optimality and its cost and responsiveness to changes. For Bluetooth to succeed as a technology on which adhoc networks can be built, it is not only essential to find lightweight solutions to the above problems, but those solutions must be fully distributed. In other words, they should not assume the existence of a central entity with access to the entire system/network state, and nodes decisions should only be based on information about their own state and that of their neighbors. However, the definition of what a node s neighborhood consists of is itself not clear. Does it consist only of nodes belonging to the same piconet(s), or does it also include other nodes within communication reach? More generally, a neighborhood could be defined as all nodes that are k or less hops away (hop count corresponds to the number of masters/piconets that need to be traversed). Clearly there is a trade-off between the accuracy (or optimality) of the decisions that can be made under different scenarios. In general, the more information is available, the better the decisions. However, this comes at the cost of a higher latency, a higher processing cost, and a higher control overhead. IV. Conclusion: Despite some of the problems, Bluetooth remains a very promising technology, with plenty of medium and long term applications. But the real test will be whether it survives the hype. Promoters are laying on it, with their unrealistic claims. This technology is probably the only one which has a good chance to become widely available among PDAs and mobile devices. Bluetooth-equipped gadgets can connect to the LAN through the Access Protocols at once.50 kilobytes per second is about all you can expect from Bluetooth. So there we are: Bluetooth is simply the best!! References [1] P. Bhagwat and R. Seigal. A routing vector method (RVM) for routing in Bluetooth scatternets. In IEEE International Workshop on Mobile Multimedia Communications (MoMuC 99), San Diego, CA, November [2] A. Das, A. Ghose, A. Razdan, H. Saran, and R. Shorey. Enhancing performance of asynchronous data traffic over the Bluetooth wireless ad-hoc network. In Proceedings of INFOCOM 2001, Anchorage, AK, April [3] B. Hajek and G. Sasaki. Link scheduling in polynomial time. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 34(5), [4] N. Muller, Bluetooth Demystified, McGraw-Hill, New York, [5] T. Mu ller, Bluetooth Security Architecture, Bluetooth SIG Inc., United Kingdom, [referred ] doc = , IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 1045
5 [6] M. Nelson, Bluetooth Interoperability Position Paper, Extended Systems, Boise, ID, February dedsystems.com. 2014, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 1046
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets
 A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
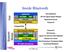 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology
 SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology
 Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology D.Annal 1, T.Indira 2, K.Poojitha 3, R.Rajashree 4 Student, Dept. of CSE, Magna College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India 1,2,3,4 ABSTRACT: The seemingly
Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology D.Annal 1, T.Indira 2, K.Poojitha 3, R.Rajashree 4 Student, Dept. of CSE, Magna College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India 1,2,3,4 ABSTRACT: The seemingly
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
101seminartopics.com. Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks
 Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Introducing Bluetooth
 Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Master. Slave. Master. Slaves. TCP/IP Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology. Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3
 / Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
/ Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a. worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the
 Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the worldwide standard for short-range wireless communication.
Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the worldwide standard for short-range wireless communication.
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN
 Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING
 A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
Modulation. Propagation. Typical frequency bands
 References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE
 Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
Bluetooth General Information White Paper
 General Information is the registered trademark of Atmel Corporation, 2325 Orchard Parkway, San Jose, CA 95131 Rev. 1993A 11/00 Introduction The wireless technology is the world s new shortrange RF transmission
General Information is the registered trademark of Atmel Corporation, 2325 Orchard Parkway, San Jose, CA 95131 Rev. 1993A 11/00 Introduction The wireless technology is the world s new shortrange RF transmission
Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Jeffrey Price Dr. Konak IST 220 Bluetooth Technology
 Jeffrey Price Dr. Konak IST 220 Bluetooth Technology 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. COMPONENTS 3. BLUETOOTH ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES 4. USES OF BLUETOOTH 5. THE FUTURE 7. DOCUMENTATION 2 1. INTRODUCTION
Jeffrey Price Dr. Konak IST 220 Bluetooth Technology 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. COMPONENTS 3. BLUETOOTH ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES 4. USES OF BLUETOOTH 5. THE FUTURE 7. DOCUMENTATION 2 1. INTRODUCTION
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
3Com Wireless Bluetooth PC Card, USB Adapter, and Printer Adapter
 DATA SHEET 3Com Wireless Bluetooth PC Card, USB Adapter, and Printer Adapter Key Benefits Simplicity Bluetooth Connection Manager provides automatic discovery and point-and-click management of devices,
DATA SHEET 3Com Wireless Bluetooth PC Card, USB Adapter, and Printer Adapter Key Benefits Simplicity Bluetooth Connection Manager provides automatic discovery and point-and-click management of devices,
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Part IX: Mobile Business
 Part IX: Mobile Business Learning Targets What is mobile business? What devices and device properties exist? How can we communicate with mobile equipment? Which are interesting mobile applications? 2 3
Part IX: Mobile Business Learning Targets What is mobile business? What devices and device properties exist? How can we communicate with mobile equipment? Which are interesting mobile applications? 2 3
A Scatternet Formation Protocol for Ad hoc Networks of Bluetooth Devices
 A Scatternet Formation Protocol for Ad hoc Networks of Bluetooth Devices Stefano Basagni Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University E-mail: basagni@ece.neu.edu Chiara Petrioli
A Scatternet Formation Protocol for Ad hoc Networks of Bluetooth Devices Stefano Basagni Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University E-mail: basagni@ece.neu.edu Chiara Petrioli
Extending or Interconnecting LANS. Physical LAN segment. Virtual LAN. Forwarding Algorithm 11/9/15. segments. VLAN2, Port3. VLAN1, Port1.
 Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Bluetooth Information Exchange Network
 Bluetooth Information Exchange Network Xiaoning (Linda) Liu A thesis submitted to AUT University In partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Engineering (ME) October 2008 School
Bluetooth Information Exchange Network Xiaoning (Linda) Liu A thesis submitted to AUT University In partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Engineering (ME) October 2008 School
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Bluetooth in Mobile Devices
 Bluetooth in Mobile Devices Vidar Rinne Mälardalen University School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Computer Science: Game Development vre03001@student.mdh.se Abstract The basic idea of Bluetooth
Bluetooth in Mobile Devices Vidar Rinne Mälardalen University School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Computer Science: Game Development vre03001@student.mdh.se Abstract The basic idea of Bluetooth
Securing A Bluetooth Device
 Securing A Bluetooth Device Mrs. Dhanashri D. Dhokate 1, Mr. Milind C. Butale 2, Mr. Babasaheb S. Patil 3 Assistant Professor, Information Technology, PVPIT, Budhgaon, India 1. Associate Professor, Electronics
Securing A Bluetooth Device Mrs. Dhanashri D. Dhokate 1, Mr. Milind C. Butale 2, Mr. Babasaheb S. Patil 3 Assistant Professor, Information Technology, PVPIT, Budhgaon, India 1. Associate Professor, Electronics
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs
 Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Bluetooth PCI Adapter
 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...2 2 Installation...2 2.1 Software Installation...2 2.1.1 Installation on Windows 95/98/ME/2000/XP...2 2.1.2 Installation on Windows NT...3 2.1.3 Installation on Linux...3
Table of Contents 1 Introduction...2 2 Installation...2 2.1 Software Installation...2 2.1.1 Installation on Windows 95/98/ME/2000/XP...2 2.1.2 Installation on Windows NT...3 2.1.3 Installation on Linux...3
Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth
 Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth Martin Connolly, Cormac J. Sreenan University College Cork Department of Computer Science Email: cjs@cs.ucc.ie Abstract The Bluetooth protocol is one of the better-known
Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth Martin Connolly, Cormac J. Sreenan University College Cork Department of Computer Science Email: cjs@cs.ucc.ie Abstract The Bluetooth protocol is one of the better-known
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY. Flavia Martelli
 Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
CALIFORNIA SOFTWARE LABS
 CALIFORNIA SOFTWARE LABS R E A L I Z E Y O U R I D E A S California Software Labs 6800 Koll Center Parkway, Suite 100 Pleasanton CA 94566, USA. Phone (925) 249 3000 Fax (925) 426 2556 info@cswl.com http://www.cswl.com
CALIFORNIA SOFTWARE LABS R E A L I Z E Y O U R I D E A S California Software Labs 6800 Koll Center Parkway, Suite 100 Pleasanton CA 94566, USA. Phone (925) 249 3000 Fax (925) 426 2556 info@cswl.com http://www.cswl.com
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Feature. What exactly is WLAN? More reading:
 The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be
 IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
In Brief TARIFF CLASSIFICATION OF CERTAIN ARTICLES USING BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY
 Ottawa, June 16, 2009 MEMORANDUM D10-14-57 In Brief TARIFF CLASSIFICATION OF CERTAIN ARTICLES USING BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY This memorandum explains the Canada Border Services Agency administrative policy
Ottawa, June 16, 2009 MEMORANDUM D10-14-57 In Brief TARIFF CLASSIFICATION OF CERTAIN ARTICLES USING BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY This memorandum explains the Canada Border Services Agency administrative policy
Bluetooth: New Freedom, New Possibilities. Value Proposition
 Bluetooth: New Freedom, New Possibilities Simon Ellis Manager Mobile Marketing, Communications Intel Corporation The Bluetooth Specification is still preliminary. All information regarding Bluetooth is
Bluetooth: New Freedom, New Possibilities Simon Ellis Manager Mobile Marketing, Communications Intel Corporation The Bluetooth Specification is still preliminary. All information regarding Bluetooth is
Seminar: Mobile Systems. Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht
 Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Logitech Advanced 2.4 GHz Technology With Unifying Technology
 Logitech Advanced 2.4 GHz Technology Revision 070709 December 8, 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION: THE MOVE TO WIRELESS PERIPHERALS IN BUSINESS... 3 2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW... 4 2.1 NETWORK TOPOLOGY...4
Logitech Advanced 2.4 GHz Technology Revision 070709 December 8, 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION: THE MOVE TO WIRELESS PERIPHERALS IN BUSINESS... 3 2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW... 4 2.1 NETWORK TOPOLOGY...4
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Bluetooth. 3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network. What is BLUETOOTH: Bluetooth 2/17/2016
 3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network Bluetooth Bluetooth Bluetooth is a high-speed, low-power microwave wireless link technology, designed to connect phones, laptops, PDAs and other portable equipment
3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network Bluetooth Bluetooth Bluetooth is a high-speed, low-power microwave wireless link technology, designed to connect phones, laptops, PDAs and other portable equipment
White Paper. Defining the Future of Multi-Gigabit Wireless Communications. July 2010
 White Paper Defining the Future of Multi-Gigabit Wireless Communications July 2010 2 Introduction The widespread availability and use of digital multimedia content has created a need for faster wireless
White Paper Defining the Future of Multi-Gigabit Wireless Communications July 2010 2 Introduction The widespread availability and use of digital multimedia content has created a need for faster wireless
IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY
 Bachelor s Thesis (UAS) Information Technology Networking and Programming 2011 IDAHOSA AKHANOLU IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY i BACHELOR S THESIS (UAS) ABSTRACT TURKU UNIVERSITY OF
Bachelor s Thesis (UAS) Information Technology Networking and Programming 2011 IDAHOSA AKHANOLU IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY i BACHELOR S THESIS (UAS) ABSTRACT TURKU UNIVERSITY OF
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech. Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, 7.1
 Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Design of Bluetooth Baseband Controller Using FPGA
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 42, No. 2, February 2003, pp. 200 205 Design of Bluetooth Baseband Controller Using FPGA Sunhee Kim and Seungjun Lee CAD and VLSI Lab.,Department of Information
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 42, No. 2, February 2003, pp. 200 205 Design of Bluetooth Baseband Controller Using FPGA Sunhee Kim and Seungjun Lee CAD and VLSI Lab.,Department of Information
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology
 Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Naveen Kumar. 1 Wi-Fi Technology
 Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Bluetooth PC Card from IBM
 Bluetooth PC Card from IBM Installation and User s Guide IBM 19K4260 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read Appendix E, Product warranties and notices on page E-1. First
Bluetooth PC Card from IBM Installation and User s Guide IBM 19K4260 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read Appendix E, Product warranties and notices on page E-1. First
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology
 LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
WZRDnet. A Low-Power Wireless Ad-Hoc Mesh Network for Austere Tactical Environments. February 14, 2018
 White Paper TELEGRID Technologies, Inc. WZRDnet A Low-Power Wireless Ad-Hoc Mesh Network for Austere Tactical Environments February 14, 2018 23 Vreeland Road Suite 290 Florham Park, NJ 07932 www.telegrid.com
White Paper TELEGRID Technologies, Inc. WZRDnet A Low-Power Wireless Ad-Hoc Mesh Network for Austere Tactical Environments February 14, 2018 23 Vreeland Road Suite 290 Florham Park, NJ 07932 www.telegrid.com
Security. Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011
 Security Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011 What is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is an open standard for short-range radio frequency (RF) communication. Bluetooth technology is used primarily to establish
Security Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011 What is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is an open standard for short-range radio frequency (RF) communication. Bluetooth technology is used primarily to establish
Protocol Based on Mobile Agents
 Bluecouts: A catternet Formation Bluecouts: A catternet Formation ergio González-Valenzuela 1 on T. Vuong 2 Victor C. M. Leung 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 2 Department of Computer
Bluecouts: A catternet Formation Bluecouts: A catternet Formation ergio González-Valenzuela 1 on T. Vuong 2 Victor C. M. Leung 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 2 Department of Computer
