Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
|
|
|
- Hilary Powell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1
2 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic Tasks 5. Resource Sharing 8. Communication 9. Low Power Design 11. Architecture Synthesis 6. Real-Time OS Software and Programming 12. Model Based Design Processing and Communication 8-2 Hardware
3 Communication is everywhere 8-3
4 Where are sensor nodes used? Logistics Maintenance Factory Automation Low resolution Sensor, Test4, Increasing frequency Acceleration (g) Time (sec) Natural Hazards Building Automation Health Care 8-4
5 Kalray MPPA 256 NoC: Network on Chip 8-5
6 Communication: Requirements Performance bandwidth and latency guaranteed behavior (real-time) Efficiency cost (material, installation, maintenance) low power Robustness fault tolerance maintainability, diagnose-ability security, safety 8-6
7 Protocol Classification arbitration time multiplex frequency multiplex synchronous asynchronous controlled access competing access covered in lecture TDMA CSMA/CR/CA Token Bus/Ring FlexRay CSMA/CD Random Bluetooth 8-7
8 Random Access Random access to communication medium no access control; requires low medium utilization access conflict improved variant: slotted random access 8-8
9 Random Access Random access to communication medium What is the optimal sending rate p in case of n stations? probability that a slot is not taken by others: probability that a station transmits successfully: determine maximum with respect to p: optimal probability that a station can successfully transmit: P optimal probability that a slot contains useful data: n P P n P 1/e n n 8-9
10 TDMA Communication in statically allocated time slots Synchronization among all nodes necessary: periodic repetition of communication frame or master node sends out a synchronization frame Examples: TTP, static portion of FlexRay, satellite networks 8-10
11 CSMA/CD Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection Try to avoid and detect collisions: before starting to transmit, check whether the channel is idle if a collision is detected (several nodes started almost simultaneously), wait for some time (backoff timer) repeated collisions result in increasing backoff times Examples: Ethernet, IEEE < t pd t pd = max end-to-end latency 8-11
12 Token Protocols Token value determines which node is transmitting and/or should transmit next Only the token holder may transmit Master/slave polling is a special form Null messages with tokens must be passed to prevent network from going idle Examples: IEEE 802.4, Profibus, TokenRing 8-12
13 Token Ring null token data ack null token A requests transmission A is token owner A sends data to C C sends acknowledge A sends null token 8-13
14 CSMA/CA Flexible TDMA (FTDMA) Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Avoidance Operation: reserve s slots for n nodes; note: slots are normally idle they are (short) time intervals, not signals; if slot is used it becomes a slice. nodes keep track of global communication state by sensing nodes start transmitting a message only during the assigned slot If s=n, no collisions; if s<n, collision may occur (see random access) Examples: , part of FlexRay 8-14
15 CSMA/CR Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Resolution Operation: Before any message transmission, there is a global arbitration arbitration message arbitration message Each node is assigned a unique identification number All nodes wishing to transmit compete by transmitting a binary signal based on their identification value A node drops out the competition if it detects a dominant state while transmitting a passive state Thus, the node with the lowest identification value wins Example: CAN Bus 8-15
16 CSMA/CR node 1 node 2 resulting channel signal node 1 recognizes dominance and drops out of competition message message 8-16
17 FlexRay FlexRay: Developed by the FlexRay consortium (BMW, Ford, Bosch, DaimlerChrysler, General Motors, Motorola, Philips). Combination of a TDMA and the Byteflight [Byteflight Consortium, 2003] (Flexible TDMA, close to CSMA/CA) protocol. High data rates can be achieved: initially targeted for ~ 10Mbit/sec; design allows much higher data rates Operation principle: Cycle is subdivided into a static and a dynamic segment. Static segment is based on a fixed allocation of time slots to nodes. Dynamic segment for transmission of ad-hoc communication with variable bandwidth requirements. 8-17
18 FlexRay Use of two independent channels to eliminate single-point failures Static segment Communication cycle Channel 1 Channel 2 Dynamic segment because of redundancy Channel 1 Channel 2 [ 8-18
19 FlexRay Basic topologies (any combination also possible): Typical physical layer (twisted pairs and differential encoding to reduce sensitivity to electromagnetic coupling): 8-19
20 FlexRay TDMA all static slots are the same length whether used or not all slots are repeated in order every communication cycle slots are lock-stepped in order on both channels 8-20
21 FlexRay Flexible TDMA: each minislot is an opportunity to send a message if message isn t sent, minislot elapses unused (short idle period) all nodes watch whether a message is sent so they can count minislots 8-21
22 Example Bluetooth 8-22
23 Who was Bluetooth? Wikinger King of Denmark Christianized, unified and controlled Denmark and Norway 8-23
24 Bluetooth Overview Design Goals small size, low cost, low energy secure transmission (encryption, authentication) robust transmission (interference with wireless LAN) Technical Data 2.4 GHz Band (open band, spectral bandwidth 79 MHz, frequency hopping and time multiplex) m transmission range, 1 Mbit/s bandwidth for each connection simultaneous transmission of multimedia streams (synchronous) and data (asynchronous) ad hoc network (spontaneous connections to neighbor nodes, dynamic network topologies, no centralized coordination, multi-hop communication) 8-24
25 Bluetooth Overview Frequency Hopping Transmitter jumps from one frequency to another with a fixed rate (1600 hops/s). The ordering (channel sequence) is determined by a pseudo random sequence of length Frequency range ( k) MHz, k = The data transmission is partitioned into time windows of length ms; each packet is transmitted by means of a different frequency. 8-25
26 Bluetooth Overview Example frequency hopping: 8-26
27 8-27
28 Network Topologies Ad-hoc networks all nodes are potentially mobile dynamic emergence of connections hierarchical structure (scatternet) of small nets (piconet) single slave piconet multi slave piconet scatternet consisting of three piconets 8-28
29 Network Topologies Piconet A piconet contains 1 master and maximally 7 slaves All nodes in a piconet use the same frequency hopping scheme (channel sequence) which is determined by the device address of the master BD_ADDR and phase which is determined by the system clock of the master. Connections are either one-to-one or between the master and all slaves (broadcast). The following connection types are possible: 432 kbit/s (duplex) or 721/56 kbit/s (asymmetric) or 3 audio channels or a combination of data and audio. 8-29
30 Netzwerktopologien Scatternet 8-30
31 Network Topologies Scatternet Several piconets with overlapping nodes form a scatternet. A node can simultaneously have the roles of slaves in several piconets and the role of a master in at most one piconet. The channel sequences of the different piconets are not synchronized. As a result, large network structures can emerge and multihop communication is possible. 8-31
32 Packet Format The access code identifies all packets between Bluetooth devices. Packet Header identifies and characterizes the connection between master and slave. 8-32
33 Addressing Bluetooth Device Address: BD_ADDR 48 Bit Unique address for each device Active Member Address AM_ADDR 3 Bit for maximally 7 active Slaves in a piconet. Address Null is a broadcast to all slaves. Parked Member Address PM_ADDR 8 Bit for parked slaves. 8-33
34 Connection Types Mixed transmission of data and audio. Synchronous Connection-Oriented (SCO) Point to point full duplex connection between master & slaves Master reserves slots to allow transmission of packets in regular intervals. Asynchronous Connection-Less (ACL) Asynchronous service No reservation of slots The master transmits spontaneously, the addressed slave answers in the following interval. 8-34
35 Frequency Hopping Time Multiplex A packet of the master is followed by a slave packet. After each packet, the channel (frequency) is switched. 8-35
36 Multi-Slot Communication Master can only start sending in even slot numbers. Packets from master or slave have length of 1, 3 or 5 slots. 8-36
37 ACL and SCO Connections 8-37
38 Modes and States Modes of operation: Inquiry (master identifies addresses of neighboring nodes) Page (master attempts connection to a slave whose address BD_ADDR is known) Connected (connection between master and slave is established) States in connection mode (sorted in decreasing order of power consumption) active (active in a connection to a master) hold (does not process data packets) sniff (awakens in regular time intervals) park (passive, in no connection with master but still synchronized) 8-38
39 States in Connection Mode master active hold sniff park Piconet 8-39
40 Synchronization in Connection Mode The channel sequence of a piconet is determined by the BD_ADDR of the master. The phase within the sequence is also determined by the master; all slaves follow. Piconet 8-40
41 Synchronization in Connection Mode 8-41
42 The Sniff State sniff active A slave in sniff state listens in regular time intervals whether there is a packet with its address. If yes, it answers. 8-42
43 From Standby to Connection Master Slave FHS 8-43
44 The Page Mode Synchronization between master and slave. It is a prerequisite for establishing a connection. page page scan Master transmits its own and slave address to slave (it uses a special channel sequence) Slave listens, whether its own address is sent from a master. Problem: Synchronization master page response Slave answers the master with its own address. slave page response Master sends FHS-packet (frequency hop synchronization) to slave. It contains the channel sequence and the phase of the piconet. 8-44
45 The Page Mode page Page scan time time 8-45
46 The Page Mode page slave page response page scan master page response synchronized 8-46
47 Protocol Hierarchy The baseband specification defines the packet formats, the physical and logical channels, the error correction, the synchronization between receiver and transmitter, and the different modes of operation and states that allow the transmission of data and audio. The audio specification defines the transmission of audio signals, in particular the coding and decoding methods. The link manager (LM) covers the authentication of a connection and the encryption, the management of a piconet (synchronous/asynchronous connection), the initiation of a connection (asynchronous/synchronous packet types, exchange of name and ID) and the transition between different modes of operation and states. 8-47
48 Protocol Hierarchy The host controller interface (HCI) defines a common standardized interface between a host and a bluetooth node; it is specified for several physical interconnections (USB, RS232, PCI,...). The link layer control and adaptation layer (L2CAP) provides an abstract interface for data communication. It segments packets (up to 64kByte) and assembles them again, it allows the multiplexing of connections (simultaneous use of several protocols and connections) and allows the exchange of quality of service information between two nodes (packet rate, packet size, latency, delay variations, maximal rate). 8-48
49 Protocol Hierarchy RFCOMM is a simple transport protocol that simulates a serial connection (~RS 232). There are several other protocols that are defined such as the telephony control protocol specification (TCS), the service discovery protocol (SDP), the OBEX (Object Exchange Protocol), and TCP/IP. Finally, the application can use the top layers of the protocol stack. 8-49
Real-Time Communications. LS 12, TU Dortmund
 Real-Time Communications Prof. Dr. Jian-Jia Chen LS 12, TU Dortmund 20, Jan., 2016 Prof. Dr. Jian-Jia Chen (LS 12, TU Dortmund) 1 / 29 Random Access no access control; requires low medium utilization Prof.
Real-Time Communications Prof. Dr. Jian-Jia Chen LS 12, TU Dortmund 20, Jan., 2016 Prof. Dr. Jian-Jia Chen (LS 12, TU Dortmund) 1 / 29 Random Access no access control; requires low medium utilization Prof.
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
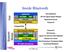 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Lecture Computer Networks
 Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Lecture Computer Networks Networks for Multimedia
Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Lecture Computer Networks Networks for Multimedia
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg
 Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing Error Detection Error Correction Media Access Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing
Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing Error Detection Error Correction Media Access Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
Lecture Objectives. Lecture and Bluetooth technology. Agenda. IEEE b. Characteristics. Center Frequencies
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and obile ystems Lecture 2 802.11 and Bluetooth technology Discuss the operation of IEEE 802.11 and Bluetooth WLANs/WANs ummarize standardization efforts and recommendations
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and obile ystems Lecture 2 802.11 and Bluetooth technology Discuss the operation of IEEE 802.11 and Bluetooth WLANs/WANs ummarize standardization efforts and recommendations
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech. Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, 7.1
 Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Lecture 6. Data Link Layer (cont d) Data Link Layer 1-1
 Lecture 6 Data Link Layer (cont d) Data Link Layer 1-1 Agenda Continue the Data Link Layer Multiple Access Links and Protocols Addressing Data Link Layer 1-2 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types
Lecture 6 Data Link Layer (cont d) Data Link Layer 1-1 Agenda Continue the Data Link Layer Multiple Access Links and Protocols Addressing Data Link Layer 1-2 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Medium Access Control. MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols
 Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Wireless Local Area Network. Internet Protocol Suite
 Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Data Link Layer Technologies
 Chapter 2.2 La 2 Data Link La Technologies 1 Content Introduction La 2: Frames Error Handling 2 Media Access Control General approaches and terms Aloha Principles CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA / CA Master-Slave
Chapter 2.2 La 2 Data Link La Technologies 1 Content Introduction La 2: Frames Error Handling 2 Media Access Control General approaches and terms Aloha Principles CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA / CA Master-Slave
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1
 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017
 ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.4: Multiple Access Protocols Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.4: Multiple Access Protocols Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527
Inside Bluetooth Low Energy
 Inside Bluetooth Low Energy Naresh Gupta BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface Acknowledgments Foreword xix xxiii xxv Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction to Wireless Communication 1 1.2 Data Rates
Inside Bluetooth Low Energy Naresh Gupta BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface Acknowledgments Foreword xix xxiii xxv Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction to Wireless Communication 1 1.2 Data Rates
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
Objectives of the Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Data Link Layer: Collisions
 Data Link Layer: Collisions 1 Multiple Access Data Link layer divided into two sublayers. The upper sublayer is responsible for datalink control, The lower sublayer is responsible for resolving access
Data Link Layer: Collisions 1 Multiple Access Data Link layer divided into two sublayers. The upper sublayer is responsible for datalink control, The lower sublayer is responsible for resolving access
The Link Layer and LANs. Chapter 6: Link layer and LANs
 The Link Layer and LANs EECS3214 2018-03-14 4-1 Chapter 6: Link layer and LANs our goals: understand principles behind link layer services: error detection, correction sharing a broadcast channel: multiple
The Link Layer and LANs EECS3214 2018-03-14 4-1 Chapter 6: Link layer and LANs our goals: understand principles behind link layer services: error detection, correction sharing a broadcast channel: multiple
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Topics. Link Layer Services (more) Link Layer Services LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS. flow control: error detection:
 1 Topics 2 LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS Multiple access: CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, token passing, channelization LAN: characteristics, i basic principles i Protocol architecture Topologies
1 Topics 2 LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS Multiple access: CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, token passing, channelization LAN: characteristics, i basic principles i Protocol architecture Topologies
Outline. Introduction to Networked Embedded Systems - Embedded systems Networked embedded systems Embedded Internet - Network properties
 Outline Introduction to Networked Embedded Systems - Embedded systems Networked embedded systems Embedded Internet - Network properties Layered Network Architectures - OSI framework descriptions of layers
Outline Introduction to Networked Embedded Systems - Embedded systems Networked embedded systems Embedded Internet - Network properties Layered Network Architectures - OSI framework descriptions of layers
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
CARRIER SENSE MULTIPLE ACCESS (CSMA):
 Lecture Handout Computer Networks Lecture No. 8 CARRIER SENSE MULTIPLE ACCESS (CSMA): There is no central control management when computers transmit on Ethernet. For this purpose the Ethernet employs CSMA
Lecture Handout Computer Networks Lecture No. 8 CARRIER SENSE MULTIPLE ACCESS (CSMA): There is no central control management when computers transmit on Ethernet. For this purpose the Ethernet employs CSMA
Extending or Interconnecting LANS. Physical LAN segment. Virtual LAN. Forwarding Algorithm 11/9/15. segments. VLAN2, Port3. VLAN1, Port1.
 Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
CS 43: Computer Networks. 27: Media Access Contd. December 3, 2018
 CS 43: Computer Networks 27: Media Access Contd. December 3, 2018 Last Class The link layer provides lots of functionality: addressing, framing, media access, error checking could be used independently
CS 43: Computer Networks 27: Media Access Contd. December 3, 2018 Last Class The link layer provides lots of functionality: addressing, framing, media access, error checking could be used independently
Redes de Computadores. Medium Access Control
 Redes de Computadores Medium Access Control Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto 1 » How to control the access of computers to a communication medium?» What is the ideal Medium
Redes de Computadores Medium Access Control Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto 1 » How to control the access of computers to a communication medium?» What is the ideal Medium
Systems. Roland Kammerer. 10. November Institute of Computer Engineering Vienna University of Technology. Communication Protocols for Embedded
 Communication Roland Institute of Computer Engineering Vienna University of Technology 10. November 2010 Overview 1. Definition of a protocol 2. Protocol properties 3. Basic Principles 4. system communication
Communication Roland Institute of Computer Engineering Vienna University of Technology 10. November 2010 Overview 1. Definition of a protocol 2. Protocol properties 3. Basic Principles 4. system communication
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Chapter 4. The Medium Access Control Sublayer. Points and Questions to Consider. Multiple Access Protocols. The Channel Allocation Problem.
 Dynamic Channel Allocation in LANs and MANs Chapter 4 The Medium Access Control Sublayer 1. Station Model. 2. Single Channel Assumption. 3. Collision Assumption. 4. (a) Continuous Time. (b) Slotted Time.
Dynamic Channel Allocation in LANs and MANs Chapter 4 The Medium Access Control Sublayer 1. Station Model. 2. Single Channel Assumption. 3. Collision Assumption. 4. (a) Continuous Time. (b) Slotted Time.
Chapter 4. The Medium Access Control Sublayer
 Chapter 4 The Medium Access Control Sublayer The Channel Allocation Problem Static Channel Allocation in LANs and MANs Dynamic Channel Allocation in LANs and MANs Dynamic Channel Allocation in LANs and
Chapter 4 The Medium Access Control Sublayer The Channel Allocation Problem Static Channel Allocation in LANs and MANs Dynamic Channel Allocation in LANs and MANs Dynamic Channel Allocation in LANs and
Master. Slave. Master. Slaves. TCP/IP Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology. Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3
 / Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
/ Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Content. Deterministic Access Polling(1) Master-Slave principles: Introduction Layer 2: Media Access Control
 Content Introduction Layer 2: Frames Error Handling Media Access Control General approaches and terms Network Topologies Media Access Principles (Random) Aloha Principles CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA / CA Media
Content Introduction Layer 2: Frames Error Handling Media Access Control General approaches and terms Network Topologies Media Access Principles (Random) Aloha Principles CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA / CA Media
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
Multiple Access Links and Protocols
 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Lecture 9: Bridging. CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren
 Lecture 9: Bridging CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Lecture 9 Overview Finishing up media access Ethernet Contention-free methods (rings) Moving beyond one wire Link technologies have limits
Lecture 9: Bridging CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Lecture 9 Overview Finishing up media access Ethernet Contention-free methods (rings) Moving beyond one wire Link technologies have limits
Lecture 2. Basics of networking in automotive systems: Network. topologies, communication principles and standardised protocols
 Lecture 2. Basics of networking in automotive systems: Network topologies, communication principles and standardised protocols Objectives Introduce basic concepts used in building networks for automotive
Lecture 2. Basics of networking in automotive systems: Network topologies, communication principles and standardised protocols Objectives Introduce basic concepts used in building networks for automotive
Multiple Access Protocols
 Multiple Access Protocols Computer Networks Lecture 2 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Multiple Access to a Shared Channel The medium (or its sub-channel) may be shared by multiple stations (dynamic allocation) just
Multiple Access Protocols Computer Networks Lecture 2 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Multiple Access to a Shared Channel The medium (or its sub-channel) may be shared by multiple stations (dynamic allocation) just
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela
 By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
Medium Access Control Sublayer Chapter 4
 Medium Access Control Sublayer Chapter 4 Channel Allocation Problem Multiple Access Protocols Ethernet Wireless LANs Broadband Wireless Bluetooth RFID Data Link Layer Switching Revised: August 2011 & February
Medium Access Control Sublayer Chapter 4 Channel Allocation Problem Multiple Access Protocols Ethernet Wireless LANs Broadband Wireless Bluetooth RFID Data Link Layer Switching Revised: August 2011 & February
MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU
 Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Data Link Layer -2- Network Access
 EITF25 Internet: Technology and Applications Data Link Layer -2- Network Access 2015, Lecture 03 Kaan Bür Previously on EITF25 Logical Link Control Sublayer Flow control Send data Wait for ACK Error control
EITF25 Internet: Technology and Applications Data Link Layer -2- Network Access 2015, Lecture 03 Kaan Bür Previously on EITF25 Logical Link Control Sublayer Flow control Send data Wait for ACK Error control
Link Layer and Ethernet
 Link Layer and Ethernet 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross traceroute Data Link Layer Multiple
Link Layer and Ethernet 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross traceroute Data Link Layer Multiple
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
EITF25 Internet Techniques and Applications L4: Network Access. Stefan Höst
 EITF25 Internet Techniques and Applications L4: Network Access Stefan Höst Repetition The link layer protocol should make sure that the data is correctly transmitted over the physical link using error
EITF25 Internet Techniques and Applications L4: Network Access Stefan Höst Repetition The link layer protocol should make sure that the data is correctly transmitted over the physical link using error
Link Layer and Ethernet
 Link Layer and Ethernet 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross traceroute Data Link Layer Multiple
Link Layer and Ethernet 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross traceroute Data Link Layer Multiple
CS 455/555 Intro to Networks and Communications. Link Layer
 CS 455/555 Intro to Networks and Communications Link Layer Dr. Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Old Dominion University mweigle@cs.odu.edu http://www.cs.odu.edu/~mweigle/cs455-s13 1 Link Layer
CS 455/555 Intro to Networks and Communications Link Layer Dr. Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Old Dominion University mweigle@cs.odu.edu http://www.cs.odu.edu/~mweigle/cs455-s13 1 Link Layer
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Introducing Bluetooth
 Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Data Link Layer -2- Network Access
 EITF25 Internet: Technology and Applications Data Link Layer -2- Network Access 2013, Lecture 03 Kaan Bür, Stefan Höst Previously on EITF25 Logical Link Control Sublayer Flow control Send data Wait for
EITF25 Internet: Technology and Applications Data Link Layer -2- Network Access 2013, Lecture 03 Kaan Bür, Stefan Höst Previously on EITF25 Logical Link Control Sublayer Flow control Send data Wait for
FlexRay International Workshop. Protocol Overview
 FlexRay International Workshop 4 th March 2003 Detroit Protocol Overview Dr. Christopher Temple - Motorola FlexRay principles Provide a communication infrastructure for future generation highspeed control
FlexRay International Workshop 4 th March 2003 Detroit Protocol Overview Dr. Christopher Temple - Motorola FlexRay principles Provide a communication infrastructure for future generation highspeed control
Chapter 5 Link Layer and LANs
 Chapter 5 Link Layer and LANs Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 4 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2007. All material copyright 1996-2007 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights
Chapter 5 Link Layer and LANs Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 4 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2007. All material copyright 1996-2007 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights
Wireless Protocols Overview
 Sami Kiminki Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science sami.kiminki@aalto.fi September 22, 2011 Introduction A primer for wireless IoT topics Brief overview on
Sami Kiminki Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science sami.kiminki@aalto.fi September 22, 2011 Introduction A primer for wireless IoT topics Brief overview on
Wireless Local Area Networks. Networks: Wireless LANs 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Networked Control Systems for Manufacturing: Parameterization, Differentiation, Evaluation, and Application. Ling Wang
 Networked Control Systems for Manufacturing: Parameterization, Differentiation, Evaluation, and Application Ling Wang ling.wang2@wayne.edu Outline Introduction Parameterization Differentiation Evaluation
Networked Control Systems for Manufacturing: Parameterization, Differentiation, Evaluation, and Application Ling Wang ling.wang2@wayne.edu Outline Introduction Parameterization Differentiation Evaluation
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic
 Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Product Specification
 Product Specification 15mm x 27mm Description One of the most capable Bluetooth modules available, the BT-21 Bluetooth OEM Module is designed for maximum flexibility. The BT-21 module includes 14 general
Product Specification 15mm x 27mm Description One of the most capable Bluetooth modules available, the BT-21 Bluetooth OEM Module is designed for maximum flexibility. The BT-21 module includes 14 general
Lecture 8 Link Layer: functionality, error detection, media access algorithm
 Lecture 8 Link Layer: functionality, error detection, media access algorithm From Kurose & Ross Book slightly modified by Romaric Duvignau duvignau@chalmers.se Thanks and enjoy! JFK/KWR All material copyright
Lecture 8 Link Layer: functionality, error detection, media access algorithm From Kurose & Ross Book slightly modified by Romaric Duvignau duvignau@chalmers.se Thanks and enjoy! JFK/KWR All material copyright
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Wireless and WiFi. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Physical Layer. Medium Access Links and Protocols. Point-to-Point protocols. Modems: Signaling. Modems Signaling. Srinidhi Varadarajan
 P Physical Layer Srinidhi Varadarajan Medium Access Links and Protocols Three types of links : point-to-point (single wire, e.g. PPP, SLIP) broadcast (shared wire or medium; e.g, Ethernet, Wavelan, etc.)
P Physical Layer Srinidhi Varadarajan Medium Access Links and Protocols Three types of links : point-to-point (single wire, e.g. PPP, SLIP) broadcast (shared wire or medium; e.g, Ethernet, Wavelan, etc.)
Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview. Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University
 Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University Medium Access Control Topology 3 Simplex and Duplex 4 FDMA TDMA CDMA DSSS FHSS Multiple Access Methods Notice: CDMA and spread spectrum
Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University Medium Access Control Topology 3 Simplex and Duplex 4 FDMA TDMA CDMA DSSS FHSS Multiple Access Methods Notice: CDMA and spread spectrum
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
