TTCsr Documentation. TTCsr Registers. Jorge Ferrer Prieto. Version 1.0
|
|
|
- Marlene Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 17 November 1997 TTCsr Documentation Jorge Ferrer Prieto Version 1.0 This documentation pretends to give information to use the TTCsr boards done at CERN by the ECP/EDO group. It s intended to be used by the software team that will write the code to use the card. TTCsr Registers MEMORY SPACE The card has 64 KB of memory space distributed as: 0x0000 (lower 16 bits): Counter 1. Number of data words written on FIFO1. 0x0000 (higher 16 bits): Counter 2. Number of data words written on FIFO2. 0x0001 (lower 16 bits): Counter 3. Number of data words written on FIFO3. 0x0002-0x3FFF: Available for user. 0x4000-0x7FFF: FIFO 1. 0x8000-0xBFFF: FIFO 2. 0xC000-0xFFFF: FIFO 3. I/O SPACE The following addresses in I/O space are used: 0x20: Old status register. There is now only one bit with useful data here, bit 2 that is the EPROM switch position. 0 means backup position and 1 means working position. 0x80: Status Register. The meaning of the bits is: Bit 11 (read only): not used (0). Bit 10 (read only): FIFO 3 50% full. If 1, FIFO 3 is at least 50% full. 1
2 FIFO Reading Protocol Bit 9 (read only): FIFO 2 50% full. If 1, FIFO 2 is at least 50% full. Bit 8 (read only): FIFO 1 50% full. If 1, FIFO 1 is at least 50% full. Bit 7 (read only): not used (0). Bit 6 (read only): Bit 5 (read only): Bit 4 (read only): Bit 3 (read/write): Bit 2 (read/write): Bit 1 (read/write): DONE. If 1, the dumping of the counters is done. NOZERO. If 1, there is new data in some of the fifos. TTCRDY. If 1 TTCrx Chip has initialized properly (reset and loading of the PROM data) and is tuned to the receiver. FIFO 3 ENABLE. Enable (1) or Disable (0) FIFO 3. FIFO 2 ENABLE. Enable (1) or Disable (0) FIFO 2. FIFO 1 ENABLE. Enable (1) or Disable (0) FIFO 1. Bit 0 (read/write): DUMPCNT. With 1 the user asks to the TTCsr the dumping of the counters. 0xC0: Set the address register and maintain address lines (used for accessing the Flash EPROM). 0xE0: Release the address lines (used for accessing the Flash EPROM). 0x40: Data register (only bits are used). Data for the Flash EPROM accessing. 0xF0: Reset the TTCsr board with a read or a write access. It s convenient after a reset of the board to check that the TTCRDY signal is set to confirm that everything went ok. Otherwise a new reset should be done until the TTCRDY becomes one. FIFO Reading Protocol In this section the protocol to be used to read the FIFOs will be described. What here is called FIFOs are indeed regions of memory where the data coming from the TTC will be stored. Each of these FIFOs (memory regions) are 16 KB long. They are located as shown in the previous section. The data that come to the FIFOs are 16-bit words, so there is space for 8Kwords of data per FIFO. The TTCsr store the data into the FIFO regions in contiguous 16-bit positions of the memory starting from the base address of each FIFO after reset (0x4000 for FIFO 1, 0x8000 for FIFO 2 and 0xC000 for FIFO 3) and continuing up to the end of the region of each FIFO, starting again from each base address in a cyclic manner. There are 3 flags and 3 counters to control the reading of the FIFOs plus some additional flags that tell about the state of the FIFOs. The flags are NOZERO, DUMPCNT and DONE. When some data comes to the TTCsr, it will be immediately stored on the appropriate FIFO by the TTCsr. Then the TTCsr will set the 2 TTCsr Documentation
3 FIFO Reading Protocol DONE flag to one, signalling that there is some data in some of the FIFOs. Then the user will be able to ask how many data is into the FIFOs by setting the flag DUMPCNT to one. When receiving DUMPCNT, the TTCsr will write onto the counters the number of words already stored on every FIFO. It s important to notice that the only thing that is dumped at this time is the 3 counters that tell how many data is stored in every FIFO, not the data itself that is always stored as soon as it arrive to the TTCsr. So this is just a 3 words writing. Once the writing of the counters is done the TTCsr will set to one the flag DONE. Then the user will be able to read the counters that will tell how many words are in each of the FIFOs and he will be able to read the data. It should be notice that from PCI side you can access to 32-bits data in one read cycle but if the number of data stored in one of the FIFOs is not even, the last 32 bit word read will contained only the lower 16-bit of significant data. The user should keep a pointer for each of the FIFOs to know in which position is the last word read because the TTCsr will write the next data starting from the next position to the last position written. So for example, if the first reading of the counters after a reset of the card says that there are 7 words written into FIFO 2, the user will find these data in the first 7 16-bit positions of FIFO 2 region. In a second reading of the counters, if there is 5 new data words in FIFO 2, they will be in positions 8 to 12 of FIFO 2 so the user will have to keep a pointer for this. To complete the protocol, once the counters are read and before or after the data is read, the user should set back the DUMPCNT signal to zero, then the TTCsr will set the DONE signal to zero and the protocol will be able to start again. Figure 1 shows graphically the process. 1 3 NOZERO DUMPCNT DONE FIGURE 1. Protocol of flags to read the FIFOs. To summarize: 1. Some new data is in the FIFOs, signal NOZERO becomes The user see the NOZERO event and ask for the counter asserting signal DUMPCNT. 3. If there is not more data coming into the FIFOs during the process, signal NOZERO will become zero when the TTCsr dumps the counters telling that there is not more new data. If there is data coming during the process, NOZERO will stay as Once the dumping is done (very quickly, because is just 3 writings at 40 MHz), signal DONE will become The user will read the counters (and the data) and it will set signal DUMPCNT to zero. The order of this 3 actions (clearing of DUMPCNT, reading of the counters and reading of the data) is irrelevant because the TTCsr will wait until a new DUMPCNT setting to overwrite the counters. TTCsr Documentation 3
4 FIFOs Format 6. After signal DUMPCNT is deactivated, TTCsr will respond deactivating signal DONE. FIFOs Format There is different data coming into the different FIFOs. This section describes the format of the data for each of the FIFOs. FIFO 1 FIFO 1 is used to store the data associated with each L1A signal occurrence. The possible data items are the Event Counter Low, Even Counter High and the Bunch Counter Identifier, being all 12-bit words. Depending on the programming of the TTCrx (see TTCrx Reference Manual), there would be one, two or all three of these items. TTCsr stores these data with the following structure: Bunch Counter Identifier Event Counter Low Event Counter High So the four higher bits indicate the type of data on the lower 12 bits. FIFO 2 The FIFO 2 is used to store all the subaddress/data issued by the TTCrx in response to an address/data cycle on the TTC network. Both data and subaddress are 8-bit data and they are stored in FIFO 2 as following: DATA SUBADDRESS 0 FIFO 3 The FIFO 3 is used to store the broadcast commands received by the TTCrx and the data issued by the TTCrx in response to a command. The commands are 6-bit words that are stored with the following format: User Commands System Commands 4 TTCsr Documentation
5 Source Code When there is data issued by the TTCrx in response to one of these commands, this data is stored on FIFO 3 with the following structure: DATA DQ Being DQ the type of data being stored (see TTCrx Reference Manual). Source Code The original source code of the card (VHDL for the FPGAs, schematics and layout) is on my CERN CAE account. The system administrators of the CAE cluster are Michel Manent and Antoine Thys. The different components can be found on the following paths: schematics & layout: /user/jferrerp/valid/ttcsr.pcb/ VHDL (PCI-FPGA): /user/jferrerp/ttcproject/pci_fpga/vhdl/ (main program: pcitop2.vhd) VHDL (TTC-FPGA): /user/jferrerp/ttcproject/ttc_fpga/vhdl/ (main program: ttc_fpga.vhd) The VHDL codes and the results of the synthesis, map, place and route of the VHDL files are also kept on a different account of the same cluster. The path is: /user/neocad/jferrerp/ttcproject/ Finally, the C programs used for the tests (slightly modified versions of the Carlos safetools) are in the MVME hard disk, jferrerp account, directories bin, EXOfiles and src. This will be described later. A CDROM is provided with a backup of all here mentioned in its latest state. TTCsr1 patch There are currently 3 TTCsr identical cards labelled as TTCsr1, TTCsr2 and TTCsr3. All of the 3 cards have the same functionality but card TTCsr1 had a problem on the making and has pin PROM_RESET of the TTCrx chip grounded. Because this and in order to save the chip, a patch on the VHDL code was made that could solve the problem. This means that we have a slightly different code for this card. If the reprogramming of the EPROM code is needed (explained in next section) this should be kept in mind. Actually, the patched code would equally work with cards TTCsr2 and TTCsr2 but if the reinitialize function is utilized (see TTCrx Reference Manual), it TTCsr Documentation 5
6 Reprogramming of the Flash EPROM won t work on a patched card. This means that TTCsr1 won t be able to use the reinitialize function. When resetting TTCsr1 there are some chances that the TTCrx of the card doesn t initialize correctly because its problem. It is then necessary to check that after the initialization time the TTCrx has the TTCRDY signal set (I/O space register 0x80, bit number 4). If the TTCRDY signal didn t changed to 1, the reset operation should be repeated. This checking should be done until a TTCRDY condition is obtained (in the tests 1 out of 2 resets didn t work). Even if TTCsr2 and 3 don t have this problem, the checking of the TTCRDY condition is recommended for every card because it is a necessary condition to start working with the card. Reprogramming of the Flash EPROM If a change of the TTCrx chip configuration bits is needed (see TTCrx Reference Manual), there is a script file to do the full process. The only thing needed will be to modify the file where these bits are into the VHDL code and then launch the process. This could be necessary also when a change of the TTCrx ID number for one card must be done. All the files and the script to run are located in the neocad account on CAE cluster. The file to modify is: /user/neocad/jferrerp/ttcproject/ttc_fpga/vhdl/prom.vhd In this small file there are some commented lines that apply for the 3 different cards. The 3 cards (labelled TTCsr1, TTCsr2 and TTCsr3) are identical but because the patch was needed to fix the TTCsr1 card problem and because every card has to get a different TTCrx ID number, if there is a need to modify the configuration bits of the TTCrx, a especial care should be taken when dealing with the commented lines that apply to every card. It should be noticed, as said in the previous section, that if the patch is applied also to cards TTCsr2 and 3, they will still work ok except the reinitialize function. In this file there are some lines like this: signal i : natural range 0 to 69; -- Card 1 -- signal i : natural range 0 to 68; -- Cards 2 and 3 This means that when generating a code for TTCsr1 card, the first line should be uncommented and the other one commented (as is in the example). There are 4 more couple of lines like this one (5 in total). There is also another single line like this: "0"& -- Card 1 This line should be uncommented for TTCsr1 and commented for the others. Finally there are the lines: 6 TTCsr Documentation
7 Test Setup " "; (TTCrx ID card 1: 21) -- " "; (TTCrx ID card 2: 22) -- " "; (TTCrx ID card 3: 23) This is where the TTCrx ID number is defined. The cards where finished with the ID numbers 21, 22 and 23 (decimal) for TTCsr1, TTCsr2 and TTCsr3 respectively as is in the example. If a change of this ID is needed for one of the cards, the bits on the proper line should be changed and uncommented leaving commented the other lines. Finally, after the modifications are completed on this file, the script should be launched. This script is: /user/neocad/jferrerp/ttcproject/ttc_fpga/gofull For the script to run correctly, there should be installed on the account the ORCA foundry version 9.1 and Galileo exemplar version Currently, neocad account has both programs set up correctly. Then, and after some time of compilation, the resulting file will be stored as: /user/neocad/jferrerp/ttcproject/ttc_fpga/prom/ttcsrprom.exo This is the file that ProgramSRecord program (from Carlos safetools) will use to reprogram the VHDL codes of the FPGAs in the TTCsr cards (where the configuration bits of the TTCrx are included). On next section it will be described the way this was done using the Test Setup and the safetools from Carlos Fernandes. Test Setup During the tests done at CERN to check the TTCsr functionality, a MVME 1604 VME card was used with a PPC603 processor card on it (instead of the originally PPC604). The login name for access to the programs used for the tests (a slightly modified version of the safetools from Carlos) is jferrerp. Once there, you have several directories: bin: main safetools programs. src: source for the bin programs. EXOfiles: files for the programming of the FPGAs. The first thing to access to the card and initialize everything is LYNX_CreateShm and then AutoTest. This can be done in one only step by using LYNX_initSPSBboard program. TTCsr Documentation 7
8 Test Setup After this if you want to reprogram the EEPROM of the card (where the FPGAs codes are), you should use the ProgramSRecord program in EXOfiles directory. But first it s necessary to check one thing. The Flash EPROM into the cards is divided in 2 banks (to hold 2 sets of codes). There is one switch into the board to choose between the 2 banks, backup set and working set. When backup set is selected, the EEPROM cannot be reprogrammed. To see which bank is selected you can use the EEPromID program. If the switch is pointing to the backup set you won t be able to see the code stored in the other bank. On the contrary, if the switch is selecting the working code you will be able to see which codes are stored in the 2 banks and also to reprogram the working and backup banks. The cards are finished with the correct codes on both safe and working banks and the switch left in the working position. If a reprogramming is needed, it can be done with ProgramSRecord program in EXOfiles directory just by doing: ProgramSRecord working.exo [backup.exo] If a backup code is not used, the existing one won t be changed (recommended, because the one stored in the backup bank is now checked and safe). After the reprogramming, the Reset program (in bin directory) and Autotest should be executed and if everything is ok the only error message should be the one related with the EPROM header recognition (in Autotest program). If there is a problem and doesn t initialize correctly, the switch of the card should be moved to backup position and then the VME should be switched off and on. After booting, the switch may be moved back again to working position if a new try with a different code is needed. The location of the EPROM switch is shown in Figure 2. EPROM Switch FIGURE 2. Location of the EPROM switch. To set the switch to working bank, the cover should be on the upper position (getting the board as in the figure). It s a very fragile switch and special care should be taken when handle it. 8 TTCsr Documentation
A[31..28] A[27..23] A[22] A[21..2] A[1] A[0] 0 Internal Memory Space SHARC A 0000 BAR[7..3] 1 Internal Memory Space SHARC B
![A[31..28] A[27..23] A[22] A[21..2] A[1] A[0] 0 Internal Memory Space SHARC A 0000 BAR[7..3] 1 Internal Memory Space SHARC B A[31..28] A[27..23] A[22] A[21..2] A[1] A[0] 0 Internal Memory Space SHARC A 0000 BAR[7..3] 1 Internal Memory Space SHARC B](/thumbs/92/109295537.jpg) MROD-Out Introduction The output part of the MROD module consists of a cluster of two output SHARCs. This cluster of SHARCs has three basic functions: 1. Drive an S-LINK 2. Connect to VMEbus 3. Receive
MROD-Out Introduction The output part of the MROD module consists of a cluster of two output SHARCs. This cluster of SHARCs has three basic functions: 1. Drive an S-LINK 2. Connect to VMEbus 3. Receive
The 9S12 in Expanded Mode - Using MSI logic to build ports Huang Chapter 14
 The 9S12 in Expanded Mode - Using MSI logic to build ports Huang Chapter 14 Using MSI Logic To Build An Output Port Many designs use standard MSI logic for microprocessor expansion This provides an inexpensive
The 9S12 in Expanded Mode - Using MSI logic to build ports Huang Chapter 14 Using MSI Logic To Build An Output Port Many designs use standard MSI logic for microprocessor expansion This provides an inexpensive
Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE Pre-Prototype
 Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE Pre-Prototype User Manual Issue: 2 Revision: 1 Reference: IPHE 2000-008, LHCb 2001-057 VELO Created: 28 February 2000 Last modified: 4 May 2001 Prepared By: Yuri Ermoline
Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE Pre-Prototype User Manual Issue: 2 Revision: 1 Reference: IPHE 2000-008, LHCb 2001-057 VELO Created: 28 February 2000 Last modified: 4 May 2001 Prepared By: Yuri Ermoline
PRINCETON (VON NEUMAN) ARCHITECTURE MICROPROCESSOR
 1 IN OUT PRINCTON (VON NUMAN) ARCHITCTUR DATA MICROPROCSSOR ALU CONTROL STATUS INSTRUCTION CONTROL CONTROL & ADDR CLOCK ADDR(N Bits) COMPUTR DATA(M Bits) CONTROL Computer with N bit address bus can access
1 IN OUT PRINCTON (VON NUMAN) ARCHITCTUR DATA MICROPROCSSOR ALU CONTROL STATUS INSTRUCTION CONTROL CONTROL & ADDR CLOCK ADDR(N Bits) COMPUTR DATA(M Bits) CONTROL Computer with N bit address bus can access
4. Verify that HDL is selected as the Top-Level Source Type, and click Next. The New Project Wizard Device Properties page appears.
 Working with the GODIL Author: Ruud Baltissen Credits: Michael Randelzhofer, Ed Spittles Date: August 2010 What is it? This document describes a way to get familiar with the Xilinx FPGAs on OHO s Godil,
Working with the GODIL Author: Ruud Baltissen Credits: Michael Randelzhofer, Ed Spittles Date: August 2010 What is it? This document describes a way to get familiar with the Xilinx FPGAs on OHO s Godil,
,879 B FAT #1 FAT #2 root directory data. Figure 1: Disk layout for a 1.44 Mb DOS diskette. B is the boot sector.
 Homework 11 Spring 2012 File Systems: Part 2 MAT 4970 April 18, 2012 Background To complete this assignment, you need to know how directories and files are stored on a 1.44 Mb diskette, formatted for DOS/Windows.
Homework 11 Spring 2012 File Systems: Part 2 MAT 4970 April 18, 2012 Background To complete this assignment, you need to know how directories and files are stored on a 1.44 Mb diskette, formatted for DOS/Windows.
µtasker Boot-loader support
 Introduction µtasker is an operating system designed especially for embedded applications where a tight control over resources is desired along with a high level of user comfort to produce efficient and
Introduction µtasker is an operating system designed especially for embedded applications where a tight control over resources is desired along with a high level of user comfort to produce efficient and
EE 308 Spring Lecture 28 March 30, 2012 Review for Exam 2. Introduction to the MC9S12 Expanded Mode
 Lecture 28 March 30, 2012 Review for Exam 2 Introduction to the MC9S12 Expanded Mode 1 Review for Exam 2 1. C Programming (a) Setting and clearing bits in registers PORTA = PORTA 0x02; PORTA = PORTA &
Lecture 28 March 30, 2012 Review for Exam 2 Introduction to the MC9S12 Expanded Mode 1 Review for Exam 2 1. C Programming (a) Setting and clearing bits in registers PORTA = PORTA 0x02; PORTA = PORTA &
Laboratory Exercise 8
 Laboratory Exercise 8 Memory Blocks In computer systems it is necessary to provide a substantial amount of memory. If a system is implemented using FPGA technology it is possible to provide some amount
Laboratory Exercise 8 Memory Blocks In computer systems it is necessary to provide a substantial amount of memory. If a system is implemented using FPGA technology it is possible to provide some amount
Kinetis Bootloader to Update Multiple Devices in a Field Bus Network
 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Document Number: AN5204 Application Note Rev. 0, 01/2016 Kinetis Bootloader to Update Multiple Devices in a Field Bus Network 1. Introduction This application note describes
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Document Number: AN5204 Application Note Rev. 0, 01/2016 Kinetis Bootloader to Update Multiple Devices in a Field Bus Network 1. Introduction This application note describes
ArduCAM-M-2MP Camera Shield
 33275-MP ArduCAM-M-2MP Camera Shield 2MP SPI Camera Hardware Application Note Rev 1.0, Mar 2015 33275-MP ArduCAM-M-2MP Hardware Application Note Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 2 2 Typical Wiring...
33275-MP ArduCAM-M-2MP Camera Shield 2MP SPI Camera Hardware Application Note Rev 1.0, Mar 2015 33275-MP ArduCAM-M-2MP Hardware Application Note Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 2 2 Typical Wiring...
Xilinx ISE8.1 and Spartan-3 Tutorial (Prepared by Kahraman Akdemir based on Professor Duckworth's Tutorials updated September 2006)
 Xilinx ISE8.1 and Spartan-3 Tutorial (Prepared by Kahraman Akdemir based on Professor Duckworth's Tutorials updated September 2006) 1 Part1) Starting a new project Simple 3-to-8 Decoder Start the Xilinx
Xilinx ISE8.1 and Spartan-3 Tutorial (Prepared by Kahraman Akdemir based on Professor Duckworth's Tutorials updated September 2006) 1 Part1) Starting a new project Simple 3-to-8 Decoder Start the Xilinx
PanelViewt 1200 Transfer Utility User Manual
 User Manual Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for the Application, Installation and Maintenance of Solid State
User Manual Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for the Application, Installation and Maintenance of Solid State
µtasker Document µtasker Bare-Minimum Boot Loader
 Embedding it better... µtasker Document µtasker Bare-Minimum Boot Loader utasker_bm_loader.doc/1.04 Copyright 2012 M.J.Butcher Consulting Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. µtasker bare-minimum loader...4
Embedding it better... µtasker Document µtasker Bare-Minimum Boot Loader utasker_bm_loader.doc/1.04 Copyright 2012 M.J.Butcher Consulting Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. µtasker bare-minimum loader...4
22 File Structure, Disk Scheduling
 Operating Systems 102 22 File Structure, Disk Scheduling Readings for this topic: Silberschatz et al., Chapters 11-13; Anderson/Dahlin, Chapter 13. File: a named sequence of bytes stored on disk. From
Operating Systems 102 22 File Structure, Disk Scheduling Readings for this topic: Silberschatz et al., Chapters 11-13; Anderson/Dahlin, Chapter 13. File: a named sequence of bytes stored on disk. From
19 File Structure, Disk Scheduling
 88 19 File Structure, Disk Scheduling Readings for this topic: Silberschatz et al., Chapters 10 11. File: a named collection of bytes stored on disk. From the OS standpoint, the file consists of a bunch
88 19 File Structure, Disk Scheduling Readings for this topic: Silberschatz et al., Chapters 10 11. File: a named collection of bytes stored on disk. From the OS standpoint, the file consists of a bunch
TPMC Digital Inputs/Outputs (Bit I/O) Version 2.0. User Manual. Issue February 2014
 The Embedded I/O Company TPMC681 64 Digital Inputs/Outputs (Bit I/O) Version 2.0 User Manual Issue 2.0.0 February 2014 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek, Germany Phone: +49 (0) 4101
The Embedded I/O Company TPMC681 64 Digital Inputs/Outputs (Bit I/O) Version 2.0 User Manual Issue 2.0.0 February 2014 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek, Germany Phone: +49 (0) 4101
CSE P567 - Winter 2010 Lab 1 Introduction to FGPA CAD Tools
 CSE P567 - Winter 2010 Lab 1 Introduction to FGPA CAD Tools This is a tutorial introduction to the process of designing circuits using a set of modern design tools. While the tools we will be using (Altera
CSE P567 - Winter 2010 Lab 1 Introduction to FGPA CAD Tools This is a tutorial introduction to the process of designing circuits using a set of modern design tools. While the tools we will be using (Altera
SD Card Controller IP Specification
 SD Card Controller IP Specification Marek Czerski Friday 30 th August, 2013 1 List of Figures 1 SoC with SD Card IP core................................ 4 2 Wishbone SD Card Controller IP Core interface....................
SD Card Controller IP Specification Marek Czerski Friday 30 th August, 2013 1 List of Figures 1 SoC with SD Card IP core................................ 4 2 Wishbone SD Card Controller IP Core interface....................
Using Synplify Pro, ISE and ModelSim
 Using Synplify Pro, ISE and ModelSim VLSI Systems on Chip ET4 351 Rene van Leuken Huib Lincklaen Arriëns Rev. 1.2 The EDA programs that will be used are: For RTL synthesis: Synplicity Synplify Pro For
Using Synplify Pro, ISE and ModelSim VLSI Systems on Chip ET4 351 Rene van Leuken Huib Lincklaen Arriëns Rev. 1.2 The EDA programs that will be used are: For RTL synthesis: Synplicity Synplify Pro For
FIRMWARE DOWNLOAD AND ON-BOARD FLASH PROM PROGRAMMING
 FIRMWARE DOWNLOAD AND ON-BOARD FLASH PROM PROGRAMMING Overview: The proposed system is to make possible, the reprogramming of the configuration PROM on the FEA On-board, so that it is not required to manually
FIRMWARE DOWNLOAD AND ON-BOARD FLASH PROM PROGRAMMING Overview: The proposed system is to make possible, the reprogramming of the configuration PROM on the FEA On-board, so that it is not required to manually
EE 308 Spring Lab on IIC Bus
 Lab on IIC Bus Next week s lab 1. Communicate with Dallas Semiconductor DS 1307 Real Time Clock (a) Set time and date in clock (b) Read time and date from clock and display 2. Display time and date on
Lab on IIC Bus Next week s lab 1. Communicate with Dallas Semiconductor DS 1307 Real Time Clock (a) Set time and date in clock (b) Read time and date from clock and display 2. Display time and date on
Using the MC9S12 in Expanded Mode External Ports S12CPUV2 Reference Manual Multiplexed External Bus Interface (MEBI) Module V3 Block User Guide
 Using the MC9S12 in Expanded Mode External Ports S12CPUV2 Reference Manual Multiplexed External Bus Interface (MEBI) Module V3 Block User Guide - Computer with N bit address bus can access 2 N bytes of
Using the MC9S12 in Expanded Mode External Ports S12CPUV2 Reference Manual Multiplexed External Bus Interface (MEBI) Module V3 Block User Guide - Computer with N bit address bus can access 2 N bytes of
475 Electronics for physicists Introduction to FPGA programming
 475 Electronics for physicists Introduction to FPGA programming Andrej Seljak, Gary Varner Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa November 18, 2015 Abstract Digital circuits based on binary
475 Electronics for physicists Introduction to FPGA programming Andrej Seljak, Gary Varner Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa November 18, 2015 Abstract Digital circuits based on binary
EE 308 Spring 2011 The MC9S12 in Expanded Mode How to get into expanded mode
 The MC9S12 in Expanded Mode How to get into expanded mode Huang Chapter 14 Module Mapping Control (MMC) V4 Block User Guide Multiplexed External Bus Interface (MEBI) Module V3 Block User Guide The MC9S12
The MC9S12 in Expanded Mode How to get into expanded mode Huang Chapter 14 Module Mapping Control (MMC) V4 Block User Guide Multiplexed External Bus Interface (MEBI) Module V3 Block User Guide The MC9S12
HCAL DCC Technical Reference E. Hazen - Revised March 27, 2007 Note: Latest version of this document should be available at:
 HCAL DCC Technical Reference E. Hazen - Revised March 27, 2007 Note: Latest version of this document should be available at: http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/cms/hcal/document/countinghouse/dcc/dcctechref.pdf Table
HCAL DCC Technical Reference E. Hazen - Revised March 27, 2007 Note: Latest version of this document should be available at: http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/cms/hcal/document/countinghouse/dcc/dcctechref.pdf Table
Dante Gonzales and Ian Doten
 Dante Gonzales and Ian Doten Overview History Game Boy and Game Boy Color Specs CPU architectures Intel 8080 Zilog Z80 Sharp LR35902 Sharp LR35902 in depth Changes from the Z80 to the LR35902 Memory Cartridge
Dante Gonzales and Ian Doten Overview History Game Boy and Game Boy Color Specs CPU architectures Intel 8080 Zilog Z80 Sharp LR35902 Sharp LR35902 in depth Changes from the Z80 to the LR35902 Memory Cartridge
MC9S12 Address Space
 MC9S12 Address Space MC9S12 has 16 address lines MC9S12 can address 2 16 distinct locations For MC9S12, each location holds one byte (eight bits) MC9S12 can address 2 16 bytes 2 16 = 65536 2 16 = 2 6 2
MC9S12 Address Space MC9S12 has 16 address lines MC9S12 can address 2 16 distinct locations For MC9S12, each location holds one byte (eight bits) MC9S12 can address 2 16 bytes 2 16 = 65536 2 16 = 2 6 2
TTC/TTS Tester (TTT) Module User Manual
 TTC/TTS Tester (TTT) Module User Manual Eric Hazen hazen@bu.edu, Christopher Woodall cwoodall@bu.edu, Charlie Hill chill90@bu.edu May 24, 2013 1 Contents 1 Overview 3 2 Quick Start Guide 4 3 Hardware Description
TTC/TTS Tester (TTT) Module User Manual Eric Hazen hazen@bu.edu, Christopher Woodall cwoodall@bu.edu, Charlie Hill chill90@bu.edu May 24, 2013 1 Contents 1 Overview 3 2 Quick Start Guide 4 3 Hardware Description
Microcontroller Systems. ELET 3232 Topic 11: General Memory Interfacing
 Microcontroller Systems ELET 3232 Topic 11: General Memory Interfacing 1 Objectives To become familiar with the concepts of memory expansion and the data and address bus To design embedded systems circuits
Microcontroller Systems ELET 3232 Topic 11: General Memory Interfacing 1 Objectives To become familiar with the concepts of memory expansion and the data and address bus To design embedded systems circuits
Using Virtual EEPROM and Flash API for Renesas MCUs RX600 Series
 Using Virtual EEPROM and Flash API for Renesas MCUs RX600 Series Description: This lab will take the user through using the Virtual EEPROM (VEE) project for RX. The user will learn to use the Virtual EEPROM
Using Virtual EEPROM and Flash API for Renesas MCUs RX600 Series Description: This lab will take the user through using the Virtual EEPROM (VEE) project for RX. The user will learn to use the Virtual EEPROM
Computer Memory Basic Concepts. Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University
 Computer Memory Basic Concepts Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University The Memory Component The memory stores the instructions and data for an
Computer Memory Basic Concepts Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University The Memory Component The memory stores the instructions and data for an
Using the KD30 Debugger
 ELEC3730 Embedded Systems Tutorial 3 Using the KD30 Debugger 1 Introduction Overview The KD30 debugger is a powerful software tool that can greatly reduce the time it takes to develop complex programs
ELEC3730 Embedded Systems Tutorial 3 Using the KD30 Debugger 1 Introduction Overview The KD30 debugger is a powerful software tool that can greatly reduce the time it takes to develop complex programs
ECE241 Digital Systems Lab 2 Altera Software Tutorial and Use
 ECE241 Digital Systems Lab 2 Altera Software Tutorial and Use Spring 2002 B. Wang, J. Zhu 1 Purpose The purpose of this lab is to learn the basics of the Altera design software: design entry, simulation
ECE241 Digital Systems Lab 2 Altera Software Tutorial and Use Spring 2002 B. Wang, J. Zhu 1 Purpose The purpose of this lab is to learn the basics of the Altera design software: design entry, simulation
5I20 ANYTHING I/O MANUAL
 5I20 ANYTHING I/O MANUAL Version 1.9 This page intentionally not blank 12 24 LOOPBACK Table of Contents GENERAL.......................................................... 1 DESCRIPTION.................................................
5I20 ANYTHING I/O MANUAL Version 1.9 This page intentionally not blank 12 24 LOOPBACK Table of Contents GENERAL.......................................................... 1 DESCRIPTION.................................................
University of Massachusetts Amherst Computer Systems Lab 1 (ECE 354) LAB 1 Reference Manual
 University of Massachusetts Amherst Computer Systems Lab 1 (ECE 354) LAB 1 Reference Manual Lab 1: Using NIOS II processor for code execution on FPGA Objectives: 1. Understand the typical design flow in
University of Massachusetts Amherst Computer Systems Lab 1 (ECE 354) LAB 1 Reference Manual Lab 1: Using NIOS II processor for code execution on FPGA Objectives: 1. Understand the typical design flow in
Implementing In-Application Programming on the ADuC702x
 Implementing In-Application Programming on the ADuC702x By Johnson Jiao [Johnson.Jiao@analog.com] and Raven Xue [Raven.Xue@analog.com] Background The ADuC702x Precision Analog Microcontroller provides
Implementing In-Application Programming on the ADuC702x By Johnson Jiao [Johnson.Jiao@analog.com] and Raven Xue [Raven.Xue@analog.com] Background The ADuC702x Precision Analog Microcontroller provides
Using the FADC250 Module (V1C - 5/5/14)
 Using the FADC250 Module (V1C - 5/5/14) 1.1 Controlling the Module Communication with the module is by standard VME bus protocols. All registers and memory locations are defined to be 4-byte entities.
Using the FADC250 Module (V1C - 5/5/14) 1.1 Controlling the Module Communication with the module is by standard VME bus protocols. All registers and memory locations are defined to be 4-byte entities.
Real-Time Systems / Real-Time Operating Systems EE445M/EE380L.6, Spring 2016
 The University of Texas at Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Real-Time Systems / Real-Time Operating Systems EE445M/EE380L.6, Spring 2016 Final Exam Date: May 12, 2016 UT EID: Printed
The University of Texas at Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Real-Time Systems / Real-Time Operating Systems EE445M/EE380L.6, Spring 2016 Final Exam Date: May 12, 2016 UT EID: Printed
Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE to ECS Interface
 Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE to ECS Interface LHCb Technical Note Issue: 1 Revision: 0 Reference: LHCb 2000-012 VELO Created: 1 February 2000 Last modified: 20 March 2000 Prepared By: Yuri Ermoline
Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE to ECS Interface LHCb Technical Note Issue: 1 Revision: 0 Reference: LHCb 2000-012 VELO Created: 1 February 2000 Last modified: 20 March 2000 Prepared By: Yuri Ermoline
RFlasher7. Getting Started and Overview. Document version
 7 Getting Started and Overview Document version 080317 Release date March 2008 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 Overview...4 2. FIRST STEPS WITH RFLASHER...5 2.1 Project options...6 2.2 File loading...7
7 Getting Started and Overview Document version 080317 Release date March 2008 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 Overview...4 2. FIRST STEPS WITH RFLASHER...5 2.1 Project options...6 2.2 File loading...7
HUNT ENGINEERING Imaging with FPGA Demo/Framework
 HUNT ENGINEERING Chestnut Court, Burton Row, Brent Knoll, Somerset, TA9 4BP, UK Tel: (+44) (0)1278 760188, Fax: (+44) (0)1278 760199, Email: sales@hunteng.co.uk www.hunteng.co.uk www.hunt-dsp.com HUNT
HUNT ENGINEERING Chestnut Court, Burton Row, Brent Knoll, Somerset, TA9 4BP, UK Tel: (+44) (0)1278 760188, Fax: (+44) (0)1278 760199, Email: sales@hunteng.co.uk www.hunteng.co.uk www.hunt-dsp.com HUNT
FPGA Interfacing of HD44780 Based LCD Using Delayed Finite State Machine (FSM)
 FPGA Interfacing of HD44780 Based LCD Using Delayed Finite State Machine (FSM) Edwin NC Mui Custom R & D Engineer Texco Enterprise Ptd. Ltd. {blackgrail2000@hotmail.com} Abstract This paper presents a
FPGA Interfacing of HD44780 Based LCD Using Delayed Finite State Machine (FSM) Edwin NC Mui Custom R & D Engineer Texco Enterprise Ptd. Ltd. {blackgrail2000@hotmail.com} Abstract This paper presents a
You will work in groups of four for the project (same groups as Project 1).
 COS/ELE 375 Prof. August Lab 2: PAW Processor Design (18 Nov 2015) Due January 12, 2015 Introduction In the prior project, you became familiar with the PAW instruction set. In this project you will design,
COS/ELE 375 Prof. August Lab 2: PAW Processor Design (18 Nov 2015) Due January 12, 2015 Introduction In the prior project, you became familiar with the PAW instruction set. In this project you will design,
Evaluation board for NXP LPC2103. User Guide. Preliminary Version updated 27 th Aug TechToys Company All Rights Reserved
 Evaluation board for NXP LPC2103 User Guide 1 SOFTWARE Download from KEIL web site at http://www.keil.com/demo/ for ARM evaluation software. Limitations to this evaluation copy have been summarized on
Evaluation board for NXP LPC2103 User Guide 1 SOFTWARE Download from KEIL web site at http://www.keil.com/demo/ for ARM evaluation software. Limitations to this evaluation copy have been summarized on
Summer 2003 Lecture 18 07/09/03
 Summer 2003 Lecture 18 07/09/03 NEW HOMEWORK Instruction Execution Times: The 8088 CPU is a synchronous machine that operates at a particular clock frequency. In the case of the original IBM PC, that clock
Summer 2003 Lecture 18 07/09/03 NEW HOMEWORK Instruction Execution Times: The 8088 CPU is a synchronous machine that operates at a particular clock frequency. In the case of the original IBM PC, that clock
AN4491 Application note
 Application note BlueNRG, BlueNRG-MS updater Introduction Note: This document describes the updater functionality of BlueNRG and BlueNRG-MS devices. The document content is valid for both BlueNRG and BlueNRG-MS
Application note BlueNRG, BlueNRG-MS updater Introduction Note: This document describes the updater functionality of BlueNRG and BlueNRG-MS devices. The document content is valid for both BlueNRG and BlueNRG-MS
NOTE: This tutorial contains many large illustrations. Page breaks have been added to keep images on the same page as the step that they represent.
 CSE 352 Tutorial # 4 Synthesizing onto an FPGA Objectives This tutorial will walk you through the steps of implementing a design made in Active-HDL onto the Altera Cyclone II FPGA NOTE: This tutorial contains
CSE 352 Tutorial # 4 Synthesizing onto an FPGA Objectives This tutorial will walk you through the steps of implementing a design made in Active-HDL onto the Altera Cyclone II FPGA NOTE: This tutorial contains
Explain the functions of the main components of a basic computer system (Part 2) S. Neebar
 Explain the functions of the main components of a basic computer system (Part 2) S. Neebar The System Unit The system unit is made up of the computer case or chassis and all the internal electronic components
Explain the functions of the main components of a basic computer system (Part 2) S. Neebar The System Unit The system unit is made up of the computer case or chassis and all the internal electronic components
Zet x86 open source SoC
 http://zet.aluzina.org v1.1 19 Feb 2010 Contents 1 2 Contents 1 2 Terasic Altera DE1 - Cyclone II FPGA http://www.terasic.com.tw Physical devices 1 FPGA 2 SDRAM 3 SRAM 4 Flash 5 SD card 6 VGA 7 50 Mhz
http://zet.aluzina.org v1.1 19 Feb 2010 Contents 1 2 Contents 1 2 Terasic Altera DE1 - Cyclone II FPGA http://www.terasic.com.tw Physical devices 1 FPGA 2 SDRAM 3 SRAM 4 Flash 5 SD card 6 VGA 7 50 Mhz
F2MC-8FX EEPROM Library
 Fujitsu Microelectronics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Application Note MCU-AN- 500019-E-23 F²MC-8FX FAMILY 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER MB95200 SERIES F2MC-8FX EEPROM Library APPLICATION NOTE Revision History Revision
Fujitsu Microelectronics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Application Note MCU-AN- 500019-E-23 F²MC-8FX FAMILY 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER MB95200 SERIES F2MC-8FX EEPROM Library APPLICATION NOTE Revision History Revision
V8-uRISC 8-bit RISC Microprocessor AllianceCORE Facts Core Specifics VAutomation, Inc. Supported Devices/Resources Remaining I/O CLBs
 V8-uRISC 8-bit RISC Microprocessor February 8, 1998 Product Specification VAutomation, Inc. 20 Trafalgar Square Nashua, NH 03063 Phone: +1 603-882-2282 Fax: +1 603-882-1587 E-mail: sales@vautomation.com
V8-uRISC 8-bit RISC Microprocessor February 8, 1998 Product Specification VAutomation, Inc. 20 Trafalgar Square Nashua, NH 03063 Phone: +1 603-882-2282 Fax: +1 603-882-1587 E-mail: sales@vautomation.com
128 CH TDC-SCALER For 10x10 GEM
 128 CH TDC-SCALER For 10x10 GEM SEA Technical Note Issue: Draft Revision: 0.9 Reference: INFN no reference Created: 25 th Nov 2010 Last modified: 1 st Feb 2013 Prepared By: A. Balla, P. Ciambrone, F.Murtas
128 CH TDC-SCALER For 10x10 GEM SEA Technical Note Issue: Draft Revision: 0.9 Reference: INFN no reference Created: 25 th Nov 2010 Last modified: 1 st Feb 2013 Prepared By: A. Balla, P. Ciambrone, F.Murtas
ECE 437 Computer Architecture and Organization Lab 6: Programming RAM and ROM Due: Thursday, November 3
 Objectives: ECE 437 Computer Architecture and Organization Lab 6: Programming RAM and ROM Due: Thursday, November 3 Build Instruction Memory and Data Memory What to hand in: Your implementation source
Objectives: ECE 437 Computer Architecture and Organization Lab 6: Programming RAM and ROM Due: Thursday, November 3 Build Instruction Memory and Data Memory What to hand in: Your implementation source
Project 1a: Hello World!
 Project 1a: Hello World! 1. Download cse465.zip from the web page. Unzip this using 7-Zip (not the Windows Utility it doesn t unzip files starting with a period) to your h:\ drive or wherever your CEC
Project 1a: Hello World! 1. Download cse465.zip from the web page. Unzip this using 7-Zip (not the Windows Utility it doesn t unzip files starting with a period) to your h:\ drive or wherever your CEC
TPMC /8 Digital Inputs (24V) 16/8 Digital Outputs (24V, 0.5A) Version 3.0. User Manual. Issue June 2014
 The Embedded I/O Company TPMC670 16/8 Digital Inputs (24V) 16/8 Digital Outputs (24V, 0.5A) Version 3.0 User Manual Issue 3.0.0 June 2014 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek, Germany Phone:
The Embedded I/O Company TPMC670 16/8 Digital Inputs (24V) 16/8 Digital Outputs (24V, 0.5A) Version 3.0 User Manual Issue 3.0.0 June 2014 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek, Germany Phone:
PCI to SH-3 AN Hitachi SH3 to PCI bus
 PCI to SH-3 AN Hitachi SH3 to PCI bus Version 1.0 Application Note FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION Complete Application Note for designing a PCI adapter or embedded system based on the Hitachi SH-3 including:
PCI to SH-3 AN Hitachi SH3 to PCI bus Version 1.0 Application Note FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION Complete Application Note for designing a PCI adapter or embedded system based on the Hitachi SH-3 including:
Homework 9: Software Design Considerations
 Homework 9: Software Design Considerations Team Code Name: Mind Readers Group No. 2 Team Member Completing This Homework: Richard Schuman E-mail Address of Team Member: _rschuman_ @ purdue.edu Evaluation:
Homework 9: Software Design Considerations Team Code Name: Mind Readers Group No. 2 Team Member Completing This Homework: Richard Schuman E-mail Address of Team Member: _rschuman_ @ purdue.edu Evaluation:
XC1700D Family of Serial Configuration PROMs. Features. Description. November 25, 1997 (Version 1.1) 0 5* Product Specification
 0 XC1700D Family of Serial Configuration PROMs November 25, 1997 (Version 1.1) 0 5* Product Specification Features Extended family of one-time programmable (OTP) bit-serial read-only memories used for
0 XC1700D Family of Serial Configuration PROMs November 25, 1997 (Version 1.1) 0 5* Product Specification Features Extended family of one-time programmable (OTP) bit-serial read-only memories used for
ECE 485/585 Microprocessor System Design
 Microprocessor System Design Lecture 4: Memory Hierarchy Memory Taxonomy SRAM Basics Memory Organization DRAM Basics Zeshan Chishti Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept Maseeh College of Engineering
Microprocessor System Design Lecture 4: Memory Hierarchy Memory Taxonomy SRAM Basics Memory Organization DRAM Basics Zeshan Chishti Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept Maseeh College of Engineering
ENGG3380: Computer Organization and Design Lab4: Buses and Peripheral Devices
 ENGG3380: Computer Organization and Design Lab4: Buses and Peripheral Devices School of Engineering, University of Guelph Winter 2017 1 Objectives: The purpose of this lab is : Learn basic bus design techniques.
ENGG3380: Computer Organization and Design Lab4: Buses and Peripheral Devices School of Engineering, University of Guelph Winter 2017 1 Objectives: The purpose of this lab is : Learn basic bus design techniques.
Lab 6: Intro to FPGAs
 Lab 6: Intro to FPGAs UC Davis Physics 116B Rev 2/22/2018 There s a saying when dealing with complex electronic systems: If you can make the LED blink, you re 90% of the way there., so in this lab you
Lab 6: Intro to FPGAs UC Davis Physics 116B Rev 2/22/2018 There s a saying when dealing with complex electronic systems: If you can make the LED blink, you re 90% of the way there., so in this lab you
PCIe-FRM16. User s Manual
 PCIe-FRM6 Users Manual (Rev.) PCIe-FRM6 User s Manual Windows, Windows000, Windows NT and Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft. We acknowledge that the trademarks or service names of all other organizations
PCIe-FRM6 Users Manual (Rev.) PCIe-FRM6 User s Manual Windows, Windows000, Windows NT and Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft. We acknowledge that the trademarks or service names of all other organizations
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL
 The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Comp 541 Digital Logic and Computer Design Prof. Montek Singh Fall 2016 Lab #5: Working with the boards! Issued Wed 9/21/16; Due Wed 9/28/16 (submit by 11:59pm)
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Comp 541 Digital Logic and Computer Design Prof. Montek Singh Fall 2016 Lab #5: Working with the boards! Issued Wed 9/21/16; Due Wed 9/28/16 (submit by 11:59pm)
and 32 bit for 32 bit. If you don t pay attention to this, there will be unexpected behavior in the ISE software and thing may not work properly!
 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE 14.7 Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Simulate the schematic circuit using ISim Part IV: Constraint, Synthesize,
This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE 14.7 Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Simulate the schematic circuit using ISim Part IV: Constraint, Synthesize,
EMU FED. --- Crate and Electronics. ESR, CERN, November B. Bylsma, S. Durkin, Jason Gilmore, Jianhui Gu, T.Y. Ling. The Ohio State University
 EMU FED --- Crate and Electronics B. Bylsma, S. Durkin, Jason Gilmore, Jianhui Gu, T.Y. Ling The Ohio State University ESR, CERN, November 2004 EMU FED Design EMU FED: Outline FED Crate & Custom Backplane
EMU FED --- Crate and Electronics B. Bylsma, S. Durkin, Jason Gilmore, Jianhui Gu, T.Y. Ling The Ohio State University ESR, CERN, November 2004 EMU FED Design EMU FED: Outline FED Crate & Custom Backplane
TPMC810. Isolated 2x CAN Bus. Version 1.1. User Manual. Issue June 2009
 The Embedded I/O Company TPMC810 Isolated 2x CAN Bus Version 1.1 User Manual Issue 1.1.6 June 2009 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek / Germany Phone: +49-(0)4101-4058-0 Fax: +49-(0)4101-4058-19
The Embedded I/O Company TPMC810 Isolated 2x CAN Bus Version 1.1 User Manual Issue 1.1.6 June 2009 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek / Germany Phone: +49-(0)4101-4058-0 Fax: +49-(0)4101-4058-19
Microprocessor Architecture. mywbut.com 1
 Microprocessor Architecture mywbut.com 1 Microprocessor Architecture The microprocessor can be programmed to perform functions on given data by writing specific instructions into its memory. The microprocessor
Microprocessor Architecture mywbut.com 1 Microprocessor Architecture The microprocessor can be programmed to perform functions on given data by writing specific instructions into its memory. The microprocessor
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. EECS 150 Spring 2000
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 150 Spring 2000 Lab #8: EPROMs This lab is to be completed with a project partner.
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 150 Spring 2000 Lab #8: EPROMs This lab is to be completed with a project partner.
PCI-FRM11. User s Manual. PCI-FRM11 User s Manual (Rev 1.1)
 PCI-FRM11 User s Manual Windows, Windows2000, Windows NT and Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft. We acknowledge that the trademarks or service names of all other organizations mentioned in this document
PCI-FRM11 User s Manual Windows, Windows2000, Windows NT and Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft. We acknowledge that the trademarks or service names of all other organizations mentioned in this document
Basic Input/Output Operations
 Basic Input/Output Operations Posted on May 9, 2008, by Ibrahim KAMAL, in Micro-controllers, tagged In this third part of the 89s52 tutorial, we are going to study the basic structure and configuration
Basic Input/Output Operations Posted on May 9, 2008, by Ibrahim KAMAL, in Micro-controllers, tagged In this third part of the 89s52 tutorial, we are going to study the basic structure and configuration
The 9S12 in Expanded Mode - How to get into expanded mode Huang Chapter 14
 The 9S2 in Expanded Mode - How to get into expanded mode Huang Chapter 4 Getting into expanded mode The HCS2 can operate in several modes: Normal Single-Chip Mode (the way we have been using the HCS2)
The 9S2 in Expanded Mode - How to get into expanded mode Huang Chapter 4 Getting into expanded mode The HCS2 can operate in several modes: Normal Single-Chip Mode (the way we have been using the HCS2)
Lab 6: Integrated the Decoder with Muti-bit Counter and Programming a FPGA
 Lab 6: Integrated the Decoder with Muti-bit Counter and Programming a FPGA For your report: The problem written in English The flowchart or function table to solve the problem if it is necessary The design
Lab 6: Integrated the Decoder with Muti-bit Counter and Programming a FPGA For your report: The problem written in English The flowchart or function table to solve the problem if it is necessary The design
The Simon State Machine Part 1
 The Simon State Machine Part 1 Lab Summary This lab is the first part to a two-part lab where you will be combining all the components you created throughout the semester into one functioning state machine.
The Simon State Machine Part 1 Lab Summary This lab is the first part to a two-part lab where you will be combining all the components you created throughout the semester into one functioning state machine.
Name EGR 2131 Lab #6 Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits
 Name EGR 2131 Lab #6 Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits Equipment and Components Quartus software and Altera DE2-115 board PART 1: Number Representation in Microsoft Calculator. First, let s
Name EGR 2131 Lab #6 Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits Equipment and Components Quartus software and Altera DE2-115 board PART 1: Number Representation in Microsoft Calculator. First, let s
Micro-Research Finland Oy Välitalontie 83 C, FI Helsinki, Finland. Four-Channel Timer 4CHTIM Technical Reference Contents
 Date: 03 June 2005 Issue: 1 Page: 1 of 17 Author: Jukka Pietarinen Four-Channel Timer 4CHTIM Technical Reference Contents Introduction...3 Four-Channel Timer Block Diagrams...3 Delay Channel...3 RF Clock
Date: 03 June 2005 Issue: 1 Page: 1 of 17 Author: Jukka Pietarinen Four-Channel Timer 4CHTIM Technical Reference Contents Introduction...3 Four-Channel Timer Block Diagrams...3 Delay Channel...3 RF Clock
ADQ14 Development Kit
 ADQ14 Development Kit Documentation : P Devices PD : ecurity Class: : Release : P Devices Page 2(of 21) ecurity class Table of Contents 1 Tools...3 2 Overview...4 2.1 High-level block overview...4 3 How
ADQ14 Development Kit Documentation : P Devices PD : ecurity Class: : Release : P Devices Page 2(of 21) ecurity class Table of Contents 1 Tools...3 2 Overview...4 2.1 High-level block overview...4 3 How
CPCI-IPC. Intelligent DSP Based Dual IndustryPack Carrier for CompactPCI systems REFERENCE MANUAL Version 2.
 CPCI-IPC Intelligent DSP Based Dual IndustryPack Carrier for CompactPCI systems REFERENCE MANUAL 724-20-000-4000 Version 2.0 May 1998 ALPHI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION 6202 S. Maple Avenue #120 Tempe, AZ 85283
CPCI-IPC Intelligent DSP Based Dual IndustryPack Carrier for CompactPCI systems REFERENCE MANUAL 724-20-000-4000 Version 2.0 May 1998 ALPHI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION 6202 S. Maple Avenue #120 Tempe, AZ 85283
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
PCI-HPDI32A-COS User Manual
 PCI-HPDI32A-COS User Manual Preliminary 8302A Whitesburg Drive Huntsville, AL 35802 Phone: (256) 880-8787 Fax: (256) 880-8788 URL: www.generalstandards.com E-mail: support@generalstandards.com User Manual
PCI-HPDI32A-COS User Manual Preliminary 8302A Whitesburg Drive Huntsville, AL 35802 Phone: (256) 880-8787 Fax: (256) 880-8788 URL: www.generalstandards.com E-mail: support@generalstandards.com User Manual
Virtual Memory (Real Memory POV)
 Virtual Memory (Real Memory POV) Computer Systems Chapter 9.1-9.6 Process Resources Each process THINKS it owns all machine resources virtual processor, virtual memory, virtual keyboard, virtual monitor,
Virtual Memory (Real Memory POV) Computer Systems Chapter 9.1-9.6 Process Resources Each process THINKS it owns all machine resources virtual processor, virtual memory, virtual keyboard, virtual monitor,
ATLAS TDAQ DATAFLOW. RoI Builder Manual. Abstract ATL-DQ-ON Document Version: 3 Document Issue: 6. Document Date: 22/2/05 Document Status:
 ATLAS ATL-DQ-ON-0005 DATAFLOW RoI Builder Manual Document Version: 3 Document Issue: 6 Document ID: Document Date: 22/2/05 Document Status: ATLAS-TDAQ-2004-XXX Abstract This report describes the ATLAS
ATLAS ATL-DQ-ON-0005 DATAFLOW RoI Builder Manual Document Version: 3 Document Issue: 6 Document ID: Document Date: 22/2/05 Document Status: ATLAS-TDAQ-2004-XXX Abstract This report describes the ATLAS
8-Bit Wonderland. Executing custom Code on the Nintendo Game Boy. Belial
 8-Bit Wonderland Executing custom Code on the Nintendo Game Boy Belial 29.05.2010 Table of contents 1 Fade In 2 Hardware 3 Software 4 Injection 5 Fade Out Belial 8-Bit Wonderland 2 / 36 Kickstart Belial
8-Bit Wonderland Executing custom Code on the Nintendo Game Boy Belial 29.05.2010 Table of contents 1 Fade In 2 Hardware 3 Software 4 Injection 5 Fade Out Belial 8-Bit Wonderland 2 / 36 Kickstart Belial
XC1701L (3.3V), XC1701 (5.0V) and XC17512L (3.3V) Serial Configuration PROMs. Features. Description
 0 XC1701L (3.3V), XC1701 (5.0V) and XC17512L (3.3V) Serial Configuration PROMs December 10, 1997 (Version 1.1) 0 5* Product Specification Features On-chip address counter, incremented by each rising edge
0 XC1701L (3.3V), XC1701 (5.0V) and XC17512L (3.3V) Serial Configuration PROMs December 10, 1997 (Version 1.1) 0 5* Product Specification Features On-chip address counter, incremented by each rising edge
ROBIN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A. Saclay - DAPNIA
 1 ROBIN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A. Saclay - DAPNIA 2 Basic principles Data flow : output < input including L2 and L3 according
1 ROBIN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A. Saclay - DAPNIA 2 Basic principles Data flow : output < input including L2 and L3 according
Board-Data Processing. VHDL Exercises. Exercise 1: Basics of VHDL Programming. Stages of the Development process using FPGA s in Xilinx ISE.
 Board-Data Processing VHDL Exercises Exercise 1: Basics of VHDL Programming Stages of the Development process using FPGA s in Xilinx ISE. Basics of VHDL VHDL (Very High Speed IC Hardware description Language)
Board-Data Processing VHDL Exercises Exercise 1: Basics of VHDL Programming Stages of the Development process using FPGA s in Xilinx ISE. Basics of VHDL VHDL (Very High Speed IC Hardware description Language)
The purpose of this course is to provide an introduction to the RL78's flash features and archectecture including security features, code and data
 1 The purpose of this course is to provide an introduction to the RL78's flash features and archectecture including security features, code and data flash organization as well as self and external programming
1 The purpose of this course is to provide an introduction to the RL78's flash features and archectecture including security features, code and data flash organization as well as self and external programming
Act! Link for Accounting Administrator Guide
 Act! Link for Accounting Administrator Guide Contents Act! Link for Accounting Introduction Page 3 Compatibility Page 5 Server Preparation Page 6 Act! Link for Accounting Program Installation Page 22 Registration
Act! Link for Accounting Administrator Guide Contents Act! Link for Accounting Introduction Page 3 Compatibility Page 5 Server Preparation Page 6 Act! Link for Accounting Program Installation Page 22 Registration
SP LOCKER USER MANUAL. v1.0
 SP LOCKER USER MANUAL v1.0 Table of Contents 1 Introduction to the SP Locker Security Software... 2 2 Before You Get Started... 2 3 Features... 2 4 Public and Secured Partition... 3 5 How to use SP Locker...
SP LOCKER USER MANUAL v1.0 Table of Contents 1 Introduction to the SP Locker Security Software... 2 2 Before You Get Started... 2 3 Features... 2 4 Public and Secured Partition... 3 5 How to use SP Locker...
Virtual Memory 1. Virtual Memory
 Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
int $0x32 // call interrupt number 50
 Kernel Programming: Process isolation, goal to make programs run fast and reliably o Processes should not affect others, unless there s a specific and allowed communication channel o Each process can act
Kernel Programming: Process isolation, goal to make programs run fast and reliably o Processes should not affect others, unless there s a specific and allowed communication channel o Each process can act
VS1000 Uart Audio Module. V1.0 Software User's Guide
 Public Document v1.0 2012-09-11 PkP VS1000 Uart Audio Module V1.0 Software User's Guide About VS1000 Uart Audio Module is an alternative software for the VS1000 Audio Module (http://www.vlsi.fi/en/products/vs1000module.html).
Public Document v1.0 2012-09-11 PkP VS1000 Uart Audio Module V1.0 Software User's Guide About VS1000 Uart Audio Module is an alternative software for the VS1000 Audio Module (http://www.vlsi.fi/en/products/vs1000module.html).
Virtual Memory 1. Virtual Memory
 Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
CISC 7310X. C08: Virtual Memory. Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College. 3/22/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College
 CISC 7310X C08: Virtual Memory Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 3/22/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Concepts of virtual address space, paging, virtual page,
CISC 7310X C08: Virtual Memory Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 3/22/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Concepts of virtual address space, paging, virtual page,
TTCrx Receiver User Manual
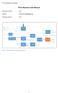 Document version: v0.1 TTCrx Receiver User Manual Author: Johan Alme (jalm@hib.no) Firmware version: v2.0 RCU BUS TTC clk 40 MHz TTC Reset TTC registers asynch TTC Ready TTC ch A cha Decoder L0 / L1a Receiving
Document version: v0.1 TTCrx Receiver User Manual Author: Johan Alme (jalm@hib.no) Firmware version: v2.0 RCU BUS TTC clk 40 MHz TTC Reset TTC registers asynch TTC Ready TTC ch A cha Decoder L0 / L1a Receiving
Summer 2009 UDP/IPv4 FPGA command protocol
 Summer 2009 UDP/IPv4 FPGA command protocol UDP/IPv4 FPGA command protocol - Harro Verkouter - verkouter@jive.nl 1 Introduction This document will serve as reference for those developers who wish to implement
Summer 2009 UDP/IPv4 FPGA command protocol UDP/IPv4 FPGA command protocol - Harro Verkouter - verkouter@jive.nl 1 Introduction This document will serve as reference for those developers who wish to implement
The FAT File System. 1. FAT Overview. 2. Boot Sector, FAT, Root Directory, and Files The FAT F 䤀耄 le System
 CIS 24 Home http://www.c jump.com/cis24/cis24syllabus.htm The FAT File System 1. FAT Overview 2. Boot Sector, FAT, Root Directory, and Files 3. FAT File System Layout 4. FAT Clusters and Sectors 5. FAT,
CIS 24 Home http://www.c jump.com/cis24/cis24syllabus.htm The FAT File System 1. FAT Overview 2. Boot Sector, FAT, Root Directory, and Files 3. FAT File System Layout 4. FAT Clusters and Sectors 5. FAT,
Chapter TEN. Memory and Memory Interfacing
 Chapter TEN Memory and Memory Interfacing OBJECTIVES this chapter enables the student to: Define the terms capacity, organization, and speed as used in semiconductor memories. Calculate the chip capacity
Chapter TEN Memory and Memory Interfacing OBJECTIVES this chapter enables the student to: Define the terms capacity, organization, and speed as used in semiconductor memories. Calculate the chip capacity
TPMC Channel Isolated Serial Interface RS232. Version 1.0. User Manual. Issue August 2017
 The Embedded I/O Company TPMC860 4 Channel Isolated Serial Interface RS232 Version 1.0 User Manual Issue 1.0.4 August 2017 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek, Germany Phone: +49 (0) 4101
The Embedded I/O Company TPMC860 4 Channel Isolated Serial Interface RS232 Version 1.0 User Manual Issue 1.0.4 August 2017 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek, Germany Phone: +49 (0) 4101
Computer Structure Lab. RESA b1monitor PROGRAM USER GUIDE
 Computer Structure Lab RESA b1monitor PROGRAM USER GUIDE Text Editor Compiler Hardware Monitor Simulator Graph Generator Hardware interface Software-hardware communication protocol FPGA Department of Systems
Computer Structure Lab RESA b1monitor PROGRAM USER GUIDE Text Editor Compiler Hardware Monitor Simulator Graph Generator Hardware interface Software-hardware communication protocol FPGA Department of Systems
