Semantic 3D Reconstruction of Heads Supplementary Material
|
|
|
- Aubrie Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
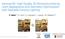
1 Semantic 3D Reconstruction of Heads Supplementary Material Fabio Maninchedda1, Christian Ha ne2,?, Bastien Jacquet3,?, Amae l Delaunoy?, Marc Pollefeys1,4 1 ETH Zurich 2 UC Berkeley 3 Kitware SAS 4 Microsoft Fig. 1: From left to right: Input image; Input labels and depth; Depth map fusion (TV-Flux fusion from [9]); Statistical model of [7] fitted into our raw input data; Our semantic reconstruction; Our result skin class only; Our model textured.? Work done while authors were at the Department of Computer Science, ETH Zu rich
2 2 F. Maninchedda, C. Häne, B. Jacquet, A. Delaunoy, M. Pollefeys 1 Additional Renderings and Visualizations Fig. 2: From left to right: Close-up of input image; Close-up of baseline using VisualSFM [8] + PMVS [2] + PSR [5]; Close-up of depth map fusion (TV-Flux fusion from [9]); Close-up of statistical face model of [7] fitted into our raw input data (depth maps + semantic labels); Close-up of our result (all classes merged). In this section we show results on two additional datasets and more comparisons as indicated in Sec. 5 of the main paper. For completeness in Fig. 1 we show all of our results, including those shown in the main paper. To point out methods that make use of prior information for the skin class we have used skin colored models. To facilitate a fair comparison of the reconstruction quality we have rendered the output of the different methods and our result in gray in Fig. 3. The surfaces of the models computed with the TV-Flux fusion approach [9] look a bit rough on some models. This is because there is a trade-off between smoothness and the amount of reconstructed geometry. If the smoothness is too strong the models shrink considerably due to the well known shrinking bias of methods penalizing the surface area. This is especially true for models where we have only captured images of the front of the head. We believe that Fig. 3 and Fig. 2 clearly show that the shape prior formulation that our method uses is effective at removing small artifacts present in the baselines that do not use any prior information while preserving details that are explained strongly by the data. The rather low quality of the reconstruction that we achieve using patch-based multi-view stereo (PMVS) [2] with subsequent Poission surface reconstruction (PSR) [5] is due to
3 Semantic Reconstruction of Heads Supplementary Material 3 the fact that the input data is captured in an uncontrolled environment without any special camera setup. The results that we achieve are very similar in quailty to the results presented in [6]. This method is very similar to PMVS and data which is used for their results on faces, is closer to the kind of data that we used than what is more commonly used for getting high quality results using PMVS and PSR. Fig. 3: From left to right: Input image; Baseline using VisualSFM [8] + PMVS [2] + PSR [5]; Baseline depth map fusion (TV-Flux fusion from [9]); Statistical face model of [7] fitted into our raw input data (depth maps + semantic labels); Our result (all classes merged).
4 4 F. Maninchedda, C. Häne, B. Jacquet, A. Delaunoy, M. Pollefeys Fig. 4: Some example 3D prints (all classes merged and skin class only). Due to the volumetric nature of our reconstructions they can naturally be 3D printed. In Fig. 4 we show some example printouts. 2 Object Shape Prior Comparison As indicated in Sec. 3.3 of the main paper we show in Fig. 5 that the proposed Wulff shape approximation is effective at removing artifacts caused by the discretization of the directions. This is due to the fact that we are directly fitting the surrogate Wulff shapes into the original training data and do not need to discretize the directions. This allows us to achieve a much smoother reconstruction of the unobserved surface between the hair and the skin on the top of the head and removes some of the edginess around the jaw bone where often the data is not very strong. At this point we also want to make two remarks about the used formulations: Despite the fact that some normal directions are discretized in this shape prior formulation it is fundamentally different form a purely discrete graphbased formulation. In a discrete graph-based formulation, in order to represent arbitrary directions, connections between not directly neighboring nodes need to be included. In the continuously inspired shape prior formulation that we are using, half spaces with arbitrary direction can be included in the Wulff shape even tough only directly neighboring voxels are linked with constraints. This is thanks to the fact that in the continuously inspired formulation the connectivity is introduced into the formulation as a discretization of the gradient operator which is independent of the surface direction. When using the original shape prior formulation of [3] the surface between the hair and the skin which is not observed gets reconstructed as facets which only have a discrete set of surface normals. This is due to the representation
5 Semantic Reconstruction of Heads Supplementary Material 5 of the Wulff shapes as polyhedra. Already in [1] it is pointed out for the 2D case that polygonal Wulff shapes lead to piecewise linear boundaries. 1 cluster 2 clusters 3 clusters General Wulff shape Fig. 5: (Left) Slice through the proposed volumetric shape prior (see main paper for more details). (Middle) Reconstruction that uses only general Wulff shapes as proposed in [3]. (Right) Proposed approach. 3 Data Term Comparison As indicated in Sec. 3 of the main paper, using the data term from [4] is not a viable choice in the presence of thin layers of semantic classes. For this experiment we collapsed the beard, eyebrow and hair label to a single hair label. Fig. 6 shows that using the data term originally proposed in [4] does not lead to satisfactory results in the presence of thin layers of semantic classes such as the facial hair on top of the skin. Fig. 6: Comparison between our proposed data term and the one from [4]: Left to right, data term from [4] with all labels and just skin label, our proposed data term with all labels and just skin label. 4 Additional Alignment Experiment To illustrate the importance of the optimization with respect to the alignment we also conducted an experiment where we omitted this part of the optimization. Therefore, the alignment is purely based on the initial landmark based registration. A comparison between with and without optimization with respect
6 6 F. Maninchedda, C. Häne, B. Jacquet, A. Delaunoy, M. Pollefeys to the alignment is shown in Fig. 7. It is clearly visible that the optimization with respect to the alignement has a siginificant impact on the reconstruction quality. Fig. 7: From left to right: Semantic model without alignment; Skin class only without alignment; Aligned semantic model; Skin class only for aligned model. References 1. Esedoglu, S., Osher, S.J.: Decomposition of images by the anisotropic rudin-osherfatemi model. Communications on pure and applied mathematics (2004) 2. Furukawa, Y., Ponce, J.: Accurate, dense, and robust multi-view stereopsis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) (2010) 3. Häne, C., Savinov, N., Pollefeys, M.: Class specific 3d object shape priors using surface normals. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014) 4. Häne, C., Zach, C., Cohen, A., Angst, R., Pollefeys, M.: Joint 3d scene reconstruction and class segmentation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2013) 5. Kazhdan, M., Bolitho, M., Hoppe, H.: Poisson surface reconstruction. In: Eurographics symposium on Geometry processing (SGP) (2006) 6. Lhuillier, M., Quan, L.: A quasi-dense approach to surface reconstruction from uncalibrated images. Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) (2005) 7. Paysan, P., Knothe, R., Amberg, B., Romdhani, S., Vetter, T.: A 3d face model for pose and illumination invariant face recognition (2009) 8. Wu, C.: Visualsfm: A visual structure from motion system. (2011) 9. Zach, C.: Fast and high quality fusion of depth maps. In: International Symposium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization and Transmission (3DPVT) (2008)
Geometric and Semantic 3D Reconstruction: Part 4A: Volumetric Semantic 3D Reconstruction. CVPR 2017 Tutorial Christian Häne UC Berkeley
 Geometric and Semantic 3D Reconstruction: Part 4A: Volumetric Semantic 3D Reconstruction CVPR 2017 Tutorial Christian Häne UC Berkeley Dense Multi-View Reconstruction Goal: 3D Model from Images (Depth
Geometric and Semantic 3D Reconstruction: Part 4A: Volumetric Semantic 3D Reconstruction CVPR 2017 Tutorial Christian Häne UC Berkeley Dense Multi-View Reconstruction Goal: 3D Model from Images (Depth
Discrete Optimization of Ray Potentials for Semantic 3D Reconstruction
 Discrete Optimization of Ray Potentials for Semantic 3D Reconstruction Marc Pollefeys Joined work with Nikolay Savinov, Christian Haene, Lubor Ladicky 2 Comparison to Volumetric Fusion Higher-order ray
Discrete Optimization of Ray Potentials for Semantic 3D Reconstruction Marc Pollefeys Joined work with Nikolay Savinov, Christian Haene, Lubor Ladicky 2 Comparison to Volumetric Fusion Higher-order ray
Multi-view Stereo. Ivo Boyadzhiev CS7670: September 13, 2011
 Multi-view Stereo Ivo Boyadzhiev CS7670: September 13, 2011 What is stereo vision? Generic problem formulation: given several images of the same object or scene, compute a representation of its 3D shape
Multi-view Stereo Ivo Boyadzhiev CS7670: September 13, 2011 What is stereo vision? Generic problem formulation: given several images of the same object or scene, compute a representation of its 3D shape
A Patch Prior for Dense 3D Reconstruction in Man-Made Environments
 A Patch Prior for Dense 3D Reconstruction in Man-Made Environments Christian Häne 1, Christopher Zach 2, Bernhard Zeisl 1, Marc Pollefeys 1 1 ETH Zürich 2 MSR Cambridge October 14, 2012 A Patch Prior for
A Patch Prior for Dense 3D Reconstruction in Man-Made Environments Christian Häne 1, Christopher Zach 2, Bernhard Zeisl 1, Marc Pollefeys 1 1 ETH Zürich 2 MSR Cambridge October 14, 2012 A Patch Prior for
3D Computer Vision. Dense 3D Reconstruction II. Prof. Didier Stricker. Christiano Gava
 3D Computer Vision Dense 3D Reconstruction II Prof. Didier Stricker Christiano Gava Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de
3D Computer Vision Dense 3D Reconstruction II Prof. Didier Stricker Christiano Gava Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de
Dense 3D Reconstruction. Christiano Gava
 Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Today: dense 3D reconstruction The matching problem
Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Today: dense 3D reconstruction The matching problem
Dense 3D Reconstruction. Christiano Gava
 Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Wide baseline matching (SIFT) Today: dense 3D reconstruction
Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Wide baseline matching (SIFT) Today: dense 3D reconstruction
Multi-view stereo. Many slides adapted from S. Seitz
 Multi-view stereo Many slides adapted from S. Seitz Beyond two-view stereo The third eye can be used for verification Multiple-baseline stereo Pick a reference image, and slide the corresponding window
Multi-view stereo Many slides adapted from S. Seitz Beyond two-view stereo The third eye can be used for verification Multiple-baseline stereo Pick a reference image, and slide the corresponding window
An Overview of Recent Progress in Volumetric Semantic 3D Reconstruction
 An Overview of Recent Progress in Volumetric Semantic 3D Reconstruction (Invited Paper) Christian Häne Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley, USA
An Overview of Recent Progress in Volumetric Semantic 3D Reconstruction (Invited Paper) Christian Häne Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley, USA
Deep Models for 3D Reconstruction
 Deep Models for 3D Reconstruction Andreas Geiger Autonomous Vision Group, MPI for Intelligent Systems, Tübingen Computer Vision and Geometry Group, ETH Zürich October 12, 2017 Max Planck Institute for
Deep Models for 3D Reconstruction Andreas Geiger Autonomous Vision Group, MPI for Intelligent Systems, Tübingen Computer Vision and Geometry Group, ETH Zürich October 12, 2017 Max Planck Institute for
SIMPLE ROOM SHAPE MODELING WITH SPARSE 3D POINT INFORMATION USING PHOTOGRAMMETRY AND APPLICATION SOFTWARE
 SIMPLE ROOM SHAPE MODELING WITH SPARSE 3D POINT INFORMATION USING PHOTOGRAMMETRY AND APPLICATION SOFTWARE S. Hirose R&D Center, TOPCON CORPORATION, 75-1, Hasunuma-cho, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, Japan Commission
SIMPLE ROOM SHAPE MODELING WITH SPARSE 3D POINT INFORMATION USING PHOTOGRAMMETRY AND APPLICATION SOFTWARE S. Hirose R&D Center, TOPCON CORPORATION, 75-1, Hasunuma-cho, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, Japan Commission
arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 22 May 2016
![arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 22 May 2016 arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 22 May 2016](/thumbs/81/83442475.jpg) Semantic 3D Reconstruction with Continuous Regularization and Ray Potentials Using a Visibility Consistency Constraint arxiv:604.02885v2 [cs.cv] 22 May 206 Nikolay Savinov, Christian Häne, L ubor Ladický
Semantic 3D Reconstruction with Continuous Regularization and Ray Potentials Using a Visibility Consistency Constraint arxiv:604.02885v2 [cs.cv] 22 May 206 Nikolay Savinov, Christian Häne, L ubor Ladický
Supplementary Material for A Multi-View Stereo Benchmark with High-Resolution Images and Multi-Camera Videos
 Supplementary Material for A Multi-View Stereo Benchmark with High-Resolution Images and Multi-Camera Videos Thomas Schöps 1 Johannes L. Schönberger 1 Silvano Galliani 2 Torsten Sattler 1 Konrad Schindler
Supplementary Material for A Multi-View Stereo Benchmark with High-Resolution Images and Multi-Camera Videos Thomas Schöps 1 Johannes L. Schönberger 1 Silvano Galliani 2 Torsten Sattler 1 Konrad Schindler
Panoramic Image Stitching
 Mcgill University Panoramic Image Stitching by Kai Wang Pengbo Li A report submitted in fulfillment for the COMP 558 Final project in the Faculty of Computer Science April 2013 Mcgill University Abstract
Mcgill University Panoramic Image Stitching by Kai Wang Pengbo Li A report submitted in fulfillment for the COMP 558 Final project in the Faculty of Computer Science April 2013 Mcgill University Abstract
Stereo Depth Map Fusion for Robot Navigation
 Stereo Depth Map Fusion for Robot Navigation Christian Häne 1, Christopher Zach 1, Jongwoo Lim 2, Ananth Ranganathan 2 and Marc Pollefeys 1 Department of Computer Science 1 ETH Zürich, Switzerland Honda
Stereo Depth Map Fusion for Robot Navigation Christian Häne 1, Christopher Zach 1, Jongwoo Lim 2, Ananth Ranganathan 2 and Marc Pollefeys 1 Department of Computer Science 1 ETH Zürich, Switzerland Honda
3D Reconstruction Of Occluded Objects From Multiple Views
 3D Reconstruction Of Occluded Objects From Multiple Views Cong Qiaoben Stanford University Dai Shen Stanford University Kaidi Yan Stanford University Chenye Zhu Stanford University Abstract In this paper
3D Reconstruction Of Occluded Objects From Multiple Views Cong Qiaoben Stanford University Dai Shen Stanford University Kaidi Yan Stanford University Chenye Zhu Stanford University Abstract In this paper
3D Fusion of Infrared Images with Dense RGB Reconstruction from Multiple Views - with Application to Fire-fighting Robots
 3D Fusion of Infrared Images with Dense RGB Reconstruction from Multiple Views - with Application to Fire-fighting Robots Yuncong Chen 1 and Will Warren 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
3D Fusion of Infrared Images with Dense RGB Reconstruction from Multiple Views - with Application to Fire-fighting Robots Yuncong Chen 1 and Will Warren 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Project Updates Short lecture Volumetric Modeling +2 papers
 Volumetric Modeling Schedule (tentative) Feb 20 Feb 27 Mar 5 Introduction Lecture: Geometry, Camera Model, Calibration Lecture: Features, Tracking/Matching Mar 12 Mar 19 Mar 26 Apr 2 Apr 9 Apr 16 Apr 23
Volumetric Modeling Schedule (tentative) Feb 20 Feb 27 Mar 5 Introduction Lecture: Geometry, Camera Model, Calibration Lecture: Features, Tracking/Matching Mar 12 Mar 19 Mar 26 Apr 2 Apr 9 Apr 16 Apr 23
Structure from Motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
Semantic 3D Reconstruction with Continuous Regularization and Ray Potentials Using a Visibility Consistency Constraint
 Semantic 3D Reconstruction with Continuous Regularization and Ray Potentials Using a Visibility Consistency Constraint Nikolay Savinov, Christian Häne, L ubor Ladický and Marc Pollefeys ETH Zürich, Switzerland
Semantic 3D Reconstruction with Continuous Regularization and Ray Potentials Using a Visibility Consistency Constraint Nikolay Savinov, Christian Häne, L ubor Ladický and Marc Pollefeys ETH Zürich, Switzerland
BIL Computer Vision Apr 16, 2014
 BIL 719 - Computer Vision Apr 16, 2014 Binocular Stereo (cont d.), Structure from Motion Aykut Erdem Dept. of Computer Engineering Hacettepe University Slide credit: S. Lazebnik Basic stereo matching algorithm
BIL 719 - Computer Vision Apr 16, 2014 Binocular Stereo (cont d.), Structure from Motion Aykut Erdem Dept. of Computer Engineering Hacettepe University Slide credit: S. Lazebnik Basic stereo matching algorithm
3D Computer Vision. Structured Light II. Prof. Didier Stricker. Kaiserlautern University.
 3D Computer Vision Structured Light II Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Introduction
3D Computer Vision Structured Light II Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Introduction
Step-by-Step Model Buidling
 Step-by-Step Model Buidling Review Feature selection Feature selection Feature correspondence Camera Calibration Euclidean Reconstruction Landing Augmented Reality Vision Based Control Sparse Structure
Step-by-Step Model Buidling Review Feature selection Feature selection Feature correspondence Camera Calibration Euclidean Reconstruction Landing Augmented Reality Vision Based Control Sparse Structure
Face Reconstruction on Mobile Devices Using a Height Map Shape Model and Fast Regularization
 Face Reconstruction on Mobile Devices Using a Height Map Shape Model and Fast Regularization Fabio Maninchedda 1, Christian Häne, Martin R. Oswald 1, and Marc Pollefeys 1,3 1 ETH Zürich, Switzerland University
Face Reconstruction on Mobile Devices Using a Height Map Shape Model and Fast Regularization Fabio Maninchedda 1, Christian Häne, Martin R. Oswald 1, and Marc Pollefeys 1,3 1 ETH Zürich, Switzerland University
Talk plan. 3d model. Applications: cultural heritage 5/9/ d shape reconstruction from photographs: a Multi-View Stereo approach
 Talk plan 3d shape reconstruction from photographs: a Multi-View Stereo approach Introduction Multi-View Stereo pipeline Carlos Hernández George Vogiatzis Yasutaka Furukawa Google Aston University Google
Talk plan 3d shape reconstruction from photographs: a Multi-View Stereo approach Introduction Multi-View Stereo pipeline Carlos Hernández George Vogiatzis Yasutaka Furukawa Google Aston University Google
Supplementary Materials for A Lighting Robust Fitting Approach of 3D Morphable Model For Face Reconstruction
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Supplementary Materials for A Lighting Robust Fitting Approach of 3D Morphable Model For Face Reconstruction Mingyang Ma Silong Peng Xiyuan Hu Received:
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Supplementary Materials for A Lighting Robust Fitting Approach of 3D Morphable Model For Face Reconstruction Mingyang Ma Silong Peng Xiyuan Hu Received:
What have we leaned so far?
 What have we leaned so far? Camera structure Eye structure Project 1: High Dynamic Range Imaging What have we learned so far? Image Filtering Image Warping Camera Projection Model Project 2: Panoramic
What have we leaned so far? Camera structure Eye structure Project 1: High Dynamic Range Imaging What have we learned so far? Image Filtering Image Warping Camera Projection Model Project 2: Panoramic
Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect
 Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect Ruizhe Wang*, Matthias Hernandez*, Jongmoo Choi, Gérard Medioni Computer Vision Lab, IRIS University of Southern California Abstract In this
Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect Ruizhe Wang*, Matthias Hernandez*, Jongmoo Choi, Gérard Medioni Computer Vision Lab, IRIS University of Southern California Abstract In this
Chaplin, Modern Times, 1936
 Chaplin, Modern Times, 1936 [A Bucket of Water and a Glass Matte: Special Effects in Modern Times; bonus feature on The Criterion Collection set] Multi-view geometry problems Structure: Given projections
Chaplin, Modern Times, 1936 [A Bucket of Water and a Glass Matte: Special Effects in Modern Times; bonus feature on The Criterion Collection set] Multi-view geometry problems Structure: Given projections
3D Wikipedia: Using online text to automatically label and navigate reconstructed geometry
 3D Wikipedia: Using online text to automatically label and navigate reconstructed geometry Bryan C. Russell et al. SIGGRAPH Asia 2013 Presented by YoungBin Kim 2014. 01. 10 Abstract Produce annotated 3D
3D Wikipedia: Using online text to automatically label and navigate reconstructed geometry Bryan C. Russell et al. SIGGRAPH Asia 2013 Presented by YoungBin Kim 2014. 01. 10 Abstract Produce annotated 3D
Computer Vision Lecture 17
 Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics 13.01.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Seminar in the summer semester
Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics 13.01.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Seminar in the summer semester
Computer Vision Lecture 17
 Announcements Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics Seminar in the summer semester Current Topics in Computer Vision and Machine Learning Block seminar, presentations in 1 st week
Announcements Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics Seminar in the summer semester Current Topics in Computer Vision and Machine Learning Block seminar, presentations in 1 st week
Direction Matters: Depth Estimation with a Surface Normal Classifier
 Direction Matters: Depth Estimation with a Surface Normal Classifier Christian Häne, L ubor Ladický, Marc Pollefeys Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich, Switzerland {christian.haene, lubor.ladicky,
Direction Matters: Depth Estimation with a Surface Normal Classifier Christian Häne, L ubor Ladický, Marc Pollefeys Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich, Switzerland {christian.haene, lubor.ladicky,
Real-Time Scene Reconstruction. Remington Gong Benjamin Harris Iuri Prilepov
 Real-Time Scene Reconstruction Remington Gong Benjamin Harris Iuri Prilepov June 10, 2010 Abstract This report discusses the implementation of a real-time system for scene reconstruction. Algorithms for
Real-Time Scene Reconstruction Remington Gong Benjamin Harris Iuri Prilepov June 10, 2010 Abstract This report discusses the implementation of a real-time system for scene reconstruction. Algorithms for
EECS 442 Computer vision. Stereo systems. Stereo vision Rectification Correspondence problem Active stereo vision systems
 EECS 442 Computer vision Stereo systems Stereo vision Rectification Correspondence problem Active stereo vision systems Reading: [HZ] Chapter: 11 [FP] Chapter: 11 Stereo vision P p p O 1 O 2 Goal: estimate
EECS 442 Computer vision Stereo systems Stereo vision Rectification Correspondence problem Active stereo vision systems Reading: [HZ] Chapter: 11 [FP] Chapter: 11 Stereo vision P p p O 1 O 2 Goal: estimate
CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick. Motion and Optic Flow. Stereo Matching
 Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
3D Reconstruction of Dynamic Textures with Crowd Sourced Data. Dinghuang Ji, Enrique Dunn and Jan-Michael Frahm
 3D Reconstruction of Dynamic Textures with Crowd Sourced Data Dinghuang Ji, Enrique Dunn and Jan-Michael Frahm 1 Background Large scale scene reconstruction Internet imagery 3D point cloud Dense geometry
3D Reconstruction of Dynamic Textures with Crowd Sourced Data Dinghuang Ji, Enrique Dunn and Jan-Michael Frahm 1 Background Large scale scene reconstruction Internet imagery 3D point cloud Dense geometry
Stereo vision. Many slides adapted from Steve Seitz
 Stereo vision Many slides adapted from Steve Seitz What is stereo vision? Generic problem formulation: given several images of the same object or scene, compute a representation of its 3D shape What is
Stereo vision Many slides adapted from Steve Seitz What is stereo vision? Generic problem formulation: given several images of the same object or scene, compute a representation of its 3D shape What is
Digital Makeup Face Generation
 Digital Makeup Face Generation Wut Yee Oo Mechanical Engineering Stanford University wutyee@stanford.edu Abstract Make up applications offer photoshop tools to get users inputs in generating a make up
Digital Makeup Face Generation Wut Yee Oo Mechanical Engineering Stanford University wutyee@stanford.edu Abstract Make up applications offer photoshop tools to get users inputs in generating a make up
Image Based Reconstruction II
 Image Based Reconstruction II Qixing Huang Feb. 2 th 2017 Slide Credit: Yasutaka Furukawa Image-Based Geometry Reconstruction Pipeline Last Lecture: Multi-View SFM Multi-View SFM This Lecture: Multi-View
Image Based Reconstruction II Qixing Huang Feb. 2 th 2017 Slide Credit: Yasutaka Furukawa Image-Based Geometry Reconstruction Pipeline Last Lecture: Multi-View SFM Multi-View SFM This Lecture: Multi-View
Additional Material (electronic only)
 Additional Material (electronic only) This additional material contains a presentation of additional capabilities of the system, a discussion of performance and temporal coherence as well as other limitations.
Additional Material (electronic only) This additional material contains a presentation of additional capabilities of the system, a discussion of performance and temporal coherence as well as other limitations.
Regularized 3D Modeling from Noisy Building Reconstructions
 Regularized 3D Modeling from Noisy Building Reconstructions Thomas Holzmann Friedrich Fraundorfer Horst Bischof Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision, Graz University of Technology, Austria {holzmann,fraundorfer,bischof}@icg.tugraz.at
Regularized 3D Modeling from Noisy Building Reconstructions Thomas Holzmann Friedrich Fraundorfer Horst Bischof Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision, Graz University of Technology, Austria {holzmann,fraundorfer,bischof}@icg.tugraz.at
3D Shape Analysis with Multi-view Convolutional Networks. Evangelos Kalogerakis
 3D Shape Analysis with Multi-view Convolutional Networks Evangelos Kalogerakis 3D model repositories [3D Warehouse - video] 3D geometry acquisition [KinectFusion - video] 3D shapes come in various flavors
3D Shape Analysis with Multi-view Convolutional Networks Evangelos Kalogerakis 3D model repositories [3D Warehouse - video] 3D geometry acquisition [KinectFusion - video] 3D shapes come in various flavors
Other Linear Filters CS 211A
 Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Dynamic 3D Shape From Multi-viewpoint Images Using Deformable Mesh Model
 Dynamic 3D Shape From Multi-viewpoint Images Using Deformable Mesh Model Shohei Nobuhara Takashi Matsuyama Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University Sakyo, Kyoto, 606-8501, Japan {nob, tm}@vision.kuee.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Dynamic 3D Shape From Multi-viewpoint Images Using Deformable Mesh Model Shohei Nobuhara Takashi Matsuyama Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University Sakyo, Kyoto, 606-8501, Japan {nob, tm}@vision.kuee.kyoto-u.ac.jp
A MULTI-RESOLUTION APPROACH TO DEPTH FIELD ESTIMATION IN DENSE IMAGE ARRAYS F. Battisti, M. Brizzi, M. Carli, A. Neri
 A MULTI-RESOLUTION APPROACH TO DEPTH FIELD ESTIMATION IN DENSE IMAGE ARRAYS F. Battisti, M. Brizzi, M. Carli, A. Neri Università degli Studi Roma TRE, Roma, Italy 2 nd Workshop on Light Fields for Computer
A MULTI-RESOLUTION APPROACH TO DEPTH FIELD ESTIMATION IN DENSE IMAGE ARRAYS F. Battisti, M. Brizzi, M. Carli, A. Neri Università degli Studi Roma TRE, Roma, Italy 2 nd Workshop on Light Fields for Computer
Continuous and Discrete Optimization Methods in Computer Vision. Daniel Cremers Department of Computer Science University of Bonn
 Continuous and Discrete Optimization Methods in Computer Vision Daniel Cremers Department of Computer Science University of Bonn Oxford, August 16 2007 Segmentation by Energy Minimization Given an image,
Continuous and Discrete Optimization Methods in Computer Vision Daniel Cremers Department of Computer Science University of Bonn Oxford, August 16 2007 Segmentation by Energy Minimization Given an image,
Translation Symmetry Detection: A Repetitive Pattern Analysis Approach
 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops Translation Symmetry Detection: A Repetitive Pattern Analysis Approach Yunliang Cai and George Baciu GAMA Lab, Department of Computing
2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops Translation Symmetry Detection: A Repetitive Pattern Analysis Approach Yunliang Cai and George Baciu GAMA Lab, Department of Computing
3D Reconstruction from Scene Knowledge
 Multiple-View Reconstruction from Scene Knowledge 3D Reconstruction from Scene Knowledge SYMMETRY & MULTIPLE-VIEW GEOMETRY Fundamental types of symmetry Equivalent views Symmetry based reconstruction MUTIPLE-VIEW
Multiple-View Reconstruction from Scene Knowledge 3D Reconstruction from Scene Knowledge SYMMETRY & MULTIPLE-VIEW GEOMETRY Fundamental types of symmetry Equivalent views Symmetry based reconstruction MUTIPLE-VIEW
Recap: Features and filters. Recap: Grouping & fitting. Now: Multiple views 10/29/2008. Epipolar geometry & stereo vision. Why multiple views?
 Recap: Features and filters Epipolar geometry & stereo vision Tuesday, Oct 21 Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Transforming and describing images; textures, colors, edges Recap: Grouping & fitting Now: Multiple
Recap: Features and filters Epipolar geometry & stereo vision Tuesday, Oct 21 Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Transforming and describing images; textures, colors, edges Recap: Grouping & fitting Now: Multiple
Automatic occlusion removal from facades for 3D urban reconstruction
 Automatic occlusion removal from facades for 3D urban reconstruction C. Engels 1, D. Tingdahl 1, M. Vercruysse 1, T. Tuytelaars 1, H. Sahli 2, and L. Van Gool 1,3 1 K.U.Leuven, ESAT-PSI/IBBT 2 V.U.Brussel,
Automatic occlusion removal from facades for 3D urban reconstruction C. Engels 1, D. Tingdahl 1, M. Vercruysse 1, T. Tuytelaars 1, H. Sahli 2, and L. Van Gool 1,3 1 K.U.Leuven, ESAT-PSI/IBBT 2 V.U.Brussel,
A Heightmap Model for Efficient 3D Reconstruction from Street-Level Video
 A Heightmap Model for Efficient 3D Reconstruction from Street-Level Video David Gallup 1, Jan-Michael Frahm 1 1 University of North Carolina Department of Computer Science {gallup,jmf}@cs.unc.edu Marc
A Heightmap Model for Efficient 3D Reconstruction from Street-Level Video David Gallup 1, Jan-Michael Frahm 1 1 University of North Carolina Department of Computer Science {gallup,jmf}@cs.unc.edu Marc
Surface Reconstruction. Gianpaolo Palma
 Surface Reconstruction Gianpaolo Palma Surface reconstruction Input Point cloud With or without normals Examples: multi-view stereo, union of range scan vertices Range scans Each scan is a triangular mesh
Surface Reconstruction Gianpaolo Palma Surface reconstruction Input Point cloud With or without normals Examples: multi-view stereo, union of range scan vertices Range scans Each scan is a triangular mesh
3D Reconstruction Using an n-layer Heightmap
 3D Reconstruction Using an n-layer Heightmap David Gallup 1, Marc Pollefeys 2, and Jan-Michael Frahm 1 1 Department of Computer Science, University of North Carolina {gallup,jmf}@cs.unc.edu 2 Department
3D Reconstruction Using an n-layer Heightmap David Gallup 1, Marc Pollefeys 2, and Jan-Michael Frahm 1 1 Department of Computer Science, University of North Carolina {gallup,jmf}@cs.unc.edu 2 Department
Structured Light II. Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov
 Structured Light II Johannes Köhler Johannes.koehler@dfki.de Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov Introduction Previous lecture: Structured Light I Active Scanning Camera/emitter
Structured Light II Johannes Köhler Johannes.koehler@dfki.de Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov Introduction Previous lecture: Structured Light I Active Scanning Camera/emitter
Static Scene Reconstruction
 GPU supported Real-Time Scene Reconstruction with a Single Camera Jan-Michael Frahm, 3D Computer Vision group, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Static Scene Reconstruction 1 Capture on campus
GPU supported Real-Time Scene Reconstruction with a Single Camera Jan-Michael Frahm, 3D Computer Vision group, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Static Scene Reconstruction 1 Capture on campus
Registration of Dynamic Range Images
 Registration of Dynamic Range Images Tan-Chi Ho 1,2 Jung-Hong Chuang 1 Wen-Wei Lin 2 Song-Sun Lin 2 1 Department of Computer Science National Chiao-Tung University 2 Department of Applied Mathematics National
Registration of Dynamic Range Images Tan-Chi Ho 1,2 Jung-Hong Chuang 1 Wen-Wei Lin 2 Song-Sun Lin 2 1 Department of Computer Science National Chiao-Tung University 2 Department of Applied Mathematics National
L2 Data Acquisition. Mechanical measurement (CMM) Structured light Range images Shape from shading Other methods
 L2 Data Acquisition Mechanical measurement (CMM) Structured light Range images Shape from shading Other methods 1 Coordinate Measurement Machine Touch based Slow Sparse Data Complex planning Accurate 2
L2 Data Acquisition Mechanical measurement (CMM) Structured light Range images Shape from shading Other methods 1 Coordinate Measurement Machine Touch based Slow Sparse Data Complex planning Accurate 2
Intrinsic3D: High-Quality 3D Reconstruction by Joint Appearance and Geometry Optimization with Spatially-Varying Lighting
 Intrinsic3D: High-Quality 3D Reconstruction by Joint Appearance and Geometry Optimization with Spatially-Varying Lighting R. Maier 1,2, K. Kim 1, D. Cremers 2, J. Kautz 1, M. Nießner 2,3 Fusion Ours 1
Intrinsic3D: High-Quality 3D Reconstruction by Joint Appearance and Geometry Optimization with Spatially-Varying Lighting R. Maier 1,2, K. Kim 1, D. Cremers 2, J. Kautz 1, M. Nießner 2,3 Fusion Ours 1
Realistic Texture Extraction for 3D Face Models Robust to Self-Occlusion
 Realistic Texture Extraction for 3D Face Models Robust to Self-Occlusion Chengchao Qu 1,2 Eduardo Monari 2 Tobias Schuchert 2 Jürgen Beyerer 2,1 1 Vision and Fusion Laboratory, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
Realistic Texture Extraction for 3D Face Models Robust to Self-Occlusion Chengchao Qu 1,2 Eduardo Monari 2 Tobias Schuchert 2 Jürgen Beyerer 2,1 1 Vision and Fusion Laboratory, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick. Motion and Optic Flow. Stereo Matching
 Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Geometric Reconstruction Dense reconstruction of scene geometry
 Lecture 5. Dense Reconstruction and Tracking with Real-Time Applications Part 2: Geometric Reconstruction Dr Richard Newcombe and Dr Steven Lovegrove Slide content developed from: [Newcombe, Dense Visual
Lecture 5. Dense Reconstruction and Tracking with Real-Time Applications Part 2: Geometric Reconstruction Dr Richard Newcombe and Dr Steven Lovegrove Slide content developed from: [Newcombe, Dense Visual
Manhattan-world Stereo and Surface Reconstruction
 Manhattan-world Stereo and Surface Reconstruction Kuan-Ting Yu CSAIL MIT Cambridge, USA peterkty@csail.mit.edu Abstract Depth estimation from 2D images has been extensively studied in the computer vision
Manhattan-world Stereo and Surface Reconstruction Kuan-Ting Yu CSAIL MIT Cambridge, USA peterkty@csail.mit.edu Abstract Depth estimation from 2D images has been extensively studied in the computer vision
Notes 9: Optical Flow
 Course 049064: Variational Methods in Image Processing Notes 9: Optical Flow Guy Gilboa 1 Basic Model 1.1 Background Optical flow is a fundamental problem in computer vision. The general goal is to find
Course 049064: Variational Methods in Image Processing Notes 9: Optical Flow Guy Gilboa 1 Basic Model 1.1 Background Optical flow is a fundamental problem in computer vision. The general goal is to find
Geometry of Multiple views
 1 Geometry of Multiple views CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University 2 Multiple views Despite the wealth of information contained in a a photograph, the depth of a scene point along the
1 Geometry of Multiple views CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University 2 Multiple views Despite the wealth of information contained in a a photograph, the depth of a scene point along the
Geometry based Repetition Detection for Urban Scene
 Geometry based Repetition Detection for Urban Scene Changchang Wu University of Washington Jan Michael Frahm UNC Chapel Hill Marc Pollefeys ETH Zürich Related Work Sparse Feature Matching [Loy et al. 06,
Geometry based Repetition Detection for Urban Scene Changchang Wu University of Washington Jan Michael Frahm UNC Chapel Hill Marc Pollefeys ETH Zürich Related Work Sparse Feature Matching [Loy et al. 06,
VIDEO FOR VIRTUAL REALITY LIGHT FIELD BASICS JAMES TOMPKIN
 VIDEO FOR VIRTUAL REALITY LIGHT FIELD BASICS JAMES TOMPKIN WHAT IS A LIGHT FIELD? Light field seems to have turned into a catch-all term for many advanced camera/display technologies. WHAT IS A LIGHT FIELD?
VIDEO FOR VIRTUAL REALITY LIGHT FIELD BASICS JAMES TOMPKIN WHAT IS A LIGHT FIELD? Light field seems to have turned into a catch-all term for many advanced camera/display technologies. WHAT IS A LIGHT FIELD?
Contents I IMAGE FORMATION 1
 Contents I IMAGE FORMATION 1 1 Geometric Camera Models 3 1.1 Image Formation............................. 4 1.1.1 Pinhole Perspective....................... 4 1.1.2 Weak Perspective.........................
Contents I IMAGE FORMATION 1 1 Geometric Camera Models 3 1.1 Image Formation............................. 4 1.1.1 Pinhole Perspective....................... 4 1.1.2 Weak Perspective.........................
Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling
 433-324 Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction to Modelling Polygonal geometry The rendering
433-324 Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction to Modelling Polygonal geometry The rendering
Multi-View Reconstruction using Narrow-Band Graph-Cuts and Surface Normal Optimization
 Multi-View Reconstruction using Narrow-Band Graph-Cuts and Surface Normal Optimization Alexander Ladikos Selim Benhimane Nassir Navab Chair for Computer Aided Medical Procedures Department of Informatics
Multi-View Reconstruction using Narrow-Band Graph-Cuts and Surface Normal Optimization Alexander Ladikos Selim Benhimane Nassir Navab Chair for Computer Aided Medical Procedures Department of Informatics
arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 21 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 21 Apr 2016 arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 21 Apr 2016](/thumbs/85/91924537.jpg) Automatic 3D Reconstruction of Manifold Meshes via Delaunay Triangulation and Mesh Sweeping arxiv:1604.06258v1 [cs.v] 21 Apr 2016 Andrea Romanoni Politecnico di Milano Italy andrea.romanoni@polimi.it Abstract
Automatic 3D Reconstruction of Manifold Meshes via Delaunay Triangulation and Mesh Sweeping arxiv:1604.06258v1 [cs.v] 21 Apr 2016 Andrea Romanoni Politecnico di Milano Italy andrea.romanoni@polimi.it Abstract
Multi-View Stereo for Static and Dynamic Scenes
 Multi-View Stereo for Static and Dynamic Scenes Wolfgang Burgard Jan 6, 2010 Main references Yasutaka Furukawa and Jean Ponce, Accurate, Dense and Robust Multi-View Stereopsis, 2007 C.L. Zitnick, S.B.
Multi-View Stereo for Static and Dynamic Scenes Wolfgang Burgard Jan 6, 2010 Main references Yasutaka Furukawa and Jean Ponce, Accurate, Dense and Robust Multi-View Stereopsis, 2007 C.L. Zitnick, S.B.
Plant and Canopy Reconstruction User Documentation. The University of Nottingham
 Plant and Canopy Reconstruction User Documentation The University of Nottingham 2014 Table of Contents Overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Program Input... 3 Point Clouds... 3 Image Sets and Camera Geometries...
Plant and Canopy Reconstruction User Documentation The University of Nottingham 2014 Table of Contents Overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Program Input... 3 Point Clouds... 3 Image Sets and Camera Geometries...
Volumetric stereo with silhouette and feature constraints
 Volumetric stereo with silhouette and feature constraints Jonathan Starck, Gregor Miller and Adrian Hilton Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing, University of Surrey, Guildford, GU2 7XH, UK.
Volumetric stereo with silhouette and feature constraints Jonathan Starck, Gregor Miller and Adrian Hilton Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing, University of Surrey, Guildford, GU2 7XH, UK.
Lecture 10: Multi view geometry
 Lecture 10: Multi view geometry Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Stereo vision Correspondence problem (Problem Set 2 (Q3)) Active stereo vision systems Structure from
Lecture 10: Multi view geometry Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Stereo vision Correspondence problem (Problem Set 2 (Q3)) Active stereo vision systems Structure from
3D Photography: Active Ranging, Structured Light, ICP
 3D Photography: Active Ranging, Structured Light, ICP Kalin Kolev, Marc Pollefeys Spring 2013 http://cvg.ethz.ch/teaching/2013spring/3dphoto/ Schedule (tentative) Feb 18 Feb 25 Mar 4 Mar 11 Mar 18 Mar
3D Photography: Active Ranging, Structured Light, ICP Kalin Kolev, Marc Pollefeys Spring 2013 http://cvg.ethz.ch/teaching/2013spring/3dphoto/ Schedule (tentative) Feb 18 Feb 25 Mar 4 Mar 11 Mar 18 Mar
Edge and Texture. CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University
 Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 16 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 16 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 16 May 2017](/thumbs/82/85992971.jpg) Automated Body Structure Extraction from Arbitrary 3D Mesh Yong Khoo, Sang Chung This paper presents an automated method for 3D character skeleton extraction that can be arxiv:1705.05508v1 [cs.gr] 16 May
Automated Body Structure Extraction from Arbitrary 3D Mesh Yong Khoo, Sang Chung This paper presents an automated method for 3D character skeleton extraction that can be arxiv:1705.05508v1 [cs.gr] 16 May
Stereo. Outline. Multiple views 3/29/2017. Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin. Multi-view geometry, matching, invariant features, stereo vision
 Stereo Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Outline Last time: Human stereopsis Epipolar geometry and the epipolar constraint Case example with parallel optical axes General case with calibrated cameras
Stereo Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Outline Last time: Human stereopsis Epipolar geometry and the epipolar constraint Case example with parallel optical axes General case with calibrated cameras
Hierarchical Upsampling for Fast Image-Based Depth Estimation
 Volume xx (200y), Number z, pp. 1 9 Hierarchical Upsampling for Fast Image-Based Depth Estimation Blake Foster and Rui Wang University of Massachusetts Amherst Abstract We propose a hierarchical upsampling
Volume xx (200y), Number z, pp. 1 9 Hierarchical Upsampling for Fast Image-Based Depth Estimation Blake Foster and Rui Wang University of Massachusetts Amherst Abstract We propose a hierarchical upsampling
Image Comparison on the Base of a Combinatorial Matching Algorithm
 Image Comparison on the Base of a Combinatorial Matching Algorithm Benjamin Drayer Department of Computer Science, University of Freiburg Abstract. In this paper we compare images based on the constellation
Image Comparison on the Base of a Combinatorial Matching Algorithm Benjamin Drayer Department of Computer Science, University of Freiburg Abstract. In this paper we compare images based on the constellation
Towards Integrated 3D Reconstruction and Semantic Interpretation of Urban Scenes
 Towards Integrated 3D Reconstruction and Semantic Interpretation of Urban Scenes MAROŠ BLAHÁ 1, CHRISTOPH VOGEL 2, AUDREY RICHARD 1, JAN D. WEGNER 1, THOMAS POCK 2 & KONRAD SCHINDLER 1 We describe recent
Towards Integrated 3D Reconstruction and Semantic Interpretation of Urban Scenes MAROŠ BLAHÁ 1, CHRISTOPH VOGEL 2, AUDREY RICHARD 1, JAN D. WEGNER 1, THOMAS POCK 2 & KONRAD SCHINDLER 1 We describe recent
3D Computer Vision & Augmented Reality
 Proceedings of Seminar and Project 3D Computer Vision & Augmented Reality Summer Semester 2013 Dr. Gabriele Bleser and Prof. Didier Stricker Department Augmented Vision University of Kaiserslautern and
Proceedings of Seminar and Project 3D Computer Vision & Augmented Reality Summer Semester 2013 Dr. Gabriele Bleser and Prof. Didier Stricker Department Augmented Vision University of Kaiserslautern and
Face Recognition At-a-Distance Based on Sparse-Stereo Reconstruction
 Face Recognition At-a-Distance Based on Sparse-Stereo Reconstruction Ham Rara, Shireen Elhabian, Asem Ali University of Louisville Louisville, KY {hmrara01,syelha01,amali003}@louisville.edu Mike Miller,
Face Recognition At-a-Distance Based on Sparse-Stereo Reconstruction Ham Rara, Shireen Elhabian, Asem Ali University of Louisville Louisville, KY {hmrara01,syelha01,amali003}@louisville.edu Mike Miller,
Stereo Wrap + Motion. Computer Vision I. CSE252A Lecture 17
 Stereo Wrap + Motion CSE252A Lecture 17 Some Issues Ambiguity Window size Window shape Lighting Half occluded regions Problem of Occlusion Stereo Constraints CONSTRAINT BRIEF DESCRIPTION 1-D Epipolar Search
Stereo Wrap + Motion CSE252A Lecture 17 Some Issues Ambiguity Window size Window shape Lighting Half occluded regions Problem of Occlusion Stereo Constraints CONSTRAINT BRIEF DESCRIPTION 1-D Epipolar Search
COMPARISON OF LASER SCANNING, PHOTOGRAMMETRY AND SfM-MVS PIPELINE APPLIED IN STRUCTURES AND ARTIFICIAL SURFACES
 COMPARISON OF LASER SCANNING, PHOTOGRAMMETRY AND SfM-MVS PIPELINE APPLIED IN STRUCTURES AND ARTIFICIAL SURFACES 2012 ISPRS Melbourne, Com III/4, S.Kiparissi Cyprus University of Technology 1 / 28 Structure
COMPARISON OF LASER SCANNING, PHOTOGRAMMETRY AND SfM-MVS PIPELINE APPLIED IN STRUCTURES AND ARTIFICIAL SURFACES 2012 ISPRS Melbourne, Com III/4, S.Kiparissi Cyprus University of Technology 1 / 28 Structure
3D Photography: Stereo Matching
 3D Photography: Stereo Matching Kevin Köser, Marc Pollefeys Spring 2012 http://cvg.ethz.ch/teaching/2012spring/3dphoto/ Stereo & Multi-View Stereo Tsukuba dataset http://cat.middlebury.edu/stereo/ Stereo
3D Photography: Stereo Matching Kevin Köser, Marc Pollefeys Spring 2012 http://cvg.ethz.ch/teaching/2012spring/3dphoto/ Stereo & Multi-View Stereo Tsukuba dataset http://cat.middlebury.edu/stereo/ Stereo
Viewpoint Invariant Features from Single Images Using 3D Geometry
 Viewpoint Invariant Features from Single Images Using 3D Geometry Yanpeng Cao and John McDonald Department of Computer Science National University of Ireland, Maynooth, Ireland {y.cao,johnmcd}@cs.nuim.ie
Viewpoint Invariant Features from Single Images Using 3D Geometry Yanpeng Cao and John McDonald Department of Computer Science National University of Ireland, Maynooth, Ireland {y.cao,johnmcd}@cs.nuim.ie
Supplementary Material for Synthesizing Normalized Faces from Facial Identity Features
 Supplementary Material for Synthesizing Normalized Faces from Facial Identity Features Forrester Cole 1 David Belanger 1,2 Dilip Krishnan 1 Aaron Sarna 1 Inbar Mosseri 1 William T. Freeman 1,3 1 Google,
Supplementary Material for Synthesizing Normalized Faces from Facial Identity Features Forrester Cole 1 David Belanger 1,2 Dilip Krishnan 1 Aaron Sarna 1 Inbar Mosseri 1 William T. Freeman 1,3 1 Google,
Template-free Shape from Texture with Perspective Cameras
 HILSMANN et al.: TEMPLATE-FREE SHAPE FROM TEXTURE 1 Template-free Shape from Texture with Perspective Cameras Anna Hilsmann 1 anna.hilsmann@hhi.fraunhofer.de David C. Schneider 1 david.schneider@hhi.fraunhofer.de
HILSMANN et al.: TEMPLATE-FREE SHAPE FROM TEXTURE 1 Template-free Shape from Texture with Perspective Cameras Anna Hilsmann 1 anna.hilsmann@hhi.fraunhofer.de David C. Schneider 1 david.schneider@hhi.fraunhofer.de
Supplementary Material: Piecewise Planar and Compact Floorplan Reconstruction from Images
 Supplementary Material: Piecewise Planar and Compact Floorplan Reconstruction from Images Ricardo Cabral Carnegie Mellon University rscabral@cmu.edu Yasutaka Furukawa Washington University in St. Louis
Supplementary Material: Piecewise Planar and Compact Floorplan Reconstruction from Images Ricardo Cabral Carnegie Mellon University rscabral@cmu.edu Yasutaka Furukawa Washington University in St. Louis
Self-supervised Multi-level Face Model Learning for Monocular Reconstruction at over 250 Hz Supplemental Material
 Self-supervised Multi-level Face Model Learning for Monocular Reconstruction at over 250 Hz Supplemental Material Ayush Tewari 1,2 Michael Zollhöfer 1,2,3 Pablo Garrido 1,2 Florian Bernard 1,2 Hyeongwoo
Self-supervised Multi-level Face Model Learning for Monocular Reconstruction at over 250 Hz Supplemental Material Ayush Tewari 1,2 Michael Zollhöfer 1,2,3 Pablo Garrido 1,2 Florian Bernard 1,2 Hyeongwoo
CSc Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography
 CSc 83010 Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography Tuesdays 11:45-1:45 1:45 Room 3305 Ioannis Stamos istamos@hunter.cuny.edu Office: 1090F, Hunter North (Entrance at 69 th bw/ / Park and Lexington Avenues)
CSc 83010 Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography Tuesdays 11:45-1:45 1:45 Room 3305 Ioannis Stamos istamos@hunter.cuny.edu Office: 1090F, Hunter North (Entrance at 69 th bw/ / Park and Lexington Avenues)
Deformable Mesh Model for Complex Multi-Object 3D Motion Estimation from Multi-Viewpoint Video
 Deformable Mesh Model for Complex Multi-Object 3D Motion Estimation from Multi-Viewpoint Video Shohei NOBUHARA Takashi MATSUYAMA Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University Sakyo, Kyoto, 606-8501,
Deformable Mesh Model for Complex Multi-Object 3D Motion Estimation from Multi-Viewpoint Video Shohei NOBUHARA Takashi MATSUYAMA Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University Sakyo, Kyoto, 606-8501,
3-D Shape Reconstruction from Light Fields Using Voxel Back-Projection
 3-D Shape Reconstruction from Light Fields Using Voxel Back-Projection Peter Eisert, Eckehard Steinbach, and Bernd Girod Telecommunications Laboratory, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Cauerstrasse 7,
3-D Shape Reconstruction from Light Fields Using Voxel Back-Projection Peter Eisert, Eckehard Steinbach, and Bernd Girod Telecommunications Laboratory, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Cauerstrasse 7,
Flow Estimation. Min Bai. February 8, University of Toronto. Min Bai (UofT) Flow Estimation February 8, / 47
 Flow Estimation Min Bai University of Toronto February 8, 2016 Min Bai (UofT) Flow Estimation February 8, 2016 1 / 47 Outline Optical Flow - Continued Min Bai (UofT) Flow Estimation February 8, 2016 2
Flow Estimation Min Bai University of Toronto February 8, 2016 Min Bai (UofT) Flow Estimation February 8, 2016 1 / 47 Outline Optical Flow - Continued Min Bai (UofT) Flow Estimation February 8, 2016 2
Evaluation of Large Scale Scene Reconstruction
 Evaluation of Large Scale Scene Reconstruction Paul Merrell, Philippos Mordohai, Jan-Michael Frahm, and Marc Pollefeys Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, USA Abstract
Evaluation of Large Scale Scene Reconstruction Paul Merrell, Philippos Mordohai, Jan-Michael Frahm, and Marc Pollefeys Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, USA Abstract
Exploring Curve Fitting for Fingers in Egocentric Images
 Exploring Curve Fitting for Fingers in Egocentric Images Akanksha Saran Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University 16-811: Math Fundamentals for Robotics Final Project Report Email: asaran@andrew.cmu.edu
Exploring Curve Fitting for Fingers in Egocentric Images Akanksha Saran Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University 16-811: Math Fundamentals for Robotics Final Project Report Email: asaran@andrew.cmu.edu
The Kinect Sensor. Luís Carriço FCUL 2014/15
 Advanced Interaction Techniques The Kinect Sensor Luís Carriço FCUL 2014/15 Sources: MS Kinect for Xbox 360 John C. Tang. Using Kinect to explore NUI, Ms Research, From Stanford CS247 Shotton et al. Real-Time
Advanced Interaction Techniques The Kinect Sensor Luís Carriço FCUL 2014/15 Sources: MS Kinect for Xbox 360 John C. Tang. Using Kinect to explore NUI, Ms Research, From Stanford CS247 Shotton et al. Real-Time
AUTOMATED 3D MODELING OF URBAN ENVIRONMENTS
 AUTOMATED 3D MODELING OF URBAN ENVIRONMENTS Ioannis Stamos Department of Computer Science Hunter College, City University of New York 695 Park Avenue, New York NY 10065 istamos@hunter.cuny.edu http://www.cs.hunter.cuny.edu/
AUTOMATED 3D MODELING OF URBAN ENVIRONMENTS Ioannis Stamos Department of Computer Science Hunter College, City University of New York 695 Park Avenue, New York NY 10065 istamos@hunter.cuny.edu http://www.cs.hunter.cuny.edu/
