Spatial Transformations. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
|
|
|
- Bethany Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sptil Trnsformtions Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Compter Science City College of New York
2 Objecties In this lectre we reiew sptil trnsformtions: - Forwrd nd inerse mppings - Trnsformtions Liner Affine Perspectie Biliner - Inferring ffine nd perspectie trnsformtions 2
3 Forwrd nd Inerse Mppings A sptil trnsformtion defines geometric reltionship between ech point in the inpt nd otpt imges. Forwrd mpping: [x, y] = [X(,), Y(,)] Inerse mpping : [, ] = [U(x,y), V(x,y)] Forwrd mpping specifies otpt coordintes (x,y) for ech inpt point (,). Inerse mpping specifies inpt point (,) for ech otpt point (x,y). Inpt Otpt (ccmltor) Forwrd mpping Inpt Otpt Inerse mpping 3
4 Liner Trnsformtions [ x, y] [, ] x 2 y Aboe eqtions re liner becse they stisfy the following two conditions necessry for ny liner fnction L(x): ) L(x+y) = L(x) + L(y) 2) L(cx) = cl(x) for ny sclr c nd position ectors x nd y. Note tht liner trnsformtion re sm of scled inpt coordinte: they do not ccont for simple trnsltion. We wnt: x y [ x, y] [,,]
5 Homogeneos Coordintes To compte inerse, the trnsformtion mtrix mst be sqre. Therefore, 2 [ x, y,] [,,] All 2-D position ectors re now represented with three components: homogeneos nottion. Third component (w) refers to the plne pon which the trnsformtion opertes. [,, ] = [, ] position ector lying on w= plne. The representtion of point in the homogeneos nottion is no longer niqe: [8, 6, 2] = [4, 8, ] = [6, 32, 4]. To recoer ny 2-D position ector p[x,y] from p h =[x, y, w ], diide by the homogeneos coordinte w. ' x [ x, y] ' w ' y ' w 5
6 6 Affine Trnsformtions (),], [,], [ y x Trnsltion T T cos sin sin cos Rottion Scle S S rows Sher H colmns Sher H
7 7 Affine Trnsformtions (2) Affine trnsformtion he 6 degrees of freedom:, 2, 3, 2, 22, 23. They cn be inferred by giing the correspondence of three 2-D points between the inpt nd otpt imges. Tht is, All points lie on the sme plne. Affine trnsformtions mp tringles onto tringles. ) 3for, s:(3for 6constrint ), ( ), ( ), ( ), ( ), ( ), ( y x y x y x y x
8 Affine Trnsformtions (3) Skew (sher) Rottion/Scle Rottion 8
9 Perspectie Trnsformtions () ' 2 3 x x ' ' ' [,, ] [,, ] ' x y w w 2 22 w 23 ' y y ' 3 w 23 not necessrily s in ffine trnsformtions Withot loss of generlity, we set 33 =. This yields 8 degrees of freedom nd llows s to mp plnr qdrilterls to plnr qdrilterls (correspondence mong 4 sets of 2-D points yields 8 coordintes). Perspectie trnsformtions introdces foreshortening effects. Stright lines re presered
10 Perspectie Trnsformtions (2)
11 Biliner Trnsforms () [ x, y] [,,,] 3 2 b b b b corner mpping mong nonplnr qdrilterls (2 nd degree de to fctors). Coneniently compted sing seprbility (see p. 57-6). Preseres spcing long edges. Stright lines in the interior no longer remin stright.
12 Biliner Trnsforms (2) 2
13 Exmples Similrity trnsformtion (RST) Affine trnsformtion Perspectie trnsformtion Polynomil trnsformtion 3
14 Scnline Algorithms Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Compter Science City College of New York
15 Objecties In this lectre we reiew scnline lgorithms: - Incrementl textre mpping - 2-pss Ctmll-Smith lgorithm Rottion Perspectie - 3-pss sher trnsformtion for rottion - Morphing 5
16 Ctmll-Smith Algorithm Two-pss trnsform First pss resmples ll rows: [, ] [x, ] [x, ] = [ F (), ] where F () = X(, ) is the forwrd mpping fct Second pss resmples ll colmns: [x, ] [x, y] [x, y] = [x, G x ()] where G x ()=Y(H x (), ) H x () is the inerse projection of x, the colmn we wish to resmple. It brings s bck from [x, ] to [, ] so tht we cn directly index into Y to get the destintion y coordintes. 6
17 7 Exmple: Rottion () cos sin cos sin into ) ( ).Sbstitte ( Compte b) cos sin sin cos tht Recll ). ( Compte ) 2 : Pss ], sin cos [ ], [ Pss: cos sin sin cos ], [ ], [ x y y H G x x H x y x x x x
18 2-Pss Rottion scle/sher rows scle/sher colmns 8
19 9 3-Pss Rottion Algorithm Rottion cn be decomposed into two scle/sher mtrices. Three pss trnsform ses on sher mtrices. Adntge of 3-pss: no scling necessry in ny pss. 2 tn sin 2 tn cos sin sin cos R cos tn sin cos cos sin sin cos R
20 3-Pss Rottion sher rows sher colmns sher rows 2
21 Softwre Implementtion The following slides contin code for initmtrix.c to prodce 3x3 perspectie trnsformtion mtrix from list of for corresponding points (e.g. imge corners). Tht mtrix is then sed in perspectie.c to resmple the imge. The code in resmple.c performs the ctl scnline resmple. 2
22 initmtrix.c () /* ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ * initmtrix: * * Gien Icorr, list of the 4 correspondence points for the corners * of imge I, compte the 3x3 perspectie mtrix in Imtrix. */ oid initmtrix(imgep I, imgep Icorr, imgep Imtrix) { int w, h; flot *p, *, 3, 23; flot x, x, x2, x3; flot y, y, y2, y3; flot dx, dx2, dx3, dy, dy2, dy3; /* init pointers */ = (flot *) Imtrix->bf[]; p = (flot *) Icorr->bf[]; /* init,,x,y rs nd print them */ x = *p++; y = *p++; x = *p++; y = *p++; x2 = *p++; y2 = *p++; x3 = *p++; y3 = *p++; 22
23 initmtrix.c (2) w = I->width; h = I->height; UI_printf("\nCorrespondence points:\n"); UI_printf("%4d %4d %6.f %6.f\n",,, x, y); UI_printf("%4d %4d %6.f %6.f\n", w,, x, y); UI_printf("%4d %4d %6.f %6.f\n", w, h, x2, y2); UI_printf("%4d %4d %6.f %6.f\n",, h, x3, y3); /* compte xiliry rs */ dx = x - x2; dx2 = x3 - x2; dx3 = x - x + x2 - x3; dy = y - y2; dy2 = y3 - y2; dy3 = y - y + y2 - y3; 23
24 initmtrix.c (3) /* compte 3x3 trnsformtion mtrix: * 2 * * */ 3 = (dx3*dy2 - dx2*dy3) / (dx*dy2 - dx2*dy); 23 = (dx*dy3 - dx3*dy) / (dx*dy2 - dx2*dy); [] = (x-x+3*x) / w; [] = (y-y+3*y) / w; [2] = 3 / w; [3] = (x3-x+23*x3) / h; [4] = (y3-y+23*y3) / h; [5] = 23 / h; [6] = x; [7] = y; [8] = ; } 24
25 perspectie.c () #define X(A, U, V) #define Y(A, U, V) #define H(A, X, V) ((A[]*U + A[3]*V + A[6]) / (A[2]*U + A[5]*V + A[8])) ((A[]*U + A[4]*V + A[7]) / (A[2]*U + A[5]*V + A[8])) ((-(A[5]*V+A[8])*X+ A[3]*V + A[6]) / (A[2]*X - A[])) /* ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ * perspectie: * * Apply perspectie imge trnsformtion on inpt I. * The 3x3 perspectie mtrix is gien in Imtrix. * The otpt is stored in I2. */ oid perspectie(imgp I, imgep Imtrix, imgep I2) { int i, w, h, ww, hh; chr *p, *p2; flot,, x, y, xmin, xmx, ymin, ymx, *, *F; imgep II; w = I->width; h = I->height; = (flot *) Imtrix->bf[]; 25
26 perspectie.c (2) xmin = xmx = X(,, ); x = X(, w, ); xmin = MIN(xmin, x); x = X(, w, h); xmin = MIN(xmin, x); x = X(,, h); xmin = MIN(xmin, x); ymin = ymx = Y(,, ); y = Y(, w, ); ymin = MIN(ymin, y); y = Y(, w, h); ymin = MIN(ymin, y); y = Y(,, h); ymin = MIN(ymin, y); xmx = MAX(xmx, x); xmx = MAX(xmx, x); xmx = MAX(xmx, x); ymx = MAX(ymx, y); ymx = MAX(ymx, y); ymx = MAX(ymx, y); ww = CEILING(xmx) - FLOOR(xmin); hh = CEILING(ymx) - FLOOR(ymin); /* llocte mpping fct bffer */ x = MAX(MAX(w, h), MAX(ww, hh)); F = (flot *) mlloc(x * sizeof(flot)); if(f == NULL) IP_bilot("perspectie: No memory"); /* llocte intermedite imge */ II = IP_llocImge(ww, h, BW_TYPE); IP_clerImge(II); p = (chr *) I->bf[]; p2 = (chr *) II->bf[]; 26
27 perspectie.c (3) /* first pss: resmple rows */ for(=; <h; ++) { /* init forwrd mpping fnction F; mp xmin to */ for(=; < w; ++) F[(int) ] = X(,, ) - xmin; } resmple(p, w,, F, p2); p += w; p2 += ww; /* disply intermedite imge */ IP_copyImge(II, NextImgeP); IP_displyImge(); /* init finl imge */ IP_copyImgeHeder(I, I2); I2->width = ww; I2->height = hh; IP_initChnnels(I2, BW_TYPE); IP_clerImge(I2); 27
28 perspectie.c (4) /* second pss: resmple colmns */ for(x=; x<ww; x++) { p = (chr *) II->bf[] + (int) x; p2 = (chr *) I2->bf[] + (int) x; /* skip pst pdding */ for(=; <h; ++,p+=ww) { if(*p) brek; /* check for nonzero pixel */ = H(, (x+xmin), ); /* else, if pixel is blck */ if(>= && <w) brek; /* then check for lid */ } /* init forwrd mpping fnction F; mp ymin to */ for(i=; <h; ++) { = H(, (x+xmin), ); = CLIP(,, w-); F[i++] = Y(,, ) - ymin; } resmple(p, i, ww, F, p2); } IP_freeImge(II); } 28
29 resmple.c () /* ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ * Resmple the len elements of src (with stride offst) into dst ccording * to the monotonic sptil mpping gien in F (len entries). * The scnline is ssmed to he been clered erlier. */ oid resmple(chr *src, int len, int offst, flot *F, chr *dst) { int,, x, xx, ix, ix, I, I, pos; doble x, x, di; if(f[] < F[len-]) pos = ; /* positie otpt stride */ else pos = ; /* negtie otpt stride */ for(=; <len-; ++) { /* index into src */ = * offst; /* otpt interl (rel nd int) for inpt pixel */ if(pos) { /* positie stride */ ix = x = F[]; ix = x = F[+]; I = src[]; I = src[+offst]; Wolberg: } Imge Processing Corse Notes 29
30 resmple.c (2) else { /* flip interl to enforce positie stride */ ix = x = F[+]; ix = x = F[]; I = src[+offst]; I = src[]; } /* index into dst */ xx = ix * offst; /* check if interl is embedded in one otpt pixel */ if(ix == ix) { dst[xx] += I * (x-x); contine; } /* else, inpt strddles more thn one otpt pixel */ /* left strddle */ dst[xx] += I * (ix+-x); 3
31 resmple.c (3) /* centrl interl */ xx += offst; di = (I-I) / (x-x); for(x=ix+; x<ix; x++,xx+=offst) dst[xx] = I + di*(x-x); } } /* right strddle */ if(x!= ix) dst[xx] += (I + di*(ix-x)) * (x-ix); 3
Rigid Body Transformations
 igid od Kinemtics igid od Trnsformtions Vij Kumr igid od Kinemtics emrk out Nottion Vectors,,, u, v, p, q, Potentil for Confusion! Mtrices,, C, g, h, igid od Kinemtics The vector nd its skew smmetric mtri
igid od Kinemtics igid od Trnsformtions Vij Kumr igid od Kinemtics emrk out Nottion Vectors,,, u, v, p, q, Potentil for Confusion! Mtrices,, C, g, h, igid od Kinemtics The vector nd its skew smmetric mtri
Lecture 5: Spatial Analysis Algorithms
 Lecture 5: Sptil Algorithms GEOG 49: Advnced GIS Sptil Anlsis Algorithms Bsis of much of GIS nlsis tod Mnipultion of mp coordintes Bsed on Eucliden coordinte geometr http://stronom.swin.edu.u/~pbourke/geometr/
Lecture 5: Sptil Algorithms GEOG 49: Advnced GIS Sptil Anlsis Algorithms Bsis of much of GIS nlsis tod Mnipultion of mp coordintes Bsed on Eucliden coordinte geometr http://stronom.swin.edu.u/~pbourke/geometr/
Stained Glass Design. Teaching Goals:
 Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
Geometric transformations
 Geometric trnsformtions Computer Grphics Some slides re bsed on Shy Shlom slides from TAU mn n n m m T A,,,,,, 2 1 2 22 12 1 21 11 Rows become columns nd columns become rows nm n n m m A,,,,,, 1 1 2 22
Geometric trnsformtions Computer Grphics Some slides re bsed on Shy Shlom slides from TAU mn n n m m T A,,,,,, 2 1 2 22 12 1 21 11 Rows become columns nd columns become rows nm n n m m A,,,,,, 1 1 2 22
Viewing and Projection
 15-462 Computer Grphics I Lecture 5 Viewing nd Projection Sher Trnsformtion Cmer Positioning Simple Prllel Projections Simple Perspective Projections [Angel, Ch. 5.2-5.4] Jnury 30, 2003 [Red s Drem, Pixr,
15-462 Computer Grphics I Lecture 5 Viewing nd Projection Sher Trnsformtion Cmer Positioning Simple Prllel Projections Simple Perspective Projections [Angel, Ch. 5.2-5.4] Jnury 30, 2003 [Red s Drem, Pixr,
a(e, x) = x. Diagrammatically, this is encoded as the following commutative diagrams / X
 4. Mon, Sept. 30 Lst time, we defined the quotient topology coming from continuous surjection q : X! Y. Recll tht q is quotient mp (nd Y hs the quotient topology) if V Y is open precisely when q (V ) X
4. Mon, Sept. 30 Lst time, we defined the quotient topology coming from continuous surjection q : X! Y. Recll tht q is quotient mp (nd Y hs the quotient topology) if V Y is open precisely when q (V ) X
Topic 3: 2D Transformations 9/10/2016. Today s Topics. Transformations. Lets start out simple. Points as Homogeneous 2D Point Coords
 Tody s Topics 3. Trnsformtions in 2D 4. Coordinte-free geometry 5. (curves & surfces) Topic 3: 2D Trnsformtions 6. Trnsformtions in 3D Simple Trnsformtions Homogeneous coordintes Homogeneous 2D trnsformtions
Tody s Topics 3. Trnsformtions in 2D 4. Coordinte-free geometry 5. (curves & surfces) Topic 3: 2D Trnsformtions 6. Trnsformtions in 3D Simple Trnsformtions Homogeneous coordintes Homogeneous 2D trnsformtions
CPSC (T1) 2nd Midterm Exam
 Signture: Fire Alrm Code: CPSC 44 2-2 (T) 2nd Midterm Exm Deprtment of Computer Science University of British Columbi K. Booth & R. Schrein Exm Instructions (Red Crefully). Sign the first pge of the exm
Signture: Fire Alrm Code: CPSC 44 2-2 (T) 2nd Midterm Exm Deprtment of Computer Science University of British Columbi K. Booth & R. Schrein Exm Instructions (Red Crefully). Sign the first pge of the exm
CS380: Computer Graphics Modeling Transformations. Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL:
 CS38: Computer Grphics Modeling Trnsformtions Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sgl.kist.c.kr/~sungeui/cg/ Clss Ojectives (Ch. 3.5) Know the clssic dt processing steps, rendering pipeline, for rendering
CS38: Computer Grphics Modeling Trnsformtions Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sgl.kist.c.kr/~sungeui/cg/ Clss Ojectives (Ch. 3.5) Know the clssic dt processing steps, rendering pipeline, for rendering
MA1008. Calculus and Linear Algebra for Engineers. Course Notes for Section B. Stephen Wills. Department of Mathematics. University College Cork
 MA1008 Clculus nd Liner Algebr for Engineers Course Notes for Section B Stephen Wills Deprtment of Mthemtics University College Cork s.wills@ucc.ie http://euclid.ucc.ie/pges/stff/wills/teching/m1008/ma1008.html
MA1008 Clculus nd Liner Algebr for Engineers Course Notes for Section B Stephen Wills Deprtment of Mthemtics University College Cork s.wills@ucc.ie http://euclid.ucc.ie/pges/stff/wills/teching/m1008/ma1008.html
AML710 CAD LECTURE 16 SURFACES. 1. Analytical Surfaces 2. Synthetic Surfaces
 AML7 CAD LECTURE 6 SURFACES. Anlticl Surfces. Snthetic Surfces Surfce Representtion From CAD/CAM point of view surfces re s importnt s curves nd solids. We need to hve n ide of curves for surfce cretion.
AML7 CAD LECTURE 6 SURFACES. Anlticl Surfces. Snthetic Surfces Surfce Representtion From CAD/CAM point of view surfces re s importnt s curves nd solids. We need to hve n ide of curves for surfce cretion.
Image interpolation. A reinterpretation of low-pass filtering. Image Interpolation
 Imge interpoltion A reinterprettion of low-pss filtering Imge Interpoltion Introduction Wht is imge interpoltion? (D-A conversion) Wh do we need it? Interpoltion Techniques 1D zero-order, first-order,
Imge interpoltion A reinterprettion of low-pss filtering Imge Interpoltion Introduction Wht is imge interpoltion? (D-A conversion) Wh do we need it? Interpoltion Techniques 1D zero-order, first-order,
3 4. Answers may vary. Sample: Reteaching Vertical s are.
 Chpter 7 Answers Alterntive Activities 7-2 1 2. Check students work. 3. The imge hs length tht is 2 3 tht of the originl segment nd is prllel to the originl segment. 4. The segments pss through the endpoints
Chpter 7 Answers Alterntive Activities 7-2 1 2. Check students work. 3. The imge hs length tht is 2 3 tht of the originl segment nd is prllel to the originl segment. 4. The segments pss through the endpoints
Orientation & Quaternions. CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2017
 Orienttion & Quternions CSE69: Computer Animtion Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 7 Orienttion Orienttion We will define orienttion to men n object s instntneous rottionl configurtion Think of
Orienttion & Quternions CSE69: Computer Animtion Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 7 Orienttion Orienttion We will define orienttion to men n object s instntneous rottionl configurtion Think of
CHAPTER III IMAGE DEWARPING (CALIBRATION) PROCEDURE
 CHAPTER III IMAGE DEWARPING (CALIBRATION) PROCEDURE 3.1 Scheimpflug Configurtion nd Perspective Distortion Scheimpflug criterion were found out to be the best lyout configurtion for Stereoscopic PIV, becuse
CHAPTER III IMAGE DEWARPING (CALIBRATION) PROCEDURE 3.1 Scheimpflug Configurtion nd Perspective Distortion Scheimpflug criterion were found out to be the best lyout configurtion for Stereoscopic PIV, becuse
B. Definition: The volume of a solid of known integrable cross-section area A(x) from x = a
 Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
CSCI 104. Rafael Ferreira da Silva. Slides adapted from: Mark Redekopp and David Kempe
 CSCI 0 fel Ferreir d Silv rfsilv@isi.edu Slides dpted from: Mrk edekopp nd Dvid Kempe LOG STUCTUED MEGE TEES Series Summtion eview Let n = + + + + k $ = #%& #. Wht is n? n = k+ - Wht is log () + log ()
CSCI 0 fel Ferreir d Silv rfsilv@isi.edu Slides dpted from: Mrk edekopp nd Dvid Kempe LOG STUCTUED MEGE TEES Series Summtion eview Let n = + + + + k $ = #%& #. Wht is n? n = k+ - Wht is log () + log ()
CS-184: Computer Graphics. Today. Clipping. Hidden Surface Removal. Tuesday, October 7, Clipping to view volume Clipping arbitrary polygons
 CS184: Computer Grphics Lecture #10: Clipping nd Hidden Surfces Prof. Jmes O Brien University of Cliforni, Berkeley V2008S101.0 1 Tody Clipping Clipping to view volume Clipping ritrry polygons Hidden Surfce
CS184: Computer Grphics Lecture #10: Clipping nd Hidden Surfces Prof. Jmes O Brien University of Cliforni, Berkeley V2008S101.0 1 Tody Clipping Clipping to view volume Clipping ritrry polygons Hidden Surfce
CS-184: Computer Graphics. Today. Lecture #10: Clipping and Hidden Surfaces ClippingAndHidden.key - October 27, 2014.
 1 CS184: Computer Grphics Lecture #10: Clipping nd Hidden Surfces!! Prof. Jmes O Brien University of Cliforni, Berkeley! V2013F101.0 Tody 2 Clipping Clipping to view volume Clipping ritrry polygons Hidden
1 CS184: Computer Grphics Lecture #10: Clipping nd Hidden Surfces!! Prof. Jmes O Brien University of Cliforni, Berkeley! V2013F101.0 Tody 2 Clipping Clipping to view volume Clipping ritrry polygons Hidden
Integration. September 28, 2017
 Integrtion September 8, 7 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my
Integrtion September 8, 7 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my
50 AMC LECTURES Lecture 2 Analytic Geometry Distance and Lines. can be calculated by the following formula:
 5 AMC LECTURES Lecture Anlytic Geometry Distnce nd Lines BASIC KNOWLEDGE. Distnce formul The distnce (d) between two points P ( x, y) nd P ( x, y) cn be clculted by the following formul: d ( x y () x )
5 AMC LECTURES Lecture Anlytic Geometry Distnce nd Lines BASIC KNOWLEDGE. Distnce formul The distnce (d) between two points P ( x, y) nd P ( x, y) cn be clculted by the following formul: d ( x y () x )
LU Decomposition. Mechanical Engineering Majors. Authors: Autar Kaw
 LU Decomposition Mechnicl Engineering Mjors Authors: Autr Kw Trnsforming Numericl Methods Eduction for STEM Undergrdutes // LU Decomposition LU Decomposition LU Decomposition is nother method to solve
LU Decomposition Mechnicl Engineering Mjors Authors: Autr Kw Trnsforming Numericl Methods Eduction for STEM Undergrdutes // LU Decomposition LU Decomposition LU Decomposition is nother method to solve
Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012
![Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012 Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012](/thumbs/96/127090604.jpg) Dynmic Progrmming Andres Klppenecker [prtilly bsed on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Dynmic Progrmming Optiml substructure An optiml solution to the problem contins within it optiml solutions to subproblems.
Dynmic Progrmming Andres Klppenecker [prtilly bsed on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Dynmic Progrmming Optiml substructure An optiml solution to the problem contins within it optiml solutions to subproblems.
Midterm 2 Sample solution
 Nme: Instructions Midterm 2 Smple solution CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fll 2012 November 28, 2012 This exm contins 9 pges, including this one. Mke sure you hve ll the pges. Write your nme on the
Nme: Instructions Midterm 2 Smple solution CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fll 2012 November 28, 2012 This exm contins 9 pges, including this one. Mke sure you hve ll the pges. Write your nme on the
Solution of Linear Algebraic Equations using the Gauss-Jordan Method
 Solution of Liner Algebric Equtions using the Guss-Jordn Method Populr pproch for solving liner equtions The Guss Jordn method depends on two properties of liner equtions: Scling one or more of ny of the
Solution of Liner Algebric Equtions using the Guss-Jordn Method Populr pproch for solving liner equtions The Guss Jordn method depends on two properties of liner equtions: Scling one or more of ny of the
Polynomial Texture Maps. Tom Malzbender Dan Gelb Hans Wolters Hewlett-Packard Laboratories
 Poynomi Textre Mps Tom Mzbender Dn Geb Hns Woters Hewett-Pckrd Lbortories Textre Mpping [ Ctm 74 ] Pro: Photogrphic inpt Simpicity Hrdwre Spport Con: Unreistic Sihoettes Sttic Lighting Bmp Mpping [ Binn
Poynomi Textre Mps Tom Mzbender Dn Geb Hns Woters Hewett-Pckrd Lbortories Textre Mpping [ Ctm 74 ] Pro: Photogrphic inpt Simpicity Hrdwre Spport Con: Unreistic Sihoettes Sttic Lighting Bmp Mpping [ Binn
CS-C3100 Computer Graphics, Fall 2016 Ray Casting II Intersection Extravaganza
 CS-C3100 Computer Grphics, Fll 2016 Ry Csting II Intersection Extrvgnz Henrik Wnn Jensen Jkko Lehtinen with lots of mteril from Frédo Durnd CS-C3100 Fll 2016 Lehtinen 1 Pinholes in Nture Flickr user Picture
CS-C3100 Computer Grphics, Fll 2016 Ry Csting II Intersection Extrvgnz Henrik Wnn Jensen Jkko Lehtinen with lots of mteril from Frédo Durnd CS-C3100 Fll 2016 Lehtinen 1 Pinholes in Nture Flickr user Picture
Math 17 - Review. Review for Chapter 12
 Mth 17 - eview Ying Wu eview for hpter 12 1. Given prmetric plnr curve x = f(t), y = g(t), where t b, how to eliminte the prmeter? (Use substitutions, or use trigonometry identities, etc). How to prmeterize
Mth 17 - eview Ying Wu eview for hpter 12 1. Given prmetric plnr curve x = f(t), y = g(t), where t b, how to eliminte the prmeter? (Use substitutions, or use trigonometry identities, etc). How to prmeterize
4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD. Study Guide. Parallel Lines and Planes P Q, O Q. Sample answers: A J, A F, and D E
 4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD Pges 142 147 Prllel Lines nd Plnes When plnes do not intersect, they re sid to e prllel. Also, when lines in the sme plne do not intersect, they re prllel. But when lines re not in
4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD Pges 142 147 Prllel Lines nd Plnes When plnes do not intersect, they re sid to e prllel. Also, when lines in the sme plne do not intersect, they re prllel. But when lines re not in
Fig.1. Let a source of monochromatic light be incident on a slit of finite width a, as shown in Fig. 1.
 Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
Solutions to Math 41 Final Exam December 12, 2011
 Solutions to Mth Finl Em December,. ( points) Find ech of the following its, with justifiction. If there is n infinite it, then eplin whether it is or. ( ) / ln() () (5 points) First we compute the it:
Solutions to Mth Finl Em December,. ( points) Find ech of the following its, with justifiction. If there is n infinite it, then eplin whether it is or. ( ) / ln() () (5 points) First we compute the it:
Union-Find Problem. Using Arrays And Chains. A Set As A Tree. Result Of A Find Operation
 Union-Find Problem Given set {,,, n} of n elements. Initilly ech element is in different set. ƒ {}, {},, {n} An intermixed sequence of union nd find opertions is performed. A union opertion combines two
Union-Find Problem Given set {,,, n} of n elements. Initilly ech element is in different set. ƒ {}, {},, {n} An intermixed sequence of union nd find opertions is performed. A union opertion combines two
Integration. October 25, 2016
 Integrtion October 5, 6 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my hve
Integrtion October 5, 6 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my hve
Functor (1A) Young Won Lim 10/5/17
 Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version 1.2 or ny lter version published
Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version 1.2 or ny lter version published
4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 4: Lagrange Multipliers
 Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
MATH 2530: WORKSHEET 7. x 2 y dz dy dx =
 MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES
 INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
Complete Coverage Path Planning of Mobile Robot Based on Dynamic Programming Algorithm Peng Zhou, Zhong-min Wang, Zhen-nan Li, Yang Li
 2nd Interntionl Conference on Electronic & Mechnicl Engineering nd Informtion Technology (EMEIT-212) Complete Coverge Pth Plnning of Mobile Robot Bsed on Dynmic Progrmming Algorithm Peng Zhou, Zhong-min
2nd Interntionl Conference on Electronic & Mechnicl Engineering nd Informtion Technology (EMEIT-212) Complete Coverge Pth Plnning of Mobile Robot Bsed on Dynmic Progrmming Algorithm Peng Zhou, Zhong-min
2D Projective transformation
 2D Projective trnsformtion The mpping of points from n N-D spce to n M-D subspce (M < N) w' w' w m m m 2 m m m 2 m m m 2 2 22 w' w' w m m m 2 m m m 2 m m 2 2 Boqun Chen 22 2D Projective trnsformtion w'
2D Projective trnsformtion The mpping of points from n N-D spce to n M-D subspce (M < N) w' w' w m m m 2 m m m 2 m m m 2 2 22 w' w' w m m m 2 m m m 2 m m 2 2 Boqun Chen 22 2D Projective trnsformtion w'
Functor (1A) Young Won Lim 8/2/17
 Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version 1.2 or ny lter version published
Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version 1.2 or ny lter version published
Visibility Algorithms
 Visibility Determintion Visibility Algorithms AKA, hidden surfce elimintion Roger Crwfis CIS 78 This set of slides reference slides used t Ohio Stte for instruction by Prof. Mchirju nd Prof. Hn-Wei Shen.
Visibility Determintion Visibility Algorithms AKA, hidden surfce elimintion Roger Crwfis CIS 78 This set of slides reference slides used t Ohio Stte for instruction by Prof. Mchirju nd Prof. Hn-Wei Shen.
Constrained Optimization. February 29
 Constrined Optimiztion Februry 9 Generl Problem min f( ) ( NLP) s.. t g ( ) i E i g ( ) i I i Modeling nd Constrints Adding constrints let s us model fr more richer set of problems. For our purpose we
Constrined Optimiztion Februry 9 Generl Problem min f( ) ( NLP) s.. t g ( ) i E i g ( ) i I i Modeling nd Constrints Adding constrints let s us model fr more richer set of problems. For our purpose we
Finite Automata. Lecture 4 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Jan 21, 2015
 Finite Automt Lecture 4 Sections 3.6-3.7 Ro T. Koether Hmpden-Sydney College Wed, Jn 21, 2015 Ro T. Koether (Hmpden-Sydney College) Finite Automt Wed, Jn 21, 2015 1 / 23 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt
Finite Automt Lecture 4 Sections 3.6-3.7 Ro T. Koether Hmpden-Sydney College Wed, Jn 21, 2015 Ro T. Koether (Hmpden-Sydney College) Finite Automt Wed, Jn 21, 2015 1 / 23 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt
15. 3D-Reconstruction from Vanishing Points
 15. 3D-Reconstruction from Vnishing Points Christin B.U. Perwss 1 nd Jon Lseny 2 1 Cvendish Lortory, Cmridge 2 C. U. Engineering Deprtment, Cmridge 15.1 Introduction 3D-reconstruction is currently n ctive
15. 3D-Reconstruction from Vnishing Points Christin B.U. Perwss 1 nd Jon Lseny 2 1 Cvendish Lortory, Cmridge 2 C. U. Engineering Deprtment, Cmridge 15.1 Introduction 3D-reconstruction is currently n ctive
Suffix trees, suffix arrays, BWT
 ALGORITHMES POUR LA BIO-INFORMATIQUE ET LA VISUALISATION COURS 3 Rluc Uricru Suffix trees, suffix rrys, BWT Bsed on: Suffix trees nd suffix rrys presenttion y Him Kpln Suffix trees course y Pco Gomez Liner-Time
ALGORITHMES POUR LA BIO-INFORMATIQUE ET LA VISUALISATION COURS 3 Rluc Uricru Suffix trees, suffix rrys, BWT Bsed on: Suffix trees nd suffix rrys presenttion y Him Kpln Suffix trees course y Pco Gomez Liner-Time
Basic Geometry and Topology
 Bsic Geometry nd Topology Stephn Stolz Septemer 7, 2015 Contents 1 Pointset Topology 1 1.1 Metric spces................................... 1 1.2 Topologicl spces................................ 5 1.3 Constructions
Bsic Geometry nd Topology Stephn Stolz Septemer 7, 2015 Contents 1 Pointset Topology 1 1.1 Metric spces................................... 1 1.2 Topologicl spces................................ 5 1.3 Constructions
Definition of Regular Expression
 Definition of Regulr Expression After the definition of the string nd lnguges, we re redy to descrie regulr expressions, the nottion we shll use to define the clss of lnguges known s regulr sets. Recll
Definition of Regulr Expression After the definition of the string nd lnguges, we re redy to descrie regulr expressions, the nottion we shll use to define the clss of lnguges known s regulr sets. Recll
A Tautology Checker loosely related to Stålmarck s Algorithm by Martin Richards
 A Tutology Checker loosely relted to Stålmrck s Algorithm y Mrtin Richrds mr@cl.cm.c.uk http://www.cl.cm.c.uk/users/mr/ University Computer Lortory New Museum Site Pemroke Street Cmridge, CB2 3QG Mrtin
A Tutology Checker loosely relted to Stålmrck s Algorithm y Mrtin Richrds mr@cl.cm.c.uk http://www.cl.cm.c.uk/users/mr/ University Computer Lortory New Museum Site Pemroke Street Cmridge, CB2 3QG Mrtin
Network Interconnection: Bridging CS 571 Fall Kenneth L. Calvert All rights reserved
 Network Interconnection: Bridging CS 57 Fll 6 6 Kenneth L. Clvert All rights reserved The Prolem We know how to uild (rodcst) LANs Wnt to connect severl LANs together to overcome scling limits Recll: speed
Network Interconnection: Bridging CS 57 Fll 6 6 Kenneth L. Clvert All rights reserved The Prolem We know how to uild (rodcst) LANs Wnt to connect severl LANs together to overcome scling limits Recll: speed
7. Texture Mapping. Idea. Examples Image Textures. Motivation. Textures can be images or procedures. Textures can be 2D or 3D
 3 4 Idea Add srface detail withot raising geometric complexity Textres can be images or procedres Textres can be D or 3D Motiation Wireframe Model + Lighting & Shading + Textre Mapping http://www.3drender.com/jbirn/prodctions.html
3 4 Idea Add srface detail withot raising geometric complexity Textres can be images or procedres Textres can be D or 3D Motiation Wireframe Model + Lighting & Shading + Textre Mapping http://www.3drender.com/jbirn/prodctions.html
CS311H: Discrete Mathematics. Graph Theory IV. A Non-planar Graph. Regions of a Planar Graph. Euler s Formula. Instructor: Işıl Dillig
 CS311H: Discrete Mthemtics Grph Theory IV Instructor: Işıl Dillig Instructor: Işıl Dillig, CS311H: Discrete Mthemtics Grph Theory IV 1/25 A Non-plnr Grph Regions of Plnr Grph The plnr representtion of
CS311H: Discrete Mthemtics Grph Theory IV Instructor: Işıl Dillig Instructor: Işıl Dillig, CS311H: Discrete Mthemtics Grph Theory IV 1/25 A Non-plnr Grph Regions of Plnr Grph The plnr representtion of
1 Drawing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrator
 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
Accuracy in Warping ECT LV Surfaces to CT Angiography Coronary Vessels
 Accurcy in Wrping ECT LV Surfces to CT Angiogrphy Coronry Vessels BC Lee, JN Kritzmn, JR Corbett, EP Ficro * University of Michign Helth System, Ann Arbor, MI Disclosure: * Receive softwre roylties from
Accurcy in Wrping ECT LV Surfces to CT Angiogrphy Coronry Vessels BC Lee, JN Kritzmn, JR Corbett, EP Ficro * University of Michign Helth System, Ann Arbor, MI Disclosure: * Receive softwre roylties from
arxiv: v1 [cs.cg] 9 Dec 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cg] 9 Dec 2016 arxiv: v1 [cs.cg] 9 Dec 2016](/thumbs/88/114661589.jpg) Some Counterexmples for Comptible Tringultions rxiv:62.0486v [cs.cg] 9 Dec 206 Cody Brnson Dwn Chndler 2 Qio Chen 3 Christin Chung 4 Andrew Coccimiglio 5 Sen L 6 Lily Li 7 Aïn Linn 8 Ann Lubiw 9 Clre Lyle
Some Counterexmples for Comptible Tringultions rxiv:62.0486v [cs.cg] 9 Dec 206 Cody Brnson Dwn Chndler 2 Qio Chen 3 Christin Chung 4 Andrew Coccimiglio 5 Sen L 6 Lily Li 7 Aïn Linn 8 Ann Lubiw 9 Clre Lyle
a < a+ x < a+2 x < < a+n x = b, n A i n f(x i ) x. i=1 i=1
 Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
TO REGULAR EXPRESSIONS
 Suject :- Computer Science Course Nme :- Theory Of Computtion DA TO REGULAR EXPRESSIONS Report Sumitted y:- Ajy Singh Meen 07000505 jysmeen@cse.iit.c.in BASIC DEINITIONS DA:- A finite stte mchine where
Suject :- Computer Science Course Nme :- Theory Of Computtion DA TO REGULAR EXPRESSIONS Report Sumitted y:- Ajy Singh Meen 07000505 jysmeen@cse.iit.c.in BASIC DEINITIONS DA:- A finite stte mchine where
CS 221: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 221: Artificil Intelligence Fll 2011 Lecture 2: Serch (Slides from Dn Klein, with help from Sturt Russell, Andrew Moore, Teg Grenger, Peter Norvig) Problem types! Fully observble, deterministic! single-belief-stte
CS 221: Artificil Intelligence Fll 2011 Lecture 2: Serch (Slides from Dn Klein, with help from Sturt Russell, Andrew Moore, Teg Grenger, Peter Norvig) Problem types! Fully observble, deterministic! single-belief-stte
Lecture 4 Single View Metrology
 Lecture 4 Single View Metrology Professor Silvio Svrese Computtionl Vision nd Geometry Lb Silvio Svrese Lecture 4-4-Jn-5 Lecture 4 Single View Metrology Review clibrtion nd 2D trnsformtions Vnishing points
Lecture 4 Single View Metrology Professor Silvio Svrese Computtionl Vision nd Geometry Lb Silvio Svrese Lecture 4-4-Jn-5 Lecture 4 Single View Metrology Review clibrtion nd 2D trnsformtions Vnishing points
Math 142, Exam 1 Information.
 Mth 14, Exm 1 Informtion. 9/14/10, LC 41, 9:30-10:45. Exm 1 will be bsed on: Sections 7.1-7.5. The corresponding ssigned homework problems (see http://www.mth.sc.edu/ boyln/sccourses/14f10/14.html) At
Mth 14, Exm 1 Informtion. 9/14/10, LC 41, 9:30-10:45. Exm 1 will be bsed on: Sections 7.1-7.5. The corresponding ssigned homework problems (see http://www.mth.sc.edu/ boyln/sccourses/14f10/14.html) At
Orthogonal line segment intersection
 Computtionl Geometry [csci 3250] Line segment intersection The prolem (wht) Computtionl Geometry [csci 3250] Orthogonl line segment intersection Applictions (why) Algorithms (how) A specil cse: Orthogonl
Computtionl Geometry [csci 3250] Line segment intersection The prolem (wht) Computtionl Geometry [csci 3250] Orthogonl line segment intersection Applictions (why) Algorithms (how) A specil cse: Orthogonl
Rational Numbers---Adding Fractions With Like Denominators.
 Rtionl Numbers---Adding Frctions With Like Denomintors. A. In Words: To dd frctions with like denomintors, dd the numertors nd write the sum over the sme denomintor. B. In Symbols: For frctions c nd b
Rtionl Numbers---Adding Frctions With Like Denomintors. A. In Words: To dd frctions with like denomintors, dd the numertors nd write the sum over the sme denomintor. B. In Symbols: For frctions c nd b
Engineer To Engineer Note
 Engineer To Engineer Note EE-186 Technicl Notes on using Anlog Devices' DSP components nd development tools Contct our technicl support by phone: (800) ANALOG-D or e-mil: dsp.support@nlog.com Or visit
Engineer To Engineer Note EE-186 Technicl Notes on using Anlog Devices' DSP components nd development tools Contct our technicl support by phone: (800) ANALOG-D or e-mil: dsp.support@nlog.com Or visit
If f(x, y) is a surface that lies above r(t), we can think about the area between the surface and the curve.
 Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the
Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the
Before We Begin. Introduction to Spatial Domain Filtering. Introduction to Digital Image Processing. Overview (1): Administrative Details (1):
 Overview (): Before We Begin Administrtive detils Review some questions to consider Winter 2006 Imge Enhncement in the Sptil Domin: Bsics of Sptil Filtering, Smoothing Sptil Filters, Order Sttistics Filters
Overview (): Before We Begin Administrtive detils Review some questions to consider Winter 2006 Imge Enhncement in the Sptil Domin: Bsics of Sptil Filtering, Smoothing Sptil Filters, Order Sttistics Filters
Pointer Analysis. CSE 501 Spring 15
 Pointer Anlysis CSE 501 Sring 15 Course Outline St8c nlysis Dtflow nd strct interret8on Alic8ons We re here Beyond generl- urose lnguges Progrm Verific8on Dynmic nlysis New comilers Tody Intro to ointer
Pointer Anlysis CSE 501 Sring 15 Course Outline St8c nlysis Dtflow nd strct interret8on Alic8ons We re here Beyond generl- urose lnguges Progrm Verific8on Dynmic nlysis New comilers Tody Intro to ointer
Lecture Overview. Knowledge-based systems in Bioinformatics, 1MB602. Procedural abstraction. The sum procedure. Integration as a procedure
 Lecture Overview Knowledge-bsed systems in Bioinformtics, MB6 Scheme lecture Procedurl bstrction Higher order procedures Procedures s rguments Procedures s returned vlues Locl vribles Dt bstrction Compound
Lecture Overview Knowledge-bsed systems in Bioinformtics, MB6 Scheme lecture Procedurl bstrction Higher order procedures Procedures s rguments Procedures s returned vlues Locl vribles Dt bstrction Compound
Stack. A list whose end points are pointed by top and bottom
 4. Stck Stck A list whose end points re pointed by top nd bottom Insertion nd deletion tke plce t the top (cf: Wht is the difference between Stck nd Arry?) Bottom is constnt, but top grows nd shrinks!
4. Stck Stck A list whose end points re pointed by top nd bottom Insertion nd deletion tke plce t the top (cf: Wht is the difference between Stck nd Arry?) Bottom is constnt, but top grows nd shrinks!
2 Computing all Intersections of a Set of Segments Line Segment Intersection
 15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
such that the S i cover S, or equivalently S
 MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
Fig.25: the Role of LEX
 The Lnguge for Specifying Lexicl Anlyzer We shll now study how to uild lexicl nlyzer from specifiction of tokens in the form of list of regulr expressions The discussion centers round the design of n existing
The Lnguge for Specifying Lexicl Anlyzer We shll now study how to uild lexicl nlyzer from specifiction of tokens in the form of list of regulr expressions The discussion centers round the design of n existing
ΕΠΛ323 - Θεωρία και Πρακτική Μεταγλωττιστών
 ΕΠΛ323 - Θωρία και Πρακτική Μταγλωττιστών Lecture 3 Lexicl Anlysis Elis Athnsopoulos elisthn@cs.ucy.c.cy Recognition of Tokens if expressions nd reltionl opertors if è if then è then else è else relop
ΕΠΛ323 - Θωρία και Πρακτική Μταγλωττιστών Lecture 3 Lexicl Anlysis Elis Athnsopoulos elisthn@cs.ucy.c.cy Recognition of Tokens if expressions nd reltionl opertors if è if then è then else è else relop
Pointwise convergence need not behave well with respect to standard properties such as continuity.
 Chpter 3 Uniform Convergence Lecture 9 Sequences of functions re of gret importnce in mny res of pure nd pplied mthemtics, nd their properties cn often be studied in the context of metric spces, s in Exmples
Chpter 3 Uniform Convergence Lecture 9 Sequences of functions re of gret importnce in mny res of pure nd pplied mthemtics, nd their properties cn often be studied in the context of metric spces, s in Exmples
Ray surface intersections
 Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Alignment of Long Sequences. BMI/CS Spring 2012 Colin Dewey
 Alignment of Long Sequences BMI/CS 776 www.biostt.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Spring 2012 Colin Dewey cdewey@biostt.wisc.edu Gols for Lecture the key concepts to understnd re the following how lrge-scle lignment
Alignment of Long Sequences BMI/CS 776 www.biostt.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Spring 2012 Colin Dewey cdewey@biostt.wisc.edu Gols for Lecture the key concepts to understnd re the following how lrge-scle lignment
Relations (3A) Young Won Lim 3/15/18
 Reltions (A) Copyright (c) 05 08 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version. or ny lter version published
Reltions (A) Copyright (c) 05 08 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version. or ny lter version published
Product of polynomials. Introduction to Programming (in C++) Numerical algorithms. Product of polynomials. Product of polynomials
 Product of polynomils Introduction to Progrmming (in C++) Numericl lgorithms Jordi Cortdell, Ricrd Gvldà, Fernndo Orejs Dept. of Computer Science, UPC Given two polynomils on one vrile nd rel coefficients,
Product of polynomils Introduction to Progrmming (in C++) Numericl lgorithms Jordi Cortdell, Ricrd Gvldà, Fernndo Orejs Dept. of Computer Science, UPC Given two polynomils on one vrile nd rel coefficients,
MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP
 MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP 30 2011 Contents 1. A brief diversion: reltively prime numbers 1 2. Lest common multiples 3 3. Finding ll solutions to x + by = c 4 Quick links to definitions/theorems Euclid
MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP 30 2011 Contents 1. A brief diversion: reltively prime numbers 1 2. Lest common multiples 3 3. Finding ll solutions to x + by = c 4 Quick links to definitions/theorems Euclid
HW Stereotactic Targeting
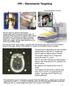 HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
UNIT 11. Query Optimization
 UNIT Query Optimiztion Contents Introduction to Query Optimiztion 2 The Optimiztion Process: An Overview 3 Optimiztion in System R 4 Optimiztion in INGRES 5 Implementing the Join Opertors Wei-Png Yng,
UNIT Query Optimiztion Contents Introduction to Query Optimiztion 2 The Optimiztion Process: An Overview 3 Optimiztion in System R 4 Optimiztion in INGRES 5 Implementing the Join Opertors Wei-Png Yng,
9.1 apply the distance and midpoint formulas
 9.1 pply the distnce nd midpoint formuls DISTANCE FORMULA MIDPOINT FORMULA To find the midpoint between two points x, y nd x y 1 1,, we Exmple 1: Find the distnce between the two points. Then, find the
9.1 pply the distnce nd midpoint formuls DISTANCE FORMULA MIDPOINT FORMULA To find the midpoint between two points x, y nd x y 1 1,, we Exmple 1: Find the distnce between the two points. Then, find the
Iterated Integrals. f (x; y) dy dx. p(x) To evaluate a type I integral, we rst evaluate the inner integral Z q(x) f (x; y) dy.
 Iterted Integrls Type I Integrls In this section, we begin the study of integrls over regions in the plne. To do so, however, requires tht we exmine the importnt ide of iterted integrls, in which inde
Iterted Integrls Type I Integrls In this section, we begin the study of integrls over regions in the plne. To do so, however, requires tht we exmine the importnt ide of iterted integrls, in which inde
Matrices and Systems of Equations
 Mtrices Mtrices nd Sstems of Equtions A mtri is rectngulr rr of rel numbers. CHAT Pre-Clculus Section 8. m m m............ n n n mn We will use the double subscript nottion for ech element of the mtri.
Mtrices Mtrices nd Sstems of Equtions A mtri is rectngulr rr of rel numbers. CHAT Pre-Clculus Section 8. m m m............ n n n mn We will use the double subscript nottion for ech element of the mtri.
Misrepresentation of Preferences
 Misrepresenttion of Preferences Gicomo Bonnno Deprtment of Economics, University of Cliforni, Dvis, USA gfbonnno@ucdvis.edu Socil choice functions Arrow s theorem sys tht it is not possible to extrct from
Misrepresenttion of Preferences Gicomo Bonnno Deprtment of Economics, University of Cliforni, Dvis, USA gfbonnno@ucdvis.edu Socil choice functions Arrow s theorem sys tht it is not possible to extrct from
Qubit allocation for quantum circuit compilers
 Quit lloction for quntum circuit compilers Nov. 10, 2017 JIQ 2017 Mrcos Yukio Sirichi Sylvin Collnge Vinícius Fernndes dos Sntos Fernndo Mgno Quintão Pereir Compilers for quntum computing The first genertion
Quit lloction for quntum circuit compilers Nov. 10, 2017 JIQ 2017 Mrcos Yukio Sirichi Sylvin Collnge Vinícius Fernndes dos Sntos Fernndo Mgno Quintão Pereir Compilers for quntum computing The first genertion
Floating Point Numbers and Interval Arithmetic
 480: 05092008 -- floting point; intervl rith Floting Point Numbers nd Intervl Arithmetic Are floting point numbers just broken? (from http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs) To mthemticin like me floting
480: 05092008 -- floting point; intervl rith Floting Point Numbers nd Intervl Arithmetic Are floting point numbers just broken? (from http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs) To mthemticin like me floting
Ray Casting II. Courtesy of James Arvo and David Kirk. Used with permission.
 y Csting II Courtesy of Jmes Arvo nd Dvid Kirk. Used with permission. MIT EECS 6.837 Frédo Durnd nd Brb Cutler Some slides courtesy of Leonrd McMilln MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler nd Durnd 1 eview of y Csting
y Csting II Courtesy of Jmes Arvo nd Dvid Kirk. Used with permission. MIT EECS 6.837 Frédo Durnd nd Brb Cutler Some slides courtesy of Leonrd McMilln MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler nd Durnd 1 eview of y Csting
ZZ - Advanced Math Review 2017
 ZZ - Advnced Mth Review Mtrix Multipliction Given! nd! find the sum of the elements of the product BA First, rewrite the mtrices in the correct order to multiply The product is BA hs order x since B is
ZZ - Advnced Mth Review Mtrix Multipliction Given! nd! find the sum of the elements of the product BA First, rewrite the mtrices in the correct order to multiply The product is BA hs order x since B is
5 Regular 4-Sided Composition
 Xilinx-Lv User Guide 5 Regulr 4-Sided Composition This tutoril shows how regulr circuits with 4-sided elements cn be described in Lv. The type of regulr circuits tht re discussed in this tutoril re those
Xilinx-Lv User Guide 5 Regulr 4-Sided Composition This tutoril shows how regulr circuits with 4-sided elements cn be described in Lv. The type of regulr circuits tht re discussed in this tutoril re those
Yoplait with Areas and Volumes
 Yoplit with Ares nd Volumes Yoplit yogurt comes in two differently shped continers. One is truncted cone nd the other is n ellipticl cylinder (see photos below). In this exercise, you will determine the
Yoplit with Ares nd Volumes Yoplit yogurt comes in two differently shped continers. One is truncted cone nd the other is n ellipticl cylinder (see photos below). In this exercise, you will determine the
Lecture 7: Building 3D Models (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Grphics (CS 4731) Lecture 7: Building 3D Models (Prt 1) Prof Emmnuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Stndrd d Unit itvectors Define y i j 1,0,0 0,1,0 k i k 0,0,1
Computer Grphics (CS 4731) Lecture 7: Building 3D Models (Prt 1) Prof Emmnuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Stndrd d Unit itvectors Define y i j 1,0,0 0,1,0 k i k 0,0,1
Thirty-fourth Annual Columbus State Invitational Mathematics Tournament. Instructions
 Thirty-fourth Annul Columbus Stte Invittionl Mthemtics Tournment Sponsored by Columbus Stte University Deprtment of Mthemtics Februry, 008 ************************* The Mthemtics Deprtment t Columbus Stte
Thirty-fourth Annul Columbus Stte Invittionl Mthemtics Tournment Sponsored by Columbus Stte University Deprtment of Mthemtics Februry, 008 ************************* The Mthemtics Deprtment t Columbus Stte
CS201 Discussion 10 DRAWTREE + TRIES
 CS201 Discussion 10 DRAWTREE + TRIES DrwTree First instinct: recursion As very generic structure, we could tckle this problem s follows: drw(): Find the root drw(root) drw(root): Write the line for the
CS201 Discussion 10 DRAWTREE + TRIES DrwTree First instinct: recursion As very generic structure, we could tckle this problem s follows: drw(): Find the root drw(root) drw(root): Write the line for the
Unit 5 Vocabulary. A function is a special relationship where each input has a single output.
 MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
EECS 281: Homework #4 Due: Thursday, October 7, 2004
 EECS 28: Homework #4 Due: Thursdy, October 7, 24 Nme: Emil:. Convert the 24-bit number x44243 to mime bse64: QUJD First, set is to brek 8-bit blocks into 6-bit blocks, nd then convert: x44243 b b 6 2 9
EECS 28: Homework #4 Due: Thursdy, October 7, 24 Nme: Emil:. Convert the 24-bit number x44243 to mime bse64: QUJD First, set is to brek 8-bit blocks into 6-bit blocks, nd then convert: x44243 b b 6 2 9
Universality of the Local Marginal Polytope
 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision nd Pttern Recognition Universlity of the Locl Mrginl Polytope Dniel Průš nd Tomáš Werner Center for Mchine Perception, Fculty of Electricl Engineering, Czech Technicl
2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision nd Pttern Recognition Universlity of the Locl Mrginl Polytope Dniel Průš nd Tomáš Werner Center for Mchine Perception, Fculty of Electricl Engineering, Czech Technicl
Unit #9 : Definite Integral Properties, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Illumination and Shading
 Illumintion nd hding In order to produce relistic imges, we must simulte the ppernce of surfces under vrious lighting conditions. Illumintion models: given the illumintion incident t point on surfce, wht
Illumintion nd hding In order to produce relistic imges, we must simulte the ppernce of surfces under vrious lighting conditions. Illumintion models: given the illumintion incident t point on surfce, wht
Digital Image Processing Chapter 5: Image Restoration
 Digital Image Processing Chapter 5: Image Restoration Concept of Image Restoration Image restoration is to restore a degraded image back to the original image while image enhancement is to maniplate the
Digital Image Processing Chapter 5: Image Restoration Concept of Image Restoration Image restoration is to restore a degraded image back to the original image while image enhancement is to maniplate the
Area & Volume. Chapter 6.1 & 6.2 September 25, y = 1! x 2. Back to Area:
 Bck to Are: Are & Volume Chpter 6. & 6. Septemer 5, 6 We cn clculte the re etween the x-xis nd continuous function f on the intervl [,] using the definite integrl:! f x = lim$ f x * i )%x n i= Where fx
Bck to Are: Are & Volume Chpter 6. & 6. Septemer 5, 6 We cn clculte the re etween the x-xis nd continuous function f on the intervl [,] using the definite integrl:! f x = lim$ f x * i )%x n i= Where fx
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Geometric Arithmetic October 31, 2012
 Fculty of Mthemtics Wterloo, Ontrio N2L 3G1 Grde 7/8 Mth Circles Geometric Arithmetic Octoer 31, 2012 Centre for Eduction in Mthemtics nd Computing Ancient Greece hs given irth to some of the most importnt
Fculty of Mthemtics Wterloo, Ontrio N2L 3G1 Grde 7/8 Mth Circles Geometric Arithmetic Octoer 31, 2012 Centre for Eduction in Mthemtics nd Computing Ancient Greece hs given irth to some of the most importnt
