If f(x, y) is a surface that lies above r(t), we can think about the area between the surface and the curve.
|
|
|
- Opal Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the intervl: Let r(t) be curve in the xy plne. If f(x, y) is surfce tht lies bove r(t), we cn think bout the re between the surfce nd the curve. 1
2 Specificlly, we think of the re enclosed bove the curve nd below the surfce. In the grph bove, the re tht we re interested in is tht shded in below the red curve on the surfce, nd bove the red curve in the xy plne. To find the vlue for this re, we evlute specific type of integrl known s the line integrl. The following theorem llows us to do so: Definition 3. If f(x, y) is continuous over the curve r(t) x(t) i + y(t) j in the xy plne, then the line integrl of f over r(t) from t to t b is f(x, y) ds f(x(t), y(t)) r (t) dt. In order to evlute line integrl over curve, we will need to prmeterize the curve by writing it s x(t) i + y(t) j, then clculte r (t). Finlly, we cn set up the integrl ccording to the theorem nd integrte s we would ny other single integrl. The theorem bove lso pplies to functions f(x, y, z) over spce curves r(t) x(t) i + y(t) j + z(t) k lmost exctly, with the obvious chnges. Exmple: A piece of tin is cut from circulr cylinder whose bse is circle of rdius 3 inches. At ny point (x, y) on the bse, the height of the object is given in inches by f(x, y) 1 + cos(πx)/4. Set up n integrl tht will yield the surfce re of the piece of tin. We cn grph the bse of the circulr cylinder in the xy plne by thinking of its defining eqution s x 2 + y 2 9: The cylinder from which we wish to cut the tin is grphed below: 2
3 The top of the piece of tin should be shped like f(x, y) 1 + cos(πx)/4: We wish to cut long the intersection of the two surfces: So the cut we mke yields the following shpe: 3
4 The line integrl of f over the region x 2 + y 2 9 will yield the surfce re of this shpe. We must first prmterize the curve x 2 + y 2 9; we cn think of it s x 3 cos t nd y 3 sin t (or r(t) 3 cos t i + 3 sin t j) on the intervl t 2π. Then r (t) 3 sin t i + 3 cos t j, nd r (t) ( 3 sin t) cos 2 t 9 3. Using the prmeteriztion, we rewrite f s f(x(t), y(t)) 1 + cos(π(3 cos t))/4. So the line integrl is f(x, y) ds 3 2π 2π f(x(t), y(t)) r (t) dt (1 + cos(π(3 cos t))/4)(3) dt 1 + cos(3π cos t) 4 dt. This is not n elementry integrl, but Mthemtic cn pproximte the vlue: 2π cos(3π cos t) dt So the surfce re of the piece of tin is pproximtely squre inches. Evlute the line integrl of f(x, y) 2 + x 2 y over the upper hlf of the unit circle x 2 + y 2 1. This is ctully the exmple from the grph t the beginning of the section: 4
5 The line integrl of f over this region will yield the re of the region below f tht lies bove the upper hlf of the circle. We need to hve prmeteriztion of the curve; we cn think of it s x cos t nd y sin t (or r(t) cos t i + sin t j) on the intervl t π. Then r (t) sin t i + cos t j, nd r (t) ( sin t) 2 + cos 2 t 1 1. Using the prmeteriztion, we rewrite f s f(x(t), y(t)) 2 + cos 2 t sin t. So the line integrl is f(x, y) ds π π f(x(t), y(t)) r (t) dt (2 + cos 2 t sin t)(1) dt 2 + cos 2 t sin t dt 2t 1 3 cos3 t π using the substitution u cos θ 2π π The number 2π is the re of the region below f tht lies bove the upper hlf of the circle. Suppose tht the curve is mde up of severl different components, s in the following grph: We cn still evlute the line integrl of function f over ; if is mde up of different curves 1, 2,..., n, then the line integrl of f over is just the sum of the line integrls over the 5
6 components; we write f(x, y) ds f(x, y) ds + 1 f(x, y) ds f(x, y) ds. n Exmple: Evlute 8xyz ds, where consists of the line segments 1 from (,, 3) to (24, 1, 3) followed by the verticl line segment 2 from (24, 1, 3) to (24, 1, ). Since we wnt to evlute line integrl over two different curves, we will write seprte integrl for ech of 1 nd 2. We need to strt by prmeterizing the line segments bove. To do so, recll tht we cn find the eqution of line in spce by finding vector prllel to the line nd point on the line. For the first line segment 1, the vector 24, 1, is prllel to the line, so the vector eqution for the line is r 1 (t) 24t i + 1t j + 3 k. Similrly,,, 3 is prllel to 2, whose vector eqution is r 2 (t) 24 i + 1 j + (3 3t) k. We will need to know r (t) for ech eqution: r 1 (t) 24 i + 1 j, nd r 2 (t) 3 k, so tht r 1 (t) nd r 2 (t) 9 3. The prmeteriztion for 1 is r 1 (t) 24t i + 1t j + 3 k, t 1, nd the prmeteriztion for 2 is r 2 (t) 24 i + 1 j + (3 3t) k, t 1. We will need this prmeteriztions to rewrite f. In the first cse, with x 24t, y 1t, nd z 3, f(x, y, z) xyz becomes 24t 1t 3 72t 2. In the second cse, with x 24, y 1, nd z 3 3t, f becomes 24 1 (3 3t) 72 72t. So the first integrl is 1 xyz ds 72t 2 26 dt t t 2 dt The second integrl is 2 xyz ds (72 72t) 3 dt ( t t t dt ) 1 6
7 So the line integrl of f over the two curves is Work As we hve seen, force cting on points in spce cn be represented by vector field. If we consider in prticulr the wy tht the force F P (x, y, z) i + Q(x, y, z) j + R(x, y, z) k cts long curve r(t) g(t) i + h(t) k + j(t) k, it mkes sense to think bout the work done by the force in moving prticle long the curve. We cn clculte the work quite esily using the following theorem: Definition 13. The work done by force F P (x, y, z) i + Q(x, y, z) j + R(x, y, z) k in moving n object over smooth curve r(t) g(t) i + h(t) k + j(t) k from t to t b is Recll tht W F ( r(t)) r (t)ds T r (t) r (t). F T ds. The theorem sys tht work cn be thought of s the line integrl of the tngentil component of the force. When clculting the integrl, we must be creful bout the order of integrtion; switching the direction of trvel long the curve r will chnge the sign of the nswer. lculting the work integrl in the given form my be difficult (since we prefer not to work in terms of the rc length prmeter s), so using one of the following equivlent forms my be helpful: W F T ds F ( r(t)) r (t)dt F d r ( P dg dt + Qdh dt + Rdj ) dt dt P dx + Q dy + R dz. Exmple Find the work done by the force field F (x, y) x 2 i xy j in moving prticle long the curve r(t) cos t i + sin t j on t π 2. To use the formul W F ( r(t)) r (t)dt, we will need to clculte F ( r(t)) nd r (t), both 7
8 of which re quite simple to do. The quntity F ( r(t)) is given by Next, we find r (t): Finlly, to evlute So the vlue for work is F ( r(t)) F (cos t, sin t) cos 2 t i cos t sin t j. r (t) sin t i + cos t j. F ( r(t)) r (t)dt, we will need to tke the dot product: F ( r(t)) r (t) (cos 2 t i cos t sin t j) ( sin t i + cos t j) W π 2 sin t cos 2 t sin t cos 2 t 2 sin t cos 2 t. F ( r(t)) r (t)dt 2 sin t cos 2 t dt 2 3 cos3 t π 2 using the substitution u cos t
a < a+ x < a+2 x < < a+n x = b, n A i n f(x i ) x. i=1 i=1
 Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
such that the S i cover S, or equivalently S
 MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
Math 35 Review Sheet, Spring 2014
 Mth 35 Review heet, pring 2014 For the finl exm, do ny 12 of the 15 questions in 3 hours. They re worth 8 points ech, mking 96, with 4 more points for netness! Put ll your work nd nswers in the provided
Mth 35 Review heet, pring 2014 For the finl exm, do ny 12 of the 15 questions in 3 hours. They re worth 8 points ech, mking 96, with 4 more points for netness! Put ll your work nd nswers in the provided
MATH 2530: WORKSHEET 7. x 2 y dz dy dx =
 MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
Math Line Integrals I
 Mth 213 - Line Integrls I Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky November 16, 2018 Homework Re-Red Section 16.2 for Mondy Work on Stewrt problems for 16.2: 1-21 (odd), 33-41 (odd), 49, 50 Begin Webwork
Mth 213 - Line Integrls I Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky November 16, 2018 Homework Re-Red Section 16.2 for Mondy Work on Stewrt problems for 16.2: 1-21 (odd), 33-41 (odd), 49, 50 Begin Webwork
Math 464 Fall 2012 Notes on Marginal and Conditional Densities October 18, 2012
 Mth 464 Fll 2012 Notes on Mrginl nd Conditionl Densities klin@mth.rizon.edu October 18, 2012 Mrginl densities. Suppose you hve 3 continuous rndom vribles X, Y, nd Z, with joint density f(x,y,z. The mrginl
Mth 464 Fll 2012 Notes on Mrginl nd Conditionl Densities klin@mth.rizon.edu October 18, 2012 Mrginl densities. Suppose you hve 3 continuous rndom vribles X, Y, nd Z, with joint density f(x,y,z. The mrginl
6.2 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method
 mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
B. Definition: The volume of a solid of known integrable cross-section area A(x) from x = a
 Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
Supplemental Notes: Line Integrals
 Nottion: Supplementl Notes: Line Integrls Let be n oriented curve prmeterized by r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) where t b. denotes the curve with its orienttion reversed. 1 + 2 mens tke curve 1 nd curve 2 nd
Nottion: Supplementl Notes: Line Integrls Let be n oriented curve prmeterized by r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) where t b. denotes the curve with its orienttion reversed. 1 + 2 mens tke curve 1 nd curve 2 nd
Area & Volume. Chapter 6.1 & 6.2 September 25, y = 1! x 2. Back to Area:
 Bck to Are: Are & Volume Chpter 6. & 6. Septemer 5, 6 We cn clculte the re etween the x-xis nd continuous function f on the intervl [,] using the definite integrl:! f x = lim$ f x * i )%x n i= Where fx
Bck to Are: Are & Volume Chpter 6. & 6. Septemer 5, 6 We cn clculte the re etween the x-xis nd continuous function f on the intervl [,] using the definite integrl:! f x = lim$ f x * i )%x n i= Where fx
Stained Glass Design. Teaching Goals:
 Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
)
 Chpter Five /SOLUTIONS Since the speed ws between nd mph during this five minute period, the fuel efficienc during this period is between 5 mpg nd 8 mpg. So the fuel used during this period is between
Chpter Five /SOLUTIONS Since the speed ws between nd mph during this five minute period, the fuel efficienc during this period is between 5 mpg nd 8 mpg. So the fuel used during this period is between
Ray surface intersections
 Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Iterated Integrals. f (x; y) dy dx. p(x) To evaluate a type I integral, we rst evaluate the inner integral Z q(x) f (x; y) dy.
 Iterted Integrls Type I Integrls In this section, we begin the study of integrls over regions in the plne. To do so, however, requires tht we exmine the importnt ide of iterted integrls, in which inde
Iterted Integrls Type I Integrls In this section, we begin the study of integrls over regions in the plne. To do so, however, requires tht we exmine the importnt ide of iterted integrls, in which inde
Math 142, Exam 1 Information.
 Mth 14, Exm 1 Informtion. 9/14/10, LC 41, 9:30-10:45. Exm 1 will be bsed on: Sections 7.1-7.5. The corresponding ssigned homework problems (see http://www.mth.sc.edu/ boyln/sccourses/14f10/14.html) At
Mth 14, Exm 1 Informtion. 9/14/10, LC 41, 9:30-10:45. Exm 1 will be bsed on: Sections 7.1-7.5. The corresponding ssigned homework problems (see http://www.mth.sc.edu/ boyln/sccourses/14f10/14.html) At
Section 10.4 Hyperbolas
 66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
MA1008. Calculus and Linear Algebra for Engineers. Course Notes for Section B. Stephen Wills. Department of Mathematics. University College Cork
 MA1008 Clculus nd Liner Algebr for Engineers Course Notes for Section B Stephen Wills Deprtment of Mthemtics University College Cork s.wills@ucc.ie http://euclid.ucc.ie/pges/stff/wills/teching/m1008/ma1008.html
MA1008 Clculus nd Liner Algebr for Engineers Course Notes for Section B Stephen Wills Deprtment of Mthemtics University College Cork s.wills@ucc.ie http://euclid.ucc.ie/pges/stff/wills/teching/m1008/ma1008.html
6.3 Volumes. Just as area is always positive, so is volume and our attitudes towards finding it.
 6.3 Volumes Just s re is lwys positive, so is volume nd our ttitudes towrds finding it. Let s review how to find the volume of regulr geometric prism, tht is, 3-dimensionl oject with two regulr fces seprted
6.3 Volumes Just s re is lwys positive, so is volume nd our ttitudes towrds finding it. Let s review how to find the volume of regulr geometric prism, tht is, 3-dimensionl oject with two regulr fces seprted
Math 17 - Review. Review for Chapter 12
 Mth 17 - eview Ying Wu eview for hpter 12 1. Given prmetric plnr curve x = f(t), y = g(t), where t b, how to eliminte the prmeter? (Use substitutions, or use trigonometry identities, etc). How to prmeterize
Mth 17 - eview Ying Wu eview for hpter 12 1. Given prmetric plnr curve x = f(t), y = g(t), where t b, how to eliminte the prmeter? (Use substitutions, or use trigonometry identities, etc). How to prmeterize
MA 124 (Calculus II) Lecture 2: January 24, 2019 Section A3. Professor Jennifer Balakrishnan,
 Wht is on tody Professor Jennifer Blkrishnn, jbl@bu.edu 1 Velocity nd net chnge 1 2 Regions between curves 3 1 Velocity nd net chnge Briggs-Cochrn-Gillett 6.1 pp. 398-46 Suppose you re driving long stright
Wht is on tody Professor Jennifer Blkrishnn, jbl@bu.edu 1 Velocity nd net chnge 1 2 Regions between curves 3 1 Velocity nd net chnge Briggs-Cochrn-Gillett 6.1 pp. 398-46 Suppose you re driving long stright
Matlab s Numerical Integration Commands
 Mtlb s Numericl Integrtion Commnds The relevnt commnds we consider re qud nd dblqud, triplequd. See the Mtlb help files for other integrtion commnds. By the wy, qud refers to dptive qudrture. To integrte:
Mtlb s Numericl Integrtion Commnds The relevnt commnds we consider re qud nd dblqud, triplequd. See the Mtlb help files for other integrtion commnds. By the wy, qud refers to dptive qudrture. To integrte:
50 AMC LECTURES Lecture 2 Analytic Geometry Distance and Lines. can be calculated by the following formula:
 5 AMC LECTURES Lecture Anlytic Geometry Distnce nd Lines BASIC KNOWLEDGE. Distnce formul The distnce (d) between two points P ( x, y) nd P ( x, y) cn be clculted by the following formul: d ( x y () x )
5 AMC LECTURES Lecture Anlytic Geometry Distnce nd Lines BASIC KNOWLEDGE. Distnce formul The distnce (d) between two points P ( x, y) nd P ( x, y) cn be clculted by the following formul: d ( x y () x )
Improper Integrals. October 4, 2017
 Improper Integrls October 4, 7 Introduction We hve seen how to clculte definite integrl when the it is rel number. However, there re times when we re interested to compute the integrl sy for emple 3. Here
Improper Integrls October 4, 7 Introduction We hve seen how to clculte definite integrl when the it is rel number. However, there re times when we re interested to compute the integrl sy for emple 3. Here
Double Integrals. MATH 375 Numerical Analysis. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Double Integrals
 Double Integrls MATH 375 Numericl Anlysis J. Robert Buchnn Deprtment of Mthemtics Fll 2013 J. Robert Buchnn Double Integrls Objectives Now tht we hve discussed severl methods for pproximting definite integrls
Double Integrls MATH 375 Numericl Anlysis J. Robert Buchnn Deprtment of Mthemtics Fll 2013 J. Robert Buchnn Double Integrls Objectives Now tht we hve discussed severl methods for pproximting definite integrls
Yoplait with Areas and Volumes
 Yoplit with Ares nd Volumes Yoplit yogurt comes in two differently shped continers. One is truncted cone nd the other is n ellipticl cylinder (see photos below). In this exercise, you will determine the
Yoplit with Ares nd Volumes Yoplit yogurt comes in two differently shped continers. One is truncted cone nd the other is n ellipticl cylinder (see photos below). In this exercise, you will determine the
4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 4: Lagrange Multipliers
 Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
Applications of the Definite Integral ( Areas and Volumes)
 Mth1242 Project II Nme: Applictions of the Definite Integrl ( Ares nd Volumes) In this project, we explore some pplictions of the definite integrl. We use integrls to find the re etween the grphs of two
Mth1242 Project II Nme: Applictions of the Definite Integrl ( Ares nd Volumes) In this project, we explore some pplictions of the definite integrl. We use integrls to find the re etween the grphs of two
Pythagoras theorem and trigonometry (2)
 HPTR 10 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry (2) 31 HPTR Liner equtions In hpter 19, Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry were used to find the lengths of sides nd the sizes of ngles in right-ngled tringles. These
HPTR 10 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry (2) 31 HPTR Liner equtions In hpter 19, Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry were used to find the lengths of sides nd the sizes of ngles in right-ngled tringles. These
Lily Yen and Mogens Hansen
 SKOLID / SKOLID No. 8 Lily Yen nd Mogens Hnsen Skolid hs joined Mthemticl Myhem which is eing reformtted s stnd-lone mthemtics journl for high school students. Solutions to prolems tht ppered in the lst
SKOLID / SKOLID No. 8 Lily Yen nd Mogens Hnsen Skolid hs joined Mthemticl Myhem which is eing reformtted s stnd-lone mthemtics journl for high school students. Solutions to prolems tht ppered in the lst
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 MATH 6 The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus (FTC) gives method of finding the signed re etween the grph of f nd the x-xis on the intervl [, ]. The theorem is: FTC: If f is
MATH 6 The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus (FTC) gives method of finding the signed re etween the grph of f nd the x-xis on the intervl [, ]. The theorem is: FTC: If f is
Unit 5 Vocabulary. A function is a special relationship where each input has a single output.
 MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
Solutions to Math 41 Final Exam December 12, 2011
 Solutions to Mth Finl Em December,. ( points) Find ech of the following its, with justifiction. If there is n infinite it, then eplin whether it is or. ( ) / ln() () (5 points) First we compute the it:
Solutions to Mth Finl Em December,. ( points) Find ech of the following its, with justifiction. If there is n infinite it, then eplin whether it is or. ( ) / ln() () (5 points) First we compute the it:
Unit #9 : Definite Integral Properties, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
8.2 Areas in the Plane
 39 Chpter 8 Applictions of Definite Integrls 8. Ares in the Plne Wht ou will lern out... Are Between Curves Are Enclosed Intersecting Curves Boundries with Chnging Functions Integrting with Respect to
39 Chpter 8 Applictions of Definite Integrls 8. Ares in the Plne Wht ou will lern out... Are Between Curves Are Enclosed Intersecting Curves Boundries with Chnging Functions Integrting with Respect to
Integration. October 25, 2016
 Integrtion October 5, 6 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my hve
Integrtion October 5, 6 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my hve
Pointwise convergence need not behave well with respect to standard properties such as continuity.
 Chpter 3 Uniform Convergence Lecture 9 Sequences of functions re of gret importnce in mny res of pure nd pplied mthemtics, nd their properties cn often be studied in the context of metric spces, s in Exmples
Chpter 3 Uniform Convergence Lecture 9 Sequences of functions re of gret importnce in mny res of pure nd pplied mthemtics, nd their properties cn often be studied in the context of metric spces, s in Exmples
It is recommended to change the limits of integration while doing a substitution.
 MAT 21 eptember 7, 216 Review Indrjit Jn. Generl Tips It is recommended to chnge the limits of integrtion while doing substitution. First write the min formul (eg. centroid, moment of inerti, mss, work
MAT 21 eptember 7, 216 Review Indrjit Jn. Generl Tips It is recommended to chnge the limits of integrtion while doing substitution. First write the min formul (eg. centroid, moment of inerti, mss, work
Fig.1. Let a source of monochromatic light be incident on a slit of finite width a, as shown in Fig. 1.
 Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
Introduction to Integration
 Introduction to Integrtion Definite integrls of piecewise constnt functions A constnt function is function of the form Integrtion is two things t the sme time: A form of summtion. The opposite of differentition.
Introduction to Integrtion Definite integrls of piecewise constnt functions A constnt function is function of the form Integrtion is two things t the sme time: A form of summtion. The opposite of differentition.
9.1 apply the distance and midpoint formulas
 9.1 pply the distnce nd midpoint formuls DISTANCE FORMULA MIDPOINT FORMULA To find the midpoint between two points x, y nd x y 1 1,, we Exmple 1: Find the distnce between the two points. Then, find the
9.1 pply the distnce nd midpoint formuls DISTANCE FORMULA MIDPOINT FORMULA To find the midpoint between two points x, y nd x y 1 1,, we Exmple 1: Find the distnce between the two points. Then, find the
Section 5.3 : Finding Area Between Curves
 MATH 9 Section 5. : Finding Are Between Curves Importnt: In this section we will lern just how to set up the integrls to find re etween curves. The finl nswer for ech emple in this hndout is given for
MATH 9 Section 5. : Finding Are Between Curves Importnt: In this section we will lern just how to set up the integrls to find re etween curves. The finl nswer for ech emple in this hndout is given for
ZZ - Advanced Math Review 2017
 ZZ - Advnced Mth Review Mtrix Multipliction Given! nd! find the sum of the elements of the product BA First, rewrite the mtrices in the correct order to multiply The product is BA hs order x since B is
ZZ - Advnced Mth Review Mtrix Multipliction Given! nd! find the sum of the elements of the product BA First, rewrite the mtrices in the correct order to multiply The product is BA hs order x since B is
x )Scales are the reciprocal of each other. e
 9. Reciprocls A Complete Slide Rule Mnul - eville W Young Chpter 9 Further Applictions of the LL scles The LL (e x ) scles nd the corresponding LL 0 (e -x or Exmple : 0.244 4.. Set the hir line over 4.
9. Reciprocls A Complete Slide Rule Mnul - eville W Young Chpter 9 Further Applictions of the LL scles The LL (e x ) scles nd the corresponding LL 0 (e -x or Exmple : 0.244 4.. Set the hir line over 4.
Integration. September 28, 2017
 Integrtion September 8, 7 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my
Integrtion September 8, 7 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my
10.5 Graphing Quadratic Functions
 0.5 Grphing Qudrtic Functions Now tht we cn solve qudrtic equtions, we wnt to lern how to grph the function ssocited with the qudrtic eqution. We cll this the qudrtic function. Grphs of Qudrtic Functions
0.5 Grphing Qudrtic Functions Now tht we cn solve qudrtic equtions, we wnt to lern how to grph the function ssocited with the qudrtic eqution. We cll this the qudrtic function. Grphs of Qudrtic Functions
Graphing Conic Sections
 Grphing Conic Sections Definition of Circle Set of ll points in plne tht re n equl distnce, clled the rdius, from fixed point in tht plne, clled the center. Grphing Circle (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 where
Grphing Conic Sections Definition of Circle Set of ll points in plne tht re n equl distnce, clled the rdius, from fixed point in tht plne, clled the center. Grphing Circle (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 where
MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP
 MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP 30 2011 Contents 1. A brief diversion: reltively prime numbers 1 2. Lest common multiples 3 3. Finding ll solutions to x + by = c 4 Quick links to definitions/theorems Euclid
MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP 30 2011 Contents 1. A brief diversion: reltively prime numbers 1 2. Lest common multiples 3 3. Finding ll solutions to x + by = c 4 Quick links to definitions/theorems Euclid
Lecture Overview. Knowledge-based systems in Bioinformatics, 1MB602. Procedural abstraction. The sum procedure. Integration as a procedure
 Lecture Overview Knowledge-bsed systems in Bioinformtics, MB6 Scheme lecture Procedurl bstrction Higher order procedures Procedures s rguments Procedures s returned vlues Locl vribles Dt bstrction Compound
Lecture Overview Knowledge-bsed systems in Bioinformtics, MB6 Scheme lecture Procedurl bstrction Higher order procedures Procedures s rguments Procedures s returned vlues Locl vribles Dt bstrction Compound
Introduction. Chapter 4: Complex Integration. Introduction (Cont d)
 Introduction Chpter 4: Complex Integrtion Li, Yongzho Stte Key Lbortory of Integrted Services Networks, Xidin University October 10, 2010 The two-dimensionl nture of the complex plne required us to generlize
Introduction Chpter 4: Complex Integrtion Li, Yongzho Stte Key Lbortory of Integrted Services Networks, Xidin University October 10, 2010 The two-dimensionl nture of the complex plne required us to generlize
APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION
 Chpter 3 DACS 1 Lok 004/05 CHAPTER 5 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 5.1 Geometricl Interprettion-Definite Integrl (pge 36) 5. Are of Region (pge 369) 5..1 Are of Region Under Grph (pge 369) Figure 5.7 shows
Chpter 3 DACS 1 Lok 004/05 CHAPTER 5 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 5.1 Geometricl Interprettion-Definite Integrl (pge 36) 5. Are of Region (pge 369) 5..1 Are of Region Under Grph (pge 369) Figure 5.7 shows
Class-XI Mathematics Conic Sections Chapter-11 Chapter Notes Key Concepts
 Clss-XI Mthemtics Conic Sections Chpter-11 Chpter Notes Key Concepts 1. Let be fixed verticl line nd m be nother line intersecting it t fixed point V nd inclined to it t nd ngle On rotting the line m round
Clss-XI Mthemtics Conic Sections Chpter-11 Chpter Notes Key Concepts 1. Let be fixed verticl line nd m be nother line intersecting it t fixed point V nd inclined to it t nd ngle On rotting the line m round
Introduction Transformation formulae Polar graphs Standard curves Polar equations Test GRAPHS INU0114/514 (MATHS 1)
 POLAR EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS GEOMETRY INU4/54 (MATHS ) Dr Adrin Jnnett MIMA CMth FRAS Polr equtions nd grphs / 6 Adrin Jnnett Objectives The purpose of this presenttion is to cover the following topics:
POLAR EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS GEOMETRY INU4/54 (MATHS ) Dr Adrin Jnnett MIMA CMth FRAS Polr equtions nd grphs / 6 Adrin Jnnett Objectives The purpose of this presenttion is to cover the following topics:
Chapter Spline Method of Interpolation More Examples Electrical Engineering
 Chpter. Spline Method of Interpoltion More Exmples Electricl Engineering Exmple Thermistors re used to mesure the temperture of bodies. Thermistors re bsed on mterils chnge in resistnce with temperture.
Chpter. Spline Method of Interpoltion More Exmples Electricl Engineering Exmple Thermistors re used to mesure the temperture of bodies. Thermistors re bsed on mterils chnge in resistnce with temperture.
1 Quad-Edge Construction Operators
 CS48: Computer Grphics Hndout # Geometric Modeling Originl Hndout #5 Stnford University Tuesdy, 8 December 99 Originl Lecture #5: 9 November 99 Topics: Mnipultions with Qud-Edge Dt Structures Scribe: Mike
CS48: Computer Grphics Hndout # Geometric Modeling Originl Hndout #5 Stnford University Tuesdy, 8 December 99 Originl Lecture #5: 9 November 99 Topics: Mnipultions with Qud-Edge Dt Structures Scribe: Mike
1 The Definite Integral
 The Definite Integrl Definition. Let f be function defined on the intervl [, b] where
The Definite Integrl Definition. Let f be function defined on the intervl [, b] where
arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 4 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 4 Jun 2012 arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 4 Jun 2012](/thumbs/76/73512534.jpg) Volumes of olids of Revolution. Unified pproch Jorge Mrtín-Morles nd ntonio M. Oller-Mrcén jorge@unizr.es, oller@unizr.es rxiv:5.v [mth.ho] Jun Centro Universitrio de l Defens - IUM. cdemi Generl Militr,
Volumes of olids of Revolution. Unified pproch Jorge Mrtín-Morles nd ntonio M. Oller-Mrcén jorge@unizr.es, oller@unizr.es rxiv:5.v [mth.ho] Jun Centro Universitrio de l Defens - IUM. cdemi Generl Militr,
f[a] x + f[a + x] x + f[a +2 x] x + + f[b x] x
![f[a] x + f[a + x] x + f[a +2 x] x + + f[b x] x f[a] x + f[a + x] x + f[a +2 x] x + + f[b x] x](/thumbs/81/84236407.jpg) Bsic Integrtion This chpter contins the fundmentl theory of integrtion. We begin with some problems to motivte the min ide: pproximtion by sum of slices. The chpter confronts this squrely, nd Chpter 3
Bsic Integrtion This chpter contins the fundmentl theory of integrtion. We begin with some problems to motivte the min ide: pproximtion by sum of slices. The chpter confronts this squrely, nd Chpter 3
5/9/17. Lesson 51 - FTC PART 2. Review FTC, PART 1. statement as the Integral Evaluation Theorem as it tells us HOW to evaluate the definite integral
 Lesson - FTC PART 2 Review! We hve seen definition/formul for definite integrl s n b A() = lim f ( i )Δ = f ()d = F() = F(b) F() n i=! where F () = f() (or F() is the ntiderivtive of f() b! And hve seen
Lesson - FTC PART 2 Review! We hve seen definition/formul for definite integrl s n b A() = lim f ( i )Δ = f ()d = F() = F(b) F() n i=! where F () = f() (or F() is the ntiderivtive of f() b! And hve seen
University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
Math 227 Problem Set V Solutions. f ds =
 Mth 7 Problem Set V Solutions If is urve with prmetriztion r(t), t b, then we define the line integrl f ds b f ( r(t) ) dr dt (t) dt. Evlute the line integrl f(x,y,z)ds for () f(x,y,z) xosz, the urve with
Mth 7 Problem Set V Solutions If is urve with prmetriztion r(t), t b, then we define the line integrl f ds b f ( r(t) ) dr dt (t) dt. Evlute the line integrl f(x,y,z)ds for () f(x,y,z) xosz, the urve with
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES
 INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD. Study Guide. Parallel Lines and Planes P Q, O Q. Sample answers: A J, A F, and D E
 4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD Pges 142 147 Prllel Lines nd Plnes When plnes do not intersect, they re sid to e prllel. Also, when lines in the sme plne do not intersect, they re prllel. But when lines re not in
4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD Pges 142 147 Prllel Lines nd Plnes When plnes do not intersect, they re sid to e prllel. Also, when lines in the sme plne do not intersect, they re prllel. But when lines re not in
Hyperbolas. Definition of Hyperbola
 CHAT Pre-Clculus Hyperols The third type of conic is clled hyperol. For n ellipse, the sum of the distnces from the foci nd point on the ellipse is fixed numer. For hyperol, the difference of the distnces
CHAT Pre-Clculus Hyperols The third type of conic is clled hyperol. For n ellipse, the sum of the distnces from the foci nd point on the ellipse is fixed numer. For hyperol, the difference of the distnces
Section 3.1: Sequences and Series
 Section.: Sequences d Series Sequences Let s strt out with the definition of sequence: sequence: ordered list of numbers, often with definite pttern Recll tht in set, order doesn t mtter so this is one
Section.: Sequences d Series Sequences Let s strt out with the definition of sequence: sequence: ordered list of numbers, often with definite pttern Recll tht in set, order doesn t mtter so this is one
P(r)dr = probability of generating a random number in the interval dr near r. For this probability idea to make sense we must have
 Rndom Numers nd Monte Crlo Methods Rndom Numer Methods The integrtion methods discussed so fr ll re sed upon mking polynomil pproximtions to the integrnd. Another clss of numericl methods relies upon using
Rndom Numers nd Monte Crlo Methods Rndom Numer Methods The integrtion methods discussed so fr ll re sed upon mking polynomil pproximtions to the integrnd. Another clss of numericl methods relies upon using
Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers
 In this section we present Lagrange s method for maximizing or minimizing a general function f(x, y, z) subject to a constraint (or side condition) of the form g(x, y, z) = k. Figure 1 shows this curve
In this section we present Lagrange s method for maximizing or minimizing a general function f(x, y, z) subject to a constraint (or side condition) of the form g(x, y, z) = k. Figure 1 shows this curve
Math Exam III Review
 Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Midterm 2 Sample solution
 Nme: Instructions Midterm 2 Smple solution CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fll 2012 November 28, 2012 This exm contins 9 pges, including this one. Mke sure you hve ll the pges. Write your nme on the
Nme: Instructions Midterm 2 Smple solution CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fll 2012 November 28, 2012 This exm contins 9 pges, including this one. Mke sure you hve ll the pges. Write your nme on the
MTH 146 Conics Supplement
 105- Review of Conics MTH 146 Conics Supplement In this section we review conics If ou ne more detils thn re present in the notes, r through section 105 of the ook Definition: A prol is the set of points
105- Review of Conics MTH 146 Conics Supplement In this section we review conics If ou ne more detils thn re present in the notes, r through section 105 of the ook Definition: A prol is the set of points
1. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES)
 Numbers nd Opertions, Algebr, nd Functions 45. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES) In sequence of terms involving eponentil growth, which the testing service lso clls geometric
Numbers nd Opertions, Algebr, nd Functions 45. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES) In sequence of terms involving eponentil growth, which the testing service lso clls geometric
Topics in Analytic Geometry
 Nme Chpter 10 Topics in Anltic Geometr Section 10.1 Lines Objective: In this lesson ou lerned how to find the inclintion of line, the ngle between two lines, nd the distnce between point nd line. Importnt
Nme Chpter 10 Topics in Anltic Geometr Section 10.1 Lines Objective: In this lesson ou lerned how to find the inclintion of line, the ngle between two lines, nd the distnce between point nd line. Importnt
f xx (x, y) = 6 + 6x f xy (x, y) = 0 f yy (x, y) = y In general, the quantity that we re interested in is
 1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
9 Graph Cutting Procedures
 9 Grph Cutting Procedures Lst clss we begn looking t how to embed rbitrry metrics into distributions of trees, nd proved the following theorem due to Brtl (1996): Theorem 9.1 (Brtl (1996)) Given metric
9 Grph Cutting Procedures Lst clss we begn looking t how to embed rbitrry metrics into distributions of trees, nd proved the following theorem due to Brtl (1996): Theorem 9.1 (Brtl (1996)) Given metric
The Basic Properties of the Integral
 The Bsic Properties of the Integrl When we compute the derivtive of complicted function, like + sin, we usull use differentition rules, like d [f()+g()] d f()+ d g(), to reduce the computtion d d d to
The Bsic Properties of the Integrl When we compute the derivtive of complicted function, like + sin, we usull use differentition rules, like d [f()+g()] d f()+ d g(), to reduce the computtion d d d to
Subtracting Fractions
 Lerning Enhncement Tem Model Answers: Adding nd Subtrcting Frctions Adding nd Subtrcting Frctions study guide. When the frctions both hve the sme denomintor (bottom) you cn do them using just simple dding
Lerning Enhncement Tem Model Answers: Adding nd Subtrcting Frctions Adding nd Subtrcting Frctions study guide. When the frctions both hve the sme denomintor (bottom) you cn do them using just simple dding
1 Drawing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrator
 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
WebAssign Lesson 1-3a Substitution Part 1 (Homework)
 WeAssign Lesson -3 Sustitution Prt (Homework) Current Score : / 3 Due : Fridy, June 7 04 :00 AM MDT Jimos Skriletz Mth 75, section 3, Summer 04 Instructor: Jimos Skriletz. /.5 points Suppose you hve the
WeAssign Lesson -3 Sustitution Prt (Homework) Current Score : / 3 Due : Fridy, June 7 04 :00 AM MDT Jimos Skriletz Mth 75, section 3, Summer 04 Instructor: Jimos Skriletz. /.5 points Suppose you hve the
Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9
 Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9 Some surfaces are defined implicitly, such as the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1. In general an implicitly defined surface has the equation
Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9 Some surfaces are defined implicitly, such as the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1. In general an implicitly defined surface has the equation
Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives
 Recall that if z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as and represent the rates of change of z in the x- and y-directions, that is, in the directions of the unit vectors i and
Recall that if z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as and represent the rates of change of z in the x- and y-directions, that is, in the directions of the unit vectors i and
Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012
![Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012 Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012](/thumbs/96/127090604.jpg) Dynmic Progrmming Andres Klppenecker [prtilly bsed on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Dynmic Progrmming Optiml substructure An optiml solution to the problem contins within it optiml solutions to subproblems.
Dynmic Progrmming Andres Klppenecker [prtilly bsed on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Dynmic Progrmming Optiml substructure An optiml solution to the problem contins within it optiml solutions to subproblems.
If you are at the university, either physically or via the VPN, you can download the chapters of this book as PDFs.
 Lecture 5 Wlks, Trils, Pths nd Connectedness Reding: Some of the mteril in this lecture comes from Section 1.2 of Dieter Jungnickel (2008), Grphs, Networks nd Algorithms, 3rd edition, which is ville online
Lecture 5 Wlks, Trils, Pths nd Connectedness Reding: Some of the mteril in this lecture comes from Section 1.2 of Dieter Jungnickel (2008), Grphs, Networks nd Algorithms, 3rd edition, which is ville online
In the last lecture, we discussed how valid tokens may be specified by regular expressions.
 LECTURE 5 Scnning SYNTAX ANALYSIS We know from our previous lectures tht the process of verifying the syntx of the progrm is performed in two stges: Scnning: Identifying nd verifying tokens in progrm.
LECTURE 5 Scnning SYNTAX ANALYSIS We know from our previous lectures tht the process of verifying the syntx of the progrm is performed in two stges: Scnning: Identifying nd verifying tokens in progrm.
Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals. Textbook: Section 16.2
 Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals Textbook: Section 16.2 Warm-Up: Derivatives of Vector Functions Suppose r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) ˆk parameterizes a curve C. The vector: is: r (t)
Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals Textbook: Section 16.2 Warm-Up: Derivatives of Vector Functions Suppose r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) ˆk parameterizes a curve C. The vector: is: r (t)
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring In-term exam April 11th. Suggested solutions
 Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus
 Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
Conic Sections Parabola Objective: Define conic section, parabola, draw a parabola, standard equations and their graphs
 Conic Sections Prol Ojective: Define conic section, prol, drw prol, stndrd equtions nd their grphs The curves creted y intersecting doule npped right circulr cone with plne re clled conic sections. If
Conic Sections Prol Ojective: Define conic section, prol, drw prol, stndrd equtions nd their grphs The curves creted y intersecting doule npped right circulr cone with plne re clled conic sections. If
called the vertex. The line through the focus perpendicular to the directrix is called the axis of the parabola.
 Review of conic sections Conic sections re grphs of the form REVIEW OF CONIC SECTIONS prols ellipses hperols P(, ) F(, p) O p =_p REVIEW OF CONIC SECTIONS In this section we give geometric definitions
Review of conic sections Conic sections re grphs of the form REVIEW OF CONIC SECTIONS prols ellipses hperols P(, ) F(, p) O p =_p REVIEW OF CONIC SECTIONS In this section we give geometric definitions
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 M Centres of Mss - Rigid bodies nd composites. Figure A continer is formed by removing right circulr solid cone of height l from uniform solid right circulr cylinder of height 6l. The centre O of the plne
M Centres of Mss - Rigid bodies nd composites. Figure A continer is formed by removing right circulr solid cone of height l from uniform solid right circulr cylinder of height 6l. The centre O of the plne
HW Stereotactic Targeting
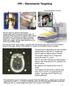 HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
Math 213 Calculus III Practice Exam 2 Solutions Fall 2002
 Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Chapter44. Polygons and solids. Contents: A Polygons B Triangles C Quadrilaterals D Solids E Constructing solids
 Chpter44 Polygons nd solids Contents: A Polygons B Tringles C Qudrilterls D Solids E Constructing solids 74 POLYGONS AND SOLIDS (Chpter 4) Opening prolem Things to think out: c Wht different shpes cn you
Chpter44 Polygons nd solids Contents: A Polygons B Tringles C Qudrilterls D Solids E Constructing solids 74 POLYGONS AND SOLIDS (Chpter 4) Opening prolem Things to think out: c Wht different shpes cn you
Math/CS 467/667 Programming Assignment 01. Adaptive Gauss Quadrature. q(x)p 4 (x) = 0
 Adptive Guss Qudrture 1. Find n orthogonl polynomil p 4 of degree 4 such tht 1 1 q(x)p 4 (x) = 0 for every polynomil q(x) of degree 3 or less. You my use Mple nd the Grm Schmidt process s done in clss.
Adptive Guss Qudrture 1. Find n orthogonl polynomil p 4 of degree 4 such tht 1 1 q(x)p 4 (x) = 0 for every polynomil q(x) of degree 3 or less. You my use Mple nd the Grm Schmidt process s done in clss.
3.5.1 Single slit diffraction
 3..1 Single slit diffrction ves pssing through single slit will lso diffrct nd produce n interference pttern. The reson for this is to do with the finite width of the slit. e will consider this lter. Tke
3..1 Single slit diffrction ves pssing through single slit will lso diffrct nd produce n interference pttern. The reson for this is to do with the finite width of the slit. e will consider this lter. Tke
Quiz2 45mins. Personal Number: Problem 1. (20pts) Here is an Table of Perl Regular Ex
 Long Quiz2 45mins Nme: Personl Numer: Prolem. (20pts) Here is n Tle of Perl Regulr Ex Chrcter Description. single chrcter \s whitespce chrcter (spce, t, newline) \S non-whitespce chrcter \d digit (0-9)
Long Quiz2 45mins Nme: Personl Numer: Prolem. (20pts) Here is n Tle of Perl Regulr Ex Chrcter Description. single chrcter \s whitespce chrcter (spce, t, newline) \S non-whitespce chrcter \d digit (0-9)
Background for Surface Integration
 Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Fall 2017 Midterm Exam 1 October 19, You may not use any books, notes, or electronic devices during this exam.
 15-112 Fll 2017 Midterm Exm 1 October 19, 2017 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: You my not use ny books, notes, or electronic devices during this exm. You my not sk questions bout the exm except for
15-112 Fll 2017 Midterm Exm 1 October 19, 2017 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: You my not use ny books, notes, or electronic devices during this exm. You my not sk questions bout the exm except for
Math 4 Review for Quarter 2 Cumulative Test
 Mth 4 Review for Qurter 2 Cumultive Test Nme: I. Right Tringle Trigonometry (3.1-3.3) Key Fcts Pythgoren Theorem - In right tringle, 2 + b 2 = c 2 where c is the hypotenuse s shown below. c b Trigonometric
Mth 4 Review for Qurter 2 Cumultive Test Nme: I. Right Tringle Trigonometry (3.1-3.3) Key Fcts Pythgoren Theorem - In right tringle, 2 + b 2 = c 2 where c is the hypotenuse s shown below. c b Trigonometric
d f(g(t), h(t)) = x dt + f ( y dt = 0. Notice that we can rewrite the relationship on the left hand side of the equality using the dot product: ( f
 Gradients and the Directional Derivative In 14.3, we discussed the partial derivatives f f and, which tell us the rate of change of the x y height of the surface defined by f in the x direction and the
Gradients and the Directional Derivative In 14.3, we discussed the partial derivatives f f and, which tell us the rate of change of the x y height of the surface defined by f in the x direction and the
Lecture 15. Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov Calculus and Vectors. Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations
 Lecture 15 Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov 10131 - Calculus and Vectors Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations Sergei Fedotov (University of Manchester) MATH10131 2011 1 / 5 Lecture 15 1 Length of a
Lecture 15 Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov 10131 - Calculus and Vectors Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations Sergei Fedotov (University of Manchester) MATH10131 2011 1 / 5 Lecture 15 1 Length of a
CS311H: Discrete Mathematics. Graph Theory IV. A Non-planar Graph. Regions of a Planar Graph. Euler s Formula. Instructor: Işıl Dillig
 CS311H: Discrete Mthemtics Grph Theory IV Instructor: Işıl Dillig Instructor: Işıl Dillig, CS311H: Discrete Mthemtics Grph Theory IV 1/25 A Non-plnr Grph Regions of Plnr Grph The plnr representtion of
CS311H: Discrete Mthemtics Grph Theory IV Instructor: Işıl Dillig Instructor: Işıl Dillig, CS311H: Discrete Mthemtics Grph Theory IV 1/25 A Non-plnr Grph Regions of Plnr Grph The plnr representtion of
