Technical Note. Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility With a Single Package. Introduction
|
|
|
- Godwin Joseph
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Technical Note Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility With a Single Package TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Introduction Introduction This technical note discusses how a single 24-ball BGA package (6 x 8mm) can support a variety of flash products, enabling designers to offer a range of densities, features and performance levels simply by replacing the installed flash device. The included details enable designers to develop a common hardware platform that can support these products: Quad SPI NOR flash: Includes legacy modes of single- or dual-bit data interface. Twin-quad SPI NOR flash: Doubles the performance and density of a traditional quad SPI device. Xccela flash: An octal SPI NOR flash device that enables designers to achieve up to 400 MB/s. Quad SPI NAND flash: Similar to Quad SPI NOR flash from an interface-perspective; storage cell is NAND, which requires E (and which is on-die and built in these devices), and it comes in higher-density options. Applies to M7xA family. This document shows the standard Quad SPI footprint and highlights the incremental changes to support all of the above devices. The end result is a single PB footprint, capable of supporting all devices mentioned in this technical note. MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 1 Products and specifications discussed herein are for evaluation and reference purposes only and are subject to change by Micron without notice. Products are only warranted by Micron to meet Micron's production data sheet specifications. All information discussed herein is provided on an "as is" basis, without warranties of any kind.
2 Quad SPI NOR Flash TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Quad SPI NOR Flash Traditional SPI flash devices can support read data widths of one, two or four bits with each clock. The figure below shows the basic footprint for a 6 x 8mm, 24-ball BGA package. The reserved for future use () balls on the perimeter of the package support forward migration to higher-performance devices. Other than the optional RESET#, all of the perimeter connections are available for expansion. Figure 1: Quad SPI NOR Flash Package A N RESET#/N B V W#/DQ2 D DQ1 DQ0 DQ3 2 E Top down ontrol Power Note: 1. See part number ordering information in the product data sheet for complete package names and details. 2. Depending on the selected device, DQ3 = DQ3/RESET or DQ3/HOLD. See part number ordering information in the product data sheet for details. Table 1: Ball Descriptions Name RESET# (optional) Description Used to reset the device ommon reference for all signals MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 2
3 TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Quad SPI NOR Flash Table 1: Ball Descriptions (ontinued) Name Description Power Supports either 1.8V or 3.3V ontrol The SPI interface has clock () and chip select (). The SPI protocol basic serial interface sends commands, addresses and data serially to and from the device synchronously with the clock. Operations occur only when the specific device is selected ( is LOW). This enables designs to support multiple devices using multiple chip selects, although only one device is enabled at a time. MT25Q SPI NOR flash devices range from 128Mb up to 2Gb. All of Micron's quad SPI NOR flash support the legacy data widths of x2 or x1. Typical performance of these devices is up to 166 MHz. Using the 166 MHz clock, STR example, and four data bit reads, a maximum of 83 MB/s performance can be achieved. If only two data bit reads are used, the maximum performance drops to 50% or 41.5 MB/s. If only a single data bit is used, the maximum read performance drops by another 50% or 21 MB/s. In addition to supporting the modes mentioned above, Micron's MT25Q quad SPI NOR flash devices feature the ability to support DTR, enabling data to be transferred on both the rising and falling edges of the clock, which is generally twice the throughput of STR. MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 3
4 Twin-Quad SPI NOR Flash TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Twin-Quad SPI NOR Flash Twin-quad SPI devices save significant board space because only one 6 x 8mm package is required with the MT25T family versus two with the MT25Q family. The figure below compares system implementations, with the left side showing an example using two discrete MT25Q devices and the right side showing an example using a single MT25T device. Figure 2: Quad SPI vs. Twin-Quad SPI omparison Two Quad SPI Packages One Twin-Quad SPI Packages Host controller (MPU/MU/So/ASI) QSPI I/O hannel 1 x4 SK MT25Q Host controller (MPU/MU/So/ASI) QSPI I/O hannel 1 x4 SK MT25T QSPI I/O hannel 2 x4 MT25Q SK QSPI I/O hannel 2 x4 (optional) SK Micron offers two versions of the MT25T device: a single-clock ()/single-chip select (), and a dual-clock/dual-chip select. The dual-clock/dual-chip select device may be the most straightforward choice when interfacing with truly independent host controllers. An example of this is when the two host controllers are operating completely separately, and the host is a multicore processor with each of the clocks operating in separate clock domains with separate controllers connected or two separate host controllers. The dual-clock/dual-chip select device may also be used in place of the singleclock/single-chip select device by tying the two signals together in the PB (which is done internally on the single-clock single/chip-select device). Figure 3 shows the single-clock/single-chip select 24-ball BGA ball assignments and routing. For ease of identification, heavy, solid black circles are drawn around the connections that are new to this particular implementation. In this case, seven new connections have been added to support the twin-quad over the original quad SPI device. Four of the new connections are additional DQ; the others are two additional ground connections and an additional power connection. The last three connections make the device more robust and improve power distribution. MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 4
5 TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Twin-Quad SPI NOR Flash Figure 3: MT25T 24-Ball BGA Package, Single-lock/Single-hip Select MT25T512 Die 1 A B N RESET# V DQ[3:0] D DQ1 DQ0 W#_1/DQ2 HOLD#_1/DQ3 DQ4 Die 2 E HOLD#_2/DQ7 W#_2/DQ6 DQ5 V DQ[7:4] Top down ontrol Power Figure 4 shows the two additional connections for the dual-clock/dual-chip select implementation. Figure 4: MT25T 24-Ball BGA Package, Dual-lock/Dual-hip Select MT25T512 Die 1 A _1 B _2 N _1 _2 RESET#/DNU V _1 DQ[3:0] D _1 DQ1 DQ0 W#_1/DQ2 HOLD#_1/DQ3 DQ4 Die 2 _2 E HOLD#_2/DQ7 W#_2/DQ6 DQ5 V _2 DQ[7:4] Top down ontrol Power MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 5
6 Xccela Flash (Octal SPI NOR Flash) TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Xccela Flash (Octal SPI NOR Flash) The MT35X Xccela flash is Micron's much-anticipated octal SPI device. The figure below shows the additional connections required to achieve the Xccela flash device's impressive performance of up to 400 MB/s. While data rates of 400 MB/s are not overly impressive by today's standards, achieving these data rates with only 11 signals (DQ[7:0],, and DQS) is impressive. The key to performance improvement is the addition of a single strobe signal, DQS, which makes it a source-synchronous interface. The addition of a DQS signal is similar to what was done in the evolution of mobile DRAM, from low-power single data rate (LPSDR) to low-power double data rate (LPDDR) devices. Like Xccela flash, LPDDR also supports a 200 MHz clock and 400 MT/s. Adding DQS to the interface makes the design of the host controller more straight-forward by simplifying the controller's task of finding the data eye. Figure 5: MT35X 24-Ball BGA Package A N RESET# Added: DQS V V PP (optional) B D V DQ1 DQS DQ0 V DQ2/W# DQ3 V PP DQ4 E DQ7 DQ6 DQ5 V Top down ontrol Power Xccela onsortium Micron understands the importance of having multiple vendors offer compatible products. To address this, Micron has formed the Xccela onsortium and has opened the specification up to other vendors. In addition, Micron is actively working with controller IP companies. This provides an alternative for companies that want to make use of Xccela flash components but might not have the resources to develop or modify their own controller. MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 6
7 Quad SPI NAND Flash Figure 6: Quad SPI NAND Flash Package TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Quad SPI NAND Flash Traditional SPI flash devices can support read data widths of one, two or four bits with each clock. The figure below shows the basic footprint for a 6 x 8mm, 24-ball BGA package. The reserved for future use () balls on the perimeter of the package support forward migration to higher-performance devices. With the exception of ball 1 (labeled as or N), most of the perimeter connections are available for expansion, and are used in the Xccela footprint as shown in Figure 5. Micron offers SPI NAND flash devices in 1Gb, 2Gb, 4Gb and 8Gb densities, making it ideal for embedded designs in need of low-cost boot or storage memory. On-die E means that the SPI NAND can often be supported with a standard SPI controller. hallenges for interfacing with SPI NAND often have to do with a flexible controller; with this device, the SPI controller must have the ability to support NAND commands as well as up to 5 bytes of NAND address. It must also accommodate the page size. Additionally, depending on the application, flash file system software may be required A N B V / W#/DQ2 D DQ1 DQ0 DQ3 E Top down ontrol Power MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 7
8 TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Performance Performance The figure below charts the performance levels of all of the SPI flash devices discussed in this technical note. Because performance is based on serial interfaces, the performance for smaller payloads is a fraction of the performance for larger payloads. This is because of the overhead that is required to input a command and three or four bytes of address for every payload. Note that random access for data sizes under eight bytes can result in unimpressive performance. But for payloads of 32 bytes or more, all of the devices discussed start to break the 50 MB/s floor, which makes implementing a cache or a buffering scheme critical to improve performance. Quad SPI NOR flash achieves a maximum of ~90 MB/s. As shown below, these devices use a total of only six signals to achieve ~90 MB/s. Twin-quad SPI NOR flash achieves ~180 MB/s or double that of the single quad SPI device. As shown below, as few as four additional signals (10 signals total) would be required to achieve~180 MB/s. Xccela flash achieves ~400 MB/s, or over double that of the twin-quad SPI device, by adding only a single DQS signal. This type of performance has generated interest in using Xccela flash as a low-pin count, execute-in-place (XIP) memory solution. Further improving on the XIP concept, Xccela flash can be used as a high-speed, nonvolatile memory that interfaces directly with the cache and memory subsystems. Assuming a 32-byte cache line, a cache line fill can be completed in about 160ns. If the cache line was 64 bytes, a line fill could be accomplished in about 240ns. Quad SPI NAND flash has a maximum read performance of 48 MB/s and supports clock frequencies of up to 133 MHz. The latest 4Gb and 8Gb devices offer a continuous read feature that is attractive for applications requiring large amounts of data to be read (like initial boot or downloading logged data). For flash densities exceeding the NOR sweet spot of under 512Mb, Micron's SPI NAND can offer lower cost, higher density solutions. Figure 7: Random Read Access Performance vs. Size Octal I/O DDR 200 MHz Twin Quad 166 MHz STR Quad I/O 166 MHz STR SPI NAND (E off) Transfer Rate (MB/s) k 2k 4k 8k 16k 32k 64k 128k 256k 512k 1M 2M Bytes per Fetch MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 8
9 TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility onclusion onclusion Micron's quad SPI NOR, twin-quad SPI NOR, Xccela (octal SPI) NOR and Quad SPI NAND flash devices are offered in a single 24-ball BGA (6 x 8mm) package, which gives designers a variety of technologies, densities, features and performance options in one PB footprint making migration between these products relatively easy. Figure 5 shows the superset ballout that enables your PB to support all of the devices mentioned in this tech note. Micron has a full line of DRAM and flash devices that are qualified to industrial and automotive temperature and quality specifications. ontact Micron for additional details on these or any other memory needs. MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 9
10 TN-25-08: Maximize SPI Flash Memory Design Flexibility Revision History Revision History Rev. 9/17 Rev. B 2/17 Rev. A 10/15 Added quad SPI NAND. Updated XTRMFlash product name to Xccela flash. Initial release 8000 S. Federal Way, P.O. Box 6, Boise, ID , Tel: Sales inquiries: Micron and the Micron logo are trademarks of Micron Technology, Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. MTD tn2508_spi_flash_design_flexibility.pdf - Rev. 9/17 EN 10
Technical Note. Reset Configurations for MT25Q, MT25T, and N25Q Flash Memory Devices. Introduction
 Technical Note Reset onfigurations for MT25Q, MT25T, and N25Q Flash Memory Devices Introduction This technical note provides a list of the reset configurations available for the MT25Q, MT25T, and N25Q
Technical Note Reset onfigurations for MT25Q, MT25T, and N25Q Flash Memory Devices Introduction This technical note provides a list of the reset configurations available for the MT25Q, MT25T, and N25Q
Maximum Monolithic Density Density Number of Stacks N25Q512Axxx. 512Mb 2 256Mb N25Q00AAxxx 1Gb 4 MT25Qxs01Gxxx. 1Gb 2 512Mb MT25Qxs02Gxxx 2Gb 4
 Technical te N25Q and MT25Q Serial Flash Stacked Devices Introduction Introduction This technical note describes the features of stacked devices for N25Q and MT25Q. These devices are memory with two or
Technical te N25Q and MT25Q Serial Flash Stacked Devices Introduction Introduction This technical note describes the features of stacked devices for N25Q and MT25Q. These devices are memory with two or
IoT, Wearable, Networking and Automotive Markets Driving External Memory Innovation Jim Cooke, Sr. Ecosystem Enabling Manager, Embedded Business Unit
 IoT, Wearable, Networking and Automotive Markets Driving External Memory Innovation Jim Cooke, Sr. Ecosystem Enabling Manager, Embedded Business Unit JCooke@Micron.com 2016Micron Technology, Inc. All rights
IoT, Wearable, Networking and Automotive Markets Driving External Memory Innovation Jim Cooke, Sr. Ecosystem Enabling Manager, Embedded Business Unit JCooke@Micron.com 2016Micron Technology, Inc. All rights
Technical Note. Migrating from Micron M25P to Micron MT25Q 128Mb. Introduction. TN-25-34: Migrating from M25P to MT25Q 128Mb.
 Technical Note TN-25-34: Migrating from to MT25Q 128Mb Introduction Migrating from Micron to Micron MT25Q 128Mb Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare the features of Micron Flash
Technical Note TN-25-34: Migrating from to MT25Q 128Mb Introduction Migrating from Micron to Micron MT25Q 128Mb Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare the features of Micron Flash
Power-Up, Power-Down, and Brownout Considerations on MT25Q, MT25T, and MT35X NOR Flash Memory
 Technical Note TN-25-38: Power Supply Considerations for NOR Flash Devices Introduction Power-Up, Power-Down, and Brownout Considerations on MT25Q, MT25T, and MT35X NOR Flash Memory Introduction This technical
Technical Note TN-25-38: Power Supply Considerations for NOR Flash Devices Introduction Power-Up, Power-Down, and Brownout Considerations on MT25Q, MT25T, and MT35X NOR Flash Memory Introduction This technical
Technical Note. Migrating from Micron M25PE to Micron MT25Q 128Mb. Introduction. TN-25-36: Migrating from M25PE to MT25Q 128Mb.
 Technical Note TN-25-36: Migrating from to MT25Q 128Mb Introduction Migrating from Micron to Micron MT25Q 128Mb Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare the features of Micron Flash
Technical Note TN-25-36: Migrating from to MT25Q 128Mb Introduction Migrating from Micron to Micron MT25Q 128Mb Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare the features of Micron Flash
Technical Note NAND Flash Performance Increase with PROGRAM PAGE CACHE MODE Command
 Technical Note NAND Flash Performance Increase with PROGRAM PAGE CACHE MODE Command TN-29-14: Increasing NAND Flash Performance Overview Overview NAND Flash devices are designed for applications requiring
Technical Note NAND Flash Performance Increase with PROGRAM PAGE CACHE MODE Command TN-29-14: Increasing NAND Flash Performance Overview Overview NAND Flash devices are designed for applications requiring
Technical Note. Improving Random Read Performance Using Micron's SNAP READ Operation. Introduction. TN-2993: SNAP READ Operation.
 Introduction Technical Note Improving Random Read Performance Using Micron's SNAP READ Operation Introduction NAND flash devices are designed for applications that require nonvolatile, high-density, fast
Introduction Technical Note Improving Random Read Performance Using Micron's SNAP READ Operation Introduction NAND flash devices are designed for applications that require nonvolatile, high-density, fast
Monitoring Ready/Busy Using the READ STATUS (70h) Command
 Introduction Technical Note Monitoring Ready/Busy Status in 2Gb, 4Gb, and 8Gb Micron NAND Flash Devices For detailed NAND Flash device information, refer to www.micron.com/products/nand/. Introduction
Introduction Technical Note Monitoring Ready/Busy Status in 2Gb, 4Gb, and 8Gb Micron NAND Flash Devices For detailed NAND Flash device information, refer to www.micron.com/products/nand/. Introduction
Technical Note. Migrating from Cypress's FL-S and FS-S to Micron's MT25Q. Introduction
 Technical Note TN-25-37: Migrating from Cypress's FL-S and FS-S to Micron's Introduction Migrating from Cypress's FL-S and FS-S to Micron's Introduction This technical note describes the process for converting
Technical Note TN-25-37: Migrating from Cypress's FL-S and FS-S to Micron's Introduction Migrating from Cypress's FL-S and FS-S to Micron's Introduction This technical note describes the process for converting
Technical Note Designing for High-Density DDR2 Memory
 Technical Note Designing for High-Density DDR2 Memory TN-47-16: Designing for High-Density DDR2 Memory Introduction Introduction DDR2 memory supports an extensive assortment of options for the system-level
Technical Note Designing for High-Density DDR2 Memory TN-47-16: Designing for High-Density DDR2 Memory Introduction Introduction DDR2 memory supports an extensive assortment of options for the system-level
Enabled (both during preconditioning and measurement) 4KB for random writes, 2MB for sequential writes
 Technical Note Introduction e.mmc Validation and Use Model Performance Introduction This technical note describes performance measurement of the Micron automotive e.mmc 5.0 device during validation and
Technical Note Introduction e.mmc Validation and Use Model Performance Introduction This technical note describes performance measurement of the Micron automotive e.mmc 5.0 device during validation and
Comparing Micron N25Q and Macronix MX25L Flash Devices
 Technical Note TN-12-14: Comparing and Flash Devices Introduction Comparing Micron and Macronix Flash Devices Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare features of the Micron (32Mb
Technical Note TN-12-14: Comparing and Flash Devices Introduction Comparing Micron and Macronix Flash Devices Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare features of the Micron (32Mb
Selecting a Flash Memory Solution for Embedded Applications
 NOR NAND Flash Guide Selecting a Flash Memory Solution for Embedded Applications When looking for flash memory for your embedded applications, Micron has the right solution: Our many years of embedded
NOR NAND Flash Guide Selecting a Flash Memory Solution for Embedded Applications When looking for flash memory for your embedded applications, Micron has the right solution: Our many years of embedded
Migrating from Spansion S25FL512S to Micron N25Q 512Mb Flash Device
 Technical Note TN-12-21: Migrating to Micron 512Mb Flash Device Introduction Migrating from Spansion 512S to Micron 512Mb Flash Device Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare features
Technical Note TN-12-21: Migrating to Micron 512Mb Flash Device Introduction Migrating from Spansion 512S to Micron 512Mb Flash Device Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare features
Product Brief LPDDR2-PCM and Mobile LPDDR2 121-Ball MCP
 Features Product Brief LPDDR2-PCM and Mobile LPDDR2 121-Ball MCP MT66R7072A10AB5ZZW.ZCA, MT66R7072A10ACUXZW.ZCA MT66R5072A10ACUXZW.ZFA Features Micron LPDDR2-PCM and LPDDR2 components RoHS-compliant, green
Features Product Brief LPDDR2-PCM and Mobile LPDDR2 121-Ball MCP MT66R7072A10AB5ZZW.ZCA, MT66R7072A10ACUXZW.ZCA MT66R5072A10ACUXZW.ZFA Features Micron LPDDR2-PCM and LPDDR2 components RoHS-compliant, green
Parallel NOR and PSRAM 88-Ball MCP Combination Memory
 Features Parallel NOR and PSRAM 88-Ball MCP Combination Memory MT38W2021A902ZQXZI.X69, MT38W2021A502ZQXZI.X69 Features Micron Parallel NOR Flash and PSRAM components RoHS-compliant, green package Space-saving
Features Parallel NOR and PSRAM 88-Ball MCP Combination Memory MT38W2021A902ZQXZI.X69, MT38W2021A502ZQXZI.X69 Features Micron Parallel NOR Flash and PSRAM components RoHS-compliant, green package Space-saving
Parallel NOR and PSRAM 56-Ball MCP Combination Memory
 Parallel NOR and PSRAM 56-Ball MCP Combination Memory MT38L3031AA03JVZZI.X7A 56-Ball MCP: 128Mb Parallel NOR and 64Mb PSRAM Features Features Micron Parallel NOR Flash and PSRAM components RoHS-compliant,
Parallel NOR and PSRAM 56-Ball MCP Combination Memory MT38L3031AA03JVZZI.X7A 56-Ball MCP: 128Mb Parallel NOR and 64Mb PSRAM Features Features Micron Parallel NOR Flash and PSRAM components RoHS-compliant,
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL256ABA 256Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL256ABA 256Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL128AB 128Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL128AB 128Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Overview. TN-29-08: Hamming Codes for NAND Flash Memory Devices Overview
 TN-9-8: Hamming Codes for NAND Flash Memory Devices Overview Technical Note Hamming Codes for NAND Flash Memory Devices For the latest NAND Flash product data sheets, see www.micron.com/products/nand/partlist.aspx.
TN-9-8: Hamming Codes for NAND Flash Memory Devices Overview Technical Note Hamming Codes for NAND Flash Memory Devices For the latest NAND Flash product data sheets, see www.micron.com/products/nand/partlist.aspx.
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QU128ABA 128Mb, 1.8V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QU128ABA 128Mb, 1.8V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and
MT29F4G08AAA, MT29F8G08BAA, MT29F8G08DAA, MT29F16G08FAA, MT29F8G08MAA, MT29F16G08QAA,
 Introduction Technical Note Improving NAND Flash Performance Using Two-Plane Command Enabled Micron Devices MT29F4G08AAA, MT29F8G08BAA, MT29F8G08DAA, MT29F16G08FAA, MT29F8G08MAA, MT29F16G08QAA, and MT29F32G08TAA
Introduction Technical Note Improving NAND Flash Performance Using Two-Plane Command Enabled Micron Devices MT29F4G08AAA, MT29F8G08BAA, MT29F8G08DAA, MT29F16G08FAA, MT29F8G08MAA, MT29F16G08QAA, and MT29F32G08TAA
Technical Note Using CellularRAM Memory to Replace Single- and Dual-Chip Select SRAM
 TN-45-7: CellularRAM Replacing Single- and Dual-CE# SRAM Introduction Technical Note Using CellularRAM Memory to Replace Single- and Dual-Chip Select SRAM Introduction Micron CellularRAM devices are designed
TN-45-7: CellularRAM Replacing Single- and Dual-CE# SRAM Introduction Technical Note Using CellularRAM Memory to Replace Single- and Dual-Chip Select SRAM Introduction Micron CellularRAM devices are designed
Technical Note. Adding ECC to a Data Bus with DDR4 x16 Components. Introduction. TN-40-41: Adding ECC With DDR4 x16 Components.
 Technical Note TN-40-41: Adding ECC With DDR4 Components Introduction Adding ECC to a Data Bus with DDR4 Components Introduction Systems with lower density memory requirements use DRAM components to save
Technical Note TN-40-41: Adding ECC With DDR4 Components Introduction Adding ECC to a Data Bus with DDR4 Components Introduction Systems with lower density memory requirements use DRAM components to save
Technical Note. Design Considerations when using NOR Flash on PCBs. Introduction and Definitions
 Technical Note Design Considerations when using NOR Flash on PCBs Introduction and Definitions TN-13-30: NOR Flash Memory: PCB Design Considerations Introduction and Definitions Table 1: Definitions Term
Technical Note Design Considerations when using NOR Flash on PCBs Introduction and Definitions TN-13-30: NOR Flash Memory: PCB Design Considerations Introduction and Definitions Table 1: Definitions Term
Technical Note. GDDR5X: The Next-Generation Graphics DRAM. Introduction. TN-ED-02: GDDR5X: The Next-Generation Graphics DRAM.
 Technical Note TN-ED-02: GDDR5X: The Next-Generation Graphics DRAM Introduction GDDR5X: The Next-Generation Graphics DRAM Introduction Since its market introduction in 2008, GDDR5 SGRAM has been the choice
Technical Note TN-ED-02: GDDR5X: The Next-Generation Graphics DRAM Introduction GDDR5X: The Next-Generation Graphics DRAM Introduction Since its market introduction in 2008, GDDR5 SGRAM has been the choice
NAND Flash and Mobile LPDRAM 168-Ball Package-on-Package (PoP) MCP Combination Memory (TI OMAP )
 NND Flash and Mobile LPDRM 168-Ball Package-on-Package (PoP) MCP Combination Memory (TI OMP ) MT29CxGxxMxxxxx Preliminary Features Features Micron NND Flash and LPDRM components RoHS-compliant, green package
NND Flash and Mobile LPDRM 168-Ball Package-on-Package (PoP) MCP Combination Memory (TI OMP ) MT29CxGxxMxxxxx Preliminary Features Features Micron NND Flash and LPDRM components RoHS-compliant, green package
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL512ABB 512Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL512ABB 512Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Optimize your system designs using Flash memory
 Optimize your system designs using Flash memory Howard Cheng Sr. Segment Applications Manager Embedded Solutions Group, Micron 2012 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Products are warranted only
Optimize your system designs using Flash memory Howard Cheng Sr. Segment Applications Manager Embedded Solutions Group, Micron 2012 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Products are warranted only
Migrating from Spansion Am29F to Micron M29F NOR Flash Memories
 Technical Note Introduction Migrating from Spansion Am29F to Micron M29F Memories Introduction This technical note explains the process for migrating an application based on Spansion Am29F200B, Am29F400B,
Technical Note Introduction Migrating from Spansion Am29F to Micron M29F Memories Introduction This technical note explains the process for migrating an application based on Spansion Am29F200B, Am29F400B,
Optimizing Your Memory Sub-System
 Optimizing Your Memory Sub-System AKA Choosing the right memories Design with Freescale Toronto Jim Cooke Ecosystems Enablement JCooke@micron.com Les Marentette FAE Manager LMarentette@tech-trek.com November
Optimizing Your Memory Sub-System AKA Choosing the right memories Design with Freescale Toronto Jim Cooke Ecosystems Enablement JCooke@micron.com Les Marentette FAE Manager LMarentette@tech-trek.com November
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Twin-Quad I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25TL256 256Mb, Twin-Quad I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 128Mb die) SPI-compatible serial
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Twin-Quad I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25TL256 256Mb, Twin-Quad I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 128Mb die) SPI-compatible serial
Technical Note. ONFI 4.0 Design Guide. Introduction. TN-29-83: ONFI 4.0 Design Guide. Introduction
 Introduction Technical Note ONFI 4.0 Design Guide Introduction The ONFI 4.0 specification enables high data rates of 667 MT/s and 800 MT/s. These high data rates, along with lower input/output capacitance,
Introduction Technical Note ONFI 4.0 Design Guide Introduction The ONFI 4.0 specification enables high data rates of 667 MT/s and 800 MT/s. These high data rates, along with lower input/output capacitance,
Technical Note Using Micron Asynchronous PSRAM with the NXP LPC2292 and LPC2294 Microcontrollers
 TN-45-29: Using Micron Async PSRAM with NXP LPC2292/2294 Introduction Technical Note Using Micron Asynchronous PSRAM with the NXP LPC2292 and LPC2294 Microcontrollers Introduction The NXP LPC2292 and LPC2294
TN-45-29: Using Micron Async PSRAM with NXP LPC2292/2294 Introduction Technical Note Using Micron Asynchronous PSRAM with the NXP LPC2292 and LPC2294 Microcontrollers Introduction The NXP LPC2292 and LPC2294
Technical Note. Micron N25Q to Micron MT25Q Migration. Introduction. TN-25-01: Micron N25Q to Micron MT25Q Migration. Introduction
 Technical Note Micron to Micron Migration TN-25-01: Micron to Micron Migration Introduction Introduction This technical note provides information to help convert a system design from the Micron Flash memory
Technical Note Micron to Micron Migration TN-25-01: Micron to Micron Migration Introduction Introduction This technical note provides information to help convert a system design from the Micron Flash memory
Making Informed Memory Choices FTF-IND-F0378
 Making Informed Memory Choices FTF-IND-F0378 Freescale Technology Forum Jim Cooke JCooke@micron.com Mike Kim MikeKim@micron.com April 10, 2014 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Products
Making Informed Memory Choices FTF-IND-F0378 Freescale Technology Forum Jim Cooke JCooke@micron.com Mike Kim MikeKim@micron.com April 10, 2014 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Products
NAND Flash Performance Improvement Using Internal Data Move
 TN-29-15: NAND Flash Internal Data Move Introduction Technical Note NAND Flash Performance Improvement Using Internal Data Move Introduction IDM Overview Micron offers a NAND Flash feature known as internal
TN-29-15: NAND Flash Internal Data Move Introduction Technical Note NAND Flash Performance Improvement Using Internal Data Move Introduction IDM Overview Micron offers a NAND Flash feature known as internal
Technical Note. Migrating from Micron M29W Devices to MT28EW NOR Flash Devices. Introduction. TN-13-50: Migrating M29W to MT28EW NOR Flash Devices
 Technical Note Migrating from Micron Devices to NOR Flash Devices TN-13-50: Migrating to NOR Flash Devices Introduction Introduction This technical note describes the process for converting a system design
Technical Note Migrating from Micron Devices to NOR Flash Devices TN-13-50: Migrating to NOR Flash Devices Introduction Introduction This technical note describes the process for converting a system design
Mobile LPDDR (only) 152-Ball Package-on-Package (PoP) TI-OMAP MT46HxxxMxxLxCG MT46HxxxMxxLxKZ
 Mobile LPDDR (only) 152-Ball Package-on-Package (PoP) TI-OMAP MT6HxxxMxxLxCG MT6HxxxMxxLxKZ 152-Ball x Mobile LPDDR (only) PoP (TI-OMAP) Features Features / = 1.70 1.95V Bidirectional data strobe per byte
Mobile LPDDR (only) 152-Ball Package-on-Package (PoP) TI-OMAP MT6HxxxMxxLxCG MT6HxxxMxxLxKZ 152-Ball x Mobile LPDDR (only) PoP (TI-OMAP) Features Features / = 1.70 1.95V Bidirectional data strobe per byte
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Twin-Quad I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25TU1G 1Gb, Twin-Quad I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 512Mb die) SPI-compatible serial
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Twin-Quad I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25TU1G 1Gb, Twin-Quad I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 512Mb die) SPI-compatible serial
Migrating from Macronix MX29GL-G/F and MX68GL-G Devices to MT28EW NOR Flash Devices
 Technical Note TN-13-38: Migrating MX29GL-G/F and MX68GL-G to MT28EW Introduction Migrating from Macronix MX29GL-G/F and MX68GL-G Devices to MT28EW Introduction This technical note describes the process
Technical Note TN-13-38: Migrating MX29GL-G/F and MX68GL-G to MT28EW Introduction Migrating from Macronix MX29GL-G/F and MX68GL-G Devices to MT28EW Introduction This technical note describes the process
Technical Note. Migrating from S29GL-S Devices to MT28FW NOR Flash Devices. Introduction. TN-13-41: Migrating S29GL-S to MT28FW NOR Flash Devices
 Technical Note Migrating from S29GL-S Devices to MT28FW NOR Flash Devices TN-3-: Migrating S29GL-S to MT28FW NOR Flash Devices Introduction Introduction This technical note describes the process for converting
Technical Note Migrating from S29GL-S Devices to MT28FW NOR Flash Devices TN-3-: Migrating S29GL-S to MT28FW NOR Flash Devices Introduction Introduction This technical note describes the process for converting
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL128ABA 128Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL128ABA 128Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB
 DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB, 2GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB, 2GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features
1. The values of t RCD and t RP for -335 modules show 18ns to align with industry specifications; actual DDR SDRAM device specifications are 15ns.
 UDIMM MT4VDDT1664A 128MB MT4VDDT3264A 256MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 128MB, 256MB (x64, SR) 184-Pin UDIMM Features Features 184-pin, unbuffered dual in-line
UDIMM MT4VDDT1664A 128MB MT4VDDT3264A 256MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 128MB, 256MB (x64, SR) 184-Pin UDIMM Features Features 184-pin, unbuffered dual in-line
Command Register Settings Description Notes
 Technical Note e.mmc Automotive 5.0 Cache Features TN-FC-50: e.mmc Automotive 5.0 Cache Features Introduction Introduction This technical note introduces an optional cache feature defined in the e.mmc
Technical Note e.mmc Automotive 5.0 Cache Features TN-FC-50: e.mmc Automotive 5.0 Cache Features Introduction Introduction This technical note introduces an optional cache feature defined in the e.mmc
Options. Data Rate (MT/s) CL = 3 CL = 2.5 CL = 2-40B PC PC PC
 DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDF6464A 512MB 1 MT16VDDF12864A 1GB 1 For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features Features 184-pin,
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDF6464A 512MB 1 MT16VDDF12864A 1GB 1 For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features Features 184-pin,
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Twin-Quad I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25TL256 256Mb, Twin-Quad I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 128Mb die) SPI-compatible serial
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Twin-Quad I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25TL256 256Mb, Twin-Quad I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 128Mb die) SPI-compatible serial
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL512AB 512Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double transfer
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL512AB 512Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double transfer
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT8VDDT3264A 256MB MT8VDDT6464A 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site:
 DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT8VDDT3264A 256MB MT8VDDT6464A 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features Features 184-pin, unbuffered
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT8VDDT3264A 256MB MT8VDDT6464A 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features Features 184-pin, unbuffered
Technical Note. Comparing Micron N25Q and M25P Flash Devices. Introduction. TN-12-12: Comparing N25Q and M25P Flash Devices.
 Technical Note Comparing Micron and Flash Devices TN-12-12: Comparing and Flash Devices Introduction Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare features of the Micron serial- Flash family
Technical Note Comparing Micron and Flash Devices TN-12-12: Comparing and Flash Devices Introduction Introduction The purpose of this technical note is to compare features of the Micron serial- Flash family
MT51J256M32 16 Meg x 32 I/O x 16 banks, 32 Meg x 16 I/O x 16 banks. Options 1. Note:
 GDDR SGRM 8Gb: x6, x GDDR SGRM Features MTJ6M 6 Meg x I/O x 6 banks, Meg x 6 I/O x 6 banks Features = =.V ±% and.v ±% Data rate: 6.0 Gb/s, 7.0 Gb/s, 8.0 Gb/s 6 internal banks Four bank groups for t CCDL
GDDR SGRM 8Gb: x6, x GDDR SGRM Features MTJ6M 6 Meg x I/O x 6 banks, Meg x 6 I/O x 6 banks Features = =.V ±% and.v ±% Data rate: 6.0 Gb/s, 7.0 Gb/s, 8.0 Gb/s 6 internal banks Four bank groups for t CCDL
DDR SDRAM UDIMM. Draft 9/ 9/ MT18VDDT6472A 512MB 1 MT18VDDT12872A 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site:
 DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT18VDDT6472A 512MB 1 MT18VDDT12872A 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB (x72, ECC, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features Features 184-pin,
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT18VDDT6472A 512MB 1 MT18VDDT12872A 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB (x72, ECC, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features Features 184-pin,
New Architecture for Code-Shadowing Applications. Anil Gupta Technical Executive, Winbond Electronics
 New Architecture for Code-Shadowing Applications Dual-buffer SPI-NAND Arch providing SPI-NOR compatibility Anil Gupta Technical Executive, Winbond Electronics Santa Clara, CA 1 Key features of New Architecture
New Architecture for Code-Shadowing Applications Dual-buffer SPI-NAND Arch providing SPI-NOR compatibility Anil Gupta Technical Executive, Winbond Electronics Santa Clara, CA 1 Key features of New Architecture
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QU256ABA 256Mb, 1.8V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QU256ABA 256Mb, 1.8V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN MAX Address Access Time
 TECHNICAL NOTE TN-00-17 TIMING SPECIFICATION DERATING FOR HIGH CAPACITANCE OUTPUT LOADING Introduction Memory systems are varied in the number of controllers, memory, and other devices that may share a
TECHNICAL NOTE TN-00-17 TIMING SPECIFICATION DERATING FOR HIGH CAPACITANCE OUTPUT LOADING Introduction Memory systems are varied in the number of controllers, memory, and other devices that may share a
Technical Note. One-Time Programmable (OTP) Operations. Introduction. TN-29-68: 2Gb: x8, x16 NAND Flash Memory. Introduction
 Technical Note Introduction Introduction This technical note describes one-time programmable () operations in the following Micron NAND Flash devices: MT29F2G08ABAEAH4 MT29F2G08ABAEAWP MT29F2G08ABBEAH4
Technical Note Introduction Introduction This technical note describes one-time programmable () operations in the following Micron NAND Flash devices: MT29F2G08ABAEAH4 MT29F2G08ABAEAWP MT29F2G08ABBEAH4
Technical Note. SMART Command Feature Set for the eu500. Introduction. TN-FD-35: eu500 eusb SMART Commands. Introduction
 Technical Note SMART Command Feature Set for the eu500 Introduction Introduction This technical note provides the self-monitoring, analysis, and reporting technology (SMART) command (B0h) feature set for
Technical Note SMART Command Feature Set for the eu500 Introduction Introduction This technical note provides the self-monitoring, analysis, and reporting technology (SMART) command (B0h) feature set for
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB Sector Erase MT25QU512ABB 512Mb, 1.8V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB Sector Erase MT25QU512ABB 512Mb, 1.8V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and
Micron Memory Support for NXP i.mx6 Platforms
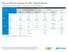 Micron Memory Support for NXP i.mx6 Platforms i.mx Processor Memory i.mx 6Quad/i.MX 6Dual/DualLite/Solo i.mx 6QuadPlus/i.MX 6DualPlus i.mx 6SoloLite i.mx 6SoloX SABRE for Automotive Infotainment SABRE
Micron Memory Support for NXP i.mx6 Platforms i.mx Processor Memory i.mx 6Quad/i.MX 6Dual/DualLite/Solo i.mx 6QuadPlus/i.MX 6DualPlus i.mx 6SoloLite i.mx 6SoloX SABRE for Automotive Infotainment SABRE
Micron Memory Support for NXP i.mx8 Platforms
 Micron Memory Support for NXP i.mx8 Platforms i.mx Processor Memory i.mx 8 Quad Max, i.mx8 Quad Plus, i.mx8 Quad i.mx8 Quad X Plus, i.mx8 Dual X Plus, i.mx8 Dual X i.mx8 M Quad / Quad Lite i.mx8 M Dual
Micron Memory Support for NXP i.mx8 Platforms i.mx Processor Memory i.mx 8 Quad Max, i.mx8 Quad Plus, i.mx8 Quad i.mx8 Quad X Plus, i.mx8 Dual X Plus, i.mx8 Dual X i.mx8 M Quad / Quad Lite i.mx8 M Dual
Technical Note Using CellularRAM to Replace UtRAM
 Technical Note Using CellularRAM to Replace UtRAM TN-45-13: CellularRAM replacing UtRAM Introduction Introduction The Micron family of CellularRAM devices is designed to be backward compatible with 6T
Technical Note Using CellularRAM to Replace UtRAM TN-45-13: CellularRAM replacing UtRAM Introduction Introduction The Micron family of CellularRAM devices is designed to be backward compatible with 6T
GLS85VM1016B / 1032B / 1064B Industrial Temp emmc NANDrive
 Features Industry Standard Embedded MultiMediaCard (emmc) Host Interface - JEDEC/MMC Standard Version 4.4 JESD84-A44 compliant - Backward compatible with emmc 4.3 Performance - emmc clock speed: Up to
Features Industry Standard Embedded MultiMediaCard (emmc) Host Interface - JEDEC/MMC Standard Version 4.4 JESD84-A44 compliant - Backward compatible with emmc 4.3 Performance - emmc clock speed: Up to
* Performance and power specifications subject to change
 Features Industry Standard Embedded MultiMediaCard (emmc) Host Interface - JEDEC/MMC Standard Version 5.1 JESD84-B51 compliant - Backward compatible with previous MMC Performance - emmc clock speed: Up
Features Industry Standard Embedded MultiMediaCard (emmc) Host Interface - JEDEC/MMC Standard Version 5.1 JESD84-B51 compliant - Backward compatible with previous MMC Performance - emmc clock speed: Up
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q512A 512Mb, Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 256Mb die) SPI-compatible serial bus interface Double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q512A 512Mb, Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 256Mb die) SPI-compatible serial bus interface Double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL512ABB 512Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL512ABB 512Mb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Single and double
Macronix MX25Lxxx45G Serial Flash DTR Introduction
 1. Introduction Macronix MX25Lxxx45G Serial NOR flash support DTR (Double Transfer Rate) Reads in the x1, x2, and x4 I/O modes. DTR allows address and data to be transferred on both the rising and falling
1. Introduction Macronix MX25Lxxx45G Serial NOR flash support DTR (Double Transfer Rate) Reads in the x1, x2, and x4 I/O modes. DTR allows address and data to be transferred on both the rising and falling
DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT8VDDT1664H 128MB 1. MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 2 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site:
 SODIMM MT8VDDT1664H 128MB 1 128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin SODIMM Features MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 2 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features
SODIMM MT8VDDT1664H 128MB 1 128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin SODIMM Features MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 2 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features
Technical Note. Software Driver for M29EW NOR Flash Memory. Introduction. TN-13-12: Software Driver for M29EW NOR Flash Memory.
 Technical Note TN-13-12: Software Driver for M29EW NOR Flash Memory Introduction Software Driver for M29EW NOR Flash Memory Introduction This technical note describes the C library source code for the
Technical Note TN-13-12: Software Driver for M29EW NOR Flash Memory Introduction Software Driver for M29EW NOR Flash Memory Introduction This technical note describes the C library source code for the
TwinDie 1.35V DDR3L SDRAM
 TwinDie 1.35R3L SDRAM MT41K4G4 256 Meg x 4 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks MT41K2G8 128 Meg x 8 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks 16Gb: x4, x8 TwinDie DDR3L SDRAM Description Description The 16Gb (TwinDie ) DDR3L SDRAM (1.35V)
TwinDie 1.35R3L SDRAM MT41K4G4 256 Meg x 4 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks MT41K2G8 128 Meg x 8 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks 16Gb: x4, x8 TwinDie DDR3L SDRAM Description Description The 16Gb (TwinDie ) DDR3L SDRAM (1.35V)
DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB
 SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25QAA 1Gb, 1.8V, Multiple I/O Serial NOR Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (four 256Mb die) SPI-compatible serial bus interface
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25QAA 1Gb, 1.8V, Multiple I/O Serial NOR Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (four 256Mb die) SPI-compatible serial bus interface
GLS85VM1004A / 1008A / 1016A / 1032A Industrial Temp emmc NANDrive
 Features Industry Standard Embedded MultiMediaCard (emmc) Host Interface - JEDEC/MMC Standard Version 4.4 JESD84-A44 compliant - Backward compatible with emmc 4.3 Performance - emmc clock speed: Up to
Features Industry Standard Embedded MultiMediaCard (emmc) Host Interface - JEDEC/MMC Standard Version 4.4 JESD84-A44 compliant - Backward compatible with emmc 4.3 Performance - emmc clock speed: Up to
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 64KB Sector Erase MT25QU2GBB 2Gb, 1.8V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (four 512Mb die) SPI-compatible serial bus interface
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 64KB Sector Erase MT25QU2GBB 2Gb, 1.8V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (four 512Mb die) SPI-compatible serial bus interface
TECHNOLOGY BRIEF. Double Data Rate SDRAM: Fast Performance at an Economical Price EXECUTIVE SUMMARY C ONTENTS
 TECHNOLOGY BRIEF June 2002 Compaq Computer Corporation Prepared by ISS Technology Communications C ONTENTS Executive Summary 1 Notice 2 Introduction 3 SDRAM Operation 3 How CAS Latency Affects System Performance
TECHNOLOGY BRIEF June 2002 Compaq Computer Corporation Prepared by ISS Technology Communications C ONTENTS Executive Summary 1 Notice 2 Introduction 3 SDRAM Operation 3 How CAS Latency Affects System Performance
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB Sector Erase MT25QL1GBBB 1Gb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 512Mb die) SPI-compatible serial
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB Sector Erase MT25QL1GBBB 1Gb, 3V Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 512Mb die) SPI-compatible serial
Image Sensor Demo System Kits
 Image Sensor Demo System Kits Introduction Introduction The Micron Imaging demonstration system family supports the full line of Micron s CMOS image sensor products. The current demonstration system is
Image Sensor Demo System Kits Introduction Introduction The Micron Imaging demonstration system family supports the full line of Micron s CMOS image sensor products. The current demonstration system is
SAMA5D2 Quad SPI (QSPI) Performance. Introduction. SMART ARM-based Microprocessor APPLICATION NOTE
 SMART ARM-based Microprocessor SAMA5D2 Quad SPI (QSPI) Performance APPLICATION NOTE Introduction The Atmel SMART SAMA5D2 Series is a high-performance, powerefficient embedded MPU based on the ARM Cortex
SMART ARM-based Microprocessor SAMA5D2 Quad SPI (QSPI) Performance APPLICATION NOTE Introduction The Atmel SMART SAMA5D2 Series is a high-performance, powerefficient embedded MPU based on the ARM Cortex
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q256A 1.8V, 256Mb: Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Double transfer rate (DTR)
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 1.8V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q256A 1.8V, 256Mb: Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface Double transfer rate (DTR)
S25FL1-K. Data Sheet. S25FL1-K Cover Sheet
 S25FL1-K S25FL116K 16 Mbit (2 Mbyte) S25FL132K 32 Mbit (4 Mbyte) S25FL164K 64 Mbit (8 Mbyte) CMOS 3.0-Volt Flash Non-Volatile Memory Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) with Multi-I/O Industrial and Extended
S25FL1-K S25FL116K 16 Mbit (2 Mbyte) S25FL132K 32 Mbit (4 Mbyte) S25FL164K 64 Mbit (8 Mbyte) CMOS 3.0-Volt Flash Non-Volatile Memory Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) with Multi-I/O Industrial and Extended
TwinDie 1.35V DDR3L SDRAM
 TwinDie 1.35R3L SDRAM MT41K2G4 128 Meg x 4 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks MT41K1G8 64 Meg x 8 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks 8Gb: x4, x8 TwinDie DDR3L SDRAM Description Description The 8Gb (TwinDie ) DDR3L SDRAM (1.35V) uses
TwinDie 1.35R3L SDRAM MT41K2G4 128 Meg x 4 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks MT41K1G8 64 Meg x 8 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks 8Gb: x4, x8 TwinDie DDR3L SDRAM Description Description The 8Gb (TwinDie ) DDR3L SDRAM (1.35V) uses
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q512A 512Mb, Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 256Mb die) SPI-compatible serial bus interface Double
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q512A 512Mb, Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features Stacked device (two 256Mb die) SPI-compatible serial bus interface Double
EDW4032BABG 8 Meg x 32 I/O x 16 banks, 16 Meg x 16 I/O x 16 banks. Options 1. Note:
 GR5 SGRM 4Gb: x16, x32 GR5 SGRM Features EW4032G 8 Meg x 32 I/O x 16 banks, 16 Meg x 16 I/O x 16 banks Features = = 1.6V/1.55V/1.5V ±3% and 1.35V ±3% ata rate: 6.0 Gb/s, 7.0 Gb/s, 8.0 Gb/s (MX) 16 internal
GR5 SGRM 4Gb: x16, x32 GR5 SGRM Features EW4032G 8 Meg x 32 I/O x 16 banks, 16 Meg x 16 I/O x 16 banks Features = = 1.6V/1.55V/1.5V ±3% and 1.35V ±3% ata rate: 6.0 Gb/s, 7.0 Gb/s, 8.0 Gb/s (MX) 16 internal
GLS85LS1002A/1004A/1008B/1016B/1032B/1064B Industrial / Commercial Temp SATA NANDrive
 Features Industry Standard Serial ATA (SATA) Host Interface - SATA 1.5 Gb/s or SATA 3.0 Gb/s 1) - ATA/ATAPI-8 compliant - Supports 48-bit address feature set Performance - Sequential data read - Up to
Features Industry Standard Serial ATA (SATA) Host Interface - SATA 1.5 Gb/s or SATA 3.0 Gb/s 1) - ATA/ATAPI-8 compliant - Supports 48-bit address feature set Performance - Sequential data read - Up to
Designing With On-Die ECC for Embedded Applications
 Designing With On-Die ECC for Embedded Applications Sathyanath Subramanian Product Line Manager, Embedded Business Unit Micron Technology, Inc. 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Information,
Designing With On-Die ECC for Embedded Applications Sathyanath Subramanian Product Line Manager, Embedded Business Unit Micron Technology, Inc. 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Information,
power supply Tamper Detect function will detect possible data modification from outside magnetic
 FEATURES High bandwidth Read and Write at 52MB/sec Quad I/O with the use of dual purpose pins to maintain a low pin count Operates in both standard, single SPI mode and high speed quad SPI mode Fast quad
FEATURES High bandwidth Read and Write at 52MB/sec Quad I/O with the use of dual purpose pins to maintain a low pin count Operates in both standard, single SPI mode and high speed quad SPI mode Fast quad
Designing with External Flash Memory on Renesas Platforms
 Designing with External Flash Memory on Renesas Platforms Douglas Crane, Segment Manager Micron Technology Class ID: CL23A Renesas Electronics America Inc. Douglas Crane Doug is a 27 year veteran in the
Designing with External Flash Memory on Renesas Platforms Douglas Crane, Segment Manager Micron Technology Class ID: CL23A Renesas Electronics America Inc. Douglas Crane Doug is a 27 year veteran in the
144-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture
 ADVAE Y71610V, Y71625V Y71612V, Y71614V 144-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 333 MHz clock for high bandwidth
ADVAE Y71610V, Y71625V Y71612V, Y71614V 144-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 333 MHz clock for high bandwidth
GLS85LP0512P / 1002P / 1004P / 1008P Industrial Grade PATA NANDrive
 Features Industry Standard ATA / IDE Bus Interface - Host Interface: 16-bit access - Supports 48-bit address feature set - Supports up to PIO Mode-6 1) - Supports up to Multi-Word DMA Mode-4 2) - Supports
Features Industry Standard ATA / IDE Bus Interface - Host Interface: 16-bit access - Supports 48-bit address feature set - Supports up to PIO Mode-6 1) - Supports up to Multi-Word DMA Mode-4 2) - Supports
Memory technology and optimizations ( 2.3) Main Memory
 Memory technology and optimizations ( 2.3) 47 Main Memory Performance of Main Memory: Latency: affects Cache Miss Penalty» Access Time: time between request and word arrival» Cycle Time: minimum time between
Memory technology and optimizations ( 2.3) 47 Main Memory Performance of Main Memory: Latency: affects Cache Miss Penalty» Access Time: time between request and word arrival» Cycle Time: minimum time between
Flash Memory Overview
 GigaDevice Semiconductor, Inc. Flash Memory Overview NOR and NAND Flash Memory are the critical Non-Volatile Memory devices that store a digital device s configuration data. GigaDevice has a large Flash
GigaDevice Semiconductor, Inc. Flash Memory Overview NOR and NAND Flash Memory are the critical Non-Volatile Memory devices that store a digital device s configuration data. GigaDevice has a large Flash
Mobile DRAM Power-Saving Features and Power Calculations
 Technical Note TN-46-12: Mobile DRAM Power-Saving Features/Calculations Introduction Mobile DRAM Power-Saving Features and Power Calculations Introduction It s important for today s mobile system designer
Technical Note TN-46-12: Mobile DRAM Power-Saving Features/Calculations Introduction Mobile DRAM Power-Saving Features and Power Calculations Introduction It s important for today s mobile system designer
NAND Flash Architecture and Specification Trends
 NAND Flash Architecture and Specification Trends Michael Abraham (mabraham@micron.com) NAND Solutions Group Architect Micron Technology, Inc. August 2011 1 Topics NAND Flash trends SSD/Enterprise application
NAND Flash Architecture and Specification Trends Michael Abraham (mabraham@micron.com) NAND Solutions Group Architect Micron Technology, Inc. August 2011 1 Topics NAND Flash trends SSD/Enterprise application
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory
 Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q256A13E124x N25Q256A13EF84x N25Q256A13ESF4x 256Mb, Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q256A13E124x N25Q256A13EF84x N25Q256A13ESF4x 256Mb, Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features Features SPI-compatible serial bus interface
DDR4 Module Part Numbering System The part numbering system is available at
 DDR4 Module Part Numbering System DDR4 SDRAM modules MT A 36 A SF 2G 72 P Z - 2G3 A 1 Product Family A = DDR4 SDRAM Printed Circuit Board Revision Die Revision (up to 2 characters) DDR4 SDRAM Module Speed
DDR4 Module Part Numbering System DDR4 SDRAM modules MT A 36 A SF 2G 72 P Z - 2G3 A 1 Product Family A = DDR4 SDRAM Printed Circuit Board Revision Die Revision (up to 2 characters) DDR4 SDRAM Module Speed
GLS85LS1004A / 1008A / 1016A / 1032A Commercial Grade SATA NANDrive
 Features Industry Standard Serial ATA (SATA) Host Interface - SATA 1.5 Gb/s or SATA 3.0 Gb/s 1) - ATA/ATAPI-8 compliant - Supports 48-bit address feature set Performance - Sustained sequential data read
Features Industry Standard Serial ATA (SATA) Host Interface - SATA 1.5 Gb/s or SATA 3.0 Gb/s 1) - ATA/ATAPI-8 compliant - Supports 48-bit address feature set Performance - Sustained sequential data read
Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide
 Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Generic
Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Generic
How Good Is Your Memory? An Architect s Look Inside SSDs
 How Good Is Your Memory? An Architect s Look Inside SSDs Michael Abraham (mabraham@micron.com) Business Line Manager Micron Technology, Inc. August 2015 1 Early Storage Optimizations µc NAND Camera SmartMedia
How Good Is Your Memory? An Architect s Look Inside SSDs Michael Abraham (mabraham@micron.com) Business Line Manager Micron Technology, Inc. August 2015 1 Early Storage Optimizations µc NAND Camera SmartMedia
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design (Part 3) Introduction Caches Main Memory (Section 2.2) Virtual Memory (Section 2.4, Appendix B.4, B.
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design (Part 3) Introduction Caches Main Memory (Section 2.2) Virtual Memory (Section 2.4, Appendix B.4, B.5) Memory Technologies Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) Optimized
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design (Part 3) Introduction Caches Main Memory (Section 2.2) Virtual Memory (Section 2.4, Appendix B.4, B.5) Memory Technologies Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) Optimized
