Partitioning. Partitioning Levels. Chip. Readings: Chapter 2. Circuits can exceed chip capacity. Partitioning
|
|
|
- Oliver Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Partitioning Readings: hapter 2 ircuits can exceed chip capacity Split circuits into chip-sized subcircuits Meet capacity constraints Reduce interconnect demand Meet performance requirements Partitioning loorplanning Placement lobal Routing etailed Routing ompaction 68 Partitioning evels nter-board Partitioning Reduce interconnect between different system board, smaller backplane nter-chip Partitioning Reduce # of board levels (interconnect) ntra-chip partitioning (quick placement) hip 69
2 ircuit Terminology We represent circuits as graphs: Nodes/ells/Vertices logic elements Nets/dges wires in the design Terminals connections between nodes and nets 70 Partitioning Terminology utset - set of nets connected to nodes in different partitions utsize - number of nets in the cutset ain - improvement in cutsize if a given node is moved 71
3 Max-flow/Min-cut [ord-ulkerson] Pick nodes S and T, and find optimum split of network such that S is in partition 1 and T is in partition 2. O M P lgorithm: ssume each edge can carry at most 1 unit of flow in either direction While we can find a path from S to T with remaining capacity ncrement flow along path low from S is cutsize, partition 1 is all nodes still reachable from S. N 72 imitations of ord-ulkerson What are the expected results on a real circuit? ow does this differ from what we want? 73
4 Size-constrained Min-cut Partition the circuit into two parts such that: 1.) ach partition has at least X% of the circuit 45%-55% is typical bound. 2.) The cutset is minimized Note1: Size-constrained bipartitioning is NP-omplete Note 2: Multi-way partitioning often extension of bipartitioning, or recursive bipartitioning. 74 roup Migration & reedy lgorithm roup migration - given an initial partitioning, move elements between partitions reedy algorithm: Move nodes, in order of gain, until no more good moves left. Make no move that violates the size constraint. 75
5 iduccia-mattheyses Size constraint: 4-6 nodes per partition 76 iduccia-mattheyses lgorithm reate initial partitioning; While cutsize is reduced { While valid moves exist { ind unlocked node in each partition that most improves/least degrades cutsize when moved to other partition; Move whichever of the two nodes most improves/least degrades cutsize while not exceeding partition size bounds; ock moved node; Update nets connected to moved nodes, and nodes connected to these nets; acktrack to the point with minimum cutsize in move series just completed; Unlock all nodes; 77
6 Performance of M reate initial partitioning; or # of iterations { /* Typically 4-5 iterations */ While valid moves { ind best node from each partition; Pick best of two nodes ock moved node; Update nets connected to moved nodes, and nodes connected to these nets; acktrack; Unlock all nodes; Performance (ignoring red): Performance of red depends on bucket data structure 78 inding est Node: ucket ata Structure rray of lists, organized by gain Max_gain points to highest occupied list ind best node: While max_gain entry is empty max_gain-- Stop if max_gain drops off bottom Update nodes: Remove moved node oreach net attached to that node adjust node gains for nodes attached to that net f any node gain > max_gain change max_gain , -2, -3-4 rray length = (Max # of node terminals)*
7 ucket ata Structure elay Update nodes: oreach attached net adjust node gains Operations = (# of times each net could change gain) * (nets * terminals/net) = (# of times each net could change gain) * (terminals) ind best node: While max_gain array is empty max_gain-- Operations = rray length + moves upwards (in update nodes) = ((Max # of terminals*2)+1) + (times each net could change gain*terminals) 80 ucket ata Structure elay (cont.) Net States: Uncut - can be cut by 1 move rozen - can t be cut by 1 move ut - can be uncut by 1 move Stuck - can t be uncut by 1 move 81
8 inal Performance of M reate initial partitioning; or # of iterations { /* Typically 4-5 iterations */ While valid moves { ind best node from each partition; Pick best of two nodes ock moved node; Update nets connected to moved nodes, and nodes connected to these nets; acktrack; Unlock all nodes; Non-red = iterations * nodes ind best node = iterations * ((Max_terminals*2+1) + 4*terminals) Update nodes = iterations * 4 * terminals Overall = 82 lustering roup nodes together into clusters lusters are nodes that probably should be in same partition xample: recursively cluster with neighbor to whom it shares the most edges Partition with clusters, then remove clustering & repeat 83
9 Multiple Runs Use multiple runs to improve expected value, reduce variance Start from multiple, random initializations
Partitioning. Course contents: Readings. Kernighang-Lin partitioning heuristic Fiduccia-Mattheyses heuristic. Chapter 7.5.
 Course contents: Partitioning Kernighang-Lin partitioning heuristic Fiduccia-Mattheyses heuristic Readings Chapter 7.5 Partitioning 1 Basic Definitions Cell: a logic block used to build larger circuits.
Course contents: Partitioning Kernighang-Lin partitioning heuristic Fiduccia-Mattheyses heuristic Readings Chapter 7.5 Partitioning 1 Basic Definitions Cell: a logic block used to build larger circuits.
Unit 5A: Circuit Partitioning
 Course contents: Unit 5A: Circuit Partitioning Kernighang-Lin partitioning heuristic Fiduccia-Mattheyses heuristic Simulated annealing based partitioning algorithm Readings Chapter 7.5 Unit 5A 1 Course
Course contents: Unit 5A: Circuit Partitioning Kernighang-Lin partitioning heuristic Fiduccia-Mattheyses heuristic Simulated annealing based partitioning algorithm Readings Chapter 7.5 Unit 5A 1 Course
CAD Algorithms. Circuit Partitioning
 CAD Algorithms Partitioning Mohammad Tehranipoor ECE Department 13 October 2008 1 Circuit Partitioning Partitioning: The process of decomposing a circuit/system into smaller subcircuits/subsystems, which
CAD Algorithms Partitioning Mohammad Tehranipoor ECE Department 13 October 2008 1 Circuit Partitioning Partitioning: The process of decomposing a circuit/system into smaller subcircuits/subsystems, which
Sec 2. Euler Circuits, cont.
 Sec 2. uler ircuits, cont. uler ircuits traverse each edge of a connected graph exactly once. Recall that all vertices must have even degree in order for an uler ircuit to exist. leury s lgorithm is a
Sec 2. uler ircuits, cont. uler ircuits traverse each edge of a connected graph exactly once. Recall that all vertices must have even degree in order for an uler ircuit to exist. leury s lgorithm is a
Mincut Placement with FM Partitioning featuring Terminal Propagation. Brett Wilson Lowe Dantzler
 Mincut Placement with FM Partitioning featuring Terminal Propagation Brett Wilson Lowe Dantzler Project Overview Perform Mincut Placement using the FM Algorithm to perform partitioning. Goals: Minimize
Mincut Placement with FM Partitioning featuring Terminal Propagation Brett Wilson Lowe Dantzler Project Overview Perform Mincut Placement using the FM Algorithm to perform partitioning. Goals: Minimize
Combined Code and Data Minimization Algorithms
 Problem Statement ombined ode and ata Minimization lgorithms March, 995 Mini onference on Ptolemy Praveen K Murthy (U erkeley, Shuvra S hattacharyya (Hitachi merica Ltd, dward Lee (U erkeley {murthy,shuvra,eal}@eecsberkeleyedu
Problem Statement ombined ode and ata Minimization lgorithms March, 995 Mini onference on Ptolemy Praveen K Murthy (U erkeley, Shuvra S hattacharyya (Hitachi merica Ltd, dward Lee (U erkeley {murthy,shuvra,eal}@eecsberkeleyedu
Preclass Warmup. ESE535: Electronic Design Automation. Motivation (1) Today. Bisection Width. Motivation (2)
 ESE535: Electronic Design Automation Preclass Warmup What cut size were you able to achieve? Day 4: January 28, 25 Partitioning (Intro, KLFM) 2 Partitioning why important Today Can be used as tool at many
ESE535: Electronic Design Automation Preclass Warmup What cut size were you able to achieve? Day 4: January 28, 25 Partitioning (Intro, KLFM) 2 Partitioning why important Today Can be used as tool at many
Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
Place and Route for FPGAs
 Place and Route for FPGAs 1 FPGA CAD Flow Circuit description (VHDL, schematic,...) Synthesize to logic blocks Place logic blocks in FPGA Physical design Route connections between logic blocks FPGA programming
Place and Route for FPGAs 1 FPGA CAD Flow Circuit description (VHDL, schematic,...) Synthesize to logic blocks Place logic blocks in FPGA Physical design Route connections between logic blocks FPGA programming
VLSI Physical Design: From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure
 Chapter Netlist and System Partitioning Original Authors: Andrew B. Kahng, Jens, Igor L. Markov, Jin Hu Chapter Netlist and System Partitioning. Introduction. Terminology. Optimization Goals. Partitioning
Chapter Netlist and System Partitioning Original Authors: Andrew B. Kahng, Jens, Igor L. Markov, Jin Hu Chapter Netlist and System Partitioning. Introduction. Terminology. Optimization Goals. Partitioning
CAD Algorithms. Placement and Floorplanning
 CAD Algorithms Placement Mohammad Tehranipoor ECE Department 4 November 2008 1 Placement and Floorplanning Layout maps the structural representation of circuit into a physical representation Physical representation:
CAD Algorithms Placement Mohammad Tehranipoor ECE Department 4 November 2008 1 Placement and Floorplanning Layout maps the structural representation of circuit into a physical representation Physical representation:
Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths
 Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths Kruskal's lgorithm Prim's lgorithm Shortest Paths pril 04, 018 inda eeren / eoffrey Tien 1 Kruskal's algorithm ata types for implementation Kruskalslgorithm()
Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths Kruskal's lgorithm Prim's lgorithm Shortest Paths pril 04, 018 inda eeren / eoffrey Tien 1 Kruskal's algorithm ata types for implementation Kruskalslgorithm()
An Introduction to FPGA Placement. Yonghong Xu Supervisor: Dr. Khalid
 RESEARCH CENTRE FOR INTEGRATED MICROSYSTEMS UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR An Introduction to FPGA Placement Yonghong Xu Supervisor: Dr. Khalid RESEARCH CENTRE FOR INTEGRATED MICROSYSTEMS UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
RESEARCH CENTRE FOR INTEGRATED MICROSYSTEMS UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR An Introduction to FPGA Placement Yonghong Xu Supervisor: Dr. Khalid RESEARCH CENTRE FOR INTEGRATED MICROSYSTEMS UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
Eu = {n1, n2} n1 n2. u n3. Iu = {n4} gain(u) = 2 1 = 1 V 1 V 2. Cutset
 Shantanu Dutt 1 and Wenyong Deng 2 A Probability-Based Approach to VLSI Circuit Partitioning Department of Electrical Engineering 1 of Minnesota University Minneapolis, Minnesota 55455 LSI Logic Corporation
Shantanu Dutt 1 and Wenyong Deng 2 A Probability-Based Approach to VLSI Circuit Partitioning Department of Electrical Engineering 1 of Minnesota University Minneapolis, Minnesota 55455 LSI Logic Corporation
ESE535: Electronic Design Automation. Today. LUT Mapping. Simplifying Structure. Preclass: Cover in 4-LUT? Preclass: Cover in 4-LUT?
 ESE55: Electronic Design Automation Day 7: February, 0 Clustering (LUT Mapping, Delay) Today How do we map to LUTs What happens when IO dominates Delay dominates Lessons for non-luts for delay-oriented
ESE55: Electronic Design Automation Day 7: February, 0 Clustering (LUT Mapping, Delay) Today How do we map to LUTs What happens when IO dominates Delay dominates Lessons for non-luts for delay-oriented
Introduction VLSI PHYSICAL DESIGN AUTOMATION
 VLSI PHYSICAL DESIGN AUTOMATION PROF. INDRANIL SENGUPTA DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Introduction Main steps in VLSI physical design 1. Partitioning and Floorplanning l 2. Placement 3.
VLSI PHYSICAL DESIGN AUTOMATION PROF. INDRANIL SENGUPTA DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Introduction Main steps in VLSI physical design 1. Partitioning and Floorplanning l 2. Placement 3.
Spanning Tree. Lecture19: Graph III. Minimum Spanning Tree (MSP)
 Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
An Iterative Enterprise Group Algorithm
 akob ruby Registers, lassifications and eoinformation ivision Neuchâtel September 2018 n terative nterprise roup lgorithm www.statistik.at The ata Raw data about enterprises and people related to them
akob ruby Registers, lassifications and eoinformation ivision Neuchâtel September 2018 n terative nterprise roup lgorithm www.statistik.at The ata Raw data about enterprises and people related to them
MATH 103: Contemporary Mathematics Study Guide for Chapter 6: Hamilton Circuits and the TSP
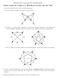 MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
Introduction. A very important step in physical design cycle. It is the process of arranging a set of modules on the layout surface.
 Placement Introduction A very important step in physical design cycle. A poor placement requires larger area. Also results in performance degradation. It is the process of arranging a set of modules on
Placement Introduction A very important step in physical design cycle. A poor placement requires larger area. Also results in performance degradation. It is the process of arranging a set of modules on
TCOM 501: Networking Theory & Fundamentals. Lecture 11 April 16, 2003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis
 TOM 50: Networking Theory & undamentals Lecture pril 6, 2003 Prof. Yannis. Korilis 2 Topics Routing in ata Network Graph Representation of a Network Undirected Graphs Spanning Trees and Minimum Weight
TOM 50: Networking Theory & undamentals Lecture pril 6, 2003 Prof. Yannis. Korilis 2 Topics Routing in ata Network Graph Representation of a Network Undirected Graphs Spanning Trees and Minimum Weight
Clustering Lecture 8. David Sontag New York University. Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein
 Clustering Lecture 8 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein Clustering: Unsupervised learning Clustering Requires
Clustering Lecture 8 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein Clustering: Unsupervised learning Clustering Requires
Key terms and concepts: Divide and conquer system partitioning floorplanning chip planning placement routing global routing detailed routing
 SICs...THE COURSE ( WEEK) SIC CONSTRUCTION Key terms and concepts: microelectronic system (or system on a chip) is the town and SICs (or system blocks) are the buildings System partitioning corresponds
SICs...THE COURSE ( WEEK) SIC CONSTRUCTION Key terms and concepts: microelectronic system (or system on a chip) is the town and SICs (or system blocks) are the buildings System partitioning corresponds
Constraint satisfaction search. Combinatorial optimization search.
 S 1571 Introduction to I Lecture 8 onstraint satisfaction search. ombinatorial optimization search. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square onstraint satisfaction problem (SP) Objective:
S 1571 Introduction to I Lecture 8 onstraint satisfaction search. ombinatorial optimization search. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square onstraint satisfaction problem (SP) Objective:
IP Forwarding Computer Networking. Routes from Node A. Graph Model. Lecture 10: Intra-Domain Routing
 IP orwarding - omputer Networking Lecture : Intra-omain Routing RIP (Routing Information Protocol) & OSP (Open Shortest Path irst) The Story So ar IP addresses are structure to reflect Internet structure
IP orwarding - omputer Networking Lecture : Intra-omain Routing RIP (Routing Information Protocol) & OSP (Open Shortest Path irst) The Story So ar IP addresses are structure to reflect Internet structure
Routing. Effect of Routing in Flow Control. Relevant Graph Terms. Effect of Routing Path on Flow Control. Effect of Routing Path on Flow Control
 Routing Third Topic of the course Read chapter of the text Read chapter of the reference Main functions of routing system Selection of routes between the origin/source-destination pairs nsure that the
Routing Third Topic of the course Read chapter of the text Read chapter of the reference Main functions of routing system Selection of routes between the origin/source-destination pairs nsure that the
Lesson 4.2. Critical Paths
 Lesson. ritical Paths It is relatively easy to find the shortest time needed to complete a project if the project consists of only a few activities. ut as the tasks increase in number, the problem becomes
Lesson. ritical Paths It is relatively easy to find the shortest time needed to complete a project if the project consists of only a few activities. ut as the tasks increase in number, the problem becomes
Large Scale Circuit Partitioning
 Large Scale Circuit Partitioning With Loose/Stable Net Removal And Signal Flow Based Clustering Jason Cong Honching Li Sung-Kyu Lim Dongmin Xu UCLA VLSI CAD Lab Toshiyuki Shibuya Fujitsu Lab, LTD Support
Large Scale Circuit Partitioning With Loose/Stable Net Removal And Signal Flow Based Clustering Jason Cong Honching Li Sung-Kyu Lim Dongmin Xu UCLA VLSI CAD Lab Toshiyuki Shibuya Fujitsu Lab, LTD Support
CSE/EE 461 Distance Vector Routing
 S/ 46 istance Vector Routing Last Time Introduction to the Network layer Internetworks atagram and virtual circuit services Internet Protocol (IP) packet format The Network layer Provides end-to-end data
S/ 46 istance Vector Routing Last Time Introduction to the Network layer Internetworks atagram and virtual circuit services Internet Protocol (IP) packet format The Network layer Provides end-to-end data
Maximum flow problem CE 377K. March 3, 2015
 Maximum flow problem CE 377K March 3, 2015 Informal evaluation results 2 slow, 16 OK, 2 fast Most unclear topics: max-flow/min-cut, WHAT WILL BE ON THE MIDTERM? Most helpful things: review at start of
Maximum flow problem CE 377K March 3, 2015 Informal evaluation results 2 slow, 16 OK, 2 fast Most unclear topics: max-flow/min-cut, WHAT WILL BE ON THE MIDTERM? Most helpful things: review at start of
Note. Out of town Thursday afternoon. Willing to meet before 1pm, me if you want to meet then so I know to be in my office
 raphs and Trees Note Out of town Thursday afternoon Willing to meet before pm, email me if you want to meet then so I know to be in my office few extra remarks about recursion If you can write it recursively
raphs and Trees Note Out of town Thursday afternoon Willing to meet before pm, email me if you want to meet then so I know to be in my office few extra remarks about recursion If you can write it recursively
Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths
 Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths Prim's algorithm ijkstra's algorithm November, 017 inda eeren / eoffrey Tien 1 Recall: S spanning tree Starting from vertex 16 9 1 6 10 13 4 3 17 5 11 7 16 13
Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths Prim's algorithm ijkstra's algorithm November, 017 inda eeren / eoffrey Tien 1 Recall: S spanning tree Starting from vertex 16 9 1 6 10 13 4 3 17 5 11 7 16 13
A New K-Way Partitioning Approach. Bernhard M. Riess, Heiko A. Giselbrecht, and Bernd Wurth. Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany
 A New K-Way Partitioning Approach for Multiple Types of s Bernhard M. Riess, Heiko A. Giselbrecht, and Bernd Wurth Institute of Electronic Design Automation Technical University of Munich, 8090 Munich,
A New K-Way Partitioning Approach for Multiple Types of s Bernhard M. Riess, Heiko A. Giselbrecht, and Bernd Wurth Institute of Electronic Design Automation Technical University of Munich, 8090 Munich,
Towards Reconfigurable Rack-Scale Networking
 1 Towards Reconfigurable Rack-Scale etworking Tyler Szepesi, ernard Wong, Tim recht, Sajjad Rizvi heriton School of omputer Science University of Waterloo pril 21, 2015 2 Rack-Scale omputing Traditional
1 Towards Reconfigurable Rack-Scale etworking Tyler Szepesi, ernard Wong, Tim recht, Sajjad Rizvi heriton School of omputer Science University of Waterloo pril 21, 2015 2 Rack-Scale omputing Traditional
Let s focus on clarifying questions. More Routing. Logic Refresher. Warning. Short Summary of Course. 10 Years from Now.
 Let s focus on clarifying questions I love the degree of interaction in this year s class More Routing all Scott Shenker http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee/ Materials with thanks to Jennifer Rexford, Ion
Let s focus on clarifying questions I love the degree of interaction in this year s class More Routing all Scott Shenker http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee/ Materials with thanks to Jennifer Rexford, Ion
Computational Geometry
 Orthogonal Range Searching omputational Geometry hapter 5 Range Searching Problem: Given a set of n points in R d, preprocess them such that reporting or counting the k points inside a d-dimensional axis-parallel
Orthogonal Range Searching omputational Geometry hapter 5 Range Searching Problem: Given a set of n points in R d, preprocess them such that reporting or counting the k points inside a d-dimensional axis-parallel
Shortest Paths and Minimum Spanning Trees
 /9/ hortest Paths and Minimum panning Trees dmin avid Kauchak cs0 pring 0 ijkstra s algorithm What about ijkstra s on? 0-0 /9/ What about ijkstra s on? ijkstra s algorithm only works for positive edge
/9/ hortest Paths and Minimum panning Trees dmin avid Kauchak cs0 pring 0 ijkstra s algorithm What about ijkstra s on? 0-0 /9/ What about ijkstra s on? ijkstra s algorithm only works for positive edge
Weekly Assignment nr.4
 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO, INSTITUTE OF INFORMATICS Weekly Assignment nr.4 1 FLOW NETWORKS Prerequisites: Graphs(directed, undirected) Degrees, neighbours, paths Depth-first, Breadth-first Lesson Plan: 1. Flow
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO, INSTITUTE OF INFORMATICS Weekly Assignment nr.4 1 FLOW NETWORKS Prerequisites: Graphs(directed, undirected) Degrees, neighbours, paths Depth-first, Breadth-first Lesson Plan: 1. Flow
CS137: Electronic Design Automation
 CS137: Electronic Design Automation Day 4: January 16, 2002 Clustering (LUT Mapping, Delay) Today How do we map to LUTs? What happens when delay dominates? Lessons for non-luts for delay-oriented partitioning
CS137: Electronic Design Automation Day 4: January 16, 2002 Clustering (LUT Mapping, Delay) Today How do we map to LUTs? What happens when delay dominates? Lessons for non-luts for delay-oriented partitioning
Chapter 6 Detailed Routing
 hapter 6 Detailed Routing 6.1 Terminology 6.2 Horizontal and Vertical onstraint Graphs 6.2.1 Horizontal onstraint Graphs 6.2.2 Vertical onstraint Graphs 6.3 hannel Routing lgorithms 6.3.1 Left-Edge lgorithm
hapter 6 Detailed Routing 6.1 Terminology 6.2 Horizontal and Vertical onstraint Graphs 6.2.1 Horizontal onstraint Graphs 6.2.2 Vertical onstraint Graphs 6.3 hannel Routing lgorithms 6.3.1 Left-Edge lgorithm
1. trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) How many different spanning. trees does the network shown in figure (b) have?
 2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
6 Randomized rounding of semidefinite programs
 6 Randomized rounding of semidefinite programs We now turn to a new tool which gives substantially improved performance guarantees for some problems We now show how nonlinear programming relaxations can
6 Randomized rounding of semidefinite programs We now turn to a new tool which gives substantially improved performance guarantees for some problems We now show how nonlinear programming relaxations can
Problem: Large Graphs
 S : ata Structures raph lgorithms raph Search Lecture Problem: Large raphs It is expensive to find optimal paths in large graphs, using S or ijkstra s algorithm (for weighted graphs) How can we search
S : ata Structures raph lgorithms raph Search Lecture Problem: Large raphs It is expensive to find optimal paths in large graphs, using S or ijkstra s algorithm (for weighted graphs) How can we search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Lecture 4 - Features and Constraints. CSPs as Graph searching problems. Example Domains. Dual Representations
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Lecture 4 - Features and Constraints Jesse Hoey School of Computer Science University of Waterloo January 22, 2018 Readings: Poole & Mackworth (2nd d.) Chapt. 4.1-4.8
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Lecture 4 - Features and Constraints Jesse Hoey School of Computer Science University of Waterloo January 22, 2018 Readings: Poole & Mackworth (2nd d.) Chapt. 4.1-4.8
A region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that is divided up by the network.
 Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees 0 OS SO LX PV OR 0 JK 0 WI 00 W MI 00 Goodrich, Tamassia Minimum Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning
Minimum Spanning Trees 0 OS SO LX PV OR 0 JK 0 WI 00 W MI 00 Goodrich, Tamassia Minimum Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. Force-Directed Partitioning Technique for 3D IC. Aysa Fakheri Tabrizi A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Force-Directed Partitioning Technique for 3D IC by Aysa Fakheri Tabrizi A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Force-Directed Partitioning Technique for 3D IC by Aysa Fakheri Tabrizi A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 S 101, Winter 2018 esign and nalysis of lgorithms Lecture 3: onnected omponents lass URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ nd of Lecture 2: s, Topological Order irected cyclic raph.g., Vertices
S 101, Winter 2018 esign and nalysis of lgorithms Lecture 3: onnected omponents lass URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ nd of Lecture 2: s, Topological Order irected cyclic raph.g., Vertices
L14 - Placement and Routing
 L14 - Placement and Routing Ajay Joshi Massachusetts Institute of Technology RTL design flow HDL RTL Synthesis manual design Library/ module generators netlist Logic optimization a b 0 1 s d clk q netlist
L14 - Placement and Routing Ajay Joshi Massachusetts Institute of Technology RTL design flow HDL RTL Synthesis manual design Library/ module generators netlist Logic optimization a b 0 1 s d clk q netlist
Lecture overview. Knowledge-based systems in Bioinformatics, 1MB602, Goal based agents. Search terminology. Specifying a search problem
 Lecture overview Knowledge-based systems in ioinformatics, 1M602, 2006 Lecture 6: earch oal based agents earch terminology pecifying a search problem earch considerations Uninformed search euristic methods
Lecture overview Knowledge-based systems in ioinformatics, 1M602, 2006 Lecture 6: earch oal based agents earch terminology pecifying a search problem earch considerations Uninformed search euristic methods
Euler and Hamilton circuits. Euler paths and circuits
 1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
CS 5114: Theory of Algorithms. Graph Algorithms. A Tree Proof. Graph Traversals. Clifford A. Shaffer. Spring 2014
 epartment of omputer Science Virginia Tech lacksburg, Virginia opyright c 04 by lifford. Shaffer : Theory of lgorithms Title page : Theory of lgorithms lifford. Shaffer Spring 04 lifford. Shaffer epartment
epartment of omputer Science Virginia Tech lacksburg, Virginia opyright c 04 by lifford. Shaffer : Theory of lgorithms Title page : Theory of lgorithms lifford. Shaffer Spring 04 lifford. Shaffer epartment
CS S-06 Binary Search Trees 1
 CS245-2008S-06 inary Search Trees 1 06-0: Ordered List T Operations: Insert an element in the list Check if an element is in the list Remove an element from the list Print out the contents of the list,
CS245-2008S-06 inary Search Trees 1 06-0: Ordered List T Operations: Insert an element in the list Check if an element is in the list Remove an element from the list Print out the contents of the list,
BACKEND DESIGN. Circuit Partitioning
 BACKEND DESIGN Circuit Partitioning Partitioning System Design Decomposition of a complex system into smaller subsystems. Each subsystem can be designed independently. Decomposition scheme has to minimize
BACKEND DESIGN Circuit Partitioning Partitioning System Design Decomposition of a complex system into smaller subsystems. Each subsystem can be designed independently. Decomposition scheme has to minimize
CprE 583 Reconfigurable Computing
 CprE / ComS 583 Reconfigurable Computing Prof. Joseph Zambreno Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Iowa State University Lecture #9 Logic Emulation Technology Recap FPGA-Based Router (FPX)
CprE / ComS 583 Reconfigurable Computing Prof. Joseph Zambreno Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Iowa State University Lecture #9 Logic Emulation Technology Recap FPGA-Based Router (FPX)
Randomized Large Neighborhood Search for Cumulative Scheduling
 Randomized arge Neighborhood Search for umulative Scheduling aniel odard and Philippe aborie and Wim Nuijten O S.. 9, rue de Verdun -. P. 85 94253 entilly edex, rance {dgodard,plaborie,wnuijten}@ilog.fr
Randomized arge Neighborhood Search for umulative Scheduling aniel odard and Philippe aborie and Wim Nuijten O S.. 9, rue de Verdun -. P. 85 94253 entilly edex, rance {dgodard,plaborie,wnuijten}@ilog.fr
Block Alignment in 3D Floorplan Using Layered TCG
 lock lignment in 3 loorplan Using Layered TG Jill H.Y. Law epartment of S hinese University of Hong hylaw@cse.cuhk.edu.hk vangeline.y. Young epartment of S hinese University of Hong fyyoung@cse.cuhk.edu.hk
lock lignment in 3 loorplan Using Layered TG Jill H.Y. Law epartment of S hinese University of Hong hylaw@cse.cuhk.edu.hk vangeline.y. Young epartment of S hinese University of Hong fyyoung@cse.cuhk.edu.hk
Shortest Paths and Minimum Spanning Trees
 // hortest Paths and Minimum panning Trees avid Kauchak cs pring dmin an resubmit homeworks - for up to half credit back l ue by the end of the week Read book // // // // // Is ijkstra s algorithm correct?
// hortest Paths and Minimum panning Trees avid Kauchak cs pring dmin an resubmit homeworks - for up to half credit back l ue by the end of the week Read book // // // // // Is ijkstra s algorithm correct?
Markov Random Fields
 3750 Machine earning ecture 4 Markov Random ields Milos auskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 ennott quare 3750 dvanced Machine earning Markov random fields Probabilistic models with symmetric dependences.
3750 Machine earning ecture 4 Markov Random ields Milos auskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 ennott quare 3750 dvanced Machine earning Markov random fields Probabilistic models with symmetric dependences.
An Interconnect-Centric Design Flow for Nanometer Technologies
 An Interconnect-Centric Design Flow for Nanometer Technologies Jason Cong UCLA Computer Science Department Email: cong@cs.ucla.edu Tel: 310-206-2775 URL: http://cadlab.cs.ucla.edu/~cong Exponential Device
An Interconnect-Centric Design Flow for Nanometer Technologies Jason Cong UCLA Computer Science Department Email: cong@cs.ucla.edu Tel: 310-206-2775 URL: http://cadlab.cs.ucla.edu/~cong Exponential Device
6 ROUTING PROBLEMS VEHICLE ROUTING PROBLEMS. Vehicle Routing Problem, VRP:
 6 ROUTING PROBLEMS VEHICLE ROUTING PROBLEMS Vehicle Routing Problem, VRP: Customers i=1,...,n with demands of a product must be served using a fleet of vehicles for the deliveries. The vehicles, with given
6 ROUTING PROBLEMS VEHICLE ROUTING PROBLEMS Vehicle Routing Problem, VRP: Customers i=1,...,n with demands of a product must be served using a fleet of vehicles for the deliveries. The vehicles, with given
Twin Binary Sequences: A Non-redundant Representation for General Non-slicing Floorplan
 Twin inary Sequences: Non-redundant Representation for General Non-slicing loorplan vangeline.y. Young, hris.n. hu and Zion ien Shen bstract The efficiency and effectiveness of many floorplanning methods
Twin inary Sequences: Non-redundant Representation for General Non-slicing loorplan vangeline.y. Young, hris.n. hu and Zion ien Shen bstract The efficiency and effectiveness of many floorplanning methods
An Effective Algorithm for Multiway Hypergraph Partitioning
 An Effective Algorithm for Multiway Hypergraph Partitioning Zhizi Zhao, Lixin Tao, Yongchang Zhao 3 Concordia University, zhao_z@cs.concordia.ca, Pace University, ltao@pace.edu, 3 retired Abstract In this
An Effective Algorithm for Multiway Hypergraph Partitioning Zhizi Zhao, Lixin Tao, Yongchang Zhao 3 Concordia University, zhao_z@cs.concordia.ca, Pace University, ltao@pace.edu, 3 retired Abstract In this
New Optimal Layer Assignment for Bus-Oriented Escape Routing
 New Optimal Layer ssignment for us-oriented scape Routing in-tai Yan epartment of omputer Science and nformation ngineering, hung-ua University, sinchu, Taiwan, R. O.. STRT n this paper, based on the optimal
New Optimal Layer ssignment for us-oriented scape Routing in-tai Yan epartment of omputer Science and nformation ngineering, hung-ua University, sinchu, Taiwan, R. O.. STRT n this paper, based on the optimal
Basic Concept of Cooperative Timing-driven Design Automation Technology for High-speed RISC Processor HARP-1
 asic oncept of ooperative Timing-driven esign Automation Technology for High-speed RIS Processor HARP-1 Hidekazu Terai(*), Kazutoshi Gemma(*), Yohsuke Nagao(**), Yasuo Satoh(**), Yasuhiro Ohno(*) Hitachi
asic oncept of ooperative Timing-driven esign Automation Technology for High-speed RIS Processor HARP-1 Hidekazu Terai(*), Kazutoshi Gemma(*), Yohsuke Nagao(**), Yasuo Satoh(**), Yasuhiro Ohno(*) Hitachi
Chapter 5 Global Routing
 Chapter 5 Global Routing 5. Introduction 5.2 Terminology and Definitions 5.3 Optimization Goals 5. Representations of Routing Regions 5.5 The Global Routing Flow 5.6 Single-Net Routing 5.6. Rectilinear
Chapter 5 Global Routing 5. Introduction 5.2 Terminology and Definitions 5.3 Optimization Goals 5. Representations of Routing Regions 5.5 The Global Routing Flow 5.6 Single-Net Routing 5.6. Rectilinear
Placement Algorithm for FPGA Circuits
 Placement Algorithm for FPGA Circuits ZOLTAN BARUCH, OCTAVIAN CREŢ, KALMAN PUSZTAI Computer Science Department, Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, 26, Bariţiu St., 3400 Cluj-Napoca, Romania {Zoltan.Baruch,
Placement Algorithm for FPGA Circuits ZOLTAN BARUCH, OCTAVIAN CREŢ, KALMAN PUSZTAI Computer Science Department, Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, 26, Bariţiu St., 3400 Cluj-Napoca, Romania {Zoltan.Baruch,
0!1. Overlaying mechanism is called tunneling. Overlay Network Nodes. ATM links can be the physical layer for IP
 epartment of lectrical ngineering and omputer Sciences University of alifornia erkeley '!$$( network defined over another set of networks The overlay addresses its own nodes Links on one layer are network
epartment of lectrical ngineering and omputer Sciences University of alifornia erkeley '!$$( network defined over another set of networks The overlay addresses its own nodes Links on one layer are network
VLSI Circuit Partitioning by Cluster-Removal Using Iterative Improvement Techniques
 VLSI Circuit Partitioning by Cluster-Removal Using Iterative Improvement Techniques Shantanu Dutt and Wenyong Deng Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 5555, USA
VLSI Circuit Partitioning by Cluster-Removal Using Iterative Improvement Techniques Shantanu Dutt and Wenyong Deng Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 5555, USA
Topological Sort. CSE 373 Data Structures Lecture 19
 Topological Sort S 373 ata Structures Lecture 19 Readings and References Reading Section 9.2 Some slides based on: S 326 by S. Wolfman, 2000 11/27/02 Topological Sort - Lecture 19 2 Topological Sort 142
Topological Sort S 373 ata Structures Lecture 19 Readings and References Reading Section 9.2 Some slides based on: S 326 by S. Wolfman, 2000 11/27/02 Topological Sort - Lecture 19 2 Topological Sort 142
Third Generation Routers
 IP orwarding 5-5- omputer Networking 5- Lecture : Routing Peter Steenkiste all www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/5-- The Story So ar IP addresses are structured to reflect Internet structure IP packet headers carry
IP orwarding 5-5- omputer Networking 5- Lecture : Routing Peter Steenkiste all www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/5-- The Story So ar IP addresses are structured to reflect Internet structure IP packet headers carry
ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE! 1. Link state flooding topology information finding the shortest paths (Dijkstra)
 ontents ÉOL POLYTHNIQU ÉÉRL LUSNN! 1. Link state flooding topology information finding the shortest paths (ijkstra)! 2. Hierarchical routing with areas! 3. OSP Link State Routing database modelling neighbor
ontents ÉOL POLYTHNIQU ÉÉRL LUSNN! 1. Link state flooding topology information finding the shortest paths (ijkstra)! 2. Hierarchical routing with areas! 3. OSP Link State Routing database modelling neighbor
What is Search? Intro to Search. Search problems. Finding goals in trees. Why is goal search not trivial? Blind Search Methods
 What is Search? lind Search Methods Search as an Tool S, DS, DS, US, ids Search is one of the most powerful approaches to problem solving in Search is a universal problem solving mechanism that Systematically
What is Search? lind Search Methods Search as an Tool S, DS, DS, US, ids Search is one of the most powerful approaches to problem solving in Search is a universal problem solving mechanism that Systematically
A Linear-Time Heuristic for Improving Network Partitions
 A Linear-Time Heuristic for Improving Network Partitions ECE 556 Project Report Josh Brauer Introduction The Fiduccia-Matteyses min-cut heuristic provides an efficient solution to the problem of separating
A Linear-Time Heuristic for Improving Network Partitions ECE 556 Project Report Josh Brauer Introduction The Fiduccia-Matteyses min-cut heuristic provides an efficient solution to the problem of separating
CAD Algorithms. Shortest Path
 lgorithms Shortest Path lgorithms Mohammad Tehranipoor epartment September 00 Shortest Path Problem: ind the best way of getting from s to t where s and t are vertices in a graph. est: Min (sum of the
lgorithms Shortest Path lgorithms Mohammad Tehranipoor epartment September 00 Shortest Path Problem: ind the best way of getting from s to t where s and t are vertices in a graph. est: Min (sum of the
Bayesian Networks and Decision Graphs
 ayesian Networks and ecision raphs hapter 7 hapter 7 p. 1/27 Learning the structure of a ayesian network We have: complete database of cases over a set of variables. We want: ayesian network structure
ayesian Networks and ecision raphs hapter 7 hapter 7 p. 1/27 Learning the structure of a ayesian network We have: complete database of cases over a set of variables. We want: ayesian network structure
VLSI Circuit Partitioning by Cluster-Removal Using Iterative Improvement Techniques
 To appear in Proc. IEEE/ACM International Conference on CAD, 996 VLSI Circuit Partitioning by Cluster-Removal Using Iterative Improvement Techniques Shantanu Dutt and Wenyong Deng Department of Electrical
To appear in Proc. IEEE/ACM International Conference on CAD, 996 VLSI Circuit Partitioning by Cluster-Removal Using Iterative Improvement Techniques Shantanu Dutt and Wenyong Deng Department of Electrical
State Transition Graph of 8-Puzzle E W W E W W 3 2 E
 rrays. Lists. inary search trees. ash tables. tacks. Queues. tate Transition raph of 8-Puzzle oal: Understand data structures by solving the puzzle problem lementary tructures 4 7 5 6 8 4 6 5 7 8. Trees
rrays. Lists. inary search trees. ash tables. tacks. Queues. tate Transition raph of 8-Puzzle oal: Understand data structures by solving the puzzle problem lementary tructures 4 7 5 6 8 4 6 5 7 8. Trees
Clustering Algorithms. Margareta Ackerman
 Clustering Algorithms Margareta Ackerman A sea of algorithms As we discussed last class, there are MANY clustering algorithms, and new ones are proposed all the time. They are very different from each
Clustering Algorithms Margareta Ackerman A sea of algorithms As we discussed last class, there are MANY clustering algorithms, and new ones are proposed all the time. They are very different from each
Automated system partitioning based on hypergraphs for 3D stacked integrated circuits. FOSDEM 2018 Quentin Delhaye
 Automated system partitioning based on hypergraphs for 3D stacked integrated circuits FOSDEM 2018 Quentin Delhaye Integrated circuits: Let s go 3D Building an Integrated Circuit (IC) Transistors to build
Automated system partitioning based on hypergraphs for 3D stacked integrated circuits FOSDEM 2018 Quentin Delhaye Integrated circuits: Let s go 3D Building an Integrated Circuit (IC) Transistors to build
Distance-Vector Routing: Distributed B-F (cont.)
 istance-vector Routing: istributed - (cont.) xample [ istributed ellman-ord lgorithm ] ssume each node i maintains an entry (R(i,x), L(i,x)), where R(i,x) is the next node along the current shortest path
istance-vector Routing: istributed - (cont.) xample [ istributed ellman-ord lgorithm ] ssume each node i maintains an entry (R(i,x), L(i,x)), where R(i,x) is the next node along the current shortest path
Logic Partition Orderings for Multi-FPGA Systems
 International Symposium on ield-programmable ate rrays, 995. Logic Partition Orderings for Multi-P Systems Scott auck, aetano orriello epartment of omputer Science and ngineering University of Washington
International Symposium on ield-programmable ate rrays, 995. Logic Partition Orderings for Multi-P Systems Scott auck, aetano orriello epartment of omputer Science and ngineering University of Washington
Placement ABOUT THIS CHAPTER 11.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER. Chris Chu Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa
 CHAPTER Placement 11 Chris Chu Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa ABOUT THIS CHAPTER Placement is the process of determining the locations of circuit devices on a die surface. It is an important stage in
CHAPTER Placement 11 Chris Chu Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa ABOUT THIS CHAPTER Placement is the process of determining the locations of circuit devices on a die surface. It is an important stage in
Genetic Algorithm for Circuit Partitioning
 Genetic Algorithm for Circuit Partitioning ZOLTAN BARUCH, OCTAVIAN CREŢ, KALMAN PUSZTAI Computer Science Department, Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, 26, Bariţiu St., 3400 Cluj-Napoca, Romania {Zoltan.Baruch,
Genetic Algorithm for Circuit Partitioning ZOLTAN BARUCH, OCTAVIAN CREŢ, KALMAN PUSZTAI Computer Science Department, Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, 26, Bariţiu St., 3400 Cluj-Napoca, Romania {Zoltan.Baruch,
Parallel repartitioning and remapping in
 Parallel repartitioning and remapping in Sébastien Fourestier François Pellegrini November 21, 2012 Joint laboratory workshop Table of contents Parallel repartitioning Shared-memory parallel algorithms
Parallel repartitioning and remapping in Sébastien Fourestier François Pellegrini November 21, 2012 Joint laboratory workshop Table of contents Parallel repartitioning Shared-memory parallel algorithms
Memory Management. (SGG, Chapter 08) Objectives. Memory Hierarchy. Outline. Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu. To describe various memory hardware"
 Objectives Memory Management (SGG, hapter 08) To describe various memory hardware To discuss various memory-management techniques, including partitions and swapping Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Department
Objectives Memory Management (SGG, hapter 08) To describe various memory hardware To discuss various memory-management techniques, including partitions and swapping Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Department
The Partitioning Problem
 The Partitioning Problem 1. Iterative Improvement The partitioning problem is the problem of breaking a circuit into two subcircuits. Like many problems in VLSI design automation, we will solve this problem
The Partitioning Problem 1. Iterative Improvement The partitioning problem is the problem of breaking a circuit into two subcircuits. Like many problems in VLSI design automation, we will solve this problem
Unit 2. Signaling and Single Area OSPF
 nit ignaling and ingle rea PF elecommunications ignaling ignaling g sed to provide all of the set up, tare down and call processing information such as: ff hook notification alling party number alled party
nit ignaling and ingle rea PF elecommunications ignaling ignaling g sed to provide all of the set up, tare down and call processing information such as: ff hook notification alling party number alled party
Memory Management. Before We Begin. Process s Memory Address Space. Process Memory. CSE 120: Principles of Operating Systems.
 SE 12: Principles of Operating Systems Lecture 7 Memory Management February 1, 26 Prof. Joe Pasquale Department of omputer Science and Engineering University of alifornia, San Diego Before We Begin Read
SE 12: Principles of Operating Systems Lecture 7 Memory Management February 1, 26 Prof. Joe Pasquale Department of omputer Science and Engineering University of alifornia, San Diego Before We Begin Read
Hardware-Software Codesign
 Hardware-Software Codesign 4. System Partitioning Lothar Thiele 4-1 System Design specification system synthesis estimation SW-compilation intellectual prop. code instruction set HW-synthesis intellectual
Hardware-Software Codesign 4. System Partitioning Lothar Thiele 4-1 System Design specification system synthesis estimation SW-compilation intellectual prop. code instruction set HW-synthesis intellectual
Data Organization: Creating Order Out Of Chaos
 ata Organization: reating Order Out Of haos 3 Non-linear data structures 5-5 Principles of omputation, arnegie Mellon University - ORTIN Trees tree is a hierarchical (usually non-linear) data structure.
ata Organization: reating Order Out Of haos 3 Non-linear data structures 5-5 Principles of omputation, arnegie Mellon University - ORTIN Trees tree is a hierarchical (usually non-linear) data structure.
mywbut.com Uninformed Search
 Uninformed Search 1 2.4 Search Searching through a state space involves the following: set of states Operators and their costs Start state test to check for goal state We will now outline the basic search
Uninformed Search 1 2.4 Search Searching through a state space involves the following: set of states Operators and their costs Start state test to check for goal state We will now outline the basic search
CSE 326: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
CS 5114: Theory of Algorithms. Graph Algorithms. A Tree Proof. Graph Traversals. Clifford A. Shaffer. Spring 2014
 epartment of omputer Science Virginia Tech lacksburg, Virginia opyright c 04 by lifford. Shaffer : Theory of lgorithms Title page : Theory of lgorithms lifford. Shaffer Spring 04 lifford. Shaffer epartment
epartment of omputer Science Virginia Tech lacksburg, Virginia opyright c 04 by lifford. Shaffer : Theory of lgorithms Title page : Theory of lgorithms lifford. Shaffer Spring 04 lifford. Shaffer epartment
Bridges. Bridge Functions. Example of No-frills Bridge. No-frills Bridges. Example of Learning Bridge. Learning Bridges
 ridge Functions To extend size of LNs either geographically or in terms number of users. Protocols that include collisions can be performed in a collision domain of limited size. In ring networks the number
ridge Functions To extend size of LNs either geographically or in terms number of users. Protocols that include collisions can be performed in a collision domain of limited size. In ring networks the number
Introduction to Parallel Computing
 Introduction to Parallel Computing George Karypis Sorting Outline Background Sorting Networks Quicksort Bucket-Sort & Sample-Sort Background Input Specification Each processor has n/p elements A ordering
Introduction to Parallel Computing George Karypis Sorting Outline Background Sorting Networks Quicksort Bucket-Sort & Sample-Sort Background Input Specification Each processor has n/p elements A ordering
Greedy Algorithms. At each step in the algorithm, one of several choices can be made.
 Greedy Algorithms At each step in the algorithm, one of several choices can be made. Greedy Strategy: make the choice that is the best at the moment. After making a choice, we are left with one subproblem
Greedy Algorithms At each step in the algorithm, one of several choices can be made. Greedy Strategy: make the choice that is the best at the moment. After making a choice, we are left with one subproblem
Clustering Lecture 14
 Clustering Lecture 14 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein Clustering: Unsupervised learning Clustering Requires
Clustering Lecture 14 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein Clustering: Unsupervised learning Clustering Requires
Graphs: Definitions and Representations (Chapter 9)
 oday s Outline Graphs: efinitions and Representations (hapter 9) dmin: HW #4 due hursday, Nov 10 at 11pm Memory hierarchy Graphs Representations SE 373 ata Structures and lgorithms 11/04/2011 1 11/04/2011
oday s Outline Graphs: efinitions and Representations (hapter 9) dmin: HW #4 due hursday, Nov 10 at 11pm Memory hierarchy Graphs Representations SE 373 ata Structures and lgorithms 11/04/2011 1 11/04/2011
Distance Vector Routing
 ÉOL POLYTHNIQU FÉÉRL LUSNN istance Vector Routing Jean Yves Le oudec 20 ontents. Routing in General 2. istance vector: theory 3. istance vector: practice (RIP) 4. Software efined Networking (SN) Textbook
ÉOL POLYTHNIQU FÉÉRL LUSNN istance Vector Routing Jean Yves Le oudec 20 ontents. Routing in General 2. istance vector: theory 3. istance vector: practice (RIP) 4. Software efined Networking (SN) Textbook
