|
|
|
- Albert Horton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 You can now find video tutorials for Blender Basics on line for each chapter. Visit: Look for the video link on the page to take you to the YouTube channel. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 2004, 2006, 2009, 2011, 2017 fifth edition by James Chronister. This document may be reproduced in whole or in part without permission from the author. Feel free to use this manual for any and all educational applications. I enjoy s from other educators, so please let me know how you re using the book. You may not bundle this tutorial with any software or documentation that is intended for commercial applications (marketing for a profit) without expressed written approval from the author. Inquiries and comments can be directed to jchronister@cdschools.org. This document, and other information, can be found at At this site, look under Academics in Technology Education. Information regarding the Blender program and development can be found at Blender users can also find information on how to use the program at Daily Blender news and tutorial links can be found at
3 Table Table of of Contents Contents Introductory Items v vi viii Introduction Rendering and Animation Basic Concepts Basic Key Commands Chapter 1- The Blender Interface The Blender Screen Viewport (Window) Types The User Preferences Window Open, Saving and Appending Files Packing Data Importing Objects (from other file formats) Moving Around in 3D Space Window and Button Control Creating Viewports Working with Basic Meshes Using Main Modifiers to Manipulate Meshes Edit Mode- Mesh Editing The Tool Shelf Proportional Editing Joining/Separating Meshes, Boolean Operations Chapter 2- Working with Viewports (windows) Chapter 3- Creating and Editing Objects Chapter 4- Blender Render Engines The Classic Render Engine The Cycles Render Engine Tweaking Cycles for Speed & Quality Chapter 5- Materials and Textures Basic Material Settings Basic Texture Settings Using Images and Movies as Textures Displacement Mapping Materials and Textures in Cycles Chapter 6- Setting Up a World 6-1 Using Color, Mist and Textures Using an Image in the Background Cycles World Settings Chapter 7- Lighting and Cameras 7-1 Camera Settings and Options Using Nodes for Depth-of-Field, Green Screen (Chroma Key), and More Lighting Types and Settings Indirect Lighting Basic Setup Options Rendering Movies and Images Network Rendering 9-2 Reflection (mirror) and Refraction (transparency) Chapter 8- Render Settings Chapter 9- Ray-Tracing (mirror, transparency, shadows) 9-1 Lighting and Shadows Chapter 10- Animation Basics Basic Key-framing and Auto Key-framing Working with the Graph Editor and Dope Sheet Animating Materials, Lamps and World Settings (and more) i
4 Table of Contents (continued) Chapter 11- Adding 3D Text Blender 3D Text Settings Converting to a Mesh Chapter 12- NURBS and Meta Shape Basics Using NURBS to create lofted shapes Liquid and droplet effects using Meta Shapes Basic Mesh Modifiers Simulation Modifiers Chapter 13- Modifiers Chapter 14- Particle Systems and Interactions Particle Settings and Material Influence (Cycles) Using the Explode Modifier Particle Interaction With Objects and Forces Using Particles for Hair and Grass Using Child-Parented Objects Adjusting Object Centers (pivot points) Chapter 15- Child-Parent Relationships Chapter 16- Working With Constraints Tracking To An Object Following Paths and Curves Using Armatures to Deform Meshes Creating Vertex Groups Using Inverse Kinematics (IK) and Other Constraints Creating Mesh Keys Using Action Editor Sliders Chapter 17- Armatures (bones and skeletons) Chapter 18- Relative Vertex Keys (shape keys) Chapter 19- Object Physics Creating Fabric and Fluid Effects with Interactions Realistic Object Interactions in Real-Time and Animations Duplicating Meshes to Create Screws and Gears Using Mesh Editing to Create Revolved Shapes Blender Add-On Meshes Setting Up the Tracking Scene Using Masks and Materials Chapter 20- Creating Springs, Screws, Gears and other Add-On Shapes Chapter 21- Video Motion Tracking Chapter 22- Game Engine Basics (real-time animation) Setting Up The Physics Engine Applying Materials Using Game Physics in Animation Using Logic Blocks Using Basic Mapping GLSL Shading Chapter 23- UV Texture Mapping Chapter 24- Video Sequence Editor Producing a Movie From Individual Clips and Images Adding an Audio Track Chapter 25-3D Printing Tools Fundamentals of 3D Printing Using Blender to Create 3D Printer Models Exporting Models Educational Standards Alignment Index ii
5 Performance Practice Exercises Tasks Chapter 1 Setting Up Your Interface Chapter 2 Multiple Viewport Configuration Chapter 3 Create a Sculpture Modeling a Landscape and Lighthouse Adding Windows to the Lighthouse Challenge Task: Creating a 3D Logo Chapter 4 Test Renderings Chapter 5 Adding Classic Materials & Textures to the Lighthouse Scene Challenge Task: Cycles Shading for the Lighthouse Scene Chapter 6 Creating an Environment for Your Scene Challenge Task: A Sculpture Environment Chapter 7 Lighting Up the Landscape Scene Challenge Task: Cycles Scene and Blur Chapter 8 Saving a Picture of Your Scene Chapter 9 Reflection and Refraction Challenge Task: Cycles Reflection and Refraction Chapter 10 Adding Motion to Your Scene Challenge Task: A Logo or Sculpture in Motion Chapter 11 Company Logo Challenge Task: Production Logo Chapter 12 The Lava Lamp Challenge Task: The Spill iii iii
6 Practice Exercises Performance Tasks Chapter 13 Common Modifiers Exercise Challenge Task: Insect Study Chapter 14 Adding Rain to Your Scene Challenge Task: A Fireworks Display& Candle... Chapter 15 The Robotic Arm Challenge Task: A Simple Character... Chapter 16 A Camera That Follows the Arm Challenge Task: A Simple Roller Coaster... Chapter 17 Create a Hand With Armatures Challenge Task: Flubber Character... Chapter 18 Cheesy Actor Monkey Chapter 19 A Waving Flag Making a Splash With Fluids Challenge Task: Rube Goldberg Invention... Chapter 20 Turning Gears Challenge Task: An Animated Spring... Chapter 21 Composite Desk Scene Chapter 22 A Simple Maze Runner Chapter 23 Creating a Texture Wrap Challenge Task: Texture Your Maze... Chapter 24 Video Portfolio Chapter 25 Chess Piece iv
7 Introduction Introduction About Blender How can Blender be free? People usually associate freeware software with the terms bad, with limited features or just a demo. Blender is fully functional. It works as an open-sourced, community development program where people from around the world contribute to its success. Blender is a rendering\animation\game development open-sourced freeware program maintained by the Blender Foundation and can be downloaded, free of charge, from The goal of the foundation can be summarized as follows: The Blender Foundation is an independent organization (a Dutch stichting ), acting as a non-profit public benefit corporation, with the following goals: 1. To establish services for active users and developers of Blender. 2. To maintain and improve the current Blender product via a public accessible source code system under the GNU GPL license. 3. To establish funding or revenue mechanisms that serve the foundation s goals and cover the foundation s expenses. 4. To give the worldwide Internet community access to 3D technology in general, with Blender as a core. Blender website (blender.org) Blender can be a difficult program to learn with limitless possibilities. What do you teach in the time you have to teach? That s a tough question because you can t teach it all. This tutorial book is designed to get you up and running in the basics of creating objects and scenes and animating. The best advice I can give you about learning this program is Don t Give Up! All rendering and animation programs have a tough learning curve. After a few weeks, things get easier. This tutorial has been developed to be used in conjunction with daily lesson planning and demonstrations. Because of this, some areas of Blender have not been described as fully as they could be. If you are using this guide as a stand-alone teaching or self-help tool, you may need to seek additional help from reputable places like and to make sense of things. These sites give you access to help forums and tutorials. There are literally thousands of Blender users world-wide that browse the forums to give and get advice. Make use of that vast knowledge base! Version Information: The current release at the time of this printing is version Since Blender is developed by a worldwide pool of individuals giving freely of their time, releases happen often. New for this edition: While most of the activities here use the classic render engine due to classroom time constraints (cycles rendering is very time intensive), a unit (and more) has been added for the cycles render engine. There are also new challenge tasks for those students that are looking for extra, or alternate, activities. Reference to education standards, reflective writing, motion tracking, and 3D printing have also been added. v
8 Rendering and Animation Rendering and Animation Basics RENDERING: A rendering is a pictorial output of a 3D scene or object. Features like materials, lighting, oversampling and shadows control the effects and quality of the rendering. The more of these features you add, the more realistic your scene become, but also lengthens rendering times. Materials and Textures: You can control the way an object appears by applying color and textures. Materials provide realism with added effects. You an control glossiness (specular), self-emitting lighting characteristics, transparency and pattern repetition. Ray-tracing can provide reflection (mirror) and refraction (transparency) effects. Textures can be made from any scanned photograph or drawn object in an image-editing or painting-type program. Images in almost any format (jpg, bitmap, png) can be used. Blender also has many built-in texture generators that can simulate a variety of surface characteristics such as wood, marble, clouds, waves and surface roughness. Lighting: Lighting provides the realism to your scene through reflections and shadows. You can control the type of light, intensity and color. Some lights can give a fog or dusty look with a halo or volume lighting effect. Illumination distances can also be set. Cameras: Your camera is your point-of-view for the scene. Just like a real camera, you can control lens length to achieve close-ups or wide angles. Clipping distance can also be set to control how far and near the camera sees. Depth-of-field can be controlled using nodes. ANIMATION: An animation is a series of rendered images that form a movie. The quality of your movie is controlled by all of the above mentioned features including frames per second (fps), output size, file type and compression. The most common method of animation is called key-framing. Key frames are created at various points in the animation while the computer generates all of the transition frames between the two keys. Basic animation options include changing size, rotation and location of objects. vi
9 Rendering Rendering and and Animation Animation Time Factors: In order to animate, you must first set the length of your animation in frames and your frames per second (fps). The length in time can be calculated from these. Frame Rate Options: NTSC- U.S. and Japan video standard of 30 fps Film- Movie standard of 24 fps PAL- European video standard of 25 fps *We typically use a frame rate of fps depending on computer speed or if we plan to save the file to DVD. Hit the PAL or NTSC setting buttons for these. Creating Keys: A key is placed at the beginning and end of a desired move, size change or rotation of an object. Think in terms of how long you want a change to occur and relate it to your fps. For example, if you want an object to move from point A to point B in 2 seconds and you have 30 fps, place 2 keys 60 frames apart. Following Paths and Objects: In most animation programs, a camera can follow a path or object (or both) as it moves. This feature saves a lot of animation time and reduces the number of keys needed. Output Options: We typically save our movies in MPEG format for Windows. This type of file plays easily on most media players and at a high quality. Depending on how you plan to use your movie (i.e. on the web, saved to DVD, played in a presentation), you may wish to use different formats. Examples include Apple Quicktime and Windows AVI formats. Different formats also allow you to adjust the quality settings. For example, AVI formats can be compressed using a variety of compressors called CODECs. Rendering sizes: Animations are saved in a measurement unit called a pixel. Your computer and TV screens display images as small dots. The more dots, or pixels, per inch, the higher the resolution. Modern displays and TVs use square pixels, but older TV sets used rectangular pixels. This made it somewhat more difficult to render images because the output from 3D animation programs needed to be compressed into a non-square ratio format. Since most TVs have been replaced by modern flat screens, we can begin to get away from these older, confusing ratios and work with 1:1 pixel ratios. vii vii
10 Basic Key Commands Rendering and Animation The next considerations deal with render sizes: 1. The older TV standard of 4:3 ratio size or the newer TV (and film)16:9 ratio size. 2. Standard Definition (SD) or High Definition (HD). This decision will most likely be controlled by the type of result you need and how much time you have to render the project. Until recently, we have always worked with DVD standard definition 4:3 renderings in the classroom. We are changing most of our projects to HDTV 720p to better fit modern TVs and online video postings. While high definition renderings can produce better projects, the cost in rendering times would make it almost impossible for us to complete projects in the classroom during the school day, even with the small render farm we have in the lab. Standard definition still looks great played back on modern TVs and renders at a fraction of the time of higher HD. Here are the frame sizes for each type of render: Real-Time Animation and Physics: Blender uses the Bullet physics engine to make objects react in your scene like they would in real life. The Bullet physics engine was used in movies like 2012 to create all of the realistic-looking animations of falling and reacting objects. Real-time animation allows you to add physical properties to your objects and use the keyboard and other features to control them. You can create actors, change masses, control dampening (friction), set force and torque in x, y, and z planes and create relationships with other objects within the scene. With time and practice, interesting 3D games, animations, and real-time architectural walk-throughs can be created. Blender allows you to use the physics engine to create animation tracks. You can now use the physics to create realistic falling, rolling, etc. animations and use them in movies. viii
11 Basic Basic Key Key Commands Commands Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details. TAB key- Toggles between edit mode (vertex editing) and object select mode. If you re in edit mode when you create a new object, it will be joined to the selected object. Ctrl Z The global UNDO command. With each press, one step will be undone (up to 32 steps possible by default). If in edit mode, it will only undo editing steps on the selected object. Space Bar- Brings up a search window to find basic commands. Z keytoggles view from wireframe to solid. Alt Z Toggles a texture/shaded view. R keyrotates an object or selected vertices. (pressing X,Y,Z after R will limit effect) S keyscales a selected object or vertices. (pressing X,Y,Z after S will limit effect) G key- Grabs or moves the object or selected vertices. (pressing X,Y,Z after G limits effect) A keywhile in edit mode it s good for selecting all vertices for commands like remove doubles and subdivide. Pressing A twice will clear selected and reselect. Alt A Plays animation in selected window. Your cursor must be in that window for it to play. Ctrl A After an object has been re-sized and/or rotated, this can reset the object s data to 1 and 0. W key- Brings up a Specials menu while in edit mode of specific edit mode options. Shift- D - Duplicates or copies selected objects or selected vertices. E keywhile in edit mode, selected vertices can be extruded by pressing E. O key- The O key (not zero) will put you into proportional vertex editing while in edit mode. Proportional editing now also works in object mode. B keygives you a box (window drag) to select multiple objects. In edit mode, works the same to select multiple vertices. C key- Gives you a circle select in edit mode that can be sized by scrolling the mouse wheel. Press LMB to select, press wheel to deselect. Right mouse click or Esc to exit. Shift- A - Brings up the tools menu where you can add meshes, cameras, lights, etc. Number Pad- Controls your views. 7 top, 1 front, 3 side, 0 camera, 5 perspective,. zooms on selected object, + and zoom in and out. The + - buttons also control affected vertices size in proportional vertex editing. MouseLeft to manipulate (LMB), right to select (RMB), center wheel to zoom and rotate view. If you hold down shift and center wheel you can pan around on the screen. Shift Key- Hold down the shift key to make multiple selections with the right mouse button. Arrow Keys-Used to advance frames in animation. Left/right goes 1 frame at a time, up/down goes 10 frames at a time. P keywhile in edit mode, pressing P will seperate selected verticies. In object mode, pressing P will cause you to enter into the game (real-time) mode. Press Esc to exit game mode. ATL/CTRL P -Creates or breaks child/parent relationships. To create C/P relationships, hold down shift key and select child first, then parent. Hit Ctrl P. To clear a relationship, do the same except hit Alt P. U keyin Object Mode, brings up the Single-User menu to unlink materials, animations (IPOs), etc. for linked or copied objects. M key- Moves selected objects to other layers. Ctrl M Mirrors an object. Select M, then X,Y,or Z to mirror on that axis. N keybrings up the numeric info. on a selected object (location, rotation and size). Info. can then be changed in the panel. ix
12 Practice Exercises Ctrl J Ctrl L - Joins selected objects together. Link mesh's data to another mesh. Good for copying materials and other object data from one object to other objects. While holding the Shift key, select all the objects with the one containing the material or other data last. Press Ctrl- L and select you option. F keymakes a face in edit mode of the selected vertices. You can only select 3-4 vertices at a time to make a face. By selecting 2 verticies and pressing F will close shape. Alt F Will Face or Fill a closed set of selected verticies. Ctrl F Brings up a Face Specials menu with other face options. Shift F Camera Flying is enabled and will cause the camera to fly through the scene. X or Delete- Delete selected objects, vertices or faces. K -LMB In edit mode, K and left mouse button will allow you to slice faces. Ctrl R In edit mode, will bring up options to slice or cut faces. Shift- S In both edit and object modes, this will give you options to locate objects or the cursor to assist in precise placement. Function Keys-F1-Load File; F2-Save File; F3-Repeat History; F11-Last Render; F12-Render I KeyThe I key is used to insert animation keys for various things. Objects can be animated with basic Rotation, Location and Size keys and combinations there of. T Key Opens the Toolbox at the side of your viewport. Ctrl T Used to create a Track To Constraint to make one object follow another (like a camera with a target). Ctrl S Used to Save your Blender file Alt C Used to convert meshes, text and curves. For example, text can be converted into a mesh for other transform options. Shift Space Toggles between multiple screens to full screen of active view port. Can also use Ctrl - Up Arrow to do the same thing. Ctrl 0 If using multiple cameras, this will switch to the selected camera. (Number pad 0 ) Armatures- Meshes can be controlled by bones or armatures. Create a mesh with vertices at the joint locations, then create an armature string within it. Child/Parent the mesh to the armature using the armature option. You can then animate in Pose Mode. Ctrl-TabPuts you into Pose mode for manipulating armatures. Import/Export- Blender accepts many different file formats through the import/export commands. When inserting other Blender files or objects into another scene, use the APPEND option from the file menu and select the appropriate options. Multiple objects can be selected with Shift-Right mouse button. Multiple Viewports- To create multiple viewports, move your cursor to the upper-right corner of an existing viewport. When your cursor turns into a + over the tab triangle, press LMB and drag to spit viewport area. To join areas, repeat the process. The Basic Blender Buttons: Editor (window) Type Scene Settings Render Setting x Object Settings World Settings Modifiers Constraints Material Settings Object Data Particles Texture Settings Physics
Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details.
 Basic Key Commands Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details. TAB key- Toggles between edit mode (vertex editing) and
Basic Key Commands Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details. TAB key- Toggles between edit mode (vertex editing) and
Blender. Basics. Second Edition. Classroom Tutorial Book. By James Chronister
 Blender Basics Second Edition Classroom Tutorial Book By James Chronister 2004, 2006 second edition by James Chronister. This document may be reproduced without permission from the author, but please let
Blender Basics Second Edition Classroom Tutorial Book By James Chronister 2004, 2006 second edition by James Chronister. This document may be reproduced without permission from the author, but please let
Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details.
 Basic Key Commands Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details. TAB key- Toggles between edit mode (vertex editing) and
Basic Key Commands Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details. TAB key- Toggles between edit mode (vertex editing) and
Chapter 12- NURBS & Meta Shape Basics
 Chapter 12- NURBS & Meta Shape Basics When you press Shift-A for Add, you will notice other object types beside meshes, cameras and lights that can be created. Two types of objects that can be created
Chapter 12- NURBS & Meta Shape Basics When you press Shift-A for Add, you will notice other object types beside meshes, cameras and lights that can be created. Two types of objects that can be created
Chapter 9- Animation Basics
 Timing, Moving, Rotating and Scaling Now that we know how to make stuff and make it look good, it s time to figure out how to move it around in your scene. Another name for an animation is Interpolation
Timing, Moving, Rotating and Scaling Now that we know how to make stuff and make it look good, it s time to figure out how to move it around in your scene. Another name for an animation is Interpolation
Blender Notes. Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 1 The Blender Interface and Basic Shapes
 Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 1 The Blender Interface and Basic Shapes Introduction Blender is a powerful modeling, animation and rendering
Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 1 The Blender Interface and Basic Shapes Introduction Blender is a powerful modeling, animation and rendering
Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects
 ` Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects Edit Mode- Mesh Editing Object Mode After you have created a mesh, you can go into Edit mode (Tab key or Mode option in window) and change its shape. In edit mode,
` Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects Edit Mode- Mesh Editing Object Mode After you have created a mesh, you can go into Edit mode (Tab key or Mode option in window) and change its shape. In edit mode,
Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects
 Working with Basic Meshes Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects Now that we know how to move around in Blender, let s start doing some basic building and shaping. In this chapter we will talk about creating
Working with Basic Meshes Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects Now that we know how to move around in Blender, let s start doing some basic building and shaping. In this chapter we will talk about creating
Chapter 23- UV Texture Mapping
 Chapter 23- UV Texture Mapping Since games need to be able to process operations as fast as possible, traditional rendering techniques (specular, ray tracing reflections and refractions) cannot typically
Chapter 23- UV Texture Mapping Since games need to be able to process operations as fast as possible, traditional rendering techniques (specular, ray tracing reflections and refractions) cannot typically
Chapter 19- Object Physics
 Chapter 19- Object Physics Flowing water, fabric, things falling, and even a bouncing ball can be difficult to animate realistically using techniques we have already discussed. This is where Blender's
Chapter 19- Object Physics Flowing water, fabric, things falling, and even a bouncing ball can be difficult to animate realistically using techniques we have already discussed. This is where Blender's
Chapter 13 - Modifiers
 Chapter 13 - Modifiers The modifier list continues to grow with each new release of Blender. We have already discussed the Subdivision Surface (SubSurf) and Ocean modifiers in previous chapters and will
Chapter 13 - Modifiers The modifier list continues to grow with each new release of Blender. We have already discussed the Subdivision Surface (SubSurf) and Ocean modifiers in previous chapters and will
Chapter 4- Materials and Textures
 Chapter 4- Materials and Textures Materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent like glass or make them look like
Chapter 4- Materials and Textures Materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent like glass or make them look like
Chapter 1- The Blender Interface
 Chapter 1- The Blender Interface The Blender Screen Years ago, when I first looked at Blender and read some tutorials I thought that this looked easy and made sense. After taking the program for a test
Chapter 1- The Blender Interface The Blender Screen Years ago, when I first looked at Blender and read some tutorials I thought that this looked easy and made sense. After taking the program for a test
Chapter 4- Blender Render Engines
 Chapter 4- Render Engines What is a Render Engine? As you make your 3D models in, your goal will probably be to generate (render) an image or a movie as a final result. The software that determines how
Chapter 4- Render Engines What is a Render Engine? As you make your 3D models in, your goal will probably be to generate (render) an image or a movie as a final result. The software that determines how
Chapter 6- Lighting and Cameras
 Lighting Types and Settings When you create a scene in Blender, you start with a few basic elements that will include a camera, but may or may not include a light. Remember that what the camera sees is
Lighting Types and Settings When you create a scene in Blender, you start with a few basic elements that will include a camera, but may or may not include a light. Remember that what the camera sees is
Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects
 ` Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects Working with Basic Meshes Now that you can move around in Blender, let s start doing some basic building and shaping. In this chapter we will talk about creating
` Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects Working with Basic Meshes Now that you can move around in Blender, let s start doing some basic building and shaping. In this chapter we will talk about creating
Chapter 4- Materials and Textures
 Chapter 4- Materials and Textures Materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent like glass or make them look like
Chapter 4- Materials and Textures Materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent like glass or make them look like
Chapter 14 Particle Systems & Interactions
 Chapter 14 Particle Systems & Interactions This is probably the nicest and most flexible of the Blender effects. When you turn an object into particles, it can be used to simulate snow, fire, smoke, clouds,
Chapter 14 Particle Systems & Interactions This is probably the nicest and most flexible of the Blender effects. When you turn an object into particles, it can be used to simulate snow, fire, smoke, clouds,
https://blenderzen.com/
 Blender Shortcut Keys Cheat Sheet Blender is a vast multi-purpose program designed to do some very complex things. Luckily for us the creators of Blender simplified the interface and squeezed most commands
Blender Shortcut Keys Cheat Sheet Blender is a vast multi-purpose program designed to do some very complex things. Luckily for us the creators of Blender simplified the interface and squeezed most commands
Actions and Graphs in Blender - Week 8
 Actions and Graphs in Blender - Week 8 Sculpt Tool Sculpting tools in Blender are very easy to use and they will help you create interesting effects and model characters when working with animation and
Actions and Graphs in Blender - Week 8 Sculpt Tool Sculpting tools in Blender are very easy to use and they will help you create interesting effects and model characters when working with animation and
Chapter 1- The Blender Interface
 The Blender Screen When I first looked at Blender and read some tutorials I thought that this looked easy and made sense. After taking the program for a test run, I decided to forget about it for a while
The Blender Screen When I first looked at Blender and read some tutorials I thought that this looked easy and made sense. After taking the program for a test run, I decided to forget about it for a while
Full Screen Layout. Main Menu Property-specific Options. Object Tools ( t ) Outliner. Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons
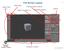 Object Tools ( t ) Full Screen Layout Main Menu Property-specific Options Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons Outliner 1 Animation Controls The Create and Add Menus 2 The Coordinate and Viewing
Object Tools ( t ) Full Screen Layout Main Menu Property-specific Options Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons Outliner 1 Animation Controls The Create and Add Menus 2 The Coordinate and Viewing
Chapter Adding 1- T Mo he tio B n le to nde Yo r ur Inte Scerfac ne e Landscape Scene Stormy Night.mp4 End 200 Default Animation frame 1 Location
 1- The Blender Interface Adding Motion to Your Scene Open your Landscape Scene file and go to your scene buttons. It s time to animate our dark and stormy night. We will start by making the correct setting
1- The Blender Interface Adding Motion to Your Scene Open your Landscape Scene file and go to your scene buttons. It s time to animate our dark and stormy night. We will start by making the correct setting
Detailed Table of content. 3D View by tools - Header. 3D View by tools - Header detailed
 3D View by tools - Header Detailed Table of content...1 Introduction...16 Header...16 All Modes - View Menu...17 All Modes - Navigation Menu...24 All Modes, all Object types - Show / Hide...29 Object Mode
3D View by tools - Header Detailed Table of content...1 Introduction...16 Header...16 All Modes - View Menu...17 All Modes - Navigation Menu...24 All Modes, all Object types - Show / Hide...29 Object Mode
Beginners Guide Maya. To be used next to Learning Maya 5 Foundation. 15 juni 2005 Clara Coepijn Raoul Franker
 Beginners Guide Maya To be used next to Learning Maya 5 Foundation 15 juni 2005 Clara Coepijn 0928283 Raoul Franker 1202596 Index Index 1 Introduction 2 The Interface 3 Main Shortcuts 4 Building a Character
Beginners Guide Maya To be used next to Learning Maya 5 Foundation 15 juni 2005 Clara Coepijn 0928283 Raoul Franker 1202596 Index Index 1 Introduction 2 The Interface 3 Main Shortcuts 4 Building a Character
3D Modeling Course Outline
 3D Modeling Course Outline Points Possible Course Hours Course Overview 4 Lab 1: Start the Course Identify computer requirements. Learn how to move through the course. Switch between windows. Lab 2: Set
3D Modeling Course Outline Points Possible Course Hours Course Overview 4 Lab 1: Start the Course Identify computer requirements. Learn how to move through the course. Switch between windows. Lab 2: Set
Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design week 4 Textures
 Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design week 4 Textures Thaleia Deniozou - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design week 4 Textures Thaleia Deniozou - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
First Animated Model Yellow Submarine
 Course: 3D Design Title: First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig (May 2012) First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Most of you are perhaps too young
Course: 3D Design Title: First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig (May 2012) First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Most of you are perhaps too young
Notes on Blender: By Matthew Evett
 Notes on Blender: By Matthew Evett A synopsis of the Wiki: http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/blender_3d:_noob_to_pro The Blender GUI is implemented via opengl. Thus the GUI is not Windowsstandard. Can resize
Notes on Blender: By Matthew Evett A synopsis of the Wiki: http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/blender_3d:_noob_to_pro The Blender GUI is implemented via opengl. Thus the GUI is not Windowsstandard. Can resize
Digital 3D Animation
 Elizabethtown Area School District Digital 3D Animation Course Number: 753 Length of Course: 1 semester 18 weeks Grade Level: 11-12 Elective Total Clock Hours: 120 hours Length of Period: 80 minutes Date
Elizabethtown Area School District Digital 3D Animation Course Number: 753 Length of Course: 1 semester 18 weeks Grade Level: 11-12 Elective Total Clock Hours: 120 hours Length of Period: 80 minutes Date
Chapter 9- Ray-Tracing
 Ray-tracing is used to produce mirrored and reflective surfaces. It is also being used to create transparency and refraction (bending of images through transparent surfaceslike a magnifying glass or a
Ray-tracing is used to produce mirrored and reflective surfaces. It is also being used to create transparency and refraction (bending of images through transparent surfaceslike a magnifying glass or a
Mesh Modeling Vase and Flower
 Course: 3D Design Title: Mesh Modeling Vase and Flower Dropbox File: VaseAndFlower.zip Blender: Version 2.45 Level: Beginning Author: Neal Hirsig (nhirsig@tufts.edu) Mesh Modeling Vase and Flower In this
Course: 3D Design Title: Mesh Modeling Vase and Flower Dropbox File: VaseAndFlower.zip Blender: Version 2.45 Level: Beginning Author: Neal Hirsig (nhirsig@tufts.edu) Mesh Modeling Vase and Flower In this
Chapter 20- Springs, Screws and Gears
 So far, we see that Blender has many features that are found in almost all 3D computer programs like the ability to extrude along paths, subtract and add meshes through Boolean expressions and now we will
So far, we see that Blender has many features that are found in almost all 3D computer programs like the ability to extrude along paths, subtract and add meshes through Boolean expressions and now we will
Animation Basics. Learning Objectives
 Animation Basics Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Work with the time slider Understand animation playback controls Understand animation and time controls Morph compound
Animation Basics Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Work with the time slider Understand animation playback controls Understand animation and time controls Morph compound
3D Studio Max Lesson 1.1: A Basic Overview of 3DSMax's Main Tool Bar
 3D Studio Max Lesson 1.1: A Basic Overview of 3DSMax's Main Tool Bar Introduction In this tutorial, we'll just be taking a look at parts of the environment of 3D Studio Max version 4.26, and helping you
3D Studio Max Lesson 1.1: A Basic Overview of 3DSMax's Main Tool Bar Introduction In this tutorial, we'll just be taking a look at parts of the environment of 3D Studio Max version 4.26, and helping you
Week 1 The Blender Interface and Basic Shapes
 Week 1 The Blender Interface and Basic Shapes Blender Blender is an open-source 3d software that we will use for this class to create our 3d game. Blender is as powerful as 3d Studio Max and Maya and has
Week 1 The Blender Interface and Basic Shapes Blender Blender is an open-source 3d software that we will use for this class to create our 3d game. Blender is as powerful as 3d Studio Max and Maya and has
Reference Image. Source:
 Mesh Modeling By Immer Baldos This document is a tutorial on mesh modeling using Blender version 2.49b. The goal is to create a model of an elevator. This tutorial will tackle creating the elevator cart,
Mesh Modeling By Immer Baldos This document is a tutorial on mesh modeling using Blender version 2.49b. The goal is to create a model of an elevator. This tutorial will tackle creating the elevator cart,
Introduction to Maya
 1 M CO PY RI GH TE D MA TE RI AL Introduction to Maya aya is a powerful 3D modeling, animation, effects, and rendering solution that has been used in everything from product design to feature films. In
1 M CO PY RI GH TE D MA TE RI AL Introduction to Maya aya is a powerful 3D modeling, animation, effects, and rendering solution that has been used in everything from product design to feature films. In
Creating the Tilt Game with Blender 2.49b
 Creating the Tilt Game with Blender 2.49b Create a tilting platform. Start a new blend. Delete the default cube right click to select then press X and choose Erase Selected Object. Switch to Top view (NUM
Creating the Tilt Game with Blender 2.49b Create a tilting platform. Start a new blend. Delete the default cube right click to select then press X and choose Erase Selected Object. Switch to Top view (NUM
This is the opening view of blender.
 This is the opening view of blender. Note that interacting with Blender is a little different from other programs that you may be used to. For example, left clicking won t select objects on the scene,
This is the opening view of blender. Note that interacting with Blender is a little different from other programs that you may be used to. For example, left clicking won t select objects on the scene,
Creating a Snowman Scene
 Creating a Snowman Scene By: Shane Trautsch Blender 2.72 What you will learn Basic Modeling Particle systems sculpting Materials and Textures Lighting Creating a Snow By now, you have created a snowman.
Creating a Snowman Scene By: Shane Trautsch Blender 2.72 What you will learn Basic Modeling Particle systems sculpting Materials and Textures Lighting Creating a Snow By now, you have created a snowman.
Blender: Introduction, Modelling and Exporting
 Blender: Introduction, Modelling and Exporting 4076/GV07: Virtual Environments (VE) MSci 4th year, MSc VIVE, EngD Will Steptoe Room 6.22, Computer Science W.Steptoe@cs.ucl.ac.uk http://www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/w.steptoe
Blender: Introduction, Modelling and Exporting 4076/GV07: Virtual Environments (VE) MSci 4th year, MSc VIVE, EngD Will Steptoe Room 6.22, Computer Science W.Steptoe@cs.ucl.ac.uk http://www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/w.steptoe
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide
 Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Chapter 5- Materials & Textures
 Chapter 5- Materials & Textures As mentioned in the past chapter, materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent
Chapter 5- Materials & Textures As mentioned in the past chapter, materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent
NURBS Sailboat on Ocean (Modeling/Animation)
 Course: 3D Design Title: NURBS Sailboat Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig (nhirsig@tufts.edu) (April 2013) NURBS Sailboat on Ocean (Modeling/Animation) The objective of this PDF
Course: 3D Design Title: NURBS Sailboat Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig (nhirsig@tufts.edu) (April 2013) NURBS Sailboat on Ocean (Modeling/Animation) The objective of this PDF
An Introduction to Maya. Maya. Used in industrial design, CAD, computer games and motion picture effects. The ambition is what get
 An Introduction to Maya Gustav Taxén gustavt@nada.kth.se 2D1640 Grafik och Interaktionsprogrammering VT 2006 Maya Used in industrial design, CAD, computer games and motion picture effects Special focus
An Introduction to Maya Gustav Taxén gustavt@nada.kth.se 2D1640 Grafik och Interaktionsprogrammering VT 2006 Maya Used in industrial design, CAD, computer games and motion picture effects Special focus
Sculpting 3D Models. Glossary
 A Array An array clones copies of an object in a pattern, such as in rows and columns, or in a circle. Each object in an array can be transformed individually. Array Flyout Array flyout is available in
A Array An array clones copies of an object in a pattern, such as in rows and columns, or in a circle. Each object in an array can be transformed individually. Array Flyout Array flyout is available in
1 INTRoduCTIon to BLENDER 1. 3 PREPARATIon 19
 INTRoduCTIoN xv 2 INTRoduCTIon to GIMP 13 Topics Covered... xv What Isn t Covered...xvi Requirements....xvi The Projects....xvi The Bat Creature... xvii The Spider Bot... xvii The Jungle Temple... xvii
INTRoduCTIoN xv 2 INTRoduCTIon to GIMP 13 Topics Covered... xv What Isn t Covered...xvi Requirements....xvi The Projects....xvi The Bat Creature... xvii The Spider Bot... xvii The Jungle Temple... xvii
Maya Lesson 8 Notes - Animated Adjustable Desk Lamp
 Maya Lesson 8 Notes - Animated Adjustable Desk Lamp To Model the Lamp: 1. Research: Google images - adjustable desk lamp. 2. Print several images of lamps for ideas to model. 3. Make a sketch of the lamp
Maya Lesson 8 Notes - Animated Adjustable Desk Lamp To Model the Lamp: 1. Research: Google images - adjustable desk lamp. 2. Print several images of lamps for ideas to model. 3. Make a sketch of the lamp
Chapter 5- Materials & Textures
 Chapter 5- Materials & Textures As mentioned in the past chapter, materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent
Chapter 5- Materials & Textures As mentioned in the past chapter, materials and textures are what change your model from being gray to brilliant. You can add color, make things glow, become transparent
Images from 3D Creative Magazine. 3D Modelling Systems
 Images from 3D Creative Magazine 3D Modelling Systems Contents Reference & Accuracy 3D Primitives Transforms Move (Translate) Rotate Scale Mirror Align 3D Booleans Deforms Bend Taper Skew Twist Squash
Images from 3D Creative Magazine 3D Modelling Systems Contents Reference & Accuracy 3D Primitives Transforms Move (Translate) Rotate Scale Mirror Align 3D Booleans Deforms Bend Taper Skew Twist Squash
User Interface Software Projects
 User Interface Software Projects Assoc. Professor Donald J. Patterson INF 134 Winter 2013 The author of this work license copyright to it according to the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share
User Interface Software Projects Assoc. Professor Donald J. Patterson INF 134 Winter 2013 The author of this work license copyright to it according to the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share
FLUID DESIGNER FOR 3D PRINTING Installing & Configuring Startup Screen
 FLUID DESIGNER FOR 3D PRINTING Installing & Configuring Startup Screen INSTALLING THE APPLICATION After downloading the file FluidDesigner3DPrinting.Zip from our web site you should install it in either
FLUID DESIGNER FOR 3D PRINTING Installing & Configuring Startup Screen INSTALLING THE APPLICATION After downloading the file FluidDesigner3DPrinting.Zip from our web site you should install it in either
3ds Max certification prep
 3ds Max certification prep Study online at quizlet.com/_25oorz 1. 24 Frames per second 2. 25 Frames per second, Europe 3. 30 Frames per second, Americas and Japan 4. Absolute mode, off set mode 5. How
3ds Max certification prep Study online at quizlet.com/_25oorz 1. 24 Frames per second 2. 25 Frames per second, Europe 3. 30 Frames per second, Americas and Japan 4. Absolute mode, off set mode 5. How
Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder
 Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder 1 2 SketchUp 1. SketchUp is free, and you can download it from the website www.sketchup.com. For some K12 use, see www.sketchup.com/3dfor/k12-education.
Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder 1 2 SketchUp 1. SketchUp is free, and you can download it from the website www.sketchup.com. For some K12 use, see www.sketchup.com/3dfor/k12-education.
User InterfaceChapter1:
 Chapter 1 User InterfaceChapter1: In this chapter you will learn about several aspects of the User Interface. You will learn about the overall layout of the UI, and then about the details of each element.
Chapter 1 User InterfaceChapter1: In this chapter you will learn about several aspects of the User Interface. You will learn about the overall layout of the UI, and then about the details of each element.
Textures and UV Mapping in Blender
 Textures and UV Mapping in Blender Categories : Uncategorised Date : 21st November 2017 1 / 25 (See below for an introduction to UV maps and unwrapping) Jim s Notes regarding Blender objects, the UV Editor
Textures and UV Mapping in Blender Categories : Uncategorised Date : 21st November 2017 1 / 25 (See below for an introduction to UV maps and unwrapping) Jim s Notes regarding Blender objects, the UV Editor
3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner
 3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner Align: to place or arrange (things) in a straight line. To use the Align tool, select at least two objects by Shift left-clicking on them or by dragging a box
3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner Align: to place or arrange (things) in a straight line. To use the Align tool, select at least two objects by Shift left-clicking on them or by dragging a box
Using Blender to Create a Trainz Asset - Preparation
 Using Blender to Create a Trainz Asset - Preparation Project Folder It's a good idea to create a folder for each project to keep the various files associated with a project together. The folder can be
Using Blender to Create a Trainz Asset - Preparation Project Folder It's a good idea to create a folder for each project to keep the various files associated with a project together. The folder can be
LIGHTCONVERSE TOOLS Interface Overview
 MANUAL 1 Contents Contents... 1 LIGHTCONVERSE TOOLS Interface Overview... 2 Tool Manager... 3 Mouse... 4 Mouse Control Operation:... 4 3D Space Area... 4 Modes... 5 Balance Calculator in Warehouse Mode...
MANUAL 1 Contents Contents... 1 LIGHTCONVERSE TOOLS Interface Overview... 2 Tool Manager... 3 Mouse... 4 Mouse Control Operation:... 4 3D Space Area... 4 Modes... 5 Balance Calculator in Warehouse Mode...
Notes 2 My Notes and Thoughts Blender Rigify. Categories : Uncategorised. Date : 19th November / 43
 Blender Rigify Categories : Uncategorised Date : 19th November 2017 1 / 43 Rigify is an incredibly useful tool for getting characters rigged in a jiffy. Instead of spending days setting up a rig by hand,
Blender Rigify Categories : Uncategorised Date : 19th November 2017 1 / 43 Rigify is an incredibly useful tool for getting characters rigged in a jiffy. Instead of spending days setting up a rig by hand,
Mesh Modeling Dice Boolean
 Course: 3D Design Title: Mesh Modeling Dice - Boolean Dropbox File: Dice.zip Blender: Version 2.41 Level: Beginning Author: Neal Hirsig (nhirsig@tufts.edu) Mesh Modeling Dice Boolean In this tutorial,
Course: 3D Design Title: Mesh Modeling Dice - Boolean Dropbox File: Dice.zip Blender: Version 2.41 Level: Beginning Author: Neal Hirsig (nhirsig@tufts.edu) Mesh Modeling Dice Boolean In this tutorial,
Author: John M Blain 2.54+
 Author: John M Blain 2.54+ Blender 3D Computer Modeling and Animation Blender 3D is a an open source freeware program maintained by the Blender Foundation. The program can be downloaded, free of charge,
Author: John M Blain 2.54+ Blender 3D Computer Modeling and Animation Blender 3D is a an open source freeware program maintained by the Blender Foundation. The program can be downloaded, free of charge,
SketchUp + Google Earth LEARNING GUIDE by Jordan Martin. Source (images): Architecture
 SketchUp + Google Earth LEARNING GUIDE by Jordan Martin Source (images): www.sketchup.com Part 1: Getting Started with SketchUp GETTING STARTED: Throughout this manual users will learn different tools
SketchUp + Google Earth LEARNING GUIDE by Jordan Martin Source (images): www.sketchup.com Part 1: Getting Started with SketchUp GETTING STARTED: Throughout this manual users will learn different tools
It is a good idea to practice View Control tools for 5 minutes at the start of every 3D session, before doing any other work.
 3D View Control Module Overview All the 2D view controls, such as Fit View, Zoom In and Out, Window Area, and Pan, can be used in 3D. As in 2D, elements to the left, right, above, or below can be excluded
3D View Control Module Overview All the 2D view controls, such as Fit View, Zoom In and Out, Window Area, and Pan, can be used in 3D. As in 2D, elements to the left, right, above, or below can be excluded
Import / Object modes: 5 Layers for organising your scene are available at the top of the screen.
 LUMION 1 VS LUMION 2 SCENES - In Lumion 2, the sky, clouds, fog, material settings, ambient shadows and reflections have been overhauled, so don't expect your Lumion 1 scenes to look identical when you
LUMION 1 VS LUMION 2 SCENES - In Lumion 2, the sky, clouds, fog, material settings, ambient shadows and reflections have been overhauled, so don't expect your Lumion 1 scenes to look identical when you
Chapter 18- Relative Vertex (Shape) Keys
 Chapter 18- Relative Vertex (Shape) Keys Creating Mesh Shape Keys We ve discussed deforming a mesh with an armature, but what if you want to deform a mesh in other ways like have it flatten, move a mouth,
Chapter 18- Relative Vertex (Shape) Keys Creating Mesh Shape Keys We ve discussed deforming a mesh with an armature, but what if you want to deform a mesh in other ways like have it flatten, move a mouth,
Animatron Tutorial. Ronald Bourret
 Animatron Tutorial Ronald Bourret http://www.rpbourret.com Table of Contents License... 2 Lesson 1: Getting Started... 3 1.1 Creating an Animatron account... 3 1.2 Animatron screen... 3 Lesson 2: Drawing...
Animatron Tutorial Ronald Bourret http://www.rpbourret.com Table of Contents License... 2 Lesson 1: Getting Started... 3 1.1 Creating an Animatron account... 3 1.2 Animatron screen... 3 Lesson 2: Drawing...
Blender Lesson Ceramic Bowl
 Blender Lesson Ceramic Bowl This lesson is going to show you how to create a ceramic looking bowl using the free program Blender. You will learn how to change the view, add, delete, scale and edit objects
Blender Lesson Ceramic Bowl This lesson is going to show you how to create a ceramic looking bowl using the free program Blender. You will learn how to change the view, add, delete, scale and edit objects
Graphical Editors used at CSC/Nada earlier. Main competitors. What is Maya? What is Maya? An Introduction to Maya. Maya
 DH2640 Grafik och interaktionsprogrammering DH2323 Datorgrafik och interaktion NA8740 Datorgrafik och användargränssnitt An Introduction to Maya original slides by Gustav Taxén Lars Kjelldahl lassekj@csc.kth.se
DH2640 Grafik och interaktionsprogrammering DH2323 Datorgrafik och interaktion NA8740 Datorgrafik och användargränssnitt An Introduction to Maya original slides by Gustav Taxén Lars Kjelldahl lassekj@csc.kth.se
Object Manipulation and Basic Animation
 Object Manipulation and Basic Animation By Immer Baldos This document is a tutorial on basic modeling and animation using Blender version 2.49b. The goals are to create a Windmill using blender s built-in
Object Manipulation and Basic Animation By Immer Baldos This document is a tutorial on basic modeling and animation using Blender version 2.49b. The goals are to create a Windmill using blender s built-in
ROTOSCOPING AND MATTE PAINTING In Blender v2.48a
 In the world of Visual Effects, Rotoscoping, Matte Painting and Garbage Painting are necessary and complementary functions. They are used each time a cut-out in the image is necessary, to remove a background
In the world of Visual Effects, Rotoscoping, Matte Painting and Garbage Painting are necessary and complementary functions. They are used each time a cut-out in the image is necessary, to remove a background
solidthinking Environment...1 Modeling Views...5 Console...13 Selecting Objects...15 Working Modes...19 World Browser...25 Construction Tree...
 Copyright 1993-2009 solidthinking, Inc. All rights reserved. solidthinking and renderthinking are trademarks of solidthinking, Inc. All other trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective
Copyright 1993-2009 solidthinking, Inc. All rights reserved. solidthinking and renderthinking are trademarks of solidthinking, Inc. All other trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective
Character Modeling COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 38 Character Modeling p a r t _ 1 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 39 Character Modeling Character Modeling 40 1Subdivision & Polygon Modeling Many of Maya's features have seen great improvements in recent updates
38 Character Modeling p a r t _ 1 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 39 Character Modeling Character Modeling 40 1Subdivision & Polygon Modeling Many of Maya's features have seen great improvements in recent updates
Computer graphics Labs: Blender (1/3) Modelling, transparency and reflection
 Computer graphics Labs: Blender (1/3) Modelling, transparency and reflection University of Liège Department of Aerospace and Mechanical engineering Designed with Blender 2.76b Introduction to the interface
Computer graphics Labs: Blender (1/3) Modelling, transparency and reflection University of Liège Department of Aerospace and Mechanical engineering Designed with Blender 2.76b Introduction to the interface
To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max.
 Job No: 01 Duration: 8H Job Title: User interface overview Objective: To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max. Students should be
Job No: 01 Duration: 8H Job Title: User interface overview Objective: To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max. Students should be
Beginning Paint 3D A Step by Step Tutorial. By Len Nasman
 A Step by Step Tutorial By Len Nasman Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Paint 3D User Interface...4 Creating 2D Shapes...5 Drawing Lines with Paint 3D...6 Straight Lines...6 Multi-Point Curves...6
A Step by Step Tutorial By Len Nasman Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Paint 3D User Interface...4 Creating 2D Shapes...5 Drawing Lines with Paint 3D...6 Straight Lines...6 Multi-Point Curves...6
Learning Autodesk Maya The Modeling & Animation Handbook. Free Models From Turbo Squid Value US $ Official Autodesk Training Guide
 Free Models From Turbo Squid Value US $239.00 Official Autodesk Training Guide Learning Autodesk Maya 2008 The Modeling & Animation Handbook A hands-on introduction to key tools and techniques in Autodesk
Free Models From Turbo Squid Value US $239.00 Official Autodesk Training Guide Learning Autodesk Maya 2008 The Modeling & Animation Handbook A hands-on introduction to key tools and techniques in Autodesk
A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015
 A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015 Written by Mitchell Youngerman Table of Contents Layout of Toolbars...pg 1 Creating Objects...pg 2 Selecting & Deselecting Objects...pg 3 Changing Perspective... pg 4 Transforming
A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015 Written by Mitchell Youngerman Table of Contents Layout of Toolbars...pg 1 Creating Objects...pg 2 Selecting & Deselecting Objects...pg 3 Changing Perspective... pg 4 Transforming
Lesson 11. Polygonal Spaceship
 11 Polygonal Spaceship In this lesson, you will build and texture map a polygonal spaceship. Starting with a polygonal cube, you will extrude facets until you have a completed ship. You will then be able
11 Polygonal Spaceship In this lesson, you will build and texture map a polygonal spaceship. Starting with a polygonal cube, you will extrude facets until you have a completed ship. You will then be able
Modify Group. Joint Move. (default keyboard shortcut Ctrl J)
 Modify Group Joint Move (default keyboard shortcut Ctrl J) Joint Mover draws lines along each bone and puts a cross hair at the base of the child bone(s), which is usually coincident with the tip of the
Modify Group Joint Move (default keyboard shortcut Ctrl J) Joint Mover draws lines along each bone and puts a cross hair at the base of the child bone(s), which is usually coincident with the tip of the
Bforartists Reference Manual - Copyright - This page is under Public Domain. Editors
 Editors Introduction...2 Hidden menus...2 The Header menu...2 Flip to Top...2 Collapse Menus...2 Hide Editortype menu...3 Maximize Area - Tile Area...3 The editor type menu...3 Area Options...3 Split area...3
Editors Introduction...2 Hidden menus...2 The Header menu...2 Flip to Top...2 Collapse Menus...2 Hide Editortype menu...3 Maximize Area - Tile Area...3 The editor type menu...3 Area Options...3 Split area...3
Sliding and Rotating Objects. Appendix 1: Author s Notes
 AnimationWorks User Guide AnimationWORKS Introduction Camera Paths Cameras Moving Objects Moving Object Paths Sliding and Rotating Objects Light Objects Class Visibility Objects Transparency Objects Appendix
AnimationWorks User Guide AnimationWORKS Introduction Camera Paths Cameras Moving Objects Moving Object Paths Sliding and Rotating Objects Light Objects Class Visibility Objects Transparency Objects Appendix
4) Finish the spline here. To complete the spline, double click the last point or select the spline tool again.
 1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
Create a Rubber Duck. This tutorial shows you how to. Create simple surfaces. Rebuild a surface. Edit surface control points. Draw and project curves
 Page 1 of 24 Create a Rubber Duck This exercise focuses on the free form, squishy aspect. Unlike the flashlight model, the exact size and placement of the objects is not critical. The overall form is the
Page 1 of 24 Create a Rubber Duck This exercise focuses on the free form, squishy aspect. Unlike the flashlight model, the exact size and placement of the objects is not critical. The overall form is the
Lathe Modeling Wine Glass
 Course: 3D Design Title: Bezier Curve Modeling Column Dropbox File: WineGlass.zip Blender: Version 2.41 Level: Beginning Author: Neal Hirsig (nhirsig@tufts.edu) Lathe Modeling Wine Glass In this tutorial,
Course: 3D Design Title: Bezier Curve Modeling Column Dropbox File: WineGlass.zip Blender: Version 2.41 Level: Beginning Author: Neal Hirsig (nhirsig@tufts.edu) Lathe Modeling Wine Glass In this tutorial,
How to...create a Video VBOX Gauge in Inkscape. So you want to create your own gauge? How about a transparent background for those text elements?
 BASIC GAUGE CREATION The Video VBox setup software is capable of using many different image formats for gauge backgrounds, static images, or logos, including Bitmaps, JPEGs, or PNG s. When the software
BASIC GAUGE CREATION The Video VBox setup software is capable of using many different image formats for gauge backgrounds, static images, or logos, including Bitmaps, JPEGs, or PNG s. When the software
Turn your movie file into the homework folder on the server called Lights, Camera, Action.
 CS32 W11 Homework 3: Due MONDAY, APRIL 18 Now let s put the ball in a world of your making and have some fun. Create a simple AND WE MEAN SIMPLE environment for one of your ball bounces. You will assign
CS32 W11 Homework 3: Due MONDAY, APRIL 18 Now let s put the ball in a world of your making and have some fun. Create a simple AND WE MEAN SIMPLE environment for one of your ball bounces. You will assign
Modeling Technology Group
 Modeling Technology Group Hiroshi Hayashi David Ogirala Matt Nedrich Jeff Ridenbaugh Spencer Smith Saba Bokhari John Gray Charles Hellstrom Bryan Linthicum Polygon Models (part-1) What are polygons? -
Modeling Technology Group Hiroshi Hayashi David Ogirala Matt Nedrich Jeff Ridenbaugh Spencer Smith Saba Bokhari John Gray Charles Hellstrom Bryan Linthicum Polygon Models (part-1) What are polygons? -
When you move an (unparented and unrotated) item in Layout, generally your mouse movements have the following effects:
 Translate Group Move (default keyboard shortcut T) When you move an (unparented and unrotated) item in Layout, generally your mouse movements have the following effects: Movement Move Left/Right LMB Up/Down
Translate Group Move (default keyboard shortcut T) When you move an (unparented and unrotated) item in Layout, generally your mouse movements have the following effects: Movement Move Left/Right LMB Up/Down
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics
 COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
As we said Procedural Textures are not images but textures that Blender creates automatically. They are good to use as a foundation to start with.
 Textures There are two types of Textures in Blender. Procedural Textures that are by default created by the program and Image Textures that use external images. We will first see how you can apply a Procedural
Textures There are two types of Textures in Blender. Procedural Textures that are by default created by the program and Image Textures that use external images. We will first see how you can apply a Procedural
Maya 2014 Introduction to Maya
 Maya 2014 Introduction to Maya Maya is an incredibly powerful animation software that can be used to create almost anything you can imagine. The purpose of this document is to help you become familiar
Maya 2014 Introduction to Maya Maya is an incredibly powerful animation software that can be used to create almost anything you can imagine. The purpose of this document is to help you become familiar
Transforming Objects and Components
 4 Transforming Objects and Components Arrow selection Lasso selection Paint selection Move Rotate Scale Universal Manipulator Soft Modification Show Manipulator Last tool used Figure 4.1 Maya s manipulation
4 Transforming Objects and Components Arrow selection Lasso selection Paint selection Move Rotate Scale Universal Manipulator Soft Modification Show Manipulator Last tool used Figure 4.1 Maya s manipulation
audio, 57 auto-orientation, 215 automatic mapping, 243 average vertices, 239 axis, 3-6, 12, 94, 126, 149, 191, 199, 290
 Index 307 Index A added attributes, 196, 205 Adobe Premiere, 256 aim constraint, 271, 272, 277 airplane, 5, 13-17, 197-199, 206-207, 252-253 Alias manuals, 54 alpha channel, 174 alpha gain, 231 ambient,
Index 307 Index A added attributes, 196, 205 Adobe Premiere, 256 aim constraint, 271, 272, 277 airplane, 5, 13-17, 197-199, 206-207, 252-253 Alias manuals, 54 alpha channel, 174 alpha gain, 231 ambient,
StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual. Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC
 StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC StickFont Editor Manual Table of Contents Welcome... 1 Registering StickFont Editor... 3 Getting Started... 5 Getting Started...
StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC StickFont Editor Manual Table of Contents Welcome... 1 Registering StickFont Editor... 3 Getting Started... 5 Getting Started...
The Wireframe Update Buttons. The Frontface and Backface Buttons. The Project Designer 265
 The Wireframe Update Buttons The speed at which objects can be manipulated in the Project Designer viewport depends in part on the complexity of the object being moved. An object that is made up of many
The Wireframe Update Buttons The speed at which objects can be manipulated in the Project Designer viewport depends in part on the complexity of the object being moved. An object that is made up of many
Blender Animation Editors
 Blender Animation Editors Animation Editors Posted on September 8, 2010 by mrsiefker Blender has several different editors for creating and fine tuning our animations. Each one is built around a specific
Blender Animation Editors Animation Editors Posted on September 8, 2010 by mrsiefker Blender has several different editors for creating and fine tuning our animations. Each one is built around a specific
ARCHITECTURE & GAMES. A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling FORM & SPACE. Industry Careers Framework. Applied. Getting Started.
 A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling One of the first introductions to form and space usually comes at a very early age. As an infant, you might have played with building blocks to help hone your motor
A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling One of the first introductions to form and space usually comes at a very early age. As an infant, you might have played with building blocks to help hone your motor
Adobe After Effects CS6 Digital Classroom
 Adobe After Effects CS6 Digital Classroom AGI Creative ISBN-13: 9781118142790 Table of Contents Starting up About Digital Classroom 1 Prerequisites 1 System requirements 1 Starting Adobe After Effects
Adobe After Effects CS6 Digital Classroom AGI Creative ISBN-13: 9781118142790 Table of Contents Starting up About Digital Classroom 1 Prerequisites 1 System requirements 1 Starting Adobe After Effects
