Micro-CT analysis of mouse long bones (proximal tibia, distal femur)
|
|
|
- Kathryn Floyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Micro-CT analysis of mouse long bones (proximal tibia, distal femur) Application note Page 1 of 13
2 2 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis Introduction The scans of mouse bones can be performed on the Skyscan 1072, 1172, 1076 micro-ct scanners. This report sets out a methodology for morphometric analysis of trabecular and cortical murine bone. Results are presented for four mouse femur samples, for both trabecular and cortical bone morphometry. Method Scan and reconstruction parameters The mouse bones were removed from alcohol storage and dried superficially on paper tissue, before being wrapped in plastic cling-film or in parafilm, to prevent drying during scanning (and associated movement artefacts). Each plastic-wrapped bone was placed in a plastic / polystyrene foam tube which was mounted vertically in the Skyscan 1172 / 1072, or horizontally in the 1076/1176 scanner sample chamber, for micro-ct imaging. The suggested parameters of the scan in the 1172 (10/11 Mpix model) are as follows: X-ray voltage X-ray current Filter 50 kv 200 µa. Image pixel size 4-5 µm Camera resolution setting Tomographic rotation Rotation step Frame averaging 0.5 mm aluminium Medium or low (2000 or 1000 pixel field width) 180 / (depending on required scan time) Scan duration Medium res min.; low res min. The suggested parameters of the scan in the 1172 (1.3 Mpix model) are as follows: X-ray voltage X-ray current Filter 50 kv 200 µa. Image pixel size 4-5 µm Camera resolution setting Tomographic rotation 0.5 mm aluminium High (1280 pixel field width) 180 /360 Page 2 of 13
3 3 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis Rotation step Frame averaging 1-2 Scan duration minutes The suggested parameters of the scan in the 1072 are as follows: X-ray voltage 50 kv X-ray current 200 µa. Filter 0.5 mm aluminium Image pixel size 4-5 µm Camera resolution setting n/a (1024 pixel field width) Tomographic rotation 180 Rotation step 0.45 Frame averaging 1-2 Scan duration minutes The suggested parameters of the scan in the 1076/1176 (not in vivo, extracted bone) are as follows: X-ray voltage X-ray current Filter 50 kv 200 µa. Image pixel size 8.9 µm Camera resolution setting Tomographic rotation Rotation step Frame averaging 1 Scan duration 0.5 mm aluminium High (4000 pixel field width) 180 / minutes The suggested parameters of the scan in the 1076/1176 (in vivo, living mouse under anaesthesia) are as follows: X-ray voltage X-ray current Filter 50 kv 200 µa. Image pixel size 8.9 µm Camera resolution setting Tomographic rotation 0.5 mm aluminium High (4000 pixel field width) 180 Page 3 of 13
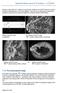
4 4 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis Rotation step Frame averaging 1 Scan duration 5-9 minutes Reconstruction parameters suggested (same for all scanners): Smoothing 0-1 Beam hardening 33% Ring reduction 5 Post-alignment Histogram limits use value calculated by Nrecon min 0; max at right end of high density tail ; refer to image to get good visible contrast Reconstruction was carried out employing a modified Feldkamp i algorithm using the Skyscan Nrecon ii software which facilitates network distributed reconstruction carried out on four pcs running simultaneously. Time for reconstruction of on scan dataset is usually much less than the scan duration. Region of interest selection for trabecular and cortical bone Both trabecular (metaphyseal) and cortical (metaphyseal-diaphyseal) were selected with reference to the growth plate. A crossectional slice was selected as a growth plate reference slice, in the following way. Moving slice-by-slice toward the growth plate from the metaphysis/diaphysis, a point is reached where a clear bridge of low density cartilage (chondrocyte seam) becomes established from one corner of the crossection to another. This bridge is established by the disappearance of the last band of fine primary spongiosal bone interrupting the chondrocyte seam (see figure 1). This landmark allows a reference level to be defined for the growth plate: trabecular and cortical volumes of interest are then defined relative to this reference level. (Note that the bridge can be at different locations in the growth plate crossection in difference bone scans, depending on the orientation of the scanned bone.) Such a reference slice can be identified in all micro-ct scans of the proximal tibia and distal femur. Note that while in the femur there are four circular islands delineated by chondrocyte seams in crossections through the upper growth plate, in the tibia there are only two such islands; none-the-less, the criterion for a growth plate reference described here can be reliably applied both for the femur and tibia. The only possible exception is in very old mice or rats Page 4 of 13
5 5 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis where the growth plate is inactive and very little or no chondrocyte seams are present. In such cases, a similar landmark can be found involving connection of the bony structures of the vestigial growth plate. Figure 1. Moving slice-by-slice toward the growth plate from the metaphysis/diaphysis, a point is reached where a clear bridge of low density cartilage (chondrocyte seam) becomes established from one corner of the crossection to another, as shown by the arrows. The two images above show the establishment of this bridge with the disappearance of the last band of fine primary spongiosal bone interrupting the chondrocyte seam. This landmark allows a reference level to be defined for the growth plate: trabecular and cortical volumes of interest are then defined relative to this reference level. (Note that the bridge can be at different locations in the growth plate crossection.) The regions of interest (ROI) were selected with reference to a growth plate reference slice, selected as described above. Trabecular and cortical regions were defined as positions along the long axis of the femur relative to the growth plate reference. The trabecular region commenced about mm (50 image slices) from the growth plate level in the direction of the metaphysis, and extended from this position for a further 1.72 mm (450 image slices). The vertical extent of the trabecular and cortical ROIs is indicated in figure 2. Note that for the trabecular ROI the value of the number of slices of the offset (interval from growth plate reference level to start of ROI, here 50 slices) and the height (here 450 slices) can be altered to allow for different bone geometries in mice of different strain, age and gender. The offset needs to be sufficient so that the trabecular ROI begins in a region of mature secondary trabecular bone, without a significant presence of the fine-structured growth-plate-associated primary spongiosa in the crossections. Within the trabecular region, separation of the trabecular from cortical bone was done using a freehand drawing tool for delineating of complex Page 5 of 13
6 6 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis regions of interest (figure 3). The boundaries of the selected trabecular ROI ran parallel and close to the endocortical boundary but excluding peripheral vestiges of the growth plate and associated primary spongiosa, as shown in fig. 3. In Skyscan CT-analyser the volume of interest (VOI) automatically interpolates or morphs the edited ROI shapes (such as freehand drawn shapes) between edited levels. The frequency of edited levels depends on how rapidly the bone crossection shape changes along the bone axis (in the z direction) and becomes less as you move from the growth plate in the direction of the diaphysis (bone shaft). The cortical region commenced about 2.15 mm (500 image slices) from the growth plate level in the direction of the metaphysis, and extended from this position for a further 0.43 mm (100 image slices). This probably represents a diaphyseal site - there were relatively few remaining thin trabecular structures, compared to the much higher relative volume and number density of trabecular structures at the metaphysis close to the growth plate. The trabecular and cortical bone ROIs were delineated as shown in figure 3. Note again that for the cortical ROI the value of the number of slices of the offset (interval from growth plate reference level to start of ROI, here 500 slices) and the height (here 100 slices) can be altered to allow for different bone geometries in mice of different strain, age and gender. Cort ROI: mm from GP ( slices); 0.43 mm section height (100 slices) Trab ROI: mm from GP ( slices); 1.72 mm section height (400 slices) Growth plate (GP) reference level Figure 2. The vertical extent of the trabecular and cortical ROIs, defined with reference to a standard growth plate reference level (see text). Page 6 of 13
7 7 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis Figure 3. Trabecular and cortical ROIs delineated by the Skyscan CTanalyser software ROI tool, by freehand drawing. Morphometric analysis 3D and 2D morphometric parameters were calculated for the trabecular and cortical selected ROIs. Single grey threshold values were applied for the trabecular and cortical ROIs respectively (68 and 120). (The lower density threshold for trabecular bone allows segmentation of the finer structures; the thicker cortical bone can have higher threshold to represent thickness and porosity more accurately.) The signal to noise ratios of the reconstructed images were high so that further image processing steps on the binarised images such as despeckle were not likely to significantly improve measurement precision. 3D parameters were based on analysis of a Marching Cubes iii type model with a rendered surface. Calculation all of 2D areas and perimeters was based on the Pratt iv algorithm. Morphometric parameters measured by CT-analyser have been validated on both virtual objects and aluminium foil and wire phantoms v. Structure thickness in 3D was calculated using the local thickness or sphere-fitting method vi, and structure model index (an indicator of the relative prevalence of plates and rods) was derived according to the method of Hildebrand and Ruegsegger vii. Degree of anisotropy was calculated by the mean intercept method viii. 3D Model construction Rendered 3D models were constructed for 3D viewing of trabecular and cortical analysed regions. Model construction was by the Double time cubes method ix, a modification of the Marching cubes method 3. Page 7 of 13
8 8 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis Results Trabecular bone Table 1 lists examples of measured morphometric parameters for trabecular bone, within the volumes of interest referenced to the growth plate, as described above. Of the four examples A-D, samples A and B have a lower trabecular percent volume (BV/TV), of 4-5%, while C and D have about double this percent volume, at 9-11%. Most of this increase in trabecular BV/TV is due to an increased spatial density of trabecular structures, as indicated by trabecular number (Tb.N) being twice as high in C and D compared to A and B. By contrast the trabecular thickness (Tb.Th) is not much different between the four samples. Images of 3d rendered models of the four samples (the analysed trabecular volumes of interest) are shown in figure 4. Cortical bone The morphometric parameters measured for four cortical bone samples are listed in table 2. Samples C and D have greater cortical thickness and crossectional area; however both periosteal and endosteal perimeter was greater in samples A and B. This implies that the cortical diaphysis was both wider and thinner in A and B. The wider bone shape in A and B compensates for the reduced cortical thickness and area in terms of cortical strength, as indicated by rotational moment of inertia, which is about the same in all four samples. Images of 3d rendered models of the four samples (the analysed cortical volumes of interest) are shown in figure 5. Page 8 of 13
9 9 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis Table 1. Trabecular morphometric parameters measured by micro-ct in mouse distal femur samples A-D. Parameter Parameter symbol x, unit Distal femur Mouse A Mouse B Mouse C Mouse D Total (tissue) volume TV (mm 3 ) Bone volume BV (mm 3 ) Percent bone volume BV/TV (%) Bone surface BS (mm 2 ) Bone surface to volume ratio Bone surface density Trabecular thickness Trabecular separation Trabecular number Trabecular pattern factor Structure model index Euler connectivity Euler connectivity density Degree of anisotropy BS/BV (mm -1 ) BS/TV (mm -1 ) Tb.Th (mm) Tb.Sp (mm) Tb.N (mm -1 ) Tb.Pf (mm -1 ) SMI E.Con E.Con.D (mm -3 ) DA Page 9 of 13
10 10 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis Table 2. Cortical morphometric parameters measured by micro-ct in mouse distal femur samples A-D. Parameter Parameter symbol 9, unit Distal femur Mouse A Mouse B Mouse C Mouse D Cortical thickness (3D) Cortical crossectional thickness (2D) Cortical periosteal perimeter Cortical endosteal perimeter Cortical crossectional area Polar moment of inertia Ct.Th (mm) Ct.Cs.Th (mm) Ct.Pe.Pm (mm) Ct.En.Pm (mm) Ct.Ar (mm 2 ) MMI(p) (mm 4 ) Eccentricity Ecc Cortical porosity Ct.Po (%) Page 10 of 13
11 11 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis (a) (b) (c) Figure 4. 3D rendered models from the trabecular ROIs from mouse femur samples A-D (d) Page 11 of 13
12 12 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 5. 3D rendered models of the cortical ROIs from the distal femurs of samples A-D. Page 12 of 13
13 13 Bruker-MicroCT method note: Long mouse bone micro-ct analysis i Feldkamp LA, Davis LC, Kress JW (1984) Practical cone-beam algorithm. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1 (6): ii Xuan Liu, Alexander Sasov (2005) Cluster reconstruction strategies for microct and nanoct scanners. In: Proceedings of the Fully Three- Dimensional Image Reconstruction Meeting in Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, July 6-9, 2005, Fort Douglas/Olympic Village, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA. iii Lorensen WE, Cline HE (1987) Marching cubes: a high resolution 3d surface construction algorithm. Computer graphics 21 (4): iv Pratt WK. Digital image processing, 2nd ed. New York: Wiley; Chapter 16. v Salmon PL, Buelens E, Sasov AY (2003) Performance of In Vivo Micro-CT Analysis of Mouse Lumbar Vertebral and Knee Trabecular Bone Architecture. J. Bone Miner. Res.18 (suppl. 2) S256. vi Hildebrand T and Ruegsegger P (1997) A new method for the model independent assessment of thickness in three dimensional images. J. Microsc.185: vii Hildebrand T and Ruegsegger P (1997) Quantification of bone microarchitecture with the structure model index. Comp. Meth. Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 1: viii Harrigan T P and Mann R W (1984) Characterisation of microstructural anisotropy in orthotropic materials using a second rank tensor. J. Mater. Sci. 19: ix Bouvier Dennis J (2004) Double-time cubes: a fast 3d surface construction algorithm for volume visualisation. University of Arkansas, 313 Engineering Hall, Fayetteville, AR72701, USA. x Parfitt AM, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR (1987) Bone Histomorphometry: standardization of nomenclature, symbols and units. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2 (6): Page 13 of 13
Applying Hounsfield unit density calibration in SkyScan CT-analyser
 1 Bruker-microCT Method note Applying Hounsfield unit density calibration in SkyScan CT-analyser Hounsfield units (HU) are a standard unit of x-ray CT density, in which air and water are ascribed values
1 Bruker-microCT Method note Applying Hounsfield unit density calibration in SkyScan CT-analyser Hounsfield units (HU) are a standard unit of x-ray CT density, in which air and water are ascribed values
Adaptive thresholding. in CTAn
 Adaptive thresholding in CTAn Method note Page 1 of 8 2 Bruker-MicroCT method note:adaptive thresholding in CTAn Introduction 2D or 3D morphometric analysis of micro-ct images always requires binarization
Adaptive thresholding in CTAn Method note Page 1 of 8 2 Bruker-MicroCT method note:adaptive thresholding in CTAn Introduction 2D or 3D morphometric analysis of micro-ct images always requires binarization
Manual for Bruker-microCT CT-Analyser v
 Setting a high value for number of projections allows a set of MIP slices to be taken through a selected part or all of the dataset. This can be a useful way of displaying quickly the structure of a scanned
Setting a high value for number of projections allows a set of MIP slices to be taken through a selected part or all of the dataset. This can be a useful way of displaying quickly the structure of a scanned
Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging
 Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging Method note Page 1 of 12 2 Method note: Dual-energy microct analysis 1. Introduction 1.1. The basis for dual energy imaging Micro-computed tomography
Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging Method note Page 1 of 12 2 Method note: Dual-energy microct analysis 1. Introduction 1.1. The basis for dual energy imaging Micro-computed tomography
The user's guide. CT-Analyser. Contents. (version )
 CT-Analyser (version 1.8.1.3) The user's guide Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. First start-up of the program 2 3. Set-up of preferences 3 4. Opening files 4 4.1. Crossection image window 8 4.2. Dataset bar
CT-Analyser (version 1.8.1.3) The user's guide Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. First start-up of the program 2 3. Set-up of preferences 3 4. Opening files 4 4.1. Crossection image window 8 4.2. Dataset bar
Using X-Ray Micro Tomography to assess the quality of Packaging Foil
 Using X-Ray Micro Tomography to assess the quality of Packaging Foil Martin Koster 1, Gerard van Dalen 2, Robert Hoeve 3 1 Unilever Research 2 Unilever Research 3 Unilever Research, Olivier van Noortlaaan
Using X-Ray Micro Tomography to assess the quality of Packaging Foil Martin Koster 1, Gerard van Dalen 2, Robert Hoeve 3 1 Unilever Research 2 Unilever Research 3 Unilever Research, Olivier van Noortlaaan
AnalyzePro Bone Microarchitecture Analysis Add-On
 AnalyzePro Bone Microarchitecture Analysis Add-On User s Manual support@analyzedirect.com www.analyzedirect.com +1.913.338.2527 2017 AnalyzeDirect, Inc 2017 Mayo Clinic Biomedical Imaging Resource Contents
AnalyzePro Bone Microarchitecture Analysis Add-On User s Manual support@analyzedirect.com www.analyzedirect.com +1.913.338.2527 2017 AnalyzeDirect, Inc 2017 Mayo Clinic Biomedical Imaging Resource Contents
Method note. Page 1 of 7
 Advanced image coregistration in Dataviewer Method note Page 1 of 7 2 Bruker microct method note: Advanced image co-registration Introduction The 2D and 3D image co-registration in Dataviewer provides
Advanced image coregistration in Dataviewer Method note Page 1 of 7 2 Bruker microct method note: Advanced image co-registration Introduction The 2D and 3D image co-registration in Dataviewer provides
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY FOR METROLOGY
 HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY FOR METROLOGY David K. Lehmann 1, Kathleen Brockdorf 1 and Dirk Neuber 2 1 phoenix x-ray Systems + Services Inc. St. Petersburg, FL, USA 2 phoenix x-ray Systems + Services
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY FOR METROLOGY David K. Lehmann 1, Kathleen Brockdorf 1 and Dirk Neuber 2 1 phoenix x-ray Systems + Services Inc. St. Petersburg, FL, USA 2 phoenix x-ray Systems + Services
MicroCT for bone and biomaterials characterization. Lea Vaiana PARALAB SL
 MicroCT for bone and biomaterials characterization Lea Vaiana PARALAB SL Distribución de equipamiento Científico para laboratorio y proceso Oficinas en Barcelona, Madrid y Bilbao. Asesoramiento pre-venta
MicroCT for bone and biomaterials characterization Lea Vaiana PARALAB SL Distribución de equipamiento Científico para laboratorio y proceso Oficinas en Barcelona, Madrid y Bilbao. Asesoramiento pre-venta
DUE to beam polychromacity in CT and the energy dependence
 1 Empirical Water Precorrection for Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Katia Sourbelle, Marc Kachelrieß, Member, IEEE, and Willi A. Kalender Abstract We propose an algorithm to correct for the cupping artifact
1 Empirical Water Precorrection for Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Katia Sourbelle, Marc Kachelrieß, Member, IEEE, and Willi A. Kalender Abstract We propose an algorithm to correct for the cupping artifact
How to make color-coded 3D models for structure thickness in CTVox
 How to make color-coded 3D models for structure thickness in CTVox Method note Page 1 of 10 2 Bruker microct method note: Color-coded structure thickness in CTVox Introduction When running a 3D analysis
How to make color-coded 3D models for structure thickness in CTVox Method note Page 1 of 10 2 Bruker microct method note: Color-coded structure thickness in CTVox Introduction When running a 3D analysis
Automatic segmentation of cortical and trabecular compartments based on a dual threshold technique for in vivo micro-ct bone analysis
 Bone 41 (2007) 505 515 www.elsevier.com/locate/bone Automatic segmentation of cortical and trabecular compartments based on a dual threshold technique for in vivo micro-ct bone analysis Helen R. Buie,
Bone 41 (2007) 505 515 www.elsevier.com/locate/bone Automatic segmentation of cortical and trabecular compartments based on a dual threshold technique for in vivo micro-ct bone analysis Helen R. Buie,
The user's guide. CT-Volume (version 2.0) Contents
 CT-Volume (version 2.0) The user's guide Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Starting CTVol 2 3. Creating 3d models 4 4. Loading a model into CTVol 6 5. Movement and rotation of a model 7 6. CTVol preferences
CT-Volume (version 2.0) The user's guide Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Starting CTVol 2 3. Creating 3d models 4 4. Loading a model into CTVol 6 5. Movement and rotation of a model 7 6. CTVol preferences
A New Quantitative Approach for Measuring Changes of 3D Structures in Trabecular Bone
 A New Quantitative Approach for Measuring Changes of 3D Structures in Trabecular Bone Norbert Marwan Peter Saparin, Jesper S. Thomsen, Jürgen Kurths Nonlinear Dynamics Group University of Potsdam MPI Colloids
A New Quantitative Approach for Measuring Changes of 3D Structures in Trabecular Bone Norbert Marwan Peter Saparin, Jesper S. Thomsen, Jürgen Kurths Nonlinear Dynamics Group University of Potsdam MPI Colloids
microct Systems for Life Science Innovation with Integrity High Resolution Microtomography for in vivo and ex vivo Applications Microtomography
 microct Systems for Life Science High Resolution Microtomography for in vivo and ex vivo Applications Innovation with Integrity Microtomography SkyScan 1278 High Throughput Large Field of View in vivo
microct Systems for Life Science High Resolution Microtomography for in vivo and ex vivo Applications Innovation with Integrity Microtomography SkyScan 1278 High Throughput Large Field of View in vivo
3D registration of micro-ct images for the identification of trabecular fracture region.
 3D registration of micro-ct images for the identification of trabecular fracture region. S. Tassani 1,2, P.A. Asvestas 3, G.K. Matsopoulos 1, and F. Baruffaldi 2 1 Institute of Communication and Computer
3D registration of micro-ct images for the identification of trabecular fracture region. S. Tassani 1,2, P.A. Asvestas 3, G.K. Matsopoulos 1, and F. Baruffaldi 2 1 Institute of Communication and Computer
Arion: a realistic projection simulator for optimizing laboratory and industrial micro-ct
 Arion: a realistic projection simulator for optimizing laboratory and industrial micro-ct J. DHAENE* 1, E. PAUWELS 1, T. DE SCHRYVER 1, A. DE MUYNCK 1, M. DIERICK 1, L. VAN HOOREBEKE 1 1 UGCT Dept. Physics
Arion: a realistic projection simulator for optimizing laboratory and industrial micro-ct J. DHAENE* 1, E. PAUWELS 1, T. DE SCHRYVER 1, A. DE MUYNCK 1, M. DIERICK 1, L. VAN HOOREBEKE 1 1 UGCT Dept. Physics
MEASURING CHANGES OF 3D STRUCTURES IN HIGH-RESOLUTION µct IMAGES OF TRABECULAR BONE
 MEASURING CHANGES OF 3D STRUCTURES IN HIGH-RESOLUTION µct IMAGES OF TRABECULAR BONE Norbert Marwan, Jürgen Kurths Nonlinear Dynamics Group, Institute of Physics, University of Potsdam, 14415 Potsdam, Germany
MEASURING CHANGES OF 3D STRUCTURES IN HIGH-RESOLUTION µct IMAGES OF TRABECULAR BONE Norbert Marwan, Jürgen Kurths Nonlinear Dynamics Group, Institute of Physics, University of Potsdam, 14415 Potsdam, Germany
Advanced Computed Tomography System for the Inspection of Large Aluminium Car Bodies
 ECNDT 2006 - Th.3.4.2 Advanced Computed Tomography System for the Inspection of Large Aluminium Car Bodies M. SIMON, I. TISEANU, C. SAUERWEIN Hans WÄLISCHMILLER, Meersburg, Germany M. SINDEL, M. BRODMANN,
ECNDT 2006 - Th.3.4.2 Advanced Computed Tomography System for the Inspection of Large Aluminium Car Bodies M. SIMON, I. TISEANU, C. SAUERWEIN Hans WÄLISCHMILLER, Meersburg, Germany M. SINDEL, M. BRODMANN,
A New Quantitative Approach for Measuring Changes of 3D Structures in Trabecular Bone
 A New Quantitative Approach for Measuring Changes of 3D Structures in Trabecular Bone Norbert Marwan Peter Saparin, Jesper S. Thomsen, Jürgen Kurths Nonlinear Dynamics Group University of Potsdam MPI Colloids
A New Quantitative Approach for Measuring Changes of 3D Structures in Trabecular Bone Norbert Marwan Peter Saparin, Jesper S. Thomsen, Jürgen Kurths Nonlinear Dynamics Group University of Potsdam MPI Colloids
How does the ROI affect the thresholding?
 How does the ROI affect the thresholding? Micro-computed tomography can be applied for the visualization of the inner structure of a material or biological tissue in a non-destructive manner. Besides visualization,
How does the ROI affect the thresholding? Micro-computed tomography can be applied for the visualization of the inner structure of a material or biological tissue in a non-destructive manner. Besides visualization,
Identifying microcracks in multi-phase crystalline rocks by X-ray CT
 Identifying microcracks in multi-phase crystalline rocks by X-ray CT Julia Behnsen 1, Oshaine O. Blake 2, Robert J. Cernik 1, Philip J. Withers 1 1 Henry Moseley X-ray Imaging Facility, Materials Science
Identifying microcracks in multi-phase crystalline rocks by X-ray CT Julia Behnsen 1, Oshaine O. Blake 2, Robert J. Cernik 1, Philip J. Withers 1 1 Henry Moseley X-ray Imaging Facility, Materials Science
Conference Biomedical Engineering
 Automatic Medical Image Analysis for Measuring Bone Thickness and Density M. Kovalovs *, A. Glazs Image Processing and Computer Graphics Department, Riga Technical University, Latvia * E-mail: mihails.kovalovs@rtu.lv
Automatic Medical Image Analysis for Measuring Bone Thickness and Density M. Kovalovs *, A. Glazs Image Processing and Computer Graphics Department, Riga Technical University, Latvia * E-mail: mihails.kovalovs@rtu.lv
Radiology. Marta Anguiano Millán. Departamento de Física Atómica, Molecular y Nuclear Facultad de Ciencias. Universidad de Granada
 Departamento de Física Atómica, Molecular y Nuclear Facultad de Ciencias. Universidad de Granada Overview Introduction Overview Introduction Tecniques of imaging in Overview Introduction Tecniques of imaging
Departamento de Física Atómica, Molecular y Nuclear Facultad de Ciencias. Universidad de Granada Overview Introduction Overview Introduction Tecniques of imaging in Overview Introduction Tecniques of imaging
MULTI-PURPOSE 3D COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM
 MULTI-PURPOSE 3D COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM M. Simon, C. Sauerwein, I. Tiseanu, S. Burdairon Hans Wälischmiller GmbH Klingleweg 8, D-88709 Meersburg, Germany e-mail: ms@hwm.com ABSTRACT A new flexible
MULTI-PURPOSE 3D COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM M. Simon, C. Sauerwein, I. Tiseanu, S. Burdairon Hans Wälischmiller GmbH Klingleweg 8, D-88709 Meersburg, Germany e-mail: ms@hwm.com ABSTRACT A new flexible
A closer look at CT scanning
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A closer look at CT scanning Author : Charissa Lee, Natalie Webster Categories : General, Vets Date : April 3, 2017 A basic
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A closer look at CT scanning Author : Charissa Lee, Natalie Webster Categories : General, Vets Date : April 3, 2017 A basic
Thresholding technique for accurate analysis of density and geometry in QCT, pqct and ÌCT images
 J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2007; 7(1):9-16 2 nd International Conference on Osteoporosis and Bone Research, October 19-23, 2005 Hylonome Thresholding technique for accurate analysis of density and
J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2007; 7(1):9-16 2 nd International Conference on Osteoporosis and Bone Research, October 19-23, 2005 Hylonome Thresholding technique for accurate analysis of density and
CT Reconstruction with Good-Orientation and Layer Separation for Multilayer Objects
 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China CT Reconstruction with Good-Orientation and Layer Separation for Multilayer Objects Tong LIU 1, Brian Stephan WONG 2, Tai
17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China CT Reconstruction with Good-Orientation and Layer Separation for Multilayer Objects Tong LIU 1, Brian Stephan WONG 2, Tai
Bone Histomorphometry: Basic Concepts and Theory
 Bone Histomorphometry: Basic Concepts and Theory Chris Jerome Inc., Langley, WA USA Modified from an original presentation given at: 29th International Sun Valley Hard Tissue Workshop August 9-13, 1999
Bone Histomorphometry: Basic Concepts and Theory Chris Jerome Inc., Langley, WA USA Modified from an original presentation given at: 29th International Sun Valley Hard Tissue Workshop August 9-13, 1999
ML reconstruction for CT
 ML reconstruction for CT derivation of MLTR rigid motion correction resolution modeling polychromatic ML model dual energy ML model Bruno De Man, Katrien Van Slambrouck, Maarten Depypere, Frederik Maes,
ML reconstruction for CT derivation of MLTR rigid motion correction resolution modeling polychromatic ML model dual energy ML model Bruno De Man, Katrien Van Slambrouck, Maarten Depypere, Frederik Maes,
Network Analysis of Grain Bulk Pore Structure Using High Resolution X-ray Computed Tomography Images
 The Canadian Society for Bioengineering The Canadian society for engineering in agricultural, food, environmental, and biological systems. La Société Canadienne de Génie Agroalimentaire et de Bioingénierie
The Canadian Society for Bioengineering The Canadian society for engineering in agricultural, food, environmental, and biological systems. La Société Canadienne de Génie Agroalimentaire et de Bioingénierie
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing SPECIAL TOPICS CT IMAGES Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 What is an image? 2 Are images only about visual concepts? We ve already seen that there are other kinds of image. In this lecture
Digital Image Processing SPECIAL TOPICS CT IMAGES Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 What is an image? 2 Are images only about visual concepts? We ve already seen that there are other kinds of image. In this lecture
Scaling Calibration in the ATRACT Algorithm
 Scaling Calibration in the ATRACT Algorithm Yan Xia 1, Andreas Maier 1, Frank Dennerlein 2, Hannes G. Hofmann 1, Joachim Hornegger 1,3 1 Pattern Recognition Lab (LME), Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg,
Scaling Calibration in the ATRACT Algorithm Yan Xia 1, Andreas Maier 1, Frank Dennerlein 2, Hannes G. Hofmann 1, Joachim Hornegger 1,3 1 Pattern Recognition Lab (LME), Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg,
FP CILIA. Customized Intelligent Life-Inspired Arrays. Integrated Project
 FP6-016039 CILIA Customized Intelligent Life-Inspired Arrays Integrated Project Information Society Technolgies Future & Emerging Technologies Proactive Initiative BIO-I3 DELIVERABLE: D1.1.2 - Public M
FP6-016039 CILIA Customized Intelligent Life-Inspired Arrays Integrated Project Information Society Technolgies Future & Emerging Technologies Proactive Initiative BIO-I3 DELIVERABLE: D1.1.2 - Public M
Developments in Dimensional Metrology in X-ray Computed Tomography at NPL
 Developments in Dimensional Metrology in X-ray Computed Tomography at NPL Wenjuan Sun and Stephen Brown 10 th May 2016 1 Possible factors influencing XCT measurements Components Influencing variables Possible
Developments in Dimensional Metrology in X-ray Computed Tomography at NPL Wenjuan Sun and Stephen Brown 10 th May 2016 1 Possible factors influencing XCT measurements Components Influencing variables Possible
Non-Stationary CT Image Noise Spectrum Analysis
 Non-Stationary CT Image Noise Spectrum Analysis Michael Balda, Björn J. Heismann,, Joachim Hornegger Pattern Recognition Lab, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen michael.balda@informatik.uni-erlangen.de
Non-Stationary CT Image Noise Spectrum Analysis Michael Balda, Björn J. Heismann,, Joachim Hornegger Pattern Recognition Lab, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen michael.balda@informatik.uni-erlangen.de
Efficient 3D Crease Point Extraction from 2D Crease Pixels of Sinogram
 Efficient 3D Crease Point Extraction from 2D Crease Pixels of Sinogram Ryo Jinnouchi 1, Yutaka Ohtake 1, Hiromasa Suzuki 1, Yukie Nagai 1 1 The University of Tokyo, Japan, e-mail: {jinnouchi, yu-ohtake,
Efficient 3D Crease Point Extraction from 2D Crease Pixels of Sinogram Ryo Jinnouchi 1, Yutaka Ohtake 1, Hiromasa Suzuki 1, Yukie Nagai 1 1 The University of Tokyo, Japan, e-mail: {jinnouchi, yu-ohtake,
Computed tomography (Item No.: P )
 Computed tomography (Item No.: P2550100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Biology Education Level: University Topic: Modern Imaging Methods Subtopic: X-ray Imaging Experiment: Computed tomography
Computed tomography (Item No.: P2550100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Biology Education Level: University Topic: Modern Imaging Methods Subtopic: X-ray Imaging Experiment: Computed tomography
An Improved Tracking Technique for Assessment of High Resolution Dynamic Radiography Kinematics
 Copyright c 2008 ICCES ICCES, vol.8, no.2, pp.41-46 An Improved Tracking Technique for Assessment of High Resolution Dynamic Radiography Kinematics G. Papaioannou 1, C. Mitrogiannis 1 and G. Nianios 1
Copyright c 2008 ICCES ICCES, vol.8, no.2, pp.41-46 An Improved Tracking Technique for Assessment of High Resolution Dynamic Radiography Kinematics G. Papaioannou 1, C. Mitrogiannis 1 and G. Nianios 1
Trabeculae Analysis Protocol for BioQuant OSTEO 2010
 Chang 7/26/2010 Trabeculae Analysis Protocol for BioQuant OSTEO 2010 Novack s lab General Info (READ FIRST) This protocol only covers a few features in the BioQuant, which are the histomorphometry analysis
Chang 7/26/2010 Trabeculae Analysis Protocol for BioQuant OSTEO 2010 Novack s lab General Info (READ FIRST) This protocol only covers a few features in the BioQuant, which are the histomorphometry analysis
LABORATORY SYSTEM FOR X-RAY NANOTOMOGRAPHY
 79 LABORATORY SYSTEM FOR X-RAY NANOTOMOGRAPHY Alexander Sasov, SkyScan, Vluchtenburgstraat 3, Aartselaar B2630, Belgium, www.skyscan.be. ABSTRACT Using advanced X-ray technologies and X-ray scattering
79 LABORATORY SYSTEM FOR X-RAY NANOTOMOGRAPHY Alexander Sasov, SkyScan, Vluchtenburgstraat 3, Aartselaar B2630, Belgium, www.skyscan.be. ABSTRACT Using advanced X-ray technologies and X-ray scattering
Empirical cupping correction: A first-order raw data precorrection for cone-beam computed tomography
 Empirical cupping correction: A first-order raw data precorrection for cone-beam computed tomography Marc Kachelrieß, a Katia Sourbelle, and Willi A. Kalender Institute of Medical Physics, University of
Empirical cupping correction: A first-order raw data precorrection for cone-beam computed tomography Marc Kachelrieß, a Katia Sourbelle, and Willi A. Kalender Institute of Medical Physics, University of
Introduction to Biomedical Imaging
 Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu X-ray Projection Imaging Computed Tomography Digital X-ray
Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu X-ray Projection Imaging Computed Tomography Digital X-ray
2D Fan Beam Reconstruction 3D Cone Beam Reconstruction
 2D Fan Beam Reconstruction 3D Cone Beam Reconstruction Mario Koerner March 17, 2006 1 2D Fan Beam Reconstruction Two-dimensional objects can be reconstructed from projections that were acquired using parallel
2D Fan Beam Reconstruction 3D Cone Beam Reconstruction Mario Koerner March 17, 2006 1 2D Fan Beam Reconstruction Two-dimensional objects can be reconstructed from projections that were acquired using parallel
Advanced Reconstruction Techniques Applied to an On-Site CT System
 2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2010 - We.1.A.4 Advanced Reconstruction Techniques Applied to an On-Site CT System Jonathan HESS, Markus EBERHORN, Markus HOFMANN, Maik LUXA Fraunhofer Development
2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2010 - We.1.A.4 Advanced Reconstruction Techniques Applied to an On-Site CT System Jonathan HESS, Markus EBERHORN, Markus HOFMANN, Maik LUXA Fraunhofer Development
3/27/2012 WHY SPECT / CT? SPECT / CT Basic Principles. Advantages of SPECT. Advantages of CT. Dr John C. Dickson, Principal Physicist UCLH
 3/27/212 Advantages of SPECT SPECT / CT Basic Principles Dr John C. Dickson, Principal Physicist UCLH Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College London Hospitals and University College London john.dickson@uclh.nhs.uk
3/27/212 Advantages of SPECT SPECT / CT Basic Principles Dr John C. Dickson, Principal Physicist UCLH Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College London Hospitals and University College London john.dickson@uclh.nhs.uk
X-ray MicroCT in Conjunction with Other Techniques for Core Analysis
 X-ray MicroCT in Conjunction with Other Techniques for Core Analysis I.V. Yakimchuk 1, A.S. Denisenko 1, B.D. Sharchilev 1, and I.A. Varfolomeev 1,2 1 Schlumberger, 119285, 13 Pudovkina str., Moscow, Russia,
X-ray MicroCT in Conjunction with Other Techniques for Core Analysis I.V. Yakimchuk 1, A.S. Denisenko 1, B.D. Sharchilev 1, and I.A. Varfolomeev 1,2 1 Schlumberger, 119285, 13 Pudovkina str., Moscow, Russia,
J. Ling Chinese Academy of Science Institute for Ceramics Shanghai, China
 DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION OF LOCAL 3-D CT RECONSTRUCTION SOFTWARE FOR IMAGING CRITICAL REGIONS IN LARGE CERAMIC TURBINE ROTORS E. A. Sivers, D. L. Holloway, and W. A. Ellingson Argonne National Laboratory
DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION OF LOCAL 3-D CT RECONSTRUCTION SOFTWARE FOR IMAGING CRITICAL REGIONS IN LARGE CERAMIC TURBINE ROTORS E. A. Sivers, D. L. Holloway, and W. A. Ellingson Argonne National Laboratory
Computed Tomography & 3D Metrology Application of the VDI/VDE Directive 2630 and Optimization of the CT system
 Computed Tomography & 3D Metrology Application of the VDI/VDE Directive 2630 and Optimization of the CT system ECNDT 2014 Prague October 6-10, 2014 Dr. Eberhard Neuser Dr. Alexander Suppes Imagination
Computed Tomography & 3D Metrology Application of the VDI/VDE Directive 2630 and Optimization of the CT system ECNDT 2014 Prague October 6-10, 2014 Dr. Eberhard Neuser Dr. Alexander Suppes Imagination
CLASS HOURS: 4 CREDIT HOURS: 4 LABORATORY HOURS: 0
 Revised 10/10 COURSE SYLLABUS TM 220 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PHYSICS CLASS HOURS: 4 CREDIT HOURS: 4 LABORATORY HOURS: 0 CATALOG COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is one of a three course set in whole body Computed
Revised 10/10 COURSE SYLLABUS TM 220 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PHYSICS CLASS HOURS: 4 CREDIT HOURS: 4 LABORATORY HOURS: 0 CATALOG COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is one of a three course set in whole body Computed
A Study of Medical Image Analysis System
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
Thickness Measurement of Metal Plate Using CT Projection Images and Nominal Shape
 Thickness Measurement of Metal Plate Using CT Projection Images and Nominal Shape Tasuku Ito 1, Yutaka Ohtake 1, Yukie Nagai 2, Hiromasa Suzuki 1 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=23662
Thickness Measurement of Metal Plate Using CT Projection Images and Nominal Shape Tasuku Ito 1, Yutaka Ohtake 1, Yukie Nagai 2, Hiromasa Suzuki 1 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=23662
CT vs. VolumeScope: image quality and dose comparison
 CT vs. VolumeScope: image quality and dose comparison V.N. Vasiliev *a, A.F. Gamaliy **b, M.Yu. Zaytsev b, K.V. Zaytseva ***b a Russian Sci. Center of Roentgenology & Radiology, 86, Profsoyuznaya, Moscow,
CT vs. VolumeScope: image quality and dose comparison V.N. Vasiliev *a, A.F. Gamaliy **b, M.Yu. Zaytsev b, K.V. Zaytseva ***b a Russian Sci. Center of Roentgenology & Radiology, 86, Profsoyuznaya, Moscow,
Computed tomography of simple objects. Related topics. Principle. Equipment TEP Beam hardening, artefacts, and algorithms
 Related topics Beam hardening, artefacts, and algorithms Principle The CT principle is demonstrated with the aid of simple objects. In the case of very simple targets, only a few images need to be taken
Related topics Beam hardening, artefacts, and algorithms Principle The CT principle is demonstrated with the aid of simple objects. In the case of very simple targets, only a few images need to be taken
Micro-CT Methodology Hasan Alsaid, PhD
 Micro-CT Methodology Hasan Alsaid, PhD Preclinical & Translational Imaging LAS, PTS, GlaxoSmithKline 20 April 2015 Provide basic understanding of technical aspects of the micro-ct Statement: All procedures
Micro-CT Methodology Hasan Alsaid, PhD Preclinical & Translational Imaging LAS, PTS, GlaxoSmithKline 20 April 2015 Provide basic understanding of technical aspects of the micro-ct Statement: All procedures
TEP Hounsfield units. Related topics Attenuation coefficient, Hounsfield units
 Hounsfield units TEP Related topics Attenuation coefficient, Hounsfield units Principle Depending on the type of CT scanner and the settings, the result of a CT scan of the same material can be different
Hounsfield units TEP Related topics Attenuation coefficient, Hounsfield units Principle Depending on the type of CT scanner and the settings, the result of a CT scan of the same material can be different
Digital Laminography and Computed Tomography with 600 kv for Aerospace Applications
 4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2012 - Tu.3.A.1 Digital Laminography and Computed Tomography with 600 kv for Aerospace Applications Malte KURFISS 1, Gerd STRECKENBACH 2 1 YXLON International
4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2012 - Tu.3.A.1 Digital Laminography and Computed Tomography with 600 kv for Aerospace Applications Malte KURFISS 1, Gerd STRECKENBACH 2 1 YXLON International
Modelling a Lamb Hind Leg
 Modelling a Lamb Hind Leg Joanne P. Crocombe Ross D. Clarke MIRINZ Food Technology & Research East Street (Ruakura Campus), PO Box 617 HAMILTON, NEW ZEALAND Andrew J. Pullan Department of Engineering Science
Modelling a Lamb Hind Leg Joanne P. Crocombe Ross D. Clarke MIRINZ Food Technology & Research East Street (Ruakura Campus), PO Box 617 HAMILTON, NEW ZEALAND Andrew J. Pullan Department of Engineering Science
SIMULATION OF BONE AGING AND VIRTUAL REALITY VISUALIZATION OF CANCELLOUS BONE STRUCTURE
 SIMULATION OF BONE AGING AND IRTUAL REALITY ISUALIZATION OF CANCELLOUS BONE STRUCTURE Ajay. Sonar, Ph.D. Candidate; James J. Carroll *, Ph.D., Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer
SIMULATION OF BONE AGING AND IRTUAL REALITY ISUALIZATION OF CANCELLOUS BONE STRUCTURE Ajay. Sonar, Ph.D. Candidate; James J. Carroll *, Ph.D., Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer
Spiral CT. Protocol Optimization & Quality Assurance. Ge Wang, Ph.D. Department of Radiology University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa 52242, USA
 Spiral CT Protocol Optimization & Quality Assurance Ge Wang, Ph.D. Department of Radiology University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa 52242, USA Spiral CT Protocol Optimization & Quality Assurance Protocol optimization
Spiral CT Protocol Optimization & Quality Assurance Ge Wang, Ph.D. Department of Radiology University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa 52242, USA Spiral CT Protocol Optimization & Quality Assurance Protocol optimization
Calculating the Distance Map for Binary Sampled Data
 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Calculating the Distance Map for Binary Sampled Data Sarah F. Frisken Gibson TR99-6 December 999 Abstract High quality rendering and physics-based
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Calculating the Distance Map for Binary Sampled Data Sarah F. Frisken Gibson TR99-6 December 999 Abstract High quality rendering and physics-based
18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, April 2012, Durban, South Africa
 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa TOWARDS ESTABLISHMENT OF STANDARDIZED PRACTICE FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPATIAL RESOLUTION AND CONTRAST OF INTERNATIONAL
18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa TOWARDS ESTABLISHMENT OF STANDARDIZED PRACTICE FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPATIAL RESOLUTION AND CONTRAST OF INTERNATIONAL
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook X-Ray Computed Tomography in Biomedical Engineering, by Robert Cierniak, Springer, 211 Computed Tomography
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook X-Ray Computed Tomography in Biomedical Engineering, by Robert Cierniak, Springer, 211 Computed Tomography
Wieblinger Weg 92a, Heidelberg, Germany, Phone: , Fax: ;
 HOW INDUSTRIAL COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY ACCELERATES PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IN THE LIGHT METAL CASTING AND INJECTION MOULDING INDUSTRY. Christof REINHART 1, Christoph POLIWODA 1, Thomas GÜNTHER 1 1 Volume Graphics
HOW INDUSTRIAL COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY ACCELERATES PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IN THE LIGHT METAL CASTING AND INJECTION MOULDING INDUSTRY. Christof REINHART 1, Christoph POLIWODA 1, Thomas GÜNTHER 1 1 Volume Graphics
DEVELOPMENT OF CONE BEAM TOMOGRAPHIC RECONSTRUCTION SOFTWARE MODULE
 Rajesh et al. : Proceedings of the National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation DEVELOPMENT OF CONE BEAM TOMOGRAPHIC RECONSTRUCTION SOFTWARE MODULE Rajesh V Acharya, Umesh Kumar, Gursharan
Rajesh et al. : Proceedings of the National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation DEVELOPMENT OF CONE BEAM TOMOGRAPHIC RECONSTRUCTION SOFTWARE MODULE Rajesh V Acharya, Umesh Kumar, Gursharan
Three dimensional visualisation and morphometry of bone samples studied in microcomputed tomography (micro-ct)
 O R I G I N L R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 73, No. 4, pp. 422 428 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2014.0064 Copyright 2014 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Three dimensional visualisation and morphometry
O R I G I N L R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 73, No. 4, pp. 422 428 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2014.0064 Copyright 2014 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Three dimensional visualisation and morphometry
SUPPLEMENTARY FILE S1: 3D AIRWAY TUBE RECONSTRUCTION AND CELL-BASED MECHANICAL MODEL. RELATED TO FIGURE 1, FIGURE 7, AND STAR METHODS.
 SUPPLEMENTARY FILE S1: 3D AIRWAY TUBE RECONSTRUCTION AND CELL-BASED MECHANICAL MODEL. RELATED TO FIGURE 1, FIGURE 7, AND STAR METHODS. 1. 3D AIRWAY TUBE RECONSTRUCTION. RELATED TO FIGURE 1 AND STAR METHODS
SUPPLEMENTARY FILE S1: 3D AIRWAY TUBE RECONSTRUCTION AND CELL-BASED MECHANICAL MODEL. RELATED TO FIGURE 1, FIGURE 7, AND STAR METHODS. 1. 3D AIRWAY TUBE RECONSTRUCTION. RELATED TO FIGURE 1 AND STAR METHODS
Traceable 3D X-Ray Measurements ZEISS METROTOM
 20 Traceable 3D X-Ray Measurements With a computer tomograph, you can successfully perform measuring and inspection jobs yourself with only one X-ray scan. The standard acceptance test, the precision engineering
20 Traceable 3D X-Ray Measurements With a computer tomograph, you can successfully perform measuring and inspection jobs yourself with only one X-ray scan. The standard acceptance test, the precision engineering
Quality control phantoms and protocol for a tomography system
 Quality control phantoms and protocol for a tomography system Lucía Franco 1 1 CT AIMEN, C/Relva 27A O Porriño Pontevedra, Spain, lfranco@aimen.es Abstract Tomography systems for non-destructive testing
Quality control phantoms and protocol for a tomography system Lucía Franco 1 1 CT AIMEN, C/Relva 27A O Porriño Pontevedra, Spain, lfranco@aimen.es Abstract Tomography systems for non-destructive testing
Characterization of Powder Injection Molded Components Using X-Ray CT. David P. Harding, Zhigang Zak Fang, C.L. Lin, Jan D. Miller
 Characterization of Powder Injection Molded Components Using X-Ray CT David P. Harding, Zhigang Zak Fang, C.L. Lin, Jan D. Miller Department of Metallurgical Engineering University of Utah 135 South 1450
Characterization of Powder Injection Molded Components Using X-Ray CT David P. Harding, Zhigang Zak Fang, C.L. Lin, Jan D. Miller Department of Metallurgical Engineering University of Utah 135 South 1450
Microgravity Application Program / Biotechnology. Mid Term Report for ESA-Project ESTEC Contract # 14592/00/NL/SH MAP AO , CCN 001, CCN 002
 Microgravity Application Program / Biotechnology Mid Term Report for ESA-Project ESTEC Contract # 14592/00/NL/SH MAP AO-99-030, CCN 001, CCN 002 2D and 3D Quantification of Bone Structure and its Changes
Microgravity Application Program / Biotechnology Mid Term Report for ESA-Project ESTEC Contract # 14592/00/NL/SH MAP AO-99-030, CCN 001, CCN 002 2D and 3D Quantification of Bone Structure and its Changes
Feldkamp-type image reconstruction from equiangular data
 Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology 9 (2001) 113 120 113 IOS Press Feldkamp-type image reconstruction from equiangular data Ben Wang a, Hong Liu b, Shiying Zhao c and Ge Wang d a Department of Elec.
Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology 9 (2001) 113 120 113 IOS Press Feldkamp-type image reconstruction from equiangular data Ben Wang a, Hong Liu b, Shiying Zhao c and Ge Wang d a Department of Elec.
An Iterative Approach to the Beam Hardening Correction in Cone Beam CT (Proceedings)
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Biomedical Engineering Faculty Research and Publications Engineering, College of 1-1-1999 An Iterative Approach to the Beam Hardening Correction in Cone Beam
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Biomedical Engineering Faculty Research and Publications Engineering, College of 1-1-1999 An Iterative Approach to the Beam Hardening Correction in Cone Beam
An Acquisition Geometry-Independent Calibration Tool for Industrial Computed Tomography
 4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2012 - Tu.3.A.3 An Acquisition Geometry-Independent Calibration Tool for Industrial Computed Tomography Jonathan HESS *, Patrick KUEHNLEIN *, Steven OECKL
4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2012 - Tu.3.A.3 An Acquisition Geometry-Independent Calibration Tool for Industrial Computed Tomography Jonathan HESS *, Patrick KUEHNLEIN *, Steven OECKL
Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings
 Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings 김보형 서울대학교컴퓨터공학부 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Lab. 2011. 3. 23 1 Computer Graphics & Image Processing Computer Graphics : Create,
Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings 김보형 서울대학교컴퓨터공학부 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Lab. 2011. 3. 23 1 Computer Graphics & Image Processing Computer Graphics : Create,
Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography
 Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography Mark A. Anastasio, Kun Wang, and Robert Schoonover Department of Biomedical Engineering Washington University in St. Louis 1 Outline Photoacoustic/thermoacoustic
Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography Mark A. Anastasio, Kun Wang, and Robert Schoonover Department of Biomedical Engineering Washington University in St. Louis 1 Outline Photoacoustic/thermoacoustic
Evaluation of tomographic reconstruction methods for small animal microct and micropet/ct
 Evaluation of tomographic reconstruction methods for small animal microct and micropet/ct S. Valton, F. Peyrin, P. Delpierre, F. Debarbieux, A. Bonissent, R. Khoury, C. Meessen, C. Morel, D. Sappey-Marinier
Evaluation of tomographic reconstruction methods for small animal microct and micropet/ct S. Valton, F. Peyrin, P. Delpierre, F. Debarbieux, A. Bonissent, R. Khoury, C. Meessen, C. Morel, D. Sappey-Marinier
Comparison of Probing Error in Dimensional Measurement by Means of 3D Computed Tomography with Circular and Helical Sampling
 nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace - We..A. Comparison of Probing Error in Dimensional Measurement by Means of D Computed Tomography with Circular and Helical Sampling Jochen HILLER, Stefan
nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace - We..A. Comparison of Probing Error in Dimensional Measurement by Means of D Computed Tomography with Circular and Helical Sampling Jochen HILLER, Stefan
Parameter Dependent Thresholding for Dimensional X-ray Computed Tomography
 International Symposium on Digital Industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography - Poster 12 Parameter Dependent Thresholding for Dimensional X-ray Computed Tomography Kim KIEKENS *, Ye TAN *, Jean-Pierre
International Symposium on Digital Industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography - Poster 12 Parameter Dependent Thresholding for Dimensional X-ray Computed Tomography Kim KIEKENS *, Ye TAN *, Jean-Pierre
Case Studies in the Use of Computed Tomography for Non-Destructive Testing, Inspection and Measurement
 SINCE2013 Singapore International NDT Conference & Exhibition 2013, 19-20 July 2013 Case Studies in the Use of Computed Tomography for Non-Destructive Testing, Inspection and Measurement Andrew A. MALCOLM,
SINCE2013 Singapore International NDT Conference & Exhibition 2013, 19-20 July 2013 Case Studies in the Use of Computed Tomography for Non-Destructive Testing, Inspection and Measurement Andrew A. MALCOLM,
VXRE Reconstruction Software Manual
 VXRE Reconstruction Software Manual Version 1.7.8 3D INDUSTRIAL IMAGING 3D Industrial Imaging Co.,Ltd. Address :#413 Institute of Computer Technology, Seoul National University, Daehak-dong, Gwanak-gu,
VXRE Reconstruction Software Manual Version 1.7.8 3D INDUSTRIAL IMAGING 3D Industrial Imaging Co.,Ltd. Address :#413 Institute of Computer Technology, Seoul National University, Daehak-dong, Gwanak-gu,
Industrial Computed Tomography Innovations
 GE Inspection Technologies Industrial Computed Tomography Innovations Premium performance for premium quality and speed. gemeasurement.com/ct Premium CT technologies. Faster than ever before. Every industrial
GE Inspection Technologies Industrial Computed Tomography Innovations Premium performance for premium quality and speed. gemeasurement.com/ct Premium CT technologies. Faster than ever before. Every industrial
Suitability of a new alignment correction method for industrial CT
 Suitability of a new alignment correction method for industrial CT Matthias Elter 1, Nicole Maass 1, Peter Koch 2 1 Siemens AG, Healthcare Sector, Erlangen, Germany, e-mail: matthias.elter@siemens.com,
Suitability of a new alignment correction method for industrial CT Matthias Elter 1, Nicole Maass 1, Peter Koch 2 1 Siemens AG, Healthcare Sector, Erlangen, Germany, e-mail: matthias.elter@siemens.com,
ND Processing Tools in NIS-Elements
 ND Processing Tools in NIS-Elements Overview This technical note describes basic uses of the ND processing tools available in NIS-Elements. These tools are specifically designed for arithmetic functions
ND Processing Tools in NIS-Elements Overview This technical note describes basic uses of the ND processing tools available in NIS-Elements. These tools are specifically designed for arithmetic functions
Micro-CT in situ study of carbonate rock microstructural evolution for geologic CO2 storage
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 10, 2018 Micro-CT in situ study of carbonate rock microstructural evolution for geologic CO2 storage Zheng, Yi; Yang, Yan; Rogowska, M.; Gundlach, Carsten Published
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 10, 2018 Micro-CT in situ study of carbonate rock microstructural evolution for geologic CO2 storage Zheng, Yi; Yang, Yan; Rogowska, M.; Gundlach, Carsten Published
Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) the new parameter of 2D texture analysis for the evaluation of 3D bone micro architecture status.
 Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) the new parameter of 2D texture analysis for the evaluation of 3D bone micro architecture status. Poster No.: C-1961 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) the new parameter of 2D texture analysis for the evaluation of 3D bone micro architecture status. Poster No.: C-1961 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Frequency-based method to optimize the number of projections for industrial computed tomography
 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18739 Frequency-based method to optimize the number of projections for industrial computed tomography Andrea Buratti 1, Soufian Ben Achour 1, Christopher
More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18739 Frequency-based method to optimize the number of projections for industrial computed tomography Andrea Buratti 1, Soufian Ben Achour 1, Christopher
Improvement of Efficiency and Flexibility in Multi-slice Helical CT
 J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.), 2008, 13(4): 408 412 DOI: 10.1007/s12204-008-0408-x Improvement of Efficiency and Flexibility in Multi-slice Helical CT SUN Wen-wu 1 ( ), CHEN Si-ping 2 ( ), ZHUANG Tian-ge
J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.), 2008, 13(4): 408 412 DOI: 10.1007/s12204-008-0408-x Improvement of Efficiency and Flexibility in Multi-slice Helical CT SUN Wen-wu 1 ( ), CHEN Si-ping 2 ( ), ZHUANG Tian-ge
Multi-spectral (W, Mo, Cu, and Ag) XCT measurements
 Multi-spectral (W, Mo, Cu, and Ag) XCT measurements Marko Katić 1, Damir Markučič 1, Gorana Baršić 1 Faculty of mechanical engineering and naval architecture, Ivana Lucica 5, Zagreb, Croatia, marko.katic@fsb.hr
Multi-spectral (W, Mo, Cu, and Ag) XCT measurements Marko Katić 1, Damir Markučič 1, Gorana Baršić 1 Faculty of mechanical engineering and naval architecture, Ivana Lucica 5, Zagreb, Croatia, marko.katic@fsb.hr
Geometrically accurate 3D FE models from medical scans created to analyse the causes of sports injuries
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 13 (2011) 422 427 5th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Geometrically accurate 3D FE models from medical scans created to
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 13 (2011) 422 427 5th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology (APCST) Geometrically accurate 3D FE models from medical scans created to
45 µm polystyrene bead embedded in scattering tissue phantom. (a,b) raw images under oblique
 Phase gradient microscopy in thick tissue with oblique back-illumination Tim N Ford, Kengyeh K Chu & Jerome Mertz Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of added versus subtracted raw OBM images 45 µm polystyrene
Phase gradient microscopy in thick tissue with oblique back-illumination Tim N Ford, Kengyeh K Chu & Jerome Mertz Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of added versus subtracted raw OBM images 45 µm polystyrene
IDL Tutorial. Working with Images. Copyright 2008 ITT Visual Information Solutions All Rights Reserved
 IDL Tutorial Working with Images Copyright 2008 ITT Visual Information Solutions All Rights Reserved http://www.ittvis.com/ IDL is a registered trademark of ITT Visual Information Solutions for the computer
IDL Tutorial Working with Images Copyright 2008 ITT Visual Information Solutions All Rights Reserved http://www.ittvis.com/ IDL is a registered trademark of ITT Visual Information Solutions for the computer
Reducing the influence of environmental scattering in industrial computed tomography by system optimisation and correction algorithms
 11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16395 Reducing the influence of environmental
11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16395 Reducing the influence of environmental
CIVA Computed Tomography Modeling
 CIVA Computed Tomography Modeling R. FERNANDEZ, EXTENDE, France S. LEGOUPIL, M. COSTIN, D. TISSEUR, A. LEVEQUE, CEA-LIST, France page 1 Summary Context From CIVA RT to CIVA CT Reconstruction Methods Applications
CIVA Computed Tomography Modeling R. FERNANDEZ, EXTENDE, France S. LEGOUPIL, M. COSTIN, D. TISSEUR, A. LEVEQUE, CEA-LIST, France page 1 Summary Context From CIVA RT to CIVA CT Reconstruction Methods Applications
Exploiting Typical Clinical Imaging Constraints for 3D Outer Bone Surface Segmentation
 Exploiting Typical Clinical Imaging Constraints for 3D Outer Bone Surface Segmentation Chris Mack, Vishali Mogallapu, Andrew Willis, Thomas P. Weldon UNC Charlotte, Department of Electrical and Computer
Exploiting Typical Clinical Imaging Constraints for 3D Outer Bone Surface Segmentation Chris Mack, Vishali Mogallapu, Andrew Willis, Thomas P. Weldon UNC Charlotte, Department of Electrical and Computer
High-resolution X-ray CT Inspection of Honeycomb Composites Using Planar Computed Tomography Technology
 2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2010 - We.4.B.4 High-resolution X-ray CT Inspection of Honeycomb Composites Using Planar Computed Tomography Technology Tong LIU, Andrew A. MALCOLM, and
2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2010 - We.4.B.4 High-resolution X-ray CT Inspection of Honeycomb Composites Using Planar Computed Tomography Technology Tong LIU, Andrew A. MALCOLM, and
INTERPRETATION OF CROP CIRCLE PATTERNS
 ERIC INTERPRETATION OF CROP CIRCLE PATTERNS Brian Tunstall Key words: Perfield Abstract Diagrams and images of selected crop circle patterns are interpreted in relation knowledge of design requirements
ERIC INTERPRETATION OF CROP CIRCLE PATTERNS Brian Tunstall Key words: Perfield Abstract Diagrams and images of selected crop circle patterns are interpreted in relation knowledge of design requirements
Freehand Voxel Carving Scanning on a Mobile Device
 Technion Institute of Technology Project in Image Processing and Analysis 234329 Freehand Voxel Carving Scanning on a Mobile Device Author: Student Number: 305950099 Supervisors: Aaron Wetzler, Yaron Honen,
Technion Institute of Technology Project in Image Processing and Analysis 234329 Freehand Voxel Carving Scanning on a Mobile Device Author: Student Number: 305950099 Supervisors: Aaron Wetzler, Yaron Honen,
Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images. Sara Rolfe 10/9/17
 Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images Sara Rolfe 10/9/17 Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images Object surface contours Image difference features Compact representation of feature differences
Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images Sara Rolfe 10/9/17 Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images Object surface contours Image difference features Compact representation of feature differences
