Computer Aided Engineering Lab (MEP72) Manual CAE LAB MANUAL- IV YEAR / VII SEMESTER Prepared by Hemanth Kumar. R Assistant Professor
|
|
|
- Elmer Carson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SRI MANAKULA VINAYAGAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to Pondicherry University) (Accredited by NBA-AICTE, New Delhi ISO 9001:2000 certified Institution & Accredited by NAAC A Grade) MADAGADIPET, PUDUCHERRY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Computer Aided Engineering Lab (MEP72) Manual CAE LAB MANUAL- IV YEAR / VII SEMESTER Prepared by Hemanth Kumar. R Assistant Professor
2 Lab Name: Computer Aided Engineering Lab Lab Code: MEP72 Contents SYLLABUS... i LIST OF EXPERIMENTS... ii CONTENTS... iii Introduction to CATIA... 1 Introduction to ANSYS... 9 Sketcher Workbench Practice D Part Modeling of given Object D Part Modeling of given Object D Modeling of - FLANGE COUPLING D Modeling of - SCREW JACK D Modeling of - PLUMMER BLOCK D Modeling Exercises for Practice Part Design Assembly Design SF & BM diagram of Simply Supported Beam with Point Load SF & BM diagram for Cantilever Beam with end Point Load SF & BM diagram OF Simply Supported Beam with Moment and Point Load Stress analysis of a Plate with a Circular Hole Von Mises Stress of a Bracket Stress distribution of Cast Iron member Heat distribution on a Thin Plate subjected to End Heating ANSYS Exercises for Practice... 45
3 SYLLABUS MEP72 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING LABORATORY ( ) OBJECTIVES To give exposure to students about computer aided design and modeling & analysis softwares. PART A COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN OF MACHINE COMPONENTS Design and drafting of the following components using TK SOLVER/ FORTRAN / C or C++/ Matlab Transmission shafts, Journal bearings, Flange couplings etc. PART-B: I. 3D MODELLING 1) Introduction to 3-D modeling sketcher, part design, assembly and drafting workbenches. 2) Generation of various 3D Models through Protrusion, revolve, shell sweep. 3) Feature based and Boolean based modeling surfaces. 4) Assembly modeling of components having a minimum of six machine elements. [Minimum of two exercises in part modeling and one exercise in assembly] II. FE Analysis: Using any of the general purpose FEA software packages solve for 1) Force and stress analysis in trusses 2) SF and BMD diagrams for different types of beams with different loading and boundary conditions. 3) Stress concentration study on plate with central hole 4) Thermal stress and heat transfer analysis of a simple plate. Note: In university practical examination, students has to answer one question each from Part A and Part B. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof i SMVEC
4 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 3 D MODELLING USING CATIA V-6. INTRODUCTION TO CATIA V D Part Modeling of Object 1 & D Modeling of FLANGE COUPLING 3. 3D Modeling of SCREW JACK 4. 3D Modeling of PLUMMER BLOCK LIST OF EXTRA EXERCISES FOR PRACTICE (CATIA). 1. Sketcher exercises practice 2. 3D Modeling of various 3D Objects 3. 3D Modeling of Knuckle Joint 4. 3D Modeling of Universal Coupling 5. 3D Modeling of Safety Valve ANALYSIS OF SYSTEMS USING ANSYS APDL INTRODUCTION TO ANSYS APDL 1. SF and BMD diagrams for all kinds of beams 2. Stress analysis of beams 3. Plane Stress Analysis on Plate with Central hole 4. Stress analysis of rectangular bracket 5. 1-D heat transfer analysis of a simple plate. LIST OF EXTRA EXERCISES FOR PRACTICE (ANSYS). 1. Wire-frame drawing analysis of a 3D Chair with loads 2. Analysis of Beam with different types of loading conditions. 3. Introduction to Ansys workbench DESGIN OF MACHINE COMPONENTS BY USING C Programming. (CYCLE - II) 1. Transmission shafts, 2. Journal bearings, 3. Flange couplings etc. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof ii SMVEC
5 Lab Name: Computer Aided Design Lab CONTENTS Lab Code: MEP72 Ex.No. Date Experiment Staff s Signature INTRODUCTION TO CATIA INTRODUCTION TO ANSYS CATIA V5 Practice Exercises Sketcher Workbench 1 3D PART MODELING OF GIVEN OBJECT 1 2 3D PART MODELING OF GIVEN OBJECT 2 3 3D MODELING OF - SCREW JACK 4 3D MODELING OF - FLANGE COUPLING 5 3D MODELING OF - PLUMMER BLOCK Practice Exercises Part Design & Assembly Design ANSYS- APDL SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAM OF SIMPLY SUPPORTED BEAM WITH POINT LOAD SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAM FOR CANTILEVER BEAM WITH END POINT LOAD SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAM OF SIMPLY SUPPORTED BEAM WITH MOMENT AND POINT LOAD STRESS ANALYSIS OF A PLATE WITH A CIRCULAR HOLE 10 VON MISES STRESS OF A BRACKET 11 STRESS DISTRIBUTION OF CAST IRON MEMBER 12 HEAT DISTRIBUTION ON A THIN PLATE SUBJECTED TO END HEATING Practice Exercises- ANSYS ADPL R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof iii SMVEC
6 Introduction to CATIA CATIA (Computer Aided Three-dimensional Interactive Application) CATIA is the most powerful multi-platform CAD/CAM/CAE/PLM software package of its kind in the world. Developed by Dassault Systèmes, the largest player in the global CAD market. The owner of Solid Works and the ACIS kernel. CATIA is Solid Works big brother. Handles any conceivable modeling task, such as: o Part modelling o Assembly modelling o Surface modelling o PDM o FEM o Optimization o CAM o Photo rendering o Mechanism simulation o Ergonomic simulation CATIA V5 Documents All files created using CATIA V5 are referred to as documents. The basis of most CATIA V5 documents is the part document. The part document is similar to the *.model file in CATIA V4. Different CATIA V5 Workbenches generate different types of documents (extension types). The following is a list of different workbenches and the extension types: Part Design *.CATPart Sketcher *.CATPart Surface Design *.CATPart Drafting *.CATDrawing Assembly Design *.CATProduct GSA *.CATAnalyis NC *.CATProcess Material *.CATMaterial Shape *.CATShape R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 1 SMVEC
7 CATIA Workbench The Application Tools are where all the Workbenches are made accessible (organized). To access the Application Tools select the Start menu located at the top left of the CATIA V5 Screen (reference Figure 1.4). The Start menu will display the Application Tools. The number of Application Tools depends on the Platform level and license package purchased. The Applications Tools shown in this section represent the P2 Platform and ED2 License package. The below shown figure displays and lists the various toolbars available in a CATIA V5. Start a new CATPart by selecting Start + Part Design (OR) File + New + Part R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 2 SMVEC
8 Toolbars in sketcher A. Profile: Create 2D elements, such as points, lines, arcs, circles and axes. B. Operation: Modify the existing elements, such as chamfer, fillet, trim, and mirror. C. Sketch tools: Provide option commands D. Constraint: Set various dimensional constraints (e.g. length, angle & radius) & geometrical constraints (e.g. coincidence, concentric, horizontal and symmetric) E. Visualization: Simplify the view R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 3 SMVEC
9 Sketcher Procedure 1. Select a plane, a Solid face, or a Planar Surface to Sketch on 2. Access the Sketcher Workbench 3. Select the Polygon icon and draw a sketch as shown and various other draw tools as shown below to draw the required sketch If you want to exit the function click on the Select icon 4. Select the Constraints icon and set dimensions. Can use other icons if necessary. 5. Change Dimensions as shown below 6. Exit the Sketcher Toolbars in part design A. Sketch-Based Features: Create a solid feature from a 2D sketch/profile B. Dress-Up Features: Add fillets/chamfers on the solid edge, add a draft onto the solid faces, Hollow the solid, offset faces R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 4 SMVEC
10 C. Transformation Features: Change the 3D position of the solid, duplicate the solid by mirroring/ patterning, scale up/down the solid D. Surface-Based Features: Split the solid with a surface/plane, adding material onto surfaces E. Reference Elements: Create a point, a line or a plane in the 3D space. F. Boolean Operations not covered in class G. Analysis (Draft analysis) not covered in class Pad & Pocket A. Pad (material added by extruding a sketch) B. Pocket (material removed by extruding a sketch) R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 5 SMVEC
11 Shaft & Groove A. Shaft (material added by rotating a sketch) B. Groove (material removed by rotating a sketch) R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 6 SMVEC
12 Assembly Design A Product stores a collection of components (parts or subproducts). The file extension is.catproduct. The major steps involved in an assembly design are: Add a part into an assembly Fix create constraints between this new part and other parts When the first part is inserted, repeat this operation with the second part Create Holes in the Box to add screws if necessary Assembly Feature Manipulation with respect to the constraints Exploded view Hyperlinks The below shown is list of toolbars (1 to 8) available in an Assembly Workbench R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 7 SMVEC
13 Constraints between components A. Coincidence Constraint (shown in below figure) B. Contact Constraint C. Distance Constraint C. Angle Constraint D. Fix Component (fix a component in space; normally we d fix at least one component) Using the above mentioned constraints and options assembly design of a product is done in CATIA. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 8 SMVEC
14 Introduction to ANSYS ANSYS is a general purpose finite element modeling package for numerically solving a wide variety of mechanical problems. These problems include: static/dynamic structural analysis (both linear and non-linear), heat transfer and fluid problems, as well as acoustic and electro-magnetic problems. In general, a finite element solution may be broken into the following three stages. This is a general guideline that can be used for setting up any finite element analysis. 1. Preprocessing: defining the problem; the major steps in preprocessing are given below: o Define keypoints/lines/areas/volumes o Define element type and material/geometric properties o Mesh lines/areas/volumes as required The amount of detail required will depend on the dimensionality of the analysis (i.e. 1D, 2D, axi-symmetric, 3D). 2. Solution: assigning loads, constraints and solving Here we specify the loads (point or pressure), constraints (translational and rotational) and finally solve the resulting set of equations. 3. Postprocessing: further processing and viewing of the results In this stage one may wish to see: o Lists of nodal displacements o Element forces and moments o Deflection plots o Stress contour diagrams ANSYS Environment The ANSYS Environment for ANSYS 12.0 contains 2 windows: the Main Window and an Output Window. Note that this is somewhat different from the previous version of ANSYS which made use of 6 different windows. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 9 SMVEC
15 1. Main Window Within the Main Window are 5 divisions: a. Utility Menu The Utility Menu contains functions that are available throughout the ANSYS session, such as file controls, selections, graphic controls and parameters. b. Input Line The Input Line shows program prompt messages and allows you to type in commands directly. c. Toolbar The Toolbar contains push buttons that execute commonly used ANSYS commands. More push buttons can be added if desired. d. Main Menu The Main Menu contains the primary ANSYS functions, organized by preprocessor, solution, general postprocessor, design optimizer. It is from this menu that the vast majority of modelling commands are issued. This is where you will note the greatest change between previous versions of ANSYS and version However, while the versions appear different, the menu structure has not changed. e. Graphics Window R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 10 SMVEC
16 The Graphic Window is where graphics are shown and graphical picking can be made. It is here where you will graphically view the model in its various stages of construction and the ensuing results from the analysis. 2. Output Window The Output Window shows text output from the program, such as listing of data etc. It is usually positioned behind the main window and can be put to the front if necessary. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 11 SMVEC
17 Drawings Sketcher Workbench Practice Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.1 Fig.2 R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 12 SMVEC
18 3D Part Modeling of given Object 1 Ex.No: Date: Aim: To draw the design and modeling of given object1 using the CATIA package. Drawing: Toolbars used Profile, Operation, Sketch tools, Constraint, Sketch-Based Features, Dress-Up Features, Transformation Features Software required CATIA V5 package R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 13 SMVEC
19 Procedure 1) Open the software tool CATIA package. 2) Start a new part design by using Start> Mechanical Design > Part Design 3) Create the new file and save it in the directory 4) Draw the 2D sketch of the required 3D object in the required view. 5) Then use the dimensional constraint option to specify the required dimension for the object 6) Then exit sketcher. 7) Use various part modeling features like pad, pocket, hole, edge fillet etc,. to complete the 3D object required 8) Save the diagram in specified directory Result Thus the required drawing was designed and modeled as per the given dimension and verified R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 14 SMVEC
20 3D Part Modeling of given Object 2 Ex.No: Aim: To draw the design and modeling of given object1 using the CATIA package Drawing: Date: Toolbars used Profile, Operation, Sketch tools, Constraint, Sketch-Based Features, Dress-Up Features, Transformation Features Software required CATIA V5 package R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 15 SMVEC
21 Procedure 1) Open the software tool CATIA package. 2) Start a new part design by using Start> Mechanical Design > Part Design 3) Create the new file and save it in the directory 4) Draw the 2D sketch of the required 3D object in the required view. 5) Then use the dimensional constraint option to specify the required dimension for the object 6) Then exit sketcher. 7) Use various part modeling features like pad, pocket, hole, edge fillet etc,. to complete the 3D object required 8) Save the diagram in specified directory Result verified. Thus the required drawing was designed and modeled as per the given dimension and R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 16 SMVEC
22 3D Modeling of - FLANGE COUPLING Ex.No: Date: Aim: To create the models of the components for the FLANGE COUPLING and assemble these components together, as shown below. Save this assembly model as Flange Coupling.asm. By using the CATIA V5 software. Application: This type of coupling is a protective type flanged coupling, the bolt heads and nuts are shielded by a peripheral protrusion, called shroud, on each flange is shown in fig.5. Alignment of the two shafts is independent of the bolts and is ensured by the provision of a turned projection, called spigot, on the flat face of the one of the flanges which fits into a corresponding recess, called socket, in the other flange. The length of the spigot projection is kept slightly less than the depth of the socket. The socket and spigot are turned to give a push fit for accurate alignment of the two shafts. The bolt holes are drilled and reamed to give a close running for the bolts in order that the load is taken smoothly without any impact. Description: Each of the flanged bosses is securely keyed to the end of each shaft using a tapered key driven from inside. While assembling, generally the two flanges are set such that the keys fitted in them are out of alignment by 90degrees to each other. The two flanges are bolted together by a number of bolts and nuts. Power is transmitted from one other through bolts. Toolbars used Profile, Operation, Sketch tools, Constraint, Sketch-Based Features, Dress-Up Features, Transformation Features Product Structure Constraints between components Procedure 1) Open the software tool CATIA package. 2) Prepare various parts required for the given FLANGE COUPLING before assembling them by using Start> Mechanical Design > Part Design and save them as individual parts 3) Start a new assembly design by using Start> Mechanical Design > Assembly Design 4) Create the new file and save it in the directory 5) Add a part created into an assembly using Existing component option 6) Fix create constraints between this new part and other parts 7) When the first part is inserted, repeat this operation with the second part and other parts until the required assembled component is achieved 8) Save the diagram in specified directory R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 17 SMVEC
23 Drawing: Result Thus the required drawing was designed, modeled and assembled as per the dimension and verified for the given FLANGE COUPLING. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 18 SMVEC
24 3D Modeling of - SCREW JACK Ex.No: Date: Aim: To create the models of the components for the SCREW JACK and assemble these components together, as shown below. Save this assembly model as Screw jack.asm. By using the CATIA V5 software. Applications: A screw jack, manually operated, is a contrivance to lift heavy objects over a smaller height with a distinct mechanical advantage. It also serves as a supporting aid in the raised position. A screw jack is actuated by a square threaded screw worked by applying a moderate effort at the end of a tommy bar inserted into the hole of the head of the screw. Description: A screw jack is shown in fig.1. Its parts are shown in Fig.2. The body Part No. 1 has an enhanced circular base which provides a large bearing area. A gun metal nut- Part No 2 is tight fitted into the body at the top. A screw spindle Part No.3 is screwed through the nut. A load bearing cup Part No.4 is mounted at the top of the screw spindle and secured to it by a washer- part No.5 and a CSK screw PART No.6 When the screw spindle is rotated, the load bearing cup moves only up or down along with the screw spindle but will not rotate with it. The tommy bar Part No.7 is inserted into the hole in the head of the screw-spindle only during working and will be detached when not in use. Toolbars used Profile, Operation, Sketch tools, Constraint, Sketch-Based Features, Dress-Up Features, Transformation Features Product Structure Constraints between components Procedure 1) Open the software tool CATIA package. 2) Prepare various parts required for the given SCREW JACK before assembling them by using Start> Mechanical Design > Part Design and save them as individual parts 3) Start a new assembly design by using Start> Mechanical Design > Assembly Design 4) Create the new file and save it in the directory 5) Add a part into an assembly using Existing component option 6) Fix create constraints between this new part and other parts 7) When the first part is inserted, repeat this operation with the second part until the required assembled component is achieved 8) Save the diagram in specified directory R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 19 SMVEC
25 Drawing: Result Thus the required drawing was designed, modeled and assembled as per the dimension and verified for the given SCREW JACK. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 20 SMVEC
26 3D Modeling of - PLUMMER BLOCK Ex.No: Date: Aim: To create the models of the components for the PLUMMER BLOCK and assemble these components together, as shown below. Save this assembly model as Plummer Block.asm. By using the CATIA V5software. Application: When a long shaft is to supported at intermediate points, bushed bearings are not used due to thei limitations, In such cases plummer blocks are used. In the plummer block bearing, the body is split horizontally along or near the axis of the shaft. This will enable to overcome the disadvantage of the bushed bearings. Description: It consists of a pedestal called body Part No.1, a cap Part No.2 two split bushes Part No.3 and Part No.4, two square headed bolts Part No.5, and hexagonal nuts Part No. 6 and Part No.7. The body made of cast iron, is provided with two bolts holes in the base plate for bolting down the bearing in position. These bolt holes will be rectangular with semicircular ends to enable the alignment of the bearing to the shaft while bolting. The bottom of the body is relieved leaving a narrow machined strip all round. This relief at the bottom requires the machining of only the narrow strip all around instead after entire bottom surface and also reduces the extent of the preparation and leveling of the bearing are relatively. Another set of two long bolt holes with square recess as their bottom ends are provided in the body. Two long square head blots - Part No.5 are introduced in these bolt holes such that their square heads are accommodated in the square recess. The split bush - Part No.3 has a projecting snug. When this split bush is fitted in the body, this prevents the rotation of the bushes along with the shaft. The other split bush Part No.4, provided with the oil hole is placed over the bottom bush Part No.3. This bush is placed after the shafts takes in position. The cap Part No.2 mounted over the top bush is held down by bolts and nuts. After assembling a small clearance will be left between the cap and the body. This clearance enables to provide the necessary clamping grip. Toolbars used Profile, Operation, Sketch tools, Constraint, Sketch-Based Features, Dress-Up Features, Transformation Features Product Structure Constraints between components R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 21 SMVEC
27 Procedure 1) Open the software tool CATIA package. 2) Prepare various parts required for the given PLUMMER BLOCK before assembling them by using Start> Mechanical Design > Part Design and save them as individual parts 3) Start a new assembly design by using Start> Mechanical Design > Assembly Design 4) Create the new file and save it in the directory 5) Add a part into an assembly using Existing component option 6) Fix create constraints between this new part and other parts 7) When the first part is inserted, repeat this operation with the second part until the required assembled component is achieved 8) Save the diagram in specified directory R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 22 SMVEC
28 Drawing: Result Thus the required drawing was designed, modeled and assembled as per the dimension and verified for the given PLUMMER BLOCK. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 23 SMVEC
29 Part Design 3D Modeling Exercises for Practice Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 24 SMVEC
30 Fig.5 Fig.6 R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 25 SMVEC
31 Assembly Design Fig.1 Knuckle Joint Fig.2 Universal Coupling R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 26 SMVEC
32 Fig.3(a) Safety Valve Part 01 R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 27 SMVEC
33 Fig.3(b) Safety Valve Part 02 R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 28 SMVEC
34 SF & BM diagram of Simply Supported Beam with Point Load Ex.No: Date: Aim: To find out shear force and bending moment diagram of simply supported beam Problem description: Simply supported beam with dimensions 0.2*0.3 m. Young s modulus- 210 Gpa. Poisson ratio I. Starting ANSYS: Click start ANSYS ANSYS product launcher: Launch ANSYS Multiphysics Run File Management browse the directory for saving and retrieving the files. II. Preprocessing: Utility Menu > Change Job Name > Enter Job Name. Utility Menu > File > Change Title > Enter New Title. Preference > Structural > OK. Preprocessor > element type > add/edit > beam > 2D elastic. Real constants > add > ok > c/s-0.2*0.3 > MI- 0.2*0.3*0.3*0.3/12 > beam height 0.3 > ok Material properties > material models > structural > linear > elastic > Isotropic > Ex 210E9 > prxy 0.27 > ok > close. Preprosessor > modelling > create > nodes > active c/s > xyz location as cs > 2 > apply > 4 apply > ok. Create > elements > autonumbered > through nodes > pick 1 and 2 > apply > pick 2 & 3 > ok. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 29 SMVEC
35 Preprossors > loads > define loads > apply > structural > displacement > on nodes > pick 1& 3 > apply DOF s constrained > UY > value=0 > ok Preprossors > loads > define loads > apply > structural > force /moments > on nodes > 2 > apply > fy > Force moment value= -20,000 (-ve) > ok. III. Solution Solution > Solve > Current LS > Ok. IV. Post processor General post preprocessor > plot- results > deformed shape > ok > contour plot > nodal solution > Dof solution > displacement vector sum > ok. Element table > define table > add > results data item > by sequence number > SMISC > SMISC, 2 > apply > SMISC, 8 > SMISC, 6- SMISC -12 > apply > ok. Plot results > contour plot > line element results > element table > item at node1 SMISC > 2 item at node > J SMISC -8 > ok. Contour plot > line element results > table item at node 1 SMISC -6 > element at node J SMISC -12 > ok List results > reaction Soln > item to be listed > all items ok Result: Thus the shear force and bending moment diagram of simply supported beam with point load are generated using ANSYS. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 30 SMVEC
36 Ex.No: SF & BM diagram for Cantilever Beam with end Point Load Date: Aim: load. To find out shear force and bending moment diagram of given cantilever beam with end point Problem description: Compute the shear force and bending moment diagrams for the beam shown and find the maximum deflection by using ANSYS. Assume Rectangular cross section area of 0.2*0.3 m, young s modulus of 210 GPA and poisson ratio 0.27 I. Starting ANSYS: Click start ANSYS ANSYS product launcher: Launch ANSYS Multiphysics File Management browse the directory for saving and retrieving the files. II. Preprocessing: Preference tick structural select h method ok Title: Utility menu file change title bracket ok Utility menu plot replot. Elements: Main menu -> preprocessor element type -> add/edit/delete -> add -> beam -> 2d elastic 3-> close Material Properties: Main menu -> preprocessor-> Material props -> material models -> structural -> linear -> elastic -> isotropic -> Young s modulus (EX = 210E9) and Poisson s ratio (PRXY = 0.27) -> ok R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 31 SMVEC
37 Modeling: Main menu -> preprocessor -> Modeling -> create -> nodes -> inactive cs -> apply -> x.y.z -> ok. Create ->elements -> Auto numbered->three nodes-> 1 and 2->o.k Preprocessor Loads -> define loads -> apply -> structural -> displacement on nodes node 1 apply A11 DOF ok Loads define loads apply structural force/moment on nodes pick node 2 apply direction of F/M Fy Force/moment value (-ve value) ok III. Solution Solution solve current LS ok close IV. Post processor Postprocessing General postprocessor Plot results deformed shape deformed and undeformed shape Element table define table Add by sequence num SMISC SMISC 2 apply SMISC 8- apply by sequence num SMISC - SMISC, 6- apply, SMISC, SMISC 2, ok- close General postprocessor plot results contour plot element results element table at node at node1- smisc2 element table item at node smis8- ok Plot results contour plot line element results element table item at node 1 SMISC 6 table SMISC 12- ok Plot control- animate deformed results- DOF solution ok Result: Thus the shear force and bending moment diagram of given cantilever beam with end point load are generated using ANSYS. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 32 SMVEC
38 SF & BM diagram OF Simply Supported Beam with Moment and Point Load Ex.No: Date: Aim: To find out the shear force and moment diagram of simply supported beam with moment and point load. Problem description: Rectangular cross section simply supported beam, with dimensions of 0.2 mm 0.3 m young s modulus E = 210 Gpa; Poisson ratio= I. Starting ANSYS: Click start ANSYS ANSYS product launcher: Launch ANSYS Multiphysics File Management browse the directory for saving and retrieving the files. II. Preprocessing: Utility Menu > Change Job Name > Enter Job Name. Utility Menu > File > Change Title > Enter New Title. Preference > Structural > OK. Element type add/edit/delete- add-beam- 2delastic 3 ok close. Real constraints-add-ok-real constraint set no1-crosssection area M.I- 0.2*0.3*(3/2) beam height 0.3-ok Material property material models- structural linear isotropic Ex-210e9-prxy-0.27-okclose. Preprocessor Modelling- create nodes-active c/s- apply-xyz (5, -2, -4) - apply-6 applyok. Create elements-auto numbered-through nodes- pitch-1, 2 apply- pick 2 3 apply pick 3 and 4-apply- pick 4, 5-ok. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 33 SMVEC
39 Preprocessor- Loads Define loads-apply-structural displacement on nodes- pick nodes 1 4 apply- DOF to be constrained-ok-structural force/moment-on nodes pick nodes 2 apply-direction of force/moment- m2 pick 2 apply direction of value of >12,000 (anticlock wise, + ve value)- apply pick- node3 apply- direction of force/ moment value 6000 (-ve value)- apply- pick node 5 apply direction as force/moment Fy Force/ moment value 6000 (-ve value)- ok III. Solution Solution-solve current ls ok-close. IV. Post processor General postprocessor- plot results deformed shape-deformed + un deformed-ok-plot results- contour plot- nodal- solution DOF displacement vector sum -ok Result: Thus the shear force and moment diagram of simply supported beam with moment and point load are generated using ANSYS. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 34 SMVEC
40 Stress analysis of a Plate with a Circular Hole Ex.No: Date: Aim To perform stress analysis of a plate with a circular hole. Problem description: In the plate with a hole under plane stress, find the deformed shape of the hole and determine the maximum stress distribution along A B. Take young s Modulus value = 210 GPA, Thickness t = 1mm, Poisson Ratio = 0.3, Diameter of the circle = 10 mm, Analysis Assumption Plane stress with thickness is used. I. Starting ANSYS: Click start ANSYS ANSYS product launcher: Launch ANSYS Multiphysics File Management browse the directory for saving and retrieving the files. II. Preprocessing: Utility Menu > Change Job Name > Enter Job Name. Utility Menu > File > Change Title > Enter New Title. Preference > Structural > OK. Preprocessor > Element Type > Add/Edit/Delete > Solid Quad 4Node 42 > Select > Options > Plane Stress/Thickness. Preprocessor > Material Properties > Material Model > Structural > Linear > Elastic > Isotropic > EX = 2E5, PRXY = 0.3. Preprocessor > Real Constant > Add/Edit/Delete > plane 42> thickness = 10 Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Areas > Rectangular by Dimension > X1, X2 = 0, 50 Y1, Y2 = 0, 50. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 35 SMVEC
41 Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Areas > Circle > Solid circle > WP X = 0, WP Y = 50 & Radius = 10 > OK. Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Subtract > Areas > Select rectangle >Apply > Select Circle > Ok. Preprocessor > Meshing > Element Edge Length = 2 > Mesh > Areas > Free. Solution > Analysis Type > New Analysis > Static > OK. Solution > Define Load > Apply > Structural > Displacement > On lines > Select Bottom Line > UY > Displacement value = 0 > OK. Solution > Define Load > On Lines > Select left line > Ok > UX > Displacement value = 0 > OK. Solution > Pressure > On Line > Select Right line > Ok > Value [100] > Ok. III. Solution Solution > Solve > Current LS > Ok. IV. Post processor Utility menu > Plot control > Style > Symmetry Expansion > Periodic > Reflect about XY. Plot control > Animate > deformed shape > Ok. General Postprocessor > Plot Result > Deformed shape > Ok. Plot Result > Plot Result > Contour Plot > Nodal Solution > Stress > Von Mises > Ok. Result: Thus the stress analysis of a plate with a circular hole is performed. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 36 SMVEC
42 Von Mises Stress of a Bracket Ex.No: Aim: To analyze the von-mises stress distribution of a rectangular bracket. Date: Problem Description: The corner bracket as figure below is subjected to a distributed load 0.2N/mm 2 on the top surface. It is fixed around the hole surfaces. The bracket is made of steel with a modulus of elasticity of 2x10 5 N/mm 2 and ν = 0.3 Plot the deformed shape Also plot the von - mises stress distribution in the bracket. I. Starting : Click start ANSYS ANSYS product launcher: Launch ANSYS Multiphysics File Management browse the directory for saving and retrieving the files. II. Preprocessing: Preference tick structural select h method ok Title: Utility menu file change title bracket ok Utility menu plot replot. Elements: Main menu preprocessor element type add/edit/delete add structural mass solid Tet.10 node (SOLID92) ok Material Properties: Main menu preprocessor Material props material models structural linear elastic isotropic Young s modulus (EX = 2x10 5 ) and Poisson s ratio (PRXY = 0.3) ok. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 37 SMVEC
43 Modeling: Main menu preprocessor Modeling create volume block by 2 corner & z enter 0, 0, 50, 75, -5 ok. Utility menu pltctrl pan zoom rotate iso close Main menu preprocessor Modeling create volume cylinder solid cylinder 25,25,7,-5 apply 25,50,7,-5 ok Main menu Preprocessor Modeling operate Boolean subtract volume select base volume ok select subtracting volume (circles) ok. Utility menu plot replot Utility menu work plane offset WP by increments enter X, Y, Z offset enter 0, 75,- 5. Utility menu work plane offset WP by increments enter XY, YZ, ZX offset enter 0,90,0. Main menu preprocessor Modeling create volume block by 2 corner & z enter 0, 0, 50, 75, -5 ok Utility menu work plane offset WP by increments enter XY, YZ, ZX offset enter 0,- 90, 0. Utility menu warplane offset WP to global origin. Utility menu Plot Multi plot Main menu preprocessor Modeling create Areas arbitrary through KPs click key points (5,2,26,25,32) ok Utility menu plot Multi plot Main menu preprocessor Modeling Operate Extrude Areas Along Normal Click area 17 Dist = -5 ok Utility menu plot cntrl hard copy to file jpeg save to: bracket. jpg ok Main menu preprocessor Meshing size cntrl smart size basic enter size level as 7 ok. Main menu preprocessor Meshing mesh volumes pick all ok. Utility menu plot ctrls hard copy to file jpeg save to: bracket mesh ok. Boundary conditions and Loads: Utility menu select entities area by num/pick by location click circular inner areas apply ok. Utility menu plot areas. Main menu solution define loads apply structural displacement on area pick all select all DOF ok Utility menu select everything. Utility menu select entities area by num/pick click top surface areas( 1&21) ok. Utility menu plot areas. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 38 SMVEC
44 Main menu solution define loads apply structural pressure on area pick all ok enter pres = 0.2 ok. Utility menu select everything Utility menu plot cntrls hard copy to file jpeg save to : bracket load.jpg ok III. Solution Main menu solution solve current LS IV. Post processor Gen. Post processor plot results contour plots nodal solu. stress von mises ok Utility menu plot ctrls hard copy to file jpeg save to : bracket stress result.jpg ok Utility menu file save as bracket.db ok Utility menu file write db log file bracket.lgw ok. Result: Thus the von - mises stress distribution in the bracket is ploted. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 39 SMVEC
45 Stress distribution of Cast Iron member Ex.No: Date: Aim : To analyse the stress distribution of hollow cast iron member when one end is fixed and other end is loaded. Problem Description: A cast iron hollow member used in machine tools structure is fixed at one end and loaded at the other end. The material properties are Young s modulus is 165GPa. and Poisson s ratio is 0.3. Analyze for the von-mises stress. I. Starting : Click start ANSYS ANSYS product launcher: Launch ANSYS Multiphysics File Management browse the directory for saving and retrieving the files. II. Preprocessing: Preference tick structural select h method ok Title: Utility menu file change title tube ok Utility menu plot replot. Elements: Main menu preprocessor element type add/edit/delete add structural mass solid Brick 8node (Solid 45) ok Material Properties: Main menu preprocessor Material props material models structural linear elastic isotropic Young s modulus (EX = 1.65e3) and Poissons ratio (PRXY = 0.3) ok. Modeling: Main menu preprocessor modeling Create Areas Rectangle by center and corner enter width = 1000: height = 250 ok. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 40 SMVEC
46 Main menu preprocessor Modeling Create Areas Rectangle By center and corner enter width = 200: height = 100 ok. Main menu preprocessor Modeling Operate Subtract Areas select base area (1) apply select area to be subtracted (2) ok. Main menu preprocessor Modeling Operate Extrude Areas by xyz offset select area (3) ok enter x,y,z value as 0,0,250 ok. Utility menu plotctrl pan,zoom,rotate iso close. Utility menu Work plane display work plane. Utility menu work plane offset WP by increments enter x,y,z offset as 500,0,125 apply. Enter XY, YZ, ZX angles as 0,0,90 ok. Main menu preprocessor Modeling Create Areas Rectangle By center and corner enter width = 200, height = 200 ok. Utility menu work plane offset WP by increments Enter XY, YZ, ZX angles as 0, 0,- 90 ok. Main menu preprocessor Modeling Operate Extrude Areas by xyz offset select area (200x200) ok enter x,y,z value as -1000,0,0 ok. Preprocessor Modeling operate subtract volumes select base volume apply select volume to be subtracted ok Utility menu plot volume. Utility menu work plane offset WP to global origin Utility menu plot cntrl hard copy to file jpeg save to: beam. jpg ok Meshing size cntrl smart size basic enter LVL as10 ok. Meshing mesh tool mesh volume pick all ok. Utility menu plot cntrl hard copy to file jpeg save to: beam mesh. jpg ok Boundary conditions and Loads: Utility menu select entities areas by num/pick apply select left side area apply ok. Utility menu select entities nodes attached to areas, all apply ok. Utility menu plot nodes. Main menu solution loads apply structural displacement on nodes pick all apply all DOF ok. Utility menu select everything Utility menu select entities lines by num/pick apply select top line of the right end apply ok. Utility menu select entities nodes attached to lines, all apply ok. Utility menu plot nodes Main menu solution loads apply force on nodes pick all ok enter F y = -50,000 ok. Utility menu select everything R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 41 SMVEC
47 Utility menu plot multiplot Utility menu plot cntrls hard copy to file jpeg save to : bracket load.jpg ok III. Solution Main menu solution solve current LS. IV. Post processor Gen. Post processor plot results contour plots nodal solu. stress von mises ok Utility menu plot ctrls hard copy to file jpeg save to : beam result.jpg ok Utility menu file save as beam.db ok Utility menu file write db log file beam.lgw ok. Result: Thus the von-mises stress analysis of hollow cast iron member is analyzed. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 42 SMVEC
48 Heat distribution on a Thin Plate subjected to End Heating Ex.No: Date: Aim: To find out the temperature distribution on a thin plate. Problem description: A thin plate is subjected to end heating with the temperature given in the figure.the thermal conductivity of the plate is k 401W/m-k xx = I. Starting ANSYS: Click start ANSYS ANSYS product launcher: Launch ANSYS Multiphysics File Management browse the directory for saving and retrieving the files. II. Preprocessing: Utility Menu > Change Job Name > Enter Job Name. Utility Menu > File > Change Title > Enter New Title. Preference > Structural > OK. Preprocessor- element type-add/edit/delete add- solid quad4 hole- 55-ok-optionelement behavior- K3- plane stress with thickness ok close. Material model-properties-thermal conductivity-isotropic-kxx-401 Modelling create area-rectangular-by meshing-mesh tool-mesh area-quad-free mesh-pick all ok-mesh tool refine-pick all-level of requirement-3 ok Loads-define loads-apply-thermal temperature- on lines select 100 C-ok. Loads-define loads-apply-thermal temperature- on lines- select 100 lines -Apply- DOF to be constrained- temp-temp value- 200 C. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 43 SMVEC
49 III. Solution Solution > Solve > Current LS > Ok. IV. Post processor General post processor-plot result- contour plot-modal solutions-dof solution-nodal temp-ok-plot controls-animate-deformed shape-dof solution-temp-ok. Result: Thus the temperature distribution on a thin plate is generated using ANSYS. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 44 SMVEC
50 ANSYS Exercises for Practice Drawings 1. Calculate and plot SFD & BMD for the beam as shown below.use Ansys APDL to do the same if the beam made of steel and cross-section is a square of side 0.05m. 2. Calculate the maximum displacement that takes place on the chair below. Also calculate the Von-mises stress acting on the chair. Draw 3D Wireframe of the chair and do the analysis. Save the animation of deformation that occurs on the chair. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 45 SMVEC
51 3. Calculate and plot SFD & BMD for the beam as shown below. 4. Calculate and plot SFD & BMD for the beam as shown below. 5. Calculate and plot SFD & BMD for the beam as shown below. 6. Calculate and plot SFD & BMD for the beam as shown below. R.Hemanth Kumar, Asst Prof 46 SMVEC
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial
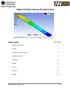
 Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
file://c:\documents and Settings\sala\Configuración local\temp\~hha54f.htm
 Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Modelling and Analysis Lab (FEA)
 Channabasaveshwara Institute of Technology (Affiliated to VTU, Belagavi & Approved by AICTE, New Delhi) (NAAC Accredited & ISO 9001:2015 Certified Institution) NH 206 (B.H. Road), Gubbi, Tumakuru 572 216.
Channabasaveshwara Institute of Technology (Affiliated to VTU, Belagavi & Approved by AICTE, New Delhi) (NAAC Accredited & ISO 9001:2015 Certified Institution) NH 206 (B.H. Road), Gubbi, Tumakuru 572 216.
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Bell Crank. Problem: Joseph Shigley and Charles Mischke. Mechanical Engineering Design 5th ed (New York: McGraw Hill, May 2002) page 87.
 Problem: A cast-iron bell-crank lever, depicted in the figure below is acted upon by forces F 1 of 250 lb and F 2 of 333 lb. The section A-A at the central pivot has a curved inner surface with a radius
Problem: A cast-iron bell-crank lever, depicted in the figure below is acted upon by forces F 1 of 250 lb and F 2 of 333 lb. The section A-A at the central pivot has a curved inner surface with a radius
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Latch Spring. Problem:
 Problem: Shown in the figure is a 12-gauge (0.1094 in) by 3/4 in latching spring which supports a load of F = 3 lb. The inside radius of the bend is 1/8 in. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer
Problem: Shown in the figure is a 12-gauge (0.1094 in) by 3/4 in latching spring which supports a load of F = 3 lb. The inside radius of the bend is 1/8 in. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis
 Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame
 Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
ANSYS. Geometry. Material Properties. E=2.8E7 psi v=0.3. ansys.fem.ir Written By:Mehdi Heydarzadeh Page 1
 Attention: This tutorial is outdated, you will be redirected automatically to the new site. If you are not redirected, click this link to the confluence site. Problem Specification Geometry Material Properties
Attention: This tutorial is outdated, you will be redirected automatically to the new site. If you are not redirected, click this link to the confluence site. Problem Specification Geometry Material Properties
ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis
 R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing
Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing
ANSYS Tutorials. Table of Contents. Grady Lemoine
 ANSYS Tutorials Grady Lemoine Table of Contents Example 1: 2-D Static Stress Analysis in ANSYS...2 Example 2: 3-D Static Stress Analysis...5 Example 3: 2-D Frame With Multiple Materials and Element Types...10
ANSYS Tutorials Grady Lemoine Table of Contents Example 1: 2-D Static Stress Analysis in ANSYS...2 Example 2: 3-D Static Stress Analysis...5 Example 3: 2-D Frame With Multiple Materials and Element Types...10
Two Dimensional Truss
 Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation
 ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
Module 1.2: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Real Constants and Material Properties 7 Meshing 9 Loads 10 Solution
Module 1.: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Real Constants and Material Properties 7 Meshing 9 Loads 10 Solution
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame
 Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
LAB MANUAL. Dharmapuri ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS. Regulation : Branch : B.E. Mechanical Engineering
 Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation : Branch : 2013 B.E. Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester : IV Year / VII Semester ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology, Dharmapuri
Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation : Branch : 2013 B.E. Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester : IV Year / VII Semester ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology, Dharmapuri
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
Dhanalakshmi College Of Engineering
 Dhanalakshmi College Of Engineering Manimangalam, Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6711 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS LABORATORY VII SEMESTER - R 2013 LABORATORY MANUAL Name
Dhanalakshmi College Of Engineering Manimangalam, Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6711 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS LABORATORY VII SEMESTER - R 2013 LABORATORY MANUAL Name
AUTO CAD LAB MANUAL. B. Tech IV Year - I Semester DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Aurora s Technological And Research Institute
 AUTO CAD LAB MANUAL B. Tech IV Year - I Semester : NAME ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 LIST OF
AUTO CAD LAB MANUAL B. Tech IV Year - I Semester : NAME ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 LIST OF
Statically Indeterminate Beam
 Problem: Using Castigliano's Theorem, determine the deflection at point A. Neglect the weight of the beam. W 1 N/m B 5 cm H 1 cm 1.35 m Overview Anticipated time to complete this tutorial: 45 minutes Tutorial
Problem: Using Castigliano's Theorem, determine the deflection at point A. Neglect the weight of the beam. W 1 N/m B 5 cm H 1 cm 1.35 m Overview Anticipated time to complete this tutorial: 45 minutes Tutorial
NonLinear Materials AH-ALBERTA Web:
 NonLinear Materials Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to describe how to include material nonlinearities in an ANSYS model. For instance, the case
NonLinear Materials Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to describe how to include material nonlinearities in an ANSYS model. For instance, the case
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
NonLinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 NonLinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline the steps required to do a simple nonlinear analysis of the beam
NonLinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline the steps required to do a simple nonlinear analysis of the beam
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame
 Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Example Plate with a hole
 Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss
 TF 3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 40 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type:
TF 3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 40 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type:
Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing
 Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing Problem Description This is a simple modal analysis of a wing of a model airplane. The wing is of uniform configuration along its length and its
Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing Problem Description This is a simple modal analysis of a wing of a model airplane. The wing is of uniform configuration along its length and its
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Example Cantilever beam
 Course in ANSYS Example0300 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the maximum deflection and locate point of maximum deflection Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained
Course in ANSYS Example0300 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the maximum deflection and locate point of maximum deflection Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained
SolidWorks. An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs
 An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
Module 3: Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam
 Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Course in ANSYS. Example0303. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0303 Example Gear axle 3D Objective: Compute the maximum stress von Mise Tasks: How should this be modeled? Topics: Element type, Real constants, modeling, Plot results, output graphics,
Course in Example0303 Example Gear axle 3D Objective: Compute the maximum stress von Mise Tasks: How should this be modeled? Topics: Element type, Real constants, modeling, Plot results, output graphics,
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS
 Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS 5.1 Introduction The problem selected to illustrate the use of ANSYS software for a three-dimensional steadystate heat conduction
Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS 5.1 Introduction The problem selected to illustrate the use of ANSYS software for a three-dimensional steadystate heat conduction
Exercise Guide. Published: August MecSoft Corpotation
 VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
Creo for Analyst. Overview
 Creo for Analyst Overview In this course, you will learn how to utilize the core functionality enhancements in Creo Parametric 2.0. First, you will become familiar with using and customizing the new ribbon
Creo for Analyst Overview In this course, you will learn how to utilize the core functionality enhancements in Creo Parametric 2.0. First, you will become familiar with using and customizing the new ribbon
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
CAD/CAM LABORATORY MANUAL
 BALAJI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE LAKNEPALLY (V), NARSAMPET (M), WARANGAL-506331 CAD/CAM LABORATORY MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING N. KISHORE KUMAR, Assistant professor LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
BALAJI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE LAKNEPALLY (V), NARSAMPET (M), WARANGAL-506331 CAD/CAM LABORATORY MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING N. KISHORE KUMAR, Assistant professor LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
Release 10. Kent L. Lawrence. Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
 ANSYS Release 10 Tutorial Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
ANSYS Release 10 Tutorial Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Course in ANSYS. Example0153. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0153 Example Offshore structure F Objective: Display the deflection figure and von Mises stress distribution Tasks: Import geometry from IGES. Display the deflection figure? Display the
Course in Example0153 Example Offshore structure F Objective: Display the deflection figure and von Mises stress distribution Tasks: Import geometry from IGES. Display the deflection figure? Display the
6. Results Combination in Hexagonal Shell
 6. Results Combination in Hexagonal Shell Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 0 minutes Discipline: Load combinations results Analysis
6. Results Combination in Hexagonal Shell Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 0 minutes Discipline: Load combinations results Analysis
ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0
 ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0 Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Release 11.0 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0 Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Release 11.0 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of. Ansys Workbench 14.0
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode 2
 5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 5 minutes Discipline: Concrete Shell Reinforcement
5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 5 minutes Discipline: Concrete Shell Reinforcement
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench
 Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
Finite Element Analysis using ANSYS Mechanical APDL & ANSYS Workbench
 Finite Element Analysis using ANSYS Mechanical APDL & ANSYS Workbench Course Curriculum (Duration: 120 Hrs.) Section I: ANSYS Mechanical APDL Chapter 1: Before you start using ANSYS a. Introduction to
Finite Element Analysis using ANSYS Mechanical APDL & ANSYS Workbench Course Curriculum (Duration: 120 Hrs.) Section I: ANSYS Mechanical APDL Chapter 1: Before you start using ANSYS a. Introduction to
IJMH - International Journal of Management and Humanities ISSN:
 EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
SOLIDWORKS - SYLLABUS
 SOLIDWORKS - SYLLABUS SolidWorks Syllabus 1 Introduction to CAD, CAE, PDM Features of SolidWorks, Total Duration : 90 Hour Various products available in SolidWorks for Product Design, Simulation, Communication
SOLIDWORKS - SYLLABUS SolidWorks Syllabus 1 Introduction to CAD, CAE, PDM Features of SolidWorks, Total Duration : 90 Hour Various products available in SolidWorks for Product Design, Simulation, Communication
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial
 Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
ANSYS EXERCISE ANSYS 5.6 Temperature Distribution in a Turbine Blade with Cooling Channels
 I. ANSYS EXERCISE ANSYS 5.6 Temperature Distribution in a Turbine Blade with Cooling Channels Copyright 2001-2005, John R. Baker John R. Baker; phone: 270-534-3114; email: jbaker@engr.uky.edu This exercise
I. ANSYS EXERCISE ANSYS 5.6 Temperature Distribution in a Turbine Blade with Cooling Channels Copyright 2001-2005, John R. Baker John R. Baker; phone: 270-534-3114; email: jbaker@engr.uky.edu This exercise
SOLIDWORKS Parametric Modeling with SDC. Covers material found on the CSWA exam. Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling
 Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2015 Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2015 Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF
TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS.
 Ex_1_2D Plate.doc 1 TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS. 1. INTRODUCTION Two-dimensional problem of the theory of elasticity is a particular
Ex_1_2D Plate.doc 1 TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS. 1. INTRODUCTION Two-dimensional problem of the theory of elasticity is a particular
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss
 ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss Lab TA: Xiaotong Huo EN 3029B xh0381@mun.ca Download link for Abaqus student edition: http://academy.3ds.com/software/simulia/abaqus-student-edition/
ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss Lab TA: Xiaotong Huo EN 3029B xh0381@mun.ca Download link for Abaqus student edition: http://academy.3ds.com/software/simulia/abaqus-student-edition/
Sliding Split Tube Telescope
 LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
Parametric Modeling with SolidWorks
 Parametric Modeling with SolidWorks 2012 LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT Assembly Project Included Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com
Parametric Modeling with SolidWorks 2012 LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT Assembly Project Included Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com
Course Modules for CATIA V6 2013x Essentials for New Users Training Online:
 Course Modules for CATIA V6 2013x - 100 Essentials for New Users Training Online: 1 Launching CATIA V6 The PLM Story Import IGI Models (Essentials) Launching CATIA V6 Choosing a Security Context 2 V6 Navigation
Course Modules for CATIA V6 2013x - 100 Essentials for New Users Training Online: 1 Launching CATIA V6 The PLM Story Import IGI Models (Essentials) Launching CATIA V6 Choosing a Security Context 2 V6 Navigation
An Overview of Computer Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis
 An Overview of Computer Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Overview... 4 2.0 General Concepts... 4 2.1 What is Computer Aided Design... 4 2.1.1 2D verses
An Overview of Computer Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Overview... 4 2.0 General Concepts... 4 2.1 What is Computer Aided Design... 4 2.1.1 2D verses
Course in ANSYS. Example0154. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0154 Example Frame 2D E = 210000N/mm 2 n = 0.3 L= 1000mm H = 1000mm a = 20mm b = 50mm c = 400mm F = 10000N I = 208333N/mm 4 Example0154 2 Example Frame 2D Objective: Compute the maximum
Course in Example0154 Example Frame 2D E = 210000N/mm 2 n = 0.3 L= 1000mm H = 1000mm a = 20mm b = 50mm c = 400mm F = 10000N I = 208333N/mm 4 Example0154 2 Example Frame 2D Objective: Compute the maximum
Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench
 Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench Contents Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 2 1. Starting Windows on the MAC... 2 2. Login into Windows... 2 3. Start ANSYS Workbench... 2 4. Configuring
Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench Contents Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 2 1. Starting Windows on the MAC... 2 2. Login into Windows... 2 3. Start ANSYS Workbench... 2 4. Configuring
 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2010 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2010 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS LABORATORY MANUAL ANSYS. Course Instructor: Dr. R.Ganesan
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS MECH 460 LABORATORY MANUAL ANSYS Course Instructor: Dr. R.Ganesan Prepared by A. Zabihollah Approved by Dr. R. Ganesan Winter 2007 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION.3 1.1 Starting
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS MECH 460 LABORATORY MANUAL ANSYS Course Instructor: Dr. R.Ganesan Prepared by A. Zabihollah Approved by Dr. R. Ganesan Winter 2007 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION.3 1.1 Starting
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Education Curriculum Surface Design Specialist
 Education Curriculum Surface Design Specialist Invest your time in imagining next generation designs. Here s what we will teach you to give shape to your imagination. CATIA Surface Design Specialist CATIA
Education Curriculum Surface Design Specialist Invest your time in imagining next generation designs. Here s what we will teach you to give shape to your imagination. CATIA Surface Design Specialist CATIA
ME Optimization of a Frame
 ME 475 - Optimization of a Frame Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus. 4 7 7 5,000 N 5,000 N 0,000 N 6 6 4 3 5 5 4 4 3 3 Figure. Full frame geometry and loading
ME 475 - Optimization of a Frame Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus. 4 7 7 5,000 N 5,000 N 0,000 N 6 6 4 3 5 5 4 4 3 3 Figure. Full frame geometry and loading
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses
 Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
SolidWorks 2013 Part II - Advanced Techniques
 SolidWorks 2013 Part II - Advanced Techniques Parts, Surfaces, Sheet Metal, SimulationXpress, Top-Down Assemblies, Core and Cavity Molds Paul Tran CSWE, CSWI Supplemental Files SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff
SolidWorks 2013 Part II - Advanced Techniques Parts, Surfaces, Sheet Metal, SimulationXpress, Top-Down Assemblies, Core and Cavity Molds Paul Tran CSWE, CSWI Supplemental Files SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff
CE Advanced Structural Analysis. Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis
 Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline a simple coupled thermal/structural analysis. A steel link, with
Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline a simple coupled thermal/structural analysis. A steel link, with
Installation Guide. Beginners guide to structural analysis
 Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame
 Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017
 Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
Solid Problem Ten. In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards:
 C h a p t e r 11 Solid Problem Ten In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards: 1. Sketch of Solid Problem Ten 2. Starting a 3D Part Drawing 3. Modifying How the UCS Icon is
C h a p t e r 11 Solid Problem Ten In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards: 1. Sketch of Solid Problem Ten 2. Starting a 3D Part Drawing 3. Modifying How the UCS Icon is
Autodesk Inventor 2018
 Parametric Modeling with Autodesk Inventor 2018 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Parametric Modeling with Autodesk Inventor 2018 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
SolidWorks 2014 Part II - Advanced Techniques
 SolidWorks 2014 Part II - Advanced Techniques Parts, Surfaces, Sheet Metal, SimulationXpress, Top-Down Assemblies, Core and Cavity Molds Paul Tran CSWE, CSWI SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
SolidWorks 2014 Part II - Advanced Techniques Parts, Surfaces, Sheet Metal, SimulationXpress, Top-Down Assemblies, Core and Cavity Molds Paul Tran CSWE, CSWI SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0
 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Course in ANSYS. Example Truss 2D. Example0150
 Course in ANSYS Example0150 Example Truss 2D Objective: Compute the maximum deflection Tasks: Display the deflection figure? Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element type, Real constants, Material, modeling,
Course in ANSYS Example0150 Example Truss 2D Objective: Compute the maximum deflection Tasks: Display the deflection figure? Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element type, Real constants, Material, modeling,
Transient Thermal Conduction Example
 Transient Thermal Conduction Example Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple transient conduction problem. Special thanks to Jesse Arnold for the analytical solution shown
Transient Thermal Conduction Example Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple transient conduction problem. Special thanks to Jesse Arnold for the analytical solution shown
Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals
 CATIA V5 Training Foils Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GPF_FI_V5R19 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course
CATIA V5 Training Foils Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GPF_FI_V5R19 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course
CATIA Surface Design
 CATIA V5 Training Exercises CATIA Surface Design Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GS1_FX_V5R19 Table of Contents (1/2) Creating Wireframe Geometry: Recap Exercises 4 Creating Wireframe Geometry:
CATIA V5 Training Exercises CATIA Surface Design Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GS1_FX_V5R19 Table of Contents (1/2) Creating Wireframe Geometry: Recap Exercises 4 Creating Wireframe Geometry:
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book:
 Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis
 Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis In this lesson you will learn different approaches to analyze the assembly using assembly analysis connection properties between assembly components. In addition
Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis In this lesson you will learn different approaches to analyze the assembly using assembly analysis connection properties between assembly components. In addition
ANSYS Element. elearning. Peter Barrett October CAE Associates Inc. and ANSYS Inc. All rights reserved.
 ANSYS Element Selection elearning Peter Barrett October 2012 2012 CAE Associates Inc. and ANSYS Inc. All rights reserved. ANSYS Element Selection What is the best element type(s) for my analysis? Best
ANSYS Element Selection elearning Peter Barrett October 2012 2012 CAE Associates Inc. and ANSYS Inc. All rights reserved. ANSYS Element Selection What is the best element type(s) for my analysis? Best
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 2 Free vibrations of a beam arget Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of elastic medium, with the use of a finite element computation system ANSYS. Program
EXERCISE 2 Free vibrations of a beam arget Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of elastic medium, with the use of a finite element computation system ANSYS. Program
SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics
 SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Additional Exercises. You will perform the following exercises to practice the concepts learnt in this course:
 Additional Exercises You will perform the following exercises to practice the concepts learnt in this course: Master Exercise : Mobile Phone Plastic Bottle Exercise 1 Master Exercise : Mobile Phone In
Additional Exercises You will perform the following exercises to practice the concepts learnt in this course: Master Exercise : Mobile Phone Plastic Bottle Exercise 1 Master Exercise : Mobile Phone In
Mechanical Design V5R19 Update
 CATIA V5 Training Foils Mechanical Design V5R19 Update Version 5 Release 19 August 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_MD2_UF_V5R19 1 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course you will be able
CATIA V5 Training Foils Mechanical Design V5R19 Update Version 5 Release 19 August 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_MD2_UF_V5R19 1 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course you will be able
ANSYS Tutorial Version 6
 ANSYS Tutorial Version 6 Fracture Analysis Consultants, Inc www.fracanalysis.com Revised: November 2011 Table of Contents: 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Tutorial 1: Crack Insertion and Growth in a Cube...
ANSYS Tutorial Version 6 Fracture Analysis Consultants, Inc www.fracanalysis.com Revised: November 2011 Table of Contents: 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Tutorial 1: Crack Insertion and Growth in a Cube...
2: Static analysis of a plate
 2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
Melting Using Element Death
 Melting Using Element Death Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to outline the steps required to use element death to model melting of a material. Element
Melting Using Element Death Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to outline the steps required to use element death to model melting of a material. Element
Preface. Version 5 Release 5. Mold Tooling Design
 Version 5 Release 5 Mold Tooling Design Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customization Workbench Description Glossary Index Preface The CATIA Version 5 Mold Tooling Design application
Version 5 Release 5 Mold Tooling Design Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customization Workbench Description Glossary Index Preface The CATIA Version 5 Mold Tooling Design application
2D CAD. Courseware Issued: DURATION: 64 hrs
 2D CAD Introduction File management Orthographic drawings View management Display management Layer management Selection methods Parametric drawings Symbol creation using block BOM / Joinery details creation
2D CAD Introduction File management Orthographic drawings View management Display management Layer management Selection methods Parametric drawings Symbol creation using block BOM / Joinery details creation
