A large number of user subroutines and utility routines is available in Abaqus, that are all programmed in Fortran. Subroutines are different for
|
|
|
- Buddy Holmes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 A large number of user subroutines and utility routines is available in Abaqus, that are all programmed in Fortran. Subroutines are different for implicit (standard) and explicit solvers. Utility routines can be called inside of subroutines to take care of standard tasks. Here a small subset of the most important routines: 4
5 For the explicit solver an own set of user subroutines is available. The VUMAT is again the most important for us. 5
6 6
7 Basic flow chart with data flow and actions from the start of the ABAQUS standard analysis until its end. 7
8 A more detailed flow of ABAQUS/Standard 8
9 The routine should be a Fortran source code or an object file *.obj. The simultaneous used of multiple subroutines has to be done in one file. If you restart, the user subroutine has to be assigned again. 9
10 10
11 11
12 12
13 Forward integration (Forward Euler (explicit)) is a simple methods, however with stability problems. The strain increment has to be chosen small, much smaller than the magnitude of the elastic strain. Hence for explicit integration the time increment hast to be controlled. Implicit or semi implicit schemes have more complicated algorithms and local iterations might be needed, however they are in general more stable and converge. 13
14 Jacobian also called Functional matrix or derivative matrix is the m x mmatrix of all 1st partial derivatives of differentiable function. 14
15 15
16 16
17 17
18 18
19 19
20 20
21 21
22 22
23 23
24 24
25 25
26 26
27 27
28 28
29 29
30 Flow direction=(deviatoric stress alpha)/predicted stress = flowrule Consistency condition 30
31 31
32 32
33 33
34 34
35 35
36 36
37 The Newton-Raphson method is a recursive method, since iterations need the results of previous iterations. The fundamental idea is to linearized the function in a point by taking its tangent. The null of the tangent is then taken as an improved approximation of the null of the function. The obtained approximation is then taken as the starting point for the next iteration, until the approximation goes under a certain limit. The iteration method converges in the best case with quadratic convergence. The number of correct decimals then doubles in each iteration. Formally said, the following procedure is repeated until a desired accuracy is met: Since solving the delta x_n with the inverse of a matrix with consecutive multiplication with f(x) is costly and numerically unfavorable, the linear equation system JDx= f is solved instead, followed by x_n+1.. To solve the system several methods exist. If the Jacobian is invertible at the null and continuous, the method converges locally quadratic, what makes it quiet useful. 37
38 However there are also other methods around that do the job much better. Newton Raphson method: In each iteration, the tangent matrix has to be calculated freshly and a linear system of equations needs to be solved. Modified Netwon Raphson method: Here the tangent stiffness matrix is only calculated at the beginning of the iteration. All consecutive iterations use the same matrix, what gave the method the name of the method of initial stiffness's. Since many iterations are needed due to low convergence rates, it is mainly used for small non linearity. Quasi Newton methods are a class of numerical methods for solving non linear minimization problems. The methods are based on the Newton method, but calculate the inverse of the Hesse matrix not directly, but approximate them only to limit the computational cost per iteration. The first algorithm was proposes in 1950 by the physicist Davidon. The most known variants are the Broyden Fletcher Goldfarb Shanno (BFGS) and Davidon Fletcher Powell (DFP), Broyden or SR1 a.s.o. 38
39 The arc length method helps to reach for non linearity in FEM applications to reach quite fast the implicit solution. It is a modification of the Newton Raphson method, that is usable for stability analysis and non linear static simulations, in particular in the domain of limit states and for buckling and post buckling. As one can see from the graph that opposite to the Newton Raphson method the aim of the equilibrium integrations is not the load amplitude but approaches the solution on a curve. This arc represents an equilibrium curve derived from the DOF values and a loading factor. For applications with large changes the radius of the acr (load factor) should be small enough. The arclength method does not work well for abrupt, unsteady non linearity like contact or elastic ideally plastic material. Variants are the Riks method. 39
40 40
41 41
42 42
43 43
44 44
45 45
46 46
47 47
48 48
49 49
50 50
51 51
52 52
53 The most popular method for integrating the plasticity equations is radial return mapping. Initially developed for J2 plasticity, it was generalized to arbitrary convex yield surfaces and yield stress functions. The principle is simple: First the stress is updated assuming that the response is elastic, then if it is outside the yield surface, the stress is projected on to the closest point of the yield surface. If the material is perfectly plastic, the yield surface is constant, but if h > 0, the yield surface expands during the plastic flow, and the stress is projected on the expanded yield surface. The data available at the beginning of the radial return update is the previous stress, equivalent plastic strain, and increment in the strain. By the end of the radial return procedure, the stress and equivalent plastic strain have been updated. Main drawback is the need for computing gradients of the flwo rule and hardening laws, what can be laborious for complicated plasticity models. 53
54 Another plastic return mapping algorithm is the Cutting plane algorithm proposed by Ortiz and Simo It avoids the need for computing the gradients of the flow rule and hardening function. The direction of the return mapping is always the steepest descent and a sequence of straight segments. Opposite to the radial return mapping, it is an explicit procedure. It converges very fast. 54
55 55
INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING
 INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING DAVID G. LUENBERGER Stanford University TT ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California London Don Mills, Ontario CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING DAVID G. LUENBERGER Stanford University TT ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California London Don Mills, Ontario CONTENTS
Experimental Data and Training
 Modeling and Control of Dynamic Systems Experimental Data and Training Mihkel Pajusalu Alo Peets Tartu, 2008 1 Overview Experimental data Designing input signal Preparing data for modeling Training Criterion
Modeling and Control of Dynamic Systems Experimental Data and Training Mihkel Pajusalu Alo Peets Tartu, 2008 1 Overview Experimental data Designing input signal Preparing data for modeling Training Criterion
David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye. Linear and Nonlinear. Programming. Fourth Edition. ö Springer
 David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye Linear and Nonlinear Programming Fourth Edition ö Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Optimization 1 1.2 Types of Problems 2 1.3 Size of Problems 5 1.4 Iterative Algorithms
David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye Linear and Nonlinear Programming Fourth Edition ö Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Optimization 1 1.2 Types of Problems 2 1.3 Size of Problems 5 1.4 Iterative Algorithms
Optimization. there will solely. any other methods presented can be. saved, and the. possibility. the behavior of. next point is to.
 From: http:/ //trond.hjorteland.com/thesis/node1.html Optimization As discussed briefly in Section 4.1, the problem we are facing when searching for stationaryy values of the action given in equation (4.1)
From: http:/ //trond.hjorteland.com/thesis/node1.html Optimization As discussed briefly in Section 4.1, the problem we are facing when searching for stationaryy values of the action given in equation (4.1)
Newton and Quasi-Newton Methods
 Lab 17 Newton and Quasi-Newton Methods Lab Objective: Newton s method is generally useful because of its fast convergence properties. However, Newton s method requires the explicit calculation of the second
Lab 17 Newton and Quasi-Newton Methods Lab Objective: Newton s method is generally useful because of its fast convergence properties. However, Newton s method requires the explicit calculation of the second
Logistic Regression
 Logistic Regression ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-05-26 Agenda Model Specification Model Fitting Bayesian Logistic Regression Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization Generative versus Discriminative Classifiers
Logistic Regression ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-05-26 Agenda Model Specification Model Fitting Bayesian Logistic Regression Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization Generative versus Discriminative Classifiers
Multi Layer Perceptron trained by Quasi Newton learning rule
 Multi Layer Perceptron trained by Quasi Newton learning rule Feed-forward neural networks provide a general framework for representing nonlinear functional mappings between a set of input variables and
Multi Layer Perceptron trained by Quasi Newton learning rule Feed-forward neural networks provide a general framework for representing nonlinear functional mappings between a set of input variables and
Example 24 Spring-back
 Example 24 Spring-back Summary The spring-back simulation of sheet metal bent into a hat-shape is studied. The problem is one of the famous tests from the Numisheet 93. As spring-back is generally a quasi-static
Example 24 Spring-back Summary The spring-back simulation of sheet metal bent into a hat-shape is studied. The problem is one of the famous tests from the Numisheet 93. As spring-back is generally a quasi-static
Introduction to Optimization
 Introduction to Optimization Second Order Optimization Methods Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart Planned Outline Gradient-based optimization (1st order methods) plain grad., steepest descent, conjugate grad.,
Introduction to Optimization Second Order Optimization Methods Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart Planned Outline Gradient-based optimization (1st order methods) plain grad., steepest descent, conjugate grad.,
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems. Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi, J.P. Escallo n Lecture December, 2013
 The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi, J.P. Escallo n Lecture 11-17 December, 2013 Institute of Structural Engineering Method of Finite Elements
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi, J.P. Escallo n Lecture 11-17 December, 2013 Institute of Structural Engineering Method of Finite Elements
Constrained and Unconstrained Optimization
 Constrained and Unconstrained Optimization Carlos Hurtado Department of Economics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign hrtdmrt2@illinois.edu Oct 10th, 2017 C. Hurtado (UIUC - Economics) Numerical
Constrained and Unconstrained Optimization Carlos Hurtado Department of Economics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign hrtdmrt2@illinois.edu Oct 10th, 2017 C. Hurtado (UIUC - Economics) Numerical
Scientific Manual FEM-Design 17.0
 Scientific Manual FEM-Design 17. 1.4.6 Calculations considering diaphragms All of the available calculation in FEM-Design can be performed with diaphragms or without diaphragms if the diaphragms were defined
Scientific Manual FEM-Design 17. 1.4.6 Calculations considering diaphragms All of the available calculation in FEM-Design can be performed with diaphragms or without diaphragms if the diaphragms were defined
Fast marching methods
 1 Fast marching methods Lecture 3 Alexander & Michael Bronstein tosca.cs.technion.ac.il/book Numerical geometry of non-rigid shapes Stanford University, Winter 2009 Metric discretization 2 Approach I:
1 Fast marching methods Lecture 3 Alexander & Michael Bronstein tosca.cs.technion.ac.il/book Numerical geometry of non-rigid shapes Stanford University, Winter 2009 Metric discretization 2 Approach I:
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1
 Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1 2 Outline
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1 2 Outline
Classical Gradient Methods
 Classical Gradient Methods Note simultaneous course at AMSI (math) summer school: Nonlin. Optimization Methods (see http://wwwmaths.anu.edu.au/events/amsiss05/) Recommended textbook (Springer Verlag, 1999):
Classical Gradient Methods Note simultaneous course at AMSI (math) summer school: Nonlin. Optimization Methods (see http://wwwmaths.anu.edu.au/events/amsiss05/) Recommended textbook (Springer Verlag, 1999):
10.7 Variable Metric Methods in Multidimensions
 10.7 Variable Metric Methods in Multidimensions 425 *fret=dbrent(ax,xx,bx,f1dim,df1dim,tol,&xmin); for (j=1;j
10.7 Variable Metric Methods in Multidimensions 425 *fret=dbrent(ax,xx,bx,f1dim,df1dim,tol,&xmin); for (j=1;j
Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering
 Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Here SolidWorks stress simulation tutorials will be re-visited to show how they
Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Here SolidWorks stress simulation tutorials will be re-visited to show how they
Under the Hood of Implicit LS-DYNA
 4 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Implicit / New Developments Under the Hood of Implicit LS-DYNA Cleve Ashcraft Roger Grimes Brad Maker May 2003 1 Implicit in LS-DYNA v. 970 LS-DYNA v. 970 has an
4 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Implicit / New Developments Under the Hood of Implicit LS-DYNA Cleve Ashcraft Roger Grimes Brad Maker May 2003 1 Implicit in LS-DYNA v. 970 LS-DYNA v. 970 has an
25. NLP algorithms. ˆ Overview. ˆ Local methods. ˆ Constrained optimization. ˆ Global methods. ˆ Black-box methods.
 CS/ECE/ISyE 524 Introduction to Optimization Spring 2017 18 25. NLP algorithms ˆ Overview ˆ Local methods ˆ Constrained optimization ˆ Global methods ˆ Black-box methods ˆ Course wrap-up Laurent Lessard
CS/ECE/ISyE 524 Introduction to Optimization Spring 2017 18 25. NLP algorithms ˆ Overview ˆ Local methods ˆ Constrained optimization ˆ Global methods ˆ Black-box methods ˆ Course wrap-up Laurent Lessard
Solving systems of nonlinear equations with arbitrary precision
 Solving systems of nonlinear equations with arbitrary precision CES Seminar January 2017 Presented by Supervisor Gregor Heiming Dr. Ralf Hannemann-Tamás Systemverfahrenstechnik AVT, RWTH Aachen University
Solving systems of nonlinear equations with arbitrary precision CES Seminar January 2017 Presented by Supervisor Gregor Heiming Dr. Ralf Hannemann-Tamás Systemverfahrenstechnik AVT, RWTH Aachen University
Efficient Tuning of SVM Hyperparameters Using Radius/Margin Bound and Iterative Algorithms
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS, VOL. 13, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 2002 1225 Efficient Tuning of SVM Hyperparameters Using Radius/Margin Bound and Iterative Algorithms S. Sathiya Keerthi Abstract This paper
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS, VOL. 13, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 2002 1225 Efficient Tuning of SVM Hyperparameters Using Radius/Margin Bound and Iterative Algorithms S. Sathiya Keerthi Abstract This paper
Multivariate Numerical Optimization
 Jianxin Wei March 1, 2013 Outline 1 Graphics for Function of Two Variables 2 Nelder-Mead Simplex Method 3 Steepest Descent Method 4 Newton s Method 5 Quasi-Newton s Method 6 Built-in R Function 7 Linear
Jianxin Wei March 1, 2013 Outline 1 Graphics for Function of Two Variables 2 Nelder-Mead Simplex Method 3 Steepest Descent Method 4 Newton s Method 5 Quasi-Newton s Method 6 Built-in R Function 7 Linear
APPLIED OPTIMIZATION WITH MATLAB PROGRAMMING
 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION WITH MATLAB PROGRAMMING Second Edition P. Venkataraman Rochester Institute of Technology WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. CONTENTS PREFACE xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1. Optimization Fundamentals
APPLIED OPTIMIZATION WITH MATLAB PROGRAMMING Second Edition P. Venkataraman Rochester Institute of Technology WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. CONTENTS PREFACE xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1. Optimization Fundamentals
A Brief Look at Optimization
 A Brief Look at Optimization CSC 412/2506 Tutorial David Madras January 18, 2018 Slides adapted from last year s version Overview Introduction Classes of optimization problems Linear programming Steepest
A Brief Look at Optimization CSC 412/2506 Tutorial David Madras January 18, 2018 Slides adapted from last year s version Overview Introduction Classes of optimization problems Linear programming Steepest
Parameters Estimation of Material Constitutive Models using Optimization Algorithms
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Parameters Estimation of Material Constitutive Models using Optimization
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Parameters Estimation of Material Constitutive Models using Optimization
Chapter 3 Numerical Methods
 Chapter 3 Numerical Methods Part 1 3.1 Linearization and Optimization of Functions of Vectors 1 Problem Notation 2 Outline 3.1.1 Linearization 3.1.2 Optimization of Objective Functions 3.1.3 Constrained
Chapter 3 Numerical Methods Part 1 3.1 Linearization and Optimization of Functions of Vectors 1 Problem Notation 2 Outline 3.1.1 Linearization 3.1.2 Optimization of Objective Functions 3.1.3 Constrained
Maximum Likelihood estimation: Stata vs. Gauss
 Maximum Likelihood estimation: Stata vs. Gauss Index Motivation Objective The Maximum Likelihood Method Capabilities: Stata vs Gauss Conclusions Motivation Stata is a powerful and flexible statistical
Maximum Likelihood estimation: Stata vs. Gauss Index Motivation Objective The Maximum Likelihood Method Capabilities: Stata vs Gauss Conclusions Motivation Stata is a powerful and flexible statistical
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering. Introduction
 Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Solving IK problems for open chains using optimization methods
 Proceedings of the International Multiconference on Computer Science and Information Technology pp. 933 937 ISBN 978-83-60810-14-9 ISSN 1896-7094 Solving IK problems for open chains using optimization
Proceedings of the International Multiconference on Computer Science and Information Technology pp. 933 937 ISBN 978-83-60810-14-9 ISSN 1896-7094 Solving IK problems for open chains using optimization
Chapter 6. Curves and Surfaces. 6.1 Graphs as Surfaces
 Chapter 6 Curves and Surfaces In Chapter 2 a plane is defined as the zero set of a linear function in R 3. It is expected a surface is the zero set of a differentiable function in R n. To motivate, graphs
Chapter 6 Curves and Surfaces In Chapter 2 a plane is defined as the zero set of a linear function in R 3. It is expected a surface is the zero set of a differentiable function in R n. To motivate, graphs
Modern Methods of Data Analysis - WS 07/08
 Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture XV (04.02.08) Contents: Function Minimization (see E. Lohrmann & V. Blobel) Optimization Problem Set of n independent variables Sometimes in addition some constraints
Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture XV (04.02.08) Contents: Function Minimization (see E. Lohrmann & V. Blobel) Optimization Problem Set of n independent variables Sometimes in addition some constraints
A Study on the Optimization Methods for Optomechanical Alignment
 A Study on the Optimization Methods for Optomechanical Alignment Ming-Ta Yu a, Tsung-Yin Lin b *, Yi-You Li a, and Pei-Feng Shu a a Dept. of Mech. Eng., National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan,
A Study on the Optimization Methods for Optomechanical Alignment Ming-Ta Yu a, Tsung-Yin Lin b *, Yi-You Li a, and Pei-Feng Shu a a Dept. of Mech. Eng., National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan,
User-defined elements, Section of the Abaqus Analysis User's Manual
 1.1.22 UEL User subroutine to define an element. Product: Abaqus/Standard References Overview Warning: This feature is intended for advanced users only. Its use in all but the simplest test examples will
1.1.22 UEL User subroutine to define an element. Product: Abaqus/Standard References Overview Warning: This feature is intended for advanced users only. Its use in all but the simplest test examples will
Recent Developments in Model-based Derivative-free Optimization
 Recent Developments in Model-based Derivative-free Optimization Seppo Pulkkinen April 23, 2010 Introduction Problem definition The problem we are considering is a nonlinear optimization problem with constraints:
Recent Developments in Model-based Derivative-free Optimization Seppo Pulkkinen April 23, 2010 Introduction Problem definition The problem we are considering is a nonlinear optimization problem with constraints:
SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS Widely used in the mathematical modeling of real world phenomena. We introduce some numerical methods for their solution. For better intuition, we examine systems of two
SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS Widely used in the mathematical modeling of real world phenomena. We introduce some numerical methods for their solution. For better intuition, we examine systems of two
Writing User Subroutines with Abaqus
 Day 1 Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture 2: User Subroutines (V)DLOAD and UTRACLOAD Lecture 3: User Subroutine FILM Workshop 1: User Subroutine FILM Lecture 4: User Subroutine (V)USDFLD Lecture 5: User Subroutine
Day 1 Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture 2: User Subroutines (V)DLOAD and UTRACLOAD Lecture 3: User Subroutine FILM Workshop 1: User Subroutine FILM Lecture 4: User Subroutine (V)USDFLD Lecture 5: User Subroutine
OPTIMIZATION OF STIFFENED LAMINATED COMPOSITE CYLINDRICAL PANELS IN THE BUCKLING AND POSTBUCKLING ANALYSIS.
 OPTIMIZATION OF STIFFENED LAMINATED COMPOSITE CYLINDRICAL PANELS IN THE BUCKLING AND POSTBUCKLING ANALYSIS. A. Korjakin, A.Ivahskov, A. Kovalev Stiffened plates and curved panels are widely used as primary
OPTIMIZATION OF STIFFENED LAMINATED COMPOSITE CYLINDRICAL PANELS IN THE BUCKLING AND POSTBUCKLING ANALYSIS. A. Korjakin, A.Ivahskov, A. Kovalev Stiffened plates and curved panels are widely used as primary
Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning
 Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning Part 2 Institute of Bioinformatics Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria Outline 1 Introduction 2 Generalization Error 3 Maximum Likelihood 4 Noise Models 5
Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning Part 2 Institute of Bioinformatics Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria Outline 1 Introduction 2 Generalization Error 3 Maximum Likelihood 4 Noise Models 5
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis
 Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Simulation in Computer Graphics. Deformable Objects. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Deformable Objects Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction forces performance collision handling visualization University
Simulation in Computer Graphics Deformable Objects Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction forces performance collision handling visualization University
Convex Optimization CMU-10725
 Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Conjugate Direction Methods Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Conjugate Direction Methods 2 Books to Read David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye: Linear and Nonlinear Programming Nesterov:
Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Conjugate Direction Methods Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Conjugate Direction Methods 2 Books to Read David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye: Linear and Nonlinear Programming Nesterov:
FORMING SIMULATION USING RIGID-PLASTIC MATERIAL MODEL IN MARC
 SESSION TITLE WILL BE COMPLETED BY MSC SOFTWARE FORMING SIMULATION USING RIGID-PLASTIC MATERIAL MODEL IN MARC Gary Huang, Simufact-Americas LLC April 8, 2013 SUMMARY When simulating large deformation in
SESSION TITLE WILL BE COMPLETED BY MSC SOFTWARE FORMING SIMULATION USING RIGID-PLASTIC MATERIAL MODEL IN MARC Gary Huang, Simufact-Americas LLC April 8, 2013 SUMMARY When simulating large deformation in
EULER-TYPE ALGORITHM APPLIED TO LEVELING PROCESS ANALYSIS
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 21, 2014, No. 3, p. 185 191 185 EULER-TYPE ALGORITHM APPLIED TO LEVELING PROCESS ANALYSIS František Šebek*, Jindřich Petruška*, Tomáš Návrat* Presented paper is focused on description
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 21, 2014, No. 3, p. 185 191 185 EULER-TYPE ALGORITHM APPLIED TO LEVELING PROCESS ANALYSIS František Šebek*, Jindřich Petruška*, Tomáš Návrat* Presented paper is focused on description
Ellipsoid Algorithm :Algorithms in the Real World. Ellipsoid Algorithm. Reduction from general case
 Ellipsoid Algorithm 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World Linear and Integer Programming II Ellipsoid algorithm Interior point methods First polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming (Khachian 79)
Ellipsoid Algorithm 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World Linear and Integer Programming II Ellipsoid algorithm Interior point methods First polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming (Khachian 79)
Optimization 3.1. for GAUSS TM. Aptech Systems, Inc.
 Optimization 3.1 for GAUSS TM Aptech Systems, Inc. Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of Aptech Systems, Inc. The software
Optimization 3.1 for GAUSS TM Aptech Systems, Inc. Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of Aptech Systems, Inc. The software
A CONJUGATE DIRECTION IMPLEMENTATION OF THE BFGS ALGORITHM WITH AUTOMATIC SCALING. Ian D Coope
 i A CONJUGATE DIRECTION IMPLEMENTATION OF THE BFGS ALGORITHM WITH AUTOMATIC SCALING Ian D Coope No. 42 December 1987 A CONJUGATE DIRECTION IMPLEMENTATION OF THE BFGS ALGORITHM WITH AUTOMATIC SCALING IAN
i A CONJUGATE DIRECTION IMPLEMENTATION OF THE BFGS ALGORITHM WITH AUTOMATIC SCALING Ian D Coope No. 42 December 1987 A CONJUGATE DIRECTION IMPLEMENTATION OF THE BFGS ALGORITHM WITH AUTOMATIC SCALING IAN
Some Aspects for the Simulation of a Non-Linear Problem with Plasticity and Contact
 Some Aspects for the Simulation of a Non-Linear Problem with Plasticity and Contact Eduardo Luís Gaertner Marcos Giovani Dropa de Bortoli EMBRACO S.A. Abstract A linear elastic model is often not appropriate
Some Aspects for the Simulation of a Non-Linear Problem with Plasticity and Contact Eduardo Luís Gaertner Marcos Giovani Dropa de Bortoli EMBRACO S.A. Abstract A linear elastic model is often not appropriate
Contents. I Basics 1. Copyright by SIAM. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
Lecture 6 - Multivariate numerical optimization
 Lecture 6 - Multivariate numerical optimization Björn Andersson (w/ Jianxin Wei) Department of Statistics, Uppsala University February 13, 2014 1 / 36 Table of Contents 1 Plotting functions of two variables
Lecture 6 - Multivariate numerical optimization Björn Andersson (w/ Jianxin Wei) Department of Statistics, Uppsala University February 13, 2014 1 / 36 Table of Contents 1 Plotting functions of two variables
OPTIMIZATION FOR AUTOMATIC HISTORY MATCHING
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 131 137 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information OPTIMIZATION FOR AUTOMATIC HISTORY MATCHING Abstract. SHUGUANG
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 131 137 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information OPTIMIZATION FOR AUTOMATIC HISTORY MATCHING Abstract. SHUGUANG
Prosurv cez Users Manual. cez Conversions. Prosurv cez Conversions has 14 functions as shown above.
 cez Conversions Prosurv cez Conversions has 14 functions as shown above. Azimuth to Bearing Enter an Azimuth and it s corresponding Bearing is computed and displayed. Note that many functions in Prosurv
cez Conversions Prosurv cez Conversions has 14 functions as shown above. Azimuth to Bearing Enter an Azimuth and it s corresponding Bearing is computed and displayed. Note that many functions in Prosurv
Locking-Free Smoothed Finite Element Method with Tetrahedral/Triangular Mesh Rezoning in Severely Large Deformation Problems
 Locking-Free Smoothed Finite Element Method with Tetrahedral/Triangular Mesh Rezoning in Severely Large Deformation Problems Yuki ONISHI, Kenji AMAYA Tokyo Institute of Technology (Japan) P. 1 P. 1 Motivation
Locking-Free Smoothed Finite Element Method with Tetrahedral/Triangular Mesh Rezoning in Severely Large Deformation Problems Yuki ONISHI, Kenji AMAYA Tokyo Institute of Technology (Japan) P. 1 P. 1 Motivation
Written exams of Robotics 2
 Written exams of Robotics 2 http://www.diag.uniroma1.it/~deluca/rob2_en.html All materials are in English, unless indicated (oldies are in Year Date (mm.dd) Number of exercises Topics 2018 07.11 4 Inertia
Written exams of Robotics 2 http://www.diag.uniroma1.it/~deluca/rob2_en.html All materials are in English, unless indicated (oldies are in Year Date (mm.dd) Number of exercises Topics 2018 07.11 4 Inertia
Nonlinear Real-time Finite Element Analysis using CUDA
 Nonlinear Real-time Finite Element Analysis using CUDA Biomechanics section KU Leuven Introduction Biomechanics & surgery application What are we trying to do? Why is FE relevant to us? FE and parallelization,
Nonlinear Real-time Finite Element Analysis using CUDA Biomechanics section KU Leuven Introduction Biomechanics & surgery application What are we trying to do? Why is FE relevant to us? FE and parallelization,
Workshop 15. Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate
 Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
Appendix E Calculating Normal Vectors
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Appendix E Calculating Normal Vectors This appendix describes how to calculate normal vectors for surfaces. You need to define normals to use
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Appendix E Calculating Normal Vectors This appendix describes how to calculate normal vectors for surfaces. You need to define normals to use
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS18. Lecture 2: Linear Regression Gradient Descent Non-linear basis functions
 COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS18 Lecture 2: Linear Regression Gradient Descent Non-linear basis functions LINEAR REGRESSION MOTIVATION Why Linear Regression? Simplest
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS18 Lecture 2: Linear Regression Gradient Descent Non-linear basis functions LINEAR REGRESSION MOTIVATION Why Linear Regression? Simplest
CHAPTER-10 DYNAMIC SIMULATION USING LS-DYNA
 DYNAMIC SIMULATION USING LS-DYNA CHAPTER-10 10.1 Introduction In the past few decades, the Finite Element Method (FEM) has been developed into a key indispensable technology in the modeling and simulation
DYNAMIC SIMULATION USING LS-DYNA CHAPTER-10 10.1 Introduction In the past few decades, the Finite Element Method (FEM) has been developed into a key indispensable technology in the modeling and simulation
Vehicle Load Area Division Wall Integrity during Frontal Crash
 Vehicle Load Area Division Wall Integrity during Frontal Crash H. Türkmen TOFAS Türk Otomobil Fabrikasi A.S. Abstract : This study addresses design efforts of a vehicle load area division wall and the
Vehicle Load Area Division Wall Integrity during Frontal Crash H. Türkmen TOFAS Türk Otomobil Fabrikasi A.S. Abstract : This study addresses design efforts of a vehicle load area division wall and the
Optimization in Scilab
 Scilab sheet Optimization in Scilab Scilab provides a high-level matrix language and allows to define complex mathematical models and to easily connect to existing libraries. That is why optimization is
Scilab sheet Optimization in Scilab Scilab provides a high-level matrix language and allows to define complex mathematical models and to easily connect to existing libraries. That is why optimization is
arxiv: v1 [cs.na] 28 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.na] 28 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.na] 28 Dec 2018](/thumbs/93/111369173.jpg) arxiv:1812.10986v1 [cs.na] 28 Dec 2018 Vilin: Unconstrained Numerical Optimization Application Marko Miladinović 1, Predrag Živadinović 2, 1,2 University of Niš, Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, Department
arxiv:1812.10986v1 [cs.na] 28 Dec 2018 Vilin: Unconstrained Numerical Optimization Application Marko Miladinović 1, Predrag Živadinović 2, 1,2 University of Niš, Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, Department
Introduction to Design Optimization
 Introduction to Design Optimization First Edition Krishnan Suresh i Dedicated to my family. They mean the world to me. ii Origins of this Text Preface Like many other textbooks, this text has evolved from
Introduction to Design Optimization First Edition Krishnan Suresh i Dedicated to my family. They mean the world to me. ii Origins of this Text Preface Like many other textbooks, this text has evolved from
Today s class. Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods. Numerical Methods, Fall 2011 Lecture 5. Prof. Jinbo Bi CSE, UConn
 Today s class Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods 1 False Position Method Although the interval [a,b] where the root becomes iteratively closer with the false position method, unlike
Today s class Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods 1 False Position Method Although the interval [a,b] where the root becomes iteratively closer with the false position method, unlike
Quiz 6 Practice Problems
 Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
course outline basic principles of numerical analysis, intro FEM
 idealization, equilibrium, solutions, interpretation of results types of numerical engineering problems continuous vs discrete systems direct stiffness approach differential & variational formulation introduction
idealization, equilibrium, solutions, interpretation of results types of numerical engineering problems continuous vs discrete systems direct stiffness approach differential & variational formulation introduction
Failure of Notched Laminates Under Out-of-Plane Bending Phase VII
 Failure of Notched Laminates Under Out-of-Plane Bending Phase VII Fall 2014 Meeting Mitchell Daniels, Levi Suryan, & John P. Parmigiani, Oregon State University Motivation and Key Issues Failure of Notched
Failure of Notched Laminates Under Out-of-Plane Bending Phase VII Fall 2014 Meeting Mitchell Daniels, Levi Suryan, & John P. Parmigiani, Oregon State University Motivation and Key Issues Failure of Notched
A Locking-free Smoothed Finite Element Formulation (Modified Selective FS/NS-FEM-T4) with Tetrahedral Mesh Rezoning for Large Deformation Problems
 A Locking-free Smoothed Finite Element Formulation (Modified Selective FS/NS-FEM-T4) with Tetrahedral Mesh Rezoning for Large Deformation Problems Yuki ONISHI, Kenji AMAYA Tokyo Institute of Technology
A Locking-free Smoothed Finite Element Formulation (Modified Selective FS/NS-FEM-T4) with Tetrahedral Mesh Rezoning for Large Deformation Problems Yuki ONISHI, Kenji AMAYA Tokyo Institute of Technology
Direction Fields; Euler s Method
 Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Module 1 Lecture Notes 2. Optimization Problem and Model Formulation
 Optimization Methods: Introduction and Basic concepts 1 Module 1 Lecture Notes 2 Optimization Problem and Model Formulation Introduction In the previous lecture we studied the evolution of optimization
Optimization Methods: Introduction and Basic concepts 1 Module 1 Lecture Notes 2 Optimization Problem and Model Formulation Introduction In the previous lecture we studied the evolution of optimization
Introduction to optimization methods and line search
 Introduction to optimization methods and line search Jussi Hakanen Post-doctoral researcher jussi.hakanen@jyu.fi How to find optimal solutions? Trial and error widely used in practice, not efficient and
Introduction to optimization methods and line search Jussi Hakanen Post-doctoral researcher jussi.hakanen@jyu.fi How to find optimal solutions? Trial and error widely used in practice, not efficient and
Curve and Surface Basics
 Curve and Surface Basics Implicit and parametric forms Power basis form Bezier curves Rational Bezier Curves Tensor Product Surfaces ME525x NURBS Curve and Surface Modeling Page 1 Implicit and Parametric
Curve and Surface Basics Implicit and parametric forms Power basis form Bezier curves Rational Bezier Curves Tensor Product Surfaces ME525x NURBS Curve and Surface Modeling Page 1 Implicit and Parametric
Object Oriented Finite Element Modeling
 Object Oriented Finite Element Modeling Bořek Patzák Czech Technical University Faculty of Civil Engineering Department of Structural Mechanics Thákurova 7, 166 29 Prague, Czech Republic January 2, 2018
Object Oriented Finite Element Modeling Bořek Patzák Czech Technical University Faculty of Civil Engineering Department of Structural Mechanics Thákurova 7, 166 29 Prague, Czech Republic January 2, 2018
Linear Separability. Linear Separability. Capabilities of Threshold Neurons. Capabilities of Threshold Neurons. Capabilities of Threshold Neurons
 Linear Separability Input space in the two-dimensional case (n = ): - - - - - - w =, w =, = - - - - - - w = -, w =, = - - - - - - w = -, w =, = Linear Separability So by varying the weights and the threshold,
Linear Separability Input space in the two-dimensional case (n = ): - - - - - - w =, w =, = - - - - - - w = -, w =, = - - - - - - w = -, w =, = Linear Separability So by varying the weights and the threshold,
NAG Library Routine Document C05RBF.1
 C05 Roots of One or More Transcendental Equations NAG Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised
C05 Roots of One or More Transcendental Equations NAG Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised
Tested Paradigm to Include Optimization in Machine Learning Algorithms
 Tested Paradigm to Include Optimization in Machine Learning Algorithms Aishwarya Asesh School of Computing Science and Engineering VIT University Vellore, India International Journal of Engineering Research
Tested Paradigm to Include Optimization in Machine Learning Algorithms Aishwarya Asesh School of Computing Science and Engineering VIT University Vellore, India International Journal of Engineering Research
Iterative Methods for Solving Linear Problems
 Iterative Methods for Solving Linear Problems When problems become too large (too many data points, too many model parameters), SVD and related approaches become impractical. Iterative Methods for Solving
Iterative Methods for Solving Linear Problems When problems become too large (too many data points, too many model parameters), SVD and related approaches become impractical. Iterative Methods for Solving
( ) 2. Integration. 1. Calculate (a) x2 (x 5) dx (b) y = x 2 6x. 2. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite.
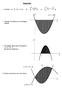 Integration 1. Calculate (a) ( 5) d (b) 4 + 3 1 d (c) ( ) + d 1 = 6. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite. 3. The diagram shows part of the graph of = 7 10. 5 = + 0 4. Find the area between
Integration 1. Calculate (a) ( 5) d (b) 4 + 3 1 d (c) ( ) + d 1 = 6. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite. 3. The diagram shows part of the graph of = 7 10. 5 = + 0 4. Find the area between
Tracking Minimum Distances between Curved Objects with Parametric Surfaces in Real Time
 Tracking Minimum Distances between Curved Objects with Parametric Surfaces in Real Time Zhihua Zou, Jing Xiao Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina Charlotte zzou28@yahoo.com, xiao@uncc.edu
Tracking Minimum Distances between Curved Objects with Parametric Surfaces in Real Time Zhihua Zou, Jing Xiao Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina Charlotte zzou28@yahoo.com, xiao@uncc.edu
Algebraic Iterative Methods for Computed Tomography
 Algebraic Iterative Methods for Computed Tomography Per Christian Hansen DTU Compute Department of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science Technical University of Denmark Per Christian Hansen Algebraic
Algebraic Iterative Methods for Computed Tomography Per Christian Hansen DTU Compute Department of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science Technical University of Denmark Per Christian Hansen Algebraic
LECTURE NOTES Non-Linear Programming
 CEE 6110 David Rosenberg p. 1 Learning Objectives LECTURE NOTES Non-Linear Programming 1. Write out the non-linear model formulation 2. Describe the difficulties of solving a non-linear programming model
CEE 6110 David Rosenberg p. 1 Learning Objectives LECTURE NOTES Non-Linear Programming 1. Write out the non-linear model formulation 2. Describe the difficulties of solving a non-linear programming model
AN UNCONSTRAINED NONLINEAR OPTIMIZATION SOLVER: A USER S GUIDE
 AN UNONSTRAINED NONLINEAR OPTIMIZATION SOLVER: A USER S GUIDE 1. Introduction This modular software package has been designed to solve the unconstrained nonlinear optimization problem. This problem entails
AN UNONSTRAINED NONLINEAR OPTIMIZATION SOLVER: A USER S GUIDE 1. Introduction This modular software package has been designed to solve the unconstrained nonlinear optimization problem. This problem entails
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURES IN FEM-BASED SOFTWARE MASTER THESIS
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURES IN FEM-BASED SOFTWARE MASTER THESIS ARCHINEER INSTITUTES FOR MEMBRANE AND SHELL TECHNOLOGIES, BUILDING AND REAL ESTATE e.v. ANHALT UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURES IN FEM-BASED SOFTWARE MASTER THESIS ARCHINEER INSTITUTES FOR MEMBRANE AND SHELL TECHNOLOGIES, BUILDING AND REAL ESTATE e.v. ANHALT UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES
CHAPTER VI BACK PROPAGATION ALGORITHM
 6.1 Introduction CHAPTER VI BACK PROPAGATION ALGORITHM In the previous chapter, we analysed that multiple layer perceptrons are effectively applied to handle tricky problems if trained with a vastly accepted
6.1 Introduction CHAPTER VI BACK PROPAGATION ALGORITHM In the previous chapter, we analysed that multiple layer perceptrons are effectively applied to handle tricky problems if trained with a vastly accepted
NAG Library Routine Document C05PBF/C05PBA
 NAG Library Routine Document /C05PBA Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
NAG Library Routine Document /C05PBA Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
EN234: Computational methods in Structural and Solid Mechanics EN234FEA TUTORIAL
 EN234: Computational methods in Structural and Solid Mechanics EN234FEA TUTORIAL School of Engineering Brown University BEFORE DOING THIS TUTORIAL YOU WILL NEED TO INSTALL FORTRAN, TECPLOT, AND ECLIPSE,
EN234: Computational methods in Structural and Solid Mechanics EN234FEA TUTORIAL School of Engineering Brown University BEFORE DOING THIS TUTORIAL YOU WILL NEED TO INSTALL FORTRAN, TECPLOT, AND ECLIPSE,
NAG Fortran Library Routine Document C05PBF.1
 C05 Roots of One or More Transcendental Equations NAG Fortran Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of
C05 Roots of One or More Transcendental Equations NAG Fortran Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of
Numerical Optimization: Introduction and gradient-based methods
 Numerical Optimization: Introduction and gradient-based methods Master 2 Recherche LRI Apprentissage Statistique et Optimisation Anne Auger Inria Saclay-Ile-de-France November 2011 http://tao.lri.fr/tiki-index.php?page=courses
Numerical Optimization: Introduction and gradient-based methods Master 2 Recherche LRI Apprentissage Statistique et Optimisation Anne Auger Inria Saclay-Ile-de-France November 2011 http://tao.lri.fr/tiki-index.php?page=courses
Discontinuous Galerkin Sparse Grid method for Maxwell s equations
 Discontinuous Galerkin Sparse Grid method for Maxwell s equations Student: Tianyang Wang Mentor: Dr. Lin Mu, Dr. David L.Green, Dr. Ed D Azevedo, Dr. Kwai Wong Motivation u We consider the Maxwell s equations,
Discontinuous Galerkin Sparse Grid method for Maxwell s equations Student: Tianyang Wang Mentor: Dr. Lin Mu, Dr. David L.Green, Dr. Ed D Azevedo, Dr. Kwai Wong Motivation u We consider the Maxwell s equations,
CS281 Section 3: Practical Optimization
 CS281 Section 3: Practical Optimization David Duvenaud and Dougal Maclaurin Most parameter estimation problems in machine learning cannot be solved in closed form, so we often have to resort to numerical
CS281 Section 3: Practical Optimization David Duvenaud and Dougal Maclaurin Most parameter estimation problems in machine learning cannot be solved in closed form, so we often have to resort to numerical
Behaviour of cold bent glass plates during the shaping process
 Behaviour of cold bent glass plates during the shaping process Kyriaki G. DATSIOU *, Mauro OVEREND a * Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge Trumpington Street, Cambridge, CB2 1PZ, UK kd365@cam.ac.uk
Behaviour of cold bent glass plates during the shaping process Kyriaki G. DATSIOU *, Mauro OVEREND a * Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge Trumpington Street, Cambridge, CB2 1PZ, UK kd365@cam.ac.uk
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
Optimization. Industrial AI Lab.
 Optimization Industrial AI Lab. Optimization An important tool in 1) Engineering problem solving and 2) Decision science People optimize Nature optimizes 2 Optimization People optimize (source: http://nautil.us/blog/to-save-drowning-people-ask-yourself-what-would-light-do)
Optimization Industrial AI Lab. Optimization An important tool in 1) Engineering problem solving and 2) Decision science People optimize Nature optimizes 2 Optimization People optimize (source: http://nautil.us/blog/to-save-drowning-people-ask-yourself-what-would-light-do)
Image Compression: An Artificial Neural Network Approach
 Image Compression: An Artificial Neural Network Approach Anjana B 1, Mrs Shreeja R 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Calicut University, Kuttippuram 2 Department of Computer Science and
Image Compression: An Artificial Neural Network Approach Anjana B 1, Mrs Shreeja R 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Calicut University, Kuttippuram 2 Department of Computer Science and
Recapitulation on Transformations in Neural Network Back Propagation Algorithm
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 4 (2013), pp. 323-328 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Recapitulation
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 4 (2013), pp. 323-328 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Recapitulation
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
Optimization with Gradient and Hessian Information Calculated Using Hyper-Dual Numbers
 Optimization with Gradient and Hessian Information Calculated Using Hyper-Dual Numbers Jeffrey A. Fike and Juan J. Alonso Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305,
Optimization with Gradient and Hessian Information Calculated Using Hyper-Dual Numbers Jeffrey A. Fike and Juan J. Alonso Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305,
AP Calculus BC Course Description
 AP Calculus BC Course Description COURSE OUTLINE: The following topics define the AP Calculus BC course as it is taught over three trimesters, each consisting of twelve week grading periods. Limits and
AP Calculus BC Course Description COURSE OUTLINE: The following topics define the AP Calculus BC course as it is taught over three trimesters, each consisting of twelve week grading periods. Limits and
C3 Numerical methods
 Verulam School C3 Numerical methods 138 min 108 marks 1. (a) The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines x = 1, x = 5 and y = 0. The region
Verulam School C3 Numerical methods 138 min 108 marks 1. (a) The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines x = 1, x = 5 and y = 0. The region
4-2 Quasi-Static Fatigue
 1 4-2 Quasi-Static Fatigue Case Description: Example Location: Composite coupon subject to tensile cyclic loading Tutorials > Fatigue > Quasi Static Fatigue Model Description: Nodes: 261; Elements: 224
1 4-2 Quasi-Static Fatigue Case Description: Example Location: Composite coupon subject to tensile cyclic loading Tutorials > Fatigue > Quasi Static Fatigue Model Description: Nodes: 261; Elements: 224
