Continuum error recognition and error analysis
|
|
|
- Austen Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Continuum error recognition and error analysis Robert Laing (ESO) 1
2 Outline Error recognition: how do you recognise and diagnose residual errors by looking at images? Image analysis: how do you extract scientifically useful numbers from images Unless otherwise specified, this talk is about continuum imaging in full polarization... but many ideas also apply to spectral-line work. 2
3 Is my image good enough? No Yes 3
4 How can I tell (1)? Look at the off-source rms noise Are there obvious artefacts? Use on-line calculators (e.g. JVLA, ALMA) or formulae Measure rms with (e.g.) casa viewer or imstat Does the image rms increase near bright sources? Is the noise random or are there ripples? Compare the noise distributions for IQUV Coherent I features <-4σ Rings, streaks etc. Properties of artefacts Additive (constant over the field) or multiplicative (scales with brightness)? Symmetric or antisymmetric around bright sources? 4
5 How can I tell (2)? Large-scale negative structures Negative bowl' around source structure Large-scale sinusoidal ripples Missing short spacings Unnatural small-scale on-source structure Deconvolution errors (often associated with Diffuse structure looks spotty poor u,v coverage Short-wavelength sinusoidal ripples 5
6 Possible causes: imaging problems (1) Is the image big enough? Are the pixels small enough to sample the beam? Aliasing Confusing sources outside the image Make a wider-field, tapered image and look Look in standard catalogues (NVSS) Are bright point sources accurately located on pixels? Wide-field issues (calculate expected effects) Averaging time too long? (Azimuthal smearing radius) Spectral channels too wide? (Radial smearing radius) w-term? ionosphere? direction dependence of antenna response (e.g. pointing errors at high frequencies; station beams at low frequencies)? 6
7 Possible causes: imaging problems (2) Missing short spacings Primary beam effects Deconvolution errors, especially with sparse u-v coverage Resolution too high? Poor choice of weighting? Bad choice of CLEAN boxes (too small, too large,...) Insufficient CLEANing single-scale CLEAN not good enough Source variability during the observations 7
8 Errors in the image and (u, v) planes Errors obey Fourier relations between (u, v) and image planes Particularly helpful in recognising additive errors e.g. single very high visibility: sinusoidal fringe Easier to recognise narrow features Orientations are orthogonal u-v amplitude errors cause symmetric errors in the image plane u-v phase errors cause antisymmetric errors in the image plane 8
9 (u, v) or image plane? Find the outliers in the u-v plane first Gross (MJy) points have gross effects on the image (these should have been flagged, but mistakes happen) A fraction f of bad data points with reasonable amplitudes give fractional error ~f in the image Low-level, but persistent errors are often easier to see in the image plane Rule of thumb: 10 deg phase error 20% amplitude error 9
10 Amplitude errors: all antennas 10% amplitude error for all antennas during one snapshot. rms 2.0 mjy No errors: peak 3.24 Jy; rms 0.11 mjy Error pattern looks like the dirty beam for a single VLA snapshot 10
11 One antenna in error at one time One antenna has 20% amplitude error during one snapshot: symmetric. rms 0.5 mjy One antenna has 10 deg phase error during one snapshot: antisymmetric. rms 0.5 mjy 11
12 One antenna in error: all times 10 deg phase error for one antenna; all times. Antisymmetric. 20% amplitude error for one antenna; all times. Symmetric. Multiplicative Can diagnose by dropping one antenna in turn and re-imaging 12
13 Non-closing errors With errors Without errors 13
14 CLEAN boxes too small Correct Too big Far too big CLEAN functions best when the area in which it finds components is restricted ( compact support ) 14
15 Deconvolution Errors VLA A+B+C configurations. Short spacings OK, but with poor A-configuration coverage Spots and ripples Conventional CLEAN fails: try multiresolution CLEAN or MEM or reduce the resolution 15
16 Multi-scale CLEAN helps 1-scale 3-scale 1-scale 3-scale Multi-scale CLEAN has removed a high-frequency ripple 16
17 Point source not on a pixel Compact source on a pixel Mis-centred by 0.5 pixel 17
18 Missing short spacings Bowl uv range < 225 kλ Messed up diffuse emission uv range kλ uv range kλ 18
19 Does the model fit the data (1)? Amplitude fits Plot amplitude against uv distance Data Model 19
20 Does the model fits the data (2) Phase fits 20
21 Does the model fit the data (3) The case of a bright source with a low-level error Error present (all antennas plotted) Nothing obvious Model subtracted (all except antenna 3 plotted). Some discrepant data 21 Model subtracted (antenna 3 only). Bad data clearly visible.
22 Summary of error recognition (u,v) plane Image plane Look for outliers (high or low) flagging tutorial Subtract the best model check residuals in amplitude and phase Do the defects look like the dirty beam? Additive or multiplicative? Symmetric or antisymmetric? Relate to possible data errors? Missing spacings? Deconvolution errors? If in doubt, simulate with realistic errors 22
23 Image Analysis Given: a well-calibrated dataset producing a high-quality image (or, in general, image cube) How can we extract scientifically useful numbers? This is a very open-ended problem, depending on: image complexity scientific goals Selected topics (excluding spectral line): Picking the correct resolution Parameter estimation Comparing images: spectra, polarization etc.; registration Getting images into your own code 23
24 Match the resolution to the problem 0.4 arcsec 1.65 arcsec Exactly the same dataset, imaged with different Gaussian tapers 24
25 Measure the off-source noise distribution Good case: rms = 7.5μJy; Gaussian noise with zero mean 25 Excess noise above Gaussian tail
26 Estimating the flux density of an extended source Use a low-resolution image, cleaned deeply The beam areas of the restored CLEAN components and residuals are not the same in general. Sum the flux density over some area (rectangular, polygonal,...) casa imstat, viewer. Remember that the total flux density is ΣI/B, where B is the integral over the beam. For a Gaussian, B = π(fwhm/pixel)2/4 ln 2. The reduction packages will calculate this for you. The reason is that the images are normalised so that a point source of flux density 1 Jy gives a peak response of 1 Jy/beam on the image. 26
27 Component fitting Image plane u-v plane Assume source components are ~Gaussian Deep cleaning restores images with Gaussian beam Size estimation quite straightforward casa imfit (although AIPS JMFIT is more reliable) More accurate for small numbers of ~point-like sources Can fit to models that are slightly more complex than point-like Accounts for imperfect sampling; noise distribution may be better understood, but no good for very complex brightness distributions Error estimates ad hoc From fitting routines By simulation 27
28 Error estimates for Gaussian fits Definitions P = peak component flux density σ = image rms noise θb = CLEAN beam size θobs = component size S = P/σ = signal/noise rms errors Error on peak flux density = σ Position error = θb/2s Assumes uncorrelated Gaussian random noise in the image plane not always true. True component size θ = (θobs2 θb2)1/2 Minimum measurable component size = θb/s1/2 S/N >100 is needed to determine a size <θb/10. 28
29 Automated image fitting Automated routines can be used to locate and fit sources (essential for surveys). SAD in AIPS is a good example. casa is weak in this area. Also adapt routines used in optical astronomy (e.g. Sextractor) beware incorrect noise model Often worthwhile to make Monte Carlo simulations to assess realistic errors in position and (especially) flux density (e.g. add model point sources). Automated fitting of images from the FIRST survey. 29
30 Basic image arithmetic Standard packages allow mathematical operations on one, two or occasionally more images (casa immath allows a lot of flexibility): Sum, product, quotient,... Polarized intensity and position angle from Q and U Spectral index α (S να) Faraday rotation measure Optical depth... Can also propagate noise and blank on input values or s/n and use masks Other image manipulations (spatial filtering, etc.) are also possible Current packages are poor at fitting functions of frequency to images at more than 2 frequencies, although they are getting better for standard operations. casa rmfit, spxfit 30
31 Basic image manipulation Often useful to make subimages Smooth images (e.g. if the restoring beam is not quite what you want) casa imsubimage Gaussian or user-supplied kernel casa imsmooth Regridding images Often needed (e.g.) to align two images with different coordinates, pixel sizes for comparison casa imregrid 31
32 Comparing images at different frequencies Match the resolutions Pick appropriate weighting and Gaussian taper to get approximately the same dirty beam FWHM Restore with the same beam Precise matching of coverage is not necessary Making the coverage of one dataset worse to match the other one often leads to disaster Error propagation Gaussian random noise in the image plane is the best case: you can only do worse Be careful near edges of the source and sharp brightness gradients 32
33 Spectral index and gradient filter 33
34 In-band spectra Total intensity at the reference frequency from casa clean with nterms = 2 Spectral index from clean, corrected for primary beam using widebandpbcor. (sign convention flipped from casa I ν-α) 2 GHz bandwidth; 5 GHz centre frequency, Jansky VLA 34
35 Integrated spectra Spectra derived by integrating the flux densities over the boxes shown on the previous slide. Note the slight flux scale error at 5 and 8.4 GHz. 35
36 Rotation Measure p exp(-kλ4) PA = PA(0) + RM λ2 36
37 Displaying polarization data p = P/I (P corrected for Ricean bias) Vectors; lengths p, directions along E-field direction + 900, after correction for Faraday rotation. 37
38 Regridding: radio optical overlay 1.4GHz radio (VLA) in red Optical (DSS) in blue 38
39 Regridding: radio X-ray overlay Radio (0.35 arcsec, 4.9 GHz, VLA) X-ray (0.6 arcsec, kev) 39
40 Issues in image registration Rationale for image combination Regridding Many astrophysical applications require multiwavelength comparison Proper motions may be important Tools available (casa imregrid) Accuracy of registration For purely radio data, ideally: Good astrometry is vital, but is not the subject of this lecture calibrator is close to the target use the same phase calibrator for all observations Watch out for errors from ionosphere, troposphere, antenna positions Use internal references if possible (e.g. point sources in the field) Beware changes in structure with frequency N.B.: images at other wavebands may have less accurate absolute astrometry 40
41 Registration errors Spectral index between and 4.9 GHz Relative shift of 0.2 FWHM 41
42 Getting data into your own code If the standard packages do not do what you want, do not be frightened of importing images into your own programs. FITS interchange standard can be read and written by all radio astronomy packages mostly standard for images (uv less so) well documented interfaces to common programming languages (python, C, fortran, IDL,...) and even to graphics manipulation packages (gimp) Easy read/write from casa to python arrays 42
43 Example: jet modelling Total intensity Vectors p/apparent B field 43
44 Summary of continuum image analysis Match the resolution to the problem For simple images, fit component parameters and derive errors Image comparison Simple mathematical operations are easy Regridding and interpolation often required Registration is an issue Noise propagation Straightforward to read images into your own code for more sophisticated modelling 44
ERROR RECOGNITION and IMAGE ANALYSIS
 PREAMBLE TO ERROR RECOGNITION and IMAGE ANALYSIS 2 Why are these two topics in the same lecture? ERROR RECOGNITION and IMAGE ANALYSIS Ed Fomalont Error recognition is used to determine defects in the data
PREAMBLE TO ERROR RECOGNITION and IMAGE ANALYSIS 2 Why are these two topics in the same lecture? ERROR RECOGNITION and IMAGE ANALYSIS Ed Fomalont Error recognition is used to determine defects in the data
ERROR RECOGNITION & IMAGE ANALYSIS. Gustaaf van Moorsel (NRAO) Ed Fomalont (NRAO) Twelfth Synthesis Imaging Workshop 2010 June 8-15
 ERROR RECOGNITION & IMAGE ANALYSIS Gustaaf van Moorsel (NRAO) Ed Fomalont (NRAO) Twelfth Synthesis Imaging Workshop 2010 June 8-15 INTRODUCTION Why are these two topics Error Recognition and Image Analysis
ERROR RECOGNITION & IMAGE ANALYSIS Gustaaf van Moorsel (NRAO) Ed Fomalont (NRAO) Twelfth Synthesis Imaging Workshop 2010 June 8-15 INTRODUCTION Why are these two topics Error Recognition and Image Analysis
Imaging and Deconvolution
 Imaging and Deconvolution Urvashi Rau National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, NM, USA The van-cittert Zernike theorem Ei E V ij u, v = I l, m e sky j 2 i ul vm dldm 2D Fourier transform : Image
Imaging and Deconvolution Urvashi Rau National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, NM, USA The van-cittert Zernike theorem Ei E V ij u, v = I l, m e sky j 2 i ul vm dldm 2D Fourier transform : Image
Lecture 17 Reprise: dirty beam, dirty image. Sensitivity Wide-band imaging Weighting
 Lecture 17 Reprise: dirty beam, dirty image. Sensitivity Wide-band imaging Weighting Uniform vs Natural Tapering De Villiers weighting Briggs-like schemes Reprise: dirty beam, dirty image. Fourier inversion
Lecture 17 Reprise: dirty beam, dirty image. Sensitivity Wide-band imaging Weighting Uniform vs Natural Tapering De Villiers weighting Briggs-like schemes Reprise: dirty beam, dirty image. Fourier inversion
Data Analysis. I have got some data, so what now? Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Australia Telescope National Facility 2 Oct 2008
 Data Analysis I have got some data, so what now? Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Australia Telescope National Facility 2 Oct 2008 1 Outline Non-imaging analysis Parameter estimation Point source fluxes,
Data Analysis I have got some data, so what now? Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Australia Telescope National Facility 2 Oct 2008 1 Outline Non-imaging analysis Parameter estimation Point source fluxes,
Synthesis Imaging. Claire Chandler, Sanjay Bhatnagar NRAO/Socorro
 Synthesis Imaging Claire Chandler, Sanjay Bhatnagar NRAO/Socorro Michelson Summer Workshop Caltech, July 24-28, 2006 Synthesis Imaging 2 Based on the van Cittert-Zernike theorem: The complex visibility
Synthesis Imaging Claire Chandler, Sanjay Bhatnagar NRAO/Socorro Michelson Summer Workshop Caltech, July 24-28, 2006 Synthesis Imaging 2 Based on the van Cittert-Zernike theorem: The complex visibility
Basic Imaging and Self- Calibration (T4 + T7)
 Basic Imaging and Self- Calibration (T4 + T7) John McKean Visibilities Fourier Transform Deconvolution AIM: 1. To make an image by taking the fast Fourier transform of the visibility data. 2. Carry out
Basic Imaging and Self- Calibration (T4 + T7) John McKean Visibilities Fourier Transform Deconvolution AIM: 1. To make an image by taking the fast Fourier transform of the visibility data. 2. Carry out
How accurately do our imaging algorithms reconstruct intensities and spectral indices of weak sources?
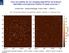 How accurately do our imaging algorithms reconstruct intensities and spectral indices of weak sources? Urvashi Rau, Sanjay Bhatnagar, Frazer Owen ( NRAO ) 29th Annual New Mexico Symposium, NRAO, Socorro,
How accurately do our imaging algorithms reconstruct intensities and spectral indices of weak sources? Urvashi Rau, Sanjay Bhatnagar, Frazer Owen ( NRAO ) 29th Annual New Mexico Symposium, NRAO, Socorro,
The Techniques of Radio Interferometry III: Imaging
 Master Astronomy and Astrophysics - 5214RAAS6Y Radio Astronomy Lecture 8 The Techniques of Radio Interferometry III: Imaging Lecturer: Michael Wise (wise@astron.nl) April 25th, 2013 Westerbork/LOFAR Field
Master Astronomy and Astrophysics - 5214RAAS6Y Radio Astronomy Lecture 8 The Techniques of Radio Interferometry III: Imaging Lecturer: Michael Wise (wise@astron.nl) April 25th, 2013 Westerbork/LOFAR Field
ADVANCED RADIO INTERFEROMETRIC IMAGING
 ADVANCED RADIO INTERFEROMETRIC IMAGING Hayden Rampadarath Based upon J. Radcliffe's DARA presentation Image courtesy of NRAO/AUI INTR ODU CT ION In the first imaging lecture, we discussed the overall and
ADVANCED RADIO INTERFEROMETRIC IMAGING Hayden Rampadarath Based upon J. Radcliffe's DARA presentation Image courtesy of NRAO/AUI INTR ODU CT ION In the first imaging lecture, we discussed the overall and
Imaging and non-imaging analysis
 1 Imaging and non-imaging analysis Greg Taylor University of New Mexico Spring 2017 Plan for the lecture-i 2 How do we go from the measurement of the coherence function (the Visibilities) to the images
1 Imaging and non-imaging analysis Greg Taylor University of New Mexico Spring 2017 Plan for the lecture-i 2 How do we go from the measurement of the coherence function (the Visibilities) to the images
Image Analysis. Jim Lovell
 Image Analysis Jim Lovell ATNF Synthesis Imaging Workshop May 2003 What Do You Want to Measure? (What you want to do and how to do it.)! Flux density of components! Absolute positions! Relative positions
Image Analysis Jim Lovell ATNF Synthesis Imaging Workshop May 2003 What Do You Want to Measure? (What you want to do and how to do it.)! Flux density of components! Absolute positions! Relative positions
Visualization & the CASA Viewer
 Visualization & the Viewer Juergen Ott & the team Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array Visualization Goals:
Visualization & the Viewer Juergen Ott & the team Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array Visualization Goals:
Fast Holographic Deconvolution
 Precision image-domain deconvolution for radio astronomy Ian Sullivan University of Washington 4/19/2013 Precision imaging Modern imaging algorithms grid visibility data using sophisticated beam models
Precision image-domain deconvolution for radio astronomy Ian Sullivan University of Washington 4/19/2013 Precision imaging Modern imaging algorithms grid visibility data using sophisticated beam models
TW Hya CASA Spectral Line Reduc6on Tutorial Imaging and Analysis
 TW Hya CASA Spectral Line Reduc6on Tutorial Imaging and Analysis Day 4, Wednesday September 9 th 12:15 HCO+(4-3) moment maps of TW Hya Tutors: Katharine Johnston Andy Biggs, Sandra Etoka, (Liz Humphreys),
TW Hya CASA Spectral Line Reduc6on Tutorial Imaging and Analysis Day 4, Wednesday September 9 th 12:15 HCO+(4-3) moment maps of TW Hya Tutors: Katharine Johnston Andy Biggs, Sandra Etoka, (Liz Humphreys),
ALMA Memo 386 ALMA+ACA Simulation Tool J. Pety, F. Gueth, S. Guilloteau IRAM, Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique 300 rue de la Piscine, F-3840
 ALMA Memo 386 ALMA+ACA Simulation Tool J. Pety, F. Gueth, S. Guilloteau IRAM, Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique 300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 Saint Martin d'h eres August 13, 2001 Abstract This
ALMA Memo 386 ALMA+ACA Simulation Tool J. Pety, F. Gueth, S. Guilloteau IRAM, Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique 300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 Saint Martin d'h eres August 13, 2001 Abstract This
FIFI-LS: Basic Cube Analysis using SOSPEX
 FIFI-LS: Basic Cube Analysis using SOSPEX Date: 1 Oct 2018 Revision: - CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 INGREDIENTS... 1 3 INSPECTING THE CUBE... 3 4 COMPARING TO A REFERENCE IMAGE... 5 5 REFERENCE VELOCITY
FIFI-LS: Basic Cube Analysis using SOSPEX Date: 1 Oct 2018 Revision: - CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 INGREDIENTS... 1 3 INSPECTING THE CUBE... 3 4 COMPARING TO A REFERENCE IMAGE... 5 5 REFERENCE VELOCITY
High Dynamic Range Imaging
 High Dynamic Range Imaging Josh Marvil CASS Radio Astronomy School 3 October 2014 CSIRO ASTRONOMY & SPACE SCIENCE High Dynamic Range Imaging Introduction Review of Clean Self- Calibration Direction Dependence
High Dynamic Range Imaging Josh Marvil CASS Radio Astronomy School 3 October 2014 CSIRO ASTRONOMY & SPACE SCIENCE High Dynamic Range Imaging Introduction Review of Clean Self- Calibration Direction Dependence
Deconvolution and Imaging ASTR 240: In-class activity, April 1, 2013
 Deconvolution and Imaging ASTR 240: In-class activity, April 1, 2013 In this activity, we will use calibrated visibilities from the Submillimeter Array to create an image of a disk around a nearby young
Deconvolution and Imaging ASTR 240: In-class activity, April 1, 2013 In this activity, we will use calibrated visibilities from the Submillimeter Array to create an image of a disk around a nearby young
OSKAR: Simulating data from the SKA
 OSKAR: Simulating data from the SKA Oxford e-research Centre, 4 June 2014 Fred Dulwich, Ben Mort, Stef Salvini 1 Overview Simulating interferometer data for SKA: Radio interferometry basics. Measurement
OSKAR: Simulating data from the SKA Oxford e-research Centre, 4 June 2014 Fred Dulwich, Ben Mort, Stef Salvini 1 Overview Simulating interferometer data for SKA: Radio interferometry basics. Measurement
Synthesis imaging using CASA
 Synthesis imaging using CASA Kuo-Song Wang ( 國松) and ARC-Taiwan team (ASIAA) UCAT Summer Student Program 2016 2016/06/30 Recap Radio interferometric observations The products from the array are Visibilities
Synthesis imaging using CASA Kuo-Song Wang ( 國松) and ARC-Taiwan team (ASIAA) UCAT Summer Student Program 2016 2016/06/30 Recap Radio interferometric observations The products from the array are Visibilities
Sky-domain algorithms to reconstruct spatial, spectral and time-variable structure of the sky-brightness distribution
 Sky-domain algorithms to reconstruct spatial, spectral and time-variable structure of the sky-brightness distribution Urvashi Rau National Radio Astronomy Observatory Socorro, NM, USA Outline : - Overview
Sky-domain algorithms to reconstruct spatial, spectral and time-variable structure of the sky-brightness distribution Urvashi Rau National Radio Astronomy Observatory Socorro, NM, USA Outline : - Overview
Radio Interferometry Bill Cotton, NRAO. Basic radio interferometry Emphasis on VLBI Imaging application
 Radio Interferometry Bill Cotton, NRAO Basic radio interferometry Emphasis on VLBI Imaging application 2 Simplest Radio Interferometer Monochromatic, point source 3 Interferometer response Adding quarter
Radio Interferometry Bill Cotton, NRAO Basic radio interferometry Emphasis on VLBI Imaging application 2 Simplest Radio Interferometer Monochromatic, point source 3 Interferometer response Adding quarter
Self-calibration: about the implementation in GILDAS. Vincent Piétu IRAM. IRAM millimeter interferometry summerschool
 Self-calibration: about the implementation in GILDAS Vincent Piétu IRAM 1 About an interferometer sensitivity One usually considers only the noise equation to assess the feasibility of an observation.
Self-calibration: about the implementation in GILDAS Vincent Piétu IRAM 1 About an interferometer sensitivity One usually considers only the noise equation to assess the feasibility of an observation.
Wideband Mosaic Imaging for VLASS
 Wideband Mosaic Imaging for VLASS Preliminary ARDG Test Report U.Rau & S.Bhatnagar 29 Aug 2018 (1) Code Validation and Usage (2) Noise, Weights, Continuum sensitivity (3) Imaging parameters (4) Understanding
Wideband Mosaic Imaging for VLASS Preliminary ARDG Test Report U.Rau & S.Bhatnagar 29 Aug 2018 (1) Code Validation and Usage (2) Noise, Weights, Continuum sensitivity (3) Imaging parameters (4) Understanding
High dynamic range imaging, computing & I/O load
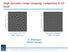 High dynamic range imaging, computing & I/O load RMS ~15µJy/beam RMS ~1µJy/beam S. Bhatnagar NRAO, Socorro Parameterized Measurement Equation Generalized Measurement Equation Obs [ S M V ij = J ij, t W
High dynamic range imaging, computing & I/O load RMS ~15µJy/beam RMS ~1µJy/beam S. Bhatnagar NRAO, Socorro Parameterized Measurement Equation Generalized Measurement Equation Obs [ S M V ij = J ij, t W
VERY LARGE TELESCOPE 3D Visualization Tool Cookbook
 European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere VERY LARGE TELESCOPE 3D Visualization Tool Cookbook VLT-SPE-ESO-19500-5652 Issue 1.0 10 July 2012 Prepared: Mark Westmoquette
European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere VERY LARGE TELESCOPE 3D Visualization Tool Cookbook VLT-SPE-ESO-19500-5652 Issue 1.0 10 July 2012 Prepared: Mark Westmoquette
GBT Memo #300: Correcting ALMA 12-m Array Data for Missing Short Spacings Using the Green Bank Telescope
 GBT Memo #300: Correcting ALMA 12-m Array Data for Missing Short Spacings Using the Green Bank Telescope Melissa Hoffman and Amanda Kepley 28 September 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Data 2 2.1 Observations
GBT Memo #300: Correcting ALMA 12-m Array Data for Missing Short Spacings Using the Green Bank Telescope Melissa Hoffman and Amanda Kepley 28 September 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Data 2 2.1 Observations
ALMA Memo No An Imaging Study for ACA. Min S. Yun. University of Massachusetts. April 1, Abstract
 ALMA Memo No. 368 An Imaging Study for ACA Min S. Yun University of Massachusetts April 1, 2001 Abstract 1 Introduction The ALMA Complementary Array (ACA) is one of the several new capabilities for ALMA
ALMA Memo No. 368 An Imaging Study for ACA Min S. Yun University of Massachusetts April 1, 2001 Abstract 1 Introduction The ALMA Complementary Array (ACA) is one of the several new capabilities for ALMA
Imaging and Deconvolution
 Imaging and Deconvolution 24-28 Sept 202 Narrabri, NSW, Australia Outline : - Synthesis Imaging Concepts - Imaging in Practice Urvashi Rau - Image-Reconstruction Algorithms National Radio Astronomy Observatory
Imaging and Deconvolution 24-28 Sept 202 Narrabri, NSW, Australia Outline : - Synthesis Imaging Concepts - Imaging in Practice Urvashi Rau - Image-Reconstruction Algorithms National Radio Astronomy Observatory
PACS Spectrometer Simulation and the Extended to Point Correction
 PACS Spectrometer Simulation and the Extended to Point Correction Jeroen de Jong February 11, 2016 Abstract This technical note describes simulating a PACS observation with a model source and its application
PACS Spectrometer Simulation and the Extended to Point Correction Jeroen de Jong February 11, 2016 Abstract This technical note describes simulating a PACS observation with a model source and its application
NRAO VLA Archive Survey
 NRAO VLA Archive Survey Jared H. Crossley, Loránt O. Sjouwerman, Edward B. Fomalont, and Nicole M. Radziwill National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 520 Edgemont Road, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA ABSTRACT
NRAO VLA Archive Survey Jared H. Crossley, Loránt O. Sjouwerman, Edward B. Fomalont, and Nicole M. Radziwill National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 520 Edgemont Road, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA ABSTRACT
CASA. Algorithms R&D. S. Bhatnagar. NRAO, Socorro
 Algorithms R&D S. Bhatnagar NRAO, Socorro Outline Broad areas of work 1. Processing for wide-field wide-band imaging Full-beam, Mosaic, wide-band, full-polarization Wide-band continuum and spectral-line
Algorithms R&D S. Bhatnagar NRAO, Socorro Outline Broad areas of work 1. Processing for wide-field wide-band imaging Full-beam, Mosaic, wide-band, full-polarization Wide-band continuum and spectral-line
Image Pixelization and Dynamic Range
 EVLA Memo 114 Image Pixelization and Dynamic Range W. D. Cotton, Juan M. Uson NRAO 1 Abstract This study investigates some of the effects of representing the sky by a rectangular grid of pixels on the
EVLA Memo 114 Image Pixelization and Dynamic Range W. D. Cotton, Juan M. Uson NRAO 1 Abstract This study investigates some of the effects of representing the sky by a rectangular grid of pixels on the
IRAM mm-interferometry School UV Plane Analysis. IRAM Grenoble
 IRAM mm-interferometry School 2004 1 UV Plane Analysis Frédéric Gueth IRAM Grenoble UV Plane analysis 2 UV Plane analysis The data are now calibrated as best as we can Caution: data are calibrated, but
IRAM mm-interferometry School 2004 1 UV Plane Analysis Frédéric Gueth IRAM Grenoble UV Plane analysis 2 UV Plane analysis The data are now calibrated as best as we can Caution: data are calibrated, but
ALMA Antenna responses in CASA imaging
 ALMA Antenna responses in CASA imaging Dirk Petry (ESO), December 2012 Outline Motivation ALBiUS/ESO work on CASA responses infrastructure and ALMA beam library First test results 1 Motivation ALMA covers
ALMA Antenna responses in CASA imaging Dirk Petry (ESO), December 2012 Outline Motivation ALBiUS/ESO work on CASA responses infrastructure and ALMA beam library First test results 1 Motivation ALMA covers
Introduction to Digital Image Processing
 Fall 2005 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain: Histograms, Arithmetic/Logic Operators, Basics of Spatial Filtering, Smoothing Spatial Filters Tuesday, February 7 2006, Overview (1): Before We Begin
Fall 2005 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain: Histograms, Arithmetic/Logic Operators, Basics of Spatial Filtering, Smoothing Spatial Filters Tuesday, February 7 2006, Overview (1): Before We Begin
esac PACS Spectrometer: forward model tool for science use
 esac European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) P.O. Box, 78 28691 Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid Spain PACS Spectrometer: forward model tool for science use Prepared by Elena Puga Reference HERSCHEL-HSC-TN-2131
esac European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) P.O. Box, 78 28691 Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid Spain PACS Spectrometer: forward model tool for science use Prepared by Elena Puga Reference HERSCHEL-HSC-TN-2131
OSKAR-2: Simulating data from the SKA
 OSKAR-2: Simulating data from the SKA AACal 2012, Amsterdam, 13 th July 2012 Fred Dulwich, Ben Mort, Stef Salvini 1 Overview OSKAR-2: Interferometer and beamforming simulator package. Intended for simulations
OSKAR-2: Simulating data from the SKA AACal 2012, Amsterdam, 13 th July 2012 Fred Dulwich, Ben Mort, Stef Salvini 1 Overview OSKAR-2: Interferometer and beamforming simulator package. Intended for simulations
Imaging and Deconvolution
 Imaging and Deconvolution Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro ATNF Radio School Narrabri, NSW 29 Sept 03 Oct 2014 #G Topics Imaging Formal Solution Discrete Data The Direct Transform The Fast Fourier Transform Weighting,
Imaging and Deconvolution Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro ATNF Radio School Narrabri, NSW 29 Sept 03 Oct 2014 #G Topics Imaging Formal Solution Discrete Data The Direct Transform The Fast Fourier Transform Weighting,
Digital Image Processing. Prof. P. K. Biswas. Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering
 Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Image Enhancement Frequency Domain Processing
Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Image Enhancement Frequency Domain Processing
Fast Camera Image Analysis. B. A. Grierson
 Fast Camera Image Analysis B. A. Grierson 9.28.2008 Introduction A high speed camera is used to image the visible light in. The camera is begins recording at the specified trigger time, and records until
Fast Camera Image Analysis B. A. Grierson 9.28.2008 Introduction A high speed camera is used to image the visible light in. The camera is begins recording at the specified trigger time, and records until
Imaging and Deconvolution
 Imaging and Deconvolution David J. Wilner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Fifteenth Synthesis Imaging Workshop 1-8 June 2016 Overview gain some intuition about interferometric imaging understand
Imaging and Deconvolution David J. Wilner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Fifteenth Synthesis Imaging Workshop 1-8 June 2016 Overview gain some intuition about interferometric imaging understand
Data products. Dario Fadda (USRA) Pipeline team Bill Vacca Melanie Clarke Dario Fadda
 Data products Dario Fadda (USRA) Pipeline team Bill Vacca Melanie Clarke Dario Fadda Pipeline (levels 1 à 2) The pipeline consists in a sequence of modules. For each module, files are created and read
Data products Dario Fadda (USRA) Pipeline team Bill Vacca Melanie Clarke Dario Fadda Pipeline (levels 1 à 2) The pipeline consists in a sequence of modules. For each module, files are created and read
Robotics. Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation. See course website for up to date information.
 Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours. Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators From Edges
CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators From Edges
Wide-Field Imaging I: Non-Coplanar Visibilities
 Wide-Field Imaging I: Non-Coplanar Visibilities Rick Perley Eleventh Synthesis Imaging Workshop Socorro, June 10-17, 2008 Review: Measurement Equation From the first lecture, we have a general relation
Wide-Field Imaging I: Non-Coplanar Visibilities Rick Perley Eleventh Synthesis Imaging Workshop Socorro, June 10-17, 2008 Review: Measurement Equation From the first lecture, we have a general relation
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 21 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 21 Jun 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 21 Jun 2017](/thumbs/92/110097439.jpg) MNRAS, 1 16 (216) Preprint 22 July 218 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3. An optimized algorithm for multi-scale wideband deconvolution of radio astronomical images A. R. Offringa 1, O. Smirnov
MNRAS, 1 16 (216) Preprint 22 July 218 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3. An optimized algorithm for multi-scale wideband deconvolution of radio astronomical images A. R. Offringa 1, O. Smirnov
From multiple images to catalogs
 Lecture 14 From multiple images to catalogs Image reconstruction Optimal co-addition Sampling-reconstruction-resampling Resolving faint galaxies Automated object detection Photometric catalogs Deep CCD
Lecture 14 From multiple images to catalogs Image reconstruction Optimal co-addition Sampling-reconstruction-resampling Resolving faint galaxies Automated object detection Photometric catalogs Deep CCD
An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory
 An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory Steven Lehar slehar@cns.bu.edu Fourier theory is pretty complicated mathematically. But there are some beautifully simple holistic concepts behind Fourier theory
An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory Steven Lehar slehar@cns.bu.edu Fourier theory is pretty complicated mathematically. But there are some beautifully simple holistic concepts behind Fourier theory
Primary Beams & Radio Interferometric Imaging Performance. O. Smirnov (Rhodes University & SKA South Africa)
 Primary Beams & Radio Interferometric Imaging Performance O. Smirnov (Rhodes University & SKA South Africa) Introduction SKA Dish CoDR (2011), as summarized by Tony Willis: My sidelobes are better than
Primary Beams & Radio Interferometric Imaging Performance O. Smirnov (Rhodes University & SKA South Africa) Introduction SKA Dish CoDR (2011), as summarized by Tony Willis: My sidelobes are better than
Contrast Optimization A new way to optimize performance Kenneth Moore, Technical Fellow
 Contrast Optimization A new way to optimize performance Kenneth Moore, Technical Fellow What is Contrast Optimization? Contrast Optimization (CO) is a new technique for improving performance of imaging
Contrast Optimization A new way to optimize performance Kenneth Moore, Technical Fellow What is Contrast Optimization? Contrast Optimization (CO) is a new technique for improving performance of imaging
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection
 Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection By Dr. Yu Cao Department of Computer Science The University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, MA 01854, USA Part of the slides
Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection By Dr. Yu Cao Department of Computer Science The University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, MA 01854, USA Part of the slides
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of Waves Waves Behaviour - Answers In 203, AS 9523 replaced AS 90520. The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. In AS 90520 there was an Evidence column with
Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of Waves Waves Behaviour - Answers In 203, AS 9523 replaced AS 90520. The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. In AS 90520 there was an Evidence column with
SSW, Radio, X-ray, and data analysis
 SSW, Radio, X-ray, and data analysis Eduard Kontar School of Physics and Astronomy University of Glasgow, UK CESRA Summer School, Glasgow, August 2015 SSW Pre-school installation guide for IDL, SSW and
SSW, Radio, X-ray, and data analysis Eduard Kontar School of Physics and Astronomy University of Glasgow, UK CESRA Summer School, Glasgow, August 2015 SSW Pre-school installation guide for IDL, SSW and
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Modeling Antenna Beams
 Modeling Antenna Beams Walter Brisken National Radio Astronomy Observatory 2011 Sept 22 1 / 24 What to learn from this talk EM simulations of antennas can be complicated Many people have spent careers
Modeling Antenna Beams Walter Brisken National Radio Astronomy Observatory 2011 Sept 22 1 / 24 What to learn from this talk EM simulations of antennas can be complicated Many people have spent careers
Spectroscopy techniques II. Danny Steeghs
 Spectroscopy techniques II Danny Steeghs Conducting long-slit spectroscopy Science goals must come first, what are the resolution and S/N requirements? Is there a restriction on exposure time? Decide on
Spectroscopy techniques II Danny Steeghs Conducting long-slit spectroscopy Science goals must come first, what are the resolution and S/N requirements? Is there a restriction on exposure time? Decide on
ALMA SIMULATIONS WITH CASA. Hsi-An Pan & ARC Taiwan Team
 ALMA SIMULATIONS WITH CASA Hsi-An Pan & ARC Taiwan Team 1 Download the scripts Prepare from the email of workshop reminder Install CASA 4.7.0 or later https://casa.nrao.edu/casa_obtaining.shtml Make sure
ALMA SIMULATIONS WITH CASA Hsi-An Pan & ARC Taiwan Team 1 Download the scripts Prepare from the email of workshop reminder Install CASA 4.7.0 or later https://casa.nrao.edu/casa_obtaining.shtml Make sure
POSSUM: analysis for early science and beyond
 POSSUM: analysis for early science and beyond Cormac Purcell, Bryan Gaensler and the POSSUM team 2016-06-02 ASKAP 2016 askap.org/possum Rotation 1 Rotation 2 Figure: O'Sullivan et al. 2012 POSSUM-12 versus
POSSUM: analysis for early science and beyond Cormac Purcell, Bryan Gaensler and the POSSUM team 2016-06-02 ASKAP 2016 askap.org/possum Rotation 1 Rotation 2 Figure: O'Sullivan et al. 2012 POSSUM-12 versus
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of Waves Waves Behaviour - Answers In 03, AS 953 replaced AS 9050. The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. In AS 9050 there was an Evidence column with the
Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of Waves Waves Behaviour - Answers In 03, AS 953 replaced AS 9050. The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. In AS 9050 there was an Evidence column with the
Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to linear, associative operators). Images
 Images (we will, eventually, come back to imaging geometry. But, now that we know how images come from the world, we will examine operations on images). Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to
Images (we will, eventually, come back to imaging geometry. But, now that we know how images come from the world, we will examine operations on images). Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to
GBT Commissioning Memo 11: Plate Scale and pointing effects of subreflector positioning at 2 GHz.
 GBT Commissioning Memo 11: Plate Scale and pointing effects of subreflector positioning at 2 GHz. Keywords: low frequency Gregorian, plate scale, focus tracking, pointing. N. VanWey, F. Ghigo, R. Maddalena,
GBT Commissioning Memo 11: Plate Scale and pointing effects of subreflector positioning at 2 GHz. Keywords: low frequency Gregorian, plate scale, focus tracking, pointing. N. VanWey, F. Ghigo, R. Maddalena,
Computer Vision 2. SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung. Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier
 Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
The maximum reachable astrometric precision. The Cramér-Rao Limit
 The maximum reachable astrometric precision The Cramér-Rao Limit Ulrich Bastian, ARI, Heidelberg, 28-04-2004 translated into English by Helmut Lenhardt, 2009 Abstract: This small investigation shall give
The maximum reachable astrometric precision The Cramér-Rao Limit Ulrich Bastian, ARI, Heidelberg, 28-04-2004 translated into English by Helmut Lenhardt, 2009 Abstract: This small investigation shall give
Interactive comment on Quantification and mitigation of the impact of scene inhomogeneity on Sentinel-4 UVN UV-VIS retrievals by S. Noël et al.
 Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss., www.atmos-meas-tech-discuss.net/5/c741/2012/ Author(s) 2012. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques Discussions
Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss., www.atmos-meas-tech-discuss.net/5/c741/2012/ Author(s) 2012. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques Discussions
Interactive comment on Quantification and mitigation of the impact of scene inhomogeneity on Sentinel-4 UVN UV-VIS retrievals by S. Noël et al.
 Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss., 5, C741 C750, 2012 www.atmos-meas-tech-discuss.net/5/c741/2012/ Author(s) 2012. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Atmospheric Measurement
Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss., 5, C741 C750, 2012 www.atmos-meas-tech-discuss.net/5/c741/2012/ Author(s) 2012. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Atmospheric Measurement
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee2031) Digital Image Processing I
 Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Adaptive selfcalibration for Allen Telescope Array imaging
 Adaptive selfcalibration for Allen Telescope Array imaging Garrett Keating, William C. Barott & Melvyn Wright Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 ABSTRACT Planned
Adaptive selfcalibration for Allen Telescope Array imaging Garrett Keating, William C. Barott & Melvyn Wright Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 ABSTRACT Planned
The ALMA Pipeline. Introduction Pipeline Subsystem Heuristics Task Interface Tests / Commissioning Results Demos. D. Muders, MPIfR L.
 The ALMA Pipeline Introduction Pipeline Subsystem Heuristics Task Interface Tests / Commissioning Results Demos D. Muders, MPIfR L. Davis, NRAO 1 Introduction ALMA must be available to all of the astronomical
The ALMA Pipeline Introduction Pipeline Subsystem Heuristics Task Interface Tests / Commissioning Results Demos D. Muders, MPIfR L. Davis, NRAO 1 Introduction ALMA must be available to all of the astronomical
Image restoration. Lecture 14. Milan Gavrilovic Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University
 Image restoration Lecture 14 Milan Gavrilovic milan@cb.uu.se Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University Computer Assisted Image Analysis 2009-05-08 M. Gavrilovic (Uppsala University) L14 Image restoration
Image restoration Lecture 14 Milan Gavrilovic milan@cb.uu.se Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University Computer Assisted Image Analysis 2009-05-08 M. Gavrilovic (Uppsala University) L14 Image restoration
ALMA simulations Rosita Paladino. & the Italian ARC
 ALMA simulations Rosita Paladino & the Italian ARC Two software tools available to help users simulate images resulting from an ALMA observations: Simulations with CASA tasks sim_observe & sim_analyze
ALMA simulations Rosita Paladino & the Italian ARC Two software tools available to help users simulate images resulting from an ALMA observations: Simulations with CASA tasks sim_observe & sim_analyze
IRAM Memo MAPPING for NOEMA: Concepts and Usage
 Original version at http://iram-institute.org/medias/uploads/mapping-noema.pdf IRAM Memo 2016-1 MAPPING for NOEMA: Concepts and Usage S. Guilloteau 1 1. LAB (Bordeaux) 14-Jul-2016 version 1.0 09-Sep-2016
Original version at http://iram-institute.org/medias/uploads/mapping-noema.pdf IRAM Memo 2016-1 MAPPING for NOEMA: Concepts and Usage S. Guilloteau 1 1. LAB (Bordeaux) 14-Jul-2016 version 1.0 09-Sep-2016
OSKAR Settings Files Revision: 8
 OSKAR Settings Files Version history: Revision Date Modification 1 212-4-23 Creation. 2 212-5-8 Added default value column to settings tables. 3 212-6-13 Updated settings for version 2..2-beta. 4 212-7-27
OSKAR Settings Files Version history: Revision Date Modification 1 212-4-23 Creation. 2 212-5-8 Added default value column to settings tables. 3 212-6-13 Updated settings for version 2..2-beta. 4 212-7-27
WSDC Subsystem Peer Review
 WSDC Subsystem Peer Review Multiband DETector () Ken Marsh (IPAC/Caltech) 1 Outline Relationship of to other WSDS pipeline modules Why multiband? Theoretical basis Procedure - Steps involved - Allowance
WSDC Subsystem Peer Review Multiband DETector () Ken Marsh (IPAC/Caltech) 1 Outline Relationship of to other WSDS pipeline modules Why multiband? Theoretical basis Procedure - Steps involved - Allowance
PSI Precision, accuracy and validation aspects
 PSI Precision, accuracy and validation aspects Urs Wegmüller Charles Werner Gamma Remote Sensing AG, Gümligen, Switzerland, wegmuller@gamma-rs.ch Contents Aim is to obtain a deeper understanding of what
PSI Precision, accuracy and validation aspects Urs Wegmüller Charles Werner Gamma Remote Sensing AG, Gümligen, Switzerland, wegmuller@gamma-rs.ch Contents Aim is to obtain a deeper understanding of what
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Computer Vision I. Announcement. Corners. Edges. Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 11
 Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_37 Monday, August 06, 2007
 Name: Date: 1. If we increase the wavelength of the light used to form a double-slit diffraction pattern: A) the width of the central diffraction peak increases and the number of bright fringes within
Name: Date: 1. If we increase the wavelength of the light used to form a double-slit diffraction pattern: A) the width of the central diffraction peak increases and the number of bright fringes within
Edge detection. Convert a 2D image into a set of curves. Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels
 Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Spherical Geometry Selection Used for Error Evaluation
 Spherical Geometry Selection Used for Error Evaluation Greg Hindman, Pat Pelland, Greg Masters Nearfield Systems Inc., Torrance, CA 952, USA ghindman@nearfield.com, ppelland@nearfield.com, gmasters@nearfield.com
Spherical Geometry Selection Used for Error Evaluation Greg Hindman, Pat Pelland, Greg Masters Nearfield Systems Inc., Torrance, CA 952, USA ghindman@nearfield.com, ppelland@nearfield.com, gmasters@nearfield.com
Experiment 5: Polarization and Interference
 Experiment 5: Polarization and Interference Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction Outline: Review
Experiment 5: Polarization and Interference Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction Outline: Review
Imaging Strategies and Postprocessing Computing Costs for Large-N SKA Designs
 Imaging Strategies and Postprocessing Computing Costs for Large-N SKA Designs Colin J. Lonsdale Sheperd S Doeleman Divya Oberoi MIT Haystack Observatory 17 July 2004 Abstract: The performance goals of
Imaging Strategies and Postprocessing Computing Costs for Large-N SKA Designs Colin J. Lonsdale Sheperd S Doeleman Divya Oberoi MIT Haystack Observatory 17 July 2004 Abstract: The performance goals of
CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours. Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators Laplacian
CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators Laplacian
Correlator Field-of-View Shaping
 Correlator Field-of-View Shaping Colin Lonsdale Shep Doeleman Vincent Fish Divya Oberoi Lynn Matthews Roger Cappallo Dillon Foight MIT Haystack Observatory Context SKA specifications extremely challenging
Correlator Field-of-View Shaping Colin Lonsdale Shep Doeleman Vincent Fish Divya Oberoi Lynn Matthews Roger Cappallo Dillon Foight MIT Haystack Observatory Context SKA specifications extremely challenging
Mu lt i s p e c t r a l
 Viewing Angle Analyser Revolutionary system for full spectral and polarization measurement in the entire viewing angle EZContrastMS80 & EZContrastMS88 ADVANCED LIGHT ANALYSIS by Field iris Fourier plane
Viewing Angle Analyser Revolutionary system for full spectral and polarization measurement in the entire viewing angle EZContrastMS80 & EZContrastMS88 ADVANCED LIGHT ANALYSIS by Field iris Fourier plane
A Modified Algorithm for CLEANing Wide-Field Maps with Extended Structures
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (1990) 11, 311 322 A Modified Algorithm for CLEANing Wide-Field Maps with Extended Structures Κ. S. Dwarakanath, A. A. Deshpande & Ν. Udaya Shankar Raman Research institute, Bangalore
J. Astrophys. Astr. (1990) 11, 311 322 A Modified Algorithm for CLEANing Wide-Field Maps with Extended Structures Κ. S. Dwarakanath, A. A. Deshpande & Ν. Udaya Shankar Raman Research institute, Bangalore
PHYSICS. Chapter 33 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 33 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 33 Wave Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the wave model of light. Slide
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 33 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 33 Wave Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the wave model of light. Slide
SPECT QA and QC. Bruce McBride St. Vincent s Hospital Sydney.
 SPECT QA and QC Bruce McBride St. Vincent s Hospital Sydney. SPECT QA and QC What is needed? Why? How often? Who says? QA and QC in Nuclear Medicine QA - collective term for all the efforts made to produce
SPECT QA and QC Bruce McBride St. Vincent s Hospital Sydney. SPECT QA and QC What is needed? Why? How often? Who says? QA and QC in Nuclear Medicine QA - collective term for all the efforts made to produce
2.) An overhead projector forms an image of a transparency on a screen:
 1.) You have measured the wavelength λ of a spectral lamp using a diffraction grating and the relation λ = d sin Θ. Your uncertainty in the grating spacing d is 0.5% and your uncertainty in your angle
1.) You have measured the wavelength λ of a spectral lamp using a diffraction grating and the relation λ = d sin Θ. Your uncertainty in the grating spacing d is 0.5% and your uncertainty in your angle
ALMA Science Pipeline Quickstart Guide
 Doc 2.13, ver. 1.0 September 2014 ALMA Science Pipeline Quickstart Guide ALMA, an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of Europe, North America and East Asia in cooperation with the Republic
Doc 2.13, ver. 1.0 September 2014 ALMA Science Pipeline Quickstart Guide ALMA, an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of Europe, North America and East Asia in cooperation with the Republic
High spatial resolution measurement of volume holographic gratings
 High spatial resolution measurement of volume holographic gratings Gregory J. Steckman, Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc., 8 E. Duarte Rd., Monrovia, CA, USA 9116 ABSTRACT The conventional approach for measuring
High spatial resolution measurement of volume holographic gratings Gregory J. Steckman, Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc., 8 E. Duarte Rd., Monrovia, CA, USA 9116 ABSTRACT The conventional approach for measuring
VLA data reduction part 1:
 VLA data reduction part 1: Post-observing, pre-calibration Loránt Sjouwerman, NRAO Outline After the observations: Obtaining your data from the archive Which CPU processes the data? (Home or NRAO) Examine
VLA data reduction part 1: Post-observing, pre-calibration Loránt Sjouwerman, NRAO Outline After the observations: Obtaining your data from the archive Which CPU processes the data? (Home or NRAO) Examine
The Completeness and Reliability of Threshold and False-discovery Rate Source Extraction Algorithms for Compact Continuum Sources
 CSIRO PUBLISHING Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia, 2012, 29, 229 243 http://dx.doi.org/10.1071/as11026 The Completeness and Reliability of Threshold and False-discovery Rate Source
CSIRO PUBLISHING Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia, 2012, 29, 229 243 http://dx.doi.org/10.1071/as11026 The Completeness and Reliability of Threshold and False-discovery Rate Source
Final Exam Study Guide
 Final Exam Study Guide Exam Window: 28th April, 12:00am EST to 30th April, 11:59pm EST Description As indicated in class the goal of the exam is to encourage you to review the material from the course.
Final Exam Study Guide Exam Window: 28th April, 12:00am EST to 30th April, 11:59pm EST Description As indicated in class the goal of the exam is to encourage you to review the material from the course.
Minimizing Noise and Bias in 3D DIC. Correlated Solutions, Inc.
 Minimizing Noise and Bias in 3D DIC Correlated Solutions, Inc. Overview Overview of Noise and Bias Digital Image Correlation Background/Tracking Function Minimizing Noise Focus Contrast/Lighting Glare
Minimizing Noise and Bias in 3D DIC Correlated Solutions, Inc. Overview Overview of Noise and Bias Digital Image Correlation Background/Tracking Function Minimizing Noise Focus Contrast/Lighting Glare
Single-epoch Measurement Algorithms Robert Lupton Applications Lead
 Single-epoch Measurement Algorithms Robert Lupton Applications Lead 2013-09-19 CDP FINAL DESIGN REVIEW September 19-20, 2013 Name of Mee)ng Loca)on Date - Change in Slide Master 1 Outline Single-epoch
Single-epoch Measurement Algorithms Robert Lupton Applications Lead 2013-09-19 CDP FINAL DESIGN REVIEW September 19-20, 2013 Name of Mee)ng Loca)on Date - Change in Slide Master 1 Outline Single-epoch
