LIGHT-REFLECTION AND REFRACTION. It is a form of energy which is needed to see things around us. It travels in a straight line.
|
|
|
- Melvyn Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LIGHT-REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Class: 10 (Boys) Sub: PHYSICS NOTES-Reflection Light: It is a form of energy which is needed to see things around us. It travels in a straight line. Nature of Light: Light has a dual nature. Wave theory of light light consists of electromagnetic waves which do not require a medium. Particle theory of light- Light is composed of particles which travel in a straight line at very high speed. Some phenomenon of light such as Reflection, refraction, shadows follows the particle theory of light. And some phenomenon of light such as Diffraction, interference, polarization follows the Wave theory of light. The modern theory of light called Quantum Theory of Light combines both the wave and particle models of light as light exhibits the properties of both waves and particles. Reflection of Light: The process of sending back the light rays which fall on the surface of an object, is called reflection of light. The ray of light which falls on the mirror surface is called incident ray. The ray of light which is sent back by the mirror is called reflected ray. The normal is a line at right angles to the mirror surface at the point of incidence. The angle of incidence is the angle made by the incident ray with the normal at the point of incidence. The angle of reflection is the angle made by the reflected ray with the normal at the point of incidence.
2 Laws of Reflection: 1 st law -The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane. 2 nd law The angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. Types of Reflection: Regular reflection In this, the parallel beam of light is reflected as parallel beam in one direction. It occurs from smooth surfaces such as plane mirrors, still water etc. Diffuse reflection In this, the parallel beam of light is reflected in different directions. It occurs in rough surfaces such as paper, book etc. Types of Images: Real images The image which can be obtained on a screen. It is formed when light rays coming from an object actually meet at a point after reflection. For ex: image at eye s retina, image formed by a projector etc Virtual images The image which cannot be obtained on a screen. It is formed when light rays coming from an object only appear to meet at a point when produced backwards after reflection. For ex: image on a TV screen, image in a mirror, image formed by convex mirror etc. Difference between Real and Virtual Images: Real Virtual 1. Can be obtained on a screen or wall Cannot be obtained on a screen or wall 2. Formed in front of the mirror Formed behind the mirror 3. The images are always are inverted. The images are always erect. 4. Can be touched Cannot be touched 5. Formed by concave mirrors only. Formed by all types of mirrors. ie. Plane, convex and concave Characteristics of the Images formed in a Plane mirror: The image formed is a virtual image. The image is erect. The size of the image is equal to that of the object.
3 The image formed is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. The image is laterally inverted. Spherical mirrors: A spherical mirror is that mirror whose reflecting surface is the part of a hollow sphere of glass. The spherical mirrors are of two types: Concave Mirror It is that spherical mirror in which the reflection of light takes place at the concave surface(cave-in) Convex Mirror It is that spherical mirror in which the reflection of light takes place at the convex surface(bulging-out) Terms related to Spherical mirrors: Aperture - It is the portion of a mirror from which the reflection of light actually takes place. The aperture of a spherical mirror is represented by the diameter of its reflecting surface. Pole It is the centre of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror. It lies on the surface of the mirror and represented by the letter P.
4 Centre of curvature It is the centre of the hollow sphere of glass of which the mirror is a part which is represented by the letter C. The centre of curvature of a concave mirror is in front of it but the centre of curvature of a convex mirror is behind it. Principal axis It is the straight line passing through the centre of curvature and pole of a spherical mirror Radius of Curvature It is the radius of the hollow sphere of glass of which the mirror is a part and represented by R. Principal Focus - The Principal Focus of concave mirror is the point on its principal axis to which all the light rays which are parallel and close to the axis, converge after reflection from the concave mirror. The concave mirror has a real focus as all the parallel rays of light converge at it focus after reflection and formed in front of the concave mirror. The Principal Focus of a convex mirror is a point on its principal axis from which a beam of light rays, initially parallel to the axis, appears to diverge after being reflected from the convex mirror. The convex mirror has a virtual focus as all the reflected rays diverge and appear to meet at its focus and formed behind the convex mirror.
5 Focal length It is the distance between its pole and principal focus. Relation between Radius of Curvature and Focal Length of a Spherical mirror: The focal length of a spherical mirror is equal to half of its radius of curvature. If, f is the focal length and R is the radius of curvature, then: f = R/2 or R = 2f Rules for obtaining images formed by spherical mirrors: 1 st Rule -A ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus for concave mirror or appear to diverge from the principal focus for convex mirror. 2 nd Rule - A ray passing through the principal focus of a concave mirror or a ray which is directed towards the principal focus of a convex mirror, after reflection, will emerge parallel to the principal axis. 3 rd Rule - A ray passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror or directed in the direction of the centre of curvature of a convex mirror, after reflection, is reflected back along the same path.
6 4 th Rule - A ray incident obliquely to the principal axis, towards a point P on the concave mirror or a convex mirror is reflected obliquely. Formation of different types of images by a concave mirror: Object at infinity: Image formed at the focus Highly diminished, point-sized Real and inverted Object beyond C Image between F and C Size is diminished Real and inverted Object at C Image formed at C Same size Real and inverted
7 Object between C and F Image formed beyond C Size is enlarged Real and inverted Object at F Image is formed at infinity Size is highly enlarged Real and inverted Object between P and F Image is formed behind the mirror Size is enlarged Virtual and erect Uses of Concave Mirrors : Used in torches, search-light and vehicles headlights to get powerful beams of light. Used as shaving mirrors to see a larger image of the face. Dentists use it to see large images of the teeth of the patients. Concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
8 Formation of different types of images by a convex mirror: At infinity: Image is formed at the focus Behind the mirror Highly diminished, point sized Virtual and erect Between infinity and pole: Image is formed between P and F, behind the mirror Diminished Virtual and Erect Uses of Convex Mirrors : Used as rear-view mirrors in vehicles: i. As it produces an erect image of the objects. ii. As the image formed is highly diminished or much smaller than the object, due to which it gives a wide field of view Used as shop security mirrors in order to help the shop owner to keep an eye on the customers. Sign convention for spherical mirrors: According to the New Cartesian Sign convention: The object is always placed to the left of the mirror. All the distances are measured from pole of the mirror as origin. Distances measured in the same direction as that of incident light are taken as positive. Distances measured against the direction of incident light are taken as negative. Distances measured upward and perpendicular to the principal axis are taken as positive. Distances measured downward and perpendicular to the principal axis are taken as negative.
9 Conclusions : The object distance(u) is always negative. For a concave mirror, if the image is formed behind, the image distance(v) is positive but if the image is formed in front of the mirror then the image distance will be negative. In convex mirror, the image is always formed on the right hand side, so v is always positive. The focus of concave mirror is in the front on the left side, so its negative but the focus of the convex mirror is behind the mirror, so its positive. The object is always placed above the principal axis in the upward direction, so the height is positive but the image can be formed above the principal axis or below, so if the image is formed above the principal axis, its height is taken as positive and if the image is formed below the principal axis, then its height is taken as negative. All the virtual images are erect and formed above principal axis, so the height of all virtual and erect images is positive but all real images are inverted and formed below the principal axis, so the height of all the real and inverted images is taken as negative. Mirror Formula : It s the relationship between object distance, image distance and focal length = 1 v u f Where u is the object distance v is the image distance f is the focal length
10 [ Magnification : Magnification produced by a spherical mirror gives the relative extent to which the image of an object is magnified with respect to the object size. Linear magnification is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object. It is represented by letter m. If h is the height of the object and h is the height of the image, then the magnification m produced by a spherical mirror is given by m= Height of the image(h ) Height of the object(h) Or m = h h Conclusions: The object is always placed above the principal axis, so the height of the object is always positive. The virtual image is always formed above the principal axis, so the height will be positive. The real image is formed below the principal axis, so the height of a real image will be negative. For virtual image, h is positive and h is also positive, so the magnification of a virtual image is always positive. So, if the magnification has a plus sign, then the image is virtual and erect. For a real image, h is negative and h is positive, so the magnification for a real image is always negative. So, if the magnification has a minus sign, then the image is real and inverted. If the magnification, m has a value greater than 1 then the image is enlarged. If the magnification, m is 1, then the image is of the same size as the object. If the magnification, m is less than 1, then the image is smaller than the object. Magnification in relation to object and image distance : The linear magnification produced by a mirror is equal to the ratio of the image distance to the object distance with a minus sign. That is, Magnification = - Image distance Object distance Or m = - v u Combining both the formulas, we get, h = - v h u ***********
CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION LIGHT Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object. Its speed is 3 10 8 m/s in vacuum. Light always travel in straight line. Reflection: The
CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION LIGHT Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object. Its speed is 3 10 8 m/s in vacuum. Light always travel in straight line. Reflection: The
LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK:
 LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK: 1. REFLECTION OF LIGHT: The phenomenon of light coming back into the same medium after it strikes a smooth surface is called reflection. 2. LAWS OF REFLECTION:
LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK: 1. REFLECTION OF LIGHT: The phenomenon of light coming back into the same medium after it strikes a smooth surface is called reflection. 2. LAWS OF REFLECTION:
STD:- VIII PHYSICS SPHERICAL MIRRORS
 STD:- VIII PHYSICS SPHERICAL MIRRORS A spherical mirror is a mirror with a curved reflective surface, which may be either convex (bulging outward) or concave (bulging inward). There are two types of spherical
STD:- VIII PHYSICS SPHERICAL MIRRORS A spherical mirror is a mirror with a curved reflective surface, which may be either convex (bulging outward) or concave (bulging inward). There are two types of spherical
PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012)
 PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012) Light Throughout most of the next 2 weeks, we will be concerned with the wave properties of light, and phenomena based on them (interference & diffraction). Light also
PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012) Light Throughout most of the next 2 weeks, we will be concerned with the wave properties of light, and phenomena based on them (interference & diffraction). Light also
Winmeen Tnpsc Group 1 & 2 Self Preparation Course Physics UNIT 9. Ray Optics. surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
 Laws of reflection Physics UNIT 9 Ray Optics The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence
Laws of reflection Physics UNIT 9 Ray Optics The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence
Propagation and Reflection of Light
 Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online tuition Pakistan Online Tutor Pakistan Propagation and Reflection of Light Q1. Define reflection of light. State the laws of reflection. Ans: REFLECTION OF LIGHT: When
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online tuition Pakistan Online Tutor Pakistan Propagation and Reflection of Light Q1. Define reflection of light. State the laws of reflection. Ans: REFLECTION OF LIGHT: When
The image is virtual and erect. When a mirror is rotated through a certain angle, the reflected ray is rotated through twice this angle.
 1 Class XII: Physics Chapter 9: Ray optics and Optical Instruments Top Concepts 1. Laws of Reflection. The reflection at a plane surface always takes place in accordance with the following two laws: (i)
1 Class XII: Physics Chapter 9: Ray optics and Optical Instruments Top Concepts 1. Laws of Reflection. The reflection at a plane surface always takes place in accordance with the following two laws: (i)
Lecture Notes (Reflection & Mirrors)
 Lecture Notes (Reflection & Mirrors) Intro: - plane mirrors are flat, smooth surfaces from which light is reflected by regular reflection - light rays are reflected with equal angles of incidence and reflection
Lecture Notes (Reflection & Mirrors) Intro: - plane mirrors are flat, smooth surfaces from which light is reflected by regular reflection - light rays are reflected with equal angles of incidence and reflection
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics 7. Reflection at a Spherical Surface L.O 7.. State laws of reflection Laws of reflection state: L.O The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics 7. Reflection at a Spherical Surface L.O 7.. State laws of reflection Laws of reflection state: L.O The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 11/18/2013 2 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain and discuss with diagrams, reflection and refraction of light
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 11/18/2013 2 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain and discuss with diagrams, reflection and refraction of light
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics. The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light.
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
CHAPTER 29: REFLECTION
 CHAPTER 29: REFLECTION 29.1 REFLECTION The return of a wave back to its original medium is called reflection. Fasten a spring to a wall and send a pulse along the spring s length. The wall is a very rigid
CHAPTER 29: REFLECTION 29.1 REFLECTION The return of a wave back to its original medium is called reflection. Fasten a spring to a wall and send a pulse along the spring s length. The wall is a very rigid
Optics II. Reflection and Mirrors
 Optics II Reflection and Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media The
Optics II Reflection and Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media The
Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors
 Purpose Theory a. To study the reflection of light Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors b. To study the formation and characteristics of images formed by different types of mirrors. When light (wave)
Purpose Theory a. To study the reflection of light Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors b. To study the formation and characteristics of images formed by different types of mirrors. When light (wave)
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
Reflection and Mirrors
 Reflection and Mirrors 1 The Law of Reflection The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. 2 The Law of Reflection When light strikes a surface it is reflected. The light ray striking the surface
Reflection and Mirrors 1 The Law of Reflection The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. 2 The Law of Reflection When light strikes a surface it is reflected. The light ray striking the surface
Geometry of image formation
 Geometry of image formation discussing here... mirrors definition of mirror types of mirrors aspects of plane mirror aspects of curved mirrors what is mirror? glass sheet with silvery / metallic coating
Geometry of image formation discussing here... mirrors definition of mirror types of mirrors aspects of plane mirror aspects of curved mirrors what is mirror? glass sheet with silvery / metallic coating
Downloaded from
 1 Class X: Physics Chapter 10: Light- Reflection and Refraction Points to remember Key learnings: 1. When light falls on a body, it may be absorbed, may be transmitted or light may come back to the same
1 Class X: Physics Chapter 10: Light- Reflection and Refraction Points to remember Key learnings: 1. When light falls on a body, it may be absorbed, may be transmitted or light may come back to the same
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
Reflection & Mirrors
 Reflection & Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media A ray of light is
Reflection & Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media A ray of light is
AP Physics: Curved Mirrors and Lenses
 The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
Light and Mirrors MIRRORS
 Light and Mirrors MIRRORS 1 Polarized Sunglasses- How do they work? light waves vibrate in more than one plane light waves can be made to vibrate in a single plane by use of polarizing filters. 2 polarizing
Light and Mirrors MIRRORS 1 Polarized Sunglasses- How do they work? light waves vibrate in more than one plane light waves can be made to vibrate in a single plane by use of polarizing filters. 2 polarizing
Optics. a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles.
 Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Section 2 Flat Mirrors. Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors.
 Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23)
 Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Ray Optics. Physics 11. Sources of Light Rays: Self-Luminous Objects. The Ray Model of Light
 Physics 11 Ray Optics Ray Model of Light Reflection Plane Mirrors Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing Images from a Concave Mirror Images from a Convex Mirror Slide 18-3 The Ray Model of Light Sources of Light
Physics 11 Ray Optics Ray Model of Light Reflection Plane Mirrors Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing Images from a Concave Mirror Images from a Convex Mirror Slide 18-3 The Ray Model of Light Sources of Light
Ray Diagrams. Ray Diagrams Used for determining location, size, orientation, and type of image
 Ray Diagrams Reflection for concave mirror: Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection. Any incident ray passing
Ray Diagrams Reflection for concave mirror: Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection. Any incident ray passing
Lecture Notes (Geometric Optics)
 Lecture Notes (Geometric Optics) Intro: - plane mirrors are flat, smooth surfaces from which light is reflected by regular reflection - light rays are reflected with equal angles of incidence and reflection
Lecture Notes (Geometric Optics) Intro: - plane mirrors are flat, smooth surfaces from which light is reflected by regular reflection - light rays are reflected with equal angles of incidence and reflection
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
The Law of Reflection
 If the surface off which the light is reflected is smooth, then the light undergoes specular reflection (parallel rays will all be reflected in the same directions). If, on the other hand, the surface
If the surface off which the light is reflected is smooth, then the light undergoes specular reflection (parallel rays will all be reflected in the same directions). If, on the other hand, the surface
Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes
 1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes. Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes. Spherical Mirrors
 1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
The branch of physics which studies light
 Mr.V The branch of physics which studies light Geometric model XVI century by W Snell Wave Model XIX century by JC Maxwell Photon Model XX century by Planck, Einstein Models of Light Basic Concept Laws
Mr.V The branch of physics which studies light Geometric model XVI century by W Snell Wave Model XIX century by JC Maxwell Photon Model XX century by Planck, Einstein Models of Light Basic Concept Laws
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction. Notes
 Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
30/08/2016. Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes. Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes. Spherical Mirrors - Images
 1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
1 Spherical Mirrors Learning Outcomes Recognise and use key words relating to mirrors. Centre of curvature Focus / focal point, focal length Pole Principal axis Use ray tracing to demonstrate reflection.
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light. Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle
 Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Lecture Outline Chapter 26. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 26 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Units of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing
Lecture Outline Chapter 26 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Units of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 17 2 18.6 Image formation with spherical mirrors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors 18.7 The thin-lens equation Sign conventions
LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 17 2 18.6 Image formation with spherical mirrors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors 18.7 The thin-lens equation Sign conventions
34.2: Two Types of Image
 Chapter 34 Images 34.2: Two Types of Image For you to see an object, your eye intercepts some of the light rays spreading from the object and then redirect them onto the retina at the rear of the eye.
Chapter 34 Images 34.2: Two Types of Image For you to see an object, your eye intercepts some of the light rays spreading from the object and then redirect them onto the retina at the rear of the eye.
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Geometric Optics Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 36! The study of light divides itself into three fields geometric optics wave optics quantum optics! In the previous chapter,
Geometric Optics Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 36! The study of light divides itself into three fields geometric optics wave optics quantum optics! In the previous chapter,
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Textbook Reference: Glencoe Physics: Chapters 16-18
 Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
P06 ray diagrams with concave mirrors and intro to problem solving.notebook
 Ray Diagrams Concave Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. For any object, millions and millions of rays are reflected in all directions. Some of these rays hit the
Ray Diagrams Concave Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. For any object, millions and millions of rays are reflected in all directions. Some of these rays hit the
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics
 PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Exam 2 is scheduled on Tuesday, March 26 @ 8 10 PM In Physics 114 It will cover four Chapters 21, 22, 23, and 24. Start reviewing lecture
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Exam 2 is scheduled on Tuesday, March 26 @ 8 10 PM In Physics 114 It will cover four Chapters 21, 22, 23, and 24. Start reviewing lecture
Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light
 Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light 25. Wave fronts and rays We are all familiar with mirrors. We see images because some light is reflected off the surface of the mirror and into our eyes. In order to describe
Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light 25. Wave fronts and rays We are all familiar with mirrors. We see images because some light is reflected off the surface of the mirror and into our eyes. In order to describe
The Ray model of Light. Reflection. Class 18
 The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
PHYSICS. Chapter 34 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 34 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 34 Ray Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the ray model of light Slide 34-2
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 34 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 34 Ray Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the ray model of light Slide 34-2
When light strikes an object there are different ways it can be affected. Light can be
 When light strikes an object there are different ways it can be affected. Light can be transmitted, reflected, refracted, and absorbed, It depends on the type of matter that it strikes. For example light
When light strikes an object there are different ways it can be affected. Light can be transmitted, reflected, refracted, and absorbed, It depends on the type of matter that it strikes. For example light
History of Light. 5 th Century B.C.
 History of Light 5 th Century B.C. Philosophers thought light was made up of streamers emitted by the eye making contact with an object Others thought that light was made of particles that traveled from
History of Light 5 th Century B.C. Philosophers thought light was made up of streamers emitted by the eye making contact with an object Others thought that light was made of particles that traveled from
Lecture 36: FRI 17 APR
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 36: FRI 17 APR 34.1 4: Geometrical optics Geometrical Optics Geometrical optics (rough approximation): light rays ( particles ) that travel in straight lines. Physical
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 36: FRI 17 APR 34.1 4: Geometrical optics Geometrical Optics Geometrical optics (rough approximation): light rays ( particles ) that travel in straight lines. Physical
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 24. Geometrical Optics. Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
The Reflection of Light
 King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences The Reflection of Light General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa Outline Introduction
King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences The Reflection of Light General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa Outline Introduction
Physics 11. Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1
 Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1 1.Review of waves In the previous section, we have investigated the nature and behaviors of waves in general. We know that all waves possess the following characteristics:
Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1 1.Review of waves In the previous section, we have investigated the nature and behaviors of waves in general. We know that all waves possess the following characteristics:
Optics and Images. Lenses and Mirrors. Matthew W. Milligan
 Optics and Images Lenses and Mirrors Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle
Optics and Images Lenses and Mirrors Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 26 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 26 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Video: The Mirror. Unit #3 - Optics. Geometric Optics. A) The Law of Reflection. applications Mirrors.
 Video: The Mirror http://vimeo.com/6212004 Unit #3 - Optics 11.1 - Mirrors Geometric Optics the science of how light reflects and bends optical device is any technology that uses light A) The Law of Reflection
Video: The Mirror http://vimeo.com/6212004 Unit #3 - Optics 11.1 - Mirrors Geometric Optics the science of how light reflects and bends optical device is any technology that uses light A) The Law of Reflection
Common terminology of reflection of light on a plane mirror. Normal : A line at right angles to the mirror s surface.
 LESSON 5.1 Understanding reflection of light Introduction : Light is a form energy that enables us to see. Light is emitted or given by hot objects, like a candle flame, or the glowing filament of light
LESSON 5.1 Understanding reflection of light Introduction : Light is a form energy that enables us to see. Light is emitted or given by hot objects, like a candle flame, or the glowing filament of light
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction
 Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
3. LENSES & PRISM
 3. LENSES & PRISM. A transparent substance bounded by two surfaces of definite geometrical shape is called lens.. A lens may be considered to be made up of a number of small prisms put together. 3. Principal
3. LENSES & PRISM. A transparent substance bounded by two surfaces of definite geometrical shape is called lens.. A lens may be considered to be made up of a number of small prisms put together. 3. Principal
Physics 1C Lecture 26A. Beginning of Chapter 26
 Physics 1C Lecture 26A Beginning of Chapter 26 Mirrors and Lenses! As we have noted before, light rays can be diverted by optical systems to fool your eye into thinking an object is somewhere that it is
Physics 1C Lecture 26A Beginning of Chapter 26 Mirrors and Lenses! As we have noted before, light rays can be diverted by optical systems to fool your eye into thinking an object is somewhere that it is
Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Ray Model of Light (pp. 172-187) Models of Light wave model of light: a model in which light is a type of wave that travels through space and transfers energy from one
Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Ray Model of Light (pp. 172-187) Models of Light wave model of light: a model in which light is a type of wave that travels through space and transfers energy from one
Chapter 5 Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
Light:- it is an agent which produces in us the sensation of sight. It is a form of energy.
 Reflection:- Light:- it is an agent which produces in us the sensation of sight. It is a form of energy. Transparent medium:- It is a medium through which light can be propagated easily.(e.g., sun, candle,
Reflection:- Light:- it is an agent which produces in us the sensation of sight. It is a form of energy. Transparent medium:- It is a medium through which light can be propagated easily.(e.g., sun, candle,
Chapter 23. Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian Reflection and Refraction at a Plane Surface The light radiate from a point object in all directions The light reflected from a plane
Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian Reflection and Refraction at a Plane Surface The light radiate from a point object in all directions The light reflected from a plane
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Light, Lenses, Mirrors
 Light, Lenses, Mirrors Optics Light is Dual in nature- has both particle and wave properties. Light = range of frequencies of electromagnetic waves that stimulates the eye s retina Facts About Light It
Light, Lenses, Mirrors Optics Light is Dual in nature- has both particle and wave properties. Light = range of frequencies of electromagnetic waves that stimulates the eye s retina Facts About Light It
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
PHYSICS. Light FORM 4. Chapter 5. Compiled by Cikgu Desikan
 PHYSICS RM 4 Chapter 5 Light Compiled by Cikgu Desikan PRE SPM PHYSICS 2016 Chapter 5 Light Dear students, The two basic processes of education are knowing and valuing. Learning bjectives : 1. Understanding
PHYSICS RM 4 Chapter 5 Light Compiled by Cikgu Desikan PRE SPM PHYSICS 2016 Chapter 5 Light Dear students, The two basic processes of education are knowing and valuing. Learning bjectives : 1. Understanding
LIGHT & OPTICS. Fundamentals of Physics 2112 Chapter 34 1
 LIGHT & OPTICS Fundamentals of Physics 22 Chapter 34 Chapter 34 Images. Two Types of Images 2. Plane Mirrors 3. Spherical Mirrors 4. Images from Spherical Mirrors 5. Spherical Refracting Surfaces 6. Thin
LIGHT & OPTICS Fundamentals of Physics 22 Chapter 34 Chapter 34 Images. Two Types of Images 2. Plane Mirrors 3. Spherical Mirrors 4. Images from Spherical Mirrors 5. Spherical Refracting Surfaces 6. Thin
9. RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
 9. RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS 1. Define the terms (a) ray of light & (b) beam of light A ray is defined as the straight line path joining the two points by which light is travelling. A beam is
9. RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS 1. Define the terms (a) ray of light & (b) beam of light A ray is defined as the straight line path joining the two points by which light is travelling. A beam is
Geometric Optics. The Law of Reflection. Physics Waves & Oscillations 3/20/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Reflection of Light. 1)Students will discover how light interacts with certain types of surfaces
 Reflection of Light 1)Students will discover how light interacts with certain types of surfaces 2) Students will understand the laws governing the phenomenon of reflection 3) Discover how images are formed,
Reflection of Light 1)Students will discover how light interacts with certain types of surfaces 2) Students will understand the laws governing the phenomenon of reflection 3) Discover how images are formed,
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Chapter 23. Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments
 Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments HITT1 A small underwater pool light is 1 m below the surface of a swimming pool. What is the radius of the circle of light on the
Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments HITT1 A small underwater pool light is 1 m below the surface of a swimming pool. What is the radius of the circle of light on the
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
INTRODUCTION REFLECTION AND REFRACTION AT BOUNDARIES. Introduction. Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface
 Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Optics Course (Phys 311) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses
 Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Welcome to: Physics I. I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide!
 Welcome to: Physics I I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide! Physics I: x Mirrors and lenses Lecture 13: 6-11-2018 Last lecture: Reflection & Refraction Reflection: Light ray hits surface Ray moves
Welcome to: Physics I I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide! Physics I: x Mirrors and lenses Lecture 13: 6-11-2018 Last lecture: Reflection & Refraction Reflection: Light ray hits surface Ray moves
Unit 11 Light and Optics Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction
 Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
Physics 1C. Lecture 23A. "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?
 Physics 1C Lecture 23A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright Mirror Equation You can mathematically relate the object distance,
Physics 1C Lecture 23A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright Mirror Equation You can mathematically relate the object distance,
GEOMETRIC OPTICS. LENSES refract light, so we need to know how light bends when entering and exiting a lens and how that interaction forms an image.
 I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
2/26/2016. Chapter 23 Ray Optics. Chapter 23 Preview. Chapter 23 Preview
 Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend...
 SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics Mirrors Plane Spherical (convex or concave) Lenses The lens equation Lensmaker s equation Combination of lenses E! Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 3, Pg Mirrors New Topic Phys
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics Mirrors Plane Spherical (convex or concave) Lenses The lens equation Lensmaker s equation Combination of lenses E! Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 3, Pg Mirrors New Topic Phys
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
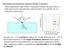 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Mirrors. N.G. Schultheiss translated and adapted by K. Schadenberg
 Mirrors N.G. Schultheiss translated and adapted by K. Schadenberg 1 Introduction This module Mirrors summarizes and extents your basic knowledge about mirrors. After this module you can proceed with the
Mirrors N.G. Schultheiss translated and adapted by K. Schadenberg 1 Introduction This module Mirrors summarizes and extents your basic knowledge about mirrors. After this module you can proceed with the
AIM To determine the frequency of alternating current using a sonometer and an electromagnet.
 EXPERIMENT 8 AIM To determine the frequency of alternating current using a sonometer and an electromagnet. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED A sonometer with a soft iron wire stretched over it, an electromagnet,
EXPERIMENT 8 AIM To determine the frequency of alternating current using a sonometer and an electromagnet. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED A sonometer with a soft iron wire stretched over it, an electromagnet,
4. Refraction. glass, air, Perspex and water.
 Mr. C. Grima 11 1. Rays and Beams A ray of light is a narrow beam of parallel light, which can be represented by a line with an arrow on it, in diagrams. A group of rays makes up a beam of light. In laboratory
Mr. C. Grima 11 1. Rays and Beams A ray of light is a narrow beam of parallel light, which can be represented by a line with an arrow on it, in diagrams. A group of rays makes up a beam of light. In laboratory
Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may draw a diagram.
 1 (a) (i) A ray of light passes through a length of curved optical fibre. Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. [1] Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may
1 (a) (i) A ray of light passes through a length of curved optical fibre. Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. [1] Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may
General Physics II. Mirrors & Lenses
 General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
Essential Physics I. Lecture 13:
 Essential Physics I E I Lecture 13: 11-07-16 Reminders No lecture: Monday 18th July (holiday) Essay due: Monday 25th July, 4:30 pm 2 weeks!! Exam: Monday 1st August, 4:30 pm Announcements 250 word essay
Essential Physics I E I Lecture 13: 11-07-16 Reminders No lecture: Monday 18th July (holiday) Essay due: Monday 25th July, 4:30 pm 2 weeks!! Exam: Monday 1st August, 4:30 pm Announcements 250 word essay
index of refraction-light speed
 AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics
 Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Sharjah Indian School, Sharjah Boys Wing
 NOTES ON Optics (Class 12-Boys Wing) Page 01 Optics deals with the study of light. Light is a form of energy that makes the things visible. There are different theories of light such as, Corpuscular theory,
NOTES ON Optics (Class 12-Boys Wing) Page 01 Optics deals with the study of light. Light is a form of energy that makes the things visible. There are different theories of light such as, Corpuscular theory,
4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb?
 1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE
 58 UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror/lens, f = R/2 Mirror formula: Magnification produced by a mirror: m = - = - Snell s law: 1
58 UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror/lens, f = R/2 Mirror formula: Magnification produced by a mirror: m = - = - Snell s law: 1
