Lesson 12: Sine 5 = 15 3
|
|
|
- Eunice Mills
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 12: Sine How did ou do on that last worksheet? Is finding the opposite side and adjacent side of an angle super-duper eas for ou now? Good, now I can show ou wh I wanted ou to learn that first. If it s still not clear, read that last lesson again. You will need a Scientific Calculator for this lesson. Below is a tall right triangle with one angle. Can ou tell me the lengths of x and with onl this much information? I bet ou can t. But I m going to teach ou a math skill that will make it possible. Isn t that incredible? I know! x The skill ou are going to learn is a Trigonometric Ratio called Sine. It is pronounced sign and it is often abbreviated sin, although it is still pronounced sine, even when abbreviated. This is the second hardest part of geometr. Man people struggle to learn this concept, but once our realize it is just a division problem it gets a lot easier. Look at the division problem below. It reads, Five equals fifteen divided b three. = 1 3 The formulas ou are about to learn in this lesson, and the next two, are in the same format as the division problem above. Look at the formula below. It is saing, The sine of Angle A is equal to the Opposite side divided b the Hpotenuse. sin A = o h This is just a division problem. The o stands for the opposite side, the h stands for the Hpotenuse, and sin A can be found with a calculator. B filling
2 in this formula we can find the two missing lengths from the triangle at the beginning of this lesson. I ll bring back that problem and show ou how to find the missing lengths. x Focus our attention on the angle. Now find the side opposite that angle. What is the length of that side? It is, so I will replace the o in the formula with. Opposite Side sin A = h Hpotenuse We don t know the length of the hpotenuse, so it will be x. sin A = x So here is the trick part. This side of the equation means the sine of the angle. Our angle is, so let s replace that side with sin. Now it sas, The sine of thirt degrees equals five divided b x. sin = x Do ou see how this is a division problem? Now all we have to do is find the sine of. But don t worr, that s a piece of cake! You just use a calculator. Some people just memorize the answer, but for me the easiest wa is to use a scientific calculator, so ou ll want to get one now. I am using a TI T-30x II s, but ou can use an scientific calculator. There is probabl one on our computer, but ou might have to change the view to scientific before ou start.
3 Each calculator is different, but basicall most are set on degrees to begin with and that s what we want. Next, tpe in 30 (ou don t have to sa degrees; that is alread set) and then press the [SIN] button. The calculator on m computer wants me to press the [SIN] button first and then 30. Tr for ourself with our calculator until ou get the answer. (point five) and then remember how ou got that answer. Now that we know the sine of 30 degrees is., we can replace that part of the equation. sin = x. = x Now we just do some basic algebra. You could do it the long wa; multipl both sides b x and then divide both sides b., but in volume VI, I showed ou the el switch-a-roo trick. It works for division equations like that one. According to el switch-a-roo, we can just switch the. with the x and we ll end up with same answer as if ou had solved it the old fashioned wa. I ll switch them around now. x =. If that confuses ou, it s no different than switching the and the 3 in the division problem below. Either wa, the equation will still be true. 3 = 1 But let s get back to our problem. We left it at x equals divided b.. x =.
4 All that s left to do is the math. I ll divide b. and get the answer to the length of the hpotenuse. x = OK, now we have the answer to x. I ll fill in the length of the hpotenuse for our triangle. Now it is time to solve for. I could use the Pthagorean Theorem to solve for, but this lesson is about sine, so let s use that. We need to find the sine of the other acute angle. Do ou know the size of the other angle? Well let s see, all triangles have a total of 180, so I ll just subtract the angles we alread know from 180 and then whatever is left is the answer. This is a right triangle, so of course this angle is 90. I ll add that to, which equals 120. So now do ou know the size of the third angle? I ll do the math, = 60. The third angle is 60.
5 We are tring to solve for. Is that side opposite or adjacent to our 60 angle? It is opposite because the flashlight is shining on that side. Which side is the hpotenuse? The side that measures is the hpotenuse. OK, so let s solve for. Some super smart mathematician figured out that the sine of this angle will be equal to the side opposite of that angle divided b the hpotenuse. Alright then, I ll write out that equation. sin 60 = OK, so what is the sine of 60? I can t reall remember, so I m going to use m Scientific Calculator to find out. M son is an engineer. He uses this kind of math nearl ever da, so he just memorizes some of these answers. I still use a calculator. So let s see, I will enter [SIN] 60 = and the screen sas , so that is the sine of 60. I will round that off and then plug that into our equation = The sine of an angle will alwas be a number between 0 and 1, and often times it will be several digits long. But mathematicians across the world agree that rounding the number down to the first four digits is close enough. Now back to our equation. Since this side is saing, divided b, I will multipl both sides b, to get b itself =
6 = 8.66 = There we go. The third side of the triangle is 8.66 units long. Prett cool, huh? 8.66 Now I ll switch it up a bit. This time I ll erase the size of the angle above and then show ou how to figure out it s size based on the length of the sides. Look at the drawing below. x 8.66 In this problem, we are tring to find the measurement of this angle, so we need to solve for x. No problem, there is a button for that on our calculators. It is called the sine INVERSE and it is written a little differentl; look at the equation below. The negative 1 in superscript makes it read, the inverse sine of x equals five over ten. That little negative 1 looks like an exponent, but it s not. sin 1 x = Since it looks so much like an exponent, often times the word Arcsin (pronounced Arc Sign) is used instead of sin -1. Either wa is acceptable and the mean the same thing. I ll write it that wa below. arcsin x =
7 Good news! Your calculator is going to do all the work, so all ou need to learn is how to enter the equation into the calculator. In Trigonometr and Pre-Calculus, ou will learn about the math that the calculator is doing, but not in this book. When ou are tring to find the inverse sine with a calculator, ou ll need to convert the fraction into a decimal number. So let s start b turning in a decimal number. I don t need a calculator for that one; I know that equals 1 which is.. 2 sin 1 x =. OK, now I need a calculator. In order to find the inverse sine of x, ou need to press two buttons. Each calculator is a little different, so look at ours and tr to find a button labeled [2 ND ] or [INV] for Inverse, or it could be [SHIFT]. You have to press this button before ou hit [SIN] and then press [x] [=] [.]. M calculator works like this: I press [2 nd ] [SIN] [=]. and magicall the screen comes up with 30. On m computer s calculator I press [.] [INV] and instantl the sin ke turns into a sin -1 ke. Once I hit the sin -1 ke, the calculator displas 30. That is the measurement of angle x! Tr it on our calculator and see if ou can get it to displa 30. Now let s find out the measurement of the other angle. Solve for x. x 8.66 The inverse sine of x will be equal to opposite over hpotenuse. sin 1 x = 8.66 First, turn that fraction into a decimal number. sin 1 x =.8660
8 I entered into m scientific calculator: [2 nd ] [SIN].8660 [=] and the screen sas, which is prett darn tootin close to 60. I ll round it up to 60. Had I not rounded the sine of 60 degrees down to four decimal points, that side would have measured Then, when ou enter [2 nd ] [SIN] = into our calculator, the answer is even closer to 60 degrees. Give it a tr. In this lesson, ou learned how to use the sine function to find the length of a right triangle s side when all ou know is the size of one angle plus the length of either the opposite side or hpotenuse. Then ou learned how to use the inverse sine function. This trigonometric function allows ou to find the size of an angle when all ou know is the length of the hpotenuse and the opposite side. You ll get a chance to practice on the next worksheet. Just remember that sine equals opposite over hpotenuse or: sin = opposite hpotenuse OR s = o h OR SOH, (pronounced as SEW) Complete the next worksheet. If ou miss more than two or if ou are confused, read this lesson again; ou ll get it.
9 Name Date Worksheet 12 page 1 of 2 Solve for x in the Right Triangles below x 2. 3 X 7 3. X x
10 Worksheet 12 page 2 of 2. Below is a sketch of Beck s Kitchen. She would like to add a corner pantr here. Stove Refrigerator Sink 2 2 Leah is going to design the face of the cabinet, which will be placed on the dotted line in the sketch above. All she needs to know is the width of the cabinet face. Use Sine to find the width of the cabinet for Beck and Leah.
Unit 4 Trigonometry. Study Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry (Section 8.1)
 Unit 4 Trigonometr Stud Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometr (Section 8.1) Objective: Evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles. Use a calculator to evaluate trigonometric functions. Use trigonometric
Unit 4 Trigonometr Stud Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometr (Section 8.1) Objective: Evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles. Use a calculator to evaluate trigonometric functions. Use trigonometric
Assignment. Pg. 567 #16-33, even pg 577 # 1-17 odd, 32-37
 Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Table of Contents. Unit 5: Trigonometric Functions. Answer Key...AK-1. Introduction... v
 These materials ma not be reproduced for an purpose. The reproduction of an part for an entire school or school sstem is strictl prohibited. No part of this publication ma be transmitted, stored, or recorded
These materials ma not be reproduced for an purpose. The reproduction of an part for an entire school or school sstem is strictl prohibited. No part of this publication ma be transmitted, stored, or recorded
SM 2. Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or
 SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
Chapter 7: Right Triangles and Trigonometry Name: Study Guide Block: Section and Objectives
 Page 1 of 22 hapter 7: Right Triangles and Trigonometr Name: Stud Guide lock: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 SOL G.8 The student will solve real-world problems involving right triangles b using the Pthagorean Theorem
Page 1 of 22 hapter 7: Right Triangles and Trigonometr Name: Stud Guide lock: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 SOL G.8 The student will solve real-world problems involving right triangles b using the Pthagorean Theorem
LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING
 LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING 137 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Plotting Points a. The -plane b. The -ais and -ais c. The origin d. Ordered
LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING 137 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Plotting Points a. The -plane b. The -ais and -ais c. The origin d. Ordered
Name: Block: What I can do for this unit:
 Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
Chapter 15 Right Triangle Trigonometry
 Chapter 15 Right Triangle Trigonometry Sec. 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry The most difficult part of Trigonometry is spelling it. Once we get by that, the rest is a piece of cake. efore we start naming
Chapter 15 Right Triangle Trigonometry Sec. 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry The most difficult part of Trigonometry is spelling it. Once we get by that, the rest is a piece of cake. efore we start naming
Connecting Algebra and Geometry with Polygons
 Connecting Algebra and Geometr with Polgons 15 Circles are reall important! Once ou know our wa around a circle, ou can use this knowledge to figure out a lot of other things! 15.1 Name That Triangle!
Connecting Algebra and Geometr with Polgons 15 Circles are reall important! Once ou know our wa around a circle, ou can use this knowledge to figure out a lot of other things! 15.1 Name That Triangle!
Algebra I Summer Math Packet
 01 Algebra I Summer Math Packet DHondtT Grosse Pointe Public Schools 5/0/01 Evaluate the power. 1.. 4. when = Write algebraic epressions and algebraic equations. Use as the variable. 4. 5. 6. the quotient
01 Algebra I Summer Math Packet DHondtT Grosse Pointe Public Schools 5/0/01 Evaluate the power. 1.. 4. when = Write algebraic epressions and algebraic equations. Use as the variable. 4. 5. 6. the quotient
Engineering and Construction F3HV 11 Maths Craft 1 RIGHT ANGLED TRIANGLES : PYTHAGORAS' THEOREM
 RIGHT NGLED TRINGLES : PYTHGORS' THEOREM ver important triangle, in terms of practical use, is the right-angled triangle. In the "real" world, the right-angled triangle is used etensivel. It is a shape
RIGHT NGLED TRINGLES : PYTHGORS' THEOREM ver important triangle, in terms of practical use, is the right-angled triangle. In the "real" world, the right-angled triangle is used etensivel. It is a shape
Lesson 11 Skills Maintenance. Activity 1. Model. The addition problem is = 4. The subtraction problem is 5 9 = 4.
 Lesson Skills Maintenance Lesson Planner Vocabular Development -coordinate -coordinate point of origin Skills Maintenance ddition and Subtraction of Positive and Negative Integers Problem Solving: We look
Lesson Skills Maintenance Lesson Planner Vocabular Development -coordinate -coordinate point of origin Skills Maintenance ddition and Subtraction of Positive and Negative Integers Problem Solving: We look
Section 1.4: Graphing Calculators and Computers
 Section 1.4: Graphing Calculators and Computers In this section we shall show some of the was that calculators can help us in mathematics. 1. Calculator Warnings Before we even consider how a calculator
Section 1.4: Graphing Calculators and Computers In this section we shall show some of the was that calculators can help us in mathematics. 1. Calculator Warnings Before we even consider how a calculator
UNIT 5 TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 5.4: Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent. Instruction. Guided Practice 5.4. Example 1
 Lesson : Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Guided Practice Example 1 Leo is building a concrete pathway 150 feet long across a rectangular courtyard, as shown in the following figure. What is the length
Lesson : Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Guided Practice Example 1 Leo is building a concrete pathway 150 feet long across a rectangular courtyard, as shown in the following figure. What is the length
Week 3. Topic 5 Asymptotes
 Week 3 Topic 5 Asmptotes Week 3 Topic 5 Asmptotes Introduction One of the strangest features of a graph is an asmptote. The come in three flavors: vertical, horizontal, and slant (also called oblique).
Week 3 Topic 5 Asmptotes Week 3 Topic 5 Asmptotes Introduction One of the strangest features of a graph is an asmptote. The come in three flavors: vertical, horizontal, and slant (also called oblique).
Topic 2 Transformations of Functions
 Week Topic Transformations of Functions Week Topic Transformations of Functions This topic can be a little trick, especiall when one problem has several transformations. We re going to work through each
Week Topic Transformations of Functions Week Topic Transformations of Functions This topic can be a little trick, especiall when one problem has several transformations. We re going to work through each
Chapter 11 Trigonometry
 hapter 11 Trigonometry Sec. 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry The most difficult part of Trigonometry is spelling it. Once we get by that, the rest is a piece of cake. efore we start naming the trigonometric
hapter 11 Trigonometry Sec. 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry The most difficult part of Trigonometry is spelling it. Once we get by that, the rest is a piece of cake. efore we start naming the trigonometric
0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY
 0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY Coordinate Geometr 0-1 Equations of Lines 0- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 0- Intersecting Lines 0- Midpoints, Distance Formula, Segment Lengths 0- Equations of Circles 0-6 Problem
0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY Coordinate Geometr 0-1 Equations of Lines 0- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 0- Intersecting Lines 0- Midpoints, Distance Formula, Segment Lengths 0- Equations of Circles 0-6 Problem
UNIT 2 RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 2: Applying Trigonometric Ratios Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: manipulating the Pythagorean Theorem given any two sides of a right triangle defining the three basic trigonometric ratios (sine,
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: manipulating the Pythagorean Theorem given any two sides of a right triangle defining the three basic trigonometric ratios (sine,
c 12 B. _ r.; = - 2 = T. .;Xplanation: 2) A 45 B. -xplanation: 5. s-,:; Student Name:
 3111201 USTestprep, Inc..USJ\~fflp naltic Geometr EOC Qui nswer Ke Geometr- (MCC9-12.G.SRT.6) Side Ratios In Right Triangles, (MCC9-12.G.SRT.7) Sine nd Cosine Of Complementar ngles 1) Student Name: Teacher
3111201 USTestprep, Inc..USJ\~fflp naltic Geometr EOC Qui nswer Ke Geometr- (MCC9-12.G.SRT.6) Side Ratios In Right Triangles, (MCC9-12.G.SRT.7) Sine nd Cosine Of Complementar ngles 1) Student Name: Teacher
CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios
 CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle. Apply inverse trigonometric ratios to
CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle. Apply inverse trigonometric ratios to
Math 26: Fall (part 1) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pythagorean Identity)
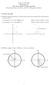 Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 8: Graphs and Functions
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 8: Graphs and Functions The Coordinate Plane A coordinate plane is formed b the intersection of a horizontal number line called the -ais and a vertical number line called the -ais.
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 8: Graphs and Functions The Coordinate Plane A coordinate plane is formed b the intersection of a horizontal number line called the -ais and a vertical number line called the -ais.
hypotenuse adjacent leg Preliminary Information: SOH CAH TOA is an acronym to represent the following three 28 m 28 m opposite leg 13 m
 On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. odel Problems II. Practice Problems III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer ey Web Resources Using the inverse sine, cosine,
On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. odel Problems II. Practice Problems III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer ey Web Resources Using the inverse sine, cosine,
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2. Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle Triangles
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2 Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle s Suggested Time: 75 minutes What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will learn through investigation, the relationship
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2 Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle s Suggested Time: 75 minutes What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will learn through investigation, the relationship
More Coordinate Graphs. How do we find coordinates on the graph?
 Lesson Problem Solving: More Coordinate Graphs Problem Solving: More Coordinate Graphs How do we find coordinates on the graph? We use coordinates to find where the dot goes on the coordinate graph. From
Lesson Problem Solving: More Coordinate Graphs Problem Solving: More Coordinate Graphs How do we find coordinates on the graph? We use coordinates to find where the dot goes on the coordinate graph. From
Intro Right Triangle Trig
 Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
LESSON 1: Trigonometry Pre-test
 LESSON 1: Trigonometry Pre-test Instructions. Answer each question to the best of your ability. If there is more than one answer, put both/all answers down. Try to answer each question, but if there is
LESSON 1: Trigonometry Pre-test Instructions. Answer each question to the best of your ability. If there is more than one answer, put both/all answers down. Try to answer each question, but if there is
Watkins Mill High School. Algebra 2. Math Challenge
 Watkins Mill High School Algebra 2 Math Challenge "This packet will help you prepare for Algebra 2 next fall. It will be collected the first week of school. It will count as a grade in the first marking
Watkins Mill High School Algebra 2 Math Challenge "This packet will help you prepare for Algebra 2 next fall. It will be collected the first week of school. It will count as a grade in the first marking
Introduction to Trigonometric Functions. Peggy Adamson and Jackie Nicholas
 Mathematics Learning Centre Introduction to Trigonometric Functions Pegg Adamson and Jackie Nicholas c 998 Universit of Sdne Acknowledgements A significant part of this manuscript has previousl appeared
Mathematics Learning Centre Introduction to Trigonometric Functions Pegg Adamson and Jackie Nicholas c 998 Universit of Sdne Acknowledgements A significant part of this manuscript has previousl appeared
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 3: ARITHMETIC PROPERTIES. Date: Lesson: Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties
 Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties CHAPTER 3: ARITHMETIC PROPERTIES Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties CHAPTER 3: ARITHMETIC PROPERTIES Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY
 MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY SECTION PAGE NUMBERS HOMEWORK Prerequisite p. 0 - # 3 Skills 4. p. 8-9 #4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,, 4. p. 37 39 #bde, acd, 3, 4acde, 5, 6ace, 7, 8, 9, 0,, 4.3 p. 46-47 #aef,, 3, 4, 5defgh,
MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY SECTION PAGE NUMBERS HOMEWORK Prerequisite p. 0 - # 3 Skills 4. p. 8-9 #4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,, 4. p. 37 39 #bde, acd, 3, 4acde, 5, 6ace, 7, 8, 9, 0,, 4.3 p. 46-47 #aef,, 3, 4, 5defgh,
Secondary Math 3- Honors. 7-4 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 Secondary Math 3- Honors 7-4 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Warm Up Fill in the Unit What You Will Learn How to restrict the domain of trigonometric functions so that the inverse can be constructed. How
Secondary Math 3- Honors 7-4 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Warm Up Fill in the Unit What You Will Learn How to restrict the domain of trigonometric functions so that the inverse can be constructed. How
Week 10. Topic 1 Polynomial Functions
 Week 10 Topic 1 Polnomial Functions 1 Week 10 Topic 1 Polnomial Functions Reading Polnomial functions result from adding power functions 1 together. Their graphs can be ver complicated, so the come up
Week 10 Topic 1 Polnomial Functions 1 Week 10 Topic 1 Polnomial Functions Reading Polnomial functions result from adding power functions 1 together. Their graphs can be ver complicated, so the come up
Albertson AP Calculus AB AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school.
 Albertson AP Calculus AB Name AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET 2017 DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the
Albertson AP Calculus AB Name AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET 2017 DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the
Implicit Differentiation - the basics
 x x 6 Implicit Differentiation - the basics Implicit differentiation is the name for the method of differentiation that we use when we have not explicitl solved for in terms of x (that means we did not
x x 6 Implicit Differentiation - the basics Implicit differentiation is the name for the method of differentiation that we use when we have not explicitl solved for in terms of x (that means we did not
LINEAR PROGRAMMING. Straight line graphs LESSON
 LINEAR PROGRAMMING Traditionall we appl our knowledge of Linear Programming to help us solve real world problems (which is referred to as modelling). Linear Programming is often linked to the field of
LINEAR PROGRAMMING Traditionall we appl our knowledge of Linear Programming to help us solve real world problems (which is referred to as modelling). Linear Programming is often linked to the field of
SPRITES Moving Two At the Same Using Game State
 If you recall our collision detection lesson, you ll likely remember that you couldn t move both sprites at the same time unless you hit a movement key for each at exactly the same time. Why was that?
If you recall our collision detection lesson, you ll likely remember that you couldn t move both sprites at the same time unless you hit a movement key for each at exactly the same time. Why was that?
20 Calculus and Structures
 0 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER FUNCTIONS Calculus and Structures Copright LESSON FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS A function f is a relationship between an input and an output and a set of instructions as to how
0 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER FUNCTIONS Calculus and Structures Copright LESSON FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS A function f is a relationship between an input and an output and a set of instructions as to how
Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry
 153 Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry Objective #1: Understanding djacent, Hypotenuse, and Opposite sides of an acute angle in a right triangle. In a right triangle, the otenuse is always the longest
153 Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry Objective #1: Understanding djacent, Hypotenuse, and Opposite sides of an acute angle in a right triangle. In a right triangle, the otenuse is always the longest
4.7 INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 Section 4.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions 4 4.7 INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS NASA What ou should learn Evaluate and graph the inverse sine function. Evaluate and graph the other inverse trigonometric
Section 4.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions 4 4.7 INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS NASA What ou should learn Evaluate and graph the inverse sine function. Evaluate and graph the other inverse trigonometric
Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8)
 Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8) Standards: Geom 19.0, Geom 20.0, Trig 7.0, Trig 8.0, Trig 12.0 Segerstrom High School -- Math Analysis Honors Name: Period:
Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8) Standards: Geom 19.0, Geom 20.0, Trig 7.0, Trig 8.0, Trig 12.0 Segerstrom High School -- Math Analysis Honors Name: Period:
turn counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. However, we could equally well get to this point by a 3 4 turn clockwise, giving (r, θ) = (1, 3π 2
 Math 133 Polar Coordinates Stewart 10.3/I,II Points in polar coordinates. The first and greatest achievement of modern mathematics was Descartes description of geometric objects b numbers, using a sstem
Math 133 Polar Coordinates Stewart 10.3/I,II Points in polar coordinates. The first and greatest achievement of modern mathematics was Descartes description of geometric objects b numbers, using a sstem
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS GRAPHING System of Equations: 2 linear equations that we try to solve at the same time. An ordered pair is a solution to a system if it makes BOTH equations true. Steps to
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS GRAPHING System of Equations: 2 linear equations that we try to solve at the same time. An ordered pair is a solution to a system if it makes BOTH equations true. Steps to
CHECK Your Understanding
 CHECK Your Understanding. State the domain and range of each relation. Then determine whether the relation is a function, and justif our answer.. a) e) 5(, ), (, 9), (, 7), (, 5), (, ) 5 5 f) 55. State
CHECK Your Understanding. State the domain and range of each relation. Then determine whether the relation is a function, and justif our answer.. a) e) 5(, ), (, 9), (, 7), (, 5), (, ) 5 5 f) 55. State
THE INVERSE GRAPH. Finding the equation of the inverse. What is a function? LESSON
 LESSON THE INVERSE GRAPH The reflection of a graph in the line = will be the graph of its inverse. f() f () The line = is drawn as the dotted line. Imagine folding the page along the dotted line, the two
LESSON THE INVERSE GRAPH The reflection of a graph in the line = will be the graph of its inverse. f() f () The line = is drawn as the dotted line. Imagine folding the page along the dotted line, the two
science. In this course we investigate problems both algebraically and graphically.
 Section. Graphs. Graphs Much of algebra is concerned with solving equations. Man algebraic techniques have been developed to provide insights into various sorts of equations and those techniques are essential
Section. Graphs. Graphs Much of algebra is concerned with solving equations. Man algebraic techniques have been developed to provide insights into various sorts of equations and those techniques are essential
AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES
 AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean
AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean
Trigonometry and the Unit Circle. Chapter 4
 Trigonometry and the Unit Circle Chapter 4 Topics Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. Develop and apply the equation of the unit circle. Solve
Trigonometry and the Unit Circle Chapter 4 Topics Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. Develop and apply the equation of the unit circle. Solve
Midpoint of a Line Segment. INVESTIGATE the Math
 .1 Midpoint of a Line Segment YOU WILL NEED grid paper, ruler, and compass, or dnamic geometr software GOAL Develop and use the formula for the midpoint of a line segment. INVESTIGATE the Math Ken s circular
.1 Midpoint of a Line Segment YOU WILL NEED grid paper, ruler, and compass, or dnamic geometr software GOAL Develop and use the formula for the midpoint of a line segment. INVESTIGATE the Math Ken s circular
Integrated Algebra A Notes/Homework Packet 9
 Name Date Integrated Algebra A Notes/Homework Packet 9 Lesson Homework Graph Using the Calculator HW # Graph with Slope/Intercept Method HW # Graph with Slope/Intercept Method-Continued HW #3 Review Put
Name Date Integrated Algebra A Notes/Homework Packet 9 Lesson Homework Graph Using the Calculator HW # Graph with Slope/Intercept Method HW # Graph with Slope/Intercept Method-Continued HW #3 Review Put
ANGLES See the Math Notes boxes in Lessons and for more information about angle relationships.
 CC1 Basic Definitions Defense Practice ANGLES 2.1.1 2.1.5 Applications of geometr in everda settings often involve the measures of angles. In this chapter we begin our stud of angle measurement. After
CC1 Basic Definitions Defense Practice ANGLES 2.1.1 2.1.5 Applications of geometr in everda settings often involve the measures of angles. In this chapter we begin our stud of angle measurement. After
2.1 The Tangent Ratio
 2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Intermediate Algebra. Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology
 Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
A trigonometric ratio is a,
 ALGEBRA II Chapter 13 Notes The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. Section 13.1 Right-Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: 1. Find the trigonometric
ALGEBRA II Chapter 13 Notes The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. Section 13.1 Right-Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: 1. Find the trigonometric
Determine Whether Two Functions Are Equivalent. Determine whether the functions in each pair are equivalent by. and g (x) 5 x 2
 .1 Functions and Equivalent Algebraic Epressions On September, 1999, the Mars Climate Orbiter crashed on its first da of orbit. Two scientific groups used different measurement sstems (Imperial and metric)
.1 Functions and Equivalent Algebraic Epressions On September, 1999, the Mars Climate Orbiter crashed on its first da of orbit. Two scientific groups used different measurement sstems (Imperial and metric)
CW High School. Advanced Math A. 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph.
 1. Functions and Math Models (10.00%) 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph. 4 Pro cient I can make connections between the algebraic
1. Functions and Math Models (10.00%) 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph. 4 Pro cient I can make connections between the algebraic
Mathematics Stage 5 PAS5.1.2 Coordinate geometry
 Mathematics Stage PAS.. Coordinate geometr Part Graphing lines Acknowledgments This publication is copright New South Wales Department of Education and Training (DET), however it ma contain material from
Mathematics Stage PAS.. Coordinate geometr Part Graphing lines Acknowledgments This publication is copright New South Wales Department of Education and Training (DET), however it ma contain material from
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3. Primary Trigonometric Ratios
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3 Suggested Time: 75 minutes Primary Trigonometric Ratios What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will use trigonometry (sin, cos, tan) to measure
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3 Suggested Time: 75 minutes Primary Trigonometric Ratios What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will use trigonometry (sin, cos, tan) to measure
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios and Pythagorean Theorem 4. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios and Pythagorean Theorem 4. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
Syllabus Objective: 3.1 The student will solve problems using the unit circle.
 Precalculus Notes: Unit 4 Trigonometr Sllabus Objective:. The student will solve problems using the unit circle. Review: a) Convert. hours into hours and minutes. Solution: hour + (0.)(60) = hour and minutes
Precalculus Notes: Unit 4 Trigonometr Sllabus Objective:. The student will solve problems using the unit circle. Review: a) Convert. hours into hours and minutes. Solution: hour + (0.)(60) = hour and minutes
Using the same procedure that was used in Project 5, enter matrix A and its label into an Excel spreadsheet:
 Math 6: Ecel Lab 6 Summer Inverse Matrices, Determinates and Applications: (Stud sections, 6, 7 and in the matri book in order to full understand the topic.) This Lab will illustrate how Ecel can help
Math 6: Ecel Lab 6 Summer Inverse Matrices, Determinates and Applications: (Stud sections, 6, 7 and in the matri book in order to full understand the topic.) This Lab will illustrate how Ecel can help
1. Let be a point on the terminal side of θ. Find the 6 trig functions of θ. (Answers need not be rationalized). b. P 1,3. ( ) c. P 10, 6.
 Q. Right Angle Trigonometry Trigonometry is an integral part of AP calculus. Students must know the basic trig function definitions in terms of opposite, adjacent and hypotenuse as well as the definitions
Q. Right Angle Trigonometry Trigonometry is an integral part of AP calculus. Students must know the basic trig function definitions in terms of opposite, adjacent and hypotenuse as well as the definitions
Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before.
 Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1 Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before. Strategy
Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1 Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before. Strategy
UNIT 2 RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 1: Exploring Trigonometric Ratios Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: measuring angles with a protractor understanding how to label angles and sides in triangles converting fractions into decimals
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: measuring angles with a protractor understanding how to label angles and sides in triangles converting fractions into decimals
8.6 Other Trigonometric Functions
 8.6 Other Trigonometric Functions I have already discussed all the trigonometric functions and their relationship to the sine and cosine functions and the x and y coordinates on the unit circle, but let
8.6 Other Trigonometric Functions I have already discussed all the trigonometric functions and their relationship to the sine and cosine functions and the x and y coordinates on the unit circle, but let
What s the Point? # 2 - Geo Fashion
 What s the Point? # 2 - Geo Fashion Graph the points and connect them with line segments. Do not connect points with DNC between them. Start (-4,1) (-5,5) (-2,2) (-4,1) DNC (2,-4) (3,-3) (4,-3) (5,-4)
What s the Point? # 2 - Geo Fashion Graph the points and connect them with line segments. Do not connect points with DNC between them. Start (-4,1) (-5,5) (-2,2) (-4,1) DNC (2,-4) (3,-3) (4,-3) (5,-4)
Geometry. Slide 1 / 202. Slide 2 / 202. Slide 3 / 202. Analytic Geometry. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 202 Slide 2 / 202 Geometr Analtic Geometr 201--02 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 202 Origin of Analtic Geometr The Distance Formula The Midpoint Formula Partitions of a Line Segment
Slide 1 / 202 Slide 2 / 202 Geometr Analtic Geometr 201--02 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 202 Origin of Analtic Geometr The Distance Formula The Midpoint Formula Partitions of a Line Segment
Pre-calculus Chapter 4 Part 1 NAME: P.
 Pre-calculus NAME: P. Date Day Lesson Assigned Due 2/12 Tuesday 4.3 Pg. 284: Vocab: 1-3. Ex: 1, 2, 7-13, 27-32, 43, 44, 47 a-c, 57, 58, 63-66 (degrees only), 69, 72, 74, 75, 78, 79, 81, 82, 86, 90, 94,
Pre-calculus NAME: P. Date Day Lesson Assigned Due 2/12 Tuesday 4.3 Pg. 284: Vocab: 1-3. Ex: 1, 2, 7-13, 27-32, 43, 44, 47 a-c, 57, 58, 63-66 (degrees only), 69, 72, 74, 75, 78, 79, 81, 82, 86, 90, 94,
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 8-1 Similarity in Right Triangles
 8 Find this vocabular word in Lesson 8-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Finding Geometric Means The geometric mean of two positive numbers is the positive square root of their. Find the geometric mean of
8 Find this vocabular word in Lesson 8-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Finding Geometric Means The geometric mean of two positive numbers is the positive square root of their. Find the geometric mean of
Unit 3, Lesson 1.3 Special Angles in the Unit Circle
 Unit, Lesson Special Angles in the Unit Circle Special angles exist within the unit circle For these special angles, it is possible to calculate the exact coordinates for the point where the terminal side
Unit, Lesson Special Angles in the Unit Circle Special angles exist within the unit circle For these special angles, it is possible to calculate the exact coordinates for the point where the terminal side
Introduction to Trigonometry
 NAME COMMON CORE GEOMETRY- Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry DATE PAGE TOPIC HOMEWORK 1/22 2-4 Lesson 1 : Incredibly Useful Ratios Homework Worksheet 1/23 5-6 LESSON 2: Using Trigonometry to find missing
NAME COMMON CORE GEOMETRY- Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry DATE PAGE TOPIC HOMEWORK 1/22 2-4 Lesson 1 : Incredibly Useful Ratios Homework Worksheet 1/23 5-6 LESSON 2: Using Trigonometry to find missing
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES
 AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio.
 14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
Understand the Slope-Intercept Equation for a Line
 Lesson Part : Introduction Understand the Slope-Intercept Equation for a Line Focus on Math Concepts CCLS 8.EE..6 How can ou show that an equation in the form 5 mx b defines a line? You have discovered
Lesson Part : Introduction Understand the Slope-Intercept Equation for a Line Focus on Math Concepts CCLS 8.EE..6 How can ou show that an equation in the form 5 mx b defines a line? You have discovered
Intro Right Triangle Trig
 Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
SECONDARY MATH Area of a Triangle and Law of Sines
 SECONDARY MATH 3 7-1 Area of a Triangle and Law of Sines Goal: Be the first team to find (r j h g f)(x). WARM UP COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS Person #1 f(x) = x 2 7x + 6 Person #2 g(x) = 2 +10 4 Person #3
SECONDARY MATH 3 7-1 Area of a Triangle and Law of Sines Goal: Be the first team to find (r j h g f)(x). WARM UP COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS Person #1 f(x) = x 2 7x + 6 Person #2 g(x) = 2 +10 4 Person #3
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
 Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
AP Calculus Summer Review Packet
 AP Calculus Summer Review Packet Name: Date began: Completed: **A Formula Sheet has been stapled to the back for your convenience!** Email anytime with questions: danna.seigle@henry.k1.ga.us Complex Fractions
AP Calculus Summer Review Packet Name: Date began: Completed: **A Formula Sheet has been stapled to the back for your convenience!** Email anytime with questions: danna.seigle@henry.k1.ga.us Complex Fractions
= = The number system. Module. Glossary Math Tools... 33
 - > + > < - %. < + a = - = = b in. F - - Module The number sstem Lesson Rational and Irrational Numbers........ 8.NS. Lesson ompare and Order Numbers......... 8 8.NS., 8.NS. Lesson Estimate the Value of
- > + > < - %. < + a = - = = b in. F - - Module The number sstem Lesson Rational and Irrational Numbers........ 8.NS. Lesson ompare and Order Numbers......... 8 8.NS., 8.NS. Lesson Estimate the Value of
4.1: Angles & Angle Measure
 4.1: Angles & Angle Measure In Trigonometry, we use degrees to measure angles in triangles. However, degree is not user friendly in many situations (just as % is not user friendly unless we change it into
4.1: Angles & Angle Measure In Trigonometry, we use degrees to measure angles in triangles. However, degree is not user friendly in many situations (just as % is not user friendly unless we change it into
Determining the 2d transformation that brings one image into alignment (registers it) with another. And
 Last two lectures: Representing an image as a weighted combination of other images. Toda: A different kind of coordinate sstem change. Solving the biggest problem in using eigenfaces? Toda Recognition
Last two lectures: Representing an image as a weighted combination of other images. Toda: A different kind of coordinate sstem change. Solving the biggest problem in using eigenfaces? Toda Recognition
Lesson 6a Exponents and Rational Functions
 Lesson 6a Eponents and Rational Functions In this lesson, we put quadratics aside for the most part (not entirely) in this lesson and move to a study of eponents and rational functions. The rules of eponents
Lesson 6a Eponents and Rational Functions In this lesson, we put quadratics aside for the most part (not entirely) in this lesson and move to a study of eponents and rational functions. The rules of eponents
M O T I O N A N D D R A W I N G
 2 M O T I O N A N D D R A W I N G Now that ou know our wa around the interface, ou re read to use more of Scratch s programming tools. In this chapter, ou ll do the following: Eplore Scratch s motion and
2 M O T I O N A N D D R A W I N G Now that ou know our wa around the interface, ou re read to use more of Scratch s programming tools. In this chapter, ou ll do the following: Eplore Scratch s motion and
Unit 2: Trigonometry. This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses.
 Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231
 1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 3: Basics of differential equations Section 6. Euler s method. for approximate solutions of IVP s
 Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 3: Basics of differential equations Section 6 Euler s method for approximate solutions of IVP s What ou need to know alread: What an initial value problem is.
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 3: Basics of differential equations Section 6 Euler s method for approximate solutions of IVP s What ou need to know alread: What an initial value problem is.
Warm Up: please factor completely
 Warm Up: please factor completely 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. vocabulary KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED: MA3A2. Students will use the circle to define the trigonometric functions. a. Define and understand angles measured
Warm Up: please factor completely 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. vocabulary KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED: MA3A2. Students will use the circle to define the trigonometric functions. a. Define and understand angles measured
Connecting the Dots Making Connections Between Arithmetic Sequences and Linear Functions
 Connecting the Dots Making Connections Between Arithmetic Sequences and Linear Functions Warm Up Use what ou know about arithmetic sequences to complete each task.. Write the first 5 terms of the sequence
Connecting the Dots Making Connections Between Arithmetic Sequences and Linear Functions Warm Up Use what ou know about arithmetic sequences to complete each task.. Write the first 5 terms of the sequence
2.1 The ReCTAngUlAR COORdInATe SySTemS And graphs
 7 CHAPTER equations ANd inequalities learning ObjeCTIveS In this section ou will: Plot ordered pairs in a Cartesian coordinate sstem. Graph equations b plotting points. Graph equations with a graphing
7 CHAPTER equations ANd inequalities learning ObjeCTIveS In this section ou will: Plot ordered pairs in a Cartesian coordinate sstem. Graph equations b plotting points. Graph equations with a graphing
Week 27 Algebra 1 Assignment:
 Week 7 Algebra Assignment: Da : p. 494 #- odd, -, 8- Da : pp. 496-497 #-9 odd, -6 Da : pp. 0-0 #-9 odd, -, -9 Da 4: p. 09 #-4, 7- Da : pp. - #-9 odd Notes on Assignment: Page 494: General notes for this
Week 7 Algebra Assignment: Da : p. 494 #- odd, -, 8- Da : pp. 496-497 #-9 odd, -6 Da : pp. 0-0 #-9 odd, -, -9 Da 4: p. 09 #-4, 7- Da : pp. - #-9 odd Notes on Assignment: Page 494: General notes for this
DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10.
 Ch 3 DECIMALS ~ Notes DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10. Since decimals are special fractions, then all the rules we have already learned for fractions should work for
Ch 3 DECIMALS ~ Notes DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10. Since decimals are special fractions, then all the rules we have already learned for fractions should work for
y = f(x) x (x, f(x)) f(x) g(x) = f(x) + 2 (x, g(x)) 0 (0, 1) 1 3 (0, 3) 2 (2, 3) 3 5 (2, 5) 4 (4, 3) 3 5 (4, 5) 5 (5, 5) 5 7 (5, 7)
 0 Relations and Functions.7 Transformations In this section, we stud how the graphs of functions change, or transform, when certain specialized modifications are made to their formulas. The transformations
0 Relations and Functions.7 Transformations In this section, we stud how the graphs of functions change, or transform, when certain specialized modifications are made to their formulas. The transformations
Tubes are Fun. By: Douglas A. Ruby Date: 6/9/2003 Class: Geometry or Trigonometry Grades: 9-12 INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES:
 Tubes are Fun B: Douglas A. Rub Date: 6/9/2003 Class: Geometr or Trigonometr Grades: 9-2 INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES: Using a view tube students will conduct an eperiment involving variation of the viewing
Tubes are Fun B: Douglas A. Rub Date: 6/9/2003 Class: Geometr or Trigonometr Grades: 9-2 INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES: Using a view tube students will conduct an eperiment involving variation of the viewing
The Sine and Cosine Functions
 Lesson -5 Lesson -5 The Sine and Cosine Functions Vocabular BIG IDEA The values of cos and sin determine functions with equations = sin and = cos whose domain is the set of all real numbers. From the eact
Lesson -5 Lesson -5 The Sine and Cosine Functions Vocabular BIG IDEA The values of cos and sin determine functions with equations = sin and = cos whose domain is the set of all real numbers. From the eact
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 4
 MATH STUDENT BOOK th Grade Unit Unit GRAPHING AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS MATH 0 GRAPHING AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS INTRODUCTION. GRAPHING 5 GRAPHING AND AMPLITUDE 5 PERIOD AND FREQUENCY VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL
MATH STUDENT BOOK th Grade Unit Unit GRAPHING AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS MATH 0 GRAPHING AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS INTRODUCTION. GRAPHING 5 GRAPHING AND AMPLITUDE 5 PERIOD AND FREQUENCY VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL
Chapter 2: Introduction to Functions
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Functions Lesson 1: Introduction to Functions Lesson 2: Function Notation Lesson 3: Composition of Functions Lesson 4: Domain and Range Lesson 5: Restricted Domain Lesson 6:
Chapter 2: Introduction to Functions Lesson 1: Introduction to Functions Lesson 2: Function Notation Lesson 3: Composition of Functions Lesson 4: Domain and Range Lesson 5: Restricted Domain Lesson 6:
Intro Right Triangle Trig
 Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse
 7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
