The Development of a 3D Self-Adaptive Goal-Oriented hp-finite Element Software for Simulations of Resistivity Logging Instruments
|
|
|
- Dwayne Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Progress Report on: The Development of a 3D Self-Adaptive Goal-Oriented hp-finite Element Software for Simulations of Resistivity Logging Instruments David Pardo (dzubiaur@yahoo.es), L. Demkowicz, C. Torres-Verdin, M. Paszynski, J. Kurtz Collaborators: Science Department of Baker-Hughes, L.E. Garcia-Castillo, W. Rachowicz December 13, 2005 Department of Petroleum and Geosystems Engineering, and Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences (ICES)
2 OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Numerical Methodology hp-finite Elements (Exponential convergence) Automatic Goal-Oriented Refinements (in the quantity of interest) 3. Current Stage of the 3D High Performance FE Software 4. Preliminary Results 5. Conclusions and Future Work
3 MOTIVATION Induction Instrument in a Deviated Well MATERIAL I LOGGING INSTRUMENT MATERIAL II MATERIAL II MATERIAL III MATERIAL III MATERIAL IV BOREHOLE Goal: Determine EM field at the receiver antennas. 2
4 MOTIVATION Through Casing Resistivity Tools MATERIAL I BOREHOLE STEEL CASING MATERIAL II MATERIAL II MATERIAL III ELECTRODES MATERIAL III MATERIAL IV Goal: Determine EM field at the receiver antennas. 3
5 MOTIVATION Electrode Problem 100 m 0.1m 99.9m BACKGROUND: 1 Ohm. m 99 m RECEIVER Loop antenna in a homogeneous media at DC. TRANSMITTER 1 m Computational domain: 100 m x 100 m. CROSS SECTION OF ANTENNAS: 0.05 m x 0.05 m 100 m 4
6 THE hp-finite ELEMENT METHOD The h-finite Element Method 1. Convergence limited by the polynomial degree, and large material contrasts. 2. Optimal h-grids do NOT converge exponentially in real applications. x z y 3. They may lock (100% error). The p-finite Element Method 1. Exponential convergence feasible for analytical ( nice ) solutions. 2. Optimal p-grids do NOT converge exponentially in real applications. x z y 3. If initial h-grid is not adequate, the p-method will fail miserably. The hp-finite Element Method 1. Exponential convergence feasible for ALL solutions. 2. Optimal hp-grids DO converge exponentially in real applications. x z y 3. If initial hp-grid is not adequate, results will still be great. 5
7 GOAL-ORIENTED ADAPTIVITY Mathematical Formulation (Goal-Oriented Adaptivity) DIRECT PROBLEM - Ψ - 2D Cross-Section DUAL PROBLEM - G - 2D Cross-Section Representation Formula for the Error in the Quantity of Interest: L(Ψ)=b(Ψ,G) = Ω σ Ψ GdV 6
8 GOAL-ORIENTED ADAPTIVITY Mathematical Formulation (Goal-Oriented Adaptivity) We define: e = Ψ Ψ hp, ǫ = G G hp. Ψ exact solution of direct problem G exact solution of dual problem Upper Bound for the Error in the Quantity of Interest: L(e) = b(e, G) = b(e, ǫ) = σ e ǫ dv Ω ALGORITHM I: σ e ǫ dv K K ALGORITHM II: σ ( e) 2 dv σ ( ǫ) 2 dv K K K 7
9 SELF-ADAPTIVE GOAL-ORIENTED hp-fem Algorithm for Goal-Oriented Adaptivity - STEP I - Solve Direct and Dual Problems on Grid hp Solve Direct and Dual Problems on Grid h/2, p+1 Use the fine grid solution to estimate the coarse grid error function. Apply the fully automatic goal-oriented hp-adaptive algorithm. Next optimal hp-grid: 8
10 SELF-ADAPTIVE GOAL-ORIENTED hp-fem Algorithm for Goal-Oriented Adaptivity - STEP II - Solve Direct and Dual Problems on Grid hp Solve Direct and Dual Problems on Grid h/2, p+1 Use the fine grid solution to estimate the coarse grid error function. Apply the fully automatic goal-oriented hp-adaptive algorithm. Next optimal hp-grid: 9
11 SELF-ADAPTIVE GOAL-ORIENTED hp-fem Algorithm for Goal-Oriented Adaptivity - STEP III - Solve Direct and Dual Problems on Grid hp Solve Direct and Dual Problems on Grid h/2, p+1 Use the fine grid solution to estimate the coarse grid error function. Apply the fully automatic goal-oriented hp-adaptive algorithm. Next optimal hp-grid: 10
12 SELF-ADAPTIVE GOAL-ORIENTED hp-fem Algorithm for Goal-Oriented Adaptivity - STEP IV - Solve Direct and Dual Problems on Grid hp Solve Direct and Dual Problems on Grid h/2, p+1 Use the fine grid solution to estimate the coarse grid error function. Apply the fully automatic goal-oriented hp-adaptive algorithm. Next optimal hp-grid: 11
13 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE 3Dhp-log Contains Several Packages: SOLVER OF LINEAR EQUATIONS ADAPTIVITY AUTOMATIC REFINEMENTS KERNEL GEOMETRY AND GRAPHICS parallel parallel version interacts with all packages Improvement needed PROBLEM SET UP 12
14 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE 3Dhp-log Contains Several Packages: METIS optimal ordering of elements MUMPS solver of linear equations interface solve1 solver of linear equations interface two_grid_hp iterative solver of linear equations ADAPTIVITY AUTOMATIC REFINEMENTS 3D hp kernel data structures mesh refinements GEOMETRY AND GRAPHICS parallel parallel version interacts with all packages External components Improvement needed PROBLEM SET UP 13
15 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE Importance of Ordering Elements (when using MUMPS) The time and memory used by the solver MUMPS depends upon the ordering of elements. The ordering of elements provided by METIS seems adequate. 14
16 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE Importance of Order of Approximation (when using MUMPS) For p=6, the solver MUMPS utilizes 50% more memory and time than for p=3. 15
17 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE Memory and Time Used by MUMPS The memory used by MUMPS depends linearly with respect to the number of unknowns. The time used by MUMPS has a quadratic dependance with respect to the number of unknowns. By using 16 processors, we expect to solve 2 million unknowns in 1 hour. 16
18 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE 3Dhp-log Contains Several Packages: METIS optimal ordering of elements MUMPS solver of linear equations interface solve1 solver of linear equations interface two_grid_hp iterative solver of linear equations goal_adapt goal oriented adaptivity h_adapt h adaptivity energy norm 3D hp kernel data structures mesh refinements GEOMETRY AND GRAPHICS hp_adapt hp adaptivity energy norm parallel parallel version interacts with all packages External components Improvement needed PROBLEM SET UP 17
19 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE Resources Needed by the Adaptive Algorithm The adaptive algorithm utilizes about half of the time used by the solver MUMPS. The amount of memory used by the adaptive algorithm is negligible, and results are not reported here. Since the final result is given by the final fine-grid solution, the adaptive algorithm does NOT need to be executed on the last iteration. For multiple logging instrument positions, the optimal grid may be reutilized without employing the adaptive algorithm. Resources needed by the adaptive algorithm are between 4% and 25% of the total resources needed by the 3D code (if MUMPS is used). 18
20 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE 3Dhp-log Contains Several Packages: METIS optimal ordering of elements MUMPS solver of linear equations interface solve1 solver of linear equations interface two_grid_hp iterative solver of linear equations goal_adapt goal oriented adaptivity h_adapt h adaptivity energy norm hp_adapt hp adaptivity energy norm 3D hp kernel data structures mesh refinements graph3d 3D graphics GMP Geometrical Modeling Package parallel parallel version interacts with all packages External components Improvement needed PROBLEM SET UP 19
21 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE Geometry and Graphics MATERIAL II LOGGING INSTRUMENT MATERIAL I MATERIAL II We are developing an interface program to automatically generate cylindrical-type grids with userprescribed angles. MATERIAL III MATERIAL III GMP utilizes isoparametric elements (i.e. approximation of the geometry coincides with that of the solution). After each refinement, an update on the geometry is performed. MATERIAL IV BOREHOLE A new graphics package shall be installed within this month. 20
22 CURRENT STAGE OF THE 3D hp-fe SOFTWARE 3Dhp-log Contains Several Packages: METIS optimal ordering of elements MUMPS solver of linear equations interface solve1 solver of linear equations interface two_grid_hp iterative solver of linear equations goal_adapt goal oriented adaptivity parallel parallel version interacts with all packages External components Improvement needed h_adapt h adaptivity energy norm hp_adapt hp adaptivity energy norm 3D hp kernel data structures mesh refinements laplace set up equation to solve problem set up problem graph3d 3D graphics GMP Geometrical Modeling Package generate_input set up geometry for the problem 21
23 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Electrode Problem 100 m 0.1m 99.9m BACKGROUND: 1 Ohm. m 99 m RECEIVER Loop antenna in a homogeneous media at DC. TRANSMITTER 1 m Computational domain: 100 m x 100 m. CROSS SECTION OF ANTENNAS: 0.05 m x 0.05 m 100 m 22
24 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Electrode Problem Final hp-grid Final solution 2D Solution: D Solution:
25 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Electrode Problem 24
26 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Fichera problem (unknown exact solution) OBJECTIVE: INTEGRAL OF SOLUTION OVER THIS BRICK z x y Equation: u = 0 Boundary Conditions: Neumann, Dirichlet z x y z x y Solution of Direct Problem Solution of Dual Problem 25
27 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Fichera problem (final hp-grids) Energy-norm: x z y x z y x z y Goal-oriented (algorithm I) Goal-oriented (algorithm II) 26
28 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Fichera problem (convergence history) Exponential Convergence in the Quantity of Interest 27
29 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The self-adaptive goal-oriented hp-adaptive strategy converges exponentially in terms of a user-prescribed quantity of interest vs. the CPU time. Preliminary results indicate that it shall be possible to simulate a variety of EM logging instruments in deviated wells by using the 3D self-adaptive goal-oriented hp-fem. The software is expected to be suitable for ALL kind of resistivity logging instruments in possibly cased wells. Cylindrical geometries can be accurately described by using higher-order elements. Department of Petroleum and Geosystems Engineering, and Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences (ICES) 28
30 FUTURE WORK Tasks and Completion Date 3D DC CODE PHASE I: NEW adaptive package and solver. COMPLETED. PHASE II: Goal-Oriented Adaptivity. COMPLETED. PHASE III: Interface for Describing Logging Problems. COMPLETED. PHASE IV: New 3D Graphics Package. 20 Jan PHASE V: Parallel Solver (MUMPS). 1 Mar PHASE VI: Logging Examples (without casing). 10 Mar PHASE VII: Iterative Solver. 10 Jun 2006 PHASE VIII: Parallel Version of 3D code. 20 Jun 2006 PHASE IX: Through Casing Resistivity Instruments. 20 Jul D AC CODE PHASE X: AC CODE USING EDGE ELEMENTS. 1 April
31 APPENDIX: SHOULD WE USE CYLINDRICAL GRIDS? Simpler geometries. The possibility of using cylindrical grids MAIN ADVANTAGES Possibly less elements needed on the azimuthal direction. MAIN DISADVANTAGES Advantages mentioned above are not clear in the case of deviated wells. Extra boundary condition needed (Ψ(0) = Ψ(2π)). Integration becomes not exact. New partial differential equations need to be implemented. Continuous elements and Nedelec elements are based on cartesian geometries. At ρ = 0 degenerated elements may be needed. FOR DEVIATED WELLS, IT IS NOT CLEAR THAT THE USE OF CYLINDRICAL GRIDS (AS OPPOSED TO CARTESIAN GRIDS) BECOMES MORE ADEQUATE 30
Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments
 Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments M. Paszyński 1,3, D. Pardo 1,2, L. Demkowicz 1, C. Torres-Verdin 2 1 Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences 2
Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments M. Paszyński 1,3, D. Pardo 1,2, L. Demkowicz 1, C. Torres-Verdin 2 1 Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences 2
3D Resistivity Logging Instruments
 Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments M.Paszyński (1), D.Pardo (2), L.Demkowicz (3), C.Torres-Verdin (2) (1) Department of Modeling and Information Technology, AGH
Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments M.Paszyński (1), D.Pardo (2), L.Demkowicz (3), C.Torres-Verdin (2) (1) Department of Modeling and Information Technology, AGH
A direct solver with reutilization of previously-computed LU factorizations for h-adaptive finite element grids with point singularities
 Maciej Paszynski AGH University of Science and Technology Faculty of Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunication Department of Computer Science al. A. Mickiewicza 30 30-059 Krakow, Poland tel.
Maciej Paszynski AGH University of Science and Technology Faculty of Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunication Department of Computer Science al. A. Mickiewicza 30 30-059 Krakow, Poland tel.
ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT
 Finite Element Methods In Linear Structural Mechanics Univ. Prof. Dr. Techn. G. MESCHKE SHORT PRESENTATION IN ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT Abdullah ALSAHLY By Shorash MIRO Computational Engineering Ruhr Universität
Finite Element Methods In Linear Structural Mechanics Univ. Prof. Dr. Techn. G. MESCHKE SHORT PRESENTATION IN ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT Abdullah ALSAHLY By Shorash MIRO Computational Engineering Ruhr Universität
Contents. I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1
 page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
3D NURBS-ENHANCED FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 7th Workshop on Numerical Methods in Applied Science and Engineering (NMASE 8) Vall de Núria, 9 a 11 de enero de 28 c LaCàN, www.lacan-upc.es 3D NURBS-ENHANCED FINITE ELEMENT METHOD R. Sevilla, S. Fernández-Méndez
7th Workshop on Numerical Methods in Applied Science and Engineering (NMASE 8) Vall de Núria, 9 a 11 de enero de 28 c LaCàN, www.lacan-upc.es 3D NURBS-ENHANCED FINITE ELEMENT METHOD R. Sevilla, S. Fernández-Méndez
Fast solvers for mesh-based computations
 Fast solvers for mesh-based computations Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer Science AGH University, Krakow, Poland home.agh.edu.pl/paszynsk Collaborators: Anna Paszyńska (Jagiellonian University,Poland)
Fast solvers for mesh-based computations Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer Science AGH University, Krakow, Poland home.agh.edu.pl/paszynsk Collaborators: Anna Paszyńska (Jagiellonian University,Poland)
Accelerating Double Precision FEM Simulations with GPUs
 Accelerating Double Precision FEM Simulations with GPUs Dominik Göddeke 1 3 Robert Strzodka 2 Stefan Turek 1 dominik.goeddeke@math.uni-dortmund.de 1 Mathematics III: Applied Mathematics and Numerics, University
Accelerating Double Precision FEM Simulations with GPUs Dominik Göddeke 1 3 Robert Strzodka 2 Stefan Turek 1 dominik.goeddeke@math.uni-dortmund.de 1 Mathematics III: Applied Mathematics and Numerics, University
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
EN 10211:2007 validation of Therm 6.3. Therm 6.3 validation according to EN ISO 10211:2007
 Therm 6.3 validation according to EN ISO 10211:2007 Therm 6.3 validation according to NBN EN ISO 10211:2007 eneral considerations and requirements for validation of calculation methods according to NBN
Therm 6.3 validation according to EN ISO 10211:2007 Therm 6.3 validation according to NBN EN ISO 10211:2007 eneral considerations and requirements for validation of calculation methods according to NBN
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1
 Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1 2 Outline
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 3, 2017, Lesson 1 2 Outline
Study of Convergence of Results in Finite Element Analysis of a Plane Stress Bracket
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Study of Convergence of Results in Finite Element Analysis of a Plane Stress Bracket Gowtham K L*, Shivashankar R. Srivatsa** *(Department of Mechanical Engineering, B. M.
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Study of Convergence of Results in Finite Element Analysis of a Plane Stress Bracket Gowtham K L*, Shivashankar R. Srivatsa** *(Department of Mechanical Engineering, B. M.
Adaptive Isogeometric Analysis by Local h-refinement with T-splines
 Adaptive Isogeometric Analysis by Local h-refinement with T-splines Michael Dörfel 1, Bert Jüttler 2, Bernd Simeon 1 1 TU Munich, Germany 2 JKU Linz, Austria SIMAI, Minisymposium M13 Outline Preliminaries:
Adaptive Isogeometric Analysis by Local h-refinement with T-splines Michael Dörfel 1, Bert Jüttler 2, Bernd Simeon 1 1 TU Munich, Germany 2 JKU Linz, Austria SIMAI, Minisymposium M13 Outline Preliminaries:
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
An Investigation into Iterative Methods for Solving Elliptic PDE s Andrew M Brown Computer Science/Maths Session (2000/2001)
 An Investigation into Iterative Methods for Solving Elliptic PDE s Andrew M Brown Computer Science/Maths Session (000/001) Summary The objectives of this project were as follows: 1) Investigate iterative
An Investigation into Iterative Methods for Solving Elliptic PDE s Andrew M Brown Computer Science/Maths Session (000/001) Summary The objectives of this project were as follows: 1) Investigate iterative
Foundations of Analytical and Numerical Field Computation
 Foundations of Analytical and Numerical Field Computation Stephan Russenschuck, CERN-AT-MEL Stephan Russenschuck CERN, TE-MCS, 1211 Geneva, Switzerland 1 Permanent Magnet Circuits 2 Rogowski profiles Pole
Foundations of Analytical and Numerical Field Computation Stephan Russenschuck, CERN-AT-MEL Stephan Russenschuck CERN, TE-MCS, 1211 Geneva, Switzerland 1 Permanent Magnet Circuits 2 Rogowski profiles Pole
The multi-level hp-method for three-dimensional problems: dynamically changing high-order mesh refinement with arbitrary hanging nodes
 The multi-level hp-method for three-dimensional problems: dynamically changing high-order mesh refinement with arbitrary hanging nodes Nils Zander 1, Tino Bog 1, Mohamed Elhaddad 1, Felix Frischmann 1,
The multi-level hp-method for three-dimensional problems: dynamically changing high-order mesh refinement with arbitrary hanging nodes Nils Zander 1, Tino Bog 1, Mohamed Elhaddad 1, Felix Frischmann 1,
A Hybrid Magnetic Field Solver Using a Combined Finite Element/Boundary Element Field Solver
 A Hybrid Magnetic Field Solver Using a Combined Finite Element/Boundary Element Field Solver Abstract - The dominant method to solve magnetic field problems is the finite element method. It has been used
A Hybrid Magnetic Field Solver Using a Combined Finite Element/Boundary Element Field Solver Abstract - The dominant method to solve magnetic field problems is the finite element method. It has been used
Lecture 7: Introduction to HFSS-IE
 Lecture 7: Introduction to HFSS-IE 2015.0 Release ANSYS HFSS for Antenna Design 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. HFSS-IE: Integral Equation Solver Introduction HFSS-IE: Technology An Integral Equation solver technology
Lecture 7: Introduction to HFSS-IE 2015.0 Release ANSYS HFSS for Antenna Design 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. HFSS-IE: Integral Equation Solver Introduction HFSS-IE: Technology An Integral Equation solver technology
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis
 Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
IMPLEMENTATION OF ANALYTICAL (MATLAB) AND NUMERICAL (HFSS) SOLUTIONS ADVANCED ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOHAIB SAADAT AFRIDI HAMMAD BUTT ZUNNURAIN AHMAD
 STUDY OF SCATTERING & RESULTANT RADIATION PATTERN: INFINITE LINE CURRENT SOURCE POSITIONED HORIZONTALLY OVER A PERFECTLY CONDUCTING INFINITE GROUND PLANE IMPLEMENTATION OF ANALYTICAL (MATLAB) AND NUMERICAL
STUDY OF SCATTERING & RESULTANT RADIATION PATTERN: INFINITE LINE CURRENT SOURCE POSITIONED HORIZONTALLY OVER A PERFECTLY CONDUCTING INFINITE GROUND PLANE IMPLEMENTATION OF ANALYTICAL (MATLAB) AND NUMERICAL
Adaptive numerical methods
 METRO MEtallurgical TRaining On-line Adaptive numerical methods Arkadiusz Nagórka CzUT Education and Culture Introduction Common steps of finite element computations consists of preprocessing - definition
METRO MEtallurgical TRaining On-line Adaptive numerical methods Arkadiusz Nagórka CzUT Education and Culture Introduction Common steps of finite element computations consists of preprocessing - definition
Combined Electrical and Magnetic Resistivity Tomography (ERT/MMR)
 Combined Electrical and Magnetic Resistivity Tomography (ERT/MMR) Gail Heath 1, John M. Svoboda 1, Birsen Canan 2, Shannon Ansley 1, David Alumbaugh 3, Douglas LaBrecque 4, Roger Sharpe 4,Roelof Versteeg
Combined Electrical and Magnetic Resistivity Tomography (ERT/MMR) Gail Heath 1, John M. Svoboda 1, Birsen Canan 2, Shannon Ansley 1, David Alumbaugh 3, Douglas LaBrecque 4, Roger Sharpe 4,Roelof Versteeg
Recent Developments in Model-based Derivative-free Optimization
 Recent Developments in Model-based Derivative-free Optimization Seppo Pulkkinen April 23, 2010 Introduction Problem definition The problem we are considering is a nonlinear optimization problem with constraints:
Recent Developments in Model-based Derivative-free Optimization Seppo Pulkkinen April 23, 2010 Introduction Problem definition The problem we are considering is a nonlinear optimization problem with constraints:
APPLICATION OF PROJECTION-BASED INTERPOLATION ALGORITHM FOR NON-STATIONARY PROBLEM
 Computer Science 7 (3) 26 http://dx.doi.org/.7494/csci.26.7.3.297 Maciej Woźniak Maciej Paszyński APPLICATION OF PROJECTION-BASED INTERPOLATION ALGORITHM FOR NON-STATIONARY PROBLEM Abstract In this paper,
Computer Science 7 (3) 26 http://dx.doi.org/.7494/csci.26.7.3.297 Maciej Woźniak Maciej Paszyński APPLICATION OF PROJECTION-BASED INTERPOLATION ALGORITHM FOR NON-STATIONARY PROBLEM Abstract In this paper,
Motivation Patch tests Numerical examples Conclusions
 Weakening the tight coupling between geometry and simulation in isogeometric analysis: from sub- and super- geometric analysis to Geometry Independent Field approximation (GIFT) Elena Atroshchenko, Gang
Weakening the tight coupling between geometry and simulation in isogeometric analysis: from sub- and super- geometric analysis to Geometry Independent Field approximation (GIFT) Elena Atroshchenko, Gang
High Order Nédélec Elements with local complete sequence properties
 High Order Nédélec Elements with local complete sequence properties Joachim Schöberl and Sabine Zaglmayr Institute for Computational Mathematics, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Austria E-mail: {js,sz}@jku.at
High Order Nédélec Elements with local complete sequence properties Joachim Schöberl and Sabine Zaglmayr Institute for Computational Mathematics, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Austria E-mail: {js,sz}@jku.at
Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models. C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak
 Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak Aerospace and Astronautics University of Washington, Seattle American Physical Society
Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak Aerospace and Astronautics University of Washington, Seattle American Physical Society
Space Filling Curves and Hierarchical Basis. Klaus Speer
 Space Filling Curves and Hierarchical Basis Klaus Speer Abstract Real world phenomena can be best described using differential equations. After linearisation we have to deal with huge linear systems of
Space Filling Curves and Hierarchical Basis Klaus Speer Abstract Real world phenomena can be best described using differential equations. After linearisation we have to deal with huge linear systems of
ADVANCES IN ADAPTIVE METHODS IN COMPUTATIONAL FLUID MECHANICS. J. Tinsley Oden. Abstract
 ADVANCES N ADAPTVE METHODS N COMPUTATONAL FLUD MECHANCS J. Tinsley Oden Texas nstitute for Computational Mechanics The University of Texas at Austin Austin, Texas 78712 Abstract Recent developments in
ADVANCES N ADAPTVE METHODS N COMPUTATONAL FLUD MECHANCS J. Tinsley Oden Texas nstitute for Computational Mechanics The University of Texas at Austin Austin, Texas 78712 Abstract Recent developments in
Schemes for improving efficiency of pixel-based inversion algorithms for electromagnetic loggingwhile-drilling
 Schemes for improving efficiency of pixel-based inversion algorithms for electromagnetic loggingwhile-drilling measurements Y. Lin, A. Abubakar, T. M. Habashy, G. Pan, M. Li and V. Druskin, Schlumberger-Doll
Schemes for improving efficiency of pixel-based inversion algorithms for electromagnetic loggingwhile-drilling measurements Y. Lin, A. Abubakar, T. M. Habashy, G. Pan, M. Li and V. Druskin, Schlumberger-Doll
Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Introduction Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus, you need
Introduction Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus, you need
Partial Differential Equations
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
June 5, Institute of Structural Analysis Graz University of Technology Lessingstr. 25/II, 8010 Graz, Austria
 Higher-order meshing of implicit geometries part I: Integration and interpolation in cut elements arxiv:706.00578v [cs.na] 2 Jun 207 T.P. Fries, S. Omerović, D. Schöllhammer, J. Steidl June 5, 207 Institute
Higher-order meshing of implicit geometries part I: Integration and interpolation in cut elements arxiv:706.00578v [cs.na] 2 Jun 207 T.P. Fries, S. Omerović, D. Schöllhammer, J. Steidl June 5, 207 Institute
Domain Decomposition and hp-adaptive Finite Elements
 Domain Decomposition and hp-adaptive Finite Elements Randolph E. Bank 1 and Hieu Nguyen 1 Department of Mathematics, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 9093-011, USA, rbank@ucsd.edu. Department
Domain Decomposition and hp-adaptive Finite Elements Randolph E. Bank 1 and Hieu Nguyen 1 Department of Mathematics, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 9093-011, USA, rbank@ucsd.edu. Department
Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 6263
 Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 66 Charles O Neill April, 00 Abstract A finite difference CFD solver was developed for transient, two-dimensional Cartesian viscous flows. Flow parameters are solved
Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 66 Charles O Neill April, 00 Abstract A finite difference CFD solver was developed for transient, two-dimensional Cartesian viscous flows. Flow parameters are solved
Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium
 Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium http://seesar.lbl.gov/anag Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory April 7, 2005 19 th IPDPS, April 7, 2005 1 Overview Motivations: Build the infrastructure in Titanium
Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium http://seesar.lbl.gov/anag Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory April 7, 2005 19 th IPDPS, April 7, 2005 1 Overview Motivations: Build the infrastructure in Titanium
ADAPTIVE APPROACH IN NONLINEAR CURVE DESIGN PROBLEM. Simo Virtanen Rakenteiden Mekaniikka, Vol. 30 Nro 1, 1997, s
 ADAPTIVE APPROACH IN NONLINEAR CURVE DESIGN PROBLEM Simo Virtanen Rakenteiden Mekaniikka, Vol. 30 Nro 1, 1997, s. 14-24 ABSTRACT In recent years considerable interest has been shown in the development
ADAPTIVE APPROACH IN NONLINEAR CURVE DESIGN PROBLEM Simo Virtanen Rakenteiden Mekaniikka, Vol. 30 Nro 1, 1997, s. 14-24 ABSTRACT In recent years considerable interest has been shown in the development
Modeling with Uncertainty Interval Computations Using Fuzzy Sets
 Modeling with Uncertainty Interval Computations Using Fuzzy Sets J. Honda, R. Tankelevich Department of Mathematical and Computer Sciences, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, U.S.A. Abstract A new method
Modeling with Uncertainty Interval Computations Using Fuzzy Sets J. Honda, R. Tankelevich Department of Mathematical and Computer Sciences, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, U.S.A. Abstract A new method
f xx + f yy = F (x, y)
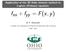 Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
An Example Eddy Currents
 An Example Eddy Currents Introduction To help you understand how to create models using the AC/DC Module, this section walks through an example in great detail. You can apply these techniques to all the
An Example Eddy Currents Introduction To help you understand how to create models using the AC/DC Module, this section walks through an example in great detail. You can apply these techniques to all the
Finite element methods
 Finite element methods Period 2, 2013/2014 Department of Information Technology Uppsala University Finite element methods, Uppsala University, Sweden, 30th October 2013 p. 1 Short Bio Patrick Henning,
Finite element methods Period 2, 2013/2014 Department of Information Technology Uppsala University Finite element methods, Uppsala University, Sweden, 30th October 2013 p. 1 Short Bio Patrick Henning,
Fictitious Domain Methods and Topology Optimization
 Fictitious Domain Methods and Topology Optimization Martin Berggren UMIT research lab Department of Computing Science Umeå University April 11, 2014 Martin Berggren (Umeå University) Fictitious Domain
Fictitious Domain Methods and Topology Optimization Martin Berggren UMIT research lab Department of Computing Science Umeå University April 11, 2014 Martin Berggren (Umeå University) Fictitious Domain
Effective adaptation of hexahedral mesh using local refinement and error estimation
 Key Engineering Materials Vols. 243-244 (2003) pp. 27-32 online at http://www.scientific.net (2003) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online Citation available & since 2003/07/15 Copyright (to be inserted
Key Engineering Materials Vols. 243-244 (2003) pp. 27-32 online at http://www.scientific.net (2003) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online Citation available & since 2003/07/15 Copyright (to be inserted
A higher-order finite volume method with collocated grid arrangement for incompressible flows
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XVII 109 A higher-order finite volume method with collocated grid arrangement for incompressible flows L. Ramirez 1, X. Nogueira 1, S. Khelladi 2, J.
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XVII 109 A higher-order finite volume method with collocated grid arrangement for incompressible flows L. Ramirez 1, X. Nogueira 1, S. Khelladi 2, J.
Collocation and optimization initialization
 Boundary Elements and Other Mesh Reduction Methods XXXVII 55 Collocation and optimization initialization E. J. Kansa 1 & L. Ling 2 1 Convergent Solutions, USA 2 Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong
Boundary Elements and Other Mesh Reduction Methods XXXVII 55 Collocation and optimization initialization E. J. Kansa 1 & L. Ling 2 1 Convergent Solutions, USA 2 Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong
13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY
 13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY Lecture 23 Dr. W. Cho Prof. N. M. Patrikalakis Copyright c 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Contents 23 F.E. and B.E. Meshing Algorithms 2
13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY Lecture 23 Dr. W. Cho Prof. N. M. Patrikalakis Copyright c 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Contents 23 F.E. and B.E. Meshing Algorithms 2
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 36
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
Advanced Surface Based MoM Techniques for Packaging and Interconnect Analysis
 Electrical Interconnect and Packaging Advanced Surface Based MoM Techniques for Packaging and Interconnect Analysis Jason Morsey Barry Rubin, Lijun Jiang, Lon Eisenberg, Alina Deutsch Introduction Fast
Electrical Interconnect and Packaging Advanced Surface Based MoM Techniques for Packaging and Interconnect Analysis Jason Morsey Barry Rubin, Lijun Jiang, Lon Eisenberg, Alina Deutsch Introduction Fast
Hypergraph Grammars in hp-adaptive Finite Element Method
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Computer Science 18 (2013 ) 1545 1554 2013 International Conference on Computational Science Hypergraph Grammars in hp-adaptive Finite Element Method
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Computer Science 18 (2013 ) 1545 1554 2013 International Conference on Computational Science Hypergraph Grammars in hp-adaptive Finite Element Method
Polynomials tend to oscillate (wiggle) a lot, even when our true function does not.
 AMSC/CMSC 460 Computational Methods, Fall 2007 UNIT 2: Spline Approximations Dianne P O Leary c 2001, 2002, 2007 Piecewise polynomial interpolation Piecewise polynomial interpolation Read: Chapter 3 Skip:
AMSC/CMSC 460 Computational Methods, Fall 2007 UNIT 2: Spline Approximations Dianne P O Leary c 2001, 2002, 2007 Piecewise polynomial interpolation Piecewise polynomial interpolation Read: Chapter 3 Skip:
H (div) approximations based on hp-adaptive curved meshes using quarter point elements
 Trabalho apresentado no CNMAC, Gramado - RS, 2016. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics H (div) approximations based on hp-adaptive curved meshes using quarter
Trabalho apresentado no CNMAC, Gramado - RS, 2016. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics H (div) approximations based on hp-adaptive curved meshes using quarter
HYBRID DIRECT AND ITERATIVE SOLVER FOR H ADAPTIVE MESHES WITH POINT SINGULARITIES
 HYBRID DIRECT AND ITERATIVE SOLVER FOR H ADAPTIVE MESHES WITH POINT SINGULARITIES Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer Science, AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland email: paszynsk@agh.edu.pl
HYBRID DIRECT AND ITERATIVE SOLVER FOR H ADAPTIVE MESHES WITH POINT SINGULARITIES Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer Science, AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland email: paszynsk@agh.edu.pl
Implementation of the Continuous-Discontinuous Galerkin Finite Element Method
 Implementation of the Continuous-Discontinuous Galerkin Finite Element Method Andrea Cangiani, John Chapman, Emmanuil Georgoulis and Max Jensen Abstract For the stationary advection-diffusion problem the
Implementation of the Continuous-Discontinuous Galerkin Finite Element Method Andrea Cangiani, John Chapman, Emmanuil Georgoulis and Max Jensen Abstract For the stationary advection-diffusion problem the
CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality
 CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality Judd Kaiser ANSYS Inc. judd.kaiser@ansys.com 2005 ANSYS, Inc. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Overview
CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality Judd Kaiser ANSYS Inc. judd.kaiser@ansys.com 2005 ANSYS, Inc. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Overview
Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Held by Prof. Dr. E. Chatzi, Dr. P. Steffen Assistants: Adrian Egger (HIL E 13.3), Harry Mylonas (HIL H33.1), Konstantinos Tatsis (HIL H33.1) Lectures homepage:
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Held by Prof. Dr. E. Chatzi, Dr. P. Steffen Assistants: Adrian Egger (HIL E 13.3), Harry Mylonas (HIL H33.1), Konstantinos Tatsis (HIL H33.1) Lectures homepage:
Accelerating Finite Element Analysis in MATLAB with Parallel Computing
 MATLAB Digest Accelerating Finite Element Analysis in MATLAB with Parallel Computing By Vaishali Hosagrahara, Krishna Tamminana, and Gaurav Sharma The Finite Element Method is a powerful numerical technique
MATLAB Digest Accelerating Finite Element Analysis in MATLAB with Parallel Computing By Vaishali Hosagrahara, Krishna Tamminana, and Gaurav Sharma The Finite Element Method is a powerful numerical technique
Modeling and Analysis of the Electric Field and Potential Distribution in a Wire-Cylinder Air Gap
 Modeling and Analysis of the Electric Field and Potential Distribution in a Wire-Cylinder Air Gap KONSTANTINOS N. KIOUSIS, ANTONIOS X. MORONIS Technological Educational Institute (TEI) of Athens Energy
Modeling and Analysis of the Electric Field and Potential Distribution in a Wire-Cylinder Air Gap KONSTANTINOS N. KIOUSIS, ANTONIOS X. MORONIS Technological Educational Institute (TEI) of Athens Energy
GEOMETRIC MULTIGRID SOLVER AND EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION IN LASER SURFACE REMELTING
 GEOMETRIC MULTIGRID SOLVER AND EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION IN LASER SURFACE REMELTING Prof. Dr. Moisés Meza Pariona Postgraduate Program in Engineering and Materials Science, State University of Ponta Grossa
GEOMETRIC MULTIGRID SOLVER AND EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION IN LASER SURFACE REMELTING Prof. Dr. Moisés Meza Pariona Postgraduate Program in Engineering and Materials Science, State University of Ponta Grossa
Finite element solution of multi-scale transport problems using the least squares based bubble function enrichment
 Finite element solution of multi-scale transport problems using the least squares based bubble function enrichment A. Yazdani a, V. Nassehi b1 a Cranfield University, School of Applied Sciences, Cranfield,
Finite element solution of multi-scale transport problems using the least squares based bubble function enrichment A. Yazdani a, V. Nassehi b1 a Cranfield University, School of Applied Sciences, Cranfield,
Finite Element Modeling Techniques (2) دانشگاه صنعتي اصفهان- دانشكده مكانيك
 Finite Element Modeling Techniques (2) 1 Where Finer Meshes Should be Used GEOMETRY MODELLING 2 GEOMETRY MODELLING Reduction of a complex geometry to a manageable one. 3D? 2D? 1D? Combination? Bulky solids
Finite Element Modeling Techniques (2) 1 Where Finer Meshes Should be Used GEOMETRY MODELLING 2 GEOMETRY MODELLING Reduction of a complex geometry to a manageable one. 3D? 2D? 1D? Combination? Bulky solids
A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for the solution of 2D Laplace equation
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):150-155 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):150-155 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for
TAU mesh deformation. Thomas Gerhold
 TAU mesh deformation Thomas Gerhold The parallel mesh deformation of the DLR TAU-Code Introduction Mesh deformation method & Parallelization Results & Applications Conclusion & Outlook Introduction CFD
TAU mesh deformation Thomas Gerhold The parallel mesh deformation of the DLR TAU-Code Introduction Mesh deformation method & Parallelization Results & Applications Conclusion & Outlook Introduction CFD
Programming, numerics and optimization
 Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture C-4: Constrained optimization Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428 June
Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture C-4: Constrained optimization Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428 June
Global and clustered approaches for stress constrained topology optimization and deactivation of design variables
 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization May 9-24, 23, Orlando, Florida, USA Global and clustered approaches for stress constrained topology optimization and deactivation of design
th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization May 9-24, 23, Orlando, Florida, USA Global and clustered approaches for stress constrained topology optimization and deactivation of design
Numerical Aspects of Special Functions
 Numerical Aspects of Special Functions Nico M. Temme In collaboration with Amparo Gil and Javier Segura, Santander, Spain. Nico.Temme@cwi.nl Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica (CWI), Amsterdam Numerics
Numerical Aspects of Special Functions Nico M. Temme In collaboration with Amparo Gil and Javier Segura, Santander, Spain. Nico.Temme@cwi.nl Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica (CWI), Amsterdam Numerics
An Embedded Boundary Method with Adaptive Mesh Refinements
 An Embedded Boundary Method with Adaptive Mesh Refinements Marcos Vanella and Elias Balaras 8 th World Congress on Computational Mechanics, WCCM8 5 th European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied
An Embedded Boundary Method with Adaptive Mesh Refinements Marcos Vanella and Elias Balaras 8 th World Congress on Computational Mechanics, WCCM8 5 th European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied
Finite element algorithm with adaptive quadtree-octree mesh refinement
 ANZIAM J. 46 (E) ppc15 C28, 2005 C15 Finite element algorithm with adaptive quadtree-octree mesh refinement G. P. Nikishkov (Received 18 October 2004; revised 24 January 2005) Abstract Certain difficulties
ANZIAM J. 46 (E) ppc15 C28, 2005 C15 Finite element algorithm with adaptive quadtree-octree mesh refinement G. P. Nikishkov (Received 18 October 2004; revised 24 January 2005) Abstract Certain difficulties
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements
 Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Approaches to Parallel Implementation of the BDDC Method
 Approaches to Parallel Implementation of the BDDC Method Jakub Šístek Includes joint work with P. Burda, M. Čertíková, J. Mandel, J. Novotný, B. Sousedík. Institute of Mathematics of the AS CR, Prague
Approaches to Parallel Implementation of the BDDC Method Jakub Šístek Includes joint work with P. Burda, M. Čertíková, J. Mandel, J. Novotný, B. Sousedík. Institute of Mathematics of the AS CR, Prague
Topology Optimization and JuMP
 Immense Potential and Challenges School of Engineering and Information Technology UNSW Canberra June 28, 2018 Introduction About Me First year PhD student at UNSW Canberra Multidisciplinary design optimization
Immense Potential and Challenges School of Engineering and Information Technology UNSW Canberra June 28, 2018 Introduction About Me First year PhD student at UNSW Canberra Multidisciplinary design optimization
Computational methods for inverse problems
 Computational methods for inverse problems Eldad Haber contributors: Stefan Heldmann, Lauren Hanson, Lior Horesh, Jan Modersitzki, Uri Ascher, Doug Oldenburg Sponsored by: DOE and NSF Motivation and examples
Computational methods for inverse problems Eldad Haber contributors: Stefan Heldmann, Lauren Hanson, Lior Horesh, Jan Modersitzki, Uri Ascher, Doug Oldenburg Sponsored by: DOE and NSF Motivation and examples
SOLVING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS ON POINT CLOUDS
 SOLVING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS ON POINT CLOUDS JIAN LIANG AND HONGKAI ZHAO Abstract. In this paper we present a general framework for solving partial differential equations on manifolds represented
SOLVING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS ON POINT CLOUDS JIAN LIANG AND HONGKAI ZHAO Abstract. In this paper we present a general framework for solving partial differential equations on manifolds represented
PARAMETRIC OPTIMIZATION OF CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARING AND COMPARE WITH FEA
 PARAMETRIC OPTIMIZATION OF CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARING AND COMPARE WITH FEA KANTHA SHOBA.M 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Thanthai Periyar Government Institute of Technology,
PARAMETRIC OPTIMIZATION OF CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARING AND COMPARE WITH FEA KANTHA SHOBA.M 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Thanthai Periyar Government Institute of Technology,
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics. D. Murrin
 Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
AC System Monitoring Device
 AC System Monitoring Device Andrew Jarrett Project Adviser: Professor Gutschlag Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering October 28, 2015 Executive Summary The alternating current (AC) system
AC System Monitoring Device Andrew Jarrett Project Adviser: Professor Gutschlag Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering October 28, 2015 Executive Summary The alternating current (AC) system
Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing
 252-0538-00L, Spring 2018 Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing Discrete Differential Geometry Differential Geometry Motivation Formalize geometric properties of shapes Roi Poranne # 2 Differential Geometry
252-0538-00L, Spring 2018 Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing Discrete Differential Geometry Differential Geometry Motivation Formalize geometric properties of shapes Roi Poranne # 2 Differential Geometry
An Efficient, Geometric Multigrid Solver for the Anisotropic Diffusion Equation in Two and Three Dimensions
 1 n Efficient, Geometric Multigrid Solver for the nisotropic Diffusion Equation in Two and Three Dimensions Tolga Tasdizen, Ross Whitaker UUSCI-2004-002 Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute University
1 n Efficient, Geometric Multigrid Solver for the nisotropic Diffusion Equation in Two and Three Dimensions Tolga Tasdizen, Ross Whitaker UUSCI-2004-002 Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute University
Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles
 Version 3.0 98-09-11 Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles W. Scholz, T. Schrefl, J. Fidler Institute of Applied and Technical Physics, Vienna University of Technology,
Version 3.0 98-09-11 Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles W. Scholz, T. Schrefl, J. Fidler Institute of Applied and Technical Physics, Vienna University of Technology,
Finite Element Methods for the Poisson Equation and its Applications
 Finite Element Methods for the Poisson Equation and its Applications Charles Crook July 30, 2013 Abstract The finite element method is a fast computational method that also has a solid mathematical theory
Finite Element Methods for the Poisson Equation and its Applications Charles Crook July 30, 2013 Abstract The finite element method is a fast computational method that also has a solid mathematical theory
SIMULATION OF AN IMPLANTED PIFA FOR A CARDIAC PACEMAKER WITH EFIELD FDTD AND HYBRID FDTD-FEM
 1 SIMULATION OF AN IMPLANTED PIFA FOR A CARDIAC PACEMAKER WITH EFIELD FDTD AND HYBRID FDTD- Introduction Medical Implanted Communication Service (MICS) has received a lot of attention recently. The MICS
1 SIMULATION OF AN IMPLANTED PIFA FOR A CARDIAC PACEMAKER WITH EFIELD FDTD AND HYBRID FDTD- Introduction Medical Implanted Communication Service (MICS) has received a lot of attention recently. The MICS
Dual Interpolants for Finite Element Methods
 Dual Interpolants for Finite Element Methods Andrew Gillette joint work with Chandrajit Bajaj and Alexander Rand Department of Mathematics Institute of Computational Engineering and Sciences University
Dual Interpolants for Finite Element Methods Andrew Gillette joint work with Chandrajit Bajaj and Alexander Rand Department of Mathematics Institute of Computational Engineering and Sciences University
Advances in 3-D Forging Process Modeling
 Advances in 3-D Forging Process Modeling W J Slagter, C J L Florie and A C J Venis MSC.Software Corporation, Groningenweg 6, 2803 PV Gouda, The Netherlands MSC/SuperForge is a new code developed for performing
Advances in 3-D Forging Process Modeling W J Slagter, C J L Florie and A C J Venis MSC.Software Corporation, Groningenweg 6, 2803 PV Gouda, The Netherlands MSC/SuperForge is a new code developed for performing
The Eikonal Equation
 The Eikonal Equation Numerical efficiency versus computational compleity Shu-Ren Hysing III Institute of Applied Mathematics LSIII University of Dortmund Level set - methodology By embedding an interface
The Eikonal Equation Numerical efficiency versus computational compleity Shu-Ren Hysing III Institute of Applied Mathematics LSIII University of Dortmund Level set - methodology By embedding an interface
Parallel Performance Studies for COMSOL Multiphysics Using Scripting and Batch Processing
 Parallel Performance Studies for COMSOL Multiphysics Using Scripting and Batch Processing Noemi Petra and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore
Parallel Performance Studies for COMSOL Multiphysics Using Scripting and Batch Processing Noemi Petra and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore
TICAM - Texas Institute for Computational and Applied Mathematics. The University of Texas at Austin. Taylor Hall Abstract
 A New Cloud-Based hp Finite Element Method J. T. Oden, C. A. M. Duarte y and O. C. Zienkiewicz z TICAM - Texas Institute for Computational and Applied Mathematics The University of Texas at Austin Taylor
A New Cloud-Based hp Finite Element Method J. T. Oden, C. A. M. Duarte y and O. C. Zienkiewicz z TICAM - Texas Institute for Computational and Applied Mathematics The University of Texas at Austin Taylor
Optical Flow Estimation with CUDA. Mikhail Smirnov
 Optical Flow Estimation with CUDA Mikhail Smirnov msmirnov@nvidia.com Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change Mikhail Smirnov Initial release Abstract Optical flow is the apparent
Optical Flow Estimation with CUDA Mikhail Smirnov msmirnov@nvidia.com Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change Mikhail Smirnov Initial release Abstract Optical flow is the apparent
Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes
 Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes Sanjay Kumar Khattri, Gunnar E. Fladmark, Helge K. Dahle Department of Mathematics, University Bergen, Norway. sanjay@mi.uib.no Summary. In this work
Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes Sanjay Kumar Khattri, Gunnar E. Fladmark, Helge K. Dahle Department of Mathematics, University Bergen, Norway. sanjay@mi.uib.no Summary. In this work
Some Aspects for the Simulation of a Non-Linear Problem with Plasticity and Contact
 Some Aspects for the Simulation of a Non-Linear Problem with Plasticity and Contact Eduardo Luís Gaertner Marcos Giovani Dropa de Bortoli EMBRACO S.A. Abstract A linear elastic model is often not appropriate
Some Aspects for the Simulation of a Non-Linear Problem with Plasticity and Contact Eduardo Luís Gaertner Marcos Giovani Dropa de Bortoli EMBRACO S.A. Abstract A linear elastic model is often not appropriate
Radiosity. Johns Hopkins Department of Computer Science Course : Rendering Techniques, Professor: Jonathan Cohen
 Radiosity Radiosity Concept Global computation of diffuse interreflections among scene objects Diffuse lighting changes fairly slowly across a surface Break surfaces up into some number of patches Assume
Radiosity Radiosity Concept Global computation of diffuse interreflections among scene objects Diffuse lighting changes fairly slowly across a surface Break surfaces up into some number of patches Assume
An introduction to mesh generation Part IV : elliptic meshing
 Elliptic An introduction to mesh generation Part IV : elliptic meshing Department of Civil Engineering, Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium Elliptic Curvilinear Meshes Basic concept A curvilinear
Elliptic An introduction to mesh generation Part IV : elliptic meshing Department of Civil Engineering, Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium Elliptic Curvilinear Meshes Basic concept A curvilinear
Department of Computing and Software
 Department of Computing and Software Faculty of Engineering McMaster University Assessment of two a posteriori error estimators for steady-state flow problems by A. H. ElSheikh, S.E. Chidiac and W. S.
Department of Computing and Software Faculty of Engineering McMaster University Assessment of two a posteriori error estimators for steady-state flow problems by A. H. ElSheikh, S.E. Chidiac and W. S.
Optimization. Industrial AI Lab.
 Optimization Industrial AI Lab. Optimization An important tool in 1) Engineering problem solving and 2) Decision science People optimize Nature optimizes 2 Optimization People optimize (source: http://nautil.us/blog/to-save-drowning-people-ask-yourself-what-would-light-do)
Optimization Industrial AI Lab. Optimization An important tool in 1) Engineering problem solving and 2) Decision science People optimize Nature optimizes 2 Optimization People optimize (source: http://nautil.us/blog/to-save-drowning-people-ask-yourself-what-would-light-do)
Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2
 Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2 David W. Trott and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County,
Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2 David W. Trott and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County,
An Interface-fitted Mesh Generator and Polytopal Element Methods for Elliptic Interface Problems
 An Interface-fitted Mesh Generator and Polytopal Element Methods for Elliptic Interface Problems Long Chen University of California, Irvine chenlong@math.uci.edu Joint work with: Huayi Wei (Xiangtan University),
An Interface-fitted Mesh Generator and Polytopal Element Methods for Elliptic Interface Problems Long Chen University of California, Irvine chenlong@math.uci.edu Joint work with: Huayi Wei (Xiangtan University),
Efficient Finite Element Geometric Multigrid Solvers for Unstructured Grids on GPUs
 Efficient Finite Element Geometric Multigrid Solvers for Unstructured Grids on GPUs Markus Geveler, Dirk Ribbrock, Dominik Göddeke, Peter Zajac, Stefan Turek Institut für Angewandte Mathematik TU Dortmund,
Efficient Finite Element Geometric Multigrid Solvers for Unstructured Grids on GPUs Markus Geveler, Dirk Ribbrock, Dominik Göddeke, Peter Zajac, Stefan Turek Institut für Angewandte Mathematik TU Dortmund,
Computational Economics and Finance
 Computational Economics and Finance Part I: Elementary Concepts of Numerical Analysis Spring 2015 Outline Computer arithmetic Error analysis: Sources of error Error propagation Controlling the error Rates
Computational Economics and Finance Part I: Elementary Concepts of Numerical Analysis Spring 2015 Outline Computer arithmetic Error analysis: Sources of error Error propagation Controlling the error Rates
Contents. I Basics 1. Copyright by SIAM. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
Code_Aster Titre : SSLV155 - Fissure lentille en traction Responsable : GÉNIAUT Samuel
 Titre SSLV155 - Fissure lentille en traction Responsable GÉNIAUT Samuel Date 14/09/2017 Page 1/23 Clé V3.04.155 SSLV155 Crack lens in traction Summary The purpose of this test is to validate the calculation
Titre SSLV155 - Fissure lentille en traction Responsable GÉNIAUT Samuel Date 14/09/2017 Page 1/23 Clé V3.04.155 SSLV155 Crack lens in traction Summary The purpose of this test is to validate the calculation
