A Bidirectional List-Sequential (BI-LISS) Equalizer for Turbo Schemes
|
|
|
- Linette Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
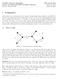
1 A Bidirectioal List-equetial BI-LI Equalizer for Turbo chemes Christia Kuh Lehrstuhl für achrichtetechik LT, Techische Uiversität Müche TUM 8090 Müche, Germay Phoe: , Fa: Abstract I the cotet of coded trasmissio over itersymbol iterferece chaels we ivestigate a bidirectioal list-sequetial equalizer BI-LI suitable for turbo schemes Especially for chaels with a umaageable high umber of states for a trellis based APP equalizatio this sequetial algorithm shows almost optimal performace with much smaller compleity Geerally, the list-sequetial LI equalizer is based o a decodig techique for covolutioal codes with high memory, amely sequetial decodig We itroduce a BI- LI equalizer which leads to a further reductio of the work amout ad provides the possibility of parallel processig For this purpose two idepedet LI equalizers are employed workig i the forward ad the backward directio respectively I ITRODUCTIO For coded trasmissio over chaels itroducig itersymbol iterferece II receivers based o the turbo priciple [, ] are kow to achieve a performace close to theoretical limits The equalizer ad decoder compoets have to be soft-i/soft-out algorithms calculatig a posteriori probabilities APP for the idividual bits I particular for chaels with a log delay spread a trellis based APP equalizer suffers from a high computatioal load ad has to be replaced with a algorithm of reduced compleity that approimates the a posteriori probabilities Followig the ideas of sequetial decodig for covolutioal codes with high memory [3] a tree based list-sequetial LI equalizer suitable for that task was itroduced i [4] Therefore, a modified Fao metric [5] is applied for eplorig a equalizer tree takig ito accout the a priori iformatio ad a appropriate legth bias for chaels with memory The tree-searchig is performed usig the stack algorithm [6] i order to fid a subset of the most probable sequeces trasmitted A soft-output is derived from those sequeces cotaied i the stack after carryig out a soft augmetatio This techique makes fully use of the a priori iformatio to improve the soft-output Basically, sequetial algorithms show a variable detectio effort Poor chael coditios reduce the effectivity of the stack algorithm ad it stops far away from the ed of the tree whe the stack is filled up Due to the soft augmetatio we are able to mitigate this problem for the uidirectioal LI equalizer but further improvemet ca be achieved usig a bidirectioal list-sequetial BI-LI equalizer I sequetial decodig origially all implemetatios aim at the hard decided maimum likelihood path to be foud after data data estimate FEC ecoder FEC decoder Fig Π Π m, a maimum umber of brach etetios A bidirectioal sequetial decodig algorithm for that purpose is suggested i [7] searchig the tree from the forward directio with a forward decoder ad idepedetly from the backward directio with a backward decoder Decodig stops wheever either the forward or the backward decoder reaches the ed of its tree Aother bidirectioal approach also workig with a forward ad a backward decoder is preseted i [8] This decodig algorithm is successful whe two appropriate partial paths of forward ad backward decoder, respectively, merge i a commo ecoder state Accordigly, the BI-LI equalizer performs a forward ad a backward LI equalizatio each with a soft augmetatio ad therefore the classical problem of ot fidig a mergig path after a fiite umber of brach etetios becomes obsolete i a turbo scheme The paper is orgaized as follows: I ectio II the system model ad basic defiitios are itroduced ectio III describes the BI-LI equalizer i detail I ectio IV simulatio results are preseted for the BI-LI equalizer ad the uidirectioal LI equalizer Fially, cocludig remarks are give i ectio V II YTEM MODEL We cosider the commuicatios system depicted i Fig Biary data is ecoded by a outer FEC ecoder typically usig a termiated or tailbited covolutioal code After imapper s II chael L e ˆ m, L ˆ m, Π BI LI y L m, Trasmissio system with iterative detectio terleavig subblocks =,,,, T etedig from time to with the vector elemets =,,, m,,, M, of legth M ad the biary digits m, = {+, } are formed Each bit sequece is mapped o a comple valued symbol s from the M -ary sigal costellatio, leadig to the symbol vector w
2 s =s,,s,,s T of legth which is appeded by L termiatig symbols ad trasmitted over the II chael The receiver observes the symbol vector y +L = y,,y,y +L T etedig from time to + L with elemets L y = h l s l + w l=0 where h = h 0,h,,h L T is the discrete time impulse respose of the chael with memory L ad uit eergy, L ie l=0 h l = The receivig process is corrupted by comple-valued additive white Gaussia oise AWG with iid oise samples w satisfyig the probability desity fuctio pdf pw = πσw e w σ w At the receiver we perform iterative equalizatio ad decodig Accordig to the turbo priciple reliability iformatio about the code bits is iterchaged betwee the soft-i/softout IO compoets The first oe is represeted by the equalizer which obtais a posteriori iformatio about the iterleaved code bits Lˆ m, usig the received symbols y +L together with the a priori iformatio L m, for all idividual bits Oly the etrisic iformatio L e ˆ m, is passed to the outer IO decoder after deiterleavig ormally, this decoder compoet applies the BCJR algorithm or oe of its approimatios [9] The etrisic part of the soft decoder output is fed back ad serves after iterleavig as a priori iput for the equalizer durig the et iteratio which is carried out usig the same set of received data Whe covergece is reached the iterative process stops ad the receiver delivers the data estimates III LIT-EQUETIAL TURBO EQUALIZATIO A APP soft-output Withi the cosidered turbo scheme the equalizer has to geerate the a posteriori log-likelihood ratio LLR Lˆ m, = l P m, =+ y +L P m, = y +L :m,=+ el P y+l = l :m,= el P y+l for each m, which ca be split up ito etrisic ad a priori parts Lˆ m, = l p y +L m, =+ p y +L m, = +lp m, =+ P m, = = L e ˆ m, +L m, 4 These LLRs ca efficietly be calculated operatig o a trellis usig the fiite state machie properties of the chael For chaels with high memory ad/or large symbol alphabets the umber of ML chael states causes a umaageable high computatioal compleity The basic idea is ow to approimate the a posteriori LLRs usig the observatio that the vast 3 majority of the cadidates cotributes a egligible amout to the total probability whe evaluatig the margializatio i 3 B APP path metric I order to fid a subset of the most probable cadidates we use a modified stack algorithm eplorig a equalizer tree, referred to as mai stack algorithm Evaluatig 3 oly for those requires their correspodig APP metric values i the log-domai which ca be stated as = lp y +L 5 = lp y +L +lp l p y +L ote that the chael part l p y +L as well as the a priori part l P of the metric ca be computed recursively i for a give sequece due to statistically idepedet oise samples w ad code bits m,, respectively Based o these properties the so-called legth bias part of the metric l p y +L ca also be determied i a sequetial maer Give the iitial ad fial chael state, the computatio of 5 ca be started either form the begiig of the block = +lp y L +lp l p y y 6 i the forward directio with = lp y L + l P l p y or from the ed of the block = + +lp y +L +L +lp l p y +L y +L +L+ 7 i the backward directio with =lp y+l +L + l P l p y +L These metric calculatios are carried out o a tree structure while performig brach etesios For a full legth path we calculate its APP metric 5 employig either the full legth forward or the full legth backward metric value +L = + =+ = [ l p y L l p y y ] = L [ + l p y L l p y y+ +L ] Durig the mai stack algorithm we perform metric computatios idepedetly i the forward ad backward directio for paths i the correspodig equalizer trees see Fig 3, solid paths I detail the chael part of the brach metric ca be epressed as l p y y L l=0 h ls l L = σw lπσw 8
3 ad for the a priori part of the brach metric we have [ M L m, l P = m, m= l e +Lm,/ + e Lm,/ ] 9 Fially, the bias parts of the forward ad backward brach metric ca be obtaied from l p y y =lp y l p y 0 ad l p y +L y +L +L+ =lp y +L +L l p y +L +L+ Although the bias term has o ifluece o the soft-output calculatio 3, it is absolutely ecessary to compare the metric values of the differet legth paths which occur while performig the mai stack algorithm Thus the legth bias is used to speed up the tree search Before presetig a procedure to determie the bias term we will give a detailed eplaatio of the mai stack algorithm C Mai stack algorithm with soft augmetatio Depedig o the equalizatio directio the two idepedet mai stack algorithms work o the mai stack or, respectively The TOP stack etry of each mai stack correspods to the path with highest metric which has ot yet reached full legth A flow chart is depicted i Fig ad i the followig we will oly poit out the differeces to the stack algorithm Origially, the stack algorithm works oly i Iitialize mai stack / with root ode metric has reached full legth I cotrast to that the mai stack algorithm stops whe the correspodig stack is filled up, ie the umber of paths i the stack reached a maimum value of ma/ ma, to use as may full legth sequeces as possible for the soft-output processig i 3 uder a give memory costrait Whe the stack is filled up with differet legth paths, a additioal improvemet of the soft-output is achieved by carryig out a full legth augmetatio without icreasig the stack size More precisely, we use the a priori iformatio L m, by meas of soft bits m, =E{ m, } =tahl m, / as well as soft symbols s =E{s } = b,,b M [ M sb,,b M m= +b m m, ], 3 b m {±}, for the augmetatio ad the required metric calculatios I Fig 3 a eample for the forward ad backward tree is preseted olid lies belog to hard decisios ad dashed lies represet the soft augmetatio These augmeted backward =+03 =+03 =+03 = 05 =+ = =+ + =+ + = = + = 05 =+ = + =+08 + =+ + = + =+08 forward Fig Eted TOP stack etry ad calculate metrics of successors Remove TOP etry from stack Isert the M ew etries i the stack which is ordered accordig to descedig metric values o tack filled up Eted all shorter paths to full legth ad update path metric usig soft values tore augmeted stack / for soft-output calculatio Flow chart for the stack algorithm with soft augmetatio Fig 3 Equalizer subtrees for BI-LI applied to BPK modulatio paths geerally cotai soft values m, ad hard decided values m, as show i Tab I k ma ma Lˆ TABLE I EXAMPLE FOR THE AUGMETED TACK OF A BI-LI EQUALIZER FOR BPK TRAMIIO WITH TACK IZE ma AD ma the forward directio ad stops whe the path with the highest
4 D Auiliary stack algorithm for bias estimatio The legth bias parts of the brach metrics 0 ad are essetial for the mai stack algorithm to be successful Evaluatig l p y =l e l py +l P 4 yields the eact value of the forward partial bias term ad l p y +L +L =l l py+l e +L +l P 5 the eact value of the backward partial bias term Ufortuately, the calculatio of 4 ad 5 is far too comple, but the correspodig sums are domiated oly by a small subset of sequeces of a particular legth These sequeces maimizig the forward partial auiliary metrics =lpy +lp or the backward partial auiliary metrics = lp y +L +L +lp, respectively, ca also be foud by eplorig the equalizer trees For this we use a slightly modified M-algorithm, referred to as auiliary stack algorithm I the forward directio this algorithm works o a auiliary stack with stack size ma = M ad recursively computes partial auiliary metric values = +lp y L +lp 6 usig the chael part 8 as well as the a priori part 9 of the brach metric, startig from =lp y L + l P Cosequetly, the forward partial bias term ca be estimated by l p y l β =l e 7 A flow chart for the auiliary stack algorithm is depicted i Fig 4 imilarly, we have for the backward directio a auiliary stack with size ma = M ad the partial auiliary metric = + +l p y+l +L +l P 8 startig from =lp y+l +L +lp A estimatio of the backward partial bias is obtaied by l p y +L +L l β =l e 9 Cotrary to the mai stacks, the auiliary stacks cotai oly sequeces of a particular legth Moreover, to reach the ed of the trees ad to guaratee limited stack sizes we have to discard paths while performig the auiliary stack algorithms for the tree depth > i the forward directio ad for i the backward directio Fig 4 Lˆ m, l Iitialize auiliary stack / with root ode Eted all stack etries ad calculate metrics of successors Remove all previous etries ad isert ew etries i the auiliary stack Compute bias estimate β / β o Ed of tree o tack filled up Order stack accordig to descedig metric values Remove all etries below positio M / M Bias complete Flow chart for the auiliary stack algorithm E oft-output processig We ow have available a set of augmeted paths i the forward mai stack ad i the backward mai stack Due to the soft augmeted part we have to modify 3 to cotrol the metric ifluece o umerator ad deomiator Therfore, we itroduce the weightig factors ± m, / which leads to + m, e + + m, e m, e + m, e 0 For the hard decided part of the tree we have almost the origial formula, but for the soft decided part we weight the metric values with the correspodig bit probabilities P m, = ± = ± m, A importat differece accordig to 3 is that we oly have the estimated bias parts l β +L ad l β L, which are i geeral differet from each other, istead of the eact value l p y +L which is valid for both directios I order to prevet BI-LI to privilege paths of the augmeted stack with the smaller estimated full legth bias, we have to use the metrics without the estimated bias terms = +l β +L, = +l β L for the evaluatio of 0 For that reaso it is oly ecessary to estimate the partial bias up to l β i the forward directio
5 ad up to l β i the backward directio I coclusio the structure of BI-LI is preseted i Fig 5 y L m, M algorithm forward auiliary stack M algorithm backward auiliary stack l β l β stack algorithm forward mai stack stack algorithm backward mai stack m, m, soft output processig Lˆ m, BER o II BI-LI, it ma = ma = 4096 LI, it ma = 89 BI-LI, it ma = ma = 048 BI-Gai BI LI equalizer 0 4 Fig 5 tructure of the BI-LI equalizer IV IMULATIO REULT The ioosphere is a very challegig physical chael which suffers from a large delay spread ad is typically modeled by two propagatio paths with equal power Therefore, we cosider the 6-tap chael h =/, 0, 0,0, 0, / T for biary trasmissio [0] Blocks of = 8 symbols are arraged i a iterleaver frame of size 89 bits The outer rate / covolutioal code is termiated ad defied by the geerator g = [ + D + D 3 + D 4, +D 3 + D 4 ] I Fig 6 the BER after decodig for a turbo receiver employig BI-LI with ma= ma = 4096 ad ma= ma= 8 is depicted ote that the full tree has 8 paths The system performace is compared to coded trasmissio over a AWG chael with APP decodig We reach this performace boud i iteratio at a BER E / i db b 0 Fig 7 BER performace after iteratios equalizatio ad decodig for = 8, various ier LI based equalizers with ma + ma= 56 ad a outer BCJR decoder for the rate /, memory 4 cov code receiver employig BI-LI with equal computatioal compleity, ie ma= ma= 4096, reaches the performace boud at a 5dB lower E b / 0 Moreover, we reduced the mai stack sizes by factors of two for the BI-LI equalizer Eve i that case, BI-LI shows a better performace V COCLUIO We have itroduced a bidirectioal list-sequetial BI-LI equalizer which overcomes the problems of former bidirectioal sequetial decodig algorithms Furthermore, the idepedet compoets of BI-LI provide the possibility of parallel processig Especially i the low E b / 0 -rage BI-LI shows a better performace tha its uidirectioal complemet LI BER it 0 it it 4 it 6 it 8 it 0 it o II E / i db b 0 Fig 6 BER performace after the decoder for = 8, a ier BI-LI equalizer with ma = ma =4096, ma= ma =8 ad a outer BCJR decoder for the rate /, memory 4 covolutioal code of 0 3 I Fig 7 a compariso of differet LI based equalizers after iteratios equalizatio ad decodig is preseted For each equalizer we have fairly small auiliary stack sizes of ma+ ma = 56 Compared to the uidirectioal LI equalizer with ma = 89, a turbo REFERECE [] C Berrou, A Glavieu, ad P Thitimajshima, ear shao limit errorcorrectig codig ad decodig: Turbo codes, i Proc of the IEEE It Cof o Commuicatios ICC, vol, pp , May 993 [] J Hageauer, The turbo priciple: Tutorial itroductio ad state of the art, i Proc of the It ymposium o Turbo Codes & Related Topics, pp, ept 997 [3] J M Wozecraft ad B Reiffe, equetial Decodig Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press, 96 [4] J Hageauer ad C Kuh, Turbo equalizatio for chaels with high memory usig a list-sequetial LI equalizer, i Proc of the It ymposium o Turbo Codes & Related Topics, pp 9 3, ept 003 [5] R Fao, A heuristic discussio of probabilistic decodig, IEEE Trasactios o Iformatio Theory, vol 9, pp 64 73, Apr 963 [6] Li ad D J Costello, Error Cotrol Codig: Fudametals ad Applicatios Pretice-Hall, Eglewood Cliffs, d ed, 004 [7] G D Forey, Fial report o a codig system desig for advaced solar missios, i Rep A-3637, Cotract AA CR7367, AA Ames Res Ctr, 967 [8] Kallel ad K Li, Bidirectioal sequetial decodig, IEEE Trasactios o Iformatio Theory, vol 43, pp 39 36, July 997 [9] J Hageauer, E Offer, ad L Papke, Iterative decodig of biary block ad covolutioal codes, IEEE Trasactios o Iformatio Theory, vol 4, pp , Mar 996 [0] R Otes ad M Tüchler, Block IO liear equalizers for turbo equalizatio i serial-toe HF modems, i Proceedigs of the orwegia igal Processig ymposium ORIG, pp 93 98, Oct 00
A New Morphological 3D Shape Decomposition: Grayscale Interframe Interpolation Method
 A ew Morphological 3D Shape Decompositio: Grayscale Iterframe Iterpolatio Method D.. Vizireau Politehica Uiversity Bucharest, Romaia ae@comm.pub.ro R. M. Udrea Politehica Uiversity Bucharest, Romaia mihea@comm.pub.ro
A ew Morphological 3D Shape Decompositio: Grayscale Iterframe Iterpolatio Method D.. Vizireau Politehica Uiversity Bucharest, Romaia ae@comm.pub.ro R. M. Udrea Politehica Uiversity Bucharest, Romaia mihea@comm.pub.ro
Joint Message-Passing Symbol-Decoding of LDPC Coded Signals over Partial-Response Channels
 Joit Message-Passig Symbol-Decodig of LDPC Coded Sigals over Partial-Respose Chaels Rathakumar Radhakrisha ad ae Vasić Departmet of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig Uiversity of Arizoa, Tucso, AZ-8572 Email:
Joit Message-Passig Symbol-Decodig of LDPC Coded Sigals over Partial-Respose Chaels Rathakumar Radhakrisha ad ae Vasić Departmet of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig Uiversity of Arizoa, Tucso, AZ-8572 Email:
Lecture Notes 6 Introduction to algorithm analysis CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming
 Lecture Notes 6 Itroductio to algorithm aalysis CSS 501 Data Structures ad Object-Orieted Programmig Readig for this lecture: Carrao, Chapter 10 To be covered i this lecture: Itroductio to algorithm aalysis
Lecture Notes 6 Itroductio to algorithm aalysis CSS 501 Data Structures ad Object-Orieted Programmig Readig for this lecture: Carrao, Chapter 10 To be covered i this lecture: Itroductio to algorithm aalysis
Chapter 3 Classification of FFT Processor Algorithms
 Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
Sorting in Linear Time. Data Structures and Algorithms Andrei Bulatov
 Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Linear Time-Invariant Systems
 9/9/00 LIEAR TIE-IVARIAT SYSTES Uit, d Part Liear Time-Ivariat Sstems A importat class of discrete-time sstem cosists of those that are Liear Priciple of superpositio Time-ivariat dela of the iput sequece
9/9/00 LIEAR TIE-IVARIAT SYSTES Uit, d Part Liear Time-Ivariat Sstems A importat class of discrete-time sstem cosists of those that are Liear Priciple of superpositio Time-ivariat dela of the iput sequece
Ones Assignment Method for Solving Traveling Salesman Problem
 Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
Improvement of the Orthogonal Code Convolution Capabilities Using FPGA Implementation
 Improvemet of the Orthogoal Code Covolutio Capabilities Usig FPGA Implemetatio Naima Kaabouch, Member, IEEE, Apara Dhirde, Member, IEEE, Saleh Faruque, Member, IEEE Departmet of Electrical Egieerig, Uiversity
Improvemet of the Orthogoal Code Covolutio Capabilities Usig FPGA Implemetatio Naima Kaabouch, Member, IEEE, Apara Dhirde, Member, IEEE, Saleh Faruque, Member, IEEE Departmet of Electrical Egieerig, Uiversity
Lecture 28: Data Link Layer
 Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) 2. Go ack N ARQ Although the Stop ad Wait ARQ is very simple, you ca easily show that it has very the low efficiecy. The low efficiecy comes from the fact that the trasmittig
Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) 2. Go ack N ARQ Although the Stop ad Wait ARQ is very simple, you ca easily show that it has very the low efficiecy. The low efficiecy comes from the fact that the trasmittig
Analysis Metrics. Intro to Algorithm Analysis. Slides. 12. Alg Analysis. 12. Alg Analysis
 Itro to Algorithm Aalysis Aalysis Metrics Slides. Table of Cotets. Aalysis Metrics 3. Exact Aalysis Rules 4. Simple Summatio 5. Summatio Formulas 6. Order of Magitude 7. Big-O otatio 8. Big-O Theorems
Itro to Algorithm Aalysis Aalysis Metrics Slides. Table of Cotets. Aalysis Metrics 3. Exact Aalysis Rules 4. Simple Summatio 5. Summatio Formulas 6. Order of Magitude 7. Big-O otatio 8. Big-O Theorems
Elementary Educational Computer
 Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic. Lecture 13 Control and Sequencing: Hardwired and Microprogrammed Control
 EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Desig with Programmable Logic Lecture 13 Cotrol ad Sequecig: Hardwired ad Microprogrammed Cotrol Refereces: Chapter s 4,5 from textbook Chapter 7 of M.M. Mao ad C.R. Kime,
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Desig with Programmable Logic Lecture 13 Cotrol ad Sequecig: Hardwired ad Microprogrammed Cotrol Refereces: Chapter s 4,5 from textbook Chapter 7 of M.M. Mao ad C.R. Kime,
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Algorithms
 Fast Fourier Trasform FFT Algorithms Relatio to the z-trasform elsewhere, ozero, z x z X x [ ] 2 ~ elsewhere,, ~ e j x X x x π j e z z X X π 2 ~ The DFS X represets evely spaced samples of the z- trasform
Fast Fourier Trasform FFT Algorithms Relatio to the z-trasform elsewhere, ozero, z x z X x [ ] 2 ~ elsewhere,, ~ e j x X x x π j e z z X X π 2 ~ The DFS X represets evely spaced samples of the z- trasform
Improving Template Based Spike Detection
 Improvig Template Based Spike Detectio Kirk Smith, Member - IEEE Portlad State Uiversity petra@ee.pdx.edu Abstract Template matchig algorithms like SSE, Covolutio ad Maximum Likelihood are well kow for
Improvig Template Based Spike Detectio Kirk Smith, Member - IEEE Portlad State Uiversity petra@ee.pdx.edu Abstract Template matchig algorithms like SSE, Covolutio ad Maximum Likelihood are well kow for
Filter design. 1 Design considerations: a framework. 2 Finite impulse response (FIR) filter design
 Filter desig Desig cosideratios: a framework C ı p ı p H(f) Aalysis of fiite wordlegth effects: I practice oe should check that the quatisatio used i the implemetatio does ot degrade the performace of
Filter desig Desig cosideratios: a framework C ı p ı p H(f) Aalysis of fiite wordlegth effects: I practice oe should check that the quatisatio used i the implemetatio does ot degrade the performace of
Computers and Scientific Thinking
 Computers ad Scietific Thikig David Reed, Creighto Uiversity Chapter 15 JavaScript Strigs 1 Strigs as Objects so far, your iteractive Web pages have maipulated strigs i simple ways use text box to iput
Computers ad Scietific Thikig David Reed, Creighto Uiversity Chapter 15 JavaScript Strigs 1 Strigs as Objects so far, your iteractive Web pages have maipulated strigs i simple ways use text box to iput
Adaptive Resource Allocation for Electric Environmental Pollution through the Control Network
 Available olie at www.sciecedirect.com Eergy Procedia 6 (202) 60 64 202 Iteratioal Coferece o Future Eergy, Eviromet, ad Materials Adaptive Resource Allocatio for Electric Evirometal Pollutio through the
Available olie at www.sciecedirect.com Eergy Procedia 6 (202) 60 64 202 Iteratioal Coferece o Future Eergy, Eviromet, ad Materials Adaptive Resource Allocatio for Electric Evirometal Pollutio through the
BASED ON ITERATIVE ERROR-CORRECTION
 A COHPARISO OF CRYPTAALYTIC PRICIPLES BASED O ITERATIVE ERROR-CORRECTIO Miodrag J. MihaljeviC ad Jova Dj. GoliC Istitute of Applied Mathematics ad Electroics. Belgrade School of Electrical Egieerig. Uiversity
A COHPARISO OF CRYPTAALYTIC PRICIPLES BASED O ITERATIVE ERROR-CORRECTIO Miodrag J. MihaljeviC ad Jova Dj. GoliC Istitute of Applied Mathematics ad Electroics. Belgrade School of Electrical Egieerig. Uiversity
Image Segmentation EEE 508
 Image Segmetatio Objective: to determie (etract) object boudaries. It is a process of partitioig a image ito distict regios by groupig together eighborig piels based o some predefied similarity criterio.
Image Segmetatio Objective: to determie (etract) object boudaries. It is a process of partitioig a image ito distict regios by groupig together eighborig piels based o some predefied similarity criterio.
are two specific neighboring points, F( x, y)
 $33/,&$7,212)7+(6(/)$92,',1* 5$1'20:$/.12,6(5('8&7,21$/*25,7+0,17+(&2/285,0$*(6(*0(17$7,21 %RJGDQ602/.$+HQU\N3$/86'DPLDQ%(5(6.$ 6LOHVLDQ7HFKQLFDO8QLYHUVLW\'HSDUWPHQWRI&RPSXWHU6FLHQFH $NDGHPLFND*OLZLFH32/$1'
$33/,&$7,212)7+(6(/)$92,',1* 5$1'20:$/.12,6(5('8&7,21$/*25,7+0,17+(&2/285,0$*(6(*0(17$7,21 %RJGDQ602/.$+HQU\N3$/86'DPLDQ%(5(6.$ 6LOHVLDQ7HFKQLFDO8QLYHUVLW\'HSDUWPHQWRI&RPSXWHU6FLHQFH $NDGHPLFND*OLZLFH32/$1'
Improving Information Retrieval System Security via an Optimal Maximal Coding Scheme
 Improvig Iformatio Retrieval System Security via a Optimal Maximal Codig Scheme Dogyag Log Departmet of Computer Sciece, City Uiversity of Hog Kog, 8 Tat Chee Aveue Kowloo, Hog Kog SAR, PRC dylog@cs.cityu.edu.hk
Improvig Iformatio Retrieval System Security via a Optimal Maximal Codig Scheme Dogyag Log Departmet of Computer Sciece, City Uiversity of Hog Kog, 8 Tat Chee Aveue Kowloo, Hog Kog SAR, PRC dylog@cs.cityu.edu.hk
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 19 Query Optimizatio Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio Query optimizatio Coducted by a query optimizer i a DBMS Goal:
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 19 Query Optimizatio Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio Query optimizatio Coducted by a query optimizer i a DBMS Goal:
Analysis of Server Resource Consumption of Meteorological Satellite Application System Based on Contour Curve
 Advaces i Computer, Sigals ad Systems (2018) 2: 19-25 Clausius Scietific Press, Caada Aalysis of Server Resource Cosumptio of Meteorological Satellite Applicatio System Based o Cotour Curve Xiagag Zhao
Advaces i Computer, Sigals ad Systems (2018) 2: 19-25 Clausius Scietific Press, Caada Aalysis of Server Resource Cosumptio of Meteorological Satellite Applicatio System Based o Cotour Curve Xiagag Zhao
Higher-order iterative methods free from second derivative for solving nonlinear equations
 Iteratioal Joural of the Phsical Scieces Vol 6(8, pp 887-89, 8 April, Available olie at http://wwwacademicjouralsorg/ijps DOI: 5897/IJPS45 ISSN 99-95 Academic Jourals Full Legth Research Paper Higher-order
Iteratioal Joural of the Phsical Scieces Vol 6(8, pp 887-89, 8 April, Available olie at http://wwwacademicjouralsorg/ijps DOI: 5897/IJPS45 ISSN 99-95 Academic Jourals Full Legth Research Paper Higher-order
Chapter 1. Introduction to Computers and C++ Programming. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 1 Itroductio to Computers ad C++ Programmig Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 1.1 Computer Systems 1.2 Programmig ad Problem Solvig 1.3 Itroductio to C++ 1.4 Testig
Chapter 1 Itroductio to Computers ad C++ Programmig Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 1.1 Computer Systems 1.2 Programmig ad Problem Solvig 1.3 Itroductio to C++ 1.4 Testig
MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fitting)
 MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fittig) I this chapter, we will eamie some methods of aalysis ad data processig; data obtaied as a result of a give
MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fittig) I this chapter, we will eamie some methods of aalysis ad data processig; data obtaied as a result of a give
Lower Bounds for Sorting
 Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
Dynamic Programming and Curve Fitting Based Road Boundary Detection
 Dyamic Programmig ad Curve Fittig Based Road Boudary Detectio SHYAM PRASAD ADHIKARI, HYONGSUK KIM, Divisio of Electroics ad Iformatio Egieerig Chobuk Natioal Uiversity 664-4 Ga Deokji-Dog Jeoju-City Jeobuk
Dyamic Programmig ad Curve Fittig Based Road Boudary Detectio SHYAM PRASAD ADHIKARI, HYONGSUK KIM, Divisio of Electroics ad Iformatio Egieerig Chobuk Natioal Uiversity 664-4 Ga Deokji-Dog Jeoju-City Jeobuk
A REDUCED-COMPLEXITY LDPC DECODING ALGORITHM WITH CHEBYSHEV POLYNOMIAL FITTING
 Joural of Theoretical ad Applied Iformatio Techology st March. Vol. 49 No. 5 - JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-95 A REDUCED-COMPLEXITY LDPC DECODING ALGORITHM WITH
Joural of Theoretical ad Applied Iformatio Techology st March. Vol. 49 No. 5 - JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-95 A REDUCED-COMPLEXITY LDPC DECODING ALGORITHM WITH
How do we evaluate algorithms?
 F2 Readig referece: chapter 2 + slides Algorithm complexity Big O ad big Ω To calculate ruig time Aalysis of recursive Algorithms Next time: Litterature: slides mostly The first Algorithm desig methods:
F2 Readig referece: chapter 2 + slides Algorithm complexity Big O ad big Ω To calculate ruig time Aalysis of recursive Algorithms Next time: Litterature: slides mostly The first Algorithm desig methods:
Evaluation scheme for Tracking in AMI
 A M I C o m m u i c a t i o A U G M E N T E D M U L T I - P A R T Y I N T E R A C T I O N http://www.amiproject.org/ Evaluatio scheme for Trackig i AMI S. Schreiber a D. Gatica-Perez b AMI WP4 Trackig:
A M I C o m m u i c a t i o A U G M E N T E D M U L T I - P A R T Y I N T E R A C T I O N http://www.amiproject.org/ Evaluatio scheme for Trackig i AMI S. Schreiber a D. Gatica-Perez b AMI WP4 Trackig:
6.854J / J Advanced Algorithms Fall 2008
 MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
Fundamental Algorithms
 Techische Uiversität Müche Fakultät für Iformatik Lehrstuhl für Effiziete Algorithme Dmytro Chibisov Sadeep Sadaada Witer Semester 2007/08 Solutio Sheet 6 November 30, 2007 Fudametal Algorithms Problem
Techische Uiversität Müche Fakultät für Iformatik Lehrstuhl für Effiziete Algorithme Dmytro Chibisov Sadeep Sadaada Witer Semester 2007/08 Solutio Sheet 6 November 30, 2007 Fudametal Algorithms Problem
CS 683: Advanced Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CS 683: Advaced Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Lecture 6, February 1, 2008 Lecturer: Joh Hopcroft Scribes: Shaomei Wu, Etha Feldma February 7, 2008 1 Threshold for k CNF Satisfiability I the previous lecture,
CS 683: Advaced Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Lecture 6, February 1, 2008 Lecturer: Joh Hopcroft Scribes: Shaomei Wu, Etha Feldma February 7, 2008 1 Threshold for k CNF Satisfiability I the previous lecture,
GPUMP: a Multiple-Precision Integer Library for GPUs
 GPUMP: a Multiple-Precisio Iteger Library for GPUs Kaiyog Zhao ad Xiaowe Chu Departmet of Computer Sciece, Hog Kog Baptist Uiversity Hog Kog, P. R. Chia Email: {kyzhao, chxw}@comp.hkbu.edu.hk Abstract
GPUMP: a Multiple-Precisio Iteger Library for GPUs Kaiyog Zhao ad Xiaowe Chu Departmet of Computer Sciece, Hog Kog Baptist Uiversity Hog Kog, P. R. Chia Email: {kyzhao, chxw}@comp.hkbu.edu.hk Abstract
Fundamentals of Media Processing. Shin'ichi Satoh Kazuya Kodama Hiroshi Mo Duy-Dinh Le
 Fudametals of Media Processig Shi'ichi Satoh Kazuya Kodama Hiroshi Mo Duy-Dih Le Today's topics Noparametric Methods Parze Widow k-nearest Neighbor Estimatio Clusterig Techiques k-meas Agglomerative Hierarchical
Fudametals of Media Processig Shi'ichi Satoh Kazuya Kodama Hiroshi Mo Duy-Dih Le Today's topics Noparametric Methods Parze Widow k-nearest Neighbor Estimatio Clusterig Techiques k-meas Agglomerative Hierarchical
The isoperimetric problem on the hypercube
 The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
Heaps. Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 201 Heaps 201 Goodrich ad Tamassia xkcd. http://xkcd.com/83/. Tree. Used with permissio uder
Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 201 Heaps 201 Goodrich ad Tamassia xkcd. http://xkcd.com/83/. Tree. Used with permissio uder
A Note on Least-norm Solution of Global WireWarping
 A Note o Least-orm Solutio of Global WireWarpig Charlie C. L. Wag Departmet of Mechaical ad Automatio Egieerig The Chiese Uiversity of Hog Kog Shati, N.T., Hog Kog E-mail: cwag@mae.cuhk.edu.hk Abstract
A Note o Least-orm Solutio of Global WireWarpig Charlie C. L. Wag Departmet of Mechaical ad Automatio Egieerig The Chiese Uiversity of Hog Kog Shati, N.T., Hog Kog E-mail: cwag@mae.cuhk.edu.hk Abstract
Bayesian approach to reliability modelling for a probability of failure on demand parameter
 Bayesia approach to reliability modellig for a probability of failure o demad parameter BÖRCSÖK J., SCHAEFER S. Departmet of Computer Architecture ad System Programmig Uiversity Kassel, Wilhelmshöher Allee
Bayesia approach to reliability modellig for a probability of failure o demad parameter BÖRCSÖK J., SCHAEFER S. Departmet of Computer Architecture ad System Programmig Uiversity Kassel, Wilhelmshöher Allee
Lecture 5. Counting Sort / Radix Sort
 Lecture 5. Coutig Sort / Radix Sort T. H. Corme, C. E. Leiserso ad R. L. Rivest Itroductio to Algorithms, 3rd Editio, MIT Press, 2009 Sugkyukwa Uiversity Hyuseug Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-2018
Lecture 5. Coutig Sort / Radix Sort T. H. Corme, C. E. Leiserso ad R. L. Rivest Itroductio to Algorithms, 3rd Editio, MIT Press, 2009 Sugkyukwa Uiversity Hyuseug Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-2018
A Study on the Performance of Cholesky-Factorization using MPI
 A Study o the Performace of Cholesky-Factorizatio usig MPI Ha S. Kim Scott B. Bade Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig Uiversity of Califoria Sa Diego {hskim, bade}@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract Cholesky-factorizatio
A Study o the Performace of Cholesky-Factorizatio usig MPI Ha S. Kim Scott B. Bade Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig Uiversity of Califoria Sa Diego {hskim, bade}@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract Cholesky-factorizatio
Pattern Recognition Systems Lab 1 Least Mean Squares
 Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Fully Parallel Window Decoder Architecture for Spatially-Coupled LDPC Codes
 Fully Parallel Widow Decoder Architecture for Spatially-Coupled LDPC Codes Najeeb Ul Hassa, Marti Schlüter, ad Gerhard P. Fettweis Vodafoe Chair Mobile Commuicatios Systems, Dresde Uiversity of Techology
Fully Parallel Widow Decoder Architecture for Spatially-Coupled LDPC Codes Najeeb Ul Hassa, Marti Schlüter, ad Gerhard P. Fettweis Vodafoe Chair Mobile Commuicatios Systems, Dresde Uiversity of Techology
Optimal Mapped Mesh on the Circle
 Koferece ANSYS 009 Optimal Mapped Mesh o the Circle doc. Ig. Jaroslav Štigler, Ph.D. Bro Uiversity of Techology, aculty of Mechaical gieerig, ergy Istitut, Abstract: This paper brigs out some ideas ad
Koferece ANSYS 009 Optimal Mapped Mesh o the Circle doc. Ig. Jaroslav Štigler, Ph.D. Bro Uiversity of Techology, aculty of Mechaical gieerig, ergy Istitut, Abstract: This paper brigs out some ideas ad
CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 11 Basic Computer Organization and Design
 College of Computer ad Iformatio Scieces Departmet of Computer Sciece CSC 220: Computer Orgaizatio Uit 11 Basic Computer Orgaizatio ad Desig 1 For the rest of the semester, we ll focus o computer architecture:
College of Computer ad Iformatio Scieces Departmet of Computer Sciece CSC 220: Computer Orgaizatio Uit 11 Basic Computer Orgaizatio ad Desig 1 For the rest of the semester, we ll focus o computer architecture:
Accuracy Improvement in Camera Calibration
 Accuracy Improvemet i Camera Calibratio FaJie L Qi Zag ad Reihard Klette CITR, Computer Sciece Departmet The Uiversity of Aucklad Tamaki Campus, Aucklad, New Zealad fli006, qza001@ec.aucklad.ac.z r.klette@aucklad.ac.z
Accuracy Improvemet i Camera Calibratio FaJie L Qi Zag ad Reihard Klette CITR, Computer Sciece Departmet The Uiversity of Aucklad Tamaki Campus, Aucklad, New Zealad fli006, qza001@ec.aucklad.ac.z r.klette@aucklad.ac.z
3D Model Retrieval Method Based on Sample Prediction
 20 Iteratioal Coferece o Computer Commuicatio ad Maagemet Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (20) (20) IACSIT Press, Sigapore 3D Model Retrieval Method Based o Sample Predictio Qigche Zhag, Ya Tag* School of Computer
20 Iteratioal Coferece o Computer Commuicatio ad Maagemet Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (20) (20) IACSIT Press, Sigapore 3D Model Retrieval Method Based o Sample Predictio Qigche Zhag, Ya Tag* School of Computer
OCR Statistics 1. Working with data. Section 3: Measures of spread
 Notes ad Eamples OCR Statistics 1 Workig with data Sectio 3: Measures of spread Just as there are several differet measures of cetral tedec (averages), there are a variet of statistical measures of spread.
Notes ad Eamples OCR Statistics 1 Workig with data Sectio 3: Measures of spread Just as there are several differet measures of cetral tedec (averages), there are a variet of statistical measures of spread.
An Improved Shuffled Frog-Leaping Algorithm for Knapsack Problem
 A Improved Shuffled Frog-Leapig Algorithm for Kapsack Problem Zhoufag Li, Ya Zhou, ad Peg Cheg School of Iformatio Sciece ad Egieerig Hea Uiversity of Techology ZhegZhou, Chia lzhf1978@126.com Abstract.
A Improved Shuffled Frog-Leapig Algorithm for Kapsack Problem Zhoufag Li, Ya Zhou, ad Peg Cheg School of Iformatio Sciece ad Egieerig Hea Uiversity of Techology ZhegZhou, Chia lzhf1978@126.com Abstract.
ECE4050 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture 6: Searching
 ECE4050 Data Structures ad Algorithms Lecture 6: Searchig 1 Search Give: Distict keys k 1, k 2,, k ad collectio L of records of the form (k 1, I 1 ), (k 2, I 2 ),, (k, I ) where I j is the iformatio associated
ECE4050 Data Structures ad Algorithms Lecture 6: Searchig 1 Search Give: Distict keys k 1, k 2,, k ad collectio L of records of the form (k 1, I 1 ), (k 2, I 2 ),, (k, I ) where I j is the iformatio associated
Cubic Polynomial Curves with a Shape Parameter
 roceedigs of the th WSEAS Iteratioal Coferece o Robotics Cotrol ad Maufacturig Techology Hagzhou Chia April -8 00 (pp5-70) Cubic olyomial Curves with a Shape arameter MO GUOLIANG ZHAO YANAN Iformatio ad
roceedigs of the th WSEAS Iteratioal Coferece o Robotics Cotrol ad Maufacturig Techology Hagzhou Chia April -8 00 (pp5-70) Cubic olyomial Curves with a Shape arameter MO GUOLIANG ZHAO YANAN Iformatio ad
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 18 Strategies for Query Processig Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio DBMS techiques to process a query Scaer idetifies
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 18 Strategies for Query Processig Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio DBMS techiques to process a query Scaer idetifies
Force Network Analysis using Complementary Energy
 orce Network Aalysis usig Complemetary Eergy Adrew BORGART Assistat Professor Delft Uiversity of Techology Delft, The Netherlads A.Borgart@tudelft.l Yaick LIEM Studet Delft Uiversity of Techology Delft,
orce Network Aalysis usig Complemetary Eergy Adrew BORGART Assistat Professor Delft Uiversity of Techology Delft, The Netherlads A.Borgart@tudelft.l Yaick LIEM Studet Delft Uiversity of Techology Delft,
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks, Queues, and Heaps Monday, February 18 / Tuesday, February 19
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
Optimum Solution of Quadratic Programming Problem: By Wolfe s Modified Simplex Method
 Volume VI, Issue III, March 7 ISSN 78-5 Optimum Solutio of Quadratic Programmig Problem: By Wolfe s Modified Simple Method Kalpaa Lokhade, P. G. Khot & N. W. Khobragade, Departmet of Mathematics, MJP Educatioal
Volume VI, Issue III, March 7 ISSN 78-5 Optimum Solutio of Quadratic Programmig Problem: By Wolfe s Modified Simple Method Kalpaa Lokhade, P. G. Khot & N. W. Khobragade, Departmet of Mathematics, MJP Educatioal
Data diverse software fault tolerance techniques
 Data diverse software fault tolerace techiques Complemets desig diversity by compesatig for desig diversity s s limitatios Ivolves obtaiig a related set of poits i the program data space, executig the
Data diverse software fault tolerace techiques Complemets desig diversity by compesatig for desig diversity s s limitatios Ivolves obtaiig a related set of poits i the program data space, executig the
Throughput-Delay Scaling in Wireless Networks with Constant-Size Packets
 Throughput-Delay Scalig i Wireless Networks with Costat-Size Packets Abbas El Gamal, James Mamme, Balaji Prabhakar, Devavrat Shah Departmets of EE ad CS Staford Uiversity, CA 94305 Email: {abbas, jmamme,
Throughput-Delay Scalig i Wireless Networks with Costat-Size Packets Abbas El Gamal, James Mamme, Balaji Prabhakar, Devavrat Shah Departmets of EE ad CS Staford Uiversity, CA 94305 Email: {abbas, jmamme,
Convergence results for conditional expectations
 Beroulli 11(4), 2005, 737 745 Covergece results for coditioal expectatios IRENE CRIMALDI 1 ad LUCA PRATELLI 2 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Bologa, Piazza di Porta Sa Doato 5, 40126 Bologa,
Beroulli 11(4), 2005, 737 745 Covergece results for coditioal expectatios IRENE CRIMALDI 1 ad LUCA PRATELLI 2 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Bologa, Piazza di Porta Sa Doato 5, 40126 Bologa,
New Results on Energy of Graphs of Small Order
 Global Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 7 (2017), pp. 2837-2848 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com New Results o Eergy of Graphs of Small Order
Global Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 7 (2017), pp. 2837-2848 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com New Results o Eergy of Graphs of Small Order
Heuristic Approaches for Solving the Multidimensional Knapsack Problem (MKP)
 Heuristic Approaches for Solvig the Multidimesioal Kapsack Problem (MKP) R. PARRA-HERNANDEZ N. DIMOPOULOS Departmet of Electrical ad Computer Eg. Uiversity of Victoria Victoria, B.C. CANADA Abstract: -
Heuristic Approaches for Solvig the Multidimesioal Kapsack Problem (MKP) R. PARRA-HERNANDEZ N. DIMOPOULOS Departmet of Electrical ad Computer Eg. Uiversity of Victoria Victoria, B.C. CANADA Abstract: -
Probability of collisions in Soft Input Decryption
 Issue 1, Volume 1, 007 1 Probability of collisios i Soft Iput Decryptio Nataša Živić, Christoph Rulad Abstract I this work, probability of collisio i Soft Iput Decryptio has bee aalyzed ad calculated.
Issue 1, Volume 1, 007 1 Probability of collisios i Soft Iput Decryptio Nataša Živić, Christoph Rulad Abstract I this work, probability of collisio i Soft Iput Decryptio has bee aalyzed ad calculated.
15-859E: Advanced Algorithms CMU, Spring 2015 Lecture #2: Randomized MST and MST Verification January 14, 2015
 15-859E: Advaced Algorithms CMU, Sprig 2015 Lecture #2: Radomized MST ad MST Verificatio Jauary 14, 2015 Lecturer: Aupam Gupta Scribe: Yu Zhao 1 Prelimiaries I this lecture we are talkig about two cotets:
15-859E: Advaced Algorithms CMU, Sprig 2015 Lecture #2: Radomized MST ad MST Verificatio Jauary 14, 2015 Lecturer: Aupam Gupta Scribe: Yu Zhao 1 Prelimiaries I this lecture we are talkig about two cotets:
Big-O Analysis. Asymptotics
 Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
IMP: Superposer Integrated Morphometrics Package Superposition Tool
 IMP: Superposer Itegrated Morphometrics Package Superpositio Tool Programmig by: David Lieber ( 03) Caisius College 200 Mai St. Buffalo, NY 4208 Cocept by: H. David Sheets, Dept. of Physics, Caisius College
IMP: Superposer Itegrated Morphometrics Package Superpositio Tool Programmig by: David Lieber ( 03) Caisius College 200 Mai St. Buffalo, NY 4208 Cocept by: H. David Sheets, Dept. of Physics, Caisius College
Structuring Redundancy for Fault Tolerance. CSE 598D: Fault Tolerant Software
 Structurig Redudacy for Fault Tolerace CSE 598D: Fault Tolerat Software What do we wat to achieve? Versios Damage Assessmet Versio 1 Error Detectio Iputs Versio 2 Voter Outputs State Restoratio Cotiued
Structurig Redudacy for Fault Tolerace CSE 598D: Fault Tolerat Software What do we wat to achieve? Versios Damage Assessmet Versio 1 Error Detectio Iputs Versio 2 Voter Outputs State Restoratio Cotiued
Designing a learning system
 CS 75 Itro to Machie Learig Lecture Desigig a learig system Milos Hauskrecht milos@pitt.edu 539 Seott Square, -5 people.cs.pitt.edu/~milos/courses/cs75/ Admiistrivia No homework assigmet this week Please
CS 75 Itro to Machie Learig Lecture Desigig a learig system Milos Hauskrecht milos@pitt.edu 539 Seott Square, -5 people.cs.pitt.edu/~milos/courses/cs75/ Admiistrivia No homework assigmet this week Please
APPLICATION NOTE PACE1750AE BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS
 APPLICATION NOTE PACE175AE BUILT-IN UNCTIONS About This Note This applicatio brief is iteded to explai ad demostrate the use of the special fuctios that are built ito the PACE175AE processor. These powerful
APPLICATION NOTE PACE175AE BUILT-IN UNCTIONS About This Note This applicatio brief is iteded to explai ad demostrate the use of the special fuctios that are built ito the PACE175AE processor. These powerful
Algorithms for Disk Covering Problems with the Most Points
 Algorithms for Disk Coverig Problems with the Most Poits Bi Xiao Departmet of Computig Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog csbxiao@comp.polyu.edu.hk Qigfeg Zhuge, Yi He, Zili Shao, Edwi
Algorithms for Disk Coverig Problems with the Most Poits Bi Xiao Departmet of Computig Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog csbxiao@comp.polyu.edu.hk Qigfeg Zhuge, Yi He, Zili Shao, Edwi
. Written in factored form it is easy to see that the roots are 2, 2, i,
 CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
Redundancy Allocation for Series Parallel Systems with Multiple Constraints and Sensitivity Analysis
 IOSR Joural of Egieerig Redudacy Allocatio for Series Parallel Systems with Multiple Costraits ad Sesitivity Aalysis S. V. Suresh Babu, D.Maheswar 2, G. Ragaath 3 Y.Viaya Kumar d G.Sakaraiah e (Mechaical
IOSR Joural of Egieerig Redudacy Allocatio for Series Parallel Systems with Multiple Costraits ad Sesitivity Aalysis S. V. Suresh Babu, D.Maheswar 2, G. Ragaath 3 Y.Viaya Kumar d G.Sakaraiah e (Mechaical
FINITE DIFFERENCE TIME DOMAIN METHOD (FDTD)
 FINIT DIFFRNC TIM DOMAIN MTOD (FDTD) The FDTD method, proposed b Yee, 1966, is aother umerical method, used widel for the solutio of M problems. It is used to solve ope-regio scatterig, radiatio, diffusio,
FINIT DIFFRNC TIM DOMAIN MTOD (FDTD) The FDTD method, proposed b Yee, 1966, is aother umerical method, used widel for the solutio of M problems. It is used to solve ope-regio scatterig, radiatio, diffusio,
New HSL Distance Based Colour Clustering Algorithm
 The 4th Midwest Artificial Itelligece ad Cogitive Scieces Coferece (MAICS 03 pp 85-9 New Albay Idiaa USA April 3-4 03 New HSL Distace Based Colour Clusterig Algorithm Vasile Patrascu Departemet of Iformatics
The 4th Midwest Artificial Itelligece ad Cogitive Scieces Coferece (MAICS 03 pp 85-9 New Albay Idiaa USA April 3-4 03 New HSL Distace Based Colour Clusterig Algorithm Vasile Patrascu Departemet of Iformatics
Random Graphs and Complex Networks T
 Radom Graphs ad Complex Networks T-79.7003 Charalampos E. Tsourakakis Aalto Uiversity Lecture 3 7 September 013 Aoucemet Homework 1 is out, due i two weeks from ow. Exercises: Probabilistic iequalities
Radom Graphs ad Complex Networks T-79.7003 Charalampos E. Tsourakakis Aalto Uiversity Lecture 3 7 September 013 Aoucemet Homework 1 is out, due i two weeks from ow. Exercises: Probabilistic iequalities
BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY
 CHAPTER 3 BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY 3.1 ISOMORPHIC PROPERTIES The ame Boolea Arithmetic was chose because it was discovered that literal Boolea Algebra could have a isomorphic umerical aspect.
CHAPTER 3 BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY 3.1 ISOMORPHIC PROPERTIES The ame Boolea Arithmetic was chose because it was discovered that literal Boolea Algebra could have a isomorphic umerical aspect.
Security of Bluetooth: An overview of Bluetooth Security
 Versio 2 Security of Bluetooth: A overview of Bluetooth Security Marjaaa Träskbäck Departmet of Electrical ad Commuicatios Egieerig mtraskba@cc.hut.fi 52655H ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to give
Versio 2 Security of Bluetooth: A overview of Bluetooth Security Marjaaa Träskbäck Departmet of Electrical ad Commuicatios Egieerig mtraskba@cc.hut.fi 52655H ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to give
Our second algorithm. Comp 135 Machine Learning Computer Science Tufts University. Decision Trees. Decision Trees. Decision Trees.
 Comp 135 Machie Learig Computer Sciece Tufts Uiversity Fall 2017 Roi Khardo Some of these slides were adapted from previous slides by Carla Brodley Our secod algorithm Let s look at a simple dataset for
Comp 135 Machie Learig Computer Sciece Tufts Uiversity Fall 2017 Roi Khardo Some of these slides were adapted from previous slides by Carla Brodley Our secod algorithm Let s look at a simple dataset for
CSC165H1 Worksheet: Tutorial 8 Algorithm analysis (SOLUTIONS)
 CSC165H1, Witer 018 Learig Objectives By the ed of this worksheet, you will: Aalyse the ruig time of fuctios cotaiig ested loops. 1. Nested loop variatios. Each of the followig fuctios takes as iput a
CSC165H1, Witer 018 Learig Objectives By the ed of this worksheet, you will: Aalyse the ruig time of fuctios cotaiig ested loops. 1. Nested loop variatios. Each of the followig fuctios takes as iput a
Big-O Analysis. Asymptotics
 Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
9.1. Sequences and Series. Sequences. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. Definition of Sequence
 _9.qxd // : AM Page Chapter 9 Sequeces, Series, ad Probability 9. Sequeces ad Series What you should lear Use sequece otatio to write the terms of sequeces. Use factorial otatio. Use summatio otatio to
_9.qxd // : AM Page Chapter 9 Sequeces, Series, ad Probability 9. Sequeces ad Series What you should lear Use sequece otatio to write the terms of sequeces. Use factorial otatio. Use summatio otatio to
k (check node degree) and j (variable node degree)
 A Parallel Turbo Decodig Message Passig Architecture for Array LDPC Codes Kira Guam, Pakaj Bhagawat, Weihuag Wag, Gwa Choi, Mark Yeary * Dept. of Electrical Egieerig, Texas A&M Uiversity, College Statio,
A Parallel Turbo Decodig Message Passig Architecture for Array LDPC Codes Kira Guam, Pakaj Bhagawat, Weihuag Wag, Gwa Choi, Mark Yeary * Dept. of Electrical Egieerig, Texas A&M Uiversity, College Statio,
Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs
 Spectral Graph Theory ad Applicatios WS 20/202 Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Su Our goal is to use the properties of the adjacecy/laplacia matrix of graphs to first uderstad
Spectral Graph Theory ad Applicatios WS 20/202 Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Su Our goal is to use the properties of the adjacecy/laplacia matrix of graphs to first uderstad
EE123 Digital Signal Processing
 Last Time EE Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 7 Block Covolutio, Overlap ad Add, FFT Discrete Fourier Trasform Properties of the Liear covolutio through circular Today Liear covolutio with Overlap ad add
Last Time EE Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 7 Block Covolutio, Overlap ad Add, FFT Discrete Fourier Trasform Properties of the Liear covolutio through circular Today Liear covolutio with Overlap ad add
CS200: Hash Tables. Prichard Ch CS200 - Hash Tables 1
 CS200: Hash Tables Prichard Ch. 13.2 CS200 - Hash Tables 1 Table Implemetatios: average cases Search Add Remove Sorted array-based Usorted array-based Balaced Search Trees O(log ) O() O() O() O(1) O()
CS200: Hash Tables Prichard Ch. 13.2 CS200 - Hash Tables 1 Table Implemetatios: average cases Search Add Remove Sorted array-based Usorted array-based Balaced Search Trees O(log ) O() O() O() O(1) O()
Introduction. Nature-Inspired Computing. Terminology. Problem Types. Constraint Satisfaction Problems - CSP. Free Optimization Problem - FOP
 Nature-Ispired Computig Hadlig Costraits Dr. Şima Uyar September 2006 Itroductio may practical problems are costraied ot all combiatios of variable values represet valid solutios feasible solutios ifeasible
Nature-Ispired Computig Hadlig Costraits Dr. Şima Uyar September 2006 Itroductio may practical problems are costraied ot all combiatios of variable values represet valid solutios feasible solutios ifeasible
Parallel Polygon Approximation Algorithm Targeted at Reconfigurable Multi-Ring Hardware
 Parallel Polygo Approximatio Algorithm Targeted at Recofigurable Multi-Rig Hardware M. Arif Wai* ad Hamid R. Arabia** *Califoria State Uiversity Bakersfield, Califoria, USA **Uiversity of Georgia, Georgia,
Parallel Polygo Approximatio Algorithm Targeted at Recofigurable Multi-Rig Hardware M. Arif Wai* ad Hamid R. Arabia** *Califoria State Uiversity Bakersfield, Califoria, USA **Uiversity of Georgia, Georgia,
Protected points in ordered trees
 Applied Mathematics Letters 008 56 50 www.elsevier.com/locate/aml Protected poits i ordered trees Gi-Sag Cheo a, Louis W. Shapiro b, a Departmet of Mathematics, Sugkyukwa Uiversity, Suwo 440-746, Republic
Applied Mathematics Letters 008 56 50 www.elsevier.com/locate/aml Protected poits i ordered trees Gi-Sag Cheo a, Louis W. Shapiro b, a Departmet of Mathematics, Sugkyukwa Uiversity, Suwo 440-746, Republic
A New Approach To Scheduling Parallel Programs Using Task Duplication
 A New Approach To Schedulig Parallel Programs Usig Task Duplicatio Ishfaq Ahmad ad Yu-Kwog Kwok Departmet of Computer Sciece Hog Kog Uiversity of Sciece ad Techology, Clear Water Bay, Kowloo, Hog Kog Abstract
A New Approach To Schedulig Parallel Programs Usig Task Duplicatio Ishfaq Ahmad ad Yu-Kwog Kwok Departmet of Computer Sciece Hog Kog Uiversity of Sciece ad Techology, Clear Water Bay, Kowloo, Hog Kog Abstract
Outline. Applications of FFT in Communications. Fundamental FFT Algorithms. FFT Circuit Design Architectures. Conclusions
 FFT Circuit Desig Outlie Applicatios of FFT i Commuicatios Fudametal FFT Algorithms FFT Circuit Desig Architectures Coclusios DAB Receiver Tuer OFDM Demodulator Chael Decoder Mpeg Audio Decoder 56/5/ 4/48
FFT Circuit Desig Outlie Applicatios of FFT i Commuicatios Fudametal FFT Algorithms FFT Circuit Desig Architectures Coclusios DAB Receiver Tuer OFDM Demodulator Chael Decoder Mpeg Audio Decoder 56/5/ 4/48
LU Decomposition Method
 SOLUTION OF SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS LU Decompositio Method Jamie Traha, Autar Kaw, Kevi Marti Uiversity of South Florida Uited States of America kaw@eg.usf.edu http://umericalmethods.eg.usf.edu Itroductio
SOLUTION OF SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS LU Decompositio Method Jamie Traha, Autar Kaw, Kevi Marti Uiversity of South Florida Uited States of America kaw@eg.usf.edu http://umericalmethods.eg.usf.edu Itroductio
Sectio 4, a prototype project of settig field weight with AHP method is developed ad the experimetal results are aalyzed. Fially, we coclude our work
 200 2d Iteratioal Coferece o Iformatio ad Multimedia Techology (ICIMT 200) IPCSIT vol. 42 (202) (202) IACSIT Press, Sigapore DOI: 0.7763/IPCSIT.202.V42.0 Idex Weight Decisio Based o AHP for Iformatio Retrieval
200 2d Iteratioal Coferece o Iformatio ad Multimedia Techology (ICIMT 200) IPCSIT vol. 42 (202) (202) IACSIT Press, Sigapore DOI: 0.7763/IPCSIT.202.V42.0 Idex Weight Decisio Based o AHP for Iformatio Retrieval
1. Introduction o Microscopic property responsible for MRI Show and discuss graphics that go from macro to H nucleus with N-S pole
 Page 1 Very Quick Itroductio to MRI The poit of this itroductio is to give the studet a sufficietly accurate metal picture of MRI to help uderstad its impact o image registratio. The two major aspects
Page 1 Very Quick Itroductio to MRI The poit of this itroductio is to give the studet a sufficietly accurate metal picture of MRI to help uderstad its impact o image registratio. The two major aspects
Task scenarios Outline. Scenarios in Knowledge Extraction. Proposed Framework for Scenario to Design Diagram Transformation
 6-0-0 Kowledge Trasformatio from Task Scearios to View-based Desig Diagrams Nima Dezhkam Kamra Sartipi {dezhka, sartipi}@mcmaster.ca Departmet of Computig ad Software McMaster Uiversity CANADA SEKE 08
6-0-0 Kowledge Trasformatio from Task Scearios to View-based Desig Diagrams Nima Dezhkam Kamra Sartipi {dezhka, sartipi}@mcmaster.ca Departmet of Computig ad Software McMaster Uiversity CANADA SEKE 08
Spectral leakage and windowing
 EEL33: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems Spectral leakage ad widowig. Itroductio Spectral leakage ad widowig I these otes, we itroduce the idea of widowig for reducig the effects of spectral leakage, ad
EEL33: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems Spectral leakage ad widowig. Itroductio Spectral leakage ad widowig I these otes, we itroduce the idea of widowig for reducig the effects of spectral leakage, ad
One advantage that SONAR has over any other music-sequencing product I ve worked
 *gajedra* D:/Thomso_Learig_Projects/Garrigus_163132/z_productio/z_3B2_3D_files/Garrigus_163132_ch17.3d, 14/11/08/16:26:39, 16:26, page: 647 17 CAL 101 Oe advatage that SONAR has over ay other music-sequecig
*gajedra* D:/Thomso_Learig_Projects/Garrigus_163132/z_productio/z_3B2_3D_files/Garrigus_163132_ch17.3d, 14/11/08/16:26:39, 16:26, page: 647 17 CAL 101 Oe advatage that SONAR has over ay other music-sequecig
Low Complexity H.265/HEVC Coding Unit Size Decision for a Videoconferencing System
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 15, No 6 Special Issue o Logistics, Iformatics ad Service Sciece Sofia 2015 Prit ISSN: 1311-9702; Olie ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI:
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 15, No 6 Special Issue o Logistics, Iformatics ad Service Sciece Sofia 2015 Prit ISSN: 1311-9702; Olie ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI:
Neuro Fuzzy Model for Human Face Expression Recognition
 IOSR Joural of Computer Egieerig (IOSRJCE) ISSN : 2278-0661 Volume 1, Issue 2 (May-Jue 2012), PP 01-06 Neuro Fuzzy Model for Huma Face Expressio Recogitio Mr. Mayur S. Burage 1, Prof. S. V. Dhopte 2 1
IOSR Joural of Computer Egieerig (IOSRJCE) ISSN : 2278-0661 Volume 1, Issue 2 (May-Jue 2012), PP 01-06 Neuro Fuzzy Model for Huma Face Expressio Recogitio Mr. Mayur S. Burage 1, Prof. S. V. Dhopte 2 1
Ch 9.3 Geometric Sequences and Series Lessons
 Ch 9.3 Geometric Sequeces ad Series Lessos SKILLS OBJECTIVES Recogize a geometric sequece. Fid the geeral, th term of a geometric sequece. Evaluate a fiite geometric series. Evaluate a ifiite geometric
Ch 9.3 Geometric Sequeces ad Series Lessos SKILLS OBJECTIVES Recogize a geometric sequece. Fid the geeral, th term of a geometric sequece. Evaluate a fiite geometric series. Evaluate a ifiite geometric
Pruning and Summarizing the Discovered Time Series Association Rules from Mechanical Sensor Data Qing YANG1,a,*, Shao-Yu WANG1,b, Ting-Ting ZHANG2,c
 Advaces i Egieerig Research (AER), volume 131 3rd Aual Iteratioal Coferece o Electroics, Electrical Egieerig ad Iformatio Sciece (EEEIS 2017) Pruig ad Summarizig the Discovered Time Series Associatio Rules
Advaces i Egieerig Research (AER), volume 131 3rd Aual Iteratioal Coferece o Electroics, Electrical Egieerig ad Iformatio Sciece (EEEIS 2017) Pruig ad Summarizig the Discovered Time Series Associatio Rules
A Generalized Set Theoretic Approach for Time and Space Complexity Analysis of Algorithms and Functions
 Proceedigs of the 10th WSEAS Iteratioal Coferece o APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Dallas, Texas, USA, November 1-3, 2006 316 A Geeralized Set Theoretic Approach for Time ad Space Complexity Aalysis of Algorithms
Proceedigs of the 10th WSEAS Iteratioal Coferece o APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Dallas, Texas, USA, November 1-3, 2006 316 A Geeralized Set Theoretic Approach for Time ad Space Complexity Aalysis of Algorithms
